Unambiguous Imaging Method for GEO-LEO Bistatic SAR Based on Joint Sequential Multiframe and Multichannel Receiving Recovery
-
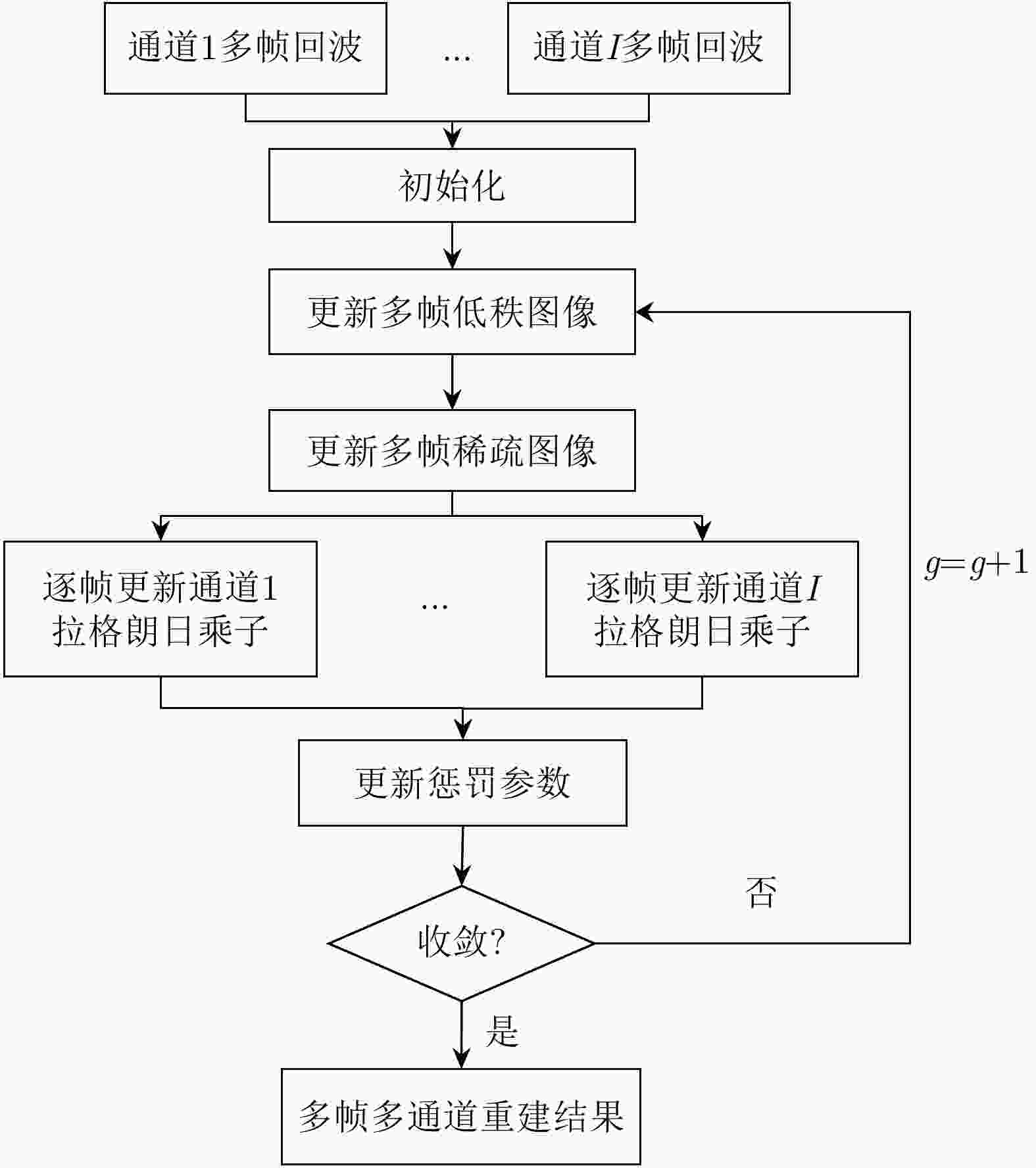
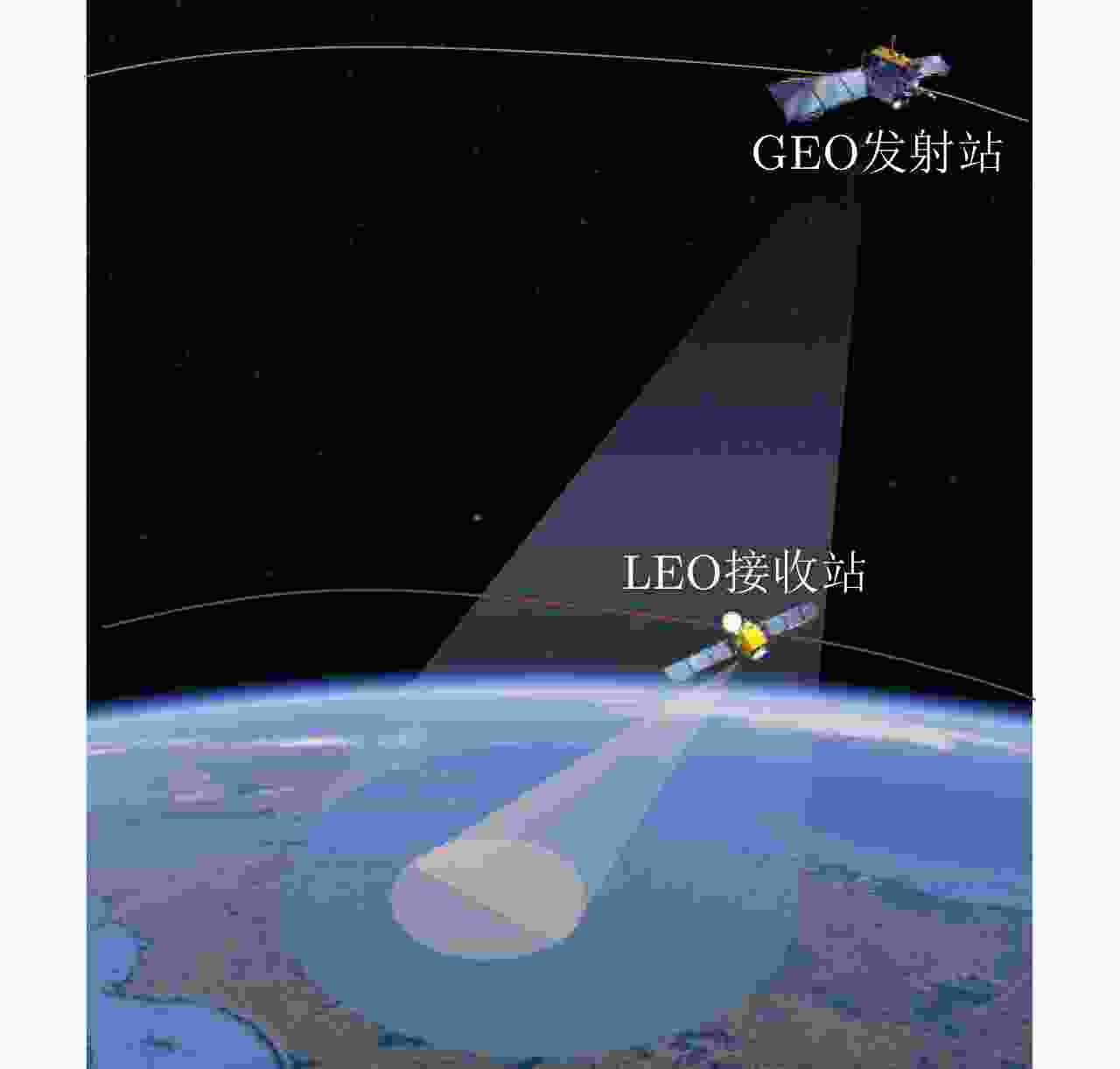
摘要: 采用地球同步轨道(GEO)卫星作为双基合成孔径雷达(SAR)的发射站,可为低轨(LEO)接收站提供大范围、持续的波束覆盖。同时,由于收发分置的系统形态,LEO接收站可以实现下视、前视、后视等多视区成像,因此,GEO-LEO双基SAR在地球测绘、侦察监视等领域具有广阔的应用前景。为实现大幅宽成像,GEO SAR发射站的脉冲重复频率较低,而LEO SAR接收站会引入大的多普勒带宽,造成GEO-LEO双基SAR方位欠采样。通过在接收站引入多通道技术虽可抑制模糊,但是面临GEO-LEO双基SAR的严重欠采样问题,多通道无模糊重建方法所需通道数过多,不利于接收系统小型化。针对方位严重欠采样条件下的复杂观测场景无模糊成像问题,该文提出了序贯多帧-多接收通道联合重建无模糊成像方法,通过利用序贯观测场景多帧图像的相关性和多接收通道的采样信息进行联合重建,实现无模糊成像。首先将GEO-LEO双基SAR无模糊成像问题建模为张量联合低秩与稀疏优化问题,然后在交替方向乘子法迭代求解中利用多接收通道信息,实现了GEO-LEO双基SAR对复杂观测场景的无模糊成像。相比于基于传统多通道重构的成像方法,该方法可显著减少无模糊成像所需的接收通道数,仿真实验验证了该方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 地球同步轨道 /
- 双基合成孔径雷达 /
- 方位欠采样 /
- 多帧-多通道联合重建 /
- 无模糊成像
Abstract: A geosynchronous (GEO) satellite can provide continuous illumination with broad beam coverage for a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) receiver, used as the transmitting station of bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR). Meanwhile, because the bistatic SAR system comprises a separate transmitter and receiver, the LEO receiver can realize multiview imaging such as downward-, forward-, and backward-looking. Therefore, GEO-LEO bistatic SAR is widely used in earth surveying and mapping to reconnaissance and surveillance application. To realize large-scene imaging, the pulse repetition rate of the GEO SAR transmitter should be low. Meanwhile, the LEO SAR receiver introduces a wide Doppler bandwidth, resulting in the azimuth undersampling of the GEO-LEO bistatic SAR. Although the multichannel technology in the receiver can suppress the ambiguity, the multichannel unambiguous recovery method requires numerous channels, resulting in the undersampling of the GEO-LEO bistatic SAR, and hindering the miniaturization of the receiving system. To address the problem of ambiguous imaging of complex observation scenes under the condition of severe azimuth subsampling condition, a sequential joint multiframe and multireceiving channel recovery unambiguous imaging method is proposed. The unambiguous imaging is recovered jointly from the correlation between sequential multiframe observation scenes and multireceiving channel sampling information. First, the unambiguous imaging problem of the GEO-LEO bistatic SAR is modeled as a joint low rank and sparse tensor optimization problem. Second, in the iterative solution of the alternating direction multiplier method, the multireceiving channel information is used to realize the unambiguous imaging of the GEO-LEO bistatic SAR for complex observation scenes. The proposed method can significantly reduce the number of receiving channels required for unambiguous imaging compared with the imaging method based on traditional multichannel The results obtained by the proposed method are validated by simulations and experiments. -
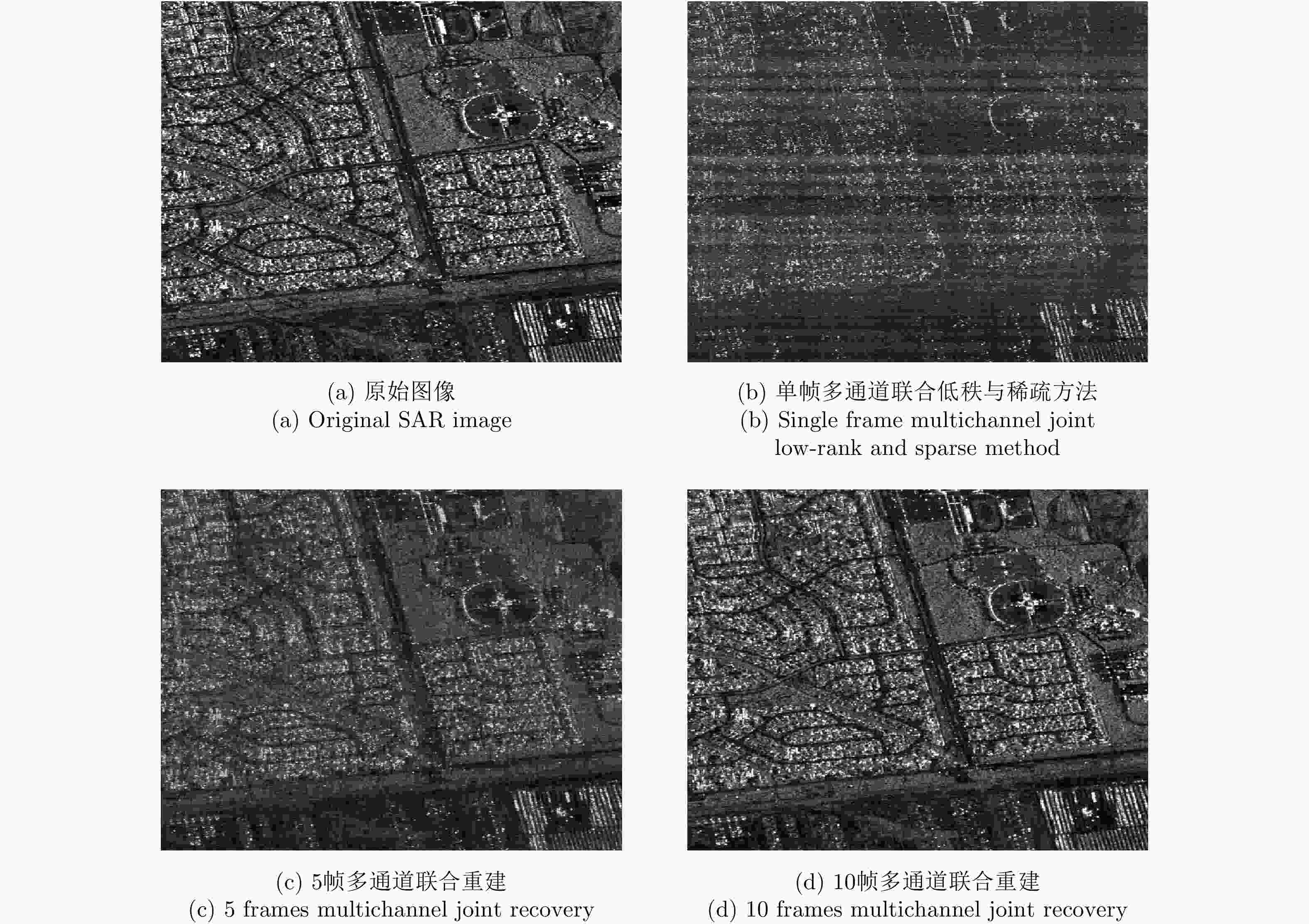
表 1 仿真系统参数
Table 1. Simulation system parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 载频 1.25 GHz 信号带宽 100 MHz 接收天线尺寸 5 m 合成孔径时间 5 s 表 2 仿真轨道参数
Table 2. Simulated orbit parameters
参数 GEO SAR数值 LEO SAR数值 半长轴 42164.17 km 6884 km 离心率 0.01 0 轨道倾角 53° 97.03° 近地点幅角 270° 270° 入射角 20.38° 58.53° 斜视角 16.5° 61.5° 表 3 不同方法的重建性能
Table 3. Reconstruction performance of different methods
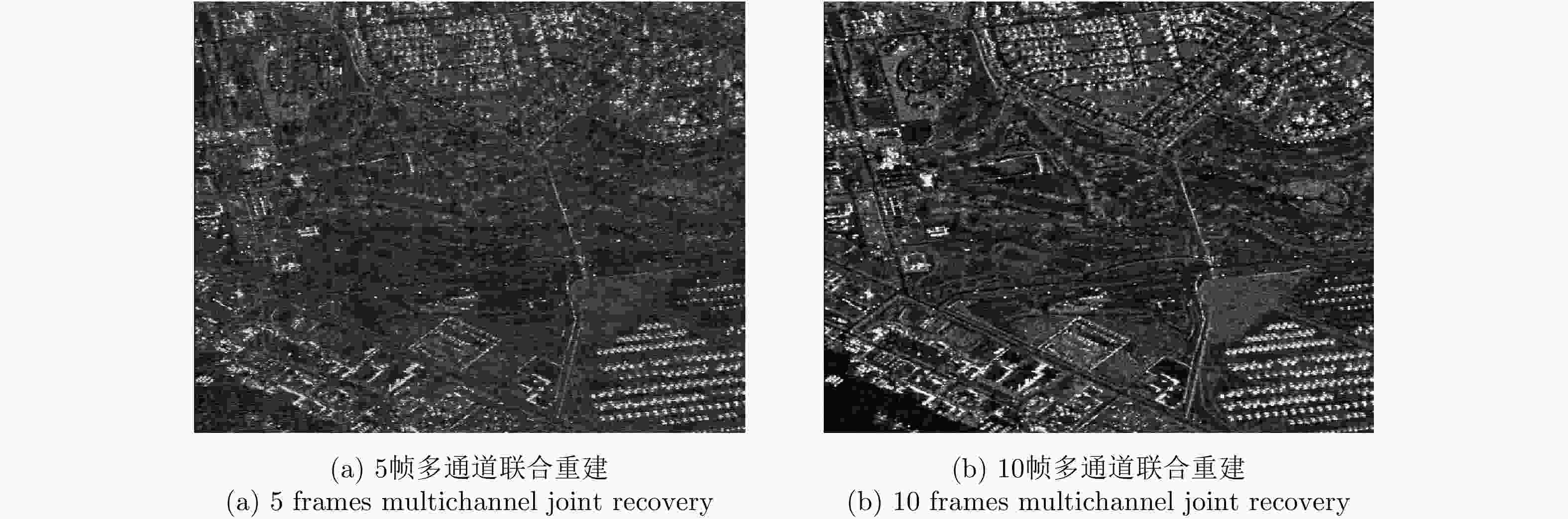
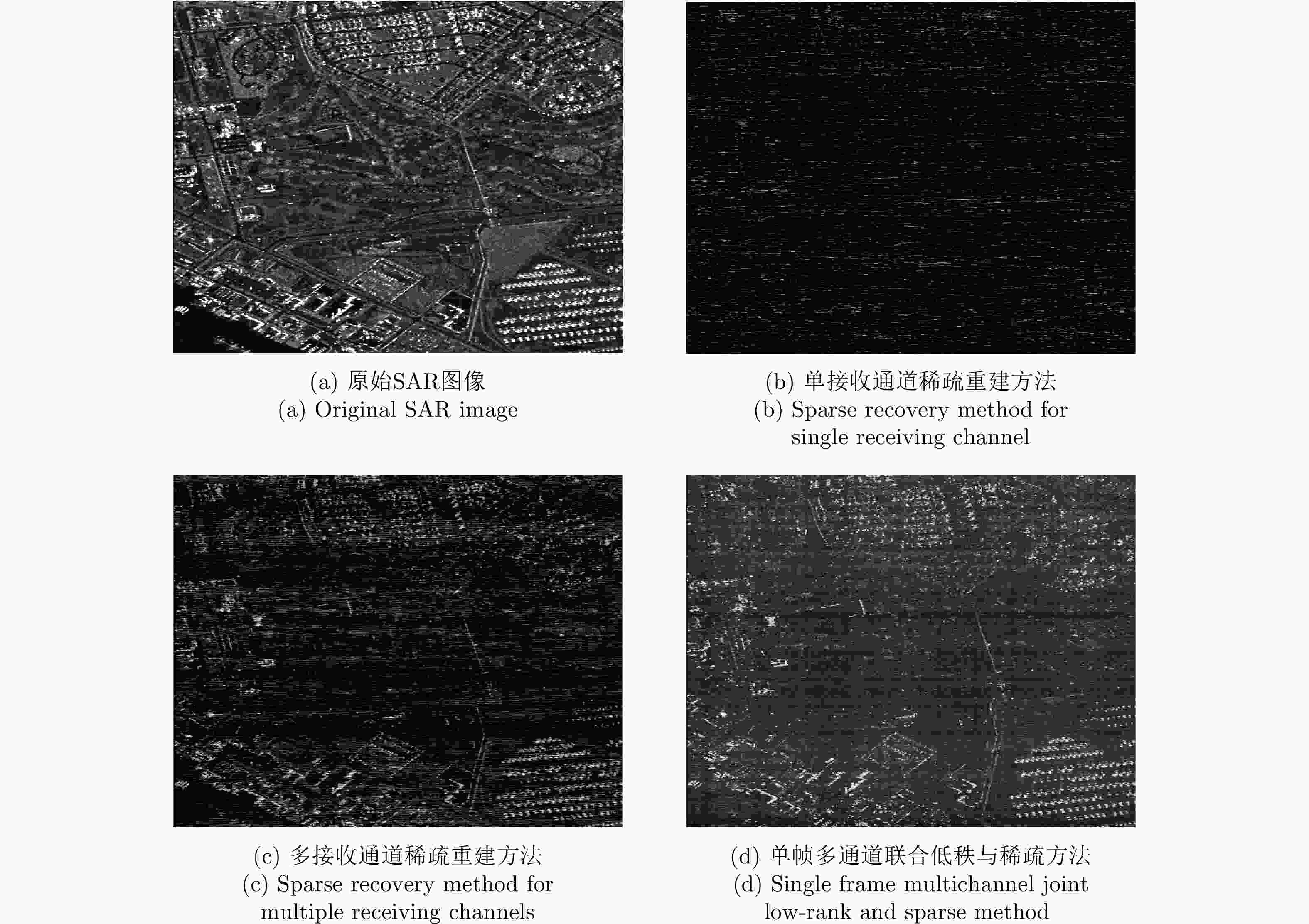
目标场景 单通道稀疏重建方法 多通道稀疏重建方法 单帧多通道联合低秩与稀疏方法 5帧多通道联合重建 10帧多通道联合重建 扩展目标场景1 10.37 dB 14.06 dB 20.06 dB 22.92 dB 26.98 dB 扩展目标场景2 9.17 dB 12.31 dB 18.19 dB 21.25 dB 26.62 dB -
[1] TOMIYASU K and PACELLI J L. Synthetic aperture radar imaging from an inclined geosynchronous orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1983, GE-21(3): 324–329. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1983.350561 [2] MADSEN S N, EDELSTEIN W, DIDOMENICO L D, et al. A geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar; for tectonic mapping, disaster management and measurements of vegetation and soil moisture[C]. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium on Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future, Sydney, Australia, 2001: 447–449. [3] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [4] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 [5] 孙稚超. 基于GEO辐射源的星机SAR成像理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.SUN Zhichao. Research on the imaging theory and algorithms of geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [6] 安洪阳. 基于高轨照射源的双基SAR成像与动目标检测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.AN Hongyang. Research on imaging and moving target detection technology of bistatic SAR with geosynchronous illuminator[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [7] GUTTRICH G L, SIEVERS W E, and TOMLJANOVICH N M. Wide area surveillance concepts based on geosynchronous illumination and bistatic unmanned airborne vehicles or satellite reception[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 126–131 . [8] LU Zheng, WANG Yuekun, XU Mingming, et al. Spacecraft formation design for bistatic SAR with GEO illuminator and LEO receiver[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 4451–4454. [9] WANG Jingen, WANG Yanfei, GE Jialong, et al. Ambiguous scattering point detection of bistatic downward-looking SAR with geostationary illuminator and LEO receiver[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 571–574. [10] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. A 2-D space-variant chirp scaling algorithm based on the RCM equalization and subband synthesis to process geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4868–4880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2285721 [11] DING Zegang, SHU Bozheng, YIN Wei, et al. A modified frequency domain algorithm based on optimal azimuth quadratic factor compensation for geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1119–1131. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2497000 [12] ZHANG Shuangxi, LI Shaojie, LIU Yanyang, et al. A novel azimuth Doppler signal reconstruction approach for the GEO-LEO bi-static multi-channel HRWS SAR system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39539–39546. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904653 [13] WANG Yuekun, LIU Yanyang, LI Zhenfang, et al. High-resolution wide-swath imaging of spaceborne multichannel bistatic SAR with inclined geosynchronous illuminator[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2380–2384. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2765675 [14] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Nonambiguous image formation for low-earth-orbit SAR with geosynchronous illumination based on multireceiving and CAMP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 348–362. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2992744 [15] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [16] RECHT B, FAZEL M, and PARRILO P A. Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization[J]. SIAM Review, 2010, 52(3): 471–501. doi: 10.1137/070697835 [17] PU Wei and WU Junjie. OSRanP: A novel way for radar imaging utilizing joint sparsity and low-rankness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 868–882. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.2993170 [18] WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LI Zhongyu, et al. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 840. doi: 10.3390/rs8100840 [19] BI Hui, BI Guoan, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. From theory to application: Real-time sparse SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2928–2936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958067 [20] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR imaging based on fast low-rank and sparse matrices recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3081099. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: