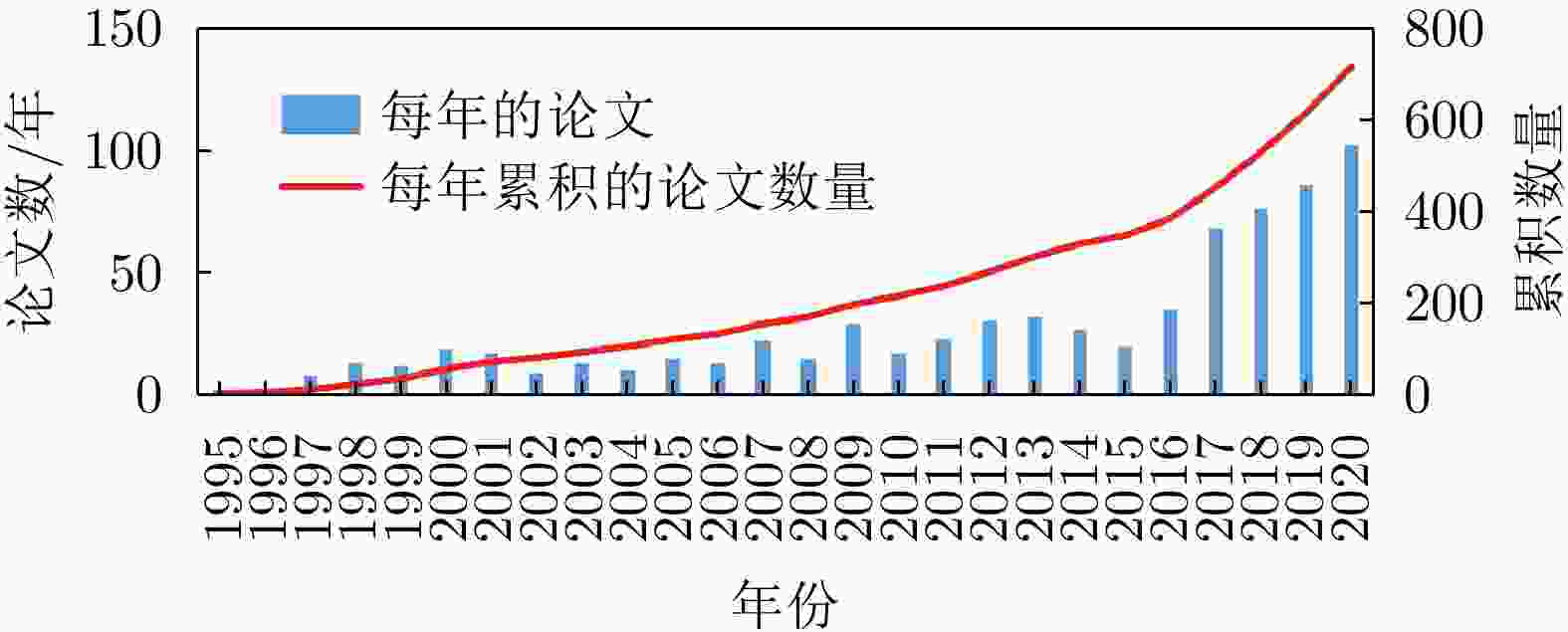
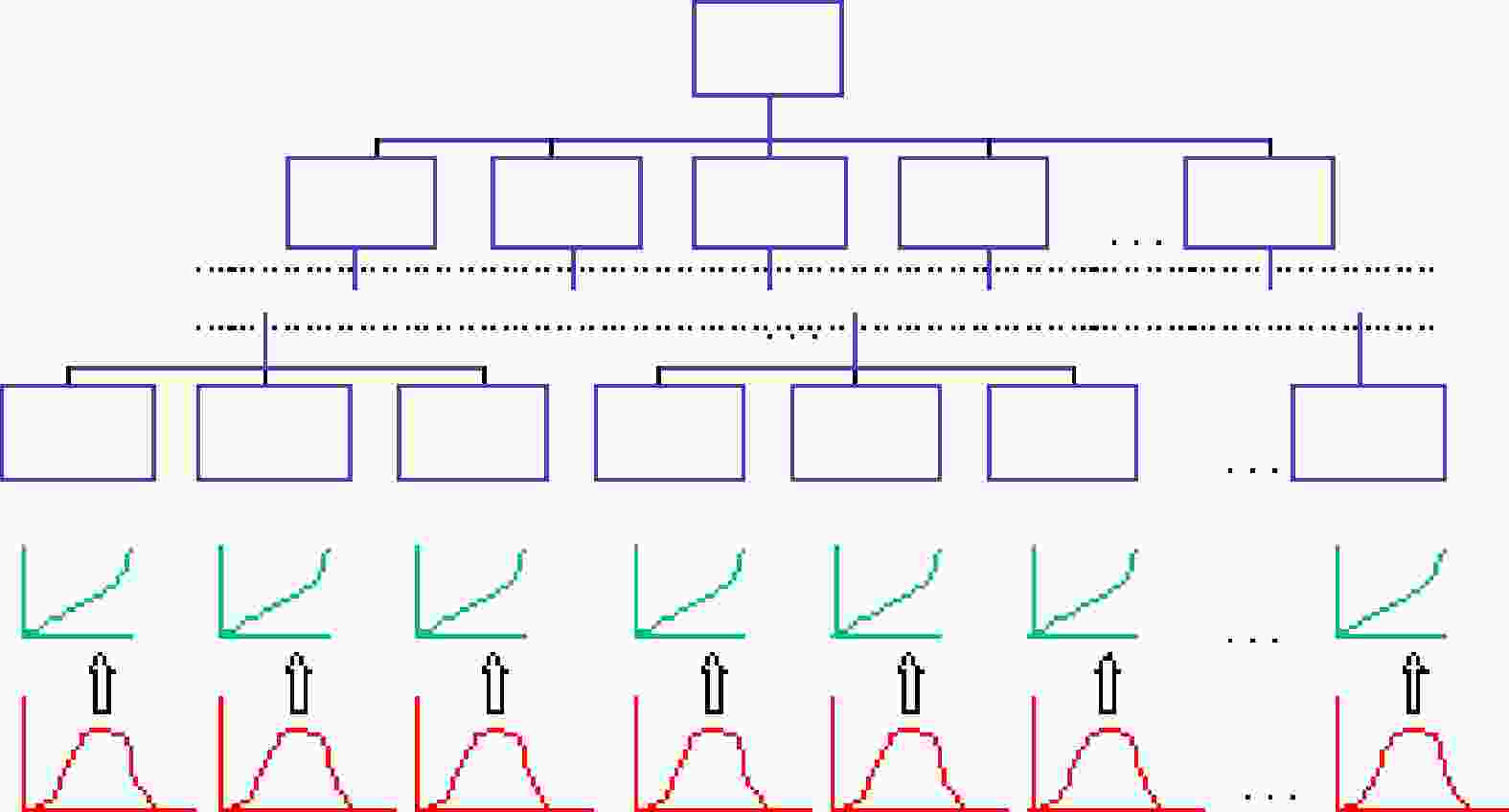
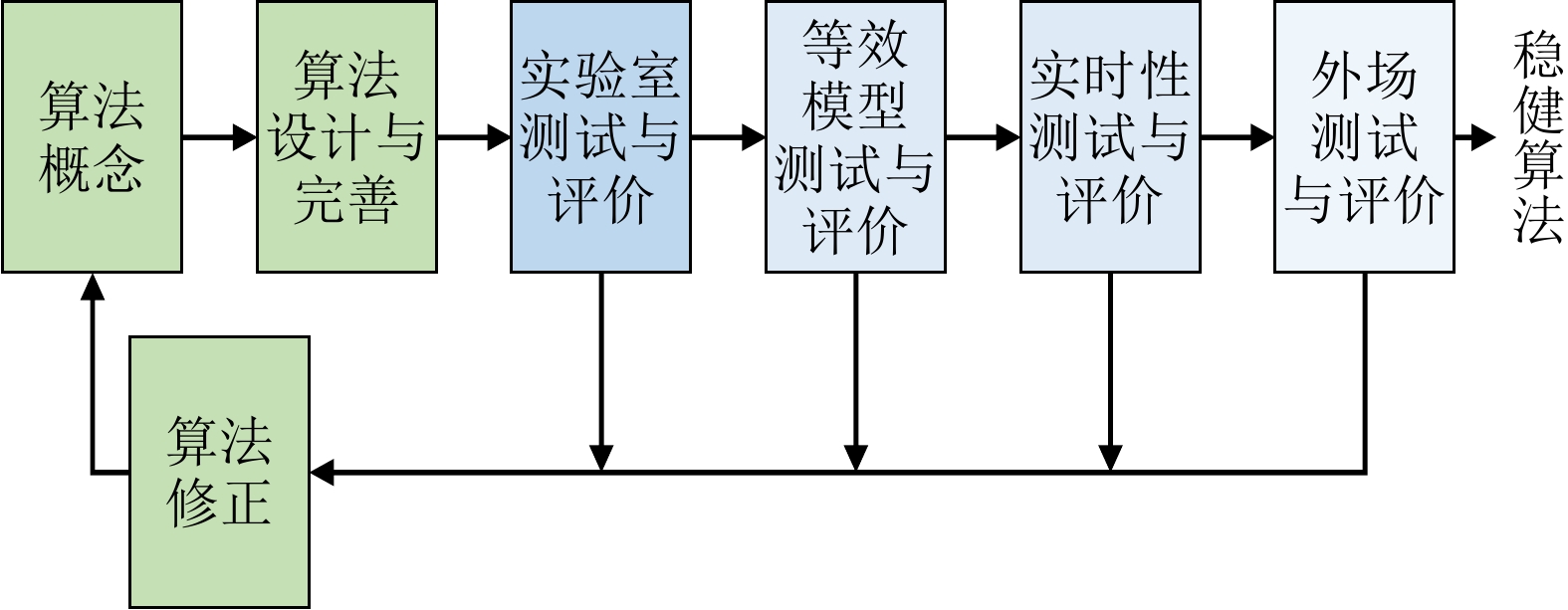
-
摘要: 自动目标识别(ATR)是一个汇集模式识别、人工智能、信息处理等多学科融合发展的技术领域,ATR评价则是将ATR算法/系统等作为研究对象的评价行为。由于ATR算法/系统面临目标非合作、工作条件复杂多样、决策者自身存在多种主观偏好等诸多困难,ATR评价贯穿ATR研制的全过程,对ATR技术发展起到重要的指导作用。该文首先阐述了ATR评价方法研究的内涵,简要回顾ATR技术发展;然后从性能指标定义、测试条件构建、推断与决策等方面详细梳理分析了ATR评价方法研究的成果、应用及最新研究进展;最后总结了若干ATR评价方法研究的发展方向。该文旨在为更好地理解ATR评价和有效使用ATR评价方法提供新的参考借鉴。Abstract: Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) is an interdisciplinary technological field related to pattern recognition, artificial intelligence, and information processing. ATR evaluation focuses on accessing ATR algorithms and systems. Due to the noncooperative targets, complex operating conditions, and multiple subjective preferences of the decision maker, ATR evaluation is performed for the entire ATR research process and shows its importance in guiding ATR development. This paper presents the connotation of ATR evaluation and briefly reviews ATR development. Furthermore, the conventional methods, applications, and latest developments in ATR evaluation are presented and discussed from the perspective of performance measures, test condition, inference and decision. Finally, several ATR evaluation research directions are summarized. This paper serves as a valuable reference for a better understanding of ATR evaluation and the effective adoption of various ATR evaluation methods.
-
表 1 常见ATR识别性能指标
Table 1. Common ATR performance measures
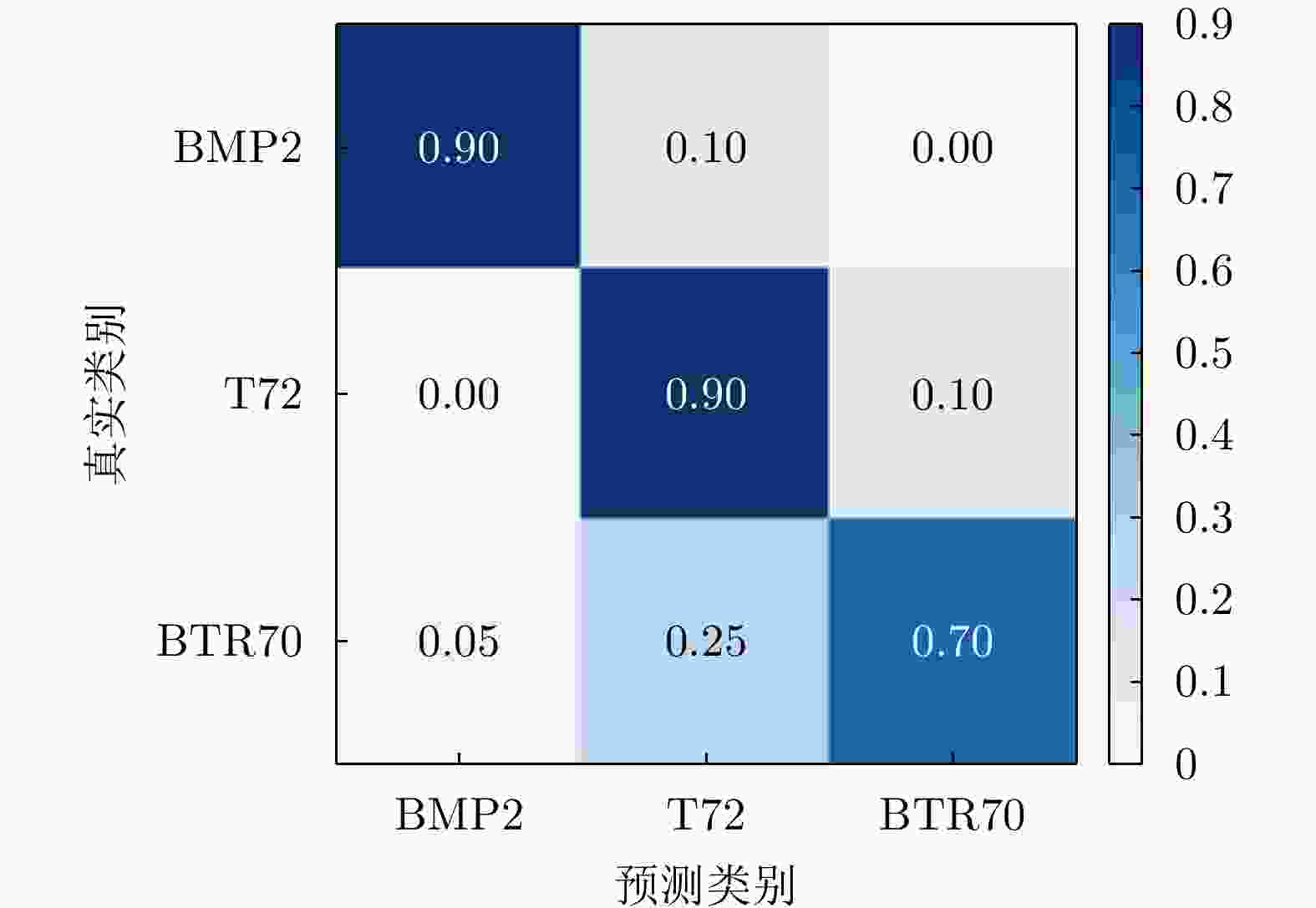
形式 典型代表 使用要点 适用范围 优/缺点 表格 混淆矩阵 每行数据记录一类目标被正确识别或错误混淆的情况 任意m类目标的分类性能评价 优点:记录所有目标类型之间的相互区分结果
缺点:目标类型数m较大时展示效果不直观概率 检测概率PD
虚警概率PFA
种类识别概率PCC
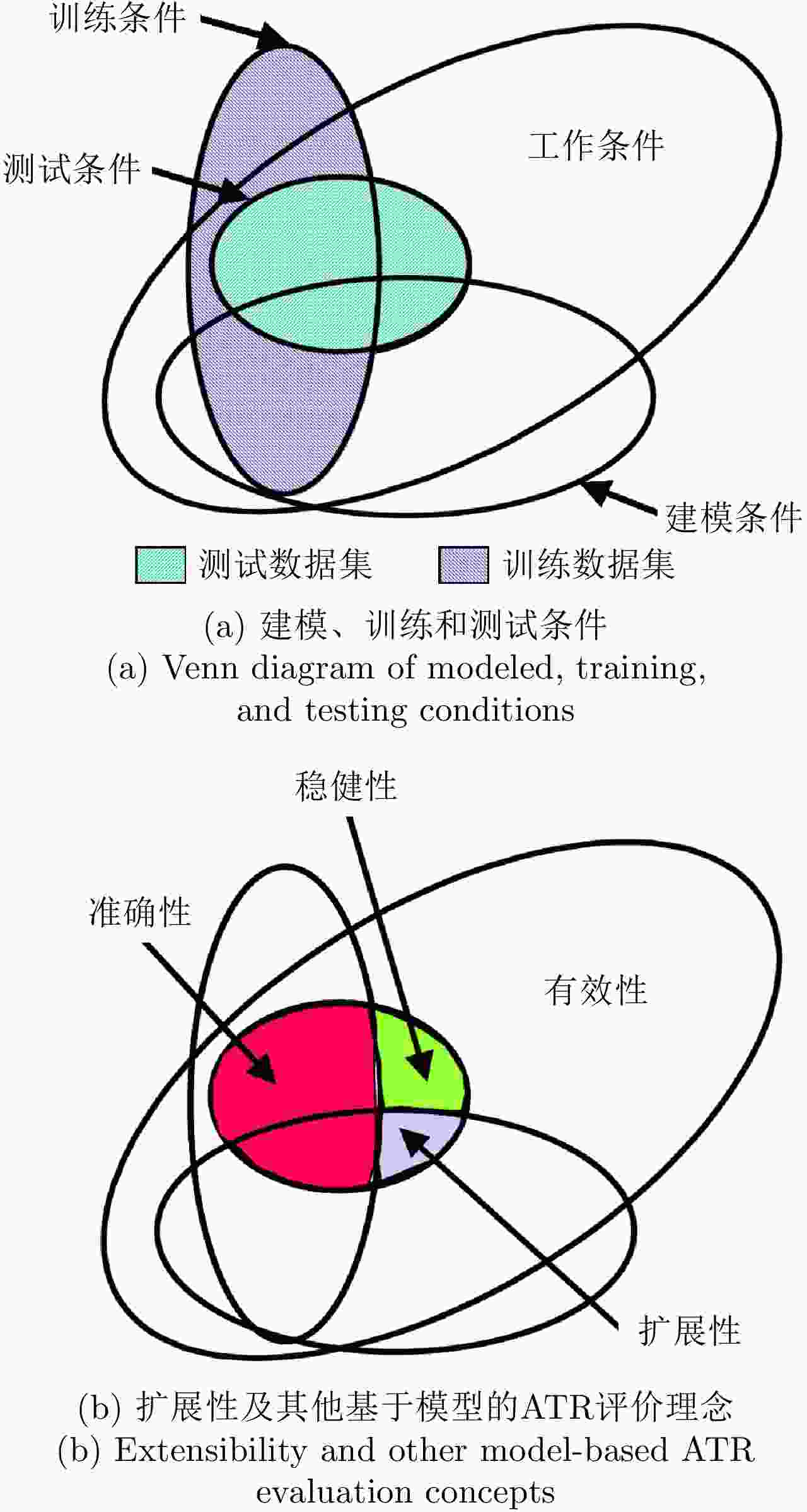
类型识别概率PID逐级识别过程中特定事件的发生概率 目标识别过程中某个决策任务结果的不确定性度量 优点:内涵清晰,指标点估计值计算简单
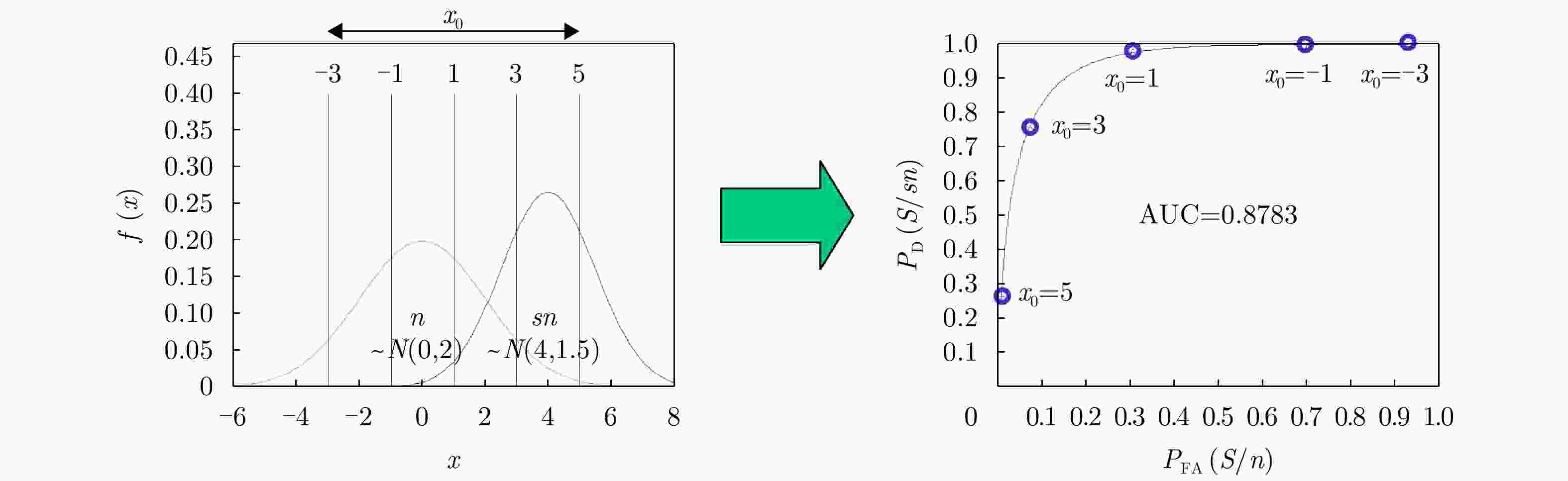
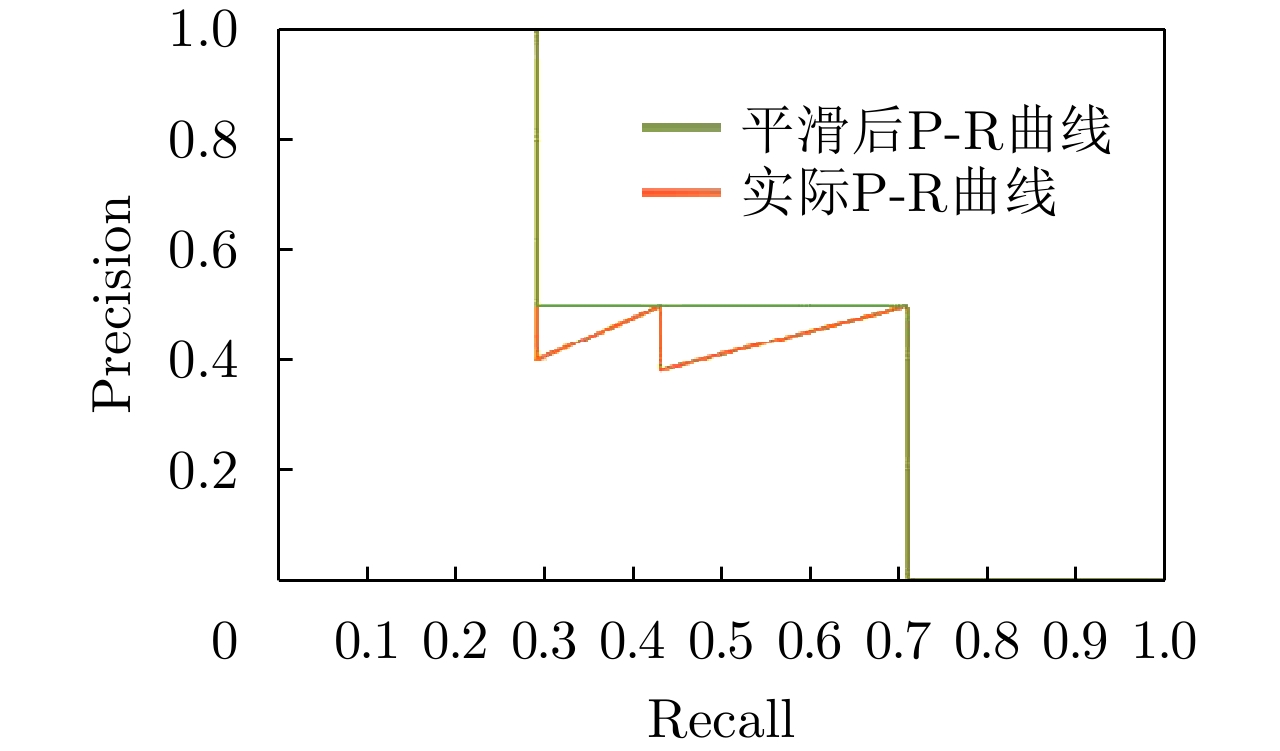
缺点:需要根据多次目标识别试验进行统计推断曲线 ROC曲线
P-R曲线转换为AUC, AP采用下面积、曲线积分的形式度量 相互制约的两方面
性能综合刻画优点:综合评价阈值变化对两个相互制约指标的影响
缺点:需调整阈值进行量化,精度受阈值离散取值的影响 -
[1] BHANU B, DUDGEON D E, ZELNIO E G, et al. Guest editorial introduction to the special issue on automatic target detection and recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 1–6. doi: 10.1109/TIP.1997.552076 [2] 胡卫东. 雷达目标识别技术的再认识[J]. 现代雷达, 2012, 34(8): 1–5. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2012.08.004HU Weidong. Restudy on the technique of radar target recognition[J]. Modern Radar, 2012, 34(8): 1–5. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2012.08.004 [3] 郁文贤. 自动目标识别的工程视角述评[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 737–752. doi: 10.12000/JR22178YU Wenxian. Automatic target recognition from an engineering perspective[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 737–752. doi: 10.12000/JR22178 [4] 张天序. 成像自动目标识别[M]. 武汉: 湖北科学技术出版社, 2005.ZHANG Tianxu. Automated Recognition of Imaged Targets[M]. Wuhan: Hubei Science and Technology Press, 2005. [5] ROSS T D and MOSSING J C. The MSTAR evaluation methodology[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 705–713. [6] ROSS T D. Confidence intervals for ATR performance metrics[C]. SPIE 4382, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VIII, Orlando, USA, 2001: 318–329. [7] MOSSING J C and ROSS T D. Evaluation of SAR ATR algorithm performance sensitivity to MSTAR extended operating conditions[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 554–565. [8] ROSS T D and MINARDI M E. Discrimination and confidence error in detector-reported scores[C]. SPIE 5427, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XI, Orlando, USA, 2004: 342–353. [9] ROSS T D, WESTERKAMP L A, ZELNIO E G, et al. Extensibility and other model-based ATR evaluation concepts[C]. SPIE 3070, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery IV, Orlando, USA, 1997: 554–565. [10] ROSS T D, BRADLEY J J, HUDSON L J, et al. SAR ATR: So what’s the problem? An MSTAR perspective[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 662–672. [11] ROSS T D, WORRELL S W, VELTEN V J, et al. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 566–573. [12] 李彦鹏. 自动目标识别效果评估——基础、理论体系及相关研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2004.LI Yanpeng. Performance evaluation in automatic target recognition—foundation, theoretic system and related research[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2004. [13] LI Yanpeng, LI Xiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. A compact methodology to understand, evaluate, and predict the performance of automatic target recognition[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(7): 11308–11350. doi: 10.3390/s140711308 [14] LI Yanpeng, SHU Shaoxian, and HE Meisheng. Fuzzy run theory and its application in performance evaluation of automatic target recognition[C]. The 9th International Symposium on Next Generation Electronics, Changsha, China, 2021. [15] KECHAGIAS-STAMATIS O and AOUF N. Evaluating 3D local descriptors for future LIDAR missiles with automatic target recognition capabilities[J]. The Imaging Science Journal, 2017, 65(7): 428–437. doi: 10.1080/13682199.2017.1361665 [16] SHARMA S, GUPTA S, GUPTA D, et al. Performance evaluation of the deep learning based convolutional neural network approach for the recognition of chest X-ray images[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12: 932496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.932496 [17] GUO Ming, LI Biao, SHAO Zhaoqun, et al. Objective image fusion evaluation method for target recognition based on target quality factor[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2022, 28(2): 495–510. doi: 10.1007/s00530-021-00850-1 [18] 齐振, 程广涛, 张友奎, 等. 基于信息熵的水声目标识别模型评估方法[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(6): 134–137. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.06.025QI Zhen, CHENG Guangtao, ZHANG Youkui, et al. Researching on evaluation method of acoustic target recognition models based on information entropy[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(6): 134–137. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2021.06.025 [19] 贺文涛, 黄学宇. 工程应用中的目标识别方法评估研究[J]. 工业控制计算机, 2020, 33(11): 78–79, 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2020.11.031HE Wentao and HUANG Xueyu. Research on evaluation of target recognition method in engineering application[J]. Industrial Control Computer, 2020, 33(11): 78–79, 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-182X.2020.11.031 [20] 周颖, 张兴敢, 王琼. 雷达目标识别算法性能优化与评估系统[J]. 南京大学学报:自然科学, 2017, 53(6): 1187–1193. doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2017.06.021ZHOU Ying, ZHANG Xinggan, and WANG Qiong. Performance optimization and evaluation system for radar target recognition algorithm[J]. Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Science, 2017, 53(6): 1187–1193. doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2017.06.021 [21] 何峻, 肖立, 刘峥, 等. ATR系统评价中的因素作用测算方法及应用[J]. 运筹与管理, 2010, 19(2): 56–62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2010.02.010HE Jun, XIAO Li, LIU Zheng, et al. A factor effect measuring method and its application in ATR system evaluation[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2010, 19(2): 56–62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2010.02.010 [22] 刘红娅, 贾鑫. 基于目标跟踪识别的ISAR干扰效果评估[J]. 运筹与管理, 2010, 19(6): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2010.06.026LIU Hongya and JIA Xin. Assessment of ISAR jamming effectiveness based on target tracking and recognizing[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2010, 19(6): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2010.06.026 [23] 庄钊文, 黎湘, 李彦鹏, 等. 自动目标识别效果评估技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2006.ZHUANG Zhaowen, LI Xiang, LI Yanpeng, et al. Performance Evaluation Technology for Automatic Target Recognition[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2006. [24] 刘伟. 自动目标识别系统效能评估方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2007.LIU Wei. Research on performance evaluation methods of automatic target recognition system[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2007. [25] 何峻. 自动目标识别评估方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2009.HE Jun. Research on automatic target recognition evaluation method[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2009. [26] 秦富童. 遥感图像目标识别效果评估研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2010.QIN Futong. Research on performance evaluation for target recognition on remote image[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2010. [27] 付强, 何峻. 自动目标识别评估方法及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.FU Qiang and HE Jun. Automatic Target Recognition Evaluation Method and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. [28] 吕金建, 丁建江, 阮崇籍, 等. 自动目标识别(ATR)算法评估研究综述[J]. 电光与控制, 2011, 18(9): 48–52, 77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2011.09.011LÜ Jinjian, DING Jianjiang, RUAN Chongji, et al. Study on ATR algorithm evaluation: A survey[J]. Electronics Optics&Control, 2011, 18(9): 48–52, 77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2011.09.011 [29] NEBABIN V G. Methods and Techniques of Radar Recognition[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1994. [30] DIEMUNSCH J R and WISSINGER J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 481–492. [31] WISSINGER J, WASHBURN R B, FRIEDLAND N S, et al. Search algorithms for model-based SAR ATR[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 279–93. [32] GILMORE J F. Knowledge-based target recognition system evolution[J]. Optical Engineering, 1991, 30(5): 557–570. doi: 10.1117/12.55829 [33] 邓志鸿, 唐世渭, 张铭, 等. Ontology研究综述[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 38(5): 730–738. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2002.05.022DENG Zhihong, TANG Shiwei, ZHANG Ming, et al. Overview of Ontology[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2002, 38(5): 730–738. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2002.05.022 [34] KEIM D A. Information visualization and visual data mining[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2002, 8(1): 1–8. doi: 10.1109/2945.981847 [35] STEINBERG A N. Context-sensitive data fusion using structural equation modeling[C]. The 12th International Conference on Information Fusion, Seattle, USA, 2009: 725–731. [36] ERNISSE B E, ROGERS S K, DESIMIO M P, et al. Complete automatic target cuer/recognition system for tactical forward-looking infrared images[J]. Optical Engineering, 1997, 36(9): 2593–2603. doi: 10.1117/1.601484 [37] INGGS M R and ROBINSON A D. Ship target recognition using low resolution radar and neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(2): 386–393. doi: 10.1109/7.766923 [38] NING Wu, CHEN Wugun, and ZHANG Xinggan. Automatic target recognition of ISAR object images based on neural network[C]. International Conference on Neural Networks and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 2003: 373–376. [39] AVCI E and COTELI R. A new automatic target recognition system based on wavelet extreme learning machine[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(16): 12340–12348. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.04.012 [40] DONG Shi, WANG Ping, and ABBAS K. A survey on deep learning and its applications[J]. Computer Science Review, 2021, 40: 100379. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100379 [41] DARGAN S, KUMAR M, AYYAGARI M R, et al. A survey of deep learning and its applications: A new paradigm to machine learning[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2020, 27(4): 1071–1092. doi: 10.1007/s11831-019-09344-w [42] ZHAI Yikui, DENG Wenbo, XU Ying, et al. Robust SAR automatic target recognition based on transferred MS-CNN with L2-regularization[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2019, 2019: 9140167. doi: 10.1155/2019/9140167 [43] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [44] ZHU Xiaoxiang, MONTAZERI S, ALI M, et al. Deep learning meets SAR: Concepts, models, pitfalls, and perspectives[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2021, 9(4): 143–172. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2020.3046356 [45] NEUPANE D and SEOK J. A review on deep learning-based approaches for automatic sonar target recognition[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(11): 1972. doi: 10.3390/electronics9111972 [46] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037 [47] POUYANFAR S, SADIQ S, YAN Yilin, et al. A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2019, 51(5): 92. doi: 10.1145/3234150 [48] 王容川, 庄志洪, 王宏波, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的雷达目标HRRP分类识别方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007WANG Rongchuan, ZHUANG Zhihong, WANG Hongbo, et al. HRRP classification and recognition method of radar target based on convolutional neural network[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007 [49] PAN Mian, LIU Ailin, YU Yanzhen, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition model based on a stacked CNN-Bi-RNN with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5100814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3055061 [50] 贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899 [51] DING Baiyuan, WEN Gongjian, MA Conghui, et al. An efficient and robust framework for SAR target recognition by hierarchically fusing global and local features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(12): 5983–5995. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2863046 [52] ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264 [53] LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137 [54] FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, ZHANG Linbin, et al. SAR target classification based on integration of ASC parts model and deep learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10213–10225. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3116979 [55] 喻玲娟, 王亚东, 谢晓春, 等. 基于FCNN和ICAE的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066YU Lingjuan, WANG Yadong, XIE Xiaochun, et al. SAR ATR based on FCNN and ICAE[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066 [56] FANG Houzhang, XIA Mingjiang, ZHOU Gang, et al. Infrared small UAV target detection based on residual image prediction via global and local dilated residual networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 7002305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3085495 [57] LI Boyang, XIAO Chao, WANG Longguang, et al. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1745–1758. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3199107 [58] DU Jinming, LU Huanzhang, HU Moufa, et al. CNN-based infrared dim small target detection algorithm using target-oriented shallow-deep features and effective small anchor[J]. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(1): 1–15. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12001 [59] LI Rui, WANG Xiaodan, WANG Jian, et al. SAR target recognition based on efficient fully convolutional attention block CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4005905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3037256 [60] GOEL A, AGARWAL A, VATSA M, et al. DNDNet: Reconfiguring CNN for adversarial robustness[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 103–110. [61] HUANG Teng, ZHANG Qixiang, LIU Jiabao, et al. Adversarial attacks on deep-learning-based SAR image target recognition[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 162: 102632. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102632 [62] ZHANG Qinghao. Improvement of online game anti-cheat system based on deep Learning[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Education, Chongqing, China, 2021: 652–655. [63] HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for SAR target classification with limited labeled data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(9): 907. doi: 10.3390/rs9090907 [64] MALMGREN-HANSEN D, KUSK A, DALL J, et al. Improving SAR automatic target recognition models with transfer learning from simulated data[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1484–1488. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2717486 [65] ZHAO Siyuan, ZHANG Zenghui, ZHANG Tao, et al. Transferable SAR image classification crossing different satellites under open set condition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4506005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3159179 [66] ZHAO Siyuan, ZHANG Zenghui, GUO Weiwei, et al. An automatic ship detection method adapting to different satellites SAR images with feature alignment and compensation loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3160727 [67] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059 [68] 柯有安. 雷达目标识别(上)[J]. 国外电子技术, 1978(4): 22–30.KE Youan. Radar target recognition[J]. Foreign Electronic Technique, 1978(4): 22–30. [69] 郁文贤, 郭桂蓉. ATR的研究现状和发展趋势[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1994(6): 25–32.YU Wenxian and GUO Guirong. The state of the arts of automatic target recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1994(6): 25–32. [70] 郁文贤. 智能化识别方法及其在舰船雷达目标识别系统中的应用[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 1992.YU Wenxian. Intelligent recognition method and its application in ship radar target recognition system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 1992. [71] MOHD M A. Performance characterization and sensitivity analysis of ATR algorithms to scene distortions[C]. SPIE 1957, Architecture, Hardware, and Forward-Looking Infrared Issues in Automatic Target Recognition, Orlando, USA, 1993: 203–214. [72] GU Yuehan, TAO Jiahui, FENG Lipeng, et al. Using VGG16 to military target classification on MSTAR dataset[C]. The 2nd China International SAR Symposium, Shanghai, China, 2021: 1–3. [73] BASSHAM C B. Automatic target recognition classification system evaluation methodology[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Air Force Institute of Technology, 2002. [74] ALEMAYEHU D and ZOU K H. Applications of ROC analysis in medical research: Recent developments and future directions[J]. Academic Radiology, 2012, 19(12): 1457–1464. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.09.006 [75] KAMARUDIN A N, COX T, and KOLAMUNNAGE-DONA R. Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: Current methods and applications[J]. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 2017, 17(1): 53. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0332-6 [76] 孙长亮. 基于ROC曲线的ATR算法性能评估方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2006.SUN Changliang. Study of ATR algorithm performance evaluation method based on ROC curve[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2006. [77] LIU Li, OUYANG Wanli, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261–318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 [78] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG Jia, SU Hao, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211–252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [79] HOIEM D, CHODPATHUMWAN Y, and DAI Qieyun. Diagnosing error in object detectors[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 340–353. [80] KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 228–242. [81] BLASCH E, MAJUMDER U, ZELNIO E, et al. Review of recent advances in AI/ML using the MSTAR data[C]. SPIE 11393, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVII, 2020. [82] 赵高丽, 宋军平. 联合多特征的MSTAR数据集SAR目标识别方法[J]. 武汉大学学报:工学版, 2022, 55(7): 732–739. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2022-07-012ZHAO Gaoli and SONG Junping. SAR target recognition of MSTAR dataset based on joint use of multiple features[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2022, 55(7): 732–739. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2022-07-012 [83] ROSS T D, BRADLEY J, and O’CONNER M. MSTAR data handbook for experiment planning[R]. AFB, OH: AFRL/SNA with Sverdrup Technology, 1997. [84] KECHAGIAS-STAMATIS O and AOUF N. Automatic target recognition on synthetic aperture radar imagery: A survey[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2021, 36(3): 56–81. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2021.3049857 [85] EVERINGHAM M, VAN GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K I, et al. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [86] EVERINGHAM M, ESLAMI S M A, VAN GOOL L, et al. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(1): 98–136. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5 [87] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. [88] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [89] KUZNETSOVA A, ROM H, ALLDRIN N, et al. The open images dataset V4: Unified image classification, object detection, and visual relationship detection at scale[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(7): 1956–1981. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01316-z [90] GUYON I, MAKHOUL J, SCHWARTZ R, et al. What size test set gives good error rate estimates?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(1): 52–64. doi: 10.1109/34.655649 [91] HE Jun and FU Qiang. Posterior probability calculation procedure for recognition rate comparison[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27(3): 700–711. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2016.00073 [92] VO T M. An 8.25b-ENOB 100kSps 290fJ-FoM asynchronous SAR capacitance to digital converter[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2022, 153: 154286. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2022.154286 [93] KLIMACK W K, BASSHAM C B, and BAUER K W JR. Application of decision analysis to automatic target recognition programmatic decisions[R]. AFIT/EN-TR-02-06, 2002. [94] KLIMACK C B. Hybrid value-utility decision analysis[R]. Operations Research Center of Excellence Technical Report DSE-TR-02-02, 2002. [95] KLIMACK W K. Robustness of multiple objective decision analysis preference functions[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Air Force Institute of Technology, 2002. [96] 仇国芳. 评估决策的信息集结理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安交通大学, 2003.QIU Guofang. A theoretical and methodological study on information aggregation in assessment processes[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2003. [97] 何峻, 赵宏钟, 付强. 基于偏好矩阵的混合型多属性决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(6): 1386–1390. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.06.028HE Jun, ZHAO Hongzhong, and FU Qiang. Method for solving hybrid multiple attribute decision making problems based on preference matrix[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(6): 1386–1390. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.06.028 [98] HE Jun, FU Ruigang, and WANG Guoyan. Prospect value function construction for pattern recognition algorithm’s accuracy metric[C]. 2022 China Automation Congress, Xiamen, China, 2022: 1409–1413. [99] 化盈盈, 张岱墀, 葛仕明. 深度学习模型可解释性的研究进展[J]. 信息安全学报, 2020, 5(3): 1–12. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2020.05.01HUA Yingying, ZHANG Daichi, and GE Shiming. Research progress in the interpretability of deep learning models[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2020, 5(3): 1–12. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2020.05.01 [100] 雷霞, 罗雄麟. 深度学习可解释性研究综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(11): 3588–3602. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021122118LEI Xia and LUO Xionglin. Review on interpretability of deep learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(11): 3588–3602. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021122118 [101] RIBEIRO M T, SINGH S, and GUESTRIN C. “Why should I trust you?”: Explaining the predictions of any classifier[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1135–1144. [102] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336–359. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01228-7 [103] 杜兰, 陈晓阳, 石钰, 等. MMRGait-1.0: 多视角多穿着条件下的雷达时频谱图步态识别数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 892–905. doi: 10.12000/JR22227.DU Lan, CHEN Xiaoyang, SHI Yu, et al. MMRGait-1.0: A radar time-frequency spectrogram dataset for gait recognition under multi-view and multi-wearing conditions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 892–905. doi: 10.12000/JR22227. [104] 陈杰, 黄志祥, 夏润繁, 等. 大规模多类SAR目标检测数据集-1.0[J/OL]. 雷达学报, https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=MSAR, 2022.CHEN Jie, HUANG Zhixiang, XIA Runfan, et al. Large-scale multi-class SAR image target detection dataset-1.0[J/OL]. Journal of Radars, https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=MSAR, 2022. [105] XIA Runfan, CHEN Jie, HUANG Zhixiang, et al. CRTransSar: A visual transformer based on contextual joint representation learning for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(6): 1488. doi: 10.3390/rs14061488 [106] 回丙伟, 宋志勇, 范红旗, 等. 地/空背景下红外图像弱小飞机目标检测跟踪数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(3): 286–297. doi: 10.11922/csdata.2019.0074.zhHUI Bingwei, SONG Zhiyong, FAN Hongqi, et al. A dataset for infrared detection and tracking of dim-small aircraft targets under ground/air background[J]. China Scientific Data, 2020, 5(3): 286–297. doi: 10.11922/csdata.2019.0074.zh [107] 傅瑞罡, 范红旗, 朱永锋, 等. 面向空地应用的红外时敏目标检测跟踪数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2022, 7(2): 206–221. doi: 10.11922/11-6035.csd.2021.0085.zhFU Ruigang, FAN Hongqi, ZHU Yongfeng, et al. A dataset for infrared time-sensitive target detection and tracking for air-ground application[J]. China Scientific Data, 2022, 7(2): 206–221. doi: 10.11922/11-6035.csd.2021.0085.zh [108] 李安然. 面向特定任务的大规模数据集质量高效评估[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2021.LI Anran. Efficient task-oriented quality assessment for large-scale datasets[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2021. [109] SEIDEL H, STAHL C, BJERKELI F, et al. Assessment of COTS IR image simulation tools for ATR development[C]. SPIE 5807, Automatic Target Recognition XV, 2005, Orlando, USA, 2005: 44–54. [110] AHMADIBENI A, JONES B, BOROOSHAK L, et al. Automatic target recognition of aerial vehicles based on synthetic SAR imagery using hybrid stacked denoising auto-encoders[C]. SPIE 11393, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVII, 2020: 71–82. [111] WESTLAKE S T, VOLONAKIS T N, JACKMAN J, et al. Deep learning for automatic target recognition with real and synthetic infrared maritime imagery[C]. SPIE 11543, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Defense Applications II, 2020, Edingburgh, UN. [112] LI Xuesong, LUO Zijuan, YANG Qirui, et al. Airborne infrared imaging simulation for target recognition[J]. IEEE Journal of Radio Frequency Identification, 2022, 6: 846–850. doi: 10.1109/JRFID.2022.3210387 [113] DIVSALAR M, AHMADI M, and NEMATI Y. A SCOR-based model to evaluate LARG supply chain performance using a hybrid MADM method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2022, 69(4): 1101–1120. doi: 10.1109/TEM.2020.2974030 [114] PENA J, NÁPOLES G, and SALGUEIRO Y. Implicit and hybrid methods for attribute weighting in multi-attribute decision-making: A review study[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54(5): 3817–3847. doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09941-3 [115] SONG Jiekun, HE Zeguo, JIANG Lina, et al. Research on hybrid multi-attribute three-way group decision making based on improved VIKOR model[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(15): 2783. doi: 10.3390/math10152783 [116] 张兴贤, 王应明. 一种基于区间信度结构的混合型多属性决策方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(1): 180–188. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.1007ZHANG Xingxian and WANG Yingming. A hybrid multi-attribute decision-making method based on interval belief structure[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(1): 180–188. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.1007 [117] LIU Sen, YU Wei, CHAN F T S, et al. A variable weight-based hybrid approach for multi-attribute group decision making under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2021, 36(2): 1015–1052. doi: 10.1002/int.22329 [118] 江文奇, 降晓璐. 面向属性关联的区间犹豫模糊型PROMETHEE决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3250–3258. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.25JIANG Wenqi and JIANG Xiaolu. Interval hesitant fuzzy PROMETHEE decision method for attribute association[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3250–3258. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.25 [119] 罗承昆, 陈云翔, 顾天一, 等. 基于前景理论和证据推理的混合型多属性决策方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2019, 41(5): 49–55. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201905008LUO Chengkun, CHEN Yunxiang, GU Tianyi, et al. Method for hybrid multi-attribute decision making based on prospect theory and evidential reasoning[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2019, 41(5): 49–55. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201905008 [120] 李明. 不确定多属性决策及其在管理中的应用[M]. 北京: 经济管理出版社, 2021.LI Ming. Uncertain Multiple Attribute Decision Making and Its Application in Management[M]. Beijing: Economic Management Press, 2021. [121] 卜凡康. 制导装置性能评价方法及其应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2020.BU Fankang. Research on performance evaluation method and its application of guidance device[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2020. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: