Review of the Method for Distributed Multi-sensor Multi-target Tracking(in English)
-
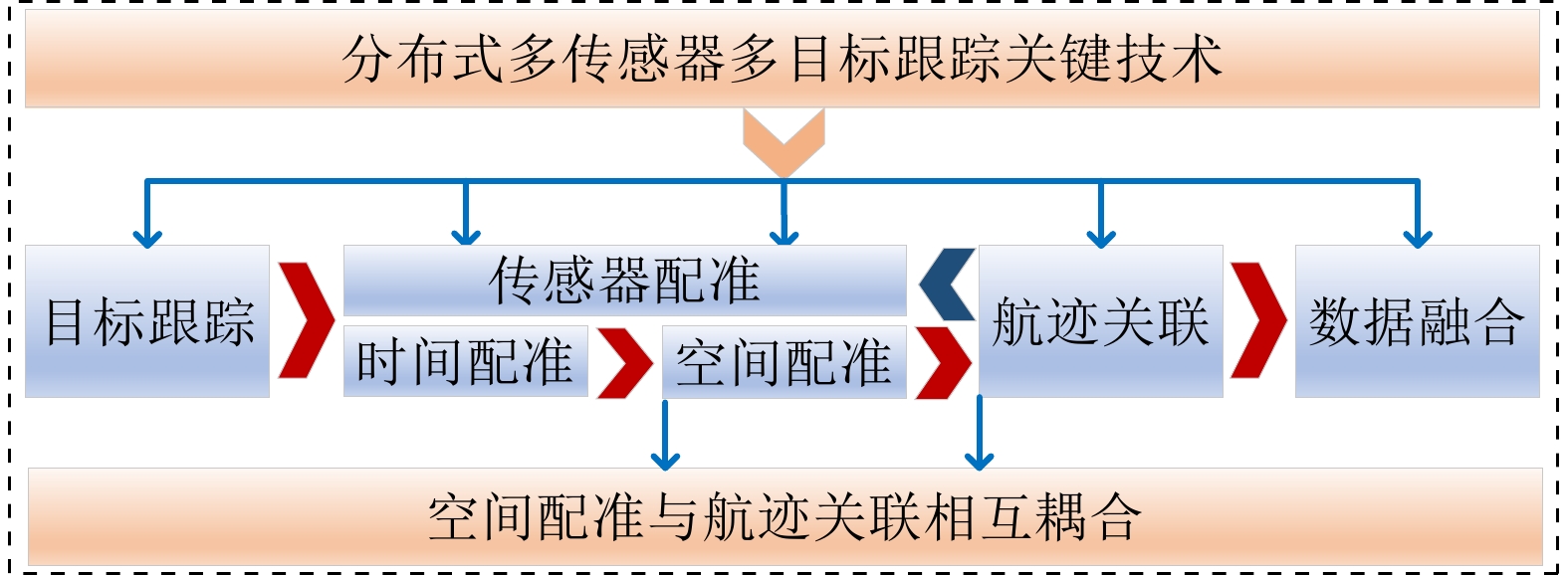
摘要: 多传感器多目标跟踪是信息融合领域的热点问题,其通过融合多个局部传感器数据,提高目标跟踪精度和稳定性。多传感器多目标跟踪按融合体系可分为分布式、集中式、混合式3类,其中分布式融合结构对网络通信带宽要求低、可靠性和稳定性强,广泛应用于军事、民用领域。该文聚焦分布式多传感器多目标跟踪涉及的目标跟踪、传感器配准、航迹关联、数据融合4项关键技术,主要分析了各关键技术的理论原理与适用条件,重点介绍了不完整测量条件下的空间配准与航迹关联,并给出仿真结果。最后,该文总结了现有分布式多传感器多目标跟踪关键技术存在的问题,并指出了其未来发展趋势。
-
关键词:
- 分布式多传感器多目标跟踪 /
- 目标跟踪 /
- 传感器配准 /
- 航迹关联 /
- 数据融合
Abstract: Multi-sensor multi-target tracking is a popular topic in the field of information fusion. It improves the accuracy and stability of target tracking by fusing multiple local sensor information. By the fusion system, the multi-sensor multi-target tracking is grouped into distributed fusion, centralized fusion, and hybrid fusion. Distributed fusion is widely applied in the military and civilian fields with the advantages of strong reliability, high stability, and low requirements on network communication bandwidth. Key techniques of distributed multi-sensor multi-target tracking include multi-target tracking, sensor registration, track-to-track association, and data fusion. This paper reviews the theoretical basis and applicable conditions of these key techniques, highlights the incomplete measurement spatial registration algorithm and track association algorithm, and provides the simulation results. Finally, the weaknesses of the key techniques of distributed multi-sensor multi-target tracking are summarized, and the future development trends of these key techniques are surveyed. -
图 5 Registration results before and after registration in the WGS84 coordinate system [ 82]
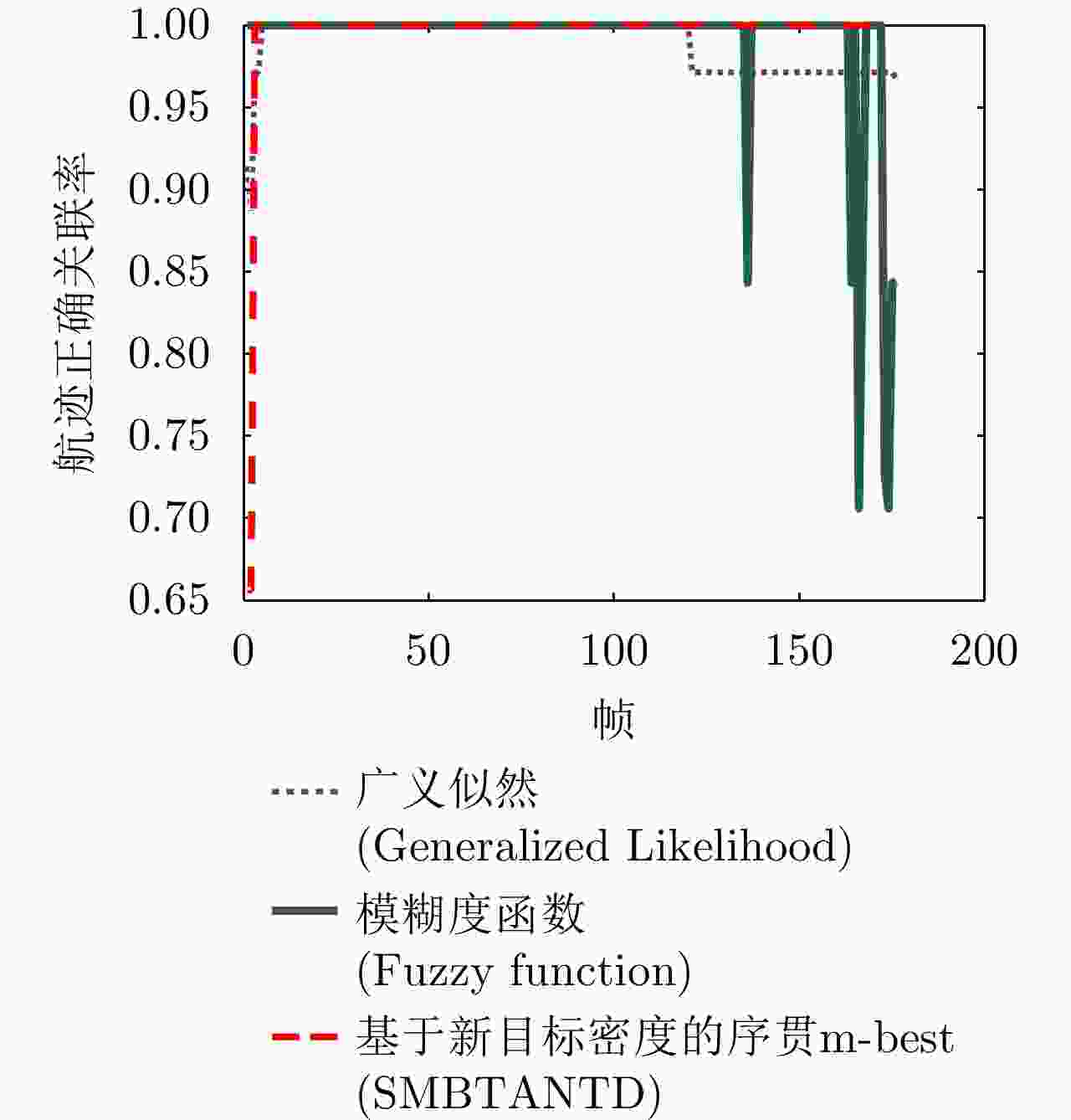
图 8 Accuracy of track association [ 82]
图 9 Relationship of track-track association and spatial registration [ 82]
表 1 典型的多目标跟踪方法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different multi-target tracking methods
多目标跟踪类型 跟踪方法 跟踪精度 运算量 数据关联类 GNN 低 低 JPDA 中等 中等 JIPDA 中等 中等 MHT 高 高 随机有限集类 PHD 低 低 CPHD 中等 中等 TPHD 中等 低 TCPHD 中等 中等 MeMBer 中等 中等 PMBM 高 中等 GLMB 高 高 LMB 高 中等 表 2 多传感器时间配准方法性能对比
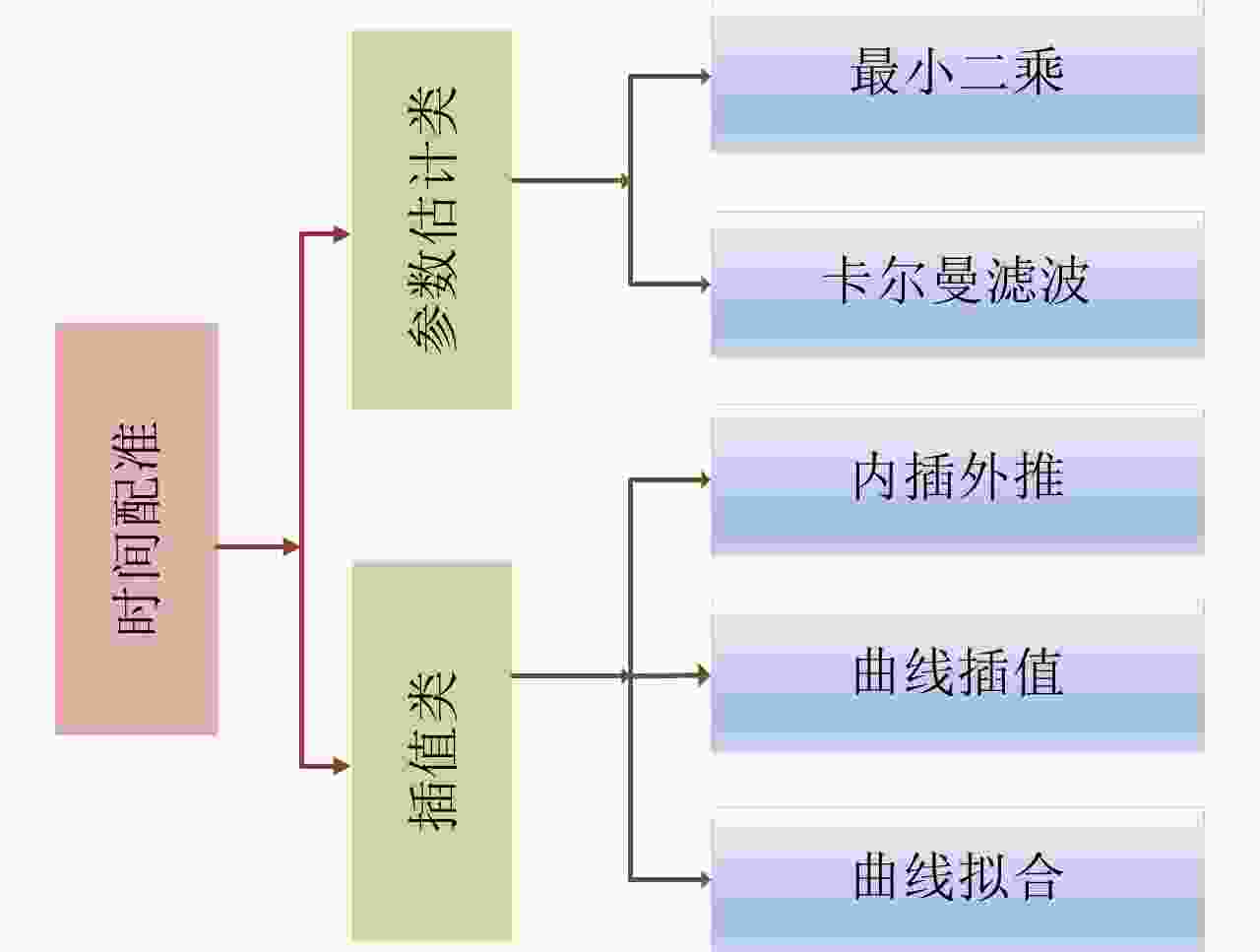
Table 2. Comparison of multi-sensor time registration methods
配准类型 配准方法 配准精度 计算量 目标运动状态 插值类 内插外推 较低 低 匀速 曲线插值 中等 较高 匀速\非匀速 曲线拟合 中等 较高 匀速\非匀速 参数估计类 最小二乘 中等 中等 匀速 卡尔曼滤波 较高 较高 匀速\非匀速 表 3 多传感器非合作目标空间配准方法分类
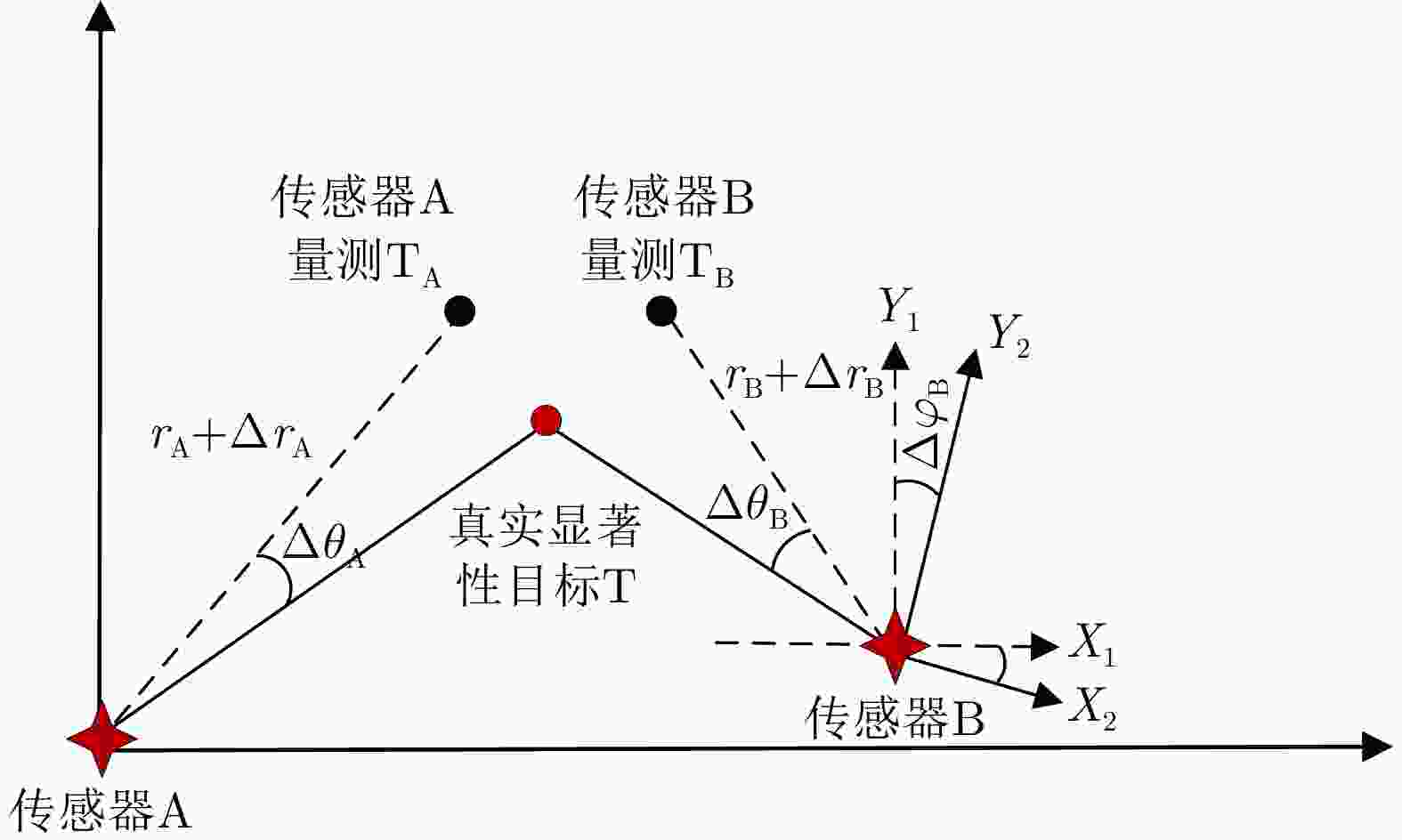
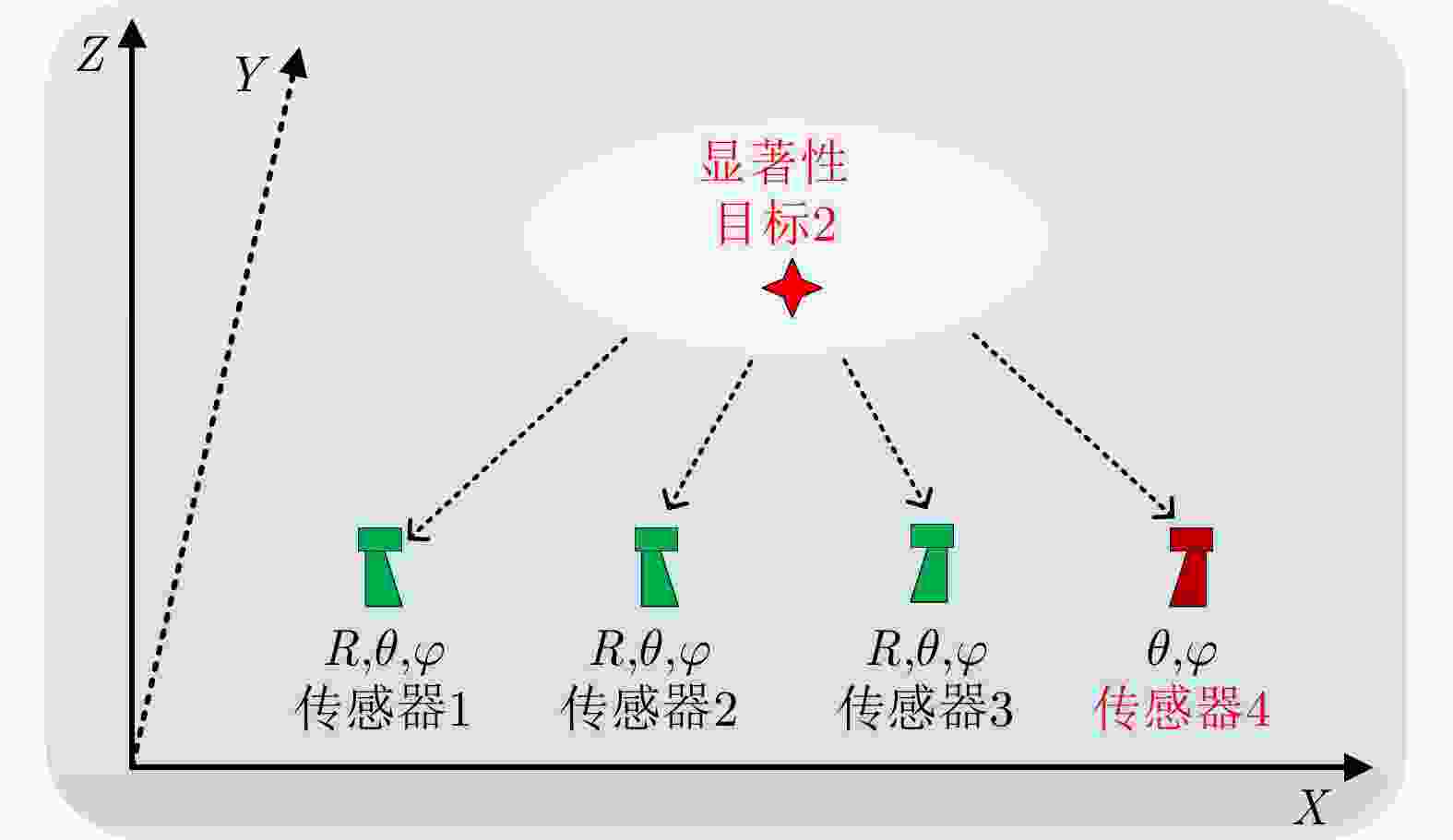
Table 3. Classification of multi-sensor spatial registration methods based on non-cooperative targets
配准方法 实时性 是否能估计
目标位置参与传感器
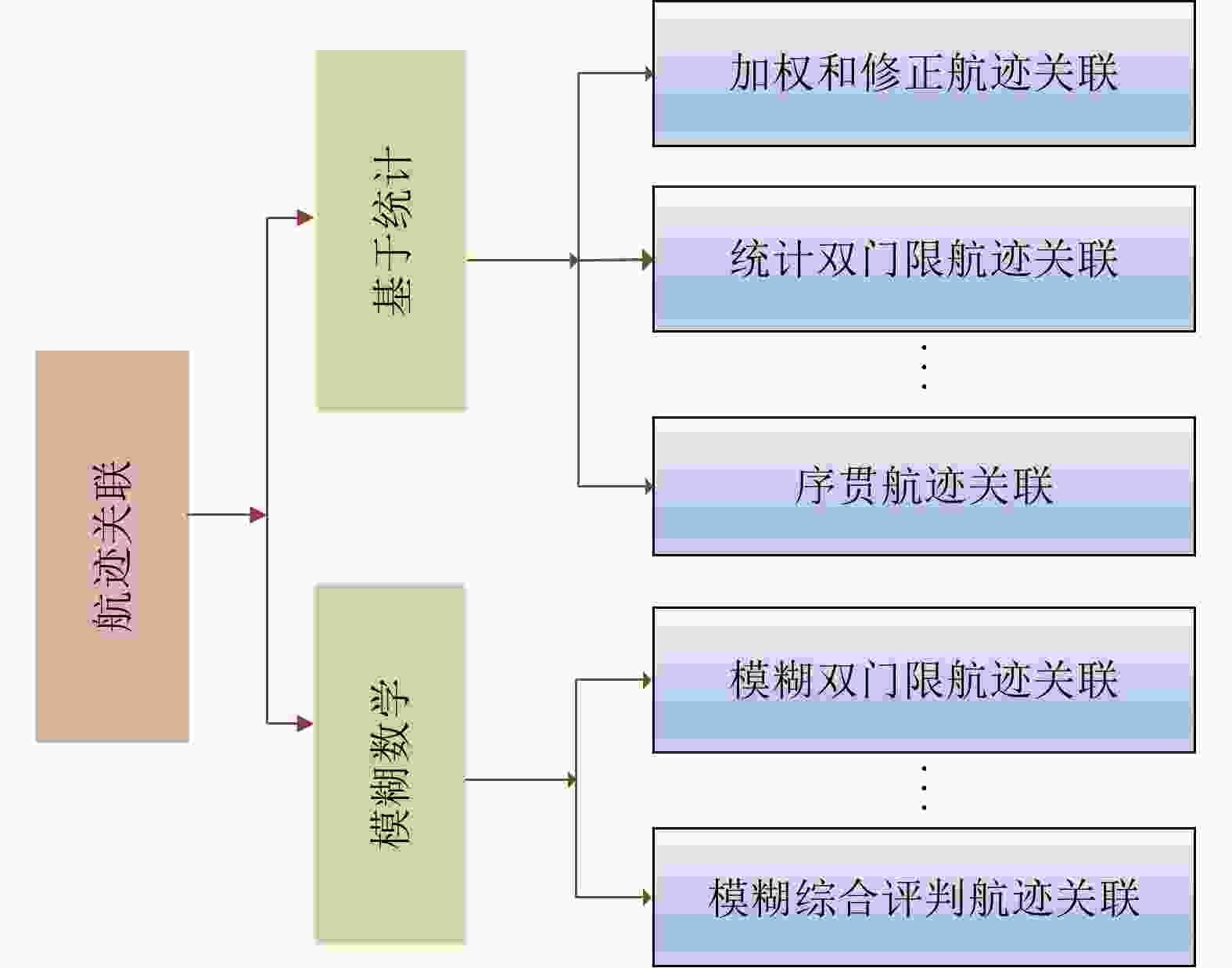
个数传感器类型 RTQC 离线 否 两个 同类 LS 离线 否 两个 同类 GLS 离线 否 两个 同类 EML 离线 是 两个 同类 KF 在线 是 多个 同类 RFS 在线 是 多个 同类 MLR 离线 是 多个 同类\异类 RBER 离线 是 多个 同类\异类 表 4 航迹关联性能对比
Table 4. Comparison of multi-sensor track-to-track association methods
表 5 多传感器估计融合方法对比
Table 5. Comparison of multi-sensor estimation fusion methods
估计融合方法 是否考虑
航迹相关计算量 融合
精度传感器
类型简单凸组合融合 否 低 低 同类 Bar-Shalom-Campo融合 是 较高 较高 同类 基于MAP 是 较高 较高 同类 CI融合 是 较高 较高 同类 GCI融合 是 较高 较高 同类/异类 AA融合 是 较高 较高 同类/异类 基于EKF融合 否 较高 较高 同类/异类 基于UKF融合 否 较高 较高 同类/异类 基于PF融合 否 高 高 同类/异类 表 6 典型的多传感器多目标跟踪方法性能对比
Table 6. Performance comparison of multi-sensor multi-target tracking methods
多目标跟踪类型 融合准则 跟踪方法 运算量 跟踪精度 数据关联类 CI融合 JPDA 中等 中等 简单凸组合融合 MHT 高 中等 随机有限集类 GCI/GA融合 PHD 低 低 CPHD 中等 中等 MeMBer 中等 中等 GLMB 高 高 LMB 中等 高 AA融合 PHD 低 低 CPHD 中等 中等 MeMBer 中等 中等 GLMB 高 高 LMB 中等 高 表 1 Performance comparison of different multi-target tracking methods
Types of multiple target tracking Tracking methods Tracking accuracy Computational complexity Data association GNN Low Low JPDA Medium Medium JIPDA Medium Medium MHT High High Random finite set PHD Low Low CPHD Medium Medium TPHD Medium Low TCPHD Medium Medium MeMBer Medium Medium PMBM High Medium GLMB High High LMB High Medium 表 2 Comparison of multi-sensor time registration methods
Registration types Registration methods Registration accuracy Computational complexity Target motion state Interpolation class Interpolation and extrapolation Lower Lower Uniform Curve interpolation Medium Higher Uniform \ Non-uniform Curve fitting Medium Higher Uniform \ Non-uniform Parameter estimation Least squares Medium Medium Uniform Kalman filter Higher Higher Uniform \ Non-uniform 表 3 Classification of multi-sensor spatial registration methods based on non-cooperative targets
Registration methods Real-time Can the target position be estimated? Number of sensors Sensor type RTQC Offline No Two Homogeneous LS Offline No Two Homogeneous GLS Offline No Two Homogeneous EML Offline Yes Two Homogeneous KF Online Yes Multiple Homogeneous RFS Online Yes Multiple Homogeneous MLR Offline Yes Multiple Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous RBER Offline Yes Multiple Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous 表 4 Comparison of multi-sensor track-to-track association methods
表 5 Comparison of multi-sensor estimation fusion methods
Estimation fusion method Whether to consider track correlation Computational
complexityFusion accuracy Sensor type Simple convex combination fusion No Low Low Homogeneous Bar-Shalom-Campo fusion Yes Higher Higher Homogeneous MAP fusion Yes Higher Higher Homogeneous CI fusion Yes Higher Higher Homogeneous GCI fusion Yes Higher Higher Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous AA fusion Yes Higher Higher Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous EKF fusion No Higher Higher Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous UKF fusion No Higher Higher Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous PF fusion No High High Homogeneous \ Heterogeneous 表 6 Performance comparison of multi-sensor multi-target tracking methods
Types of multiple target tracking Fusion criteria Tracking methods Computational complexity Tracking accuracy Data association CI Fusion JPDA Medium Medium Simple convex combination fusion MHT High Medium Random finite set GCI/GA fusion PHD Low Low CPHD Medium Medium MeMBer Medium Medium GLMB High High LMB Medium High AA fusion PHD Low Low CPHD Medium Medium MeMBer Medium Medium GLMB High High LMB Medium High -
[1] 韩崇昭, 朱洪艳, 段战胜, 等. 多源信息融合[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 1–13.HAN Chongzhao, ZHU Hongyan, DUAN Zhansheng, et al. Multi-Source Information Fusion[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 1–13. [2] 陈科文, 张祖平, 龙军. 多源信息融合关键问题、研究进展与新动向[J]. 计算机科学, 2013, 40(8): 6–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2013.08.002.CHEN Kewen, ZHANG Zuping, and LONG Jun. Multisource information fusion: Key issues, research progress and new trends[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 40(8): 6–13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2013.08.002. [3] 李龙飘. 多传感器系统中信息融合技术的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中北大学, 2009.LI Longpiao. Research on data fusion technique of multi-sensor system[D]. [Master dissertation], North University of China, 2009. [4] 苏军平. 多传感器信息融合关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.SU Junping. Research on the key technology of the multi-sensor information fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [5] 王晓丽. 基于雷达组网提高空中目标航迹测量精度的数据融合方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012.WANG Xiaoli. Research on data fusion based on netted radar to improve measurement precision of aerial targets’ flight track[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012. [6] ZHU Shanshan. Multi-source information fusion technology and its engineering application[J]. Research in Health Science, 2020, 4(4): 408–422. doi: 10.22158/rhs.v4n4p408. [7] ANITHA R, RENUKA S, and ABUDHAHIR A. Multi sensor data fusion algorithms for target tracking using multiple measurements[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, Enathi, India, 2013: 1–4. [8] AEBERHARD M, SCHLICHTHARLE S, KAEMPCHEN N, et al. Track-to-track fusion with asynchronous sensors using information matrix fusion for surround environment perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1717–1726. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2202229. [9] SHEN Qiang, LIU Jieyu, ZHOU Xiaogang, et al. Centralized fusion methods for multi-sensor system with bounded disturbances[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 141612–141626. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943163. [10] 赵蕊, 贺建军. 多传感器信息融合技术[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2007, 15(9): 1124–1126, 1134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2007.09.001.ZHAO Rui and HE Jianjun. Technology of multi-sensor information fusion[J]. Computer Measurement &Control, 2007, 15(9): 1124–1126, 1134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2007.09.001. [11] 吕漫丽, 孙灵芳. 多传感器信息融合技术[J]. 自动化技术与应用, 2008, 27(2): 79–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2008.02.025.LV Manli and SUN Lingfang. Multi-sensor information fusion technology[J]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2008, 27(2): 79–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2008.02.025. [12] 何友, 彭应宁, 陆大絟. 多传感器数据融合模型综述[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 1996, 36(9): 14–20.HE You, PENG Yingning, and LU Dajin. Survey of multisensor data fusion models[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 1996, 36(9): 14–20. [13] WANG Zhangjing, WU Yu, and NIU Qingqing. Multi-sensor fusion in automated driving: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 2847–2868. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962554. [14] LIN Xiangdong, BAR-SHALOM Y, and KIRUBARAJAN T. Multisensor multitarget bias estimation for general asynchronous sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(3): 899–921. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1541438. [15] 何友, 王国宏, 陆大絟, 等. 多传感器信息融合及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2000: 2–11.HE You, WANG Guohong, LU Dajin, et al. Multisensor Information Fusion with Applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2000: 2–11. [16] 高青. 多传感器数据融合算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2008.GAO Qing. Algorithms research on multisensor data fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2008. [17] 肖斌. 多传感器信息融合及其在工业中的应用[D]. [硕士论文], 太原理工大学, 2008.XIAO Bin. Multi-sensor information fusion and its application in industry[D]. [Master dissertation], Taiyuan University of Technology, 2008. [18] 陈文辉, 马铁华. 多传感器信息融合技术的研究与进展[J]. 科技情报开发与经济, 2006, 16(19): 212–213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2006.19.124.CHEN Wenhui and MA Tiehua. The research and progress of multi-sensor information fusion techniques[J]. Sci-Tech Information Development &Economy, 2006, 16(19): 212–213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2006.19.124. [19] NAZARI M, PASHAZADEH S, and MOHAMMAD-KHANLI L. An adaptive density-based fuzzy clustering track association for distributed tracking system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 135972–135981. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941184. [20] DASH D and JAYARAMAN V. A probabilistic model for sensor fusion using range-only measurements in multistatic radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(6): 1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.2993589. [21] SHARMA A and CHAUHAN S. Sensor fusion for distributed detection of mobile intruders in surveillance wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(24): 15224–15231. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3009828. [22] KUMAR M, GARG D P, and ZACHERY R A. A method for judicious fusion of inconsistent multiple sensor data[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2007, 7(5): 723–733. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2007.894905. [23] LLINAS J and HALL D L. An introduction to multi-sensor data fusion[C]. The 1998 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits & Systems, Monterey, USA, 1998: 537–540. [24] HU Jinwen, ZHENG Boyin, WANG Ce, et al. A survey on multi-sensor fusion based obstacle detection for intelligent ground vehicles in off-road environments[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology &Electronic Engineering, 2020, 21(5): 675–692. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1900518. [25] XIAO Fuyuan. Multi-sensor data fusion based on the belief divergence measure of evidences and the belief entropy[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 46: 23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.04.003. [26] KHALEGHI B, KHAMIS A, KARRAY F O, et al. Multisensor data fusion: A review of the state-of-the-art[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(1): 28–44. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.001. [27] LIGGINS II M, POULARIKAS A D, HALL D, et al. Handbook of Multisensor Data Fusion: Theory and Practice[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009: 3–16. [28] GAO Shesheng, ZHONG Yongmin, and LI Wei. Random weighting method for multisensor data fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2011, 11(9): 1955–1961. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2107896. [29] CARON F, DAVY M, DUFLOS E, et al. Particle filtering for multisensor data fusion with switching observation models: Application to land vehicle positioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(6): 2703–2719. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.893914. [30] MITCHELL H B. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion: An Introduction[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 1–22. [31] MAHLER R P S. Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston: Artech House, Inc., 2007: 305–682. [32] DALEY R. Estimating the wind field from chemical constituent observations: Experiments with a one-dimensional extended Kalman filter[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1995, 123(1): 181–198. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1995)123<0181:ETWFFC>2.0.CO;2. [33] WAN E A and VAN DER MERWE R. The Unscented Kalman Filter[M]. HAYKIN S. Kalman Filtering and Neural Networks. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2001: 221–280. [34] ARASARATNAM I and HAYKIN S. Cubature Kalman filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(6): 1254–1269. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2019800. [35] GUSTAFSSON F. Particle filter theory and practice with positioning applications[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2010, 25(7): 53–82. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2010.5546308. [36] VO B N, MALLICK M, BAR-SHALOM Y, et al. Multitarget Tracking[M]. WEBSTER J G. Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2015: 1–11. [37] BAR-SHALOM Y. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Applications and Advances[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1990: 2–9. [38] FORTMANN T, BAR-SHALOM Y, and SCHEFFE M. Sonar tracking of multiple targets using joint probabilistic data association[J]. IEEE journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1983, 8(3): 173–184. doi: 10.1109/JOE.1983.1145560. [39] COLGROVE S B, DAVIS A W, and AYLIFFE J K. Track initiation and nearest neighbours incorporated into probabilistic data association[J]. Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineers,Australia, 1986, 6(3): 191–198. [40] CHANG K C and BAR-SHALOM Y. Joint probabilistic data association for multitarget tracking with possibly unresolved measurements and maneuvers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1984, 29(7): 585–594. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1984.1103597. [41] MUSICKI D and EVANS R. Joint integrated probabilistic data association-JIPDA[C]. The 5th International Conference on Information Fusion, Annapolis, USA, 2002: 1120–1125. [42] SINGER R A and SEA R G. New results in optimizing surveillance system tracking and data correlation performance in dense multitarget environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1973, 18(6): 571–582. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1973.1100421. [43] SONG T L, LEE D G, and RYU J. A probabilistic nearest neighbor filter algorithm for tracking in a clutter environment[J]. Signal Processing, 2005, 85(10): 2044–2053. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.01.016. [44] REID D B. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets[J]. IEEE transactions on Automatic Control, 1979, 24(6): 843–854. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1979.1102177. [45] BLACKMAN S S. Multiple hypothesis tracking for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 5–18. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263228. [46] MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119. [47] MAHLER R. PHD filters of higher order in target number[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(4): 1523–1543. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4441756. [48] GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F and SVENSSON L. Trajectory PHD and CPHD filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(22): 5702–5714. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2943234. [49] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. On multi-Bernoulli approximations to the Bayes multi-target filter[C]. International Conference on Information Fusion, Xi’an, China, 2007: 1–8. [50] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924. [51] VO B T and VO B N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(13): 3460–3475. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2259822. [52] PAPI F, VO B N, VO B T, et al. Generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli approximation of multi-object densities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(20): 5487–5497. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2454478. [53] REUTER S, VO B T, VO B N, et al. The Labeled multi-Bernoulli filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(12): 3246–3260. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2323064. [54] GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, WILLIAMS J L, GRANSTRÖM K, et al. Poisson multi-Bernoulli mixture filter: Direct derivation and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1883–1901. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805153. [55] LIN Xiangdong, BAR-SHALOM Y, and KIRUBARAJAN T. Exact multisensor dynamic bias estimation with local tracks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(2): 576–590. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1310006. [56] BLAIR W D, RICE T R, ALOUANI A T, et al. Asynchronous data fusion for target tracking with a multitasking radar and optical sensor[C]. The SPIE of 1482, Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing V, Orlando, USA, 1991: 234–245. [57] 李莉. 最小二乘法时间配准在测量数据融合中的应用[J]. 仪表技术, 2017(12): 35–36, 49. doi: 10.19432/j.cnki.issn1006-2394.2017.12.010.LI Li. Application of time registration of the least square method in measurement data fusion[J]. Instrumentation Technology, 2017(12): 35–36, 49. doi: 10.19432/j.cnki.issn1006-2394.2017.12.010. [58] 吴聪, 王红, 李志淮, 等. 基于最小二乘曲线拟合的时间配准方法研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2013, 36(4): 44–47, 51. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2013.04.018.WU Cong, WANG Hong, LI Zhihuai, et al. Research into time registration method based on least-square curve fitting[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2013, 36(4): 44–47, 51. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2013.04.018. [59] 张圣华, 王书基, 孙潮义. 多雷达数据融合中时间对准问题的研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2001, 21(2): 23–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2001.02.005.ZHANG Shenghua, WANG Shuji, and SUN Chaoyi. Research on time registration in multi-radar data fusion[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2001, 21(2): 23–25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2001.02.005. [60] 梁凯, 潘泉, 宋国明, 等. 基于曲线拟合的多传感器时间对准方法研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2006, 31(12): 51–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.12.015.LIANG Kai, PAN Quan, SONG Guoming, et al. The study of multi-sensor time registration method based on curve fitting[J]. Fire Control and Command Control, 2006, 31(12): 51–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2006.12.015. [61] YU Hongbo, WANG Guohong, and CAO Qian. A novel approach for time registration of multi-radar data[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 385/386: 1377–1380. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.385-386.1377. [62] LI Song, CHENG Yongmei, BROWN D, et al. Comprehensive time-offset estimation for multisensor target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2351–2373. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2948517. [63] TAGHAVI E, THARMARASA R, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. A practical bias estimation algorithm for multisensor-multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(1): 2–19. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140574. [64] OKELLO N N and CHALLA S. Joint sensor registration and track-to-track fusion for distributed trackers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 808–823. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337456. [65] RHODE S, USEVICH K, MARKOVSKY I, et al. A recursive restricted total least-squares algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5652–5662. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2350959. [66] FORTUNATI S, FARINA A, GINI F, et al. Least squares estimation and Cramér-Rao type lower bounds for relative sensor registration process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(3): 1075–1087. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2097258. [67] PULFORD G W. Analysis of a nonlinear least squares procedure used in global positioning systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(9): 4526–4534. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2050061. [68] BAI Shulin and ZHANG Yumei. Error registration of netted radar by using GLS algorithm[C]. The 33rd Chinese Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 2014: 7430–7433. [69] LU Chenyang, WANG Xiaorui, and KOUTSOUKOS X. Feedback utilization control in distributed real-time systems with end-to-end tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2005, 16(6): 550–561. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2005.73. [70] ZHOU Yifeng, LEUNG H, and YIP P C. An exact maximum likelihood registration algorithm for data fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(6): 1560–1573. doi: 10.1109/78.599998. [71] CHITOUR Y and PASCAL F. Exact maximum likelihood estimates for SIRV covariance matrix: Existence and algorithm analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(10): 4563–4573. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.927464. [72] OKELLO N N and RISTIC B. Maximum likelihood registration for multiple dissimilar sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 1074–1083. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238759. [73] MCMICHAEL D W and OKELLO N N. Maximum likelihood registration of dissimilar sensors[C]. The 1st Australian Data Fusion Symposium, Adelaide, Australia, 1996: 31–34. [74] HELMICK R E and RICE T R. Removal of alignment errors in an integrated system of two 3-D sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(4): 1333–1343. doi: 10.1109/7.259537. [75] KOSUGE Y and OKADA T. Bias estimation of two 3-dimensional radars using Kalman filter[C]. The 4th IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control, Mie, Japan, 1996: 377–382. [76] NABAA N and BISHOP R H. Solution to a multisensor tracking problem with sensor registration errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(1): 354–363. doi: 10.1109/7.745706. [77] LI W, LEUNG H, and ZHOU Yifeng. Space-time registration of radar and ESM using unscented Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 824–836. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337457. [78] 胡洪涛, 敬忠良, 胡士强. 一种基于Unscented卡尔曼滤波的多平台多传感器配准算法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2005, 39(9): 1518–1521. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2005.09.030.HU Hongtao, JING Zhongliang, and HU Shiqiang. An unscented Kalman filter based multi-platform multi-sensor registration[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2005, 39(9): 1518–1521. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2005.09.030. [79] LI Wenling, JIA Yingmin, DU Junping, et al. Gaussian mixture PHD filter for multi-sensor multi-target tracking with registration errors[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(1): 86–99. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.06.030. [80] LI Minzhe, JING Zhongliang, PAN Han, et al. Joint registration and multi-target tracking based on labelled random finite set and expectation maximisation[J]. IET Radar,Sonar &Navigation, 2018, 12(3): 312–322. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0137. [81] LIAN Feng, HAN Chongzhao, LIU Weifeng, et al. Joint spatial registration and multi-target tracking using an extended probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IET Radar,Sonar &Navigation, 2011, 5(4): 441–448. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2010.0057. [82] WANG Jun, ZENG Yajun, WEI Shaoming, et al. Multi-sensor track-to-track association and spatial registration algorithm under incomplete measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 3337–3350. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3084533. [83] KANYUCK A J and SINGER R A. Correlation of multiple-site track data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1970, AES-6(2): 180–187. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1970.310100. [84] BAR-SHALOM Y. On the track-to-track correlation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1981, 26(2): 571–572. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1981.1102635. [85] 何友, 唐劲松, 王国宏. 多雷达跟踪系统中航迹质量管理的优化[J]. 现代雷达, 1995, 17(1): 14–19, 54. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1995.01.002.HE You, TANG Jinsong, and WANG Guohong. Optimal tracking-quality-management in multiradar tracking systems[J]. Modern Radar, 1995, 17(1): 14–19, 54. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.1995.01.002. [86] 黄晓冬, 何友, 赵峰. 几种典型情况下的航迹关联研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2005, 17(9): 2085–2088, 2174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2005.09.011.HUANG Xiaodong, HE You, and ZHAO Feng. Study of track association in typical cases[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2005, 17(9): 2085–2088, 2174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2005.09.011. [87] 齐林, 王海鹏, 刘瑜. 基于统计双门限的中断航迹配对关联算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(3): 301–308. doi: 10.12000/JR14077.QI Lin, WANG Haipeng, and LIU Yu. Track segment association algorithm based on statistical binary thresholds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(3): 301–308. doi: 10.12000/JR14077. [88] HONG Shuaixin, PENG Dongliang, and SHI Yifang. Track-to-track association using fuzzy membership function and clustering for distributed information fusion[C]. The 37th Chinese Control Conference, Wuhan, China, 2018: 4028–4032. [89] AZIZ A M. A new fuzzy clustering approach for data association and track fusion in multisensor-multitarget environment[C]. 2011 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2011: 1–10. [90] 徐亚圣, 丁赤飚, 任文娟, 等. 基于直方统计特征的多特征组合航迹关联[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 25–35. doi: 10.12000/JR18028.XU Yasheng, DING Chibiao, REN Wenjuan, et al. Multi-feature combination track-to-track association based on histogram statistics feature[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 25–35. doi: 10.12000/JR18028. [91] POORE A P and RIJAVEC N. A lagrangian relaxation algorithm for multidimensional assignment problems arising from multitarget tracking[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 1993, 3(3): 544–563. doi: 10.1137/0803027. [92] POPP R L, PATTIPATI K R, and BAR-SHALOM Y. M-best S-D assignment algorithm with application to multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(1): 22–39. doi: 10.1109/7.913665. [93] BAR-SHALOM Y. On the sequential track correlation algorithm in a multisensor data fusion system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(1): 396–396. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4517016. [94] 宋文彬. 传感器数据空间配准算法研究进展[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2012, 31(8): 5–8. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-97872012.08.027.SONG Wenbin. Research progress of spatial registration algorithms for sensor data[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2012, 31(8): 5–8. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-97872012.08.027. [95] TIAN Wei, WANG Yue, SHAN Xiuming, et al. Track-to-track association for biased data based on the reference topology feature[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(4): 449–453. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2305305. [96] TIAN Wei. Reference pattern-based track-to-track association with biased data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(1): 501–512. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140433. [97] LI Zhenhua, CHEN Siyue, LEUNG H, et al. Joint data association, registration, and fusion using EM-KF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 496–507. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461637. [98] 田威, 王钺, 山秀明, 等. 稳健的联合航迹关联与系统误差估计[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 53(7): 946–950. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2013.07.009.TIAN Wei, WANG Yue, SHAN Xiuming, et al. Robust method for joint track association and sensor bias estimation[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2013, 53(7): 946–950. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2013.07.009. [99] LEVEDAHL M. Explicit pattern matching assignment algorithm[C]. The SPIE of 4728, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2002, Orlando, USA, 2002: 461–469. [100] SHI Yue, WANG Yue, and SHAN Xiuming. A novel fuzzy pattern recognition data association method for biased sensor data[C]. The 9th International Conference on Information Fusion, Florence, Italy, 2006: 1–5. [101] CHAIR Z and VARSHNEY P K. Optimal data fusion in multiple sensor detection systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(1): 98–101. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310699. [102] SINGER R A and KANYUCK A J. Computer control of multiple site track correlation[J]. Automatica, 1971, 7(4): 455–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(71)90096-3. [103] ROECKER J A and MCGILLEM C D. Comparison of two-sensor tracking methods based on state vector fusion and measurement fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1988, 24(4): 447–449. doi: 10.1109/7.7186. [104] BAR-SHALOM Y and CAMPO L. The effect of the common process noise on the two-sensor fused-track covariance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(6): 803–805. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310815. [105] UHLMANN J K. General data fusion for estimates with unknown cross covariances[C]. The SPIE of 2755, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition V, Orlando, USA, 1996: 536–547. [106] HURLEY M B. An information theoretic justification for covariance intersection and its generalization[C]. The 5th International Conference on Information Fusion, Annapolis, USA, 2002: 505–511. [107] CHANG K C, TIAN Zhi, and MORI S. Performance evaluation for MAP state estimate fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(2): 706–714. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1310015. [108] DRUMMOND O E. Track fusion with feedback[C]. The SPIE of 2759, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1996, Orlando, USA, 1996: 342–360. [109] DRUMMOND O E. Hybrid sensor fusion algorithm architecture and tracklets[C]. The SPIE of 3163, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1997, San Diego, USA, 1997: 512–524. [110] ZHU Yunmin, YOU Zhisheng, ZHAO Juan, et al. The optimality for the distributed Kalman filtering fusion with feedback[J]. Automatica, 2001, 37(9): 1489–1493. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(01)00074-7. [111] YUAN Ting, BAR-SHALOM Y, and TIAN Xin. Heterogeneous track-to-track fusion[C]. The 14th International Conference on Information Fusion, Chicago, USA, 2011: 1–8. [112] CHANG K C, SAHA R K, and BAR-SHALOM Y. On optimal track-to-track fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1997, 33(4): 1271–1276. doi: 10.1109/7.625124. [113] TIAN Xin. Track-to-track fusion configurations and association in a sliding window[J]. Journal of Advances in Information Fusion, 2009, 4(2): 146–164. [114] LI Tiancheng, FAN Hongqi, GARCÍA J, et al. Second-order statistics analysis and comparison between arithmetic and geometric average fusion: Application to multi-sensor target tracking[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 51: 233–243. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.02.009. [115] LI Tiancheng, WANG Xiaoxu, LIANG Yan, et al. On arithmetic average fusion and its application for distributed multi-Bernoulli multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2883–2896. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2985643. [116] LI Tiancheng and HLAWATSCH F. A distributed particle-PHD filter using arithmetic-average fusion of Gaussian mixture parameters[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 111–124. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.020. [117] LI Tiancheng, CORCHADO J M, and SUN Shudong. Partial consensus and conservative fusion of Gaussian mixtures for distributed PHD fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(5): 2150–2163. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2882960. [118] TIAN Xin, BAR-SHALOM Y, YUAN Ting, et al. A generalized information matrix fusion based heterogeneous track-to-track fusion algorithm[C]. The SPIE 8050, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition XX, Orlando, USA, 2011: 805015. [119] TIAN Xin, YUAN Ting, and BAR-SHALOM Y. Track-to-track Fusion in Linear and Nonlinear Systems[M]. CHOUKROUN D, OSHMAN Y, THIENEL J, et al. Advances in Estimation, Navigation, and Spacecraft Control. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2015: 21–41. [120] MALLICK M, CHANG K C, ARULAMPALAM S, et al. Heterogeneous track-to-track fusion in 3-D using IRST sensor and air MTI radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3062–3079. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2898302. [121] MENEGAZ H M T, ISHIHARA J Y, and KUSSABA H T M. Unscented Kalman filters for riemannian state-space systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(4): 1487–1502. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2846684. [122] YEE D, REILLY J P, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Approximate conditional mean particle filtering for linear/nonlinear dynamic state space models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(12): 5790–5803. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.929660. [123] BATTISTELLI G, CHISCI L, FANTACCI C, et al. Distributed peer-to-peer multitarget tracking with association-based track fusion[C]. The 17th International Conference on Information Fusion, Salamanca, Spain, 2014: 1–7. [124] CHONG C Y, MORI S, and CHANG K C. Information fusion in distributed sensor networks[C]. American Control Conference, Boston, USA, 1985: 830–835. [125] CORALUPPI S, RAGO C, CARTHEL C, et al. Distributed MHT with passive sensors[C]. The 24th International Conference on Information Fusion, Sun City, South Africa, 2021: 1–8. [126] ÜNEY M, CLARK D E, and JULIER S J. Distributed fusion of PHD filters via exponential mixture densities[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 521–531. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2257162. [127] BATTISTELLI G, CHISCI L, FANTACCI C, et al. Consensus CPHD filter for distributed multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 508–520. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2250911. [128] WANG Bailu, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Distributed fusion with multi-Bernoulli filter based on generalized covariance intersection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(1): 242–255. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2617825. [129] FANTACCI C, VO B N, VO B T, et al. Robust fusion for multisensor multiobject tracking[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(5): 640–644. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2811750. [130] LI Suqi, BATTISTELLI G, CHISCI L, et al. Multi-sensor multi-object tracking with different fields-of-view using the LMB filter[C]. The 21st International Conference on Information Fusion, Cambridge, UK, 2018: 1201–1208. [131] LI Suqi, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust distributed fusion with labeled random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(2): 278–293. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2760286. [132] GAO Lin, BATTISTELLI G, and CHISCI L. Multiobject fusion with minimum information loss[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 201–205. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2963817. [133] GAO Lin, BATTISTELLI G, and CHISCI L. Fusion of labeled RFS densities with minimum information loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 5855–5868. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3028496. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: