-
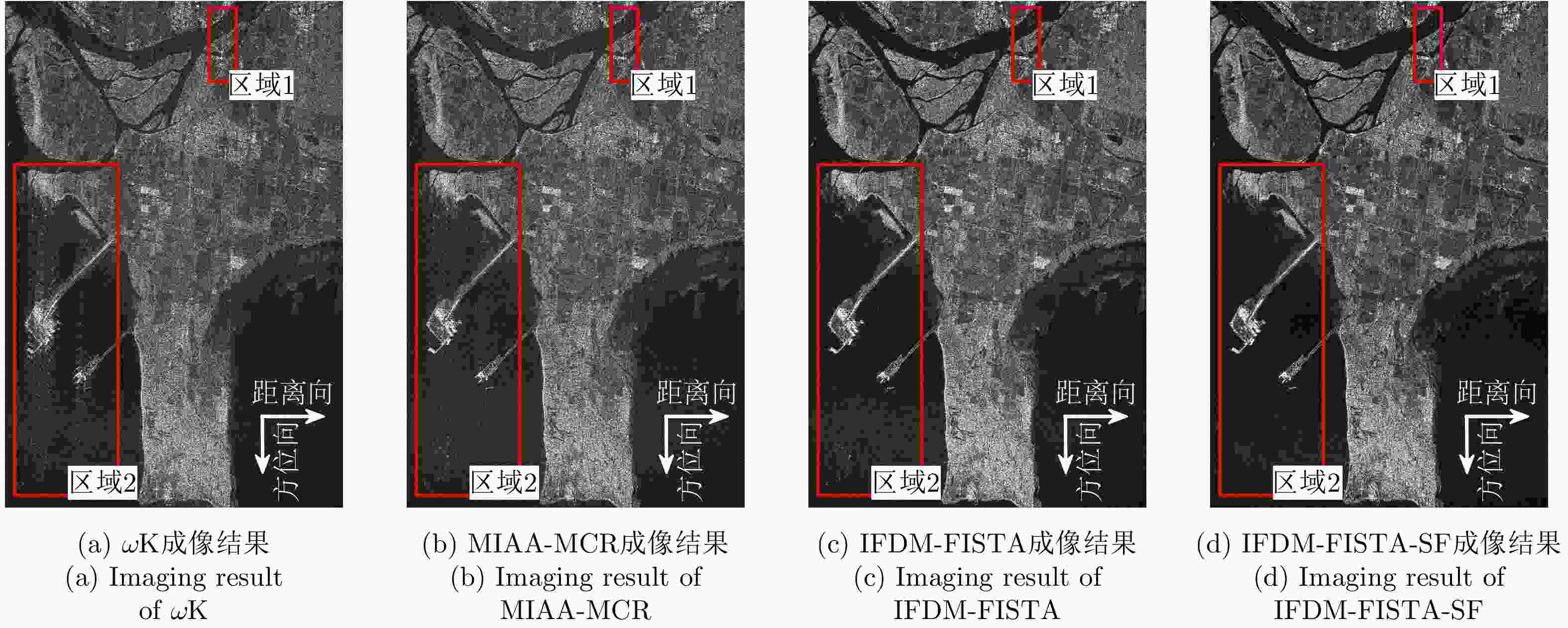
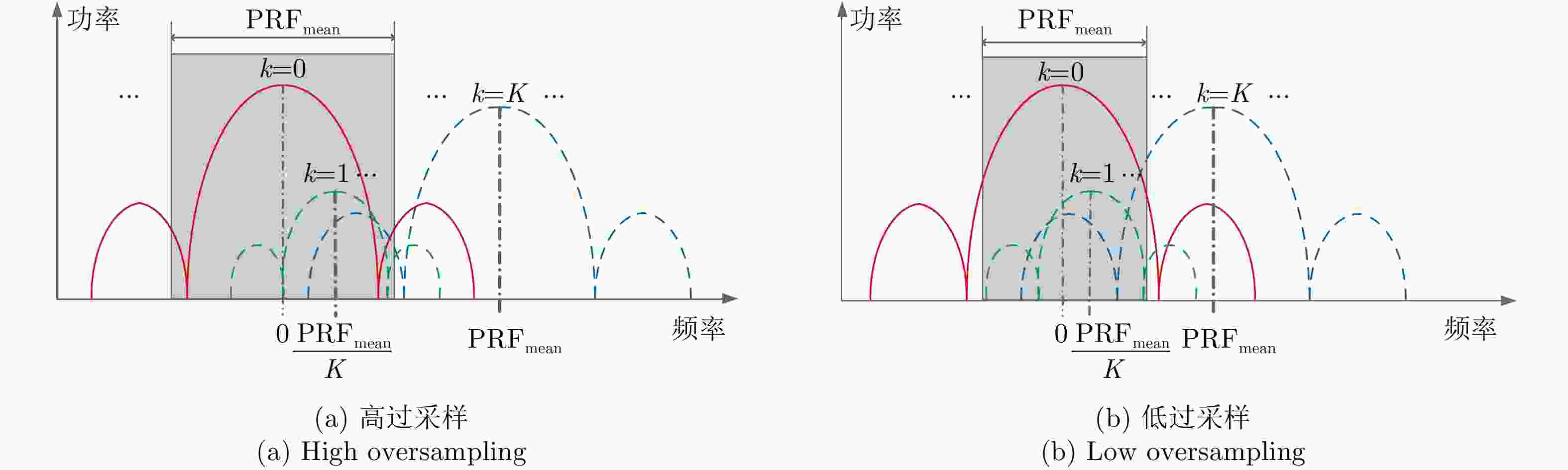
摘要: 低过采样Staggered SAR利用变脉冲重复间隔技术有效分散盲区,可实现连续观测的高分宽幅成像,同时采用低过采样率可降低系统对数据存储的要求,因此具有重要的研究价值。然而,低过采样Staggered SAR存在的非均匀采样、回波丢失和非理想方位天线方向图(AAP)问题会导致成像结果中出现严重的方位模糊。该文提出了一种基于压缩感知的成像方法,可解决已有方法模糊抑制性能差和效率低的问题。首先,建立了准确描述低过采样Staggered SAR非均匀采样、回波丢失和距离徙动的创新性频域模型(IFDM),利用二维快速迭代收缩阈值算法对基于该IFDM构造的优化问题进行迭代求解可抑制非均匀采样和回波丢失造成的方位模糊;然后,利用选择滤波方法处理迭代结果可抑制非理想AAP造成的方位模糊。实验结果表明该文方法在成像性能和效率上均优于已有方法。Abstract: Low-oversampled staggered synthetic aperture radar can achieve continuously observed high-resolution and wide-swath imaging by utilizing the variable pulse repetition interval to distribute blind ranges. Moreover, adopting a low oversampling ratio can reduce the data storage requirements, contributing to its research significance. However, non-uniform sampling, echo data loss, and non-ideal Azimuth Antenna Pattern (AAP) cause severe azimuth ambiguities in a directly focused image. This study proposes a compressive sensing-based method with better ambiguity removal performance and higher efficiency compared to existing methods. First, an Innovative Frequency-Domain Model (IFDM) is constructed, which accurately describes the non-uniform sampling, echo data loss, and coupled range cell migration. Based on the IFDM, an optimization problem is constructed and solved by the two-dimensional fast iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithm to remove the ambiguity caused by non-uniform sampling and echo data loss. Subsequently, selective filtering is used to suppress the ambiguity caused by the AAP. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can more effectively and efficiently suppress the azimuth ambiguities compared to existing methods.
-
表 1 IFDM-FISTA-SF流程
Table 1. The process of IFDM-FISTA-S
输入:距离压缩后的Staggered SAR回波数据${\boldsymbol{S}}$,稀疏算子$\Psi $ 输出:方位模糊被抑制的高质量成像结果${{\boldsymbol{X}}_{ {\text{final} } } }$ 初始化:${\lambda _1},\bar \lambda > 0$, $\beta \in \left( {0,1} \right)$, ${\sigma _0} = {\sigma _1} = 1$, $L > 0$, $l = 0$,
${{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(0)} } = {{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(1)} } = {\boldsymbol{0} }$IFDM-FISTA:当满足$l \le L$时,进行以下迭代
步骤1 ${{\boldsymbol{Z}} ^{(l)} } = {{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(l)} } + \left( { {\sigma _{l - 1} } - 1} \right)/{\sigma _l} \cdot \left( { {{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(l)} } - {{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(l - 1)} } } \right)$步骤2 ${\hat {\boldsymbol{X}}^{(l)} } = {\Psi ^{ - 1} }\left( { {{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} ^{(l)} } } \right)$ 步骤3 ${\boldsymbol{E} } = {\boldsymbol{B} } \odot \left\{ { {\tilde {\boldsymbol F} }_{\text{t} }^{\text{H} }\left[ {\left( {({ {\boldsymbol{F} }_{\text{a} } }{\boldsymbol{X} }) \circ { { { {\tilde {\boldsymbol F} } } }_{\text{r} } } } \right) \odot {\boldsymbol{D} } } \right]{\boldsymbol{F} }_{{\tau } }^{\text{H} } } \right\} - {\boldsymbol{S} }$ 步骤4 $\nabla g\left( {\boldsymbol{\varGamma} } \right) = \Psi \left\{ { {\boldsymbol{F} }_{\text{a} }^{\text{H} }\left[ {\left( {\left( { { {\tilde {\boldsymbol{F}}}_{\text{t} } }{\boldsymbol{E}}{{\boldsymbol{F}}_{ {\tau } } } } \right) \odot {{\boldsymbol{D}}^*} } \right) \circ \tilde {\boldsymbol{F}}_{\text{r} }^{\text{H} } } \right]} \right\}$ 步骤5 ${ {\boldsymbol{U} }^{(l)} } = { {\boldsymbol{Z} }^{(l)} } - 1/{\ell _{\rm{f} } } \cdot \nabla g\left({ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma} } ^{(l)} }\right)$ 步骤6 ${ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma} } ^{(l + 1)} } = { {\rm{soft} } } \left( { { {\boldsymbol{U} }^{(l)} },{\lambda _l}/{\ell _{\rm{f}}} } \right)$ 步骤7 ${\sigma _{l + 1} } = \left(1 + \sqrt {4\sigma _l^2 + 1} \right)/2$ 步骤8 ${\lambda _{l + 1}} = \max \left( {\beta {\lambda _l},\bar \lambda } \right)$ 步骤9 $l = l + 1$ SF:${{\boldsymbol{X}}_{ {\text{final} } } }{\text{ = SF} }\left( {\tilde {\boldsymbol{X}}} \right) = {\text{SF} }\left( { { {\hat {\boldsymbol{X}}}^{(L)} } } \right)$ 表 2 低过采样Staggered SAR仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters for low-oversampled Staggered SAR
参数 数值 参数 数值 轨道高度(km) 760 最大PRI (s) 1/1500 平台速度(m/s) 7473 最小PRI (s) 1/1800 参考斜距史(km) 981.8 发射过采样率 1.1 发射信号带宽(MHz) 20 有效接收采样率 0.9 多普勒带宽(Hz) 1495 中心频率(GHz) 10 表 3 不同方法对点目标模糊抑制性能的评估结果
Table 3. Evaluation results of the azimuth-ambiguity-removal performance for different methods
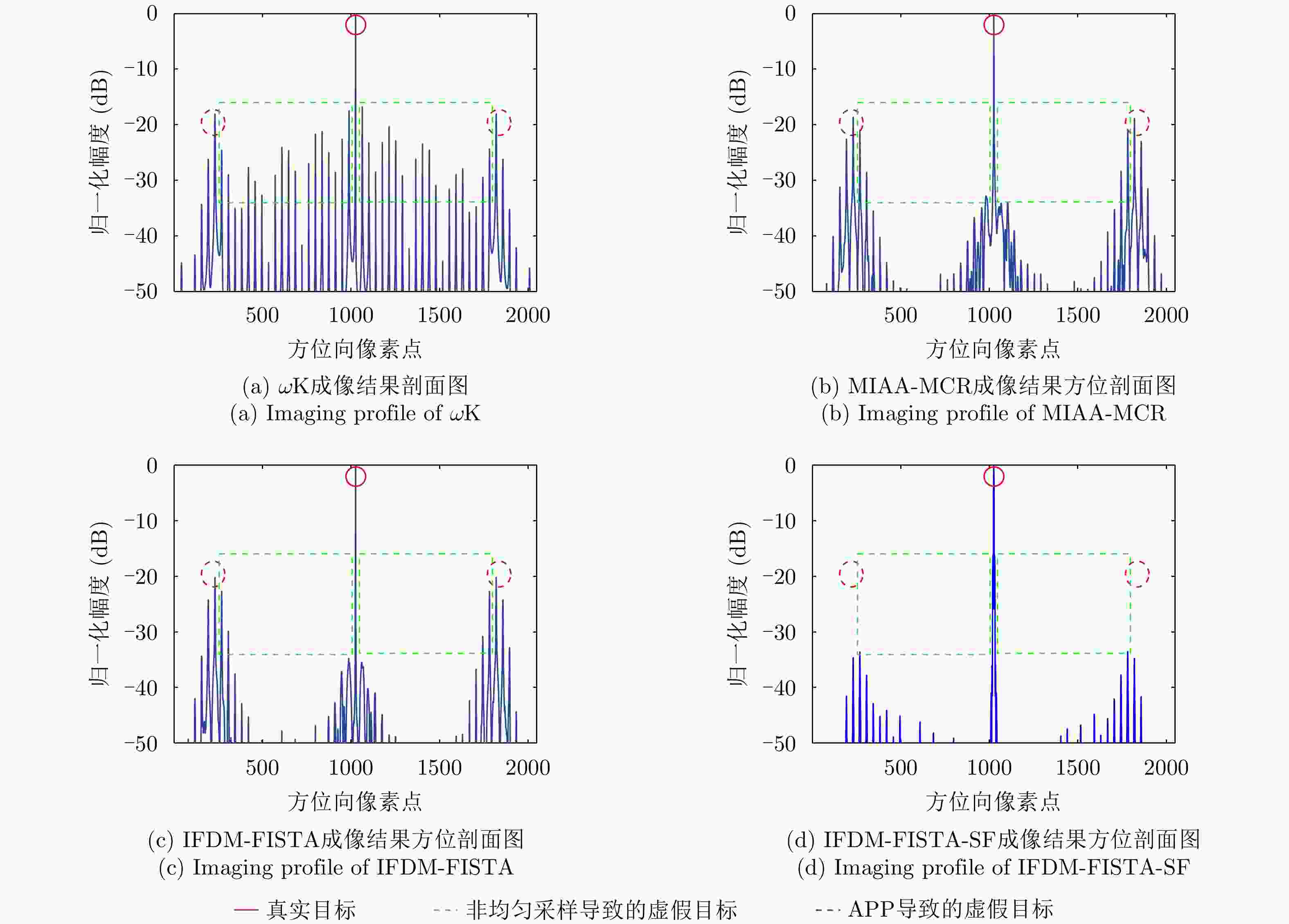
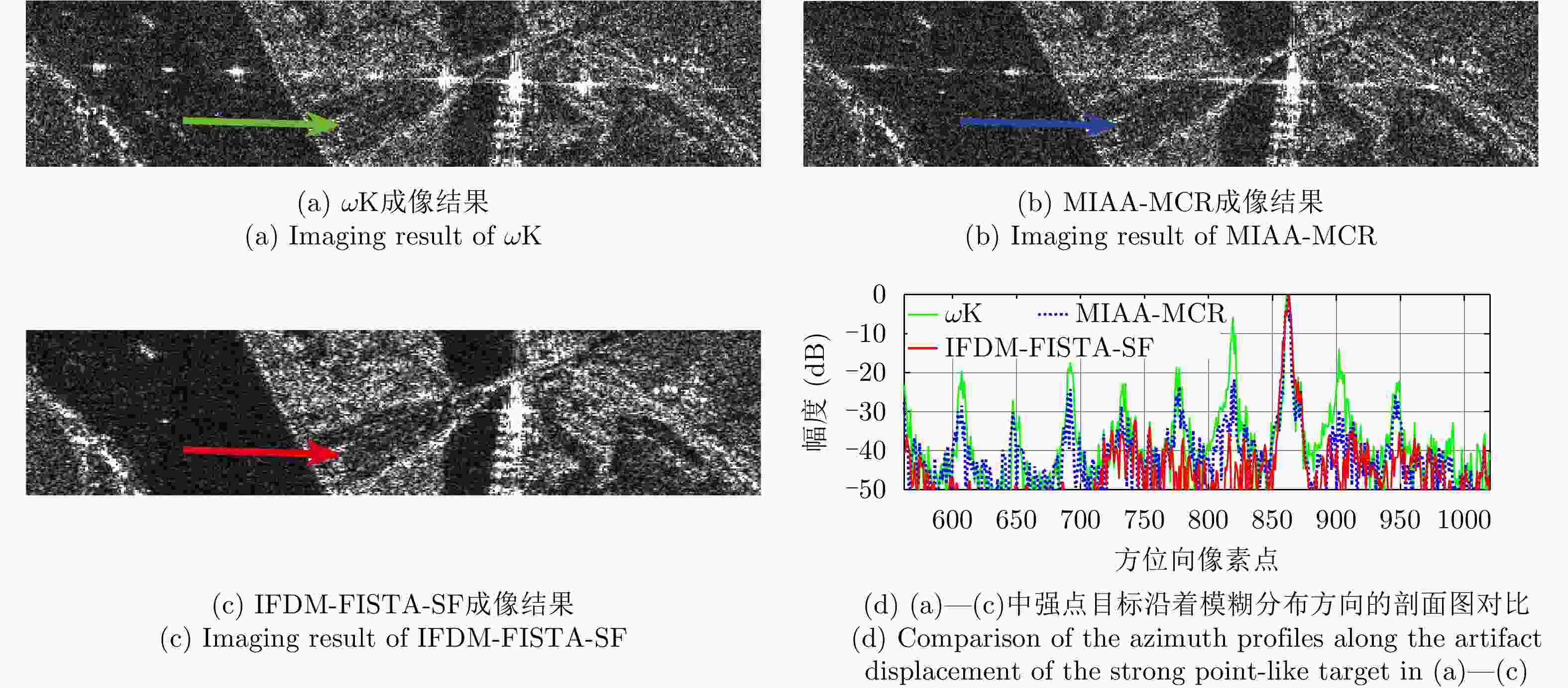
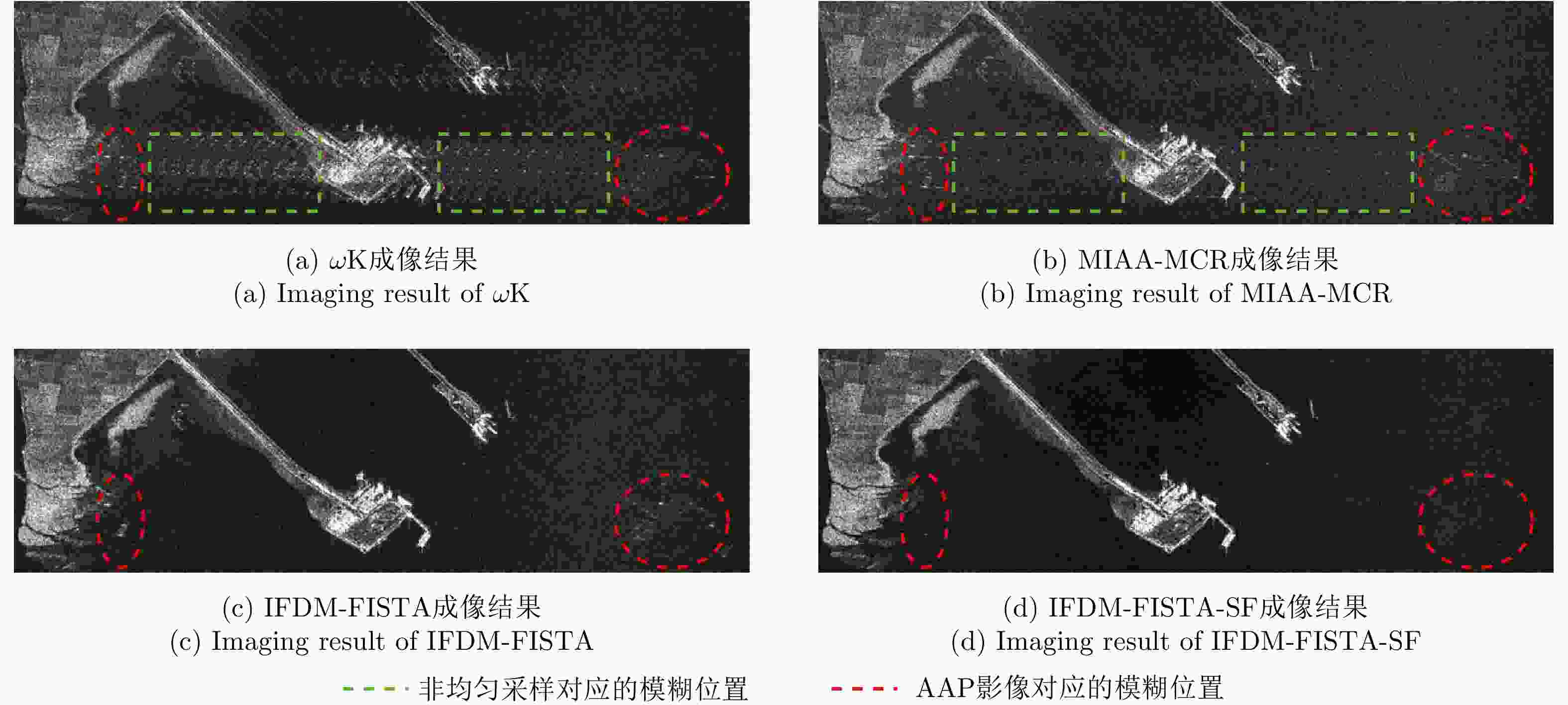
Method ATR (dB) ISLR (dB) $\omega {\text{K}}$ –18.04 –7.20 MIAA-MCR –18.65 –11.34 IFDM-FISTA –20.17 –12.58 IFDM-FISTA-SF –33.56 –14.18 表 4 各方法计算复杂度以及处理图3对应宽幅场景耗时
Table 4. Different methods’ computation complexity and time for the scene given by Fig. 3
Method 计算复杂度 耗时 (min) $ \omega {\text{K}} $ $ O\left( {MN{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_2}\left( {MN} \right)} \right) $ 1 MIAA-MCR $O\left( {LMNM_{\text{d}}^2} \right)$ 273 IFDM-FISTA by NUDFT $ O\left( {LMN\left( {M + N} \right)} \right) $ 1676 IFDM-FISTA/IFDM-FISTA-SF $ O\left( {LMN{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_2}\left( {MN} \right)} \right) $ 47 -
[1] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered SAR: High-resolution wide-swath imaging by continuous PRI variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4462–4479. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282192 [2] HUBER S, DE ALMEIDA F Q, VILLANO M, et al. Tandem-L: A technical perspective on future spaceborne SAR sensors for earth observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4792–4807. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2837673 [3] LUO Xiulian, WANG Robert, XU Wei, et al. Modification of multichannel reconstruction algorithm on the SAR with linear variation of PRI[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(7): 3050–3059. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2298242 [4] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, JÄGER M, et al. Staggered SAR: Performance analysis and experiments with real data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6617–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731047 [5] WANG Xiangyu, WANG Robert, DENG Yunkai, et al. SAR signal recovery and reconstruction in staggered mode with low oversampling factors[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 704–708. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2805311 [6] PINHEIRO M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, et al. Analysis of low-oversampled staggered SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 241–255. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2959092 [7] STOICA P, LI Jian, and LING Jun. Missing data recovery via a nonparametric iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2009, 16(4): 241–244. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2009.2014114 [8] CANDES E J and WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 [9] HERMAN M A and STROHMER T. High-resolution radar via compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(6): 2275–2284. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2014277 [10] WEI Shunjun, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Sparse reconstruction for SAR imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2010, 109: 63–81. doi: 10.2528/PIER10080805 [11] FANG Jian, XU Zongben, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Fast compressed sensing SAR imaging based on approximated observation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(1): 352–363. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2263309 [12] DONG Xiao and ZHANG Yunhua. A novel compressive sensing algorithm for SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(2): 708–720. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2291578 [13] 顾福飞, 张群, 杨秋, 等. 基于NCS算子的大斜视SAR压缩感知成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(1): 16–24. doi: 10.12000/JR15035GU Fufei, ZHANG Qun, YANG Qiu, et al. Compressed sensing imaging algorithm for high-squint SAR based on NCS operator[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(1): 16–24. doi: 10.12000/JR15035 [14] 胡静秋, 刘发林, 周崇彬, 等. 一种新的基于Omega-K算法的稀疏场景压缩感知SAR成像方法(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027HU Jingqiu, LIU Falin, ZHOU Chongbin, et al. CS-SAR imaging method based on inverse Omega-K algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027 [15] ABERMAN K and ELDAR Y C. Sub-Nyquist SAR via Fourier domain range Doppler processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6228–6244. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2723620 [16] YANG Xiaoyu, LI Gang, SUN Jinping, et al. High-resolution and wide-swath SAR imaging via Poisson disk sampling and iterative shrinkage thresholding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7): 4692–4704. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2892471 [17] ZHANG Bingchen, JIANG Chenglong, ZHANG Zhe, et al. Azimuth ambiguity suppression for SAR imaging based on group sparse reconstruction[C]. 2nd International Workshop on Compressed Sensing applied to Radar (CoSeRa 2013), Bonn, Germany, 2013. [18] WIMALAJEEWA T, ELDAR Y C, and VARSHNEY P K. Recovery of sparse matrices via matrix sketching[J]. arXiv: 1311.2448, 2013. [19] CUMMING L G, WONG F H, 洪文, 胡东辉, 译. 合成孔径雷达成像——算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007: 90–91.CUMMING L G, WONG F H, HONG Wen, HU Donghui, translation. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007: 90–91. [20] DI MARTINO G, IODICE A, RICCIO D, et al. Filtering of azimuth ambiguity in stripmap synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(9): 3967–3978. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320155 [21] DAUBECHIES I. Orthonormal bases of compactly supported wavelets[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 1988, 41(7): 909–996. doi: 10.1002/cpa.3160410705 [22] LIU Zhe, LIAO Xingxing, and WU Junjie. Image reconstruction for low-oversampled staggered SAR via HDM-FISTA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3065575. [23] GUARNIERI A M. Adaptive removal of azimuth ambiguities in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 625–633. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.842476 [24] BECK A and TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183–202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 [25] HANSEN P C and O’LEARY D P. The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete Ill-posed problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1993, 14(6): 1487–1503. doi: 10.1137/0914086 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: