Multistation Cooperative Radar Target Recognition Based on an Angle-guided Transformer Fusion Network
-
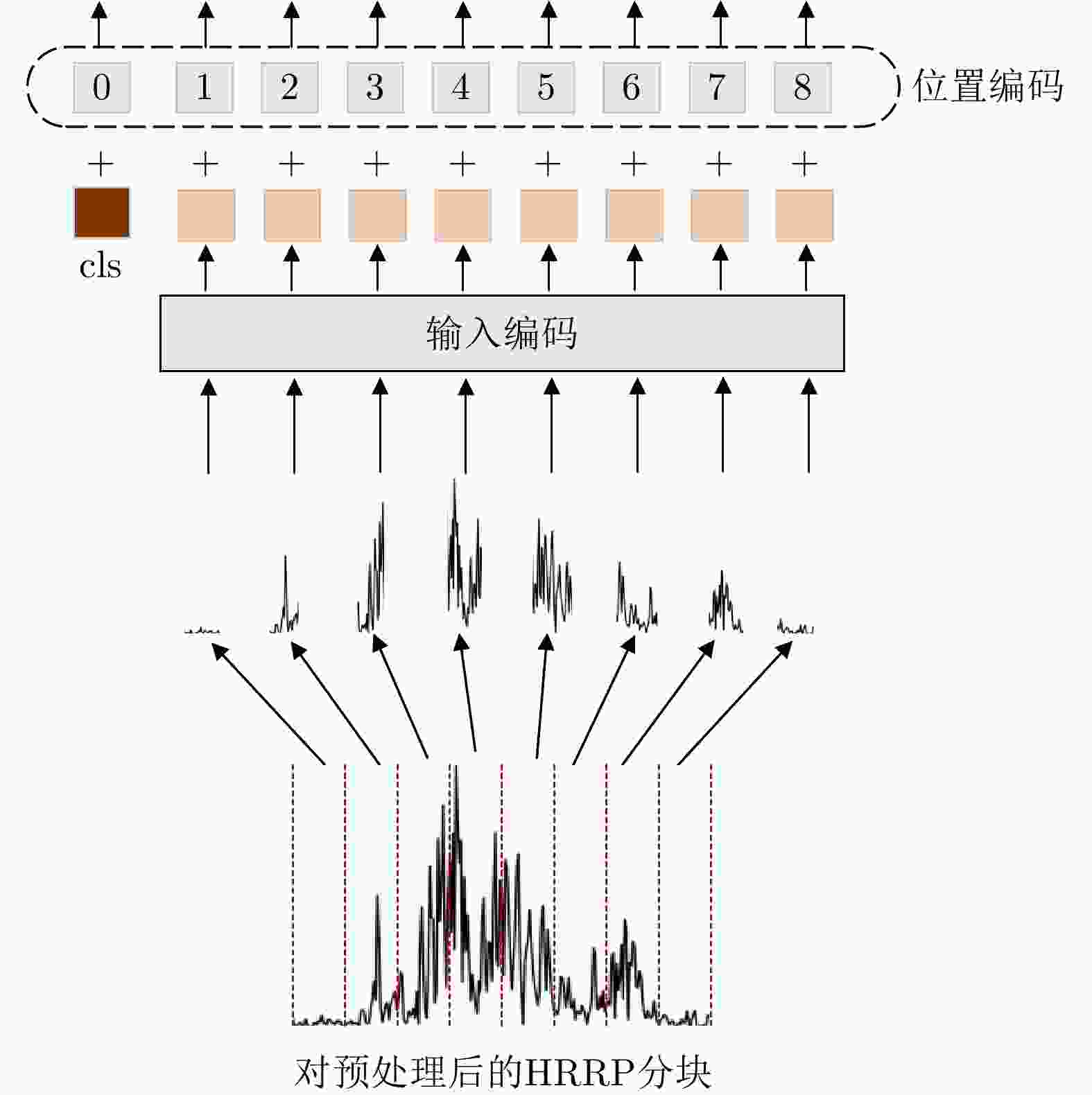
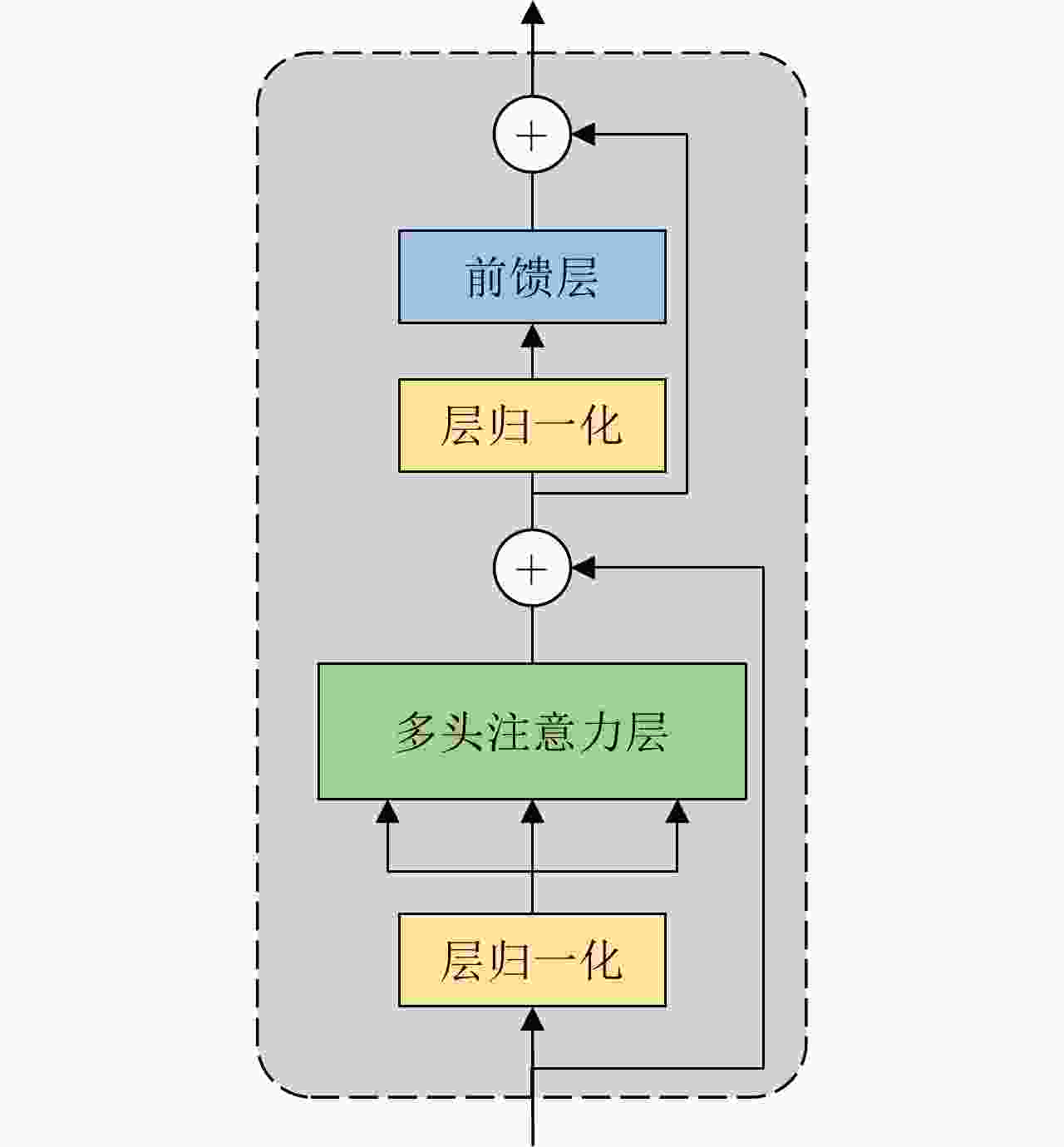
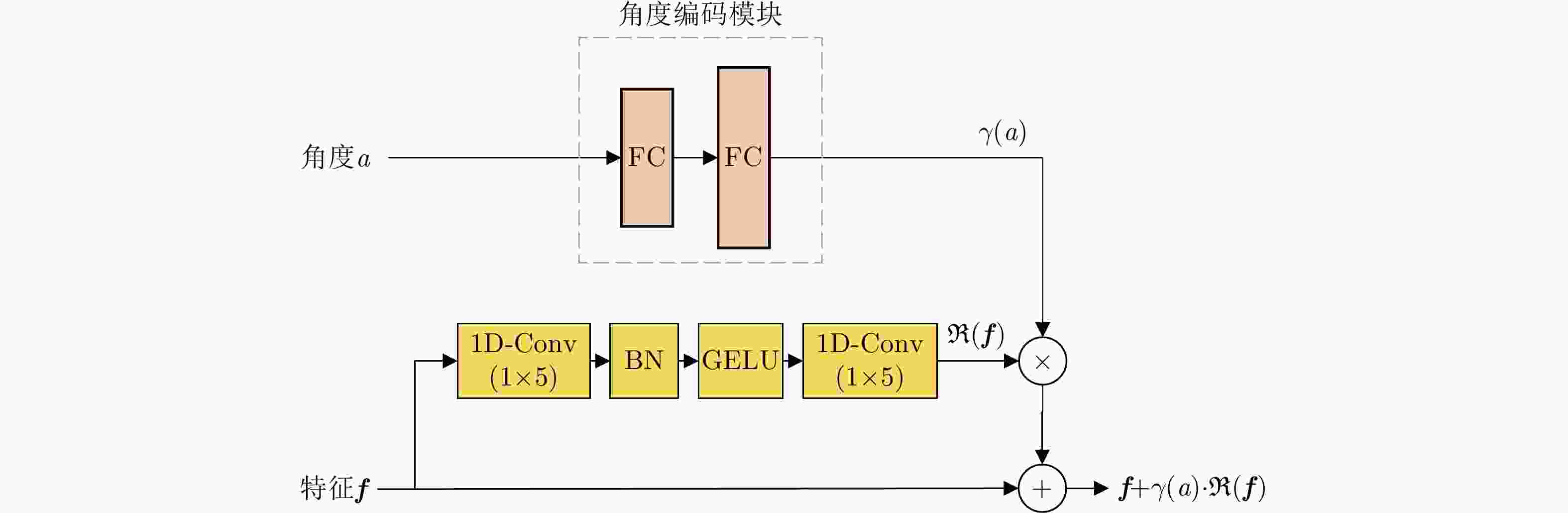
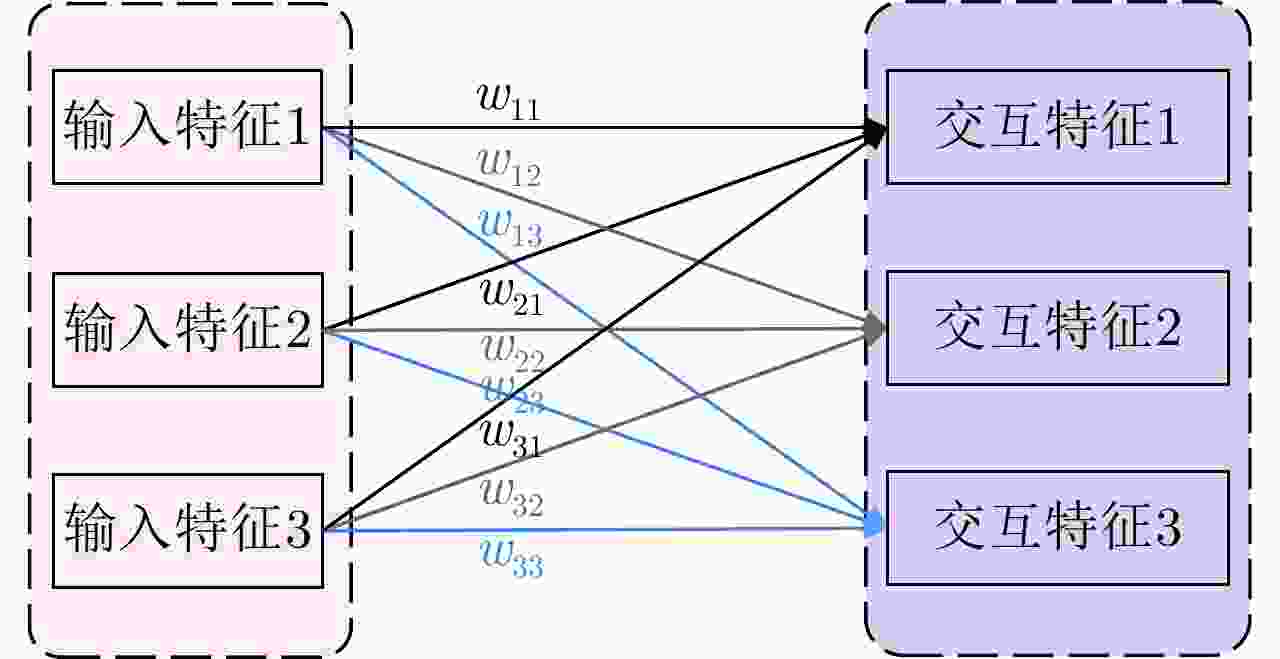
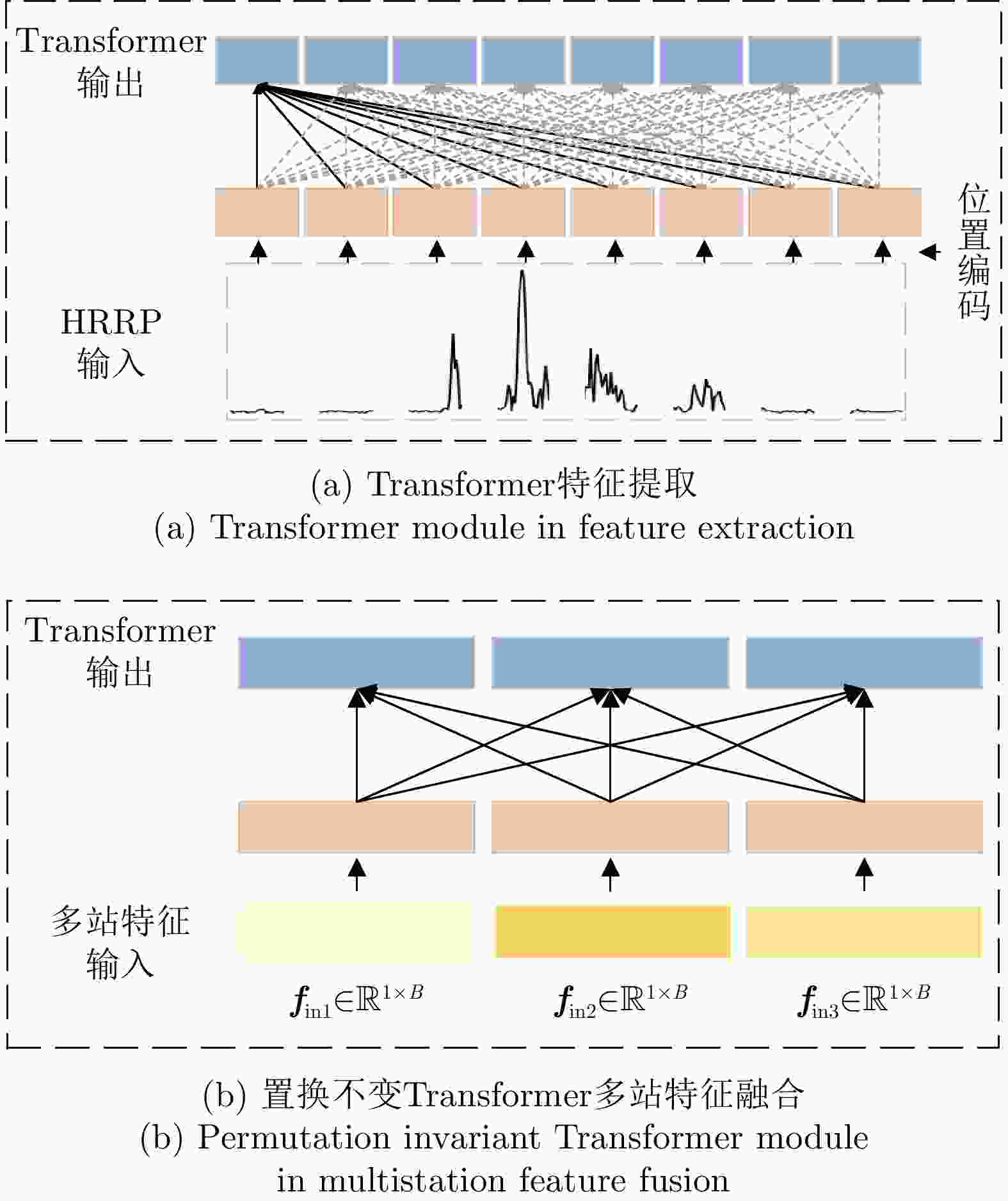
摘要: 多站协同雷达目标识别旨在利用多站信息的互补性提升识别性能。传统多站协同目标识别方法未直接考虑站间数据差异问题,且通常采用相对简单的融合策略,难以取得准确、稳健的识别性能。该文针对多站协同雷达高分辨距离像(HRRP)目标识别问题,提出了一种基于角度引导的Transformer融合网络。该网络以Transformer作为特征提取主体结构,提取单站HRRP的局部和全局特征。并在此基础上设计了3个新的辅助模块促进多站特征融合学习,角度引导模块、前级特征交互模块以及深层注意力特征融合模块。首先,角度引导模块使用目标方位角度对站间数据差异进行建模,强化了所提特征与多站视角的对应关系,提升了特征稳健性与一致性。其次,前级特征交互模块和深层注意力特征融合模块相结合的融合策略,实现了对各站特征的多阶段层次化融合。最后,基于实测数据模拟多站场景进行协同识别实验,结果表明所提方法能够有效地提升多站协同时的目标识别性能。
-
关键词:
- 多站协同雷达目标识别 /
- 高分辨距离像(HRRP) /
- 角度引导 /
- 注意力特征融合 /
- Transformer融合网络
Abstract: Multistation cooperative radar target recognition aims to enhance recognition performance by utilizing the complementarity between multistation information. Conventional multistation cooperative target recognition methods do not explicitly consider the issue of interstation data differences and typically adopt relatively simple fusion strategies, which makes it difficult to obtain accurate and robust recognition performance. In this study, we propose an angle-guided transformer fusion network for multistation radar High-Resolution Range Profile (HRRP) target recognition. The extraction of the local and global features of the single-station HRRP is conducted via feature extraction, which employs a transformer as its main structure. Furthermore, three new auxiliary modules are created to facilitate fusion learning: the angle-guided module, the prefeature interaction module, and the deep attention feature fusion module. First, the angle guidance module enhances the robustness and consistency of features via modeling data differences between multiple stations and reinforces individual features associated with the observation perspective. Second, the fusion approach is optimized, and the multilevel hierarchical fusion of multistation features is achieved by combining the prefeature interaction module and the deep attention feature fusion module. Finally, the experiments are conducted on the basis of the simulated multistation scenarios with measured data, and the outcomes demonstrate that our approach can effectively enhance the performance of target recognition in multistation coordination. -
表 1 雷达参数
Table 1. Parameters of radar
参数 数值 信号带宽 400 MHz 距离分辨率 0.375 m 表 2 目标物理参数
Table 2. Parameters of targets
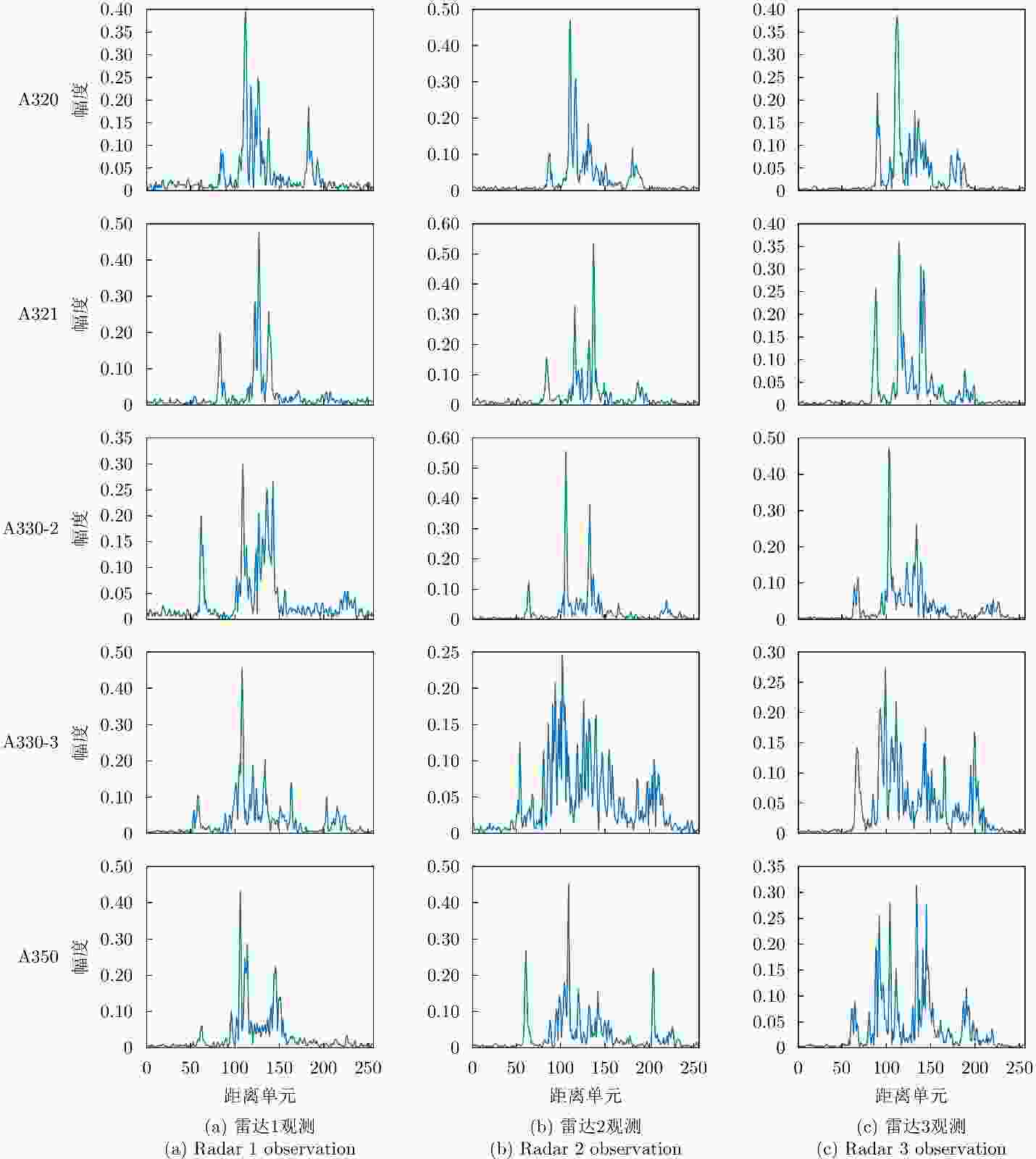
飞机型号 机身长度(m) 翼展宽度(m) 机高(m) A320 37.57 34.10 11.76 A321 44.51 34.09 11.76 A330-2 58.80 60.30 17.40 A330-3 63.60 60.30 16.85 A350 66.80 64.75 17.05 表 3 数据集样本分布
Table 3. Dataset samples distribution
飞机型号 训练样本数 测试样本数 A320 2636 2594 A321 2482 2398 A330-2 2556 2569 A330-3 2785 2572 A350 2890 2181 表 4 实验参数配置
Table 4. Experimental parameters configuration
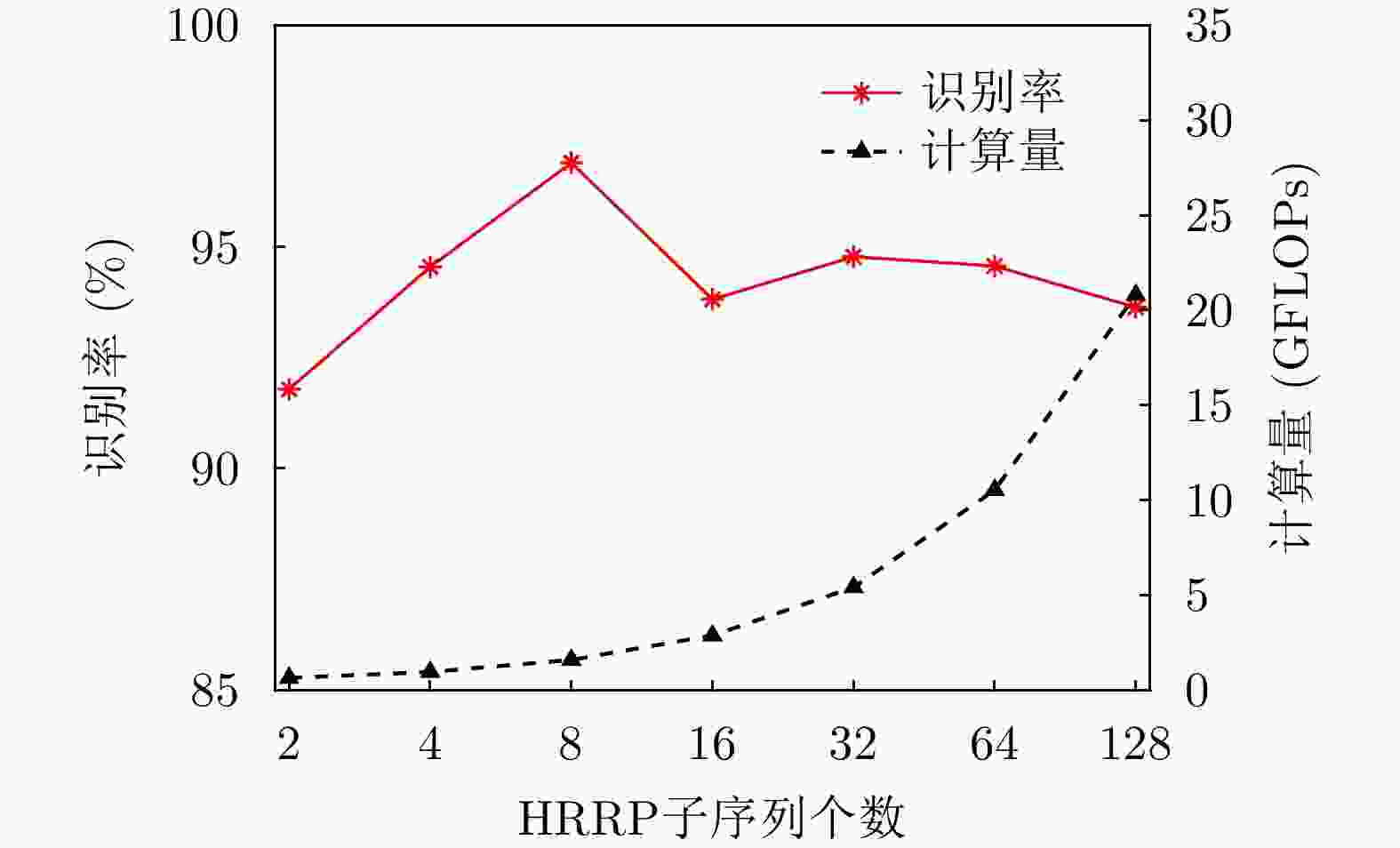
实验配置 参数 训练轮次 200 批量大小 64 初始学习率 1E–3 优化器 AdamW 丢弃率 0.1 HRRP子序列的个数N 8 子序列编码维度D 128 Transformer模块数 3 注意力头数 4 角度编码全连接层输出维度 (128, 1152) 特征交互主支路权重 0.6 特征交互其余支路权重 0.2 深层注意力融合模块数 1 损失函数 Cross Entropy Loss 表 5 实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results
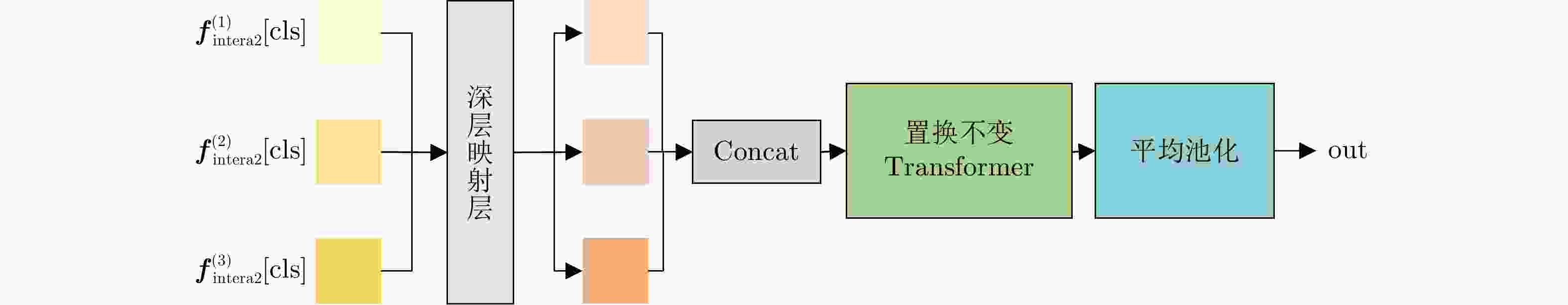
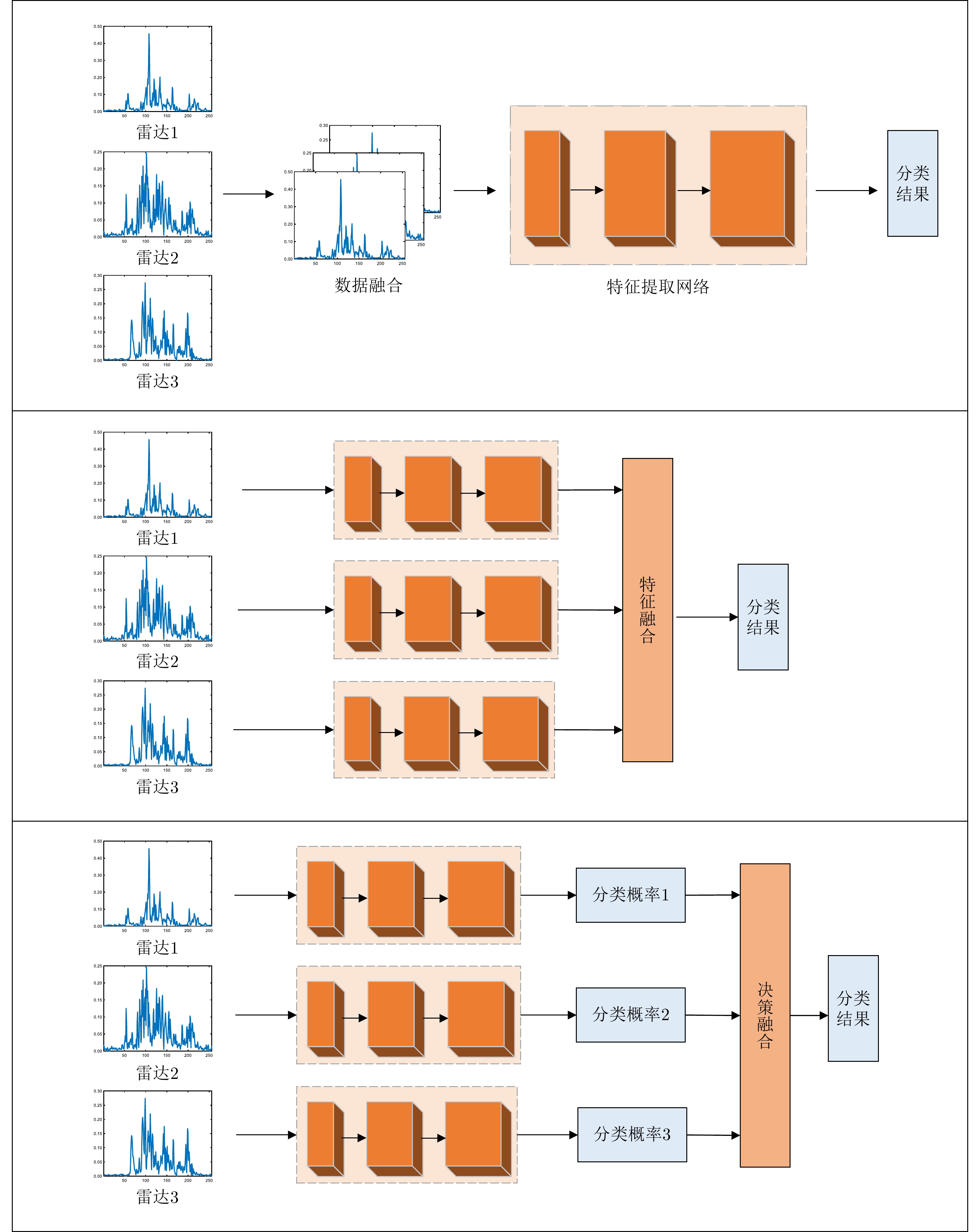
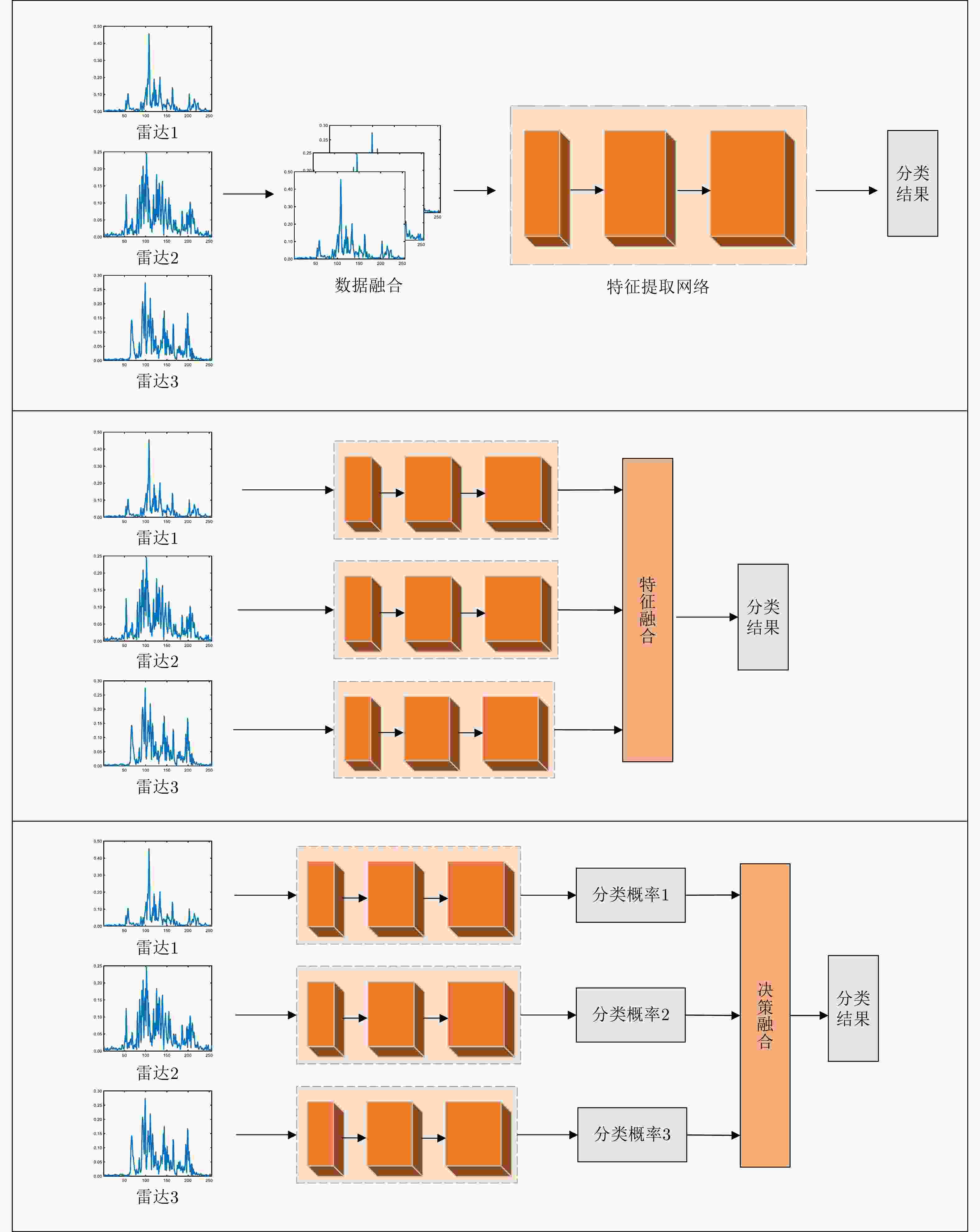
方法 融合策略 识别率(%) 参数量(M) 计算量(GFLOPs) CNN单站 雷达1 81.56 4.19 0.30 雷达2 87.27 4.19 0.30 雷达3 90.71 4.19 0.30 CNN多站 数据融合 86.35 4.19 0.30 特征融合 90.08 12.59 1.76 决策融合 90.96 12.59 1.76 Transformer单站 雷达1 87.12 0.89 0.46 雷达2 88.03 0.89 0.46 雷达3 93.21 0.89 0.46 Transformer多站 特征融合 93.60 2.51 1.38 本文方法 方位角度引导+前级
特征交互+深层注意
力特征融合96.90 3.39 1.60 表 6 消融实验结果
Table 6. Results of ablation experiment
方法 角度引导 前级特征
交互深层注意力
特征融合识别率(%) Transformer
多站特征融合– – – 93.60 √ – – 94.50(+0.90) – √ – 93.20(–0.40) – – √ 93.70(+0.10) √ √ – 93.77(+0.17) – √ √ 94.47(+0.87) √ – √ 95.68(+2.08) 本文方法 √ √ √ 96.90(+3.30) -
[1] DING Beicheng and CHEN Penghui. HRRP feature extraction and recognition method of radar ground target using convolutional neural network[C]. 2019 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Granada, Spain, 2019: 658–661. [2] WAN Jinwei, CHEN Bo, YUAN Yijun, et al. Radar HRRP recognition using attentional CNN with multi-resolution spectrograms[C]. 2019 International Radar Conference (RADAR), Toulon, France, 2019: 1–4. [3] WANG Penghui, DU Lan, PAN Mian, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on linear dynamic model[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 662–665. [4] YANG Xiuzhu, ZHANG Xinyue, DING Yi, et al. Indoor activity and vital sign monitoring for moving people with multiple radar data fusion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3791. doi: 10.3390/rs13183791 [5] YANG Jiachen, ZHANG Zhou, MAO Wei, et al. IoT-based critical infrastructure enabled radar information fusion[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2022, 98: 107723. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107723 [6] WU Hao, DAI Dahai, JI Penghui, et al. High-resolution range profile recognition method of vehicle targets based on accelerated T-SNE with multi-polarization fusion[C]. 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Nanjing, China, 2021: 72–76. [7] LIU Chang, ANTYPENKO R, SUSHKO I, et al. Marine distributed radar signal identification and classification based on deep learning[J]. Traitement du Signal, 2021, 38(5): 1541–1548. doi: 10.18280/ts.380531 [8] HUANG Yuchen, LI Wei, DOU Zhiyang, et al. Activity recognition based on millimeter-wave radar by fusing point cloud and range-Doppler information[J]. Signals, 2022, 3(2): 266–283. doi: 10.3390/signals3020017 [9] AGUILETA A A, BRENA R F, MAYORA O, et al. Multi-sensor fusion for activity recognition—A survey[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(17): 3808. doi: 10.3390/s19173808 [10] 周宁宁, 朱士涛, 年毅恒, 等. 一种基于多模态OAM波束的目标特征智能识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(5): 760–772. doi: 10.12000/JR21056ZHOU Ningning, ZHU Shitao, NIAN Yiheng, et al. An intelligent target feature recognition method based on multi-mode OAM beams[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(5): 760–772. doi: 10.12000/JR21056 [11] 邓冬虎, 张群, 罗迎, 等. 双基地ISAR系统中分辨率分析及微多普勒效应研究(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 152–167. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13039DENG Donghu, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Resolution and micro-Doppler effect in Bi-ISAR system (in English)[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 152–167. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13039 [12] 冯存前, 李靖卿, 贺思三, 等. 组网雷达中弹道目标微动特征提取与识别综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 609–620. doi: 10.12000/JR15084FENG Cunqian, LI Jingqing, HE Sisan, et al. Micro-Doppler feature extraction and recognition based on netted radar for ballistic targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 609–620. doi: 10.12000/JR15084 [13] 章鹏飞, 李刚, 霍超颖, 等. 基于双雷达微动特征融合的无人机分类识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061ZHANG Pengfei, LI Gang, HUO Chaoying, et al. Classification of drones based on micro-Doppler radar signatures using dual radar sensors[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061 [14] RYKUNOV M, DE GREEF E, KHALID H U R, et al. Multi-radar fusion for failure-tolerant vulnerable road users classification[C]. 2021 18th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), London, United Kingdom, 2022: 337–340. [15] SHU Haining and LIANG Qilian. Data fusion in a multi-target radar sensor network[C]. 2007 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, Long Beach, USA, 2007: 129–132. [16] DU Lan, WANG Penghui, LIU Hongwei, et al. Bayesian spatiotemporal multitask learning for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3182–3196. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2141664 [17] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. [18] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021. [19] WANG Qiang, LI Bei, XIAO Tong, et al. Learning deep transformer models for machine translation[C]. 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 1810–1822. [20] CAO Kaidi, RONG Yu, LI Cheng, et al. Pose-robust face recognition via deep residual equivariant mapping[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 5187–5196. [21] SUN Yuanshuang, WANG Yinghua, LIU Hongwei, et al. SAR target recognition with limited training data based on angular rotation generative network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(11): 1928–1932. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2958379 [22] LOSHCHILOV I and HUTTER F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019. [23] YUAN Lele. A time-frequency feature fusion algorithm based on neural network for HRRP[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2017, 55: 63–71. doi: 10.2528/PIERM16123002 [24] QUAN Daying, TANG Zeyu, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. LPI radar signal recognition based on dual-Channel CNN and feature fusion[J]. Symmetry, 2022, 14(3): 570. doi: 10.3390/sym14030570 [25] ZHU Lijun. Selection of multi-level deep features via spearman rank correlation for synthetic aperture radar target recognition using decision fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 133914–133927. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010969 [26] CHEN Wenchao, CHEN Bo, PENG Xiaojun, et al. Tensor RNN with Bayesian nonparametric mixture for radar HRRP modeling and target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1995–2009. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3065847 [27] GUO Dandan, CHEN Bo, CHEN Wenchao, et al. Variational temporal deep generative model for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5795–5809. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3027470 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: