Coprime Array Based Direct Position Determination of Signals with Single Moving Observation
-
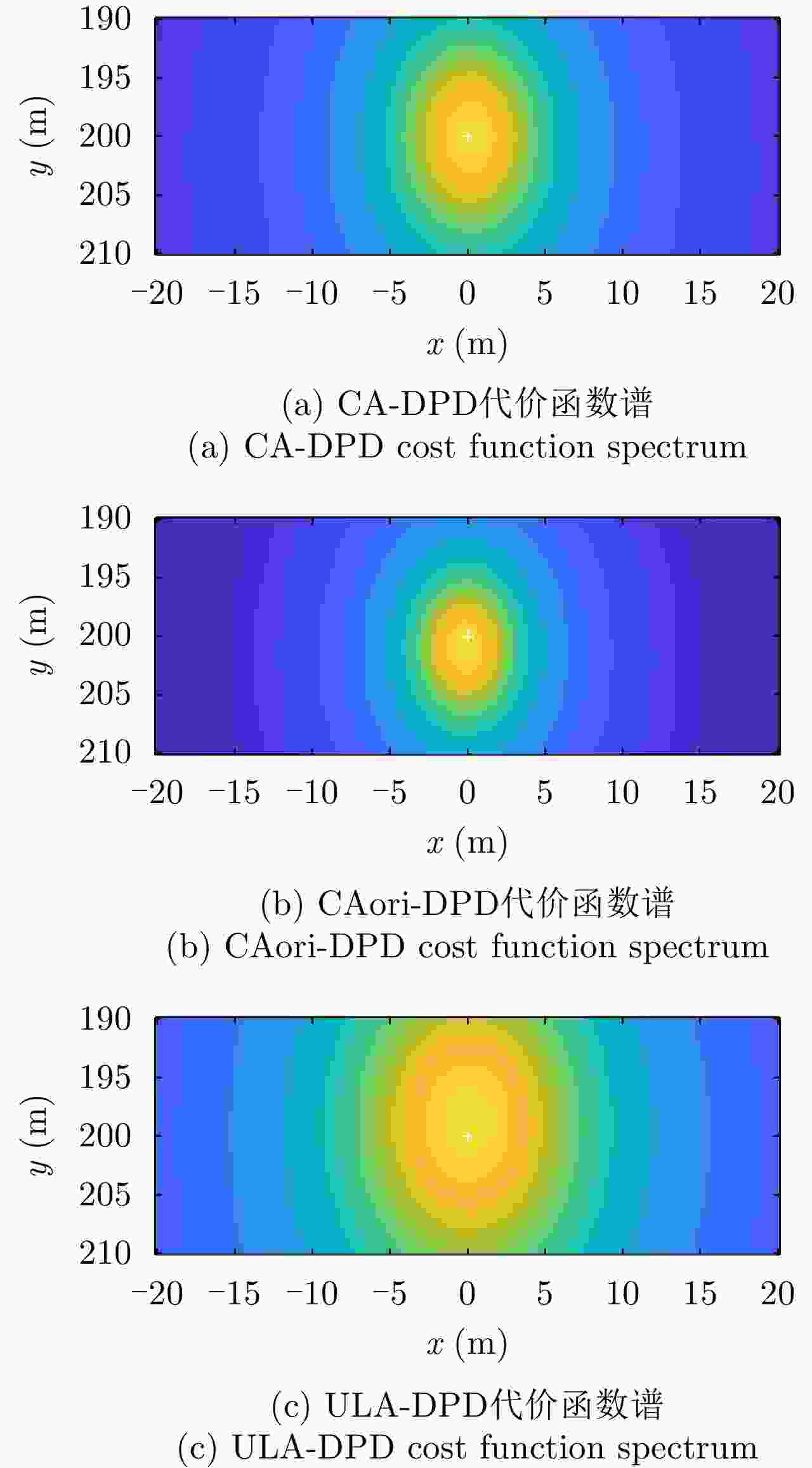
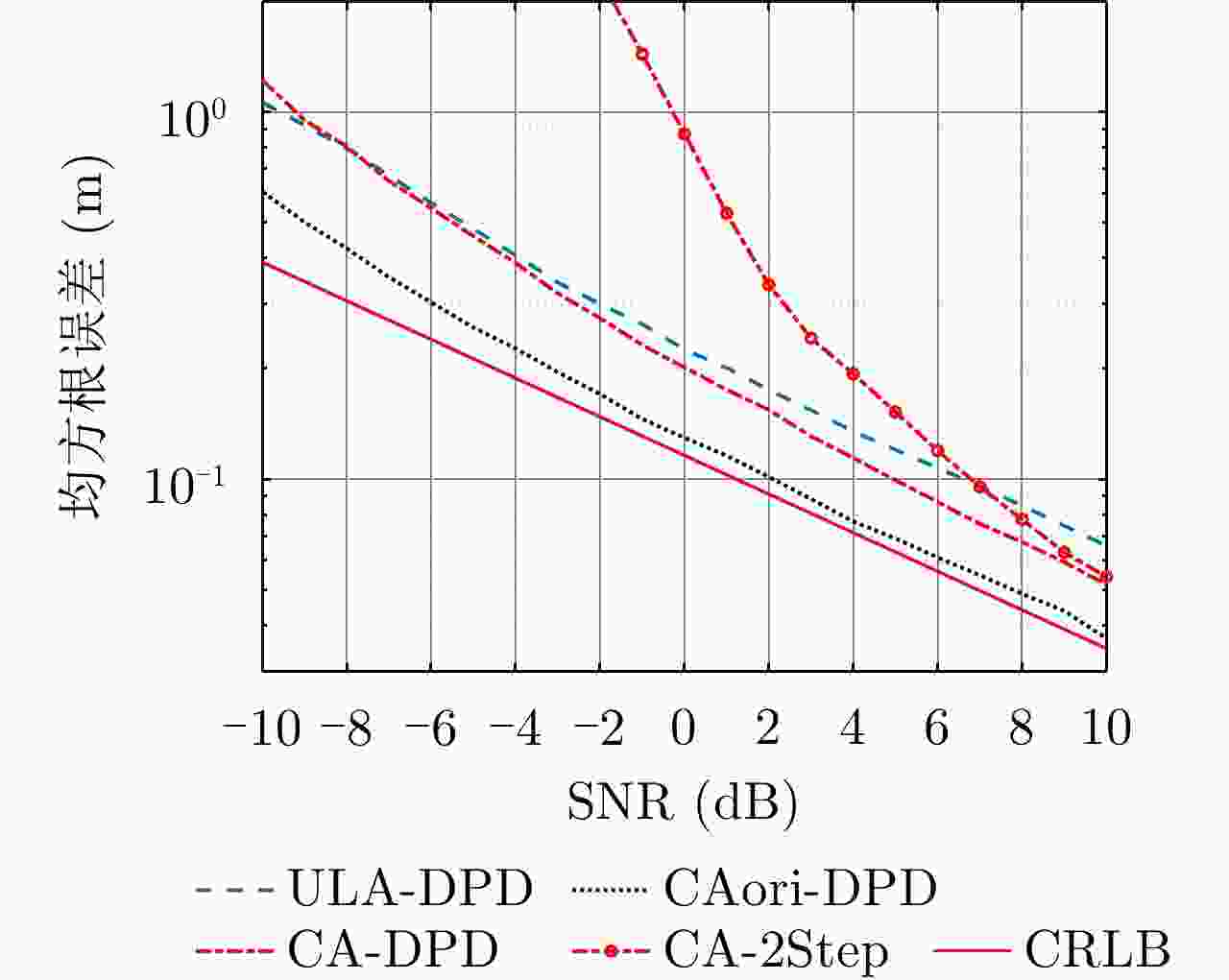
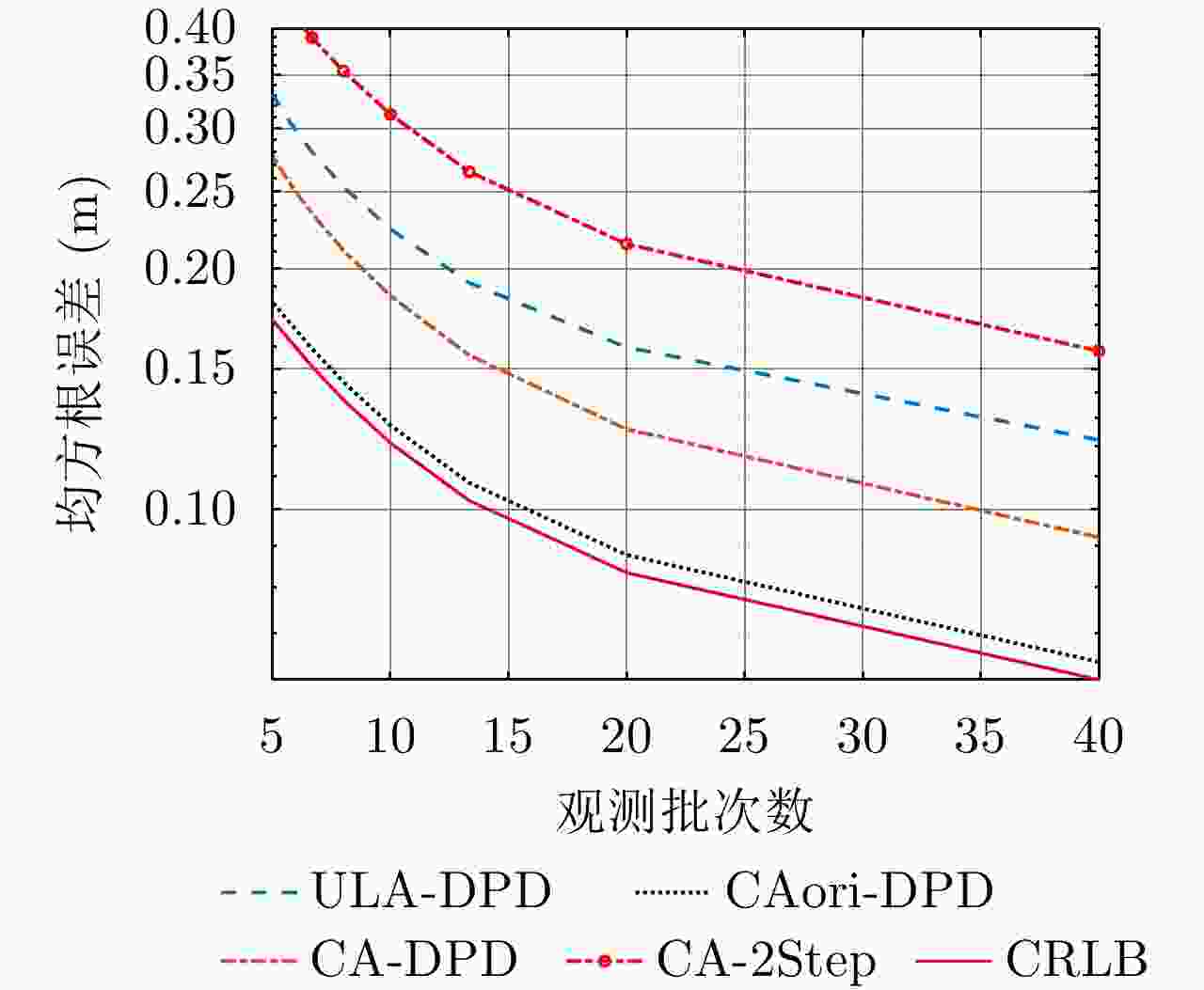
摘要: 信号直接定位方法是一种新型无源定位体制,具有适应低信噪比、无需参数关联等优势。为适应复杂电磁环境,该文提出了一种基于互质阵列的运动单站信号直接定位方法。以典型窄带信号为例,该文首先构建了互质阵列截获信号模型,然后推导了其差分共性阵对应的等效信号数学模型,最后使用空间谱技术构建了直接定位代价函数,实现了定位。经仿真分析验证,采用相同互质阵列时,该方法在分辨率和精度稍有损失的情况下可大幅提升传统直接定位方法的自由度,且与基于均匀线阵的直接定位方法相比,该方法在自由度、分辨率和定位精度等方面都具有优势。Abstract: Signal Direct Position Determination (DPD) is a novel passive localization technology, which shows superior performance in terms of low signal noise rate adaptability and no parameter association necessity. To adapt to the complex electromagnetic environment, this study proposes a coprime array-based DPD method with single moving observation. Considering narrowband signals as an example, this study first formulates the intercepted signal model, then derives its equivalent model related to the corresponding difference co-array, and finally builds the DPD cost function via spatial spectrum technology. Simulation results show that the proposed method can greatly improve the degree of freedom compared to the traditional DPD with a minor loss of resolution and accuracy when an identical coprime array is used. Meanwhile, compared to the uniform linear array-based DPD, the proposed method shows superior performance in terms of the degree of freedom, resolution, and accuracy of localization.
-
表 1 算法耗时
Table 1. Elapsed time of algorithms
算法 耗时(ms) ULA-DPD 1192.0 CA-DPD 1337.1 CAori-DPD 1197.3 CA-2Step 276.9 -
[1] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [2] MCCLOUD M L and SCHARF L L. A new subspace identification algorithm for high-resolution DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(10): 1382–1390. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2002.805244 [3] RAJ A G and MCCLELLAN J H. Single snapshot super-resolution DOA Estimation for arbitrary array geometries[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(1): 119–123. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2881927 [4] SELVA J. Efficient wideband DOA estimation through function evaluation techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(12): 3112–3123. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2824256 [5] YANG J R. Measurement of amplitude and phase differences between two RF signals by using signal power detection[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2014, 24(3): 206–208. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2013.2293665 [6] BALLAL T and BLEAKLEY C J. Phase-difference ambiguity resolution for a single-frequency signal in the near-field using a receiver triplet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(11): 5920–5926. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2062180 [7] BALLAL T and BLEAKLEY C J. Phase-difference ambiguity resolution for a single-frequency signal[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15: 853–856. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.2005439 [8] CARTER G C. Coherence and Time Delay Estimation[M]. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1993. [9] CHAN Y T and HO K C. A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(8): 1905–1915. doi: 10.1109/78.301830 [10] HO K C. Bias reduction for an explicit solution of source localization using TDOA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(5): 2101–2114. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2187283 [11] HO K C and CHAN Y T. Solution and performance analysis of geolocation by TDOA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(4): 1311–1322. doi: 10.1109/7.259534 [12] ULMAN R and GERANIOTIS E. Wideband TDOA/FDOA processing using summation of short-time CAF’s[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1999, 47(12): 3193–3200. doi: 10.1109/78.806065 [13] HO K C, LU Xiaoning, and KOVAVISARUCH L. Source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements in the presence of receiver location errors: Analysis and solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(2): 684–696. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.885744 [14] BELLO P. Joint estimation of delay, Doppler, and Doppler rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1960, 6(3): 330–341. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1960.1057562 [15] ABATZOGLOU T. Fast maximum likelihood joint estimation of frequency and frequency rate[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Tokyo, Japan, 1986: 4019–4012. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1986.1168717. [16] ZHANG Shuangri and XING Mengdao. A novel Doppler chirp rate and baseline estimation approach in the time domain based on weighted local Maximum-Likelihood for an MCHRWS SAR system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(3): 299–303. [17] ZHANG Weiqiang. Fast Doppler rate estimation based on fourth-order moment spectrum[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(23): 1926–1928. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.2182 [18] TRINH-HOANG M, VIBERG M, and PESAVENTO M. Partial relaxation approach: An eigenvalue-based DOA estimator framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(23): 6190–6203. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2875853 [19] WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A high-resolution DOA estimation method with a family of nonconvex penalties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 4925–4938. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2817638 [20] XU Xu, YE Zhongfu, and ZHANG Yufeng. DOA estimation for mixed signals in the presence of mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(9): 3523–3532. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2021919 [21] CATOVIC A and SAHINOGLU Z. The Cramer-Rao bounds of hybrid TOA/RSS and TDOA/RSS location estimation schemes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2004, 8(10): 626–628. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2004.835319 [22] LI Xinrong. RSS-based location estimation with unknown pathloss model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2006, 5(12): 3626–3633. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2006.256985 [23] PATWARI N, HERO A O, PERKINS M, et al. Relative location estimation in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(8): 2137–2148. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2003.814469 [24] WANG Gang and YANG Kehu. A new approach to sensor node localization using RSS measurements in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(5): 1389–1395. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.031611.101585 [25] WEISS A J. On the accuracy of a cellular location system based on RSS measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2003, 52(6): 1508–1518. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2003.819613 [26] 郭福成, 樊昀, 周一宇, 等. 空间电子侦察定位原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012: 44–47.GUO Fucheng, FAN Yun, ZHOU Yiyu, et al. Localization Principles in Space Electronic Reconnaissance[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012: 44–47. [27] 宋科康, 冯文涛. 采用Direct算法的外辐射源雷达高效直接定位方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(1): 149–154. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.018SONG Kefeng and FENG Wentao. An efficient method of direct position determination of passive radar with direct algorithm[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(1): 149–154. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.018 [28] 余婉婷, 于宏毅, 杜剑平, 等. 辐射源信号波形已知的超视距目标直接定位方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(11): 2368–2377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.11.019YU Wanting, YU Hongyi, DU Jianping, et al. A direct position determination method for over-the-horizon target on known radiation source waveforms[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(11): 2368–2377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.11.019 [29] ZHAO Hanying, ZHANG Ning, and SHEN Yuan. Beamspace direct localization for large-scale antenna array systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3529–3544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2996155 [30] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Advances in direct position determination[C]. Processing Workshop Proceedings, 2004 Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal, Barcelona, Spain, 2004: 584–588. [31] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Direct position determination in the presence of model errors—known waveforms[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2006, 16(1): 52–83. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2005.03.003 [32] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Analysis of direct position determination approach in the presence of model errors[C]. IEEE/SP 13th Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, 2005, Bordeaux, France, 2005: 521–524. [33] WANG Ding and WU Ying. Statistical performance analysis of direct position determination method based on Doppler shifts in presence of model errors[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 28(1): 149–182. doi: 10.1007/s11045-015-0338-3 [34] WEISS A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 [35] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Direct position determination (DPD) of multiple known and unknown radio-frequency signals[C]. 2004 12th European Signal Processing Conference, Vienna, Austria, 2004: 1115–1118. [36] WEISS A J and AMAR A. Direct position determination of multiple radio signals[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2005, 2005(1): 653549. doi: 10.1155/ASP.2005.37 [37] LU Zhiyu, BA Bin, WANG Jianhui, et al. A direct position determination method with combined TDOA and FDOA based on particle filter[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(1): 161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2017.11.007 [38] ZHOU Longjian, ZHU Weiqiang, LUO Jingqing, et al. Direct positioning maximum likelihood estimator using TDOA and FDOA for coherent short-pulse radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1505–1511. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0437 [39] 王云龙, 吴瑛. 联合时延与多普勒频率的直接定位改进算法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(4): 123–129. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201504020WANG Yunlong and WU Ying. An improved direct position determination algorithm with combined time delay and Doppler[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(4): 123–129. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201504020 [40] TIRER T and WEISS A J. High resolution localization of narrowband radio emitters based on doppler frequency shifts[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 288–298. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.06.019 [41] TIRER T and WEISS A J. High resolution direct position determination of radio frequency sources[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(2): 192–196. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2503921 [42] WU Guizhu, ZHANG Ming, and GUO Fucheng. High-resolution direct position determination based on eigenspace using a single moving ULA[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2019, 13(5): 887–894. doi: 10.1007/s11760-019-01425-4 [43] OISPUU M and NICKEL U. 3D passive source localization by a multi-array network: Noncoherent vs. coherent processing[C]. 2010 International ITG Workshop on Smart Antennas (WSA), Bremem, Germany, 2010: 300–305. [44] WU Guizhou, ZHANG Min, HE Chaoxin, et al. Direct position determination using single moving rotating linear array: Noncoherent and coherent processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2020, 33(2): 688–700. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.07.027 [45] VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with Co-prime samplers and arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 573–586. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2089682 [46] PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Nested arrays: A novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(8): 4167–4181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2049264 [47] QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, and AMIN M G. Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(6): 1377–1390. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2393838 [48] LIU Chunlin and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Super nested arrays: Linear sparse arrays with reduced mutual coupling—part I: Fundamentals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(15): 3997–4012. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2558159 [49] LIU Jianyan, ZHANG Yanmei, LU Yilong, et al. Augmented nested arrays with enhanced DOF and reduced mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(21): 5549–5563. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2736493 [50] ZHANG Yankui, BA Bin, WANG Daming, et al. Direct position determination of multiple non-circular sources with a moving coprime array[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1479. doi: 10.3390/s18051479 [51] KUMAR G, PONNUSAMY P, and AMIRI I S. Direct localization of multiple noncircular sources with a moving nested array[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 101106–101116. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929805 [52] CZARNECKI S V, JOHNSON J A, GRAY C M, et al. Self-resolving LBI triangulation[P/OL]. US, 5835060A, 1998. http://fx.gfkd.chaoxing.com/detail_38502727e7500f26da641ed9afec03488195a6654876bab11921b0a3ea25510133e7f87ae1903bd666c0a358461822c556999c638672b0c5948ab7aaa01c6a6c8cfe3d4a29101f7e57ea89991e2828e1? [53] QIAN Yang, YANG Zhongtian, and ZENG Haowei. Direct position determination for augmented coprime arrays via weighted subspace data fusion method[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 2825025. doi: 10.1155/2021/2825025 [54] TORRIERI D J. Statistical theory of passive location systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1984, 20(2): 182–98. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1984.310439 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: