Constant Modulus Waveform Design for Low-resolution Quantization MIMO Radar Based on an Alternating Direction Penalty Method
-
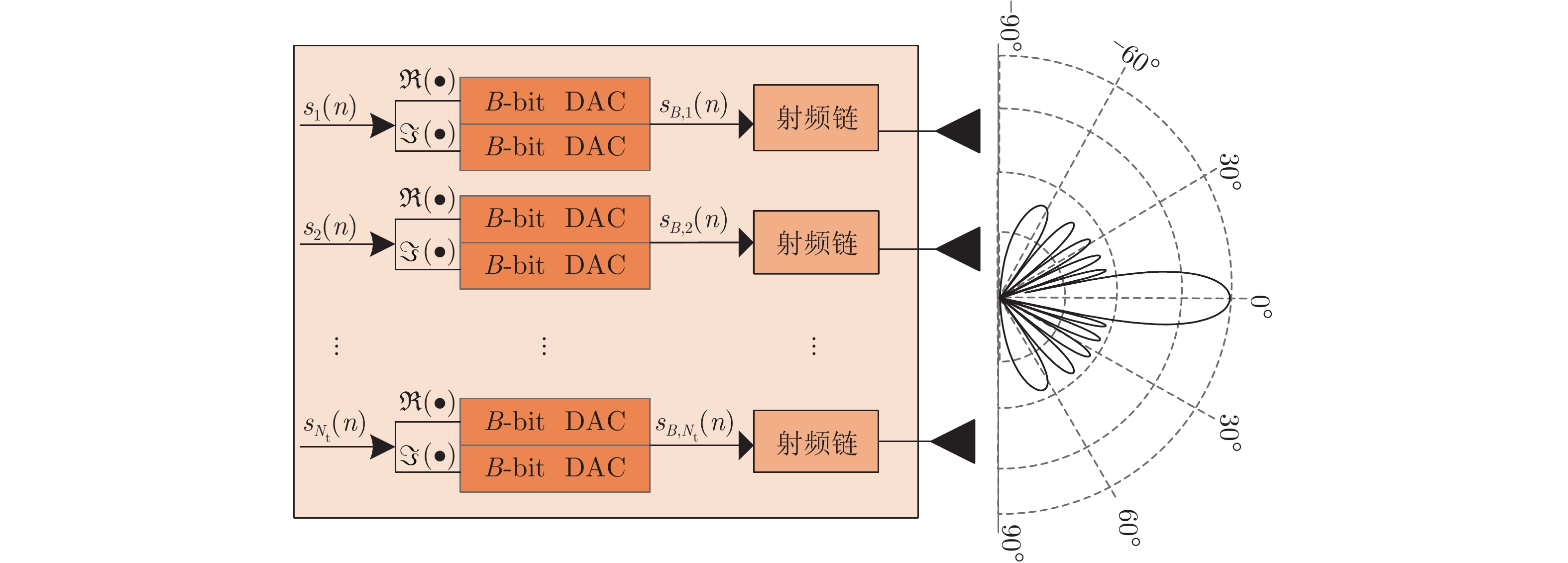
摘要: 在MIMO雷达中配备大量有源天线单元可以获得优异的波束形成性能,但会导致系统能耗大、电路复杂及成本高等问题。采用低精度的DAC组件可有效克服上述问题,但现有基于无限精度DAC条件所设计的MIMO雷达波形往往难以直接适用于低精度DAC系统。为此,该文提出了一种离散相位约束下基于最小化积分副主瓣比的低精度量化MIMO雷达恒模波形设计方法。该方法首先采用丁克尔巴赫(Dinkelbach)算法将目标函数二次分数形式转换成减法形式,再利用交替方向惩罚法求解非凸恒模离散相位约束问题。最后通过数值仿真与其他方法进行对比,分析了所提方法的发射方向图与积分副主瓣比性能,验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: Outstanding beamforming performance of the Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar can be achieved by deploying a large number of active antenna elements. Nonetheless, this will significantly increase power consumption, circuit complexity and hardware cost. These problems can be overcome by utilizing low-resolution Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) components. However, MIMO radar waveforms designed under the condition of infinite-resolution DACs are usually inapplicable to systems with low-resolution DACs. Therefore, under the constraints of discrete phases, this paper proposes a MIMO radar constant modulus waveform design method based on Integrated Sidelobe-to-Mainlobe Ratio (ISMR) minimization. The Dinkelbach algorithm is first used to convert the objective function with quadratic fractional form into a subtraction form. Then, the alternating direction penalty method is employed to solve the nonconvex constant modulus discrete phase constraint problem. Finally, by comparison with other methods through numerical simulations, the behavior of the transmit beampattern and the performance of ISMR are analyzed, and the effectiveness of the method is verified.
-
表 1 丁克尔巴赫交替方向惩罚法的低精度量化MIMO雷达恒模波形设计算法
Table 1. MIMO radar constant modulus waveform design algorithm with low-precision quantized based on DADPM
输入:${\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(0)}$, ${\xi ^{(0)}}$, B, $\delta $, $\nu $, $\epsilon$; 输出:${\boldsymbol{s} }_B^{ \star }$; 步骤1:设置 $k = 0$; 步骤2:初始化:${\varrho ^{(0)}}$, ${{\boldsymbol{p}}^{(0)}}$; 步骤3:计算${{\boldsymbol{\varXi}} ^{(k)}} = {{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{\text{s}}} - {\xi ^{(k)}}{{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{\text{m}}}$; 步骤4:设置 $t = 0$; 步骤5:更新${\boldsymbol{\tilde s}}_B^{(t + 1)}$与${\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(t + 1)}$,分别通过解问题(16)与问题(23); 步骤6:更新${\varrho ^{(t + 1)}}$和${{\boldsymbol{p}}^{(t + 1)}}$,通过式(28)与式(29); 步骤7:更新内循环迭代次数,令$t = t + 1$; 步骤8:重复步骤5—步骤7,直到满足式(32)中任一停止条件,存
储${\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(t + 1)}$;步骤9:令${\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(k + 1)} = {\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(t + 1)}$,计算${\xi ^{(k + 1)}} = {\text{ISMR}}({\boldsymbol{s}}_B^{(k + 1)})$; 步骤10:更新外循环迭代次数,令$k = k + 1$; 步骤11:重复步骤2—步骤10,直到$f({{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{B}^{(k+1)},{\xi }^{(k+1)})\le \epsilon$; 步骤12:返回 :问题(8)的解${\boldsymbol{s} }_B^{{\star} } = {\boldsymbol{s} }_B^{(k + 1)}$。 表 2 主瓣对称下极低精度量化波形算法性能统计表
Table 2. Performance statistics table of the extreme low precision quantized waveform algorithm for symmetrical mainlobe
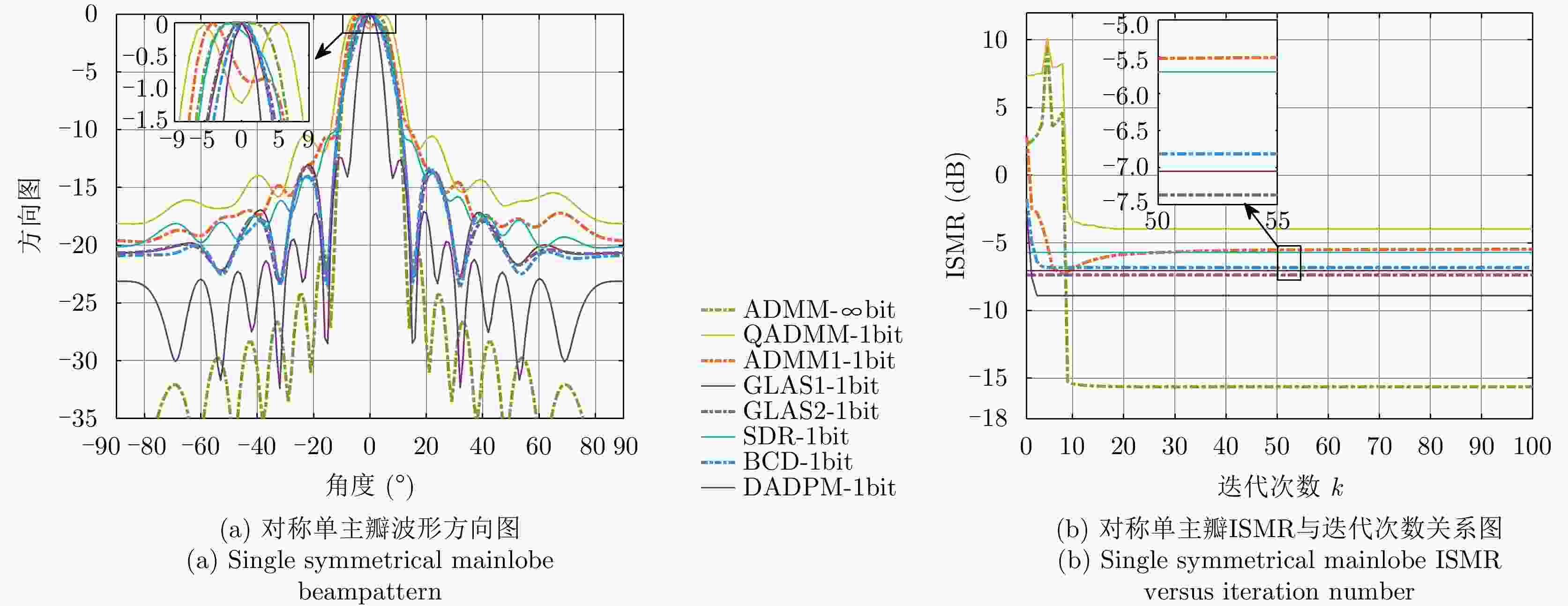
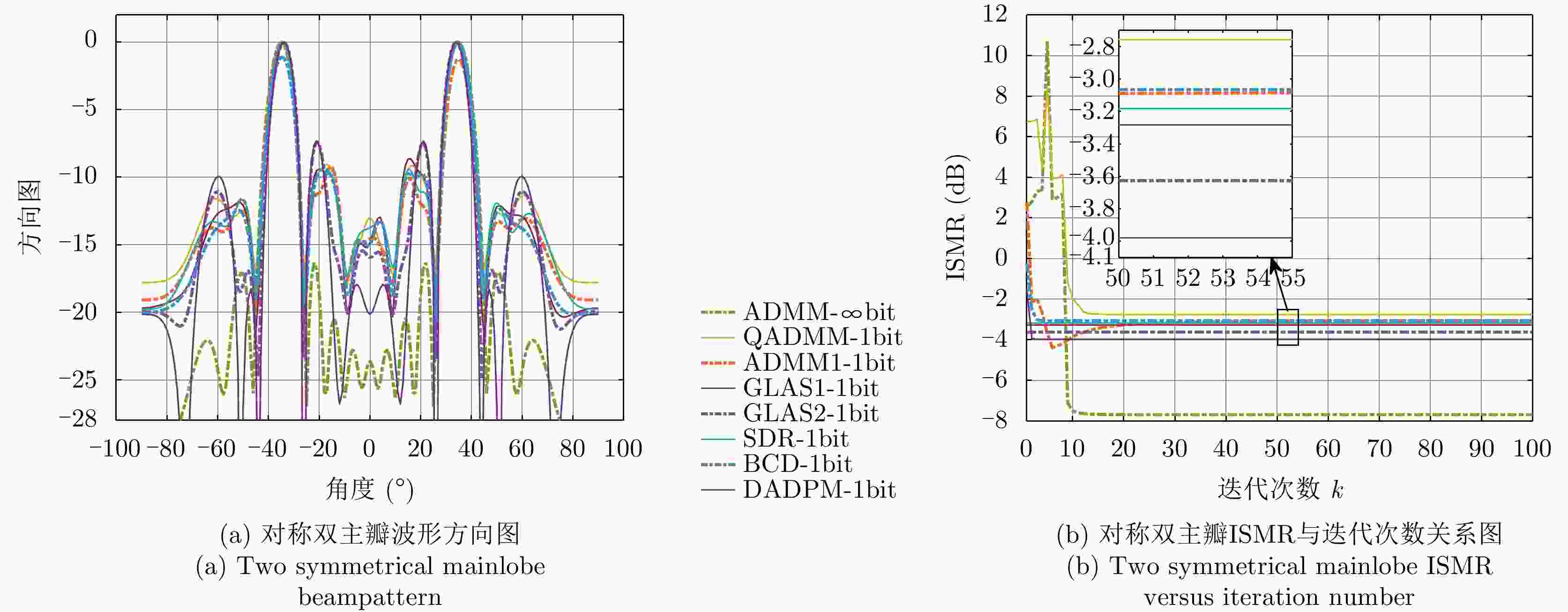
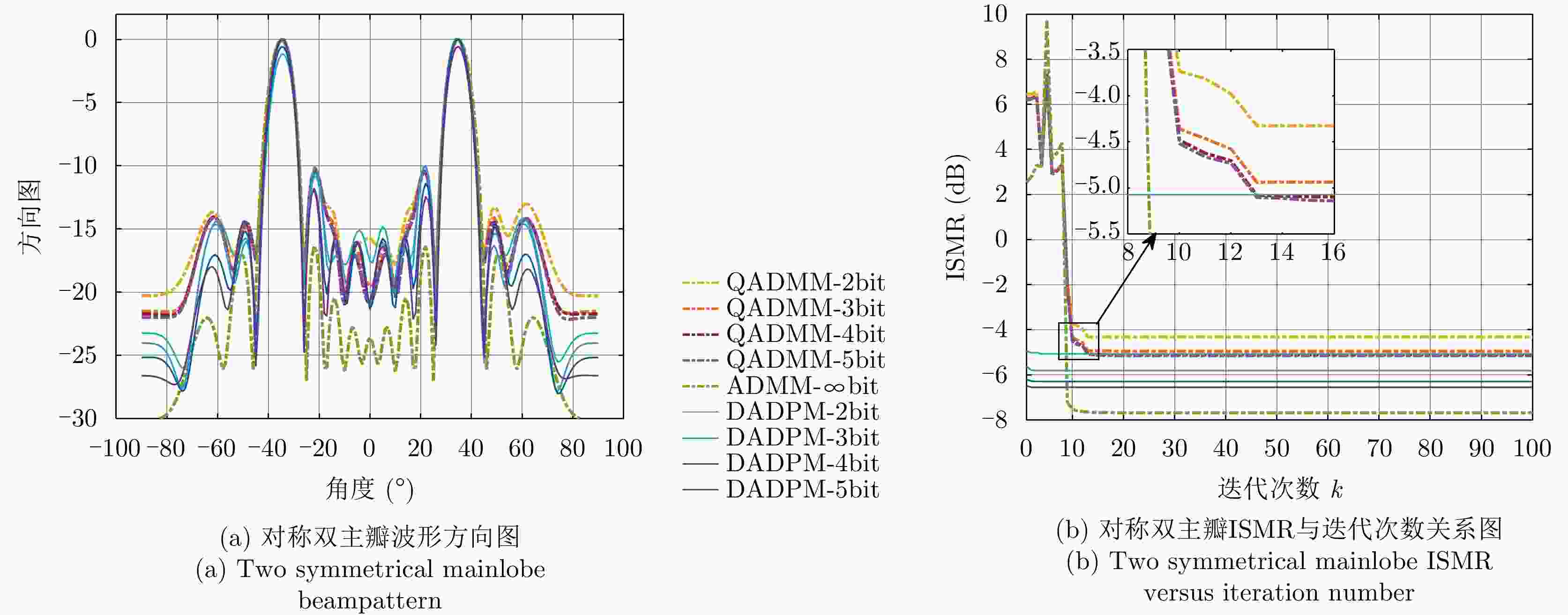
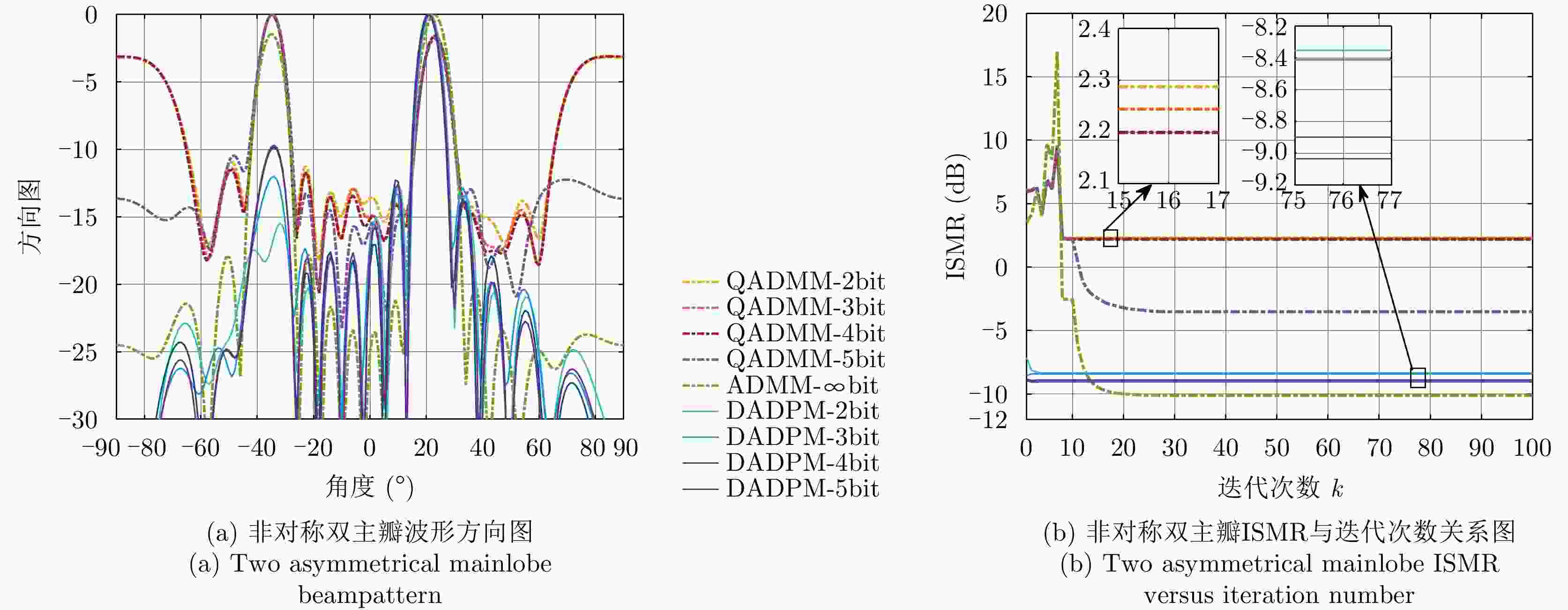
主瓣对称情况下方法 最小ISMR (dB) 最大ISMR (dB) 平均ISMR (dB) 运算时间(s) 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 ADMM-$\infty $bit –15.7192 –7.6825 11.1782 9.4329 –15.1842 –7.3031 2.3527 2.0368 QADMM-1bit –4.1057 –3.9953 10.1032 –1.3280 –4.2891 –3.9872 2.3865 2.1003 ADMM-1bit –7.1965 –6.7244 2.3044 –4.6130 –5.3700 –5.1329 3.1457 2.6269 GLAS1-1bit –7.6930 –7.7134 –6.9940 –6.6514 –7.3283 –7.1467 0.0106 0.0104 GLAS2-1bit –7.6170 –8.3327 –6.5995 –7.6447 –7.0952 –7.9970 0.0736 0.0748 SDR-1bit –5.9636 –7.0137 –5.5988 –6.7182 –5.7154 –6.8256 37.8250 38.0630 BCD-1bit –6.8706 –3.0849 –2.0389 –0.2157 –6.8327 –3.0587 0.1972 0.1964 DADPM-1bit –8.8275 –3.9973 –2.5693 –1.7831 –8.6527 –3.9812 8.5147 8.3249 表 3 低精度量化的对称主瓣波形算法性能统计表
Table 3. Performance statistics table of the low precision algorithm for symmetrical mainlobe
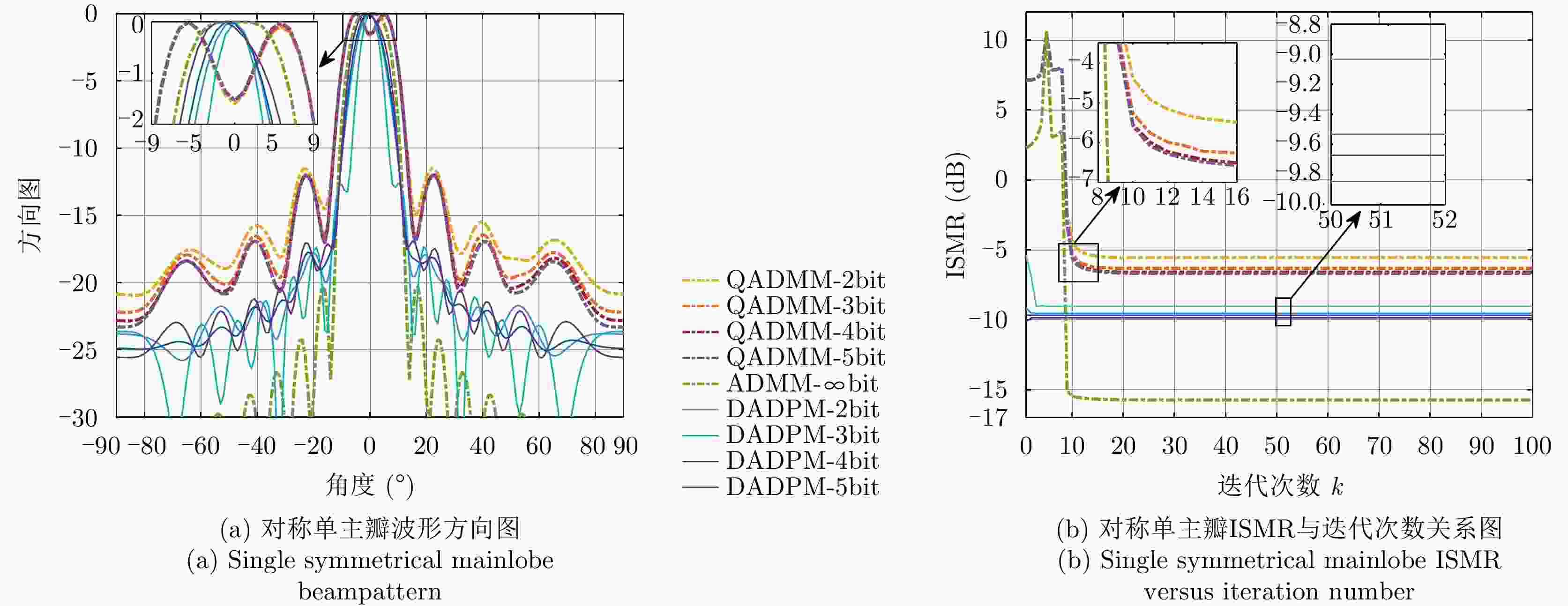
主瓣对称情况下算法 最小ISMR (dB) 最大ISMR (dB) 平均ISMR (dB) 运算时间(s) 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 单主瓣 双主瓣 QADMM-2bit –5.5427 –4.3245 11.0237 7.7345 –5.4178 –4.0784 2.3814 2.1377 QADMM-3bit –6.3020 –4.9560 11.0532 7.7081 –6.0587 –4.6564 2.3468 2.1597 QADMM-4bit –6.5840 –5.1091 11.0863 7.6597 –6.1687 –4.9790 2.1527 2.3519 QADMM-5bit –6.6815 –5.1490 11.1027 7.6038 –6.2214 –5.0074 2.2527 2.4368 ADMM-$\infty $bit –15.7192 –7.6825 11.1782 9.4329 –15.1842 –7.3031 2.3527 2.0368 DADPM-2bit –9.0532 –5.0738 –4.8751 –4.9024 –8.7875 –4.7015 8.7756 8.2487 DADPM-3bit –9.5309 –5.8123 –9.4311 –5.7812 –9.1178 –5.4725 8.7874 8.1834 DADPM-4bit –9.6694 –6.2968 –9.6103 –6.1025 –9.2789 –6.1034 8.8743 8.2981 DADPM-5bit –10.1160 –6.5541 –9.9715 –6.3251 –9.8321 –6.2753 8.8975 8.3546 -
[1] FORSYTHE K W, BLISS D W, and FAWCETT G S. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar: Performance issues[C]. The Thirty-Eighth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2004: 310–315. [2] XU Haisheng, BLUM R S, WANG Jian, et al. Colocated MIMO radar waveform design for transmit beampattern formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1558–1568. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140249 [3] 朱圣棋, 余昆, 许京伟, 等. 波形分集阵列新体制雷达研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188ZHU Shengqi, YU Kun, XU Jingwei, et al. Research progress and prospect for the noval waveform diverse array radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 795–810. doi: 10.12000/JR21188 [4] GODRICH H, HAIMOVICH A M, and BLUM R S. Target localization accuracy gain in MIMO radar-based systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(6): 2783–2803. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2046246 [5] STOICA P, HE Hao, and LI Jian. Optimization of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(4): 1730–1740. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2179652 [6] CAO Siyang and ZHENG Yuanfang. Recent developments in radar waveforms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 603–621. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14044 [7] GAO Xiang, EDFORS O, RUSEK F, et al. Massive MIMO performance evaluation based on measured propagation data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(7): 3899–3911. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2414413 [8] AHMED S and ALOUINI M S. MIMO radar transmit beampattern design without synthesising the covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(9): 2278–2289. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2310435 [9] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, YU Guoyang, et al. MIMO radar waveform design for quasi-equiripple transmit beampattern synthesis via weighted ${l_p}$ -minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3397–3411. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2917871[10] SINGH J, DABEER O, and MADHOW U. On the limits of communication with low-precision analog-to-digital conversion at the receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2009, 57(12): 3629–3639. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2009.12.080559 [11] LANDAU L and FETTWEIS G. On reconstructable ASK-sequences for receivers employing 1-Bit quantization and oversampling[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-WideBand (ICUWB), Paris, France, 2014: 180–184. [12] RISI C, PERSSON D, and LARSSON E G. Massive MIMO with 1-bit ADC[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1404.7736v1, 2014. [13] HOYOS S, SADLER B M, and ARCE G R. Monobit digital receivers for ultrawideband communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2005, 4(4): 1337–1344. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2005.850270 [14] MO Jianhua and HEATH R W. Capacity analysis of one-bit quantized MIMO systems with transmitter channel state information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(20): 5498–5512. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2455527 [15] STOICA P, LI Jian, and XIE Yao. On probing signal design for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(8): 4151–4161. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894398 [16] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, and HUANG Yongwei. MIMO radar beampattern design via PSL/ISL optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(15): 3955–3967. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2543207 [17] ZHANG Xiaojun, HE Zishu, RAYMAN-BACCHUS L, et al. MIMO radar transmit beampattern matching design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(8): 2049–2056. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2398841 [18] ZHANG Weijian, HU Jinfeng, ZHOU Qihang, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for colocated MIMO radar: A convex relaxation approach[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 117: 103141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103141 [19] YU Xianxiang, QIU Hui, YANG Jing, et al. Multispectrally constrained MIMO radar beampattern design via sequential convex approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2935–2949. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3150619 [20] CHENG Ziyang, HAN Chunlin, LIAO Bin, et al. Communication-aware waveform design for MIMO radar with good transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5549–5562. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2868042 [21] HONG Mingyi, RAZAVIYAYN M, LUO Zhiquan, et al. A unified algorithmic framework for block-structured optimization involving big data: With applications in machine learning and signal processing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(1): 57–77. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2015.2481563 [22] DENG Minglong, CHENG Ziyang, LU Xiaoying, et al. Binary waveform design for MIMO radar with good transmit beampattern performance[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(19): 1061–1063. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.1602 [23] WEI Tong, CHU Ping, CHENG Ziyang, et al. Transmit beampattern design for MIMO radar with one-bit DACs via block-sparse SDR[C]. 2020 IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5. [24] CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Transmit signal design for large-scale MIMO system with 1-bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(9): 4466–4478. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2925343 [25] WEI Tong, CHENG Ziyang, and LIAO Bin. Transmit beampattern synthesis for MIMO radar with one-bit digital-to-analog converters[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 188: 108228. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108228 [26] CHENG Ziyang, SHI Shengnan, HE Zishu, et al. Transmit sequence design for dual-function radar-communication system with one-bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5846–5860. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3070586 [27] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, and LI Jian. Constant modulus MIMO radar waveform design with minimum peak sidelobe transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(16): 4207–4222. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2847636 [28] ALDAYEL O, MONGA V, and RANGASWAMY M. Tractable transmit MIMO beampattern design under a constant modulus constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(10): 2588–2599. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2664040 [29] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, ZHANG Shengmiao, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for MIMO radar transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(18): 4912–4923. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2718976 [30] HU Jinfeng, ZHANG Weijian, ZHU Haoming, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for MIMO radar via manifold optimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 190: 108322. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108322 [31] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7): 492–498. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.13.7.492 [32] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. Quadratic optimization for unimodular sequence design via an ADPM framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3619–3634. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2998637 [33] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [34] GHADIMI E, TEIXEIRA A, SHAMES I, et al. Optimal parameter selection for the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM): Quadratic problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(3): 644–658. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2354892 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: