-
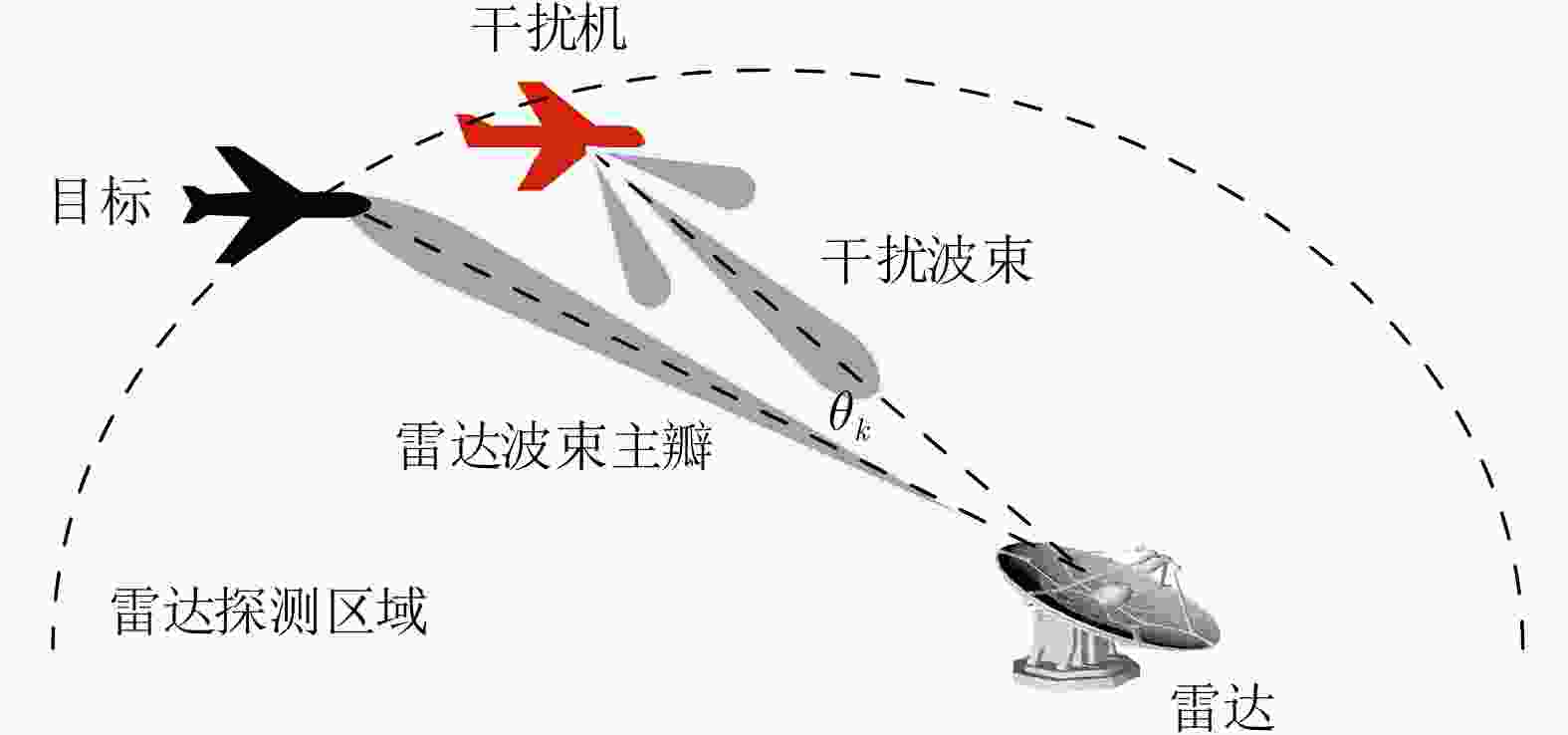
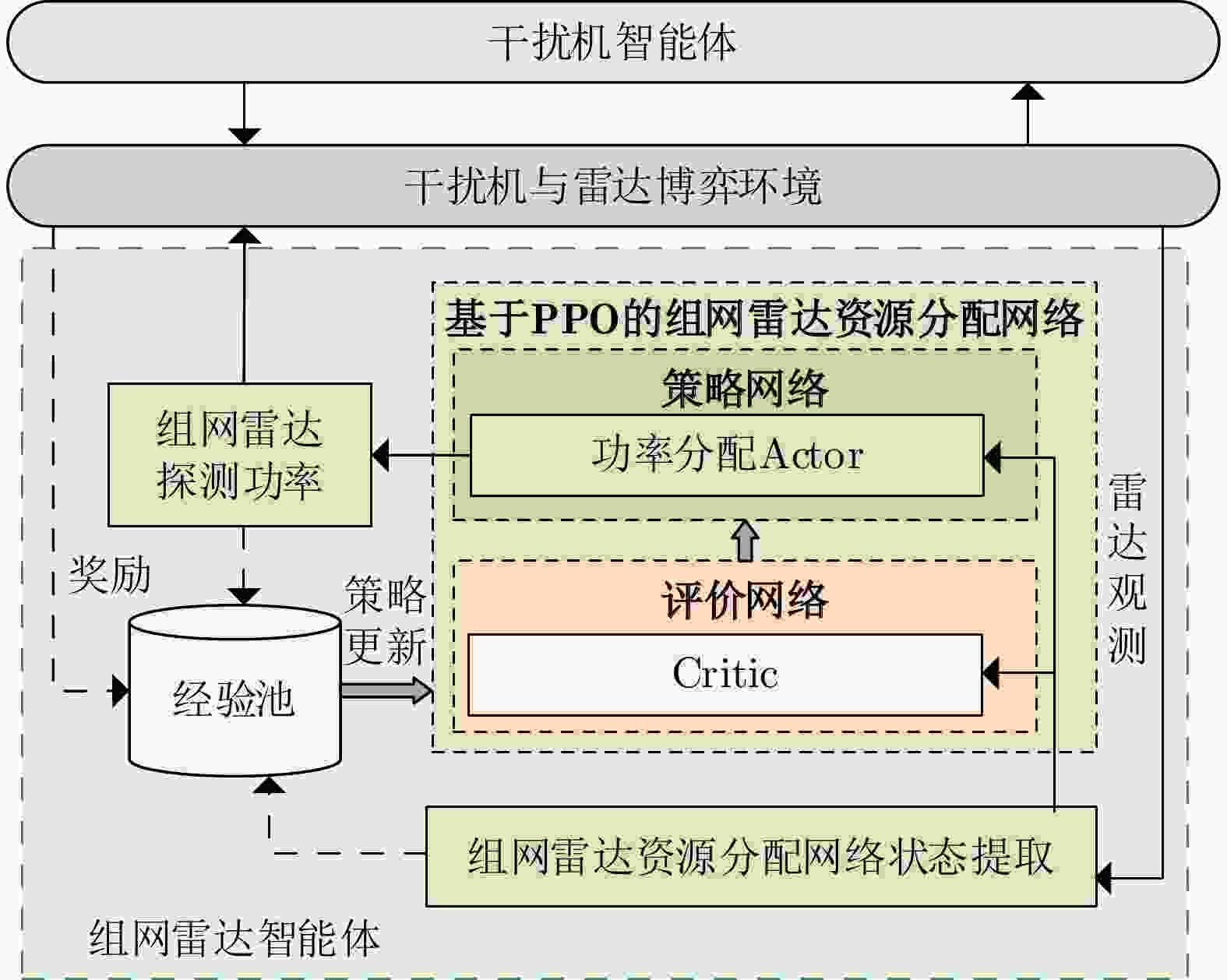
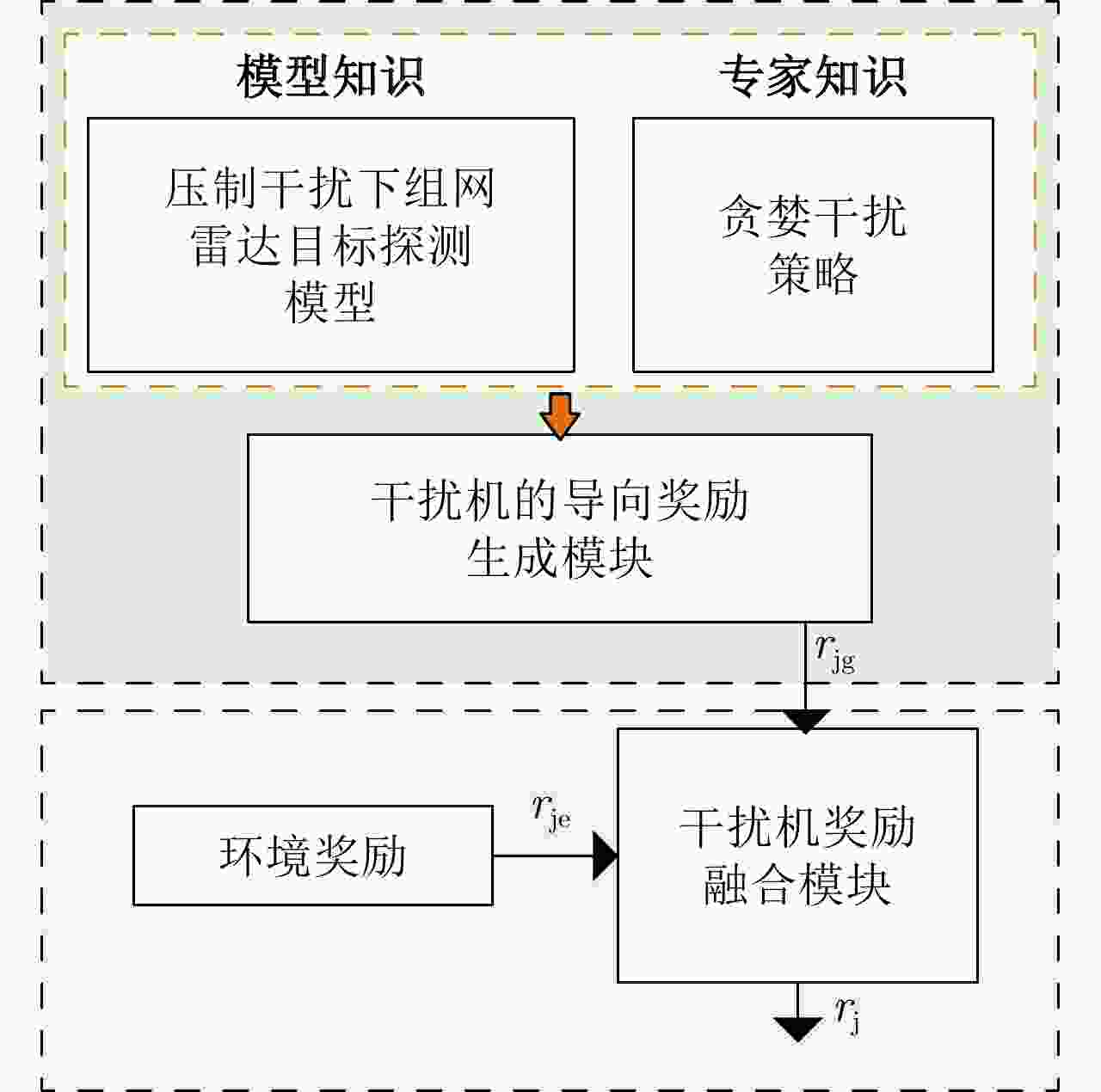
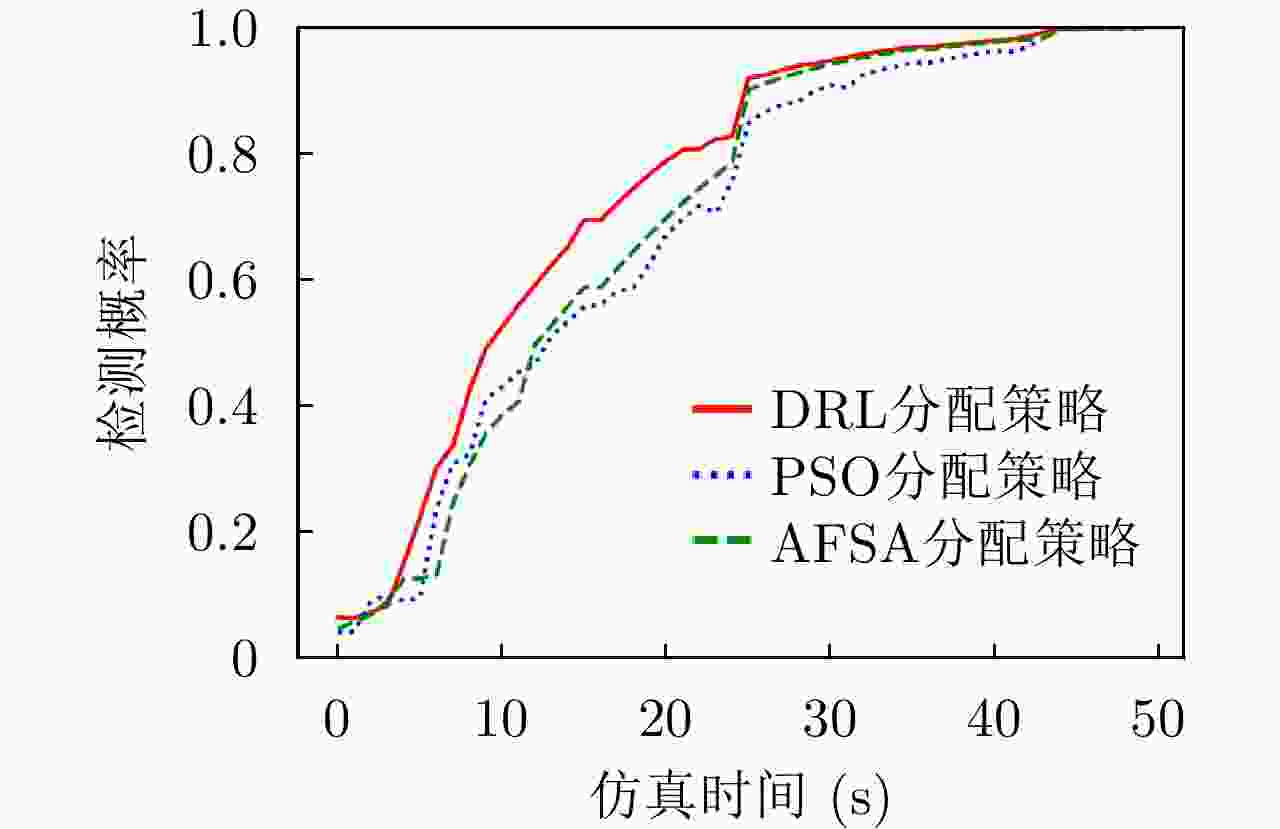
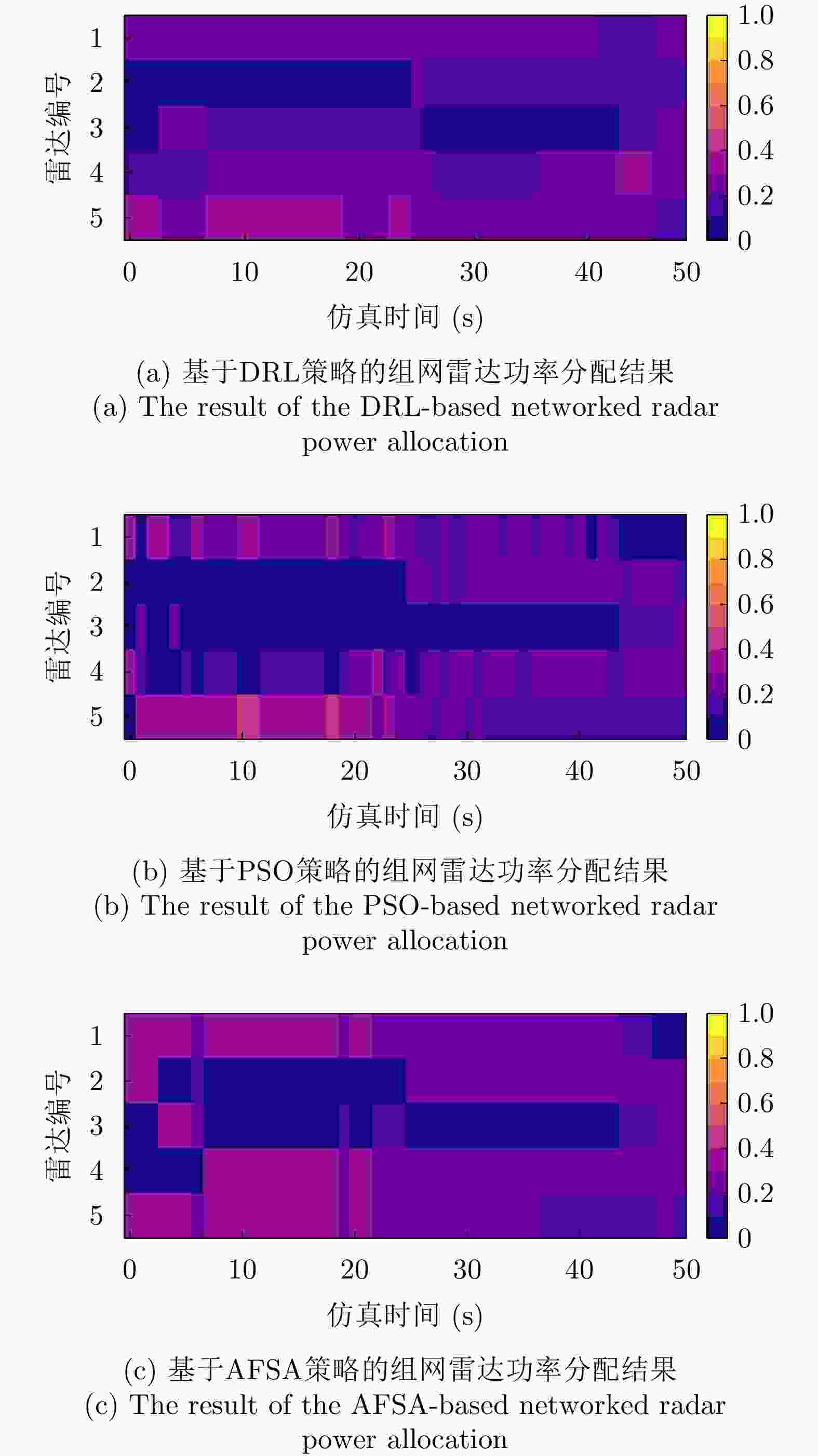
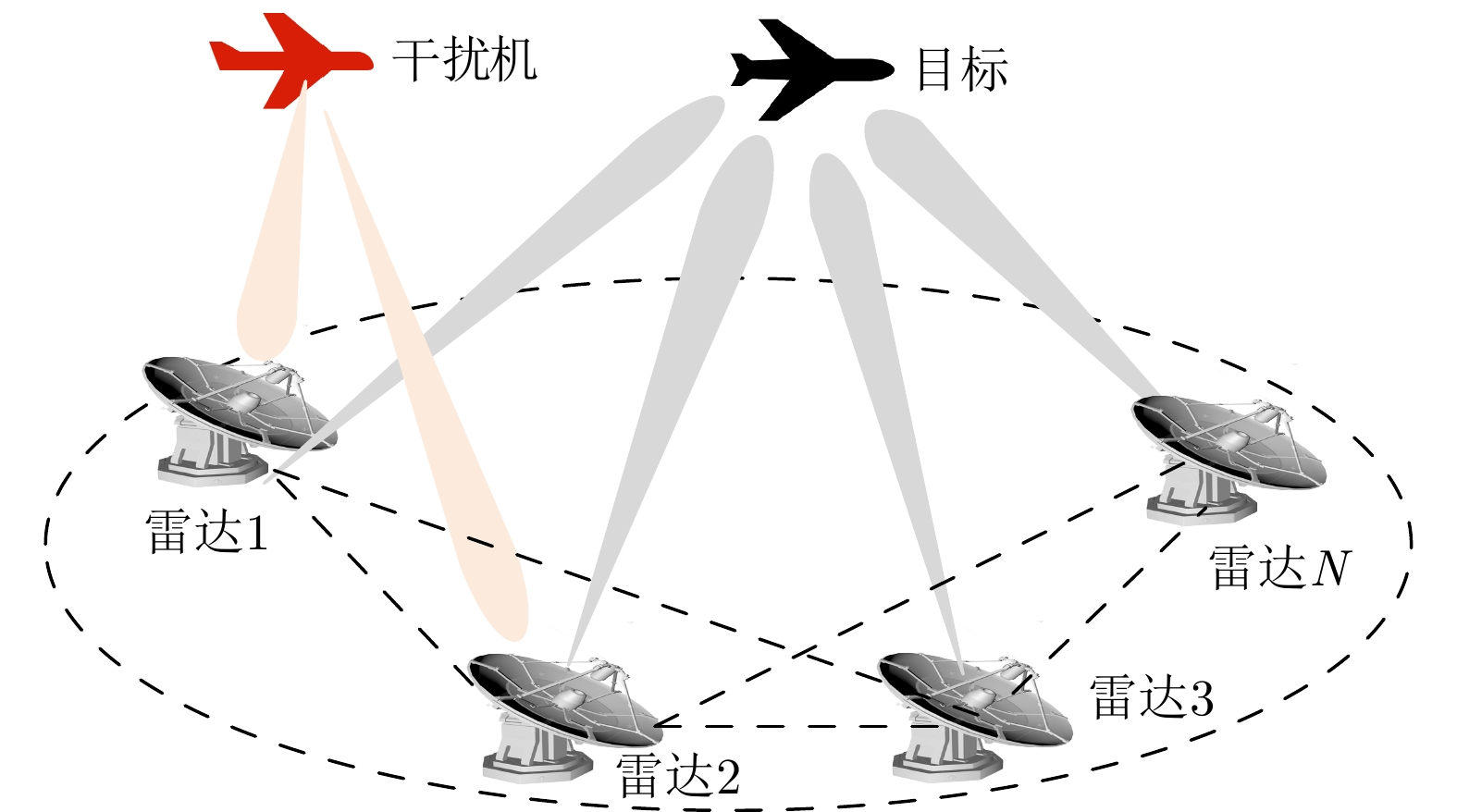
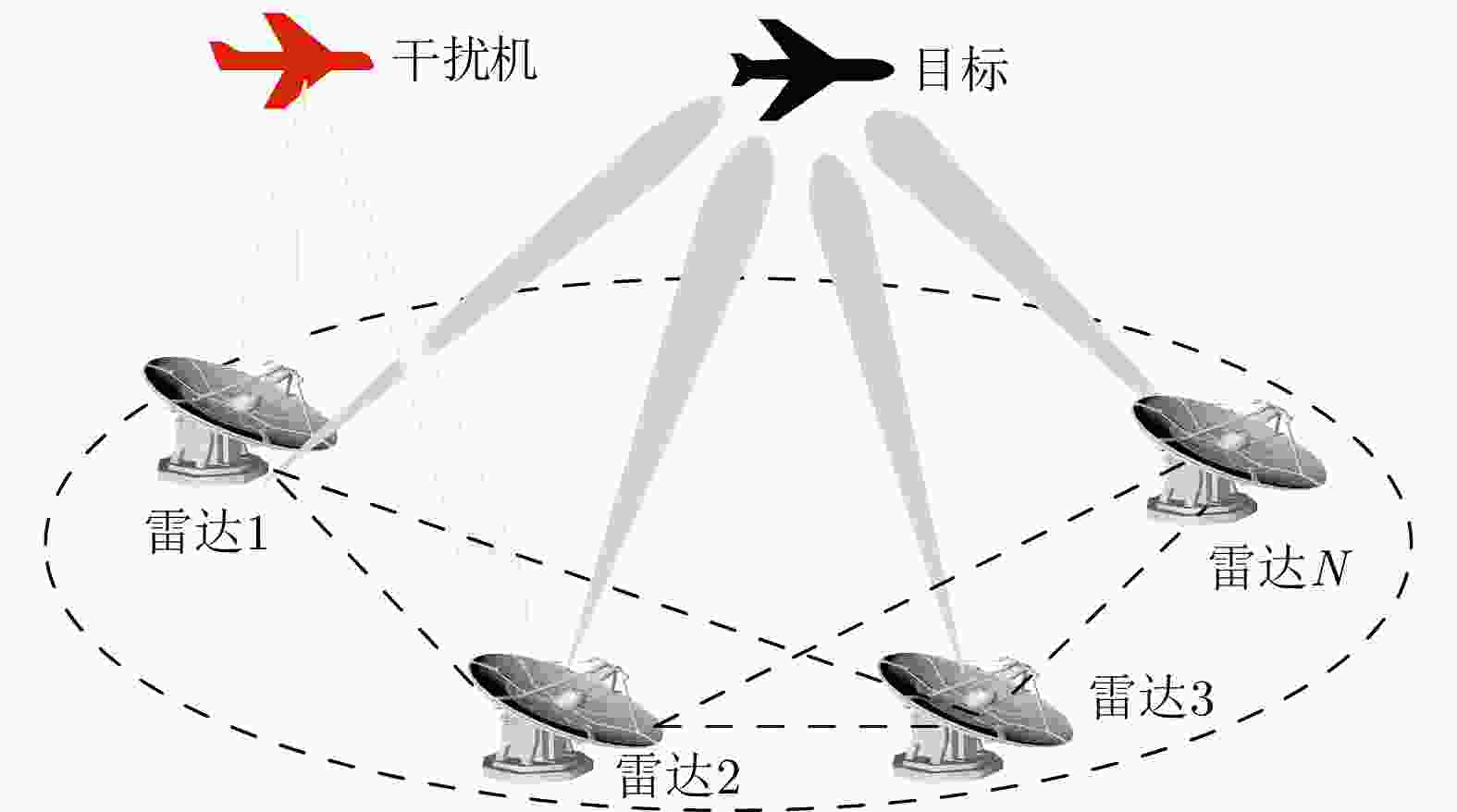
摘要: 传统的组网雷达功率分配一般在干扰模型给定的情况下进行优化,而干扰机资源优化是在雷达功率分配方式给定情况下,这样的研究缺乏博弈和交互。考虑到日益严重的雷达和干扰机相互博弈的作战场景,该文提出了伴随压制干扰下组网雷达功率分配深度博弈问题,其中智能化的目标压制干扰采用深度强化学习(DRL)训练。首先在该问题中干扰机和组网雷达被映射为两个智能体,根据干扰模型和雷达检测模型建立了压制干扰下组网雷达的目标检测模型和最大化目标检测概率优化目标函数。在组网雷达智能体方面,由近端策略优化(PPO)策略网络生成雷达功率分配向量;在干扰机智能体方面,设计了混合策略网络来同时生成波束选择动作和功率分配动作;引入领域知识构建更加有效的奖励函数,目标检测模型、等功率分配策略和贪婪干扰功率分配策略3种领域知识分别用于生成组网雷达智能体和干扰机智能体的导向奖励,从而提高智能体的学习效率和性能。最后采用交替训练方法来学习两个智能体的策略网络参数。实验结果表明;当干扰机采用基于DRL的资源分配策略时,采用基于DRL的组网雷达功率分配在目标检测概率和运行速度两种指标上明显优于基于粒子群的组网雷达功率分配和基于人工鱼群的组网雷达功率分配。Abstract: The traditional networked radar power allocation is typically optimized with a given jamming model, while the jammer resource allocation is optimized with a given radar power allocation method; such research lack gaming and interaction. Given the rising seriousness of combat scenarios in which radars and jammers compete, this study suggests a deep game problem of networked radar power allocation under escort suppression jamming, in which intelligent target jamming is trained using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). First, the jammer and the networked radar are mapped as two agents in this problem. Based on the jamming model and the radar detection model, the target detection model of the networked radar under suppressed jamming and the optimized objective function for maximizing the target detection probability are established. In terms of the networked radar agent, the radar power allocation vector is generated by the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) policy network. In terms of the jammer agent, a hybrid policy network is designed to simultaneously create beam selection and power allocation actions. Domain knowledge is introduced to construct more effective reward functions. Three kinds of domain knowledge, namely target detection model, equal power allocation strategy, and greedy interference power allocation strategy, are employed to produce guided rewards for the networked radar agent and the jammer agent, respectively. Consequently, the learning efficiency and performance of the agent are improved. Lastly, alternating training is used to learn the policy network parameters of both agents. The experimental results show that when the jammer adopts the DRL-based resource allocation strategy, the DRL-based networked radar power allocation is significantly better than the particle swarm-based and the artificial fish swarm-based networked radar power allocation in both target detection probability and run time metrics.
-
表 1 雷达工作参数
Table 1. The working parameters of the radars
参数 数值 参数 数值 发射总功率$P_{\text{r}}^{{\text{total}}}$ 10 mW 工作频率 100 GHz 最小发射功率$P_{\text{r}}^{\min }$ 0 最大发射功率$P_{\text{r}}^{\max }$ 2 mW 天线增益${G_{\text{r} } }$ 45 dB 虚警概率${P_{\text{f}}}$ 10–6 表 2 干扰机工作参数
Table 2. The working parameters of the jammer
参数 数值 参数 数值 干扰总功率$ P_{\text{j}}^{{\text{total}}} $ 60 W 干扰天线增益${G_{\text{j}}}$ 10 dB 最小发射功率$ P_{\text{j}}^{\min } $ 0 最大发射功率$ P_{\text{j}}^{\max } $ 60 W 干扰波束个数L 3 天线波瓣宽度$ {\theta _{0.5}} $ 3° 工作频率 100 GHz 极化失配损失$ {\gamma _{\text{j}}} $ 0.5 表 3 算法参数设置
Table 3. The algorithm parameters setting
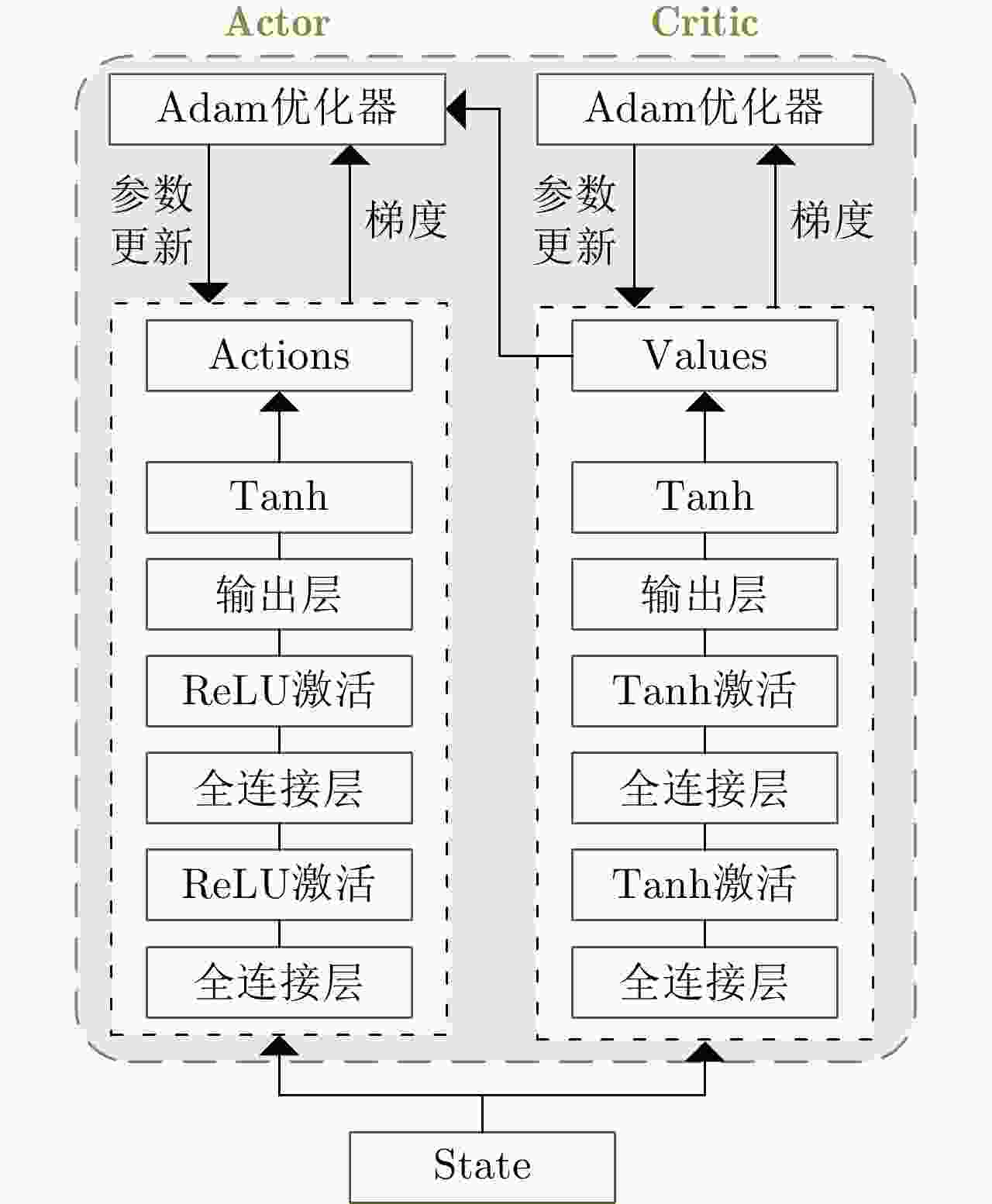
参数 取值 参数 取值 离散Actor的NN层数/节点数 3/128 离散Actor网络学习率 3e–3 连续Actor的NN层数/节点数 3/128 连续Actor网络学习率 3e–3 批量训练样本大小 128 经验回放区大小 1024 Critic网络学习率 3e–3 执行性奖励权重 0.15 PPO裁剪参数 0.2 检测概率奖励权重 0.85 折扣因子 0.998 优化器 Adam 衰减因子$\beta $ 0.9999 导向奖励参数${b_1},{b_2}$ 0.5, 0.1 表 4 各策略的资源调度运行时间
Table 4. The resource scheduling running time of each strategy
调度策略 资源调度运行时间(s) 基于DRL的分配策略 0.009237 基于PSO的分配策略 5.227107 基于AFSA的分配策略 67.365983 -
[1] 郝宇航, 蒋威, 王增福, 等. 分布式MIMO体制天波超视距雷达仿真系统[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20220625.1328.008.html, 2022.HAO Yuhang, JIANG Wei, WANG Zengfu, et al. A distributed MIMO sky-wave over-the-horizon-radar simulation system[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2422.TN.20220625.1328.008.html, 2022. [2] 潘泉, 王增福, 梁彦, 等. 信息融合理论的基本方法与进展(II)[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(10): 1233–1244. doi: 10.7641/j.issn.1000-8152.2012.10.CCTA111336PAN Quan, WANG Zengfu, LIANG Yan, et al. Basic methods and progress of information fusion (II)[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2012, 29(10): 1233–1244. doi: 10.7641/j.issn.1000-8152.2012.10.CCTA111336 [3] WANG Yuedong, LIANG Yan, ZHANG Huixia, et al. Domain knowledge-assisted deep reinforcement learning power allocation for MIMO radar detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(23): 23117–23128. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3211606 [4] 闫实, 贺静, 王跃东, 等. 基于强化学习的多机协同传感器管理[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(8): 1726–1733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.08.12YAN Shi, HE Jing, WANG Yuedong et al. Multi-airborne cooperative sensor management based on reinforcement learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(8): 1726–1733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.08.12 [5] YAN Junkun, JIAO Hao, PU Wenqiang, et al. Radar sensor network resource allocation for fused target tracking: a brief review[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 86/87: 104–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.06.009 [6] 严俊坤, 陈林, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于机会约束的MIMO雷达多波束稳健功率分配算法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(6): 1230–1235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.007YAN Junkun, CHEN Lin, LIU Hongwei, et al. Chance constrained based robust multibeam power allocation algorithm for MIMO radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(6): 1230–1235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.007 [7] 时晨光, 董璟, 周建江. 频谱共存下面向多目标跟踪的组网雷达功率时间联合优化算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 590–601. doi: 10.12000/JR22146SHI Chenguang, DONG Jing, and ZHOU Jianjiang. Joint transmit power and dwell time allocation for multitarget tracking in radar networks under spectral coexistence[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 590–601. doi: 10.12000/JR22146 [8] 程婷, 恒思宇, 李中柱. 基于脉冲交错的分布式雷达组网系统波束驻留调度[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 616–628. doi: 10.12000/JR22211CHENG Ting, HENG Siyu, and LI Zhongzhu. Real-time dwell scheduling algorithm for distributed phased array radar network based on pulse interleaving[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 616–628. doi: 10.12000/JR22211 [9] 孙俊, 张大琳, 易伟. 多机协同干扰组网雷达的资源调度方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2022, 20(3): 237–244, 254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.03.001SUN Jun, ZHANG Dalin, and YI Wei. Resource allocation for multi-Jammer cooperatively jamming netted radar systems[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2022, 20(3): 237–244, 254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2022.03.001 [10] 张大琳, 易伟, 孔令讲. 面向组网雷达干扰任务的多干扰机资源联合优化分配方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 595–606. doi: 10.12000/JR21071ZHANG Dalin, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Optimal joint allocation of multijammer resources for jamming netted radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 595–606. doi: 10.12000/JR21071 [11] 黄星源, 李岩屹. 基于双Q学习算法的干扰资源分配策略[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33(8): 1801–1808. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.20-0253HUANG Xingyuan and LI Yanyi. The allocation of jamming resources based on double Q-learning algorithm[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(8): 1801–1808. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.20-0253 [12] 段燕辉. 雷达智能抗干扰决策方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021.DUAN Yanhui. Research on radar intelligent anti-jamming decision method[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. [13] 宋佰霖, 许华, 齐子森, 等. 一种基于深度强化学习的协同通信干扰决策算法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(6): 1301–1309. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210814SONG Bailin, XU Hua, QI Zisen, et al. A collaborative communication jamming decision algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(6): 1301–1309. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210814 [14] 肖悦, 张贞凯, 杜聪. 基于改进麻雀搜索算法的雷达功率与带宽联合分配算法[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2022(5): 38–43, 92. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220077XIAO Yue, ZHANG Zhenkai, and DU Cong. Joint power and bandwidth allocation of radar based on improved sparrow search algorithm[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2022(5): 38–43, 92. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220077 [15] 靳标, 邝晓飞, 彭宇, 等. 基于合作博弈的组网雷达分布式功率分配方法[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(1): 324776. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24776JIN Biao, KUANG Xiaofei, PENG Yu, et al. Distributed power allocation method for netted radar based on cooperative game theory[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 324776. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24776 [16] SHI Chenguang, WANG Fei, SELLATHURAI M, et al. Non-cooperative game-theoretic distributed power control technique for radar network based on low probability of intercept[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2018, 12(8): 983–991. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2017.0355 [17] 李伟, 王泓霖, 郑家毅, 等. 博弈条件下雷达波形设计策略研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2654–2660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190114LI Wei, WANG Honglin, ZHENG Jiayi, et al. Research on radar waveform design strategy under game condition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2654–2660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190114 [18] HE Jin, WANG Yuedong, LIANG Yan, et al. Learning-based airborne sensor task assignment in unknown dynamic environments[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 111: 104747. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104747 [19] MU Xingchi, ZHAO Xiaohui, and LIANG Hui. Power allocation based on reinforcement learning for MIMO system with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(7): 7622–7633. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2993275 [20] RUMMERY G A and NIRANJAN M. On-Line Q-learning Using Connectionist Systems[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University, 1994: 6–7. [21] LI Jun and SHEN Xiaofeng. Robust jamming resource allocation for cooperatively suppressing multi-station radar systems in multi-jammer systems[C]. 2022 25th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Linköping, Sweden, 2022: 1–8. [22] YAO Zekun, TANG Chuanbin, WANG Chao, et al. Cooperative jamming resource allocation model and algorithm for netted radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2022, 58(22): 834–836. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12611 [23] ZHANG Dalin, SUN Jun, YI Wei, et al. Joint jamming beam and power scheduling for suppressing netted radar system[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021: 1–6. [24] 夏成龙, 李祥, 刘辰烨, 等. 基于深度强化学习的智能干扰方法研究[J]. 电声技术, 2022, 46(5): 144–149. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2022.05.035XIA Chenglong, LI Xiang, LIU Chenye, et al. Reserch of intelligent interference methods based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Audio Engineering, 2022, 46(5): 144–149. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2022.05.035 [25] LIU Weijian, WANG Yongliang, LIU Jun, et al. Performance analysis of adaptive detectors for point targets in subspace interference and Gaussian noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 429–441. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2760718 [26] 王国良, 申绪涧, 汪连栋, 等. 基于秩K融合规则的组网雷达系统干扰效果评估[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2009, 21(23): 7678–7680. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2009.23.017WANG Guoliang, SHEN Xujian, WANG Liandong, et al. Effect evaluation for noise blanket jamming against netted radars Based on Rank-K information fusion rules[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(23): 7678–7680. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2009.23.017 [27] SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018: 327–331. [28] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.53yu.com/abs/1707.06347, 2017. [29] WU Zhaodong, HU Shengliang, LUO Yasong, et al. Optimal distributed cooperative jamming resource allocation for multi-missile threat scenario[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(1): 113–128. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12168 [30] BARTON D K. Radar System Analysis and Modeling[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004: 88–89. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: