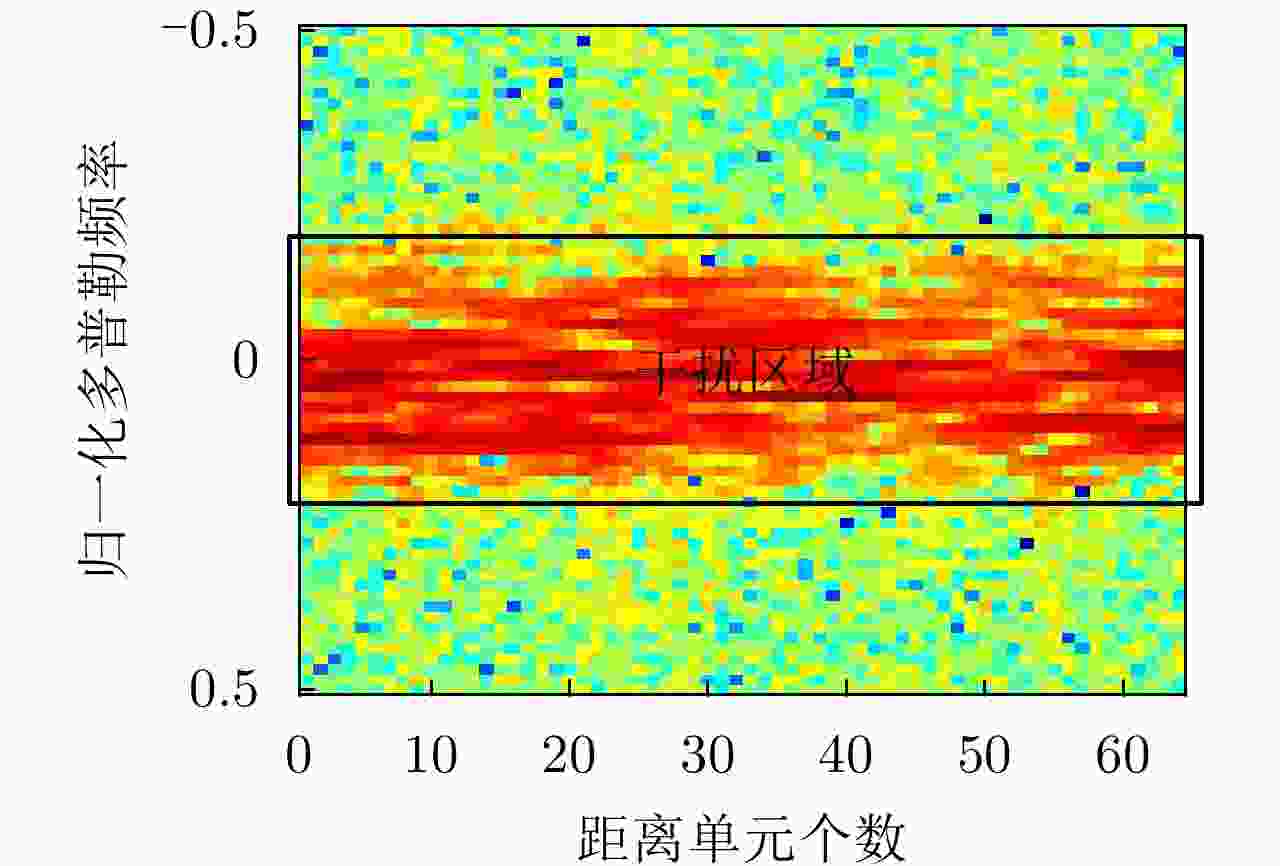
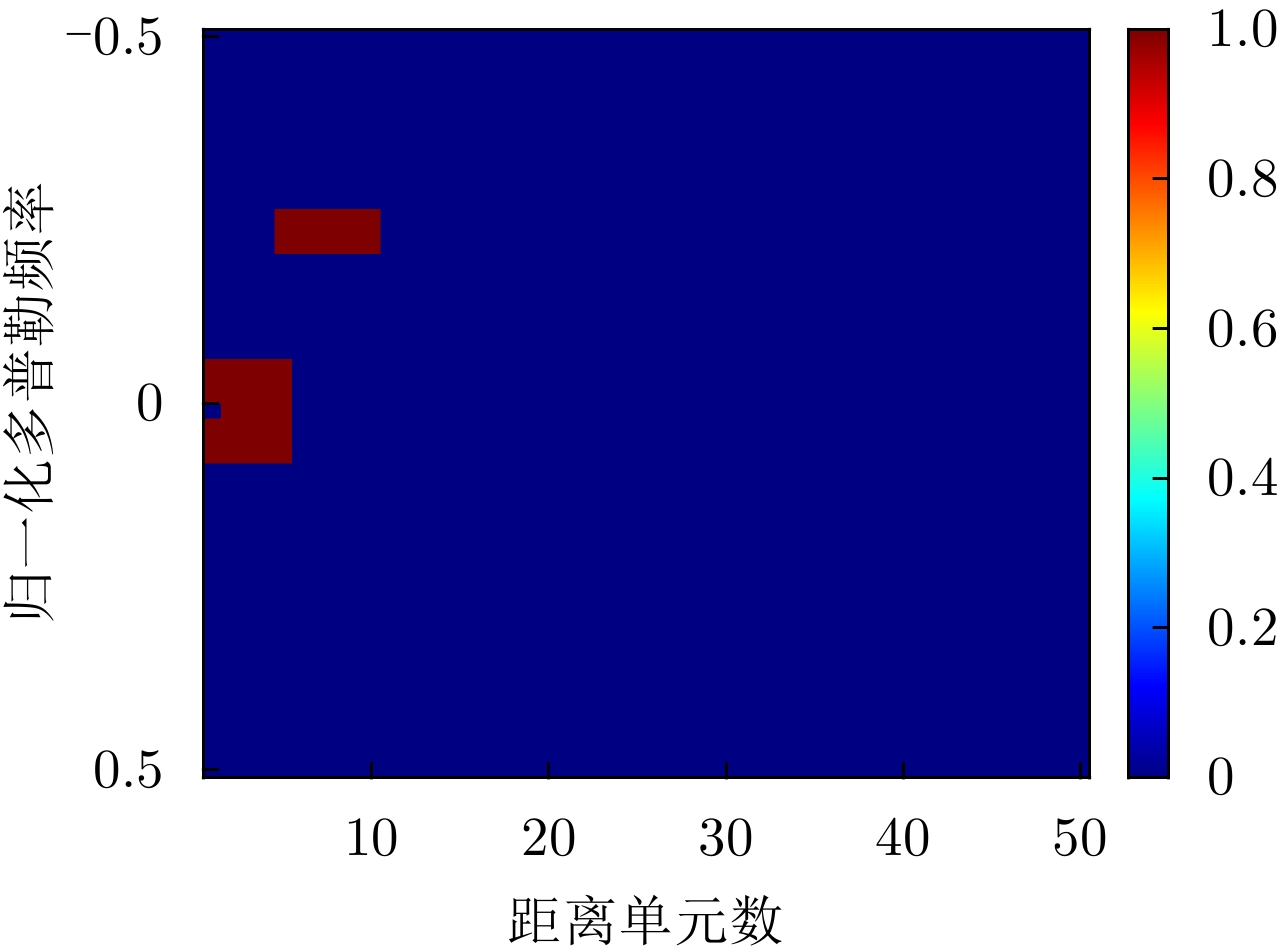
-
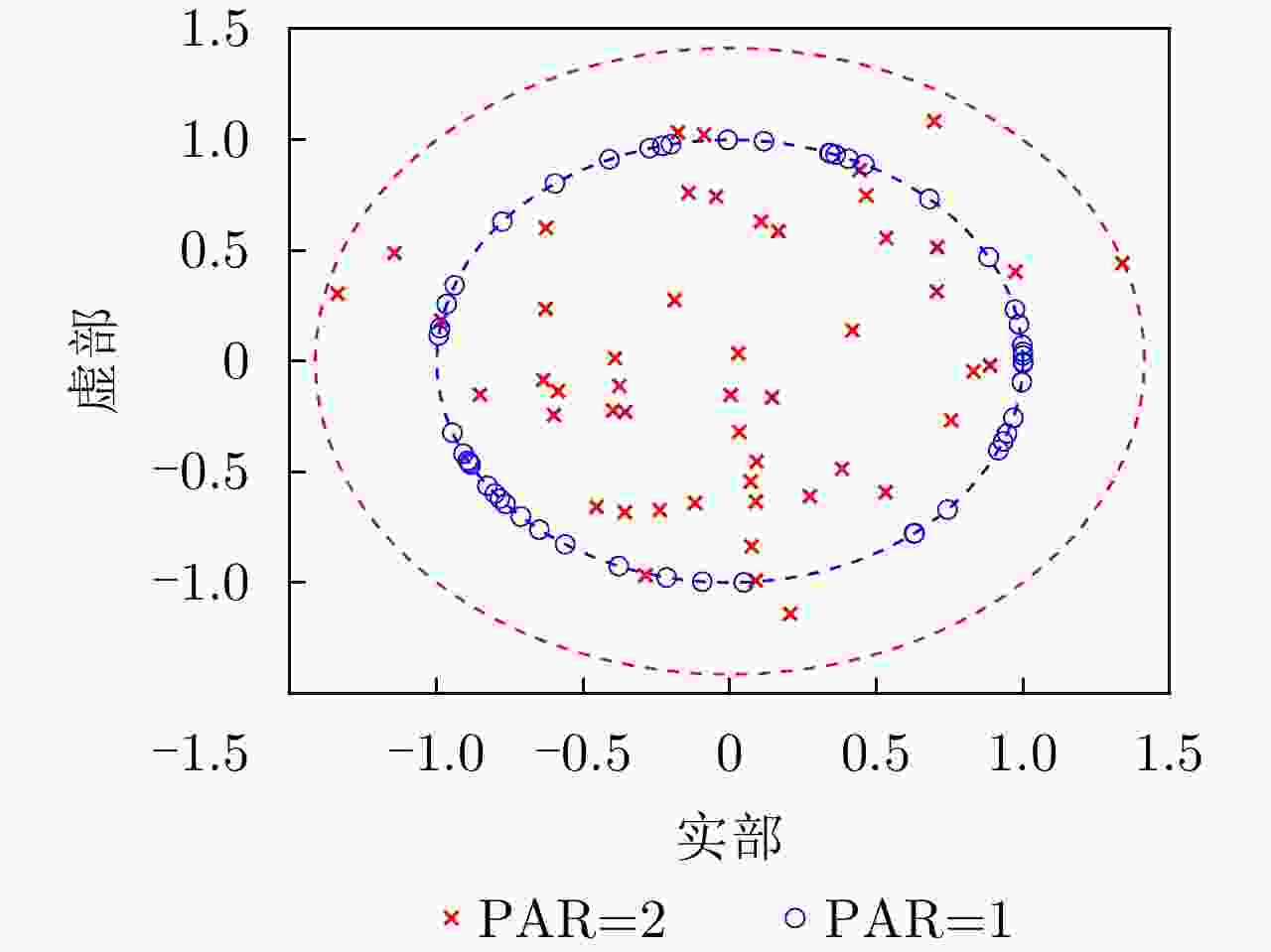
摘要: 在开展认知雷达波形设计时,由于发射波形与接收滤波器的非匹配体制,互模糊函数赋形相比传统模糊函数赋形优化自由度更高。该文针对强杂波条件下微弱运动目标检测问题,以最大化信干噪比为优化准则,提出了一种联合发射相位编码序列与接收滤波器设计的互模糊函数赋形方法。在恒模约束下,优化问题被建模为二次分式规划形式;然后通过引入辅助变量,并利用共轭梯度法求解Stiefel流形空间上的最小化问题,非凸优化据此转化为恒模约束二次优化问题;通过交替循环和类幂迭代算法求得最优解。此外考虑到发射波形受硬件限制而难以实现严格恒模,该文构建了一种低峰均比约束二次优化问题模型,并利用最近邻向量法求得最优解。最后,不同参数下的仿真与实测数据实验表明,该文赋形方法相较于传统方法具有较高的信干噪比增益和收敛速度。Abstract: Due to the mismatch between transmit waveforms and receive filters, Cross-Ambiguity Function (CAF) shaping plays an important role in the design of cognitive radar waveforms and allows more freedom for waveform optimization problem than conventional ambiguity function shaping. A CAF shaping method is proposed for designing phase-shift keying transmit waveforms and receive filters jointly to maximize the output Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR), thereby solving the problem of weaking-moving target detection under strong clutter conditions. The optimization problem is first modeled as a quadratic fractional programming problem under the Constant Modulus (CM) constraint of the transmit waveform. The conjugated gradient method is utilized to solve the minimization problem of the Stiefel manifold space through the introduction of auxiliary variables; furthermore the nonconvex optimization problem is converted into a unimodular quadratic programming problem. An algorithm based on alternately iterative maximization and power method-like iteration is proposed to solve the quadratic optimization problem. Since transmit waveforms are limited by hardware and achieving CM is difficult, the nearest vector method is employed under the constraint of a low peak-to-average power ratio. Finally, the experiments with simulated and real measured data under different parameters reveal that the transmit waveforms and receive filters designed using the proposed method exhibit better SINR performance and faster convergence speed compared with other existing algorithms.
-
1 基于PML的恒模发射波形与接收滤波器联合互模糊函数设计
1. CAF shaping for CM transmit waveforms and receive filters based on PML
输入:干扰能量分布矩阵${\boldsymbol{\sigma }}$,噪声能量${{\boldsymbol{\sigma }}_n}$,目标散射系数${\alpha _{\rm target}}$ 输出:优化发射波形x,优化接收滤波器h 1 Initialization: 初始化发射波形${{\boldsymbol{x}}_0}$,初始化接收滤波器${{\boldsymbol{h}}_0}$,参
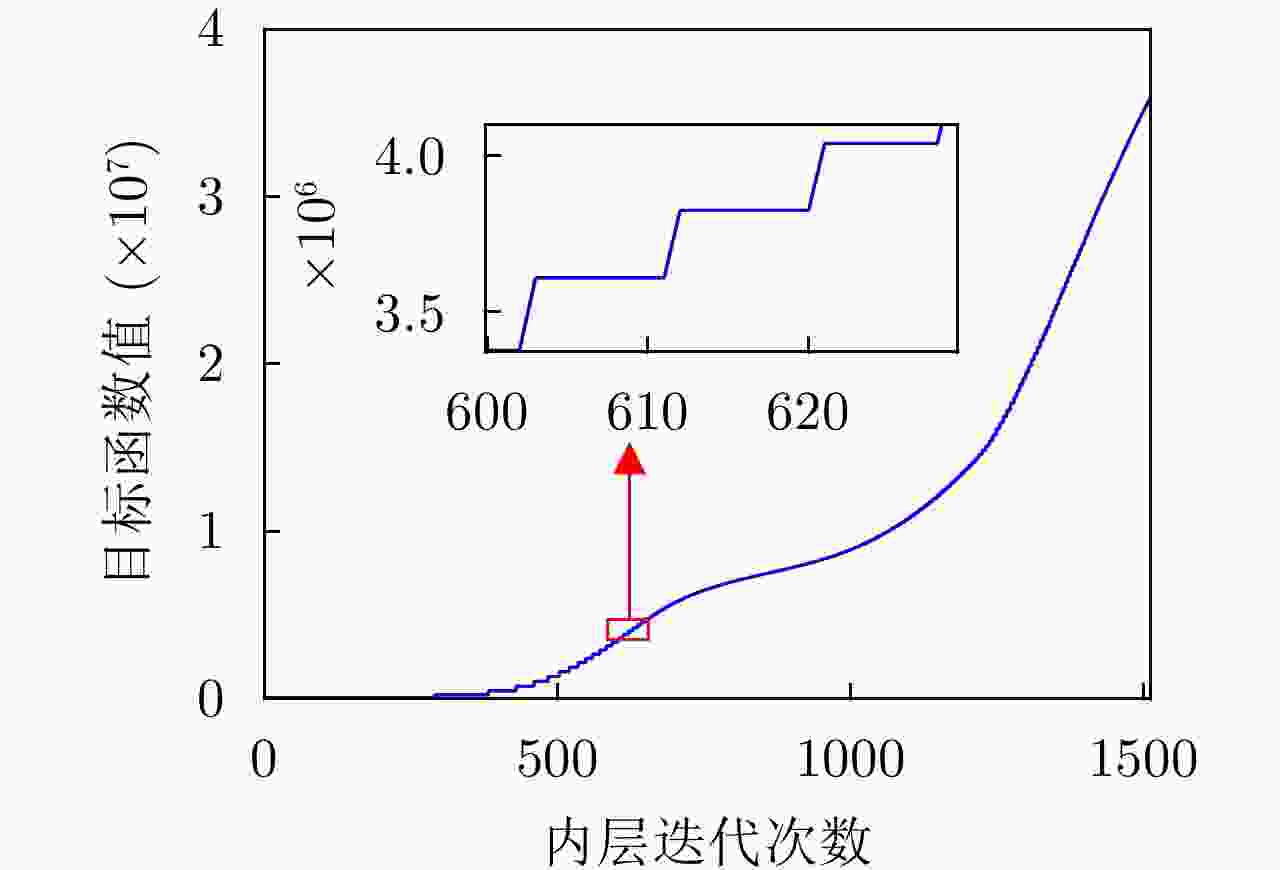
数$\lambda $,参数$\mu $。迭代终止条件${\varepsilon _1}$, ${\varepsilon _2}$2 while ${\text{error } } \ge {\varepsilon _1}$ do 3 式(13)、式(14)更新A, B 4 共轭梯度法在Stiefel流形空间求解U 5 条件式(29)更新$\mu $ 6 式(28)更新$\lambda $ 7 式(22)更新Q 8 求Q最大特征值$\gamma $,并更新${\boldsymbol{\hat Q}}$ 9 while ${\text{error } } \ge {\varepsilon _2}$ do 10 式(26)进行类幂内层迭代 11 end while 12 式(11)计算接收滤波器h 13 end while 14 return ${\boldsymbol{x}},{\boldsymbol{h}}$ 2 低PAR约束下最近邻向量问题求解方法
2. Nearest vector method with low PAR
输入: 发射波形${ {\boldsymbol{x} } }^{(s)}$,发射波形能量约束E,发射波形PAR约束
$\rho $,矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{\hat Q}} $输出:发射波形${ {\boldsymbol{x} }^{(s + 1)} }$ 1 Initialization: 单位化${{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(s)}}$, $\xi = \sqrt {E\rho /N} $, $k = 0$ 2 选取${{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(s)}}$中模长最小的$\left( {N - k} \right)$个元素的索引构成集合${{\mathcal{M}}}$,若
${{\mathcal{M}}}$不唯一,$k = k + 1$,重复步骤23 if $\forall m \in {{\mathcal{M}}}$, $ x_m^{(s)} = 0 $ do 4 if $m \in {{\mathcal{M}}}$ do 5 $x{_m^{(s + 1)} } = \sqrt {\left( {E - k{\xi ^2} } \right)/\left( {N - k} \right)}$ 6 else do 7 $x_m^{{(s + 1)} } = \xi { {\rm{e} }^{ {\text{j} }\arg x_m^{{(s)} } } }$ 8 return ${{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(s + 1)}}$ 9 else do
10 $\varpi = \sqrt {\left( {E - k{\xi ^2} } \right)/\sum\limits_{m \in { {\mathcal{M} } } } { { {\left| {x_m^{{(s)} } } \right|}^2} } }$11 if $\forall m \in {{\mathcal{M}}}$, $\varpi x_m^{{(s)} } > \xi$ do 12 $k = k + 1$,返回步骤2 13 else do 14 if $m \in {{\mathcal{M}}}$ do 15 $x{_m^{(s + 1)} } = \varpi x_m^{(s)}$ 16 else do 17 $x_m^{{(s + 1)} } = \xi { {\rm{e} }^{ {\text{j} }\arg x_m^{{(s)} } } }$ 18 end 19 end 20 end 21 return ${{\boldsymbol{x}}^{(s + 1)}}$ 表 1 不同码长下5种算法性能统计
Table 1. Performance statistics table of five algorithms under different code length
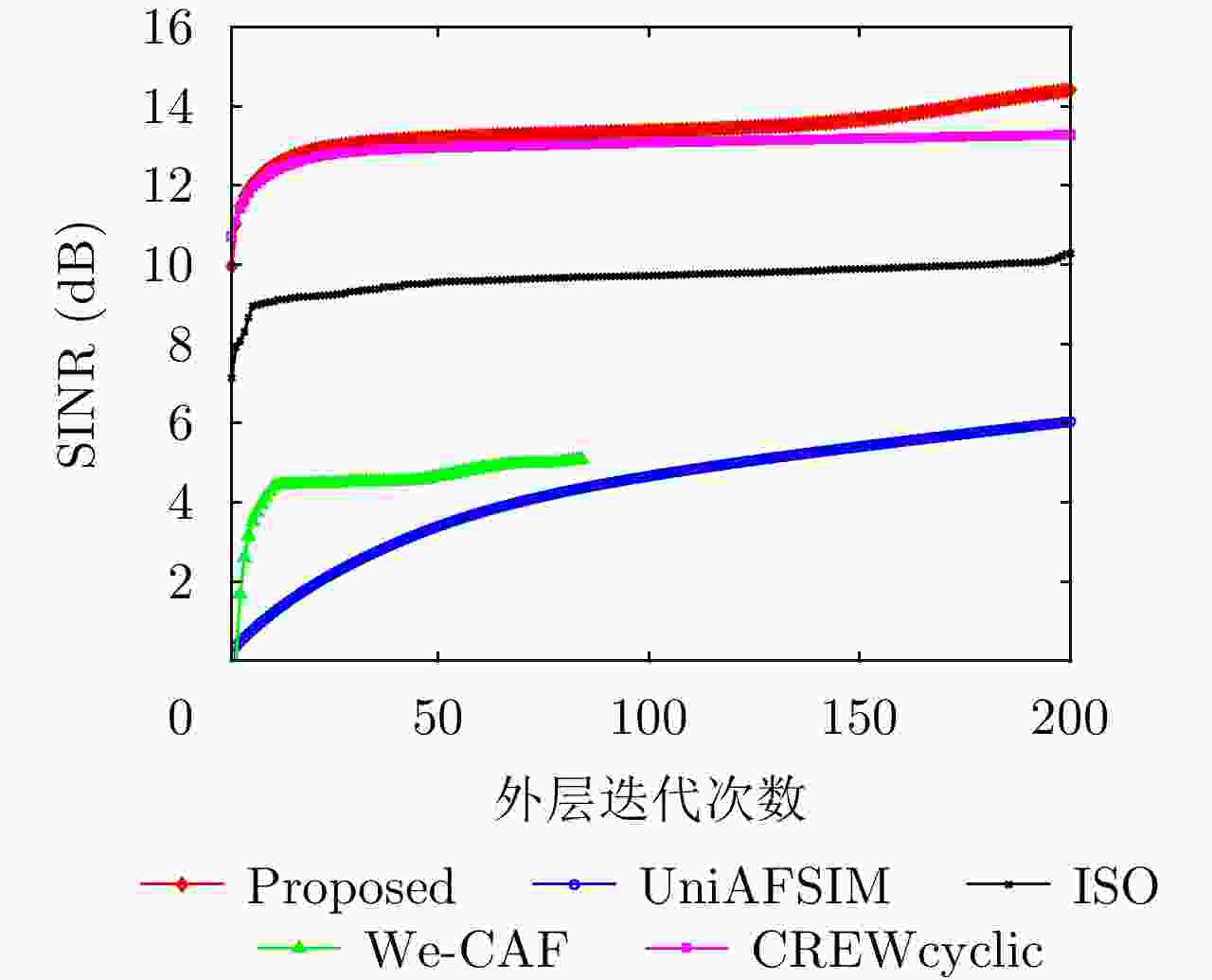
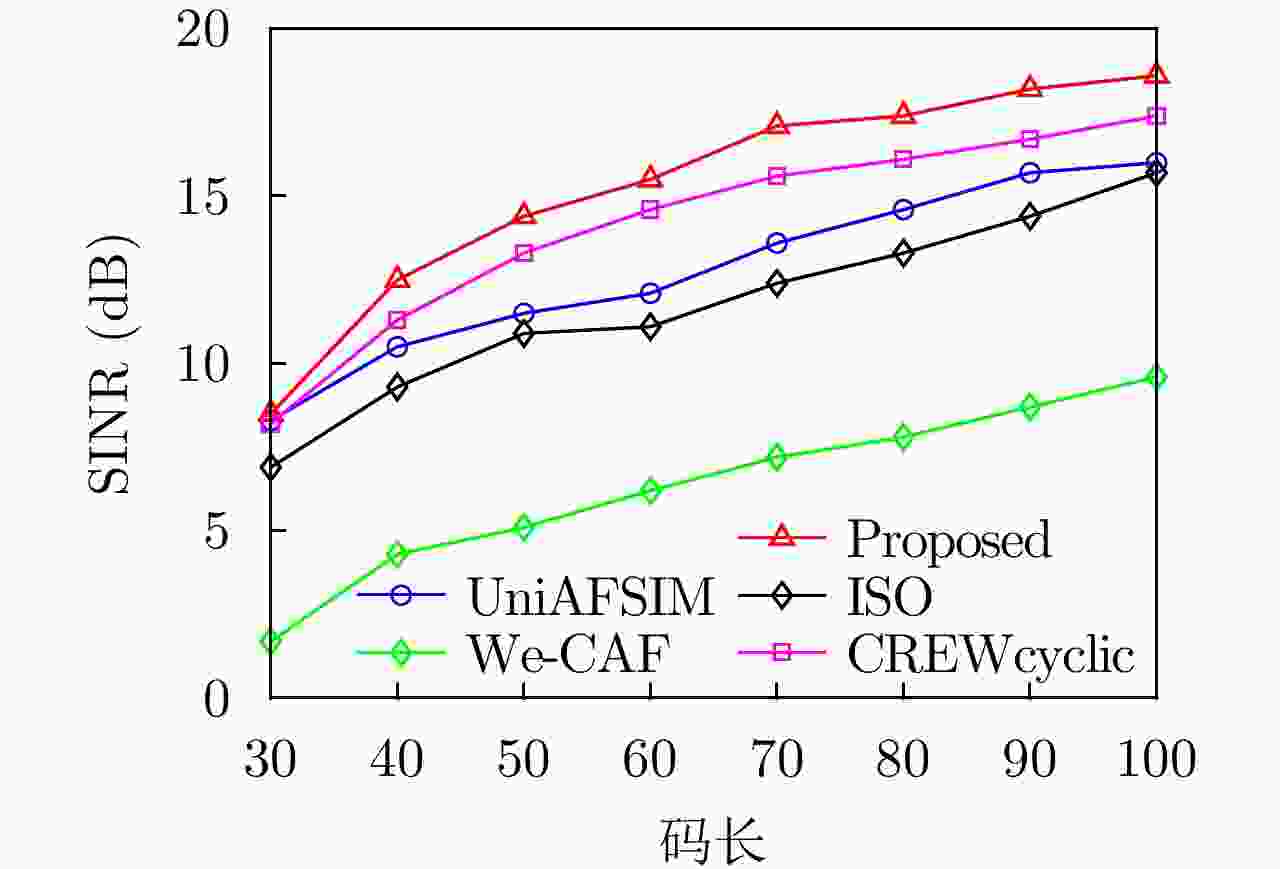
码长N 收敛时SINR (dB) 收敛时运行时间(s) 所提方法 We-CAF UniAFSIM ISO CREWcyclic 所提方法 We-CAF UniAFSIM ISO CREWcyclic 30 8.5 1.7 8.3 6.9 8.2 54.0 2.7 39.0 65.5 31.7 40 12.5 4.3 10.5 9.3 11.3 159.8 19.7 155.8 290.3 162.2 50 14.7 5.1 11.5 10.9 13.3 256.9 31.9 365.4 346.9 256.3 60 15.5 6.2 12.1 11.1 14.6 304.1 68.6 346.1 358.0 288.6 70 17.1 7.2 13.6 12.4 15.6 477.4 161.9 426.2 372.2 342.8 80 17.4 7.8 14.6 13.3 16.1 691.0 238.6 687.8 664.4 506.9 90 18.2 8.7 15.7 14.4 16.7 745.8 373.0 721.5 807.1 622.5 100 18.6 9.6 16.0 15.7 17.4 820.9 477.9 1113.8 1066.4 822.5 表 2 实测数据实验下的雷达参数
Table 2. Radar parameters in real measured data experiment
参数 数值 采样率 1 GHz 带宽 400 MHz 脉冲重复频率 2000 Hz 脉冲宽度 10 μs 高度 1.5 km 俯仰角 30° 方位角 0° 波束宽度 5° -
[1] STOICA P, HE Hao, and LI Jian. Optimization of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(4): 1730–1740. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2179652 [2] STOICA P, LI Jian, and XUE Ming. Transmit codes and receive filters for radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(6): 94–109. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.929231 [3] 余若峰, 杨威, 付耀文, 等. 面向不同雷达任务的认知波形优化综述[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(3): 726–752. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211068YU Ruofeng, YANG Wei, FU Yaowen, et al. A review on cognitive waveform optimization for different radar missions[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(3): 726–752. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211068 [4] LEVANON N and MOZESON E. Radar Signals[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2004: 7–9. [5] CUI Guolong, FU Yue, YU Xianxiang, et al. Local ambiguity function shaping via uni-modular sequence design[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(7): 977–981. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2017.2700396 [6] HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/msp.2006.1593335 [7] ARLERY F, KASSAB R, TAN U, et al. Efficient gradient method for locally optimizing the periodic/aperiodic ambiguity function[C]. IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6 [8] ARLERY F, KASSAB R, TAN U, et al. Efficient optimization of the ambiguity functions of multi-static radar waveforms[C]. 17th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Krakow, Poland, 2016: 1–6. [9] WANG Fulai, FENG Sijia, YIN Jiapeng, et al. Unimodular sequence and receiving filter design for local ambiguity function shaping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5113012. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3171253 [10] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, JIANG Bo, et al. Ambiguity function shaping for cognitive radar via complex quartic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(22): 5603–5619. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273885 [11] QIU Xiangfeng, JIANG Weidong, ZHANG Xinyu, et al. Quartic riemannian trust region algorithm for cognitive radar ambiguity function shaping[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4022005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3151679 [12] WU Linlong, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Cognitive radar-based sequence design via sinr maximization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 779–793. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2016.2621723 [13] HE Hao, STOICA P, and LI Jian. On synthesizing cross ambiguity functions[C]. IEEE Internationl Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 3536–3539 [14] CHEN Zihao, LIANG Junli, WANG Tao, et al. Generalized MBI algorithm for designing sequence set and mismatched filter bank with ambiguity function constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 2918–2933. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3181346 [15] HE Hao, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems: A Computational Approach[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 106–121. [16] SOLTANALIAN M, TANG Bo, LI Jian, et al. Joint design of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(5): 423–426. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2013.2250279 [17] ESMAEILI-NAJAFABADI H, LEUNG H, and MOO P W. Unimodular waveform design with desired ambiguity function for cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2489–2496. doi: 10.1109/taes.2019.2942411 [18] 付月, 崔国龙, 余显祥. 信号相关杂波背景下稳健的恒模序列与接收滤波器设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 292–299. doi: 10.12000/JR16158FU Yue, CUI Guolong, and YU Xianxiang. Robust design of constant modulus sequence and receiver filter in the presence of signal-dependent clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 292–299. doi: 10.12000/JR16158 [19] LIU Tianjun, FAN Pingzhi, ZHOU Zhengchun, et al. Unimodular sequence design with good local auto- and cross-ambiguity function for MSPSR system[C], IEEE 89th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Spring), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2019: 1–5. [20] WU Linlong, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Transmit waveform/receive filter design for MIMO radar with multiple waveform constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(6): 1526–1540. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2017.2787115 [21] 邱祥风, 姜卫东, 张新禹, 等. 认知MIMO雷达发射波形与接收滤波器联合优化设计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(2): 386–393. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.02.08QIU Xiangfeng, JIANG Weidong, ZHANG Xinyu, et al. Joint optimization design method for cognitive MIMO radar transmit waveform and receive filter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 386–393. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.02.08 [22] AUBRY A, DEMAIO A, FARINA A, et al. Knowledge-aided (potentially cognitive) transmit signal and receive filter design in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 93–117. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404093 [23] SOLTANALIAN M and STOICA P. Designing unimodular codes via quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(5): 1221–1234. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2013.2296883 [24] GHARANJIK A, SOLTANALIAN M, SHANKAR M R B, et al. Grab-n-Pull: A max-min fractional quadratic programming framework with applications in signal and information processing[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 160: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.02.006 [25] TROPP J A, DHILLON I S, HEATH R W, et al. Designing structured tight frames via an alternating projection method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(1): 188–209. doi: 10.1109/tit.2004.839492 [26] 张贤达. 矩阵分析与应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013: 447–450.ZHANG Xianda. Matrix Analysis and Applications[M]. 2nd ed, Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013: 447–450. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: