Element Configuration Optimization of Hybrid Distributed PA-MIMO Radar System Based on Target Detection
-
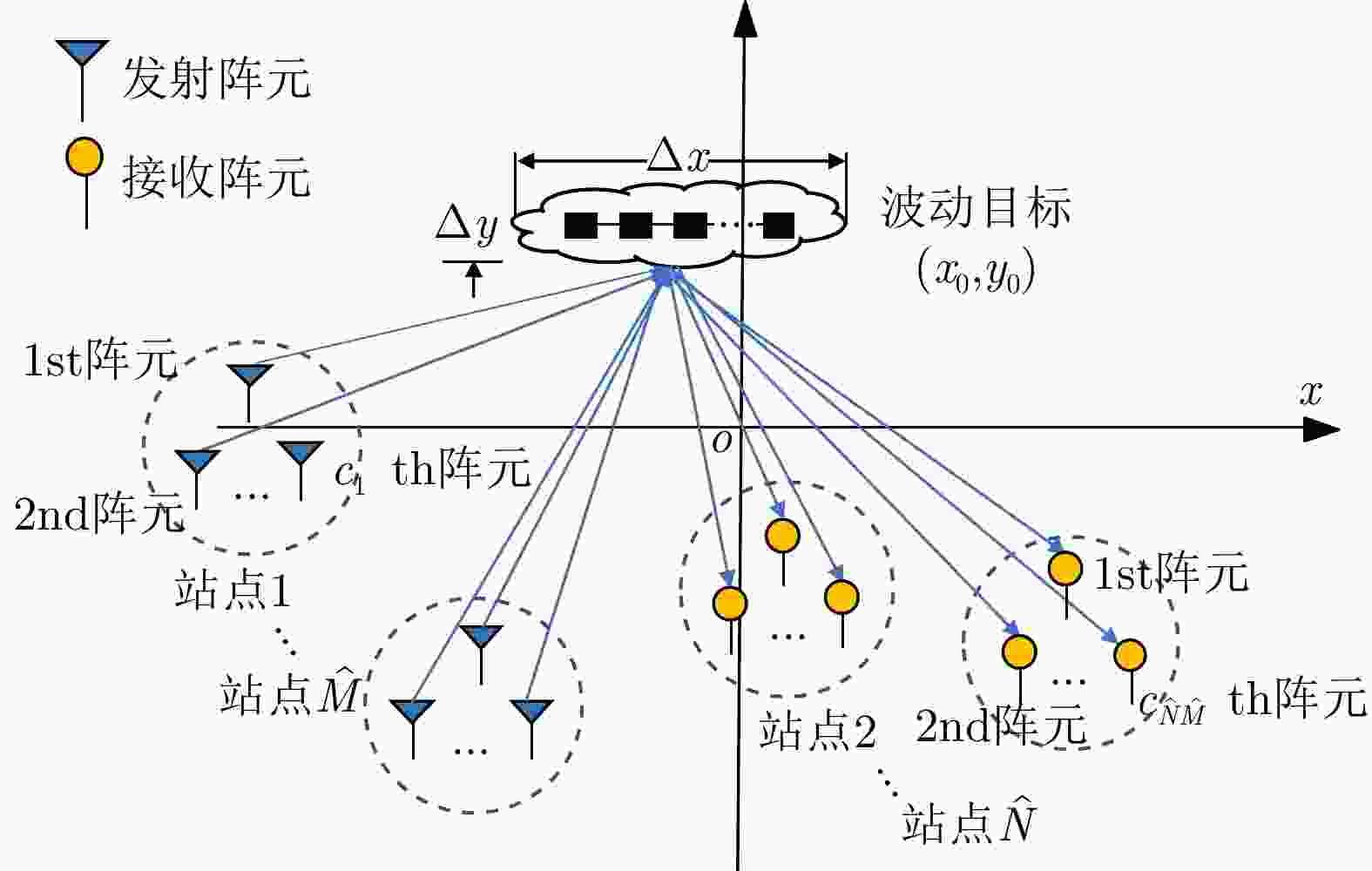
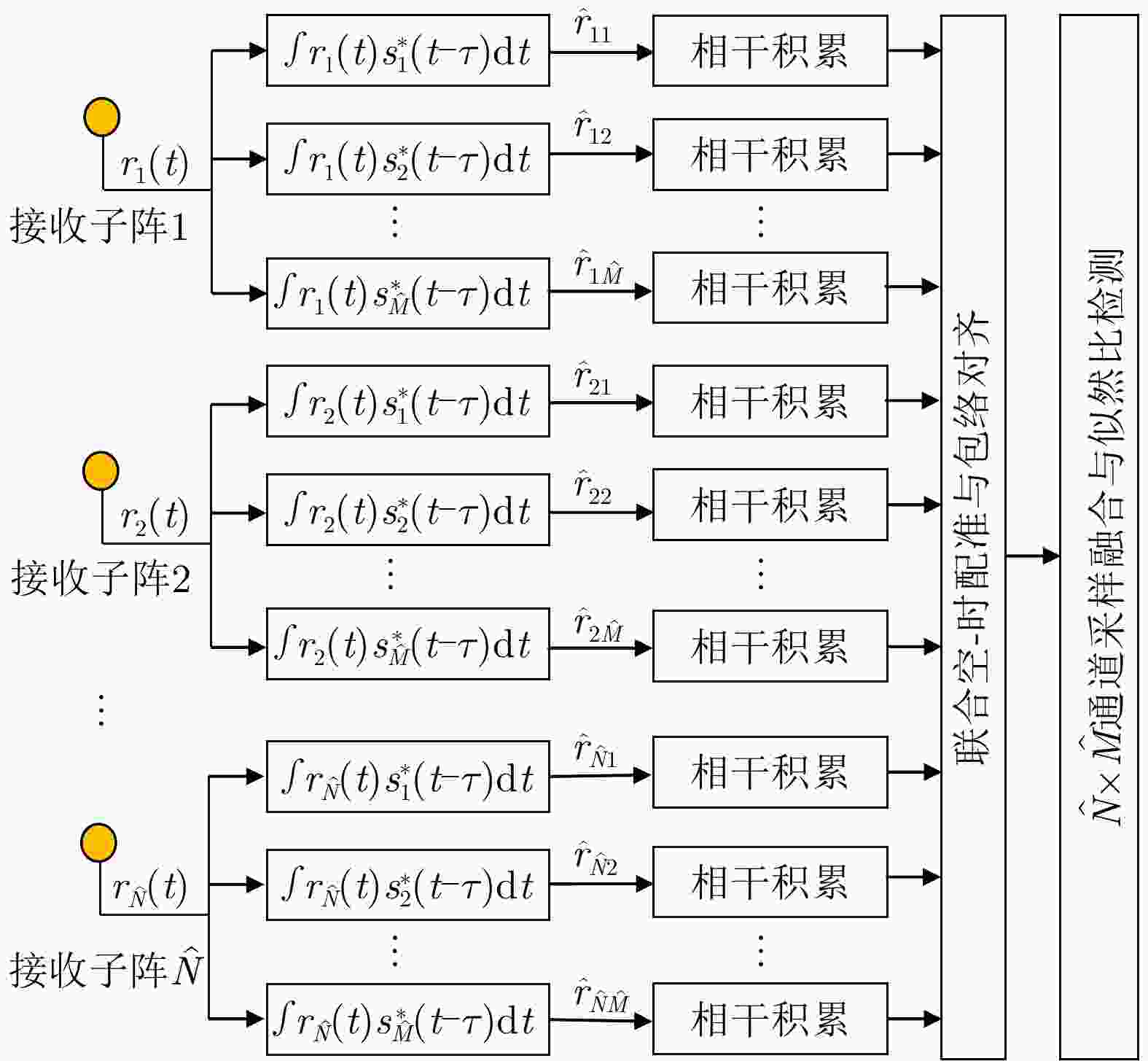
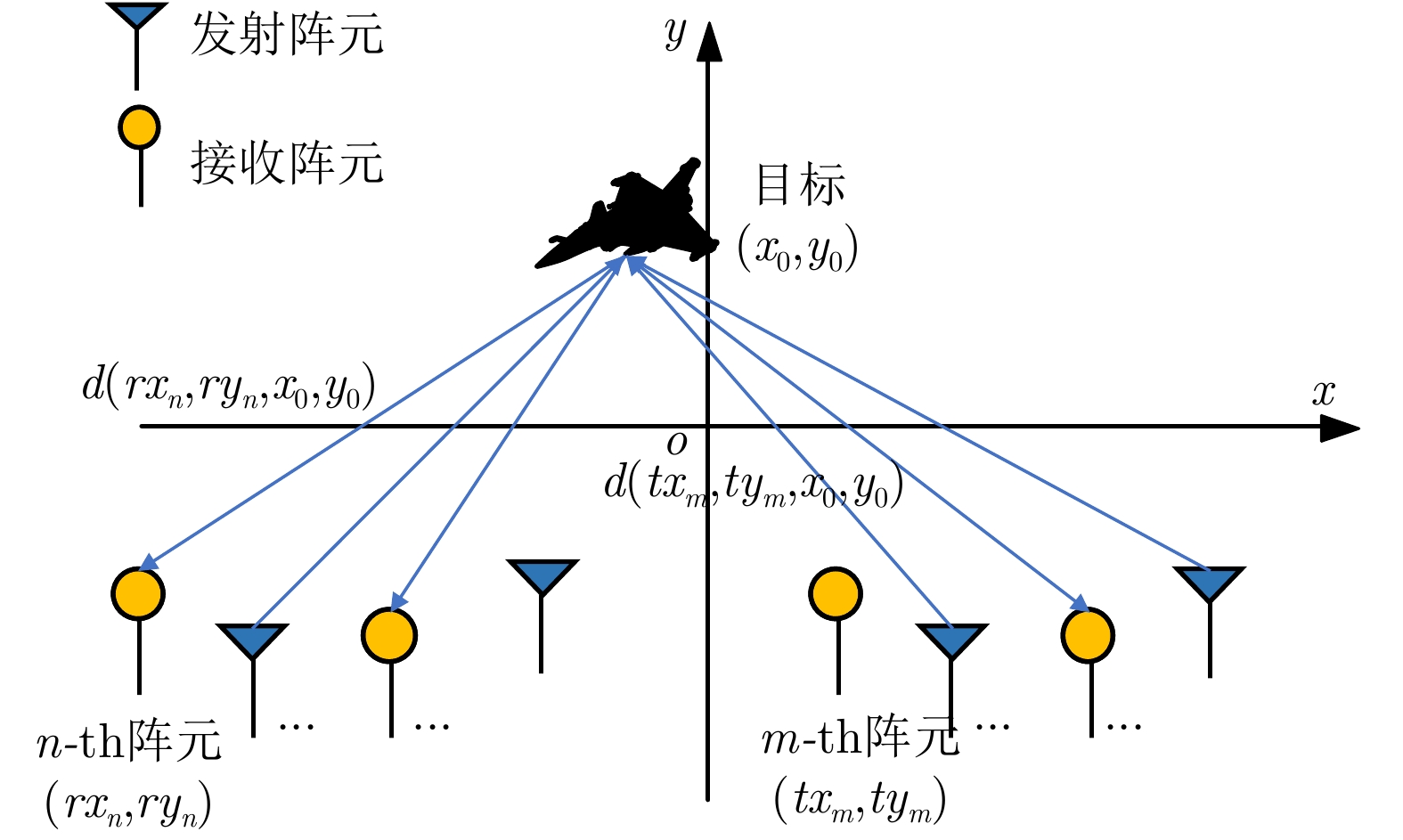
摘要: 该文建立混合分布式相控阵-多输入多输出(PA-MIMO)雷达系统模型,推导出基于Neyman-Pearson (NP)准则的似然比检测(LRT)器,在收发两端实施子阵级和阵元级优化部署,达到对雷达系统中相参增益和空间分集增益协调优化的目的。针对整数规划的子阵、阵元部署模型,提出基于量子粒子群优化的随机取整(SR-QPSO)求解算法,在较少的迭代步骤内获得最优阵元配置策略,实现子阵级和阵元级之间的联合优化。最后,通过对3个典型优化问题进行数值仿真,所提出的混合分布式PA-MIMO雷达系统优化配置较其他典型雷达系统有较大提升,探测概率达到0.98,有效距离达到1166.3 km,探测性能得到显著提升。Abstract: This paper establishes a hybrid distributed Phased-Array Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (PA-MIMO) radar system model, which combines coherent processing gain and spatial diversity gain to synergistically improve the target detection performance. We derive a Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) detector based on the Neyman-Pearson (NP) criterion for the hybrid distributed PA-MIMO radar system. The coherent processing gain and spatial diversity gain are jointly optimized by implementing subarray-level and array element–level optimal configurations at the transceiver and transmitter ends. Moreover, a Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization-based Stochastic Rounding (SR-QPSO) algorithm is proposed for the integer programming-based configuration model. This algorithm ensures that the optimal array-element configuration strategy is obtained with less iteration and achieves the joint optimization of subarray and array-element levels. Finally, simulations verify that the proposed optimal configuration offers substantial improvements compared to other typical radar systems, with a detection probability of 0.98 and an effective range of 1166.3 km, as well as a considerably improved detection performance.
-
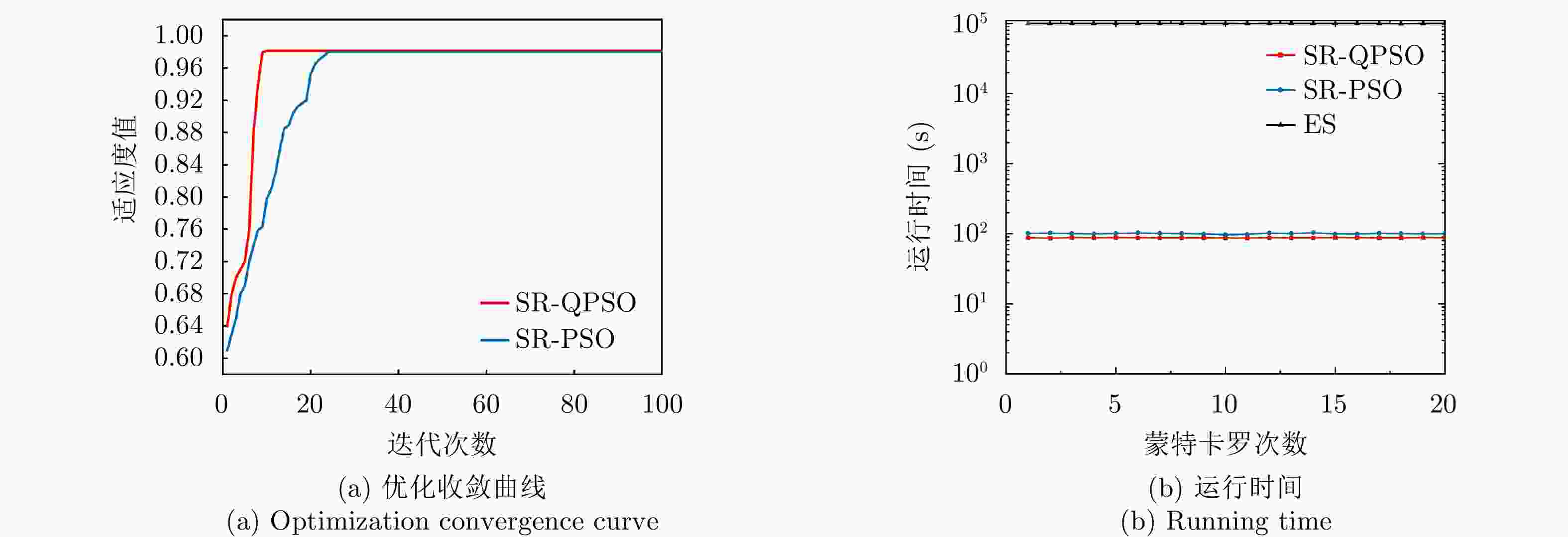
表 1 基于量子粒子群优化的随机取整求解算法流程
Table 1. SR-QPSO algorithm solution flow
(1) 初始化解空间,设定搜索维度D、种群规模W和最大迭代次
数Q,缩扩张因子$ \alpha = 0.8 $;(2) 粒子均匀随机散布于$ {\text{[}} - P_{{\text{min}}}^{},P_{{\text{max}}}^{}{\text{]}} $,记粒子位置初始值$ P_{i,t}^j $; (3) 规格化各粒子的位置参数,按照其小数位作为随机概率取整; (4) 计算个体当前位置$ {P_{i,j}}{\text{(1)}} $与全局最优位置$ {P_{\text{g}}}{\text{(}}t{\text{)}} $; (5) 设定收缩因子的上下界${\alpha _0}$和${\alpha _1}$; (6) 计算量子行为粒子的吸引子$ p_{i,j}^{}{\text{(}}t{\text{)}} $; (7) for $ t = 1 $ to Q do (8) 计算t 时刻迭代时的平均最好个体位置; (9) for $ i = 1 $ to W do (10) 计算粒子并更新粒子位置$ P_{i,j}^{}{\text{(}}t{\text{)}} $,按照其小数
位作为随机概率取整;(11) 若$ P_{i,j}^{}{\text{(}}t{\text{)}} \notin {\text{[}} - P_{{\text{min}}}^{},P_{{\text{max}}}^{}{\text{]}} $,设置$ P_{i,j}^{}{\text{(}}t + 1{\text{)}} $
为最近的边界值;(12) end for (13) end for 表 2 各算法计算复杂度对比
Table 2. Algorithm computational complexity comparison
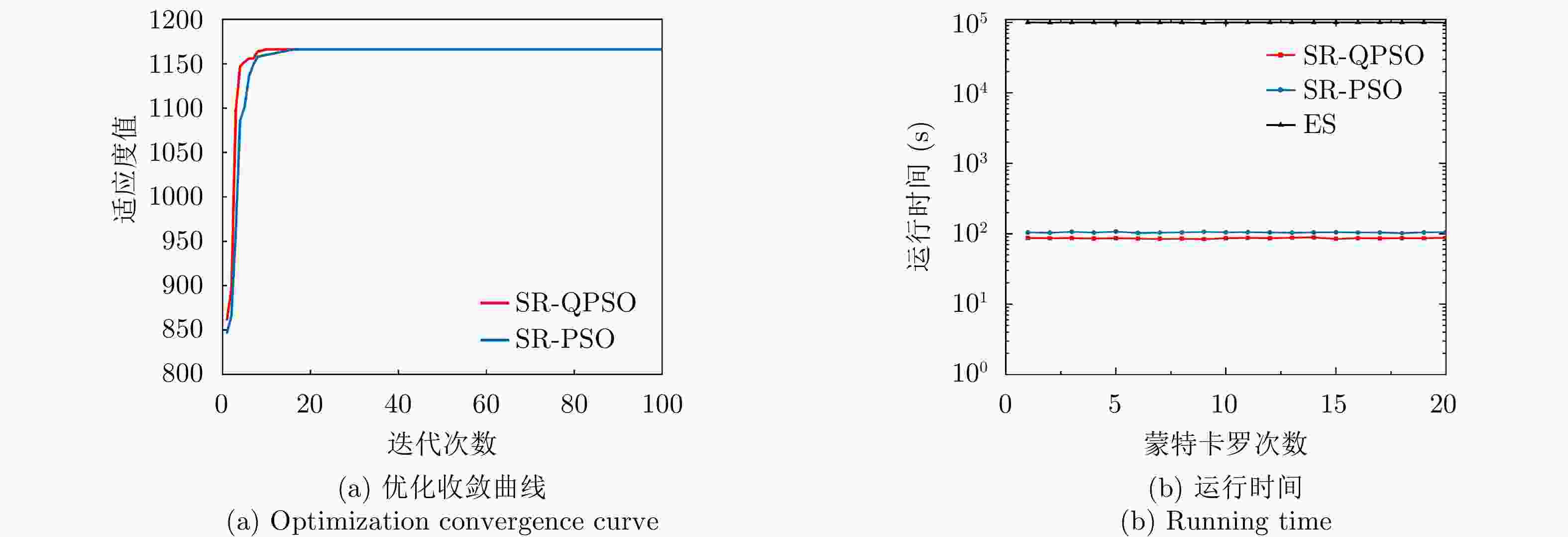
算法 计算复杂度 SR-QPSO ${\mathcal{O} }(QW)$ SR-PSO ${\mathcal{O} }(QW)$ 穷举搜索法 $ > {\mathcal{O}}({2^{M + N}}) $ 表 3 优化效果分析
Table 3. Optimization effect analysis
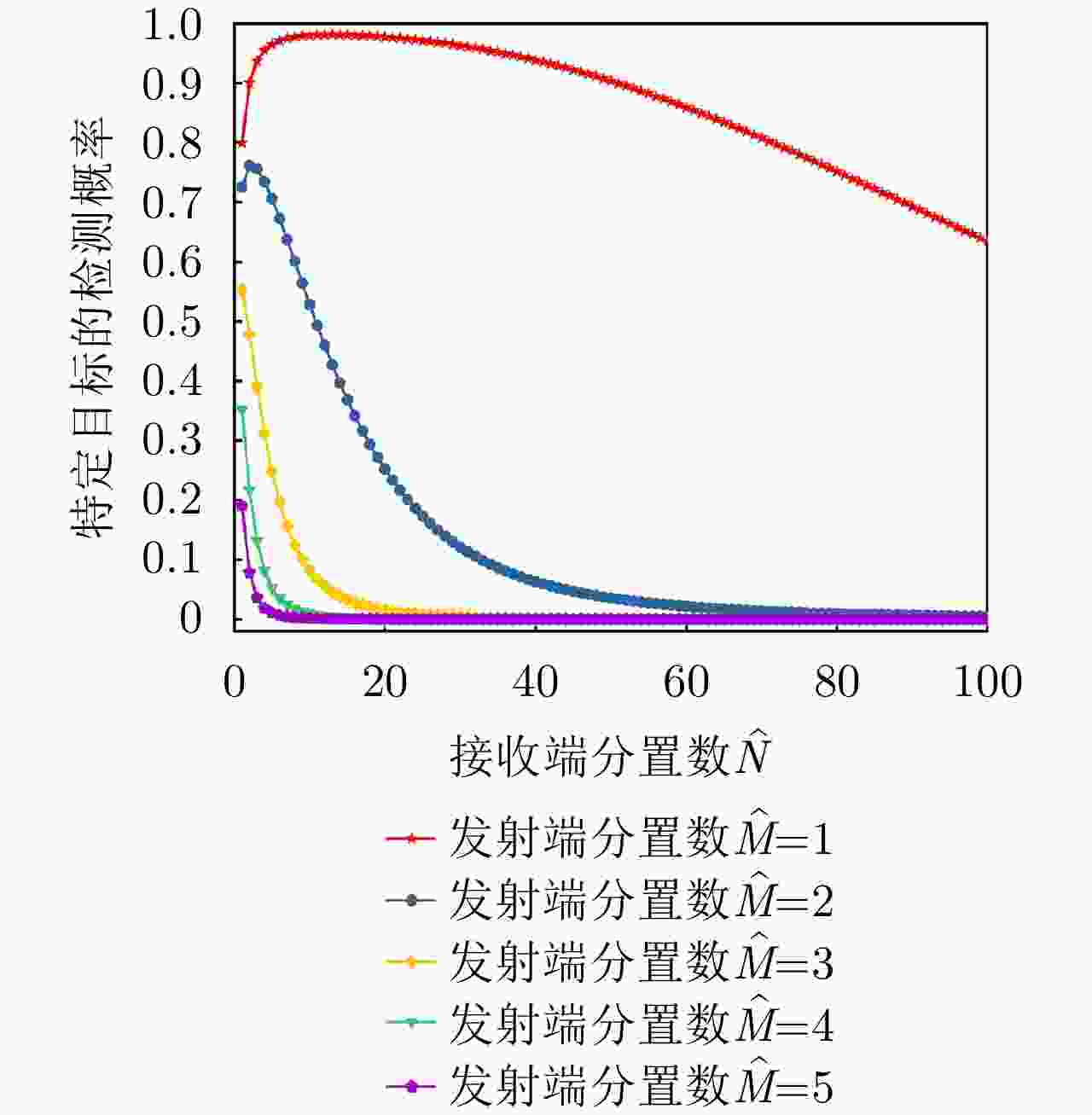
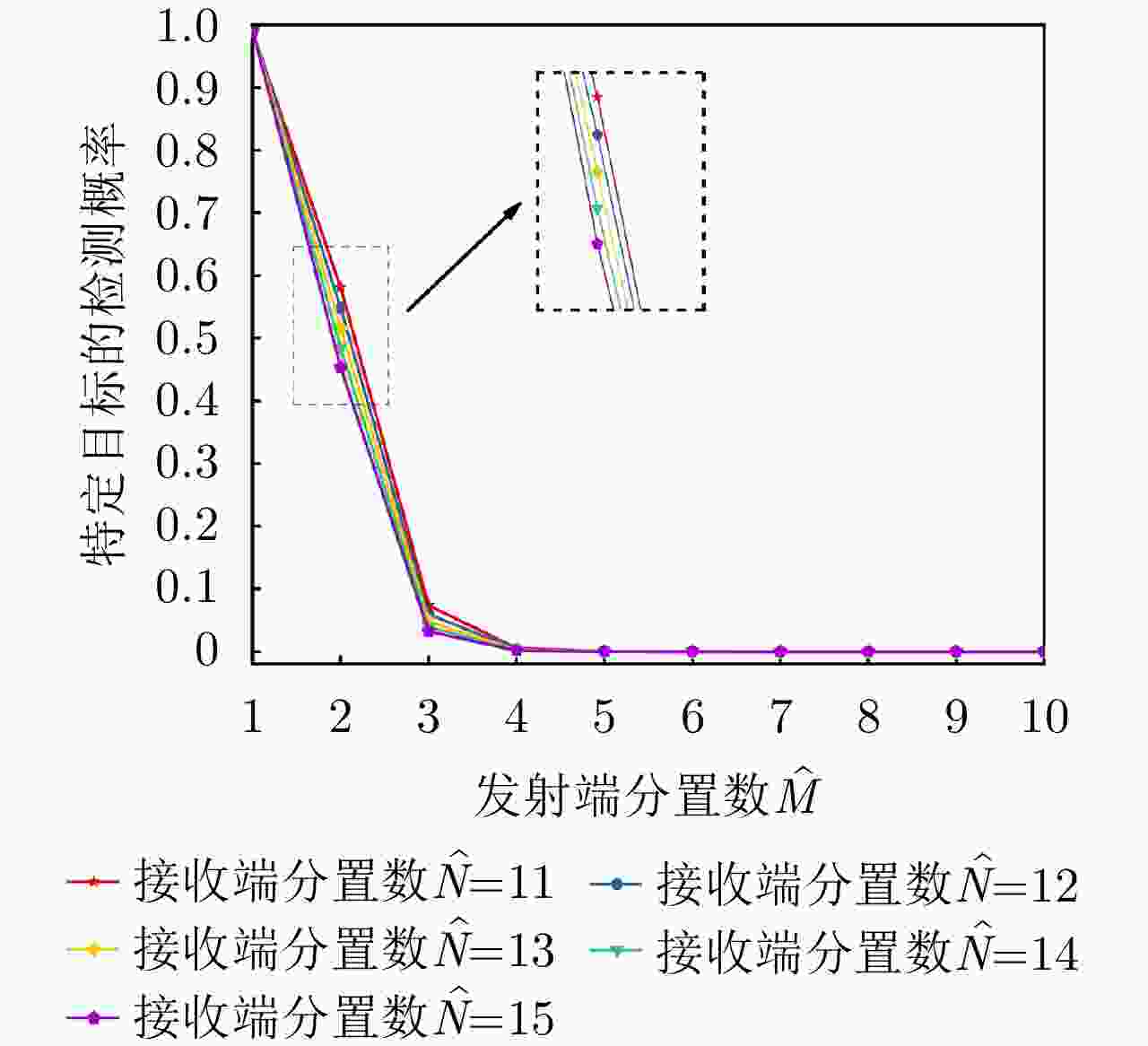
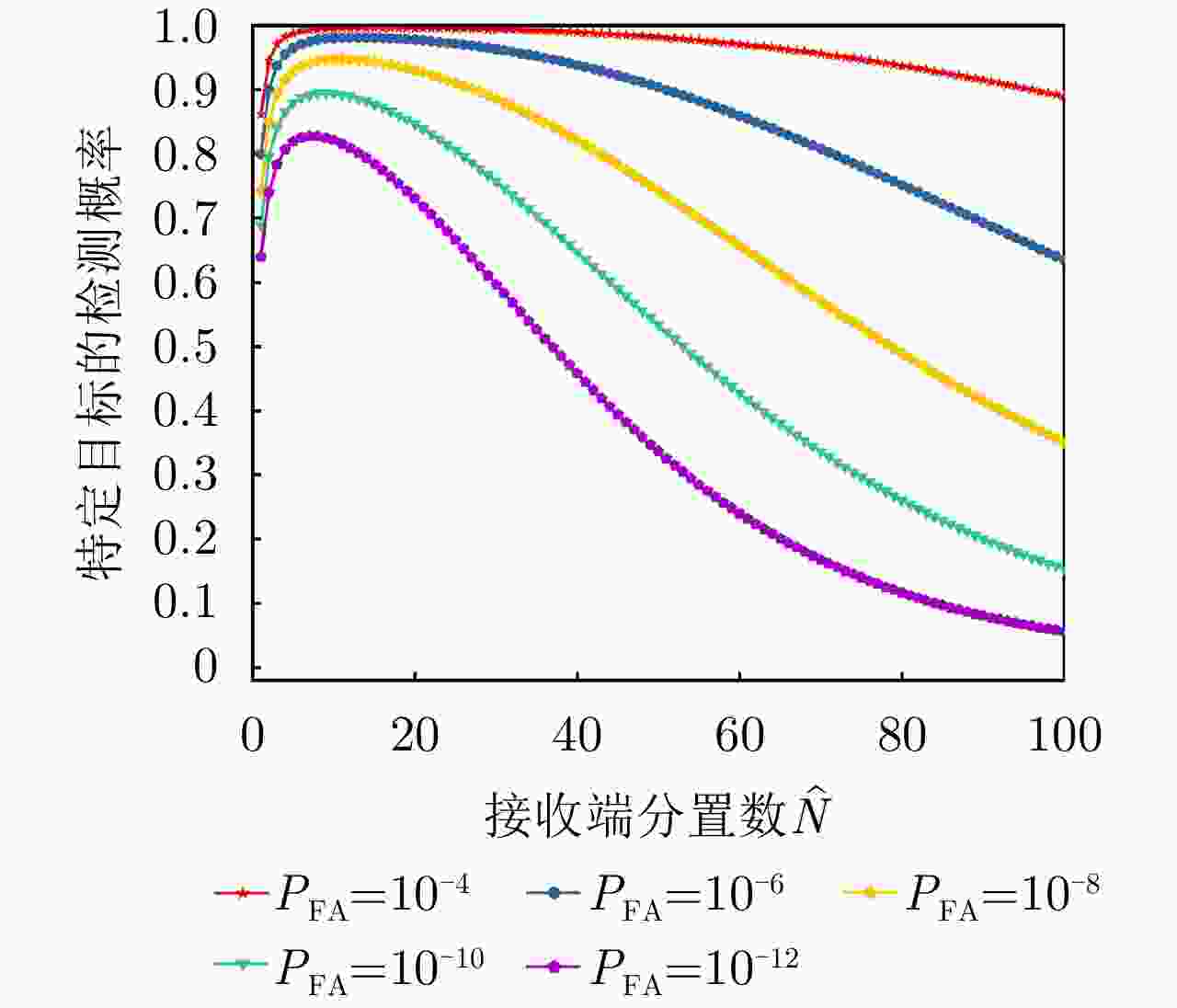
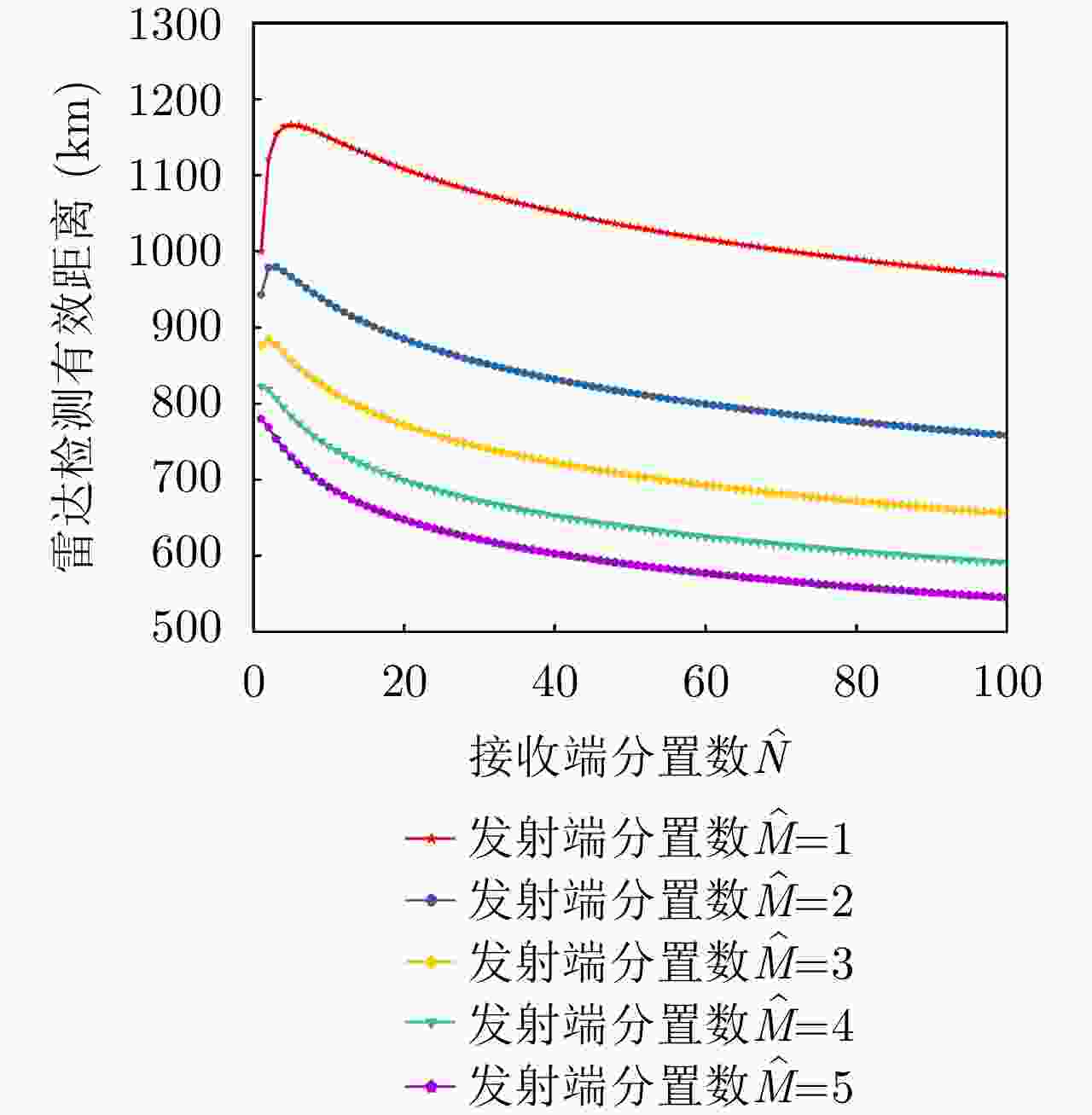
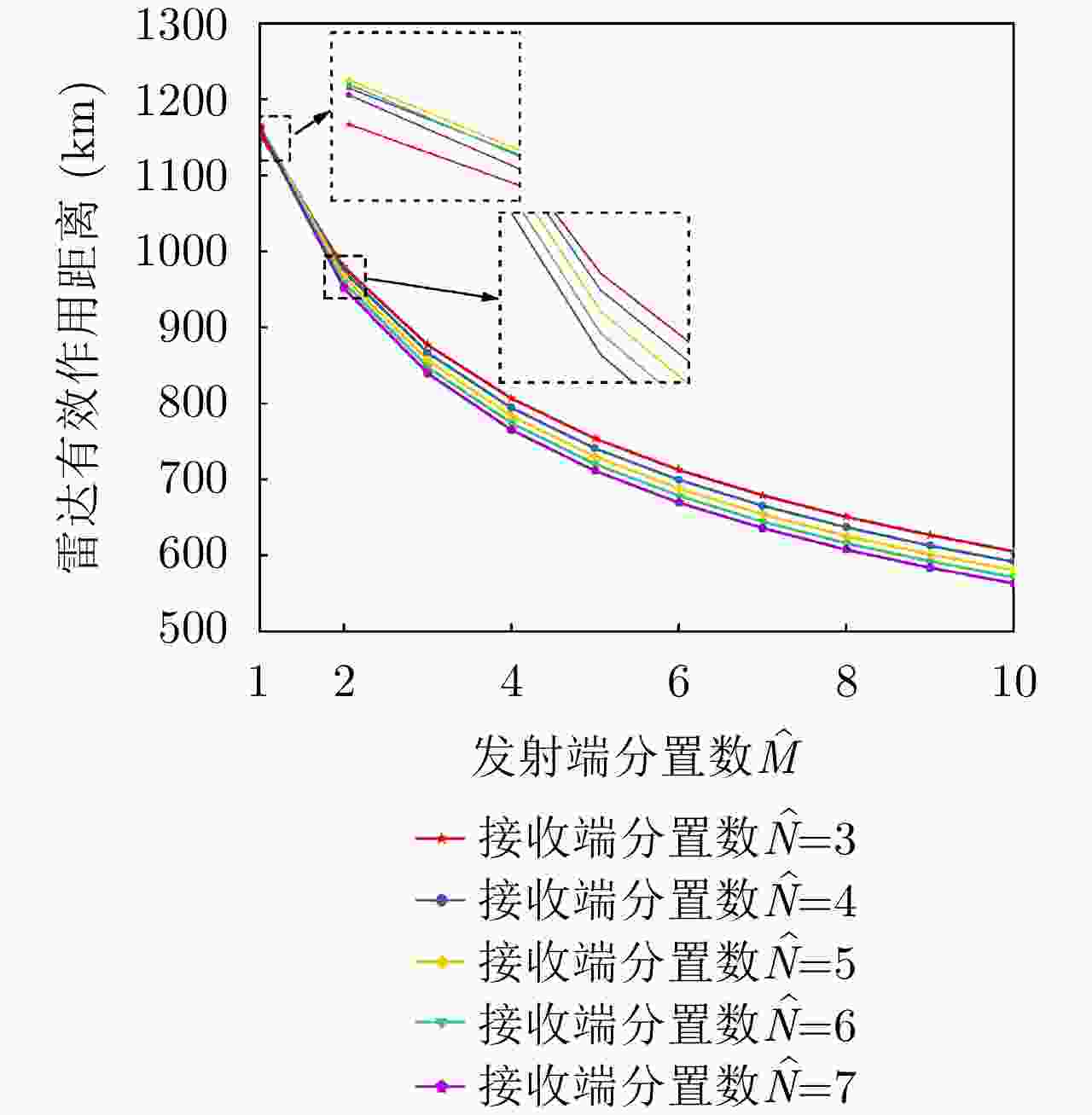
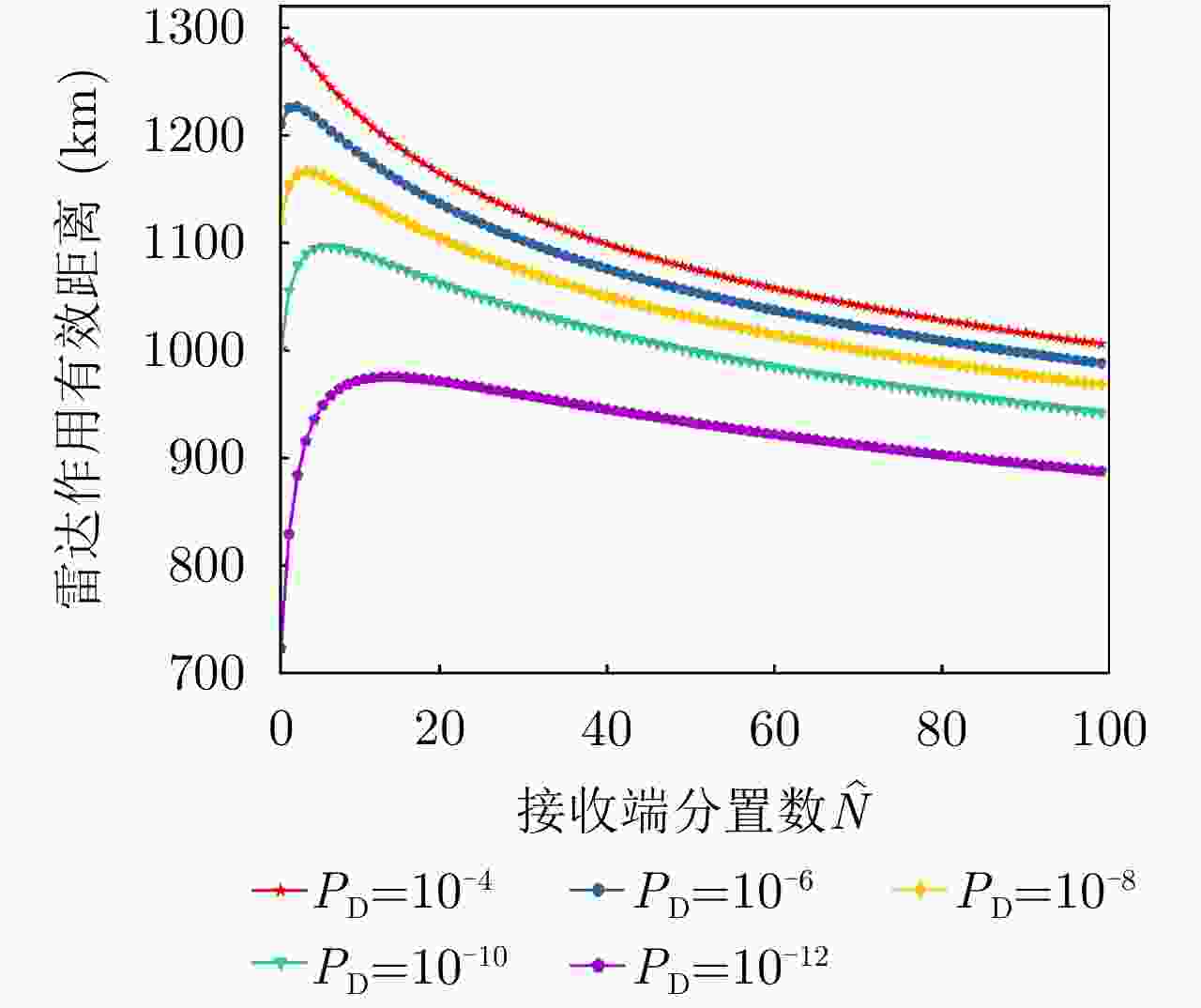
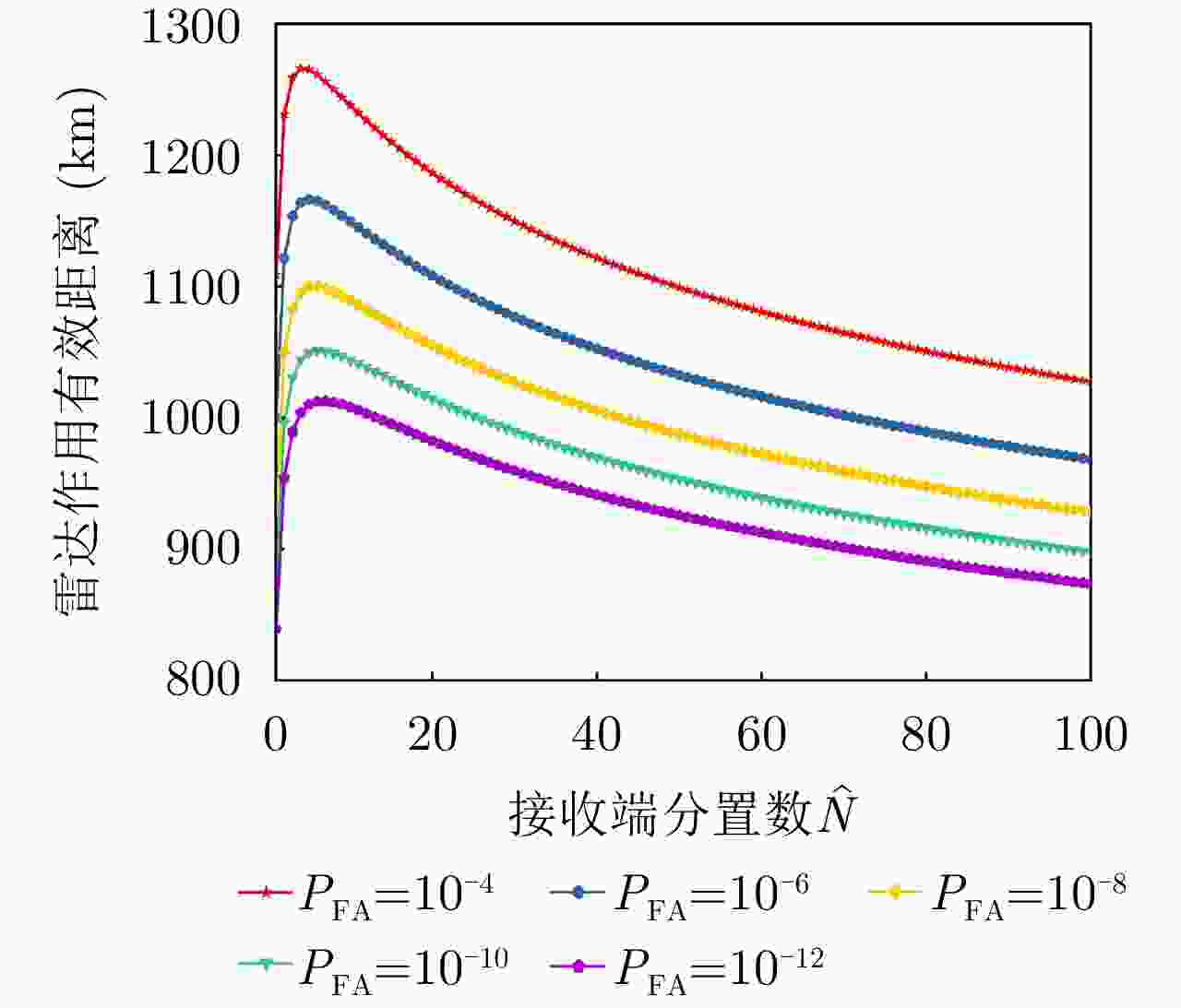
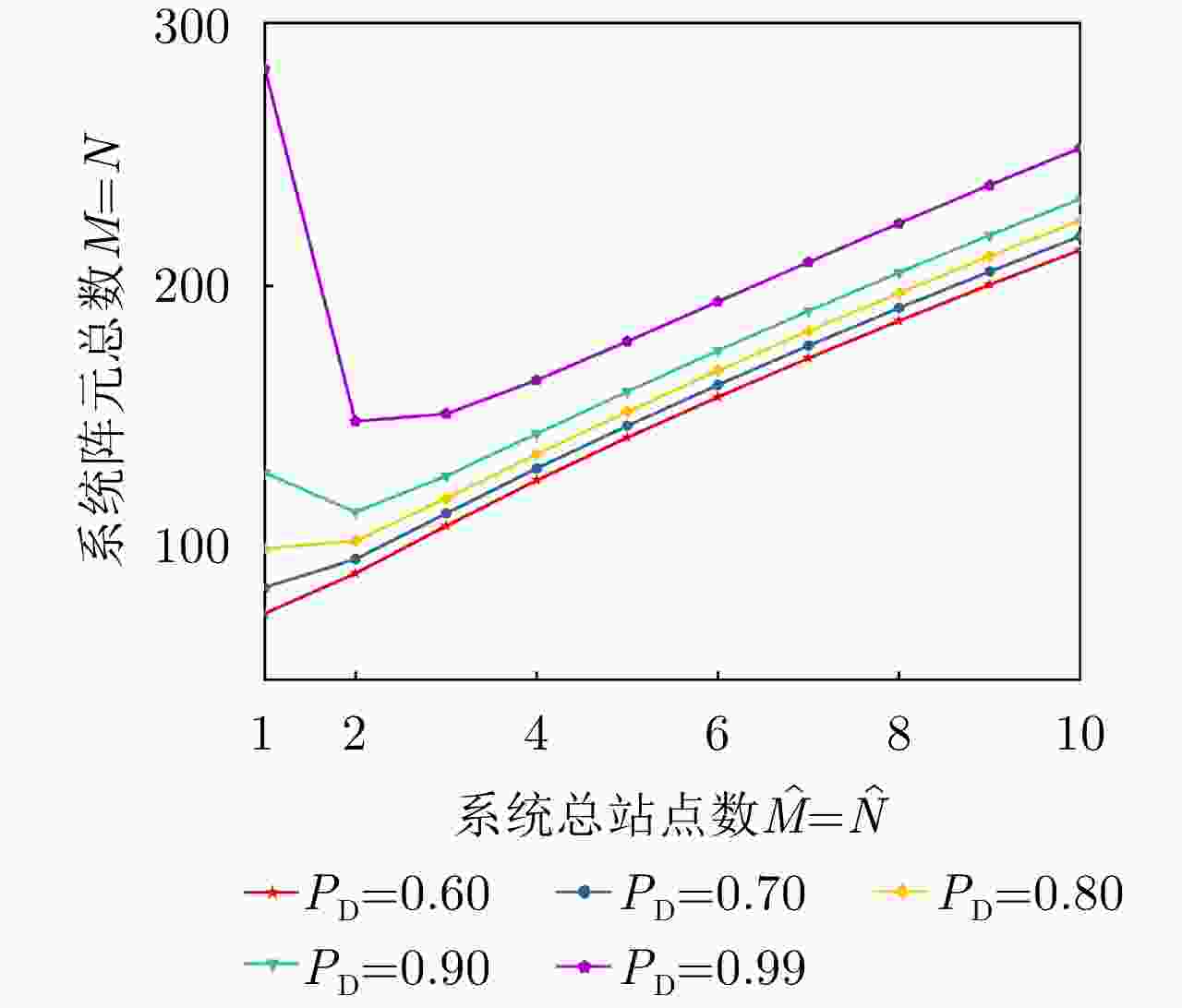
项目 最优指标值 配置策略 收敛时间 优化问题1 $ {P_{{\text{D}}\max }} = 0.98 $ $ {\text{(}}\hat M,\hat N{\text{)}} = {\text{(}}1,13{\text{)}} $ 87.275 s 优化问题2 ${R_{{\rm{E}}\max } } = 1166.3\;{\text{km} }$ $ {\text{(}}\hat M,\hat N{\text{)}} = {\text{(}}1,5{\text{)}} $ 86.778 s 优化问题3 $ M,\hat M $ 取决于$ {P_{{\text{FA}}}} $, $ {P_{\text{D}}} $ / MIMO雷达 ${P_{\text{D} } } = 0.63,\;{R_{\rm{E}}} = 1006\;{\text{km} }$ $ {\text{(}}\hat M,\hat N{\text{)}} = {\text{(}}100,100{\text{)}} $ / 相控阵雷达 ${P_{\text{D} } } = 0.80,\;{R_{\rm{E}}} = 1000\;{\text{km} }$ $ {\text{(}}\hat M,\hat N{\text{)}} = {\text{(}}1,1{\text{)}} $ / -
[1] MALANOWSKI M and KULPA K. Detection of moving targets with continuous-wave noise radar: Theory and measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(9): 3502–3509. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2181521 [2] ZHU Zhenghan, KAY S, and RAGHAVAN R S. Information-theoretic optimal radar waveform design[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(3): 274–278. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2655879 [3] YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, PU Wenqiang, et al. Joint beam selection and power allocation for multiple target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(24): 6417–6427. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2607147 [4] XU Luzhou, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Target detection and parameter estimation for MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 927–939. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655353 [5] SHI Chenguang, WANG Yijie, SALOUS S, et al. Joint transmit resource management and waveform selection strategy for target tracking in distributed phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2762–2778. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3138869 [6] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, XIE Junwei, et al. Joint subarray selection and power allocation for cognitive target tracking in large-scale MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 2569–2580. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2960401 [7] YAN Junkun, ZHANG Peng, DAI Jinhui, et al. Target capacity based simultaneous multibeam power allocation scheme for multiple target tracking application[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 178: 107794. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107794 [8] ZHANG Haowei, ZHOU Hao, ZONG Binfeng, et al. A fast power allocation strategy for multibeam tracking multiple targets in clutter[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(1): 1249–1257. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3059257 [9] YAN Junkun, DAI Jinhui, PU Wenqiang, et al. Target capacity based resource optimization for multiple target tracking in radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 2410–2421. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3071173 [10] YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, JIU Bo, et al. Simultaneous multibeam resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3110–3122. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2417504 [11] 张大琳, 易伟, 孔令讲. 面向组网雷达干扰任务的多干扰机资源联合优化分配方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 595–606. doi: 10.12000/JR21071ZHANG Dalin, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Optimal joint allocation of multijammer resources for jamming netted radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 595–606. doi: 10.12000/JR21071 [12] FISHLER E, HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R, et al. MIMO radar: An idea whose time has come[C]. Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37509), Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 71–78. [13] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Joint target assignment and resource optimization framework for multitarget tracking in phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 4379–4390. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3025867 [14] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812 [15] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMINI L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448 [16] FISHLER E, HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R S, et al. Spatial diversity in radars—models and detection performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 823–838. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862813 [17] 张光义. 相控阵雷达原理[M]. 国防工业出版社, 2009, 13–18.ZHANG Guangyi, Principle of Phased Array Radar[M]. National Defense Industry Press, 2009, 13–18. [18] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1990, 236–243. [19] BUTT F A, NAQVI I H, and RIAZ U. Hybrid phased-MIMO radar: A novel approach with optimal performance under electronic countermeasures[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(6): 1184–1187. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2828408 [20] HASSANIEN A and VOROBYOV S A. Phased-MIMO radar: A tradeoff between phased-array and MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(6): 3137–3151. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2043976 [21] DELIGIANNIS A, AMIN M, LAMBOTHARAN S, et al. Optimum sparse subarray design for multitask receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(2): 939–950. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2867258 [22] YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, LEUNG H, et al. Joint placement of transmitters and receivers for distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(1): 122–134. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2649338 [23] RADMARD M, CHITGARHA M M, MAJD M N, et al. Antenna placement and power allocation optimization in MIMO detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1468–1478. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120776 [24] XU Jia, DAI Xizeng, XIA Xianggen, et al. Optimizations of multisite radar system with MIMO radars for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2329–2343. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034636 [25] 费太勇, 谭贤四, 张堃, 等. 分布式MIMO数字阵列雷达阵元优化配置[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(8): 22–27. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.006FEI Taiyong, TAN Xiansi, ZHANG Kun, et al. Optimizations of elements configurations for distributed MIMO digital array radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(8): 22–27. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.006 [26] 费太勇, 谭贤四, 林强, 等. 分布式MIMO数字阵列雷达检测性能研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 45(12): 80–85. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.171213FEI Taiyong, TAN Xiansi, LIN Qiang, et al. Research on detection performance for distributed MIMO digital array radar[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2017, 45(12): 80–85. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.171213 [27] ZHOU Shenghua, LIU Hongwei, ZHAO Yongbo, et al. Target spatial and frequency scattering diversity property for diversity MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91(2): 269–276. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.07.004 [28] SIDIROPOULOS N D, GINI F, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Academic Press Library in Signal Processing: Volume 2: Communications and Radar Signal Processing[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 329–408. [29] XU Jia, DAI Xizeng, XIA Xianggen, et al. Optimal transmitting diversity degree-of-freedom for statistical MIMO radar[C]. 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2010: 437–440. [30] SUN Jun, XU Wenbo, and FENG Bin. A global search strategy of quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization[C]. IEEE Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems, 2004, Singapore, 2004: 111–116. [31] SUN Jun, XU Wenbo, and FENG Bin. Adaptive parameter control for quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization on individual level[C]. 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Waikoloa, USA, 2005: 3049–3054. [32] ZHANG Haowei, SHI Junpeng, ZHANG Qiliang, et al. Antenna selection for target tracking in collocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 423–436. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3031767 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: