Real-time Dwell Scheduling Algorithm for Distributed Phased Array Radar Network Based on Pulse Interleaving
-
摘要: 该文针对分布式雷达组网系统提出了一种基于脉冲交错的实时波束驻留调度算法。该算法引入时间指针向量,用于指示何时选择具有最高综合优先级的波束驻留任务,该任务被分配至交错时间利用程度最低的雷达节点,有效减少了调度过程中引入的时间空隙;同时,脉冲交错分析方法决定对于被分配的波束驻留任务是否可以在相应的雷达节点成功调度执行,其中,引入时隙占用矩阵和能量消耗矩阵来表征各个雷达节点的时间与能量资源使用情况,简化了交错分析过程,并实现了具有不同脉冲重复周期与个数的波束驻留任务之间的交错。此外,为了提高波束驻留调度的效率,所提算法还引入交错时间利用率门限自适应选择时间指针的滑动步长。仿真结果表明,该文所提算法能实现分布式雷达组网系统实时的波束驻留调度,并能获得较现有波束驻留调度算法更好的调度性能。Abstract: In this study, a real-time dwell scheduling algorithm based on pulse interleaving is proposed for a distributed radar network system. A time pointer vector is introduced to indicate the moment when the dwell task with the highest synthetic priority should be chosen. This task is further allocated to the radar node with the lowest interleaving time utilization ratio, effectively reducing the time gaps during scheduling. Meanwhile, the pulse interleaving analysis determines whether the assigned dwell task can be scheduled successfully on the corresponding radar node. The time slot occupation matrix and energy assumption matrix are introduced to indicate the time and energy resource consumption of radar nodes, which not only simplifies the pulse interleaving analysis process but also enables pulse interleaving among the tasks with different pulse repetition intervals and numbers. Furthermore, to improve the efficiency of dwell scheduling, a threshold of interleaving time utilization ratio is set to adaptively choose the sliding step of the time pointer. The simulation results reveal that the proposed algorithm can execute real-time dwell scheduling for a distributed radar network system and achieve better scheduling performance than the existing dwell scheduling algorithm.
-
表 1 基于脉冲交错的分布式雷达组网系统波束驻留调度算法步骤
Table 1. The steps of the dwell scheduling algorithm for distributed radar network system based on pulse interleaving
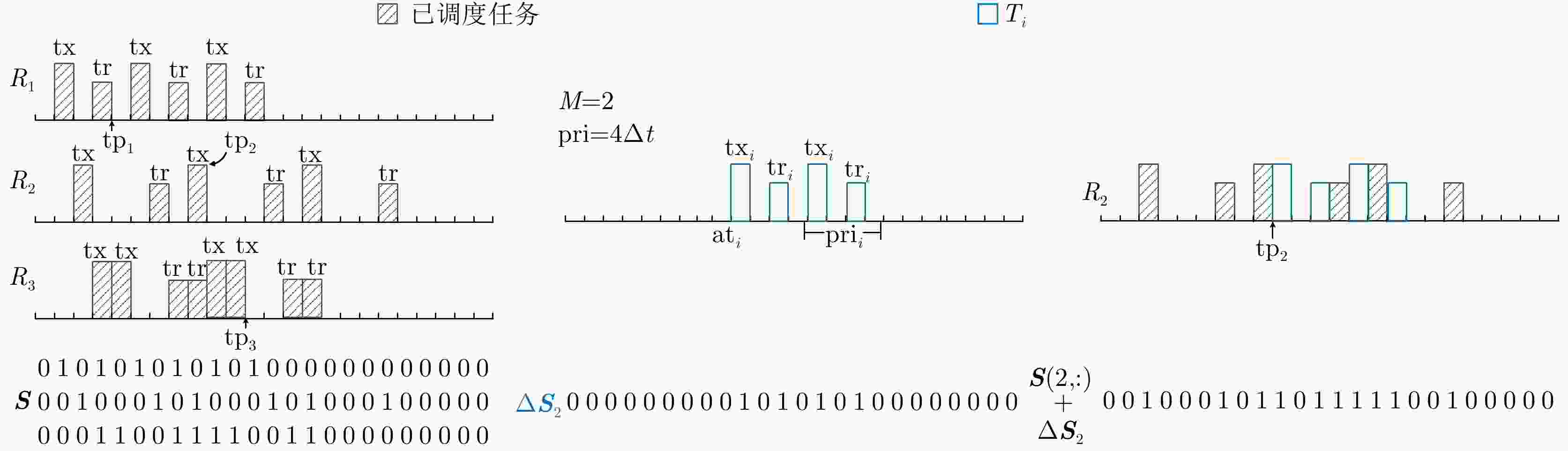
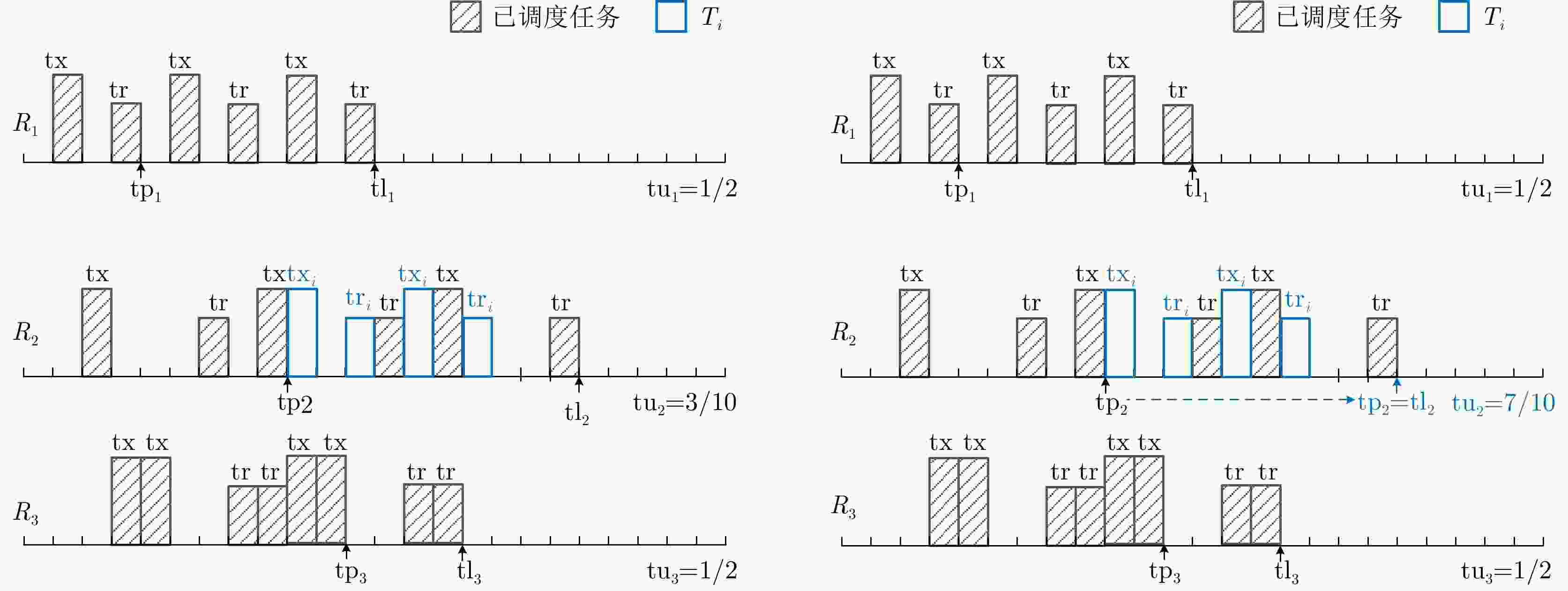
初始化${\bf{tp}} = [{t_0}{\text{ }}{t_0}{\text{ }} \cdots {\text{ }}{t_0}]$, ${\bf{tl} } = [{{\rm{tl}}_1}{\text{ t} }{ {\text{l} }_2}{\text{ } } \cdots {\text{ t} }{ {\text{l} }_M}] = [{t_0}{\text{ } }{t_0}{\text{ } } \cdots {\text{ } }{t_0}]$, $ S = {\bf{0}} $,根据式(18)初始化E; While T不为空且$\min ({\bf{tp}}) < {t_0} + {t_{{\text{SI}}}}$ 选出任务请求队列T中满足$ {\text{d}}{{\text{t}}_i} + {l_i} < \min ({\bf{tp}}) $的任务,将它们从中删除,并将其存入任务删除队列; 选出任务请求队列T中满足$ \max ({\bf{tp}}) \ge {\text{d}}{{\text{t}}_i} - {l_i} $的所有任务,假设选出任务有X个; if $ X > 0 $ 按照式(23)计算选出任务的优先级,并将这X个任务按综合优先级从大到小排序; for $ {\text{itp}} $=1:X 从排序后的队列中选取第$ {\text{itp}} $个任务,选出可用于调度执行${T_{{\text{itp}}}}$的雷达集合${{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$,${{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$中的雷达$ {R_j} $应满足
${\text{d} }{ {\text{t} }_{ {\text{itp} } } } - {l_{ {\text{itp} } } } \le {\text{t} }{ {\text{p} }_j} \le {\text{d} }{ {\text{t} }_{ {\text{itp} } } } + {l_{ {\text{itp} } } } \cap {\text{t} }{ {\text{p} }_j} + {\text{d} }{ {\text{w} }_{ {\text{itp} } } } \le {t_0} + {t_{ {\text{SI} } } },{R_j} \in {{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$;If ${{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$不为空 根据式(24),选出在${{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$中具有最小交错时间利用率的雷达$ {R_{j*}} $; 根据3.1节分析${T_{{\text{itp}}}}$能否在$ {\text{t}}{{\text{p}}_{j*}} $时刻在$ {R_{j*}} $上交错执行; if 脉冲交错分析成功 将${T_{{\text{itp}}}}$放入$ {R_{j*}} $的任务执行队列中,并把${T_{{\text{itp}}}}$从T中删除; 更新${\boldsymbol{S}}(j*,:) = {\boldsymbol{S}}(j*,:){\bf{ + } }\Delta { {\boldsymbol{S} }_{j*} }$, ${\boldsymbol{E}}(j*,:) = {\boldsymbol{E}}(j*,:){\bf{ + } }\Delta {{\boldsymbol{E}}_{j*} }$; 更新$ {\text{t}}{{\text{l}}_{j*}} = \max \left( {{\text{t}}{{\text{l}}_{j*}},{\text{t}}{{\text{p}}_{j*}} + {\text{pr}}{{\text{i}}_{{\text{itp}}}} \times \left( {{M_{{\text{itp}}}} - 1} \right) + \left( {{\text{t}}{{\text{x}}_{{\text{itp}}}} + {\text{t}}{{\text{w}}_{{\text{itp}}}} + {\text{t}}{{\text{r}}_{{\text{itp}}}}} \right)} \right) $; end 按照式(24)计算${{\rm{tu}}_{j*} }$,并根据式(27)更新${{\rm{tp}}_{j*} }$; break; end if ${\rm{itp}} = = X$且${{\boldsymbol{R}}_{ {\text{itp} } } }$为空 $ \min ({\bf{tp}}) = \min ({\bf{tp}}) + \Delta t $; ${\bf{tl}} = \max ({\bf{tp}},{\bf{tl}})$; end end else $ \min ({\bf{tp}}) = \min ({\bf{tp}}) + \Delta t $; ${\bf{tl}} = \max ({\bf{tp}},{\bf{tl}})$ end end 表 2 雷达波束驻留任务参数表
Table 2. The parameters of dwell tasks
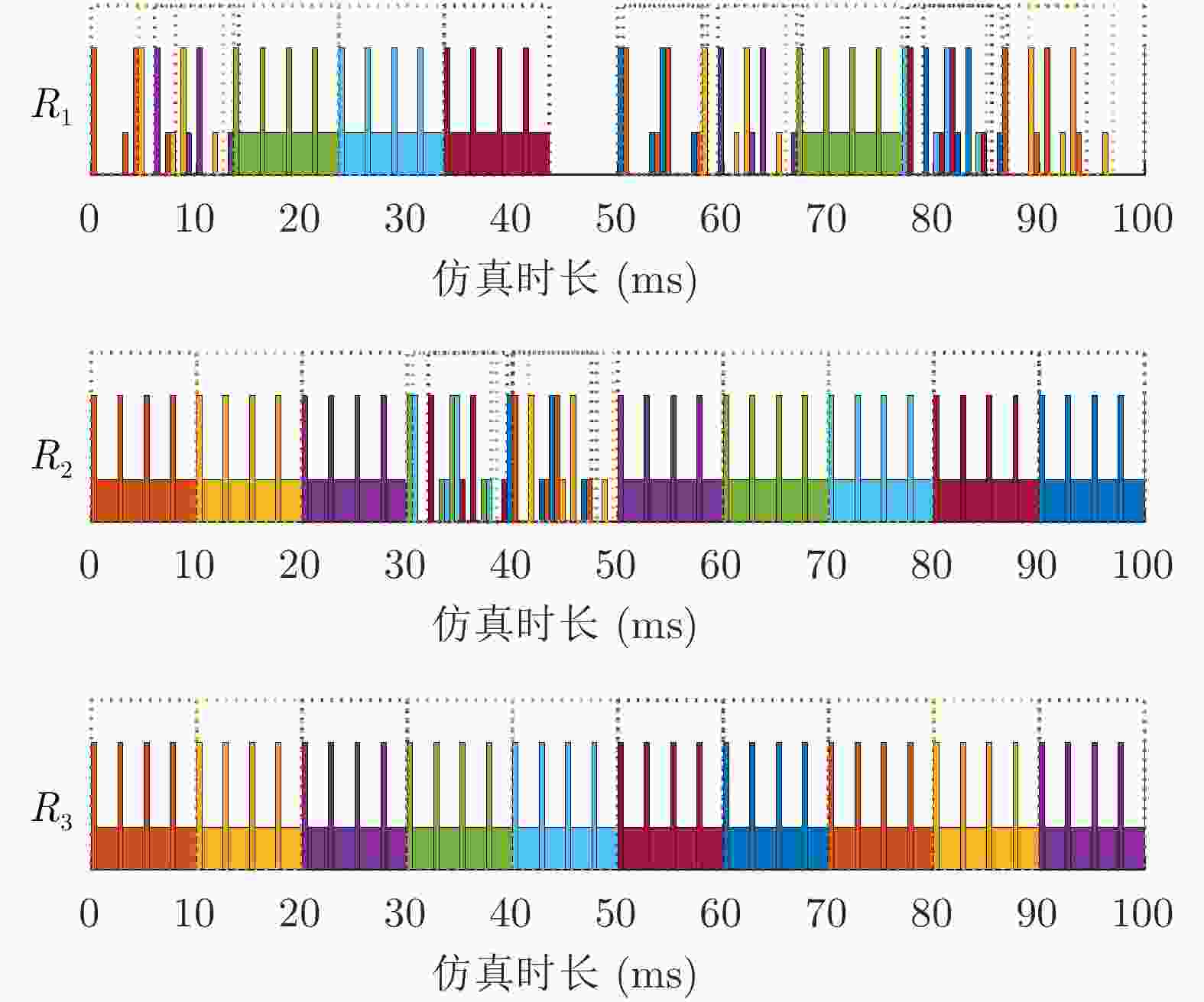
任务类型 W 驻留数目 周期(ms) 时间窗(ms) ${\text{tx}}$/${\text{tw}}$/${\text{tr}}$ (ms) ${\text{pri}}$ (ms) M 验证 5 1 – 15 0.5/2.5/0.5 4.0 2 精密跟踪 4 1 250 15 0.5/1.0/0.5 2.5 2 普通跟踪 3 1 500 25 0.5/2.5/0.5 4.0 2 地平线搜索1 2 80 2000 – 0.5/–/2.5 3.0 4 地平线搜索2 2 80 2000 – 0.5/–/2.5 3.0 4 地平线搜索3 2 80 2000 – 0.5/–/2.5 3.0 4 空域搜索1 1 120 4000 – 0.5/-/2.0 2.5 4 空域搜索2 1 120 4000 – 0.5/–/2.0 2.5 4 空域搜索3 1 120 4000 – 0.5/–/2.0 2.5 4 -
[1] 周文辉. 相控阵雷达及组网跟踪系统资源管理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2004.ZHOU Wenhui. Research on resource management technology for phased array radar and its network in tracking system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Defense Technology, 2004. [2] YUAN Ye, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust power allocation for resource-aware multi-target tracking with colocated MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 443–458. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047519 [3] YUAN Ye, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Scaled accuracy based power allocation for multi-target tracking with colocated MIMO radars[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 158: 227–240. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.01.014 [4] 卢建斌, 胡卫东, 郁文贤. 多功能相控阵雷达实时任务调度研究[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(4): 732–736. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.04.032LU Jianbin, HU Weidong, and YU Wenxian. Study on real-time task scheduling of multifunction phased array radars[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(4): 732–736. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.04.032 [5] ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, ZONG Binfeng, et al. Dynamic priority scheduling method for the air-defence phased array radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(7): 1140–1146. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0549 [6] QU Zhen, DING Zhen, and MOO P. Dual-side scheduling for radar resource management[C]. 21st International Radar Symposium, Warsaw, Poland, 2020: 260–263. [7] CHENG Ting, HE Zishu, and TANG Ting. Dwell scheduling algorithm for multifunction phased array radars based on the scheduling gain[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 19(3): 479–485. doi: 10.1016/S1004-4132(08)60110-3 [8] CHEN Yijun, ZHANG Qun, YUAN Ning, et al. An adaptive ISAR-imaging-considered task scheduling algorithm for multi-function phased array radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(19): 5096–5110. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2449251 [9] 段毅, 谭贤四, 曲智国, 等. 基于可变时间窗的相控阵雷达事件调度方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2018, 40(2): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.02.001DUAN Yi, TAN Xiansi, QU Zhiguo, et al. Phased array radar scheduling method based on variable time window[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40(2): 1–6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.02.001 [10] TAN Qianqian, CHENG Ting, and LI Xi. Online adaptive dwell scheduling based on dynamic template for PAR[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(5): 1119–1129. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000096 [11] CHENG Ting, LI Zhongzhu, TAN Qianqian, et al. Real-time adaptive dwell scheduling for digital array radar based on virtual dynamic template[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3197–3208. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3145773 [12] YANG Shanchao, TIAN Kangsheng, and LIU Renzheng. Task scheduling algorithm based on value optimisation for anti-missile phased array radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(11): 1883–1889. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0163 [13] MENG Fanqing and TIAN Kangsheng. Phased-array radar task scheduling method for hypersonic-glide vehicles[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 221288–221298. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3043338 [14] ABDELAZIZ F B and MIR H. An optimization model and tabu search heuristic for scheduling of tasks on a radar sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(17): 6694–6702. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2587730 [15] QU Zhen, DING Zhen, and MOO P. A machine learning radar scheduling method based on the EST algorithm[C]. IEEE 18th International Conference on Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing, Milan, Italy, 2019: 22–27. [16] QU Zhen, DING Zhen, and MOO P. A machine learning task selection method for radar resource management (poster)[C]. 22th International Conference on Information Fusion, Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–6. [17] ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, et al. A hybrid adaptively genetic algorithm for task scheduling problem in the phased array radar[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 272(3): 868–878. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.07.012 [18] ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, et al. An entropy-based PSO for DAR task scheduling problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 73: 862–873. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.09.022 [19] ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, HU Qiyong, et al. A hybrid DPSO with levy flight for scheduling MIMO radar tasks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 71: 242–254. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.028 [20] SHAGHAGHI M and ADVE R S. Task selection and scheduling in multifunction multichannel radars[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 969–974. [21] SHAGHAGHI M and ADVE R S. Machine learning based cognitive radar resource management[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 1433–1438. [22] SHAGHAGHI M, ADVE R S, and DING Zhen. Multifunction cognitive radar task scheduling using Monte Carlo tree search and policy networks[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1437–1447. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5276 [23] TIAN Tuanwei, ZHANG Tianxian, and KONG Lingjiang. Timeliness constrained task scheduling for multifunction radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(2): 525–534. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2878795 [24] LI Xueting, XU Longxiao, ZHANG Tianxian, et al. A scheduling method of generalized tasks for multifunctional radar network[C]. International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–6. [25] XU Longxiao, ZHANG Tianxian, WANG Yuanhang, et al. Resources conversion and complementarity based tasks scheduling for multifunction radar network[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–5. [26] XU Longxiao and ZHANG Tianxian. Reinforcement learning based dynamic task scheduling for multifunction radar network[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. [27] LIU Xiaowen, ZHANG Qun, CHEN Yichang, et al. Task allocation optimization for multi-target ISAR imaging in radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(1): 122–132. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2771804 [28] LIU Xiaowen, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. ISAR imaging task allocation for multi-target in radar network based on potential game[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(23): 11192–11204. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2936423 [29] LIU Xiaowen, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Radar network time scheduling for multi-target ISAR task with game theory and multiagent reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(4): 4462–4473. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3029430 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: