-
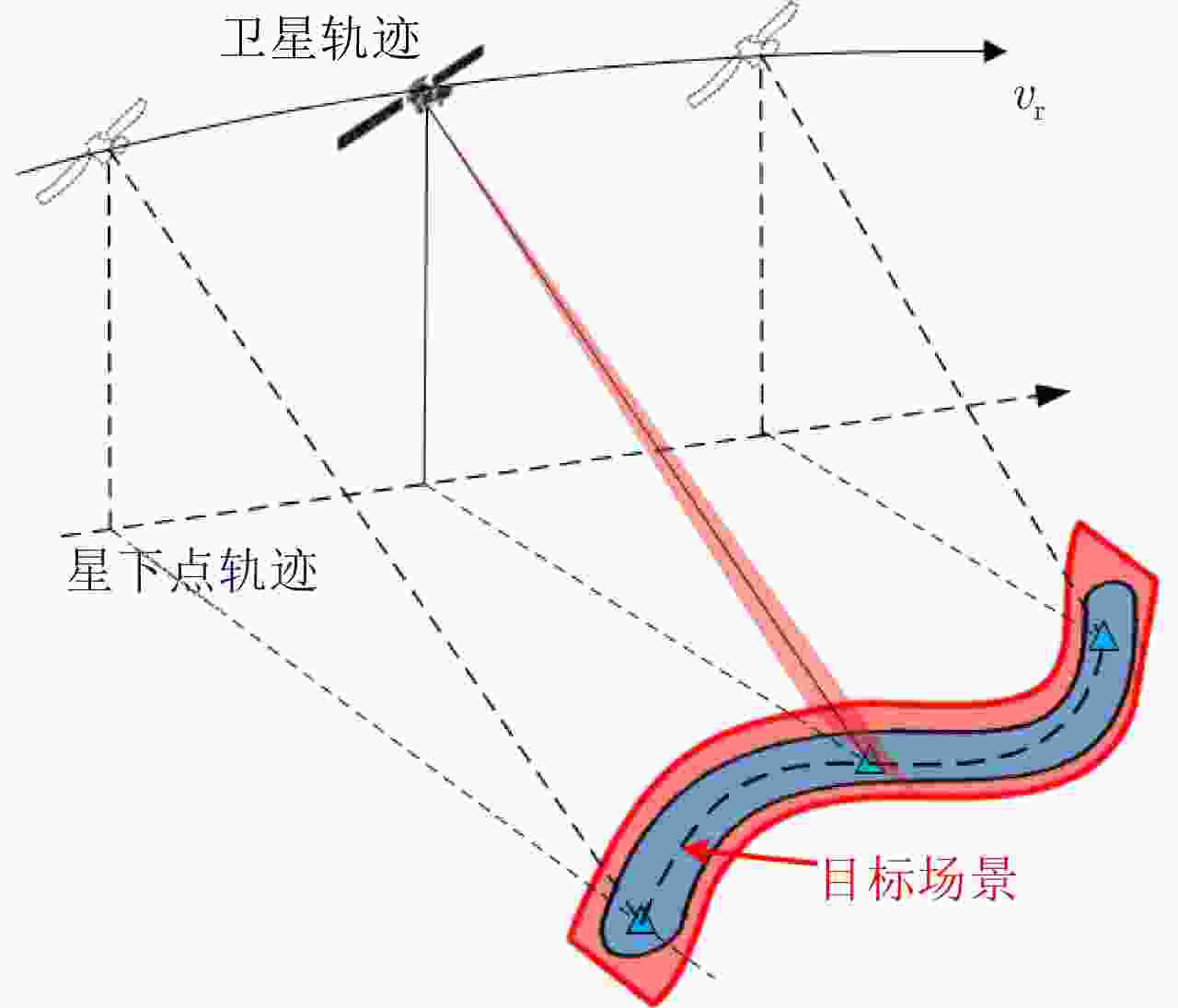
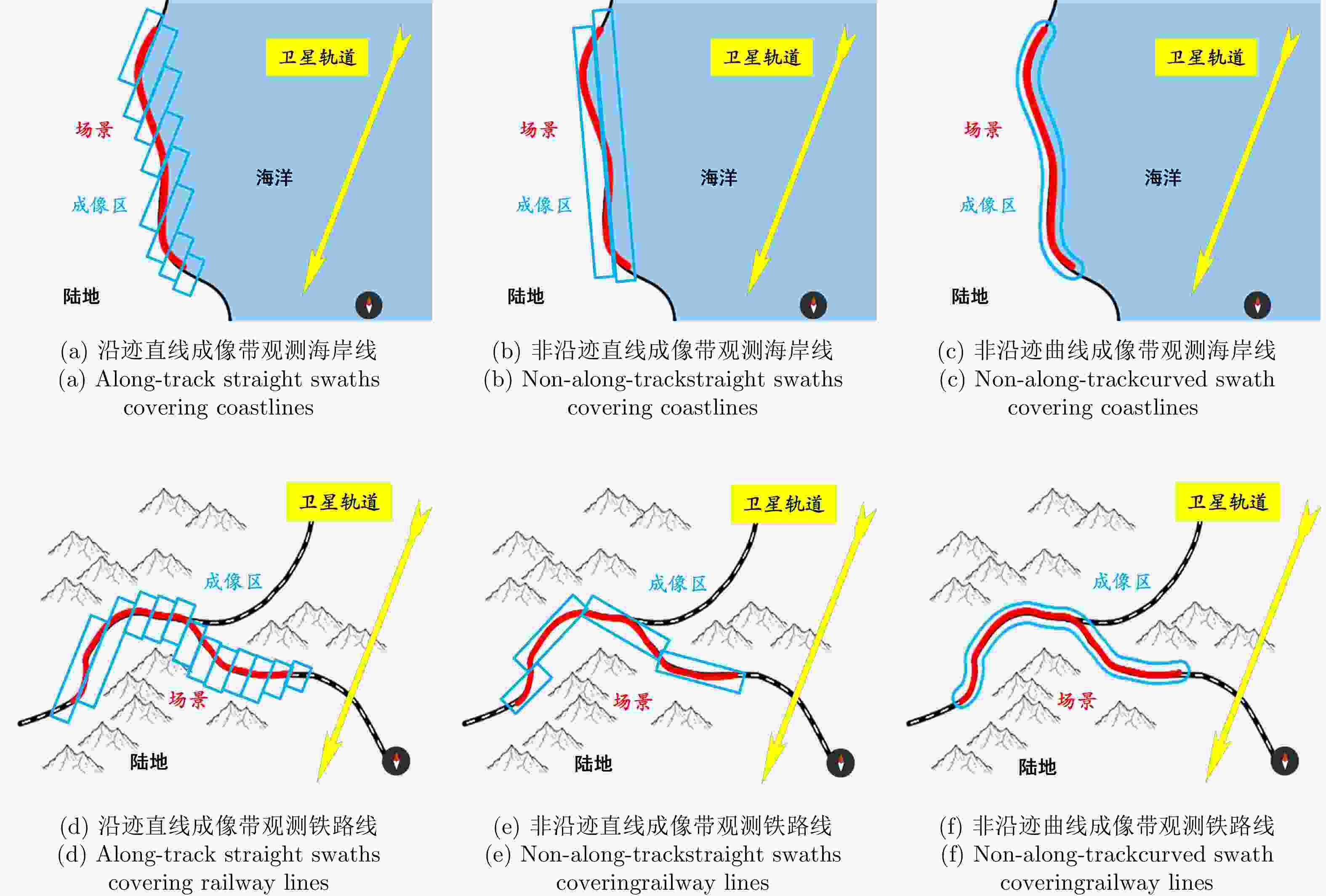
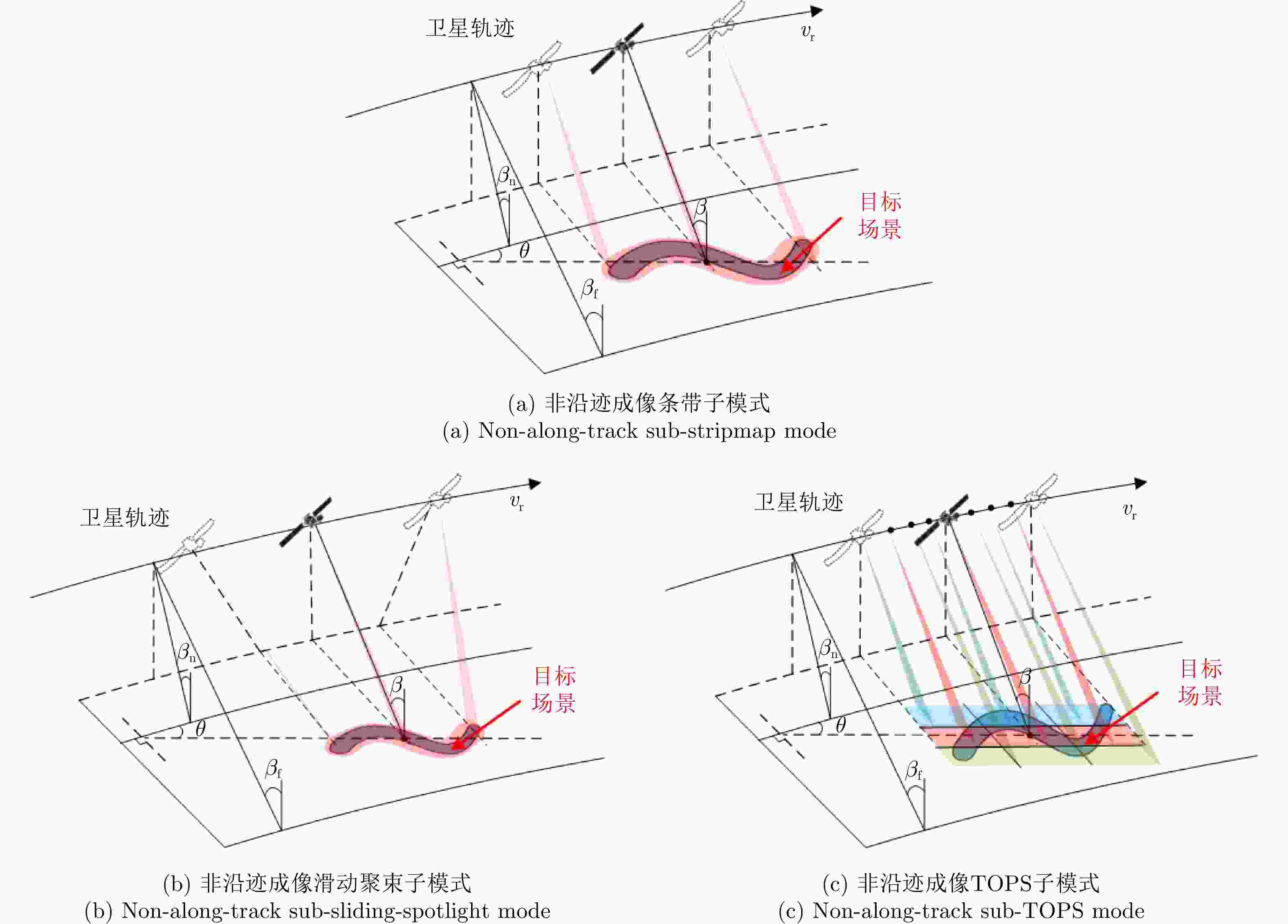
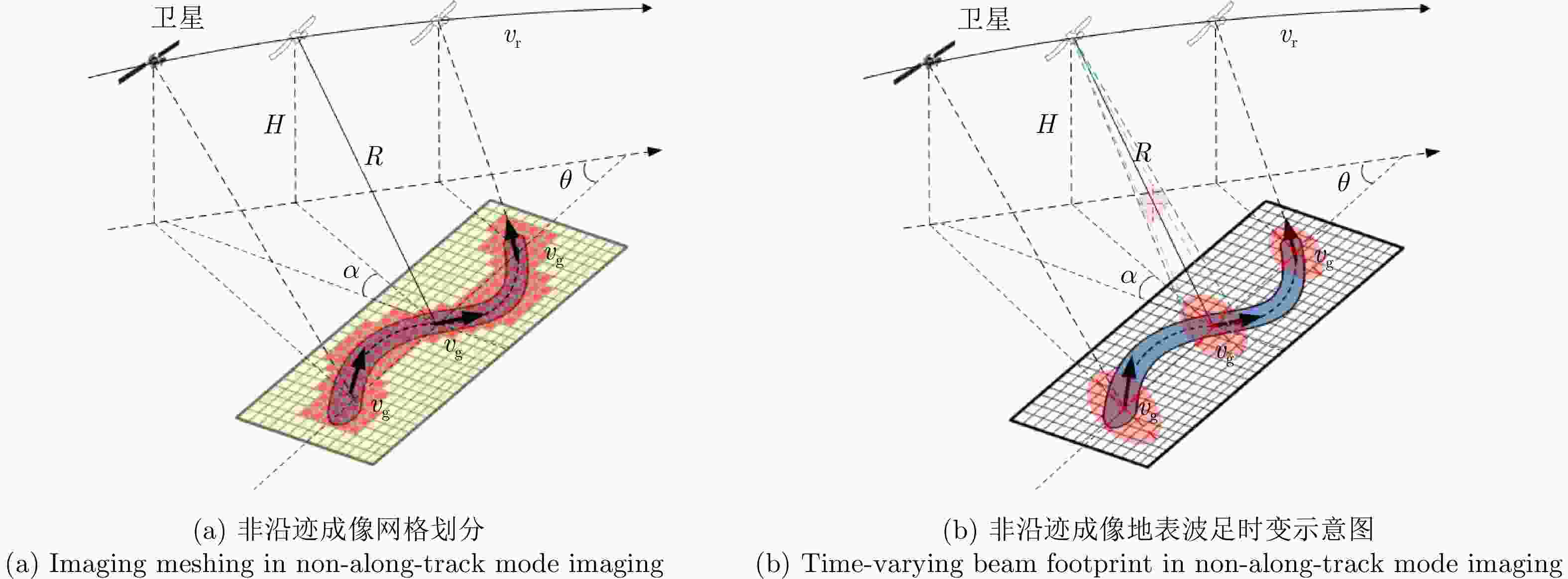
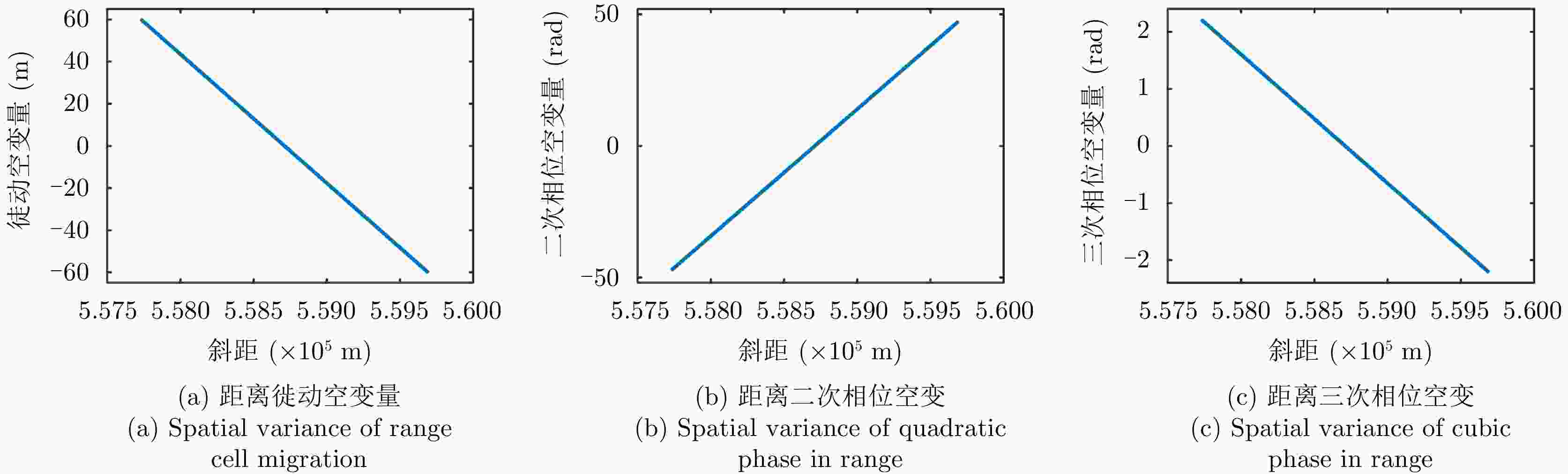
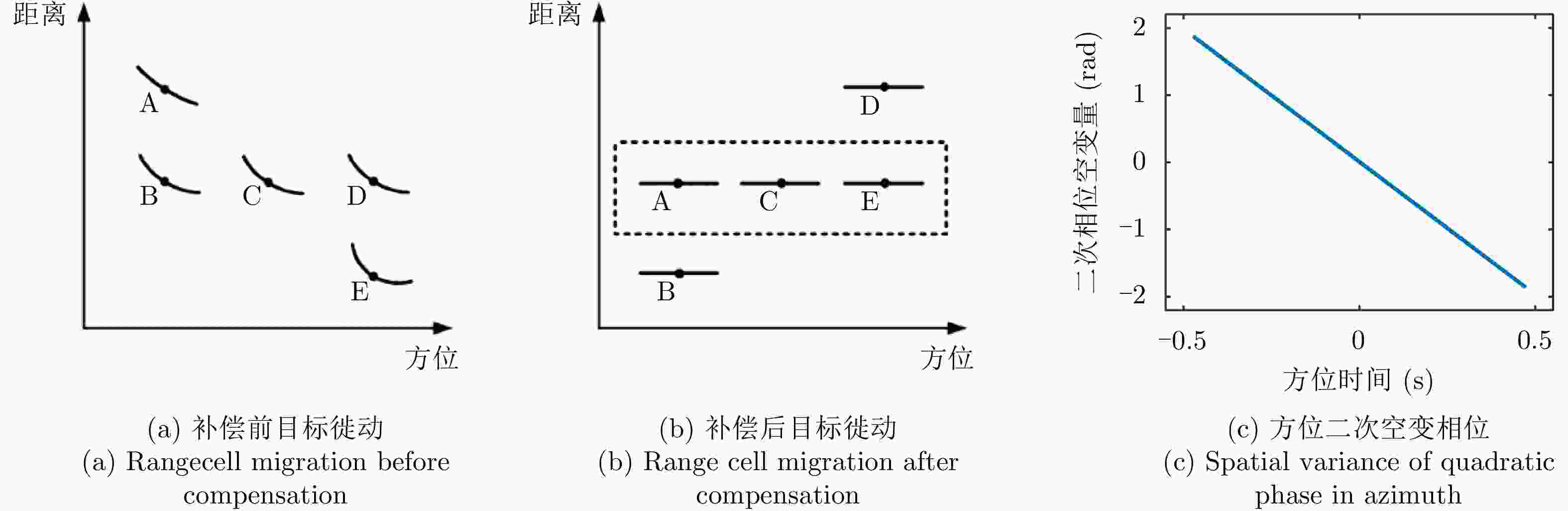
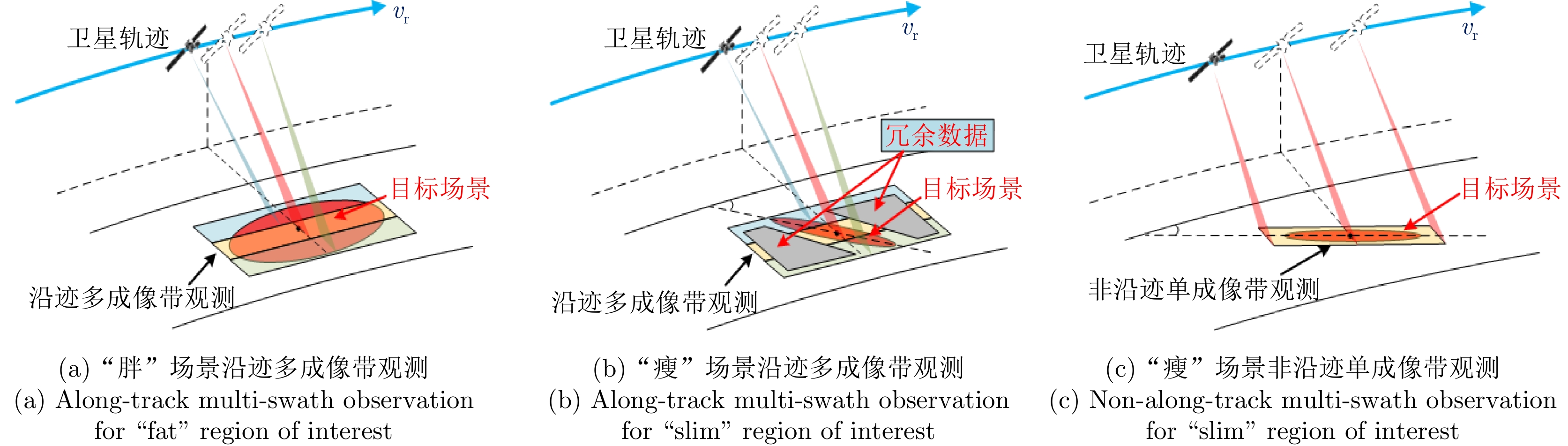
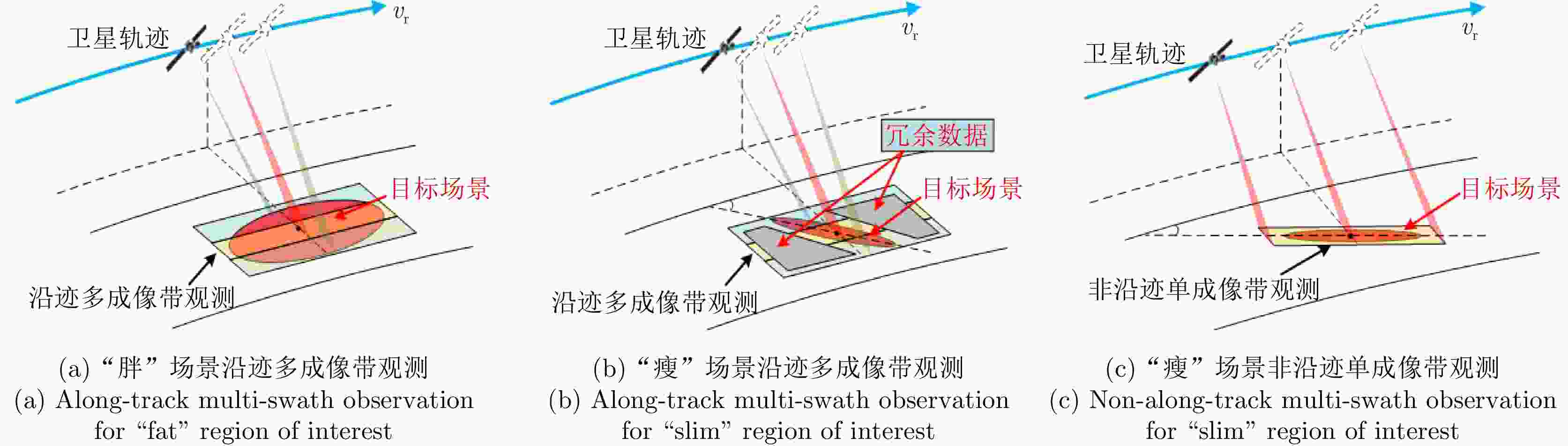
摘要: 星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)通过采用不同成像模式,实现分辨率与成像带宽度的不同性能组合。常规星载SAR模式的成像带沿着卫星航迹方向,走向单一;但实际目标场景的地理走向多种多样,与沿卫星航迹方向的成像带地理走向不匹配的情况普遍出现,导致数采周期长或方位分辨低、存储与计算资源浪费。星载SAR非沿迹成像模式是解决该问题的新思路,其通过生成与卫星航迹不同向的直线型或曲线型的成像带,匹配于目标场景的实际地理走向,对目标场景进行“地理定制化”成像。该文主要从信息获取、成像处理等方面,讨论了星载SAR非沿迹成像新模式的主要机遇与挑战,并通过计算机仿真实现了星载SAR非沿迹成像模式的原理性验证。Abstract: Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) can achieve various performance combinations of resolution and observation bandwidth by adjusting the working modes. The imaging swath of the traditional spaceborne SAR working mode is along the satellite orbit, and the geographical trend is single; however, the geographical shape and direction of the surface scene are diverse and generally do not match the imaging swath along the orbit, resulting in a long data acquisition period, low azimuth resolution, and storage waste of computing resources. To this end, the spaceborne SAR Non-along-track imaging mode is a new method for spaceborne SAR scene matching that is characterized by an imaging zone that is no longer mechanically along the satellite orbit but is generated according to the actual geographical direction of the scene to achieve “customization” that matches the scene imaging. In this paper, the main opportunities and challenges faced by the new mode of spaceborne SAR scene matching are discussed from the aspects of information acquisition and imaging processing, and the principled verification of the spaceborne SAR Non-along-track imaging mode is provided through a computer simulation.
-
Key words:
- Spaceborne SAR /
- Non-along-track imaging mode /
- Data acquisition /
- Imaging processing
-
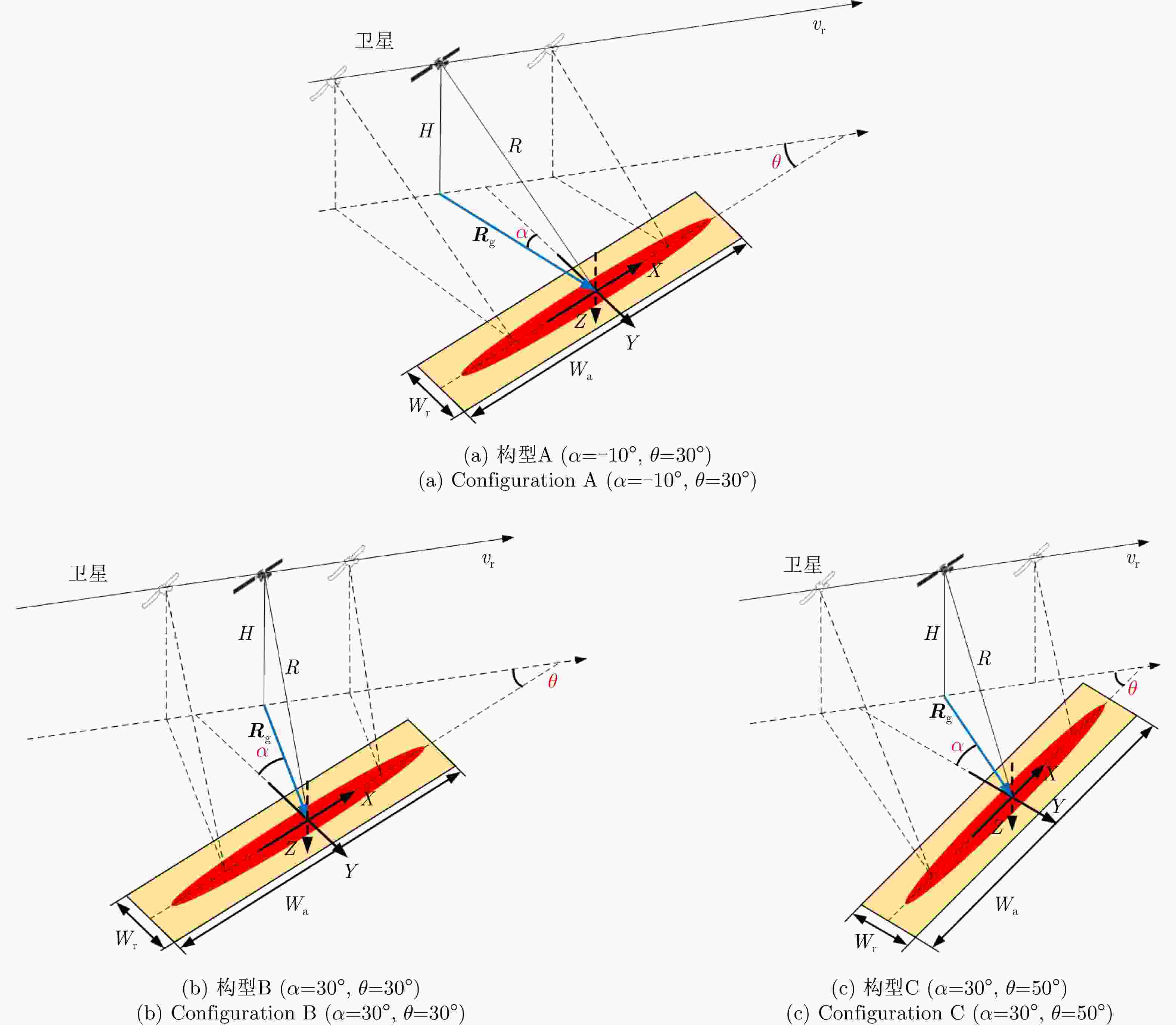
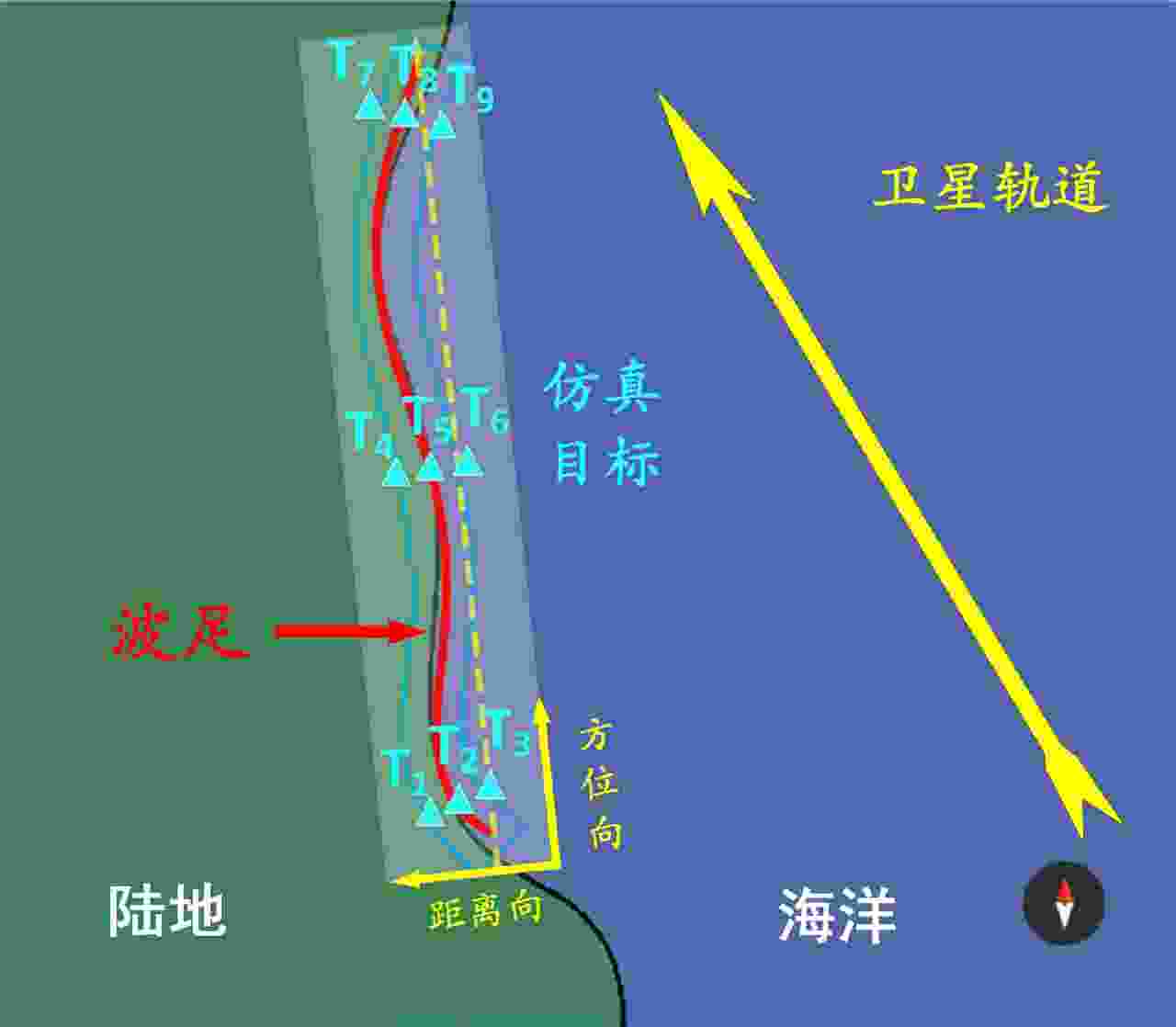
表 1 主要仿真参数
Table 1. Key simulation parameters
参数 数值 载频 10 GHz 脉冲宽度 20 μs 轨道高度 550 km 距离向波束宽度 0.6° 方位向波束宽度 0.6° 带宽 88.5 MHz 方位点数 147765 距离点数 163664 -
[1] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991: 4–8. [2] 刘永坦. 雷达成像技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2014: 26–28.LIU Yongtan. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 26–28. [3] 魏钟铨. 合成孔径雷达卫星[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 67–68.WEI Zhongquan. Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 67–68. [4] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004: 4–5. [5] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 3–6.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 3–6. [6] 皮亦鸣, 杨建宇, 付毓生, 等. 合成孔径雷达成像原理[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 2007: 51–52.PI Yiming, YANG Jianyu, FU Yusheng, et al. Principle of Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging[M]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Press, 2007: 51–52. [7] VILLANO M, PINHEIRO M, KRIEGER G, et al. Gapless imaging with the NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission: Challenges and opportunities of staggered SAR[C]. The 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018. [8] MOORE R K, CLAASSEN J P, and LIN Y H. Scanning spaceborne synthetic aperture radar with integrated radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1981, AES-17(3): 410–421. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1981.309069 [9] DE ZAN F and GUARNIERI A M. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(9): 2352–2360. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.873853 [10] ZHENG Ge, YAO Yiping, HE Dongsheng, et al. Optimization design of global low-orbit satellite constellation for multi-fold coverage[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Engineering, Xi’an, China, 2020. [11] EUGENIO F, MARCELLO J, and MARTIN J. High-resolution maps of bathymetry and benthic habitats in shallow-water environments using multispectral remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 3539–3549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2377300 [12] WU Xueling, LIU Chaoxian, and WU Guofeng. Spatial-temporal analysis and stability investigation of coastline changes: A case study in Shenzhen, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 45–56. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755444 [13] CHEN Ninghua, NI Nina, KAPP P, et al. Structural analysis of the hero range in the Qaidam Basin, Northwestern China, using integrated UAV, terrestrial LiDAR, Landsat 8, and 3-D seismic data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(9): 4581–4591. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2440171 [14] WANG Xiaoqing, DOU Aixia, DING Xiang, et al. The development of rapid extraction and publishing system of earthquake damage based on remote sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018. [15] QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, ZHANG Lu, et al. Structural health and stability assessment of high-speed railways via thermal dilation mapping with time-series InSAR analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2999–3010. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2719025 [16] BABU A and BAUMGARTNER S V. Road surface quality assessment using polarimetric airborne SAR[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020. [17] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995: 4−5. [18] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [19] QUEGAN S. Spotlight synthetic aperture radar: Signal processing algorithms: Carrara W. G., Goodman R. S. and Majewski R. M., 1995, 554 pp. Artech House, Boston, London, £63, hb, ISBN 0-89006-728-7[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 1997, 59(5): 597–598. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(97)83336-6 [20] FRANCESCHETTI G, GUIDA R, IODICE A, et al. Efficient simulation of hybrid stripmap/spotlight SAR raw signals from extended scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2385–2396. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834763 [21] BELCHER D P and BAKER C J. High resolution processing of hybrid strip-map/spotlight mode SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(6): 366–374. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960790 [22] META A, MITTERMAYER J, PRATS P, et al. TOPS imaging with TerraSAR-X: Mode design and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 759–769. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2026743 [23] WANG Yan, LI Jingwen, YANG Jian, et al. Spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR: Positive terrain tracking by continuous beam scanning in elevation[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(11): 1014–1022. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1212416 [24] WANG Yan, LI Zhe, DING Zegang, et al. Spaceborne large-squint terrain-matching synthetic aperture radar: Concept and technology[C]. The 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–6. [25] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, XU Pei, et al. Strip layering diagram-based optimum continuously varying pulse interval sequence design for extremely high-resolution spaceborne sliding spotlight SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6751–6770. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3028973 [26] WANG Yan, YANG Jian, and LI Jingwen. Data acquisition for a novel spaceborne azimuth-range sweep synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, United States, 2017: 6004–6007. [27] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, JI Weiwei, et al. Time-varying nadir echo suppression for spaceborne stripmap range sweep synthetic aperture radar via waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(5): 826–830. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2989375 [28] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Ambiguities and image quality in staggered SAR[C]. The 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, Singapore, 2015: 204–209. [29] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, JÄGER M, et al. Staggered SAR: Performance analysis and experiments with real data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6617–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731047 [30] SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1999: 486–539. [31] BAMLER R and EINEDER M. ScanSAR processing using standard high precision SAR algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(1): 212–218. doi: 10.1109/36.481905 [32] DAVIDSON G W and CUMMING I. Signal properties of spaceborne squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(3): 611–617. doi: 10.1109/36.581976 [33] LUO Yunhua, ZHAO Bingji, HAN Xiaolei, et al. A novel high-order range model and imaging approach for high-resolution LEO SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3473–3485. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2273086 [34] SUN Guangcai, JIANG Xiuwei, XING Mengdao, et al. Focus improvement of highly squinted data based on azimuth nonlinear scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2308–2322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2102040 [35] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, ZENG Tao, et al. Interpolation free wide nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 621–625. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930537 [36] WANG Yan, LI Jingwen, and YANG Jian. Wide nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6922–6936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2737031 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: