-
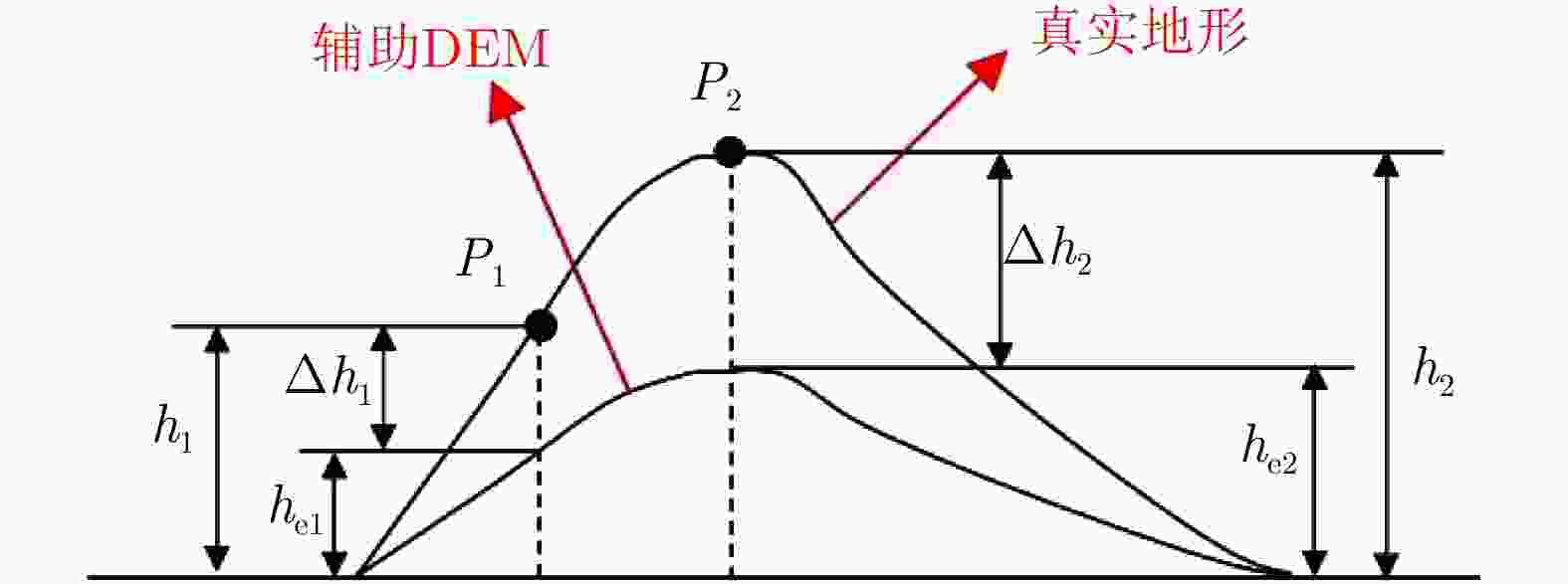
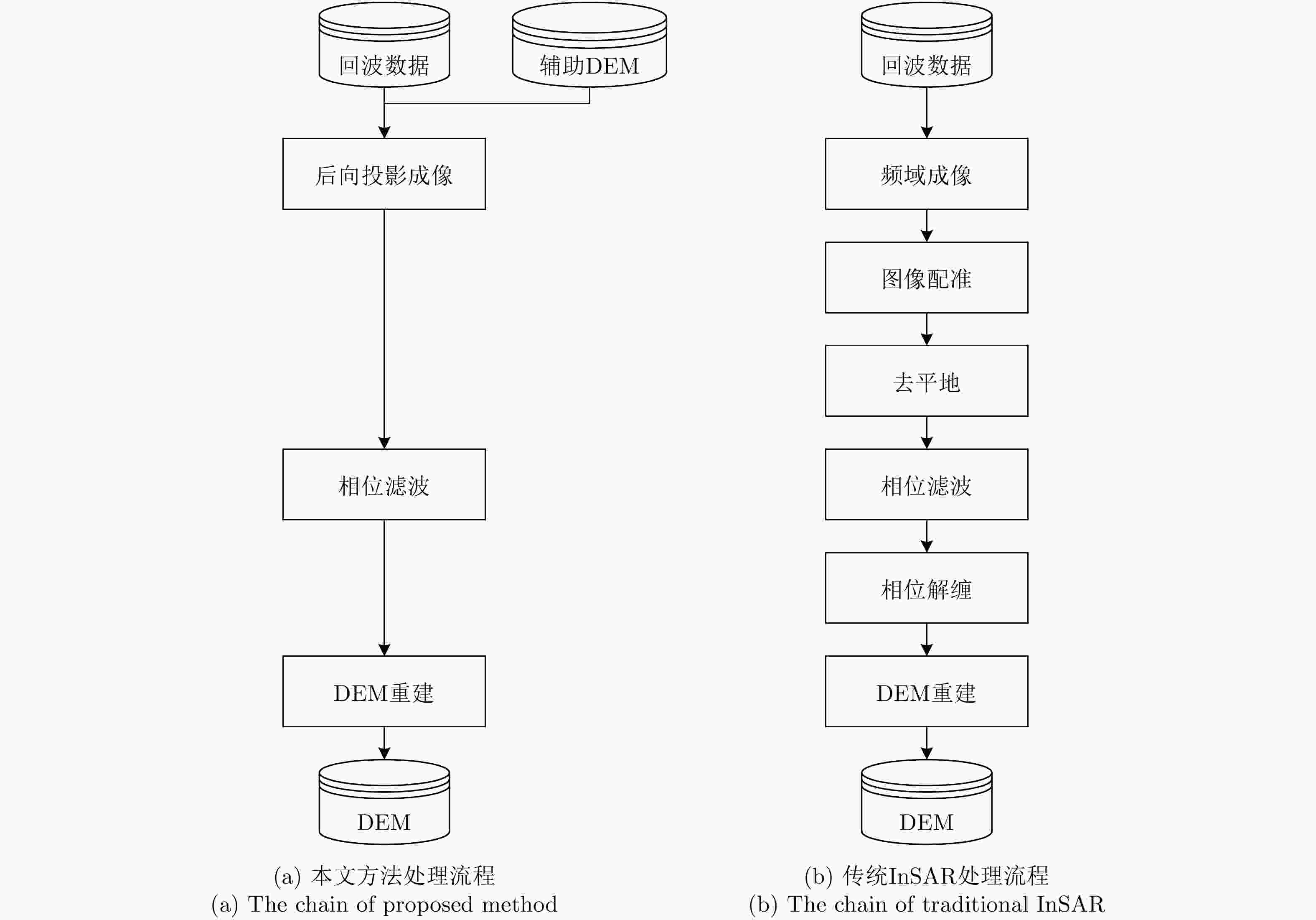
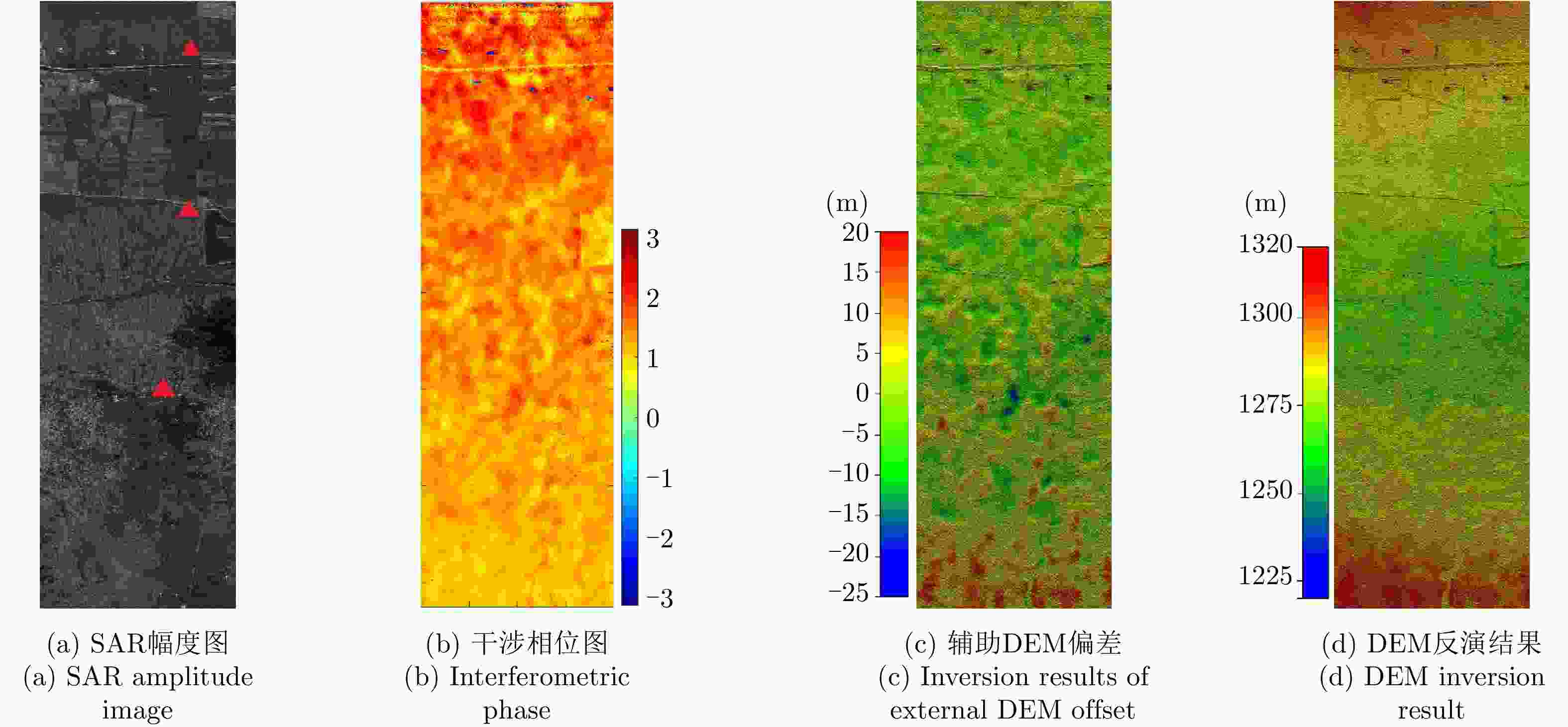
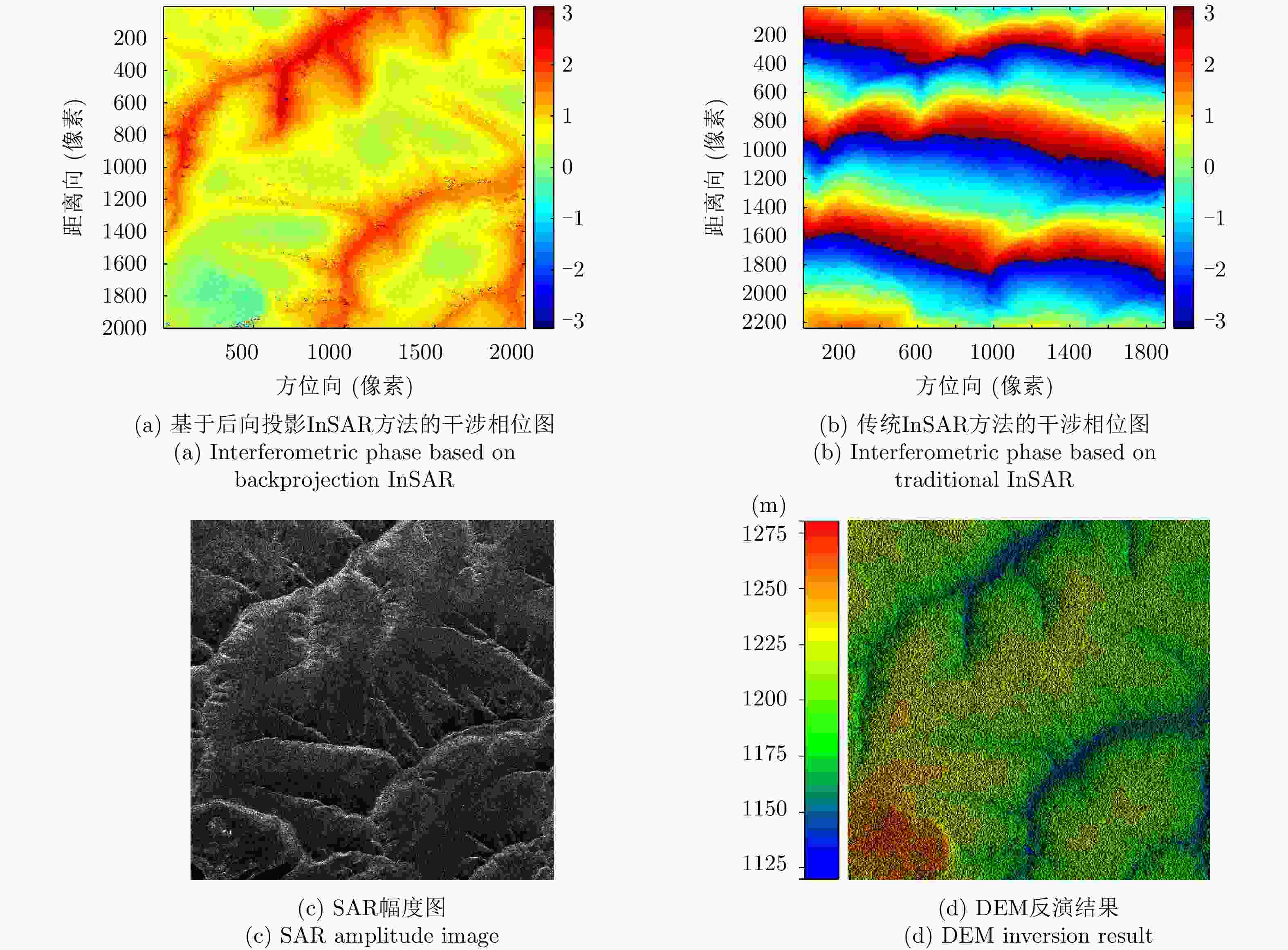
摘要: 利用干涉合成孔径雷达(InSAR)技术获取数字高程模型(DEM)时,在地形起伏剧烈区域,干涉条纹十分密集,增加了相位解缠的难度,影响相位展开和高程反演的精度。为了解决该问题,该文提出了一种基于DEM辅助后向投影模型的InSAR高程反演方法。该方法可以在统一的后向投影成像空间中实现成像和InSAR高程反演,并且引入外源DEM作为辅助信息,去除大部分地形相位,有效地降低了干涉条纹的密度,减少了干涉相位的缠绕。此外,该方法在多数情况下可以避免图像配准和相位解缠过程,简化了传统InSAR的处理流程,并且可以实现高精度的高程反演。通过仿真实验和X波段机载双天线InSAR数据的处理验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: When Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) is used to obtain the Digital Elevation Model (DEM), highly sloped terrains will make interferometric fringes dense and increase the difficulty of phase unwrapping, which will affect the accuracy of phase unwrapping and elevation inversion. To solve this problem, an InSAR elevation inversion method based on BackProjection (BP) model with an external DEM is proposed. This model achieves imaging and InSAR DEM inversion in a uniform BP geographic space and introduces an external DEM as auxiliary information. These processes, in turn, can remove most phases of the terrain and reduce the density of interferometric fringes and phase wrapping. Additionally, the proposed method can avoid the procedures of image registration and phase unwrapping in most cases, which simplifies traditional InSAR processing and achieves high processing accuracy. A simulation experiment and X-band InSAR data processing were performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Elevation inversion /
- InSAR /
- External DEM /
- BackProjection (BP) algorithm /
- SAR
-
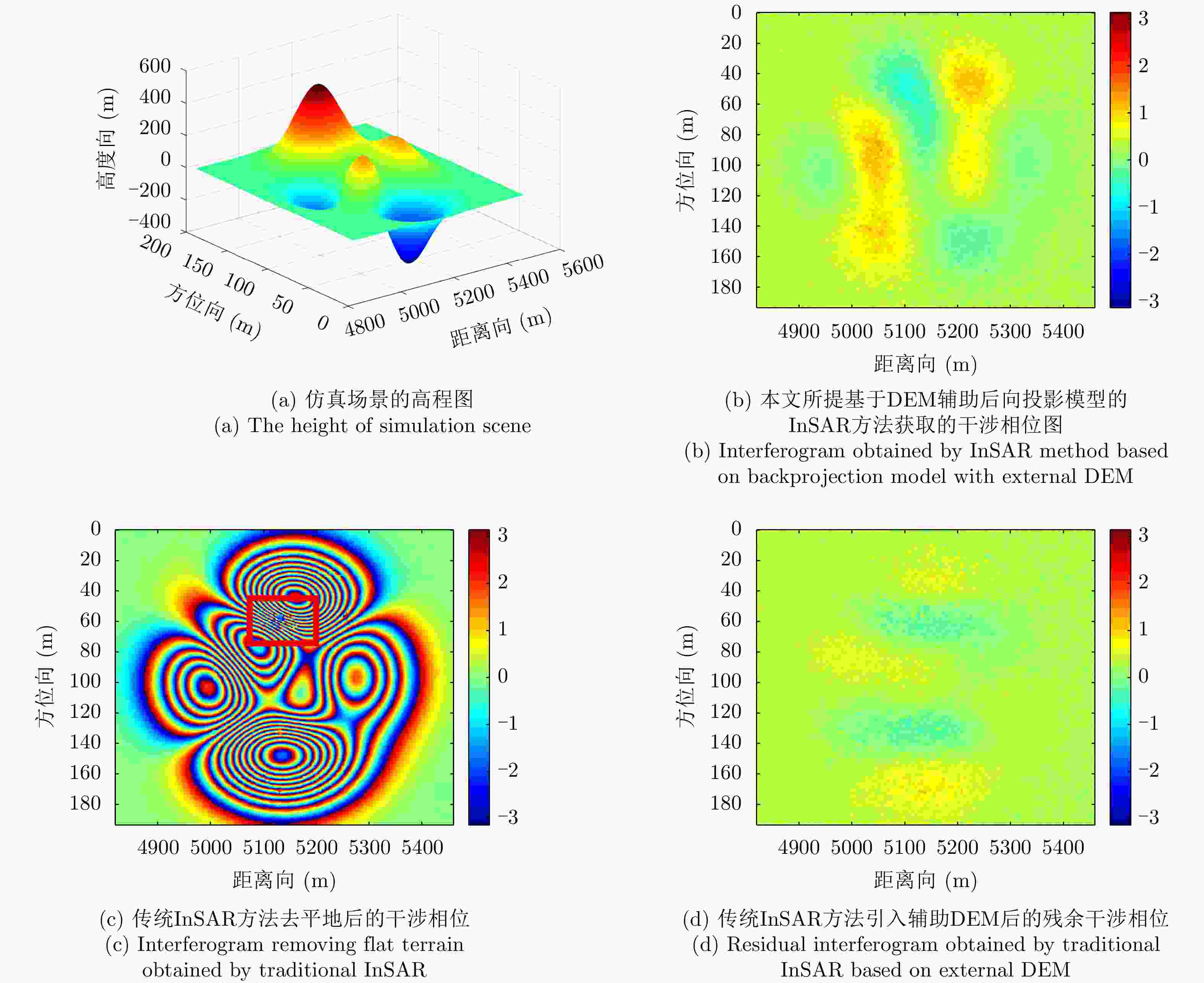
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
成像仿真参数 数值 载频(GHz) 9.6 距离向带宽(MHz) 100 距离向采样率(MHz) 120 脉冲宽度(μs) 3.7 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 300 平台平均速度(m/s) 113.5 平台平均高度(m) 3286.5 中心下视角(rad) 0.8727 基线长度(m) 2.189 基线倾角(rad) 0 表 2 X波段机载InSAR系统参数
Table 2. X-band airborne InSAR system parameters
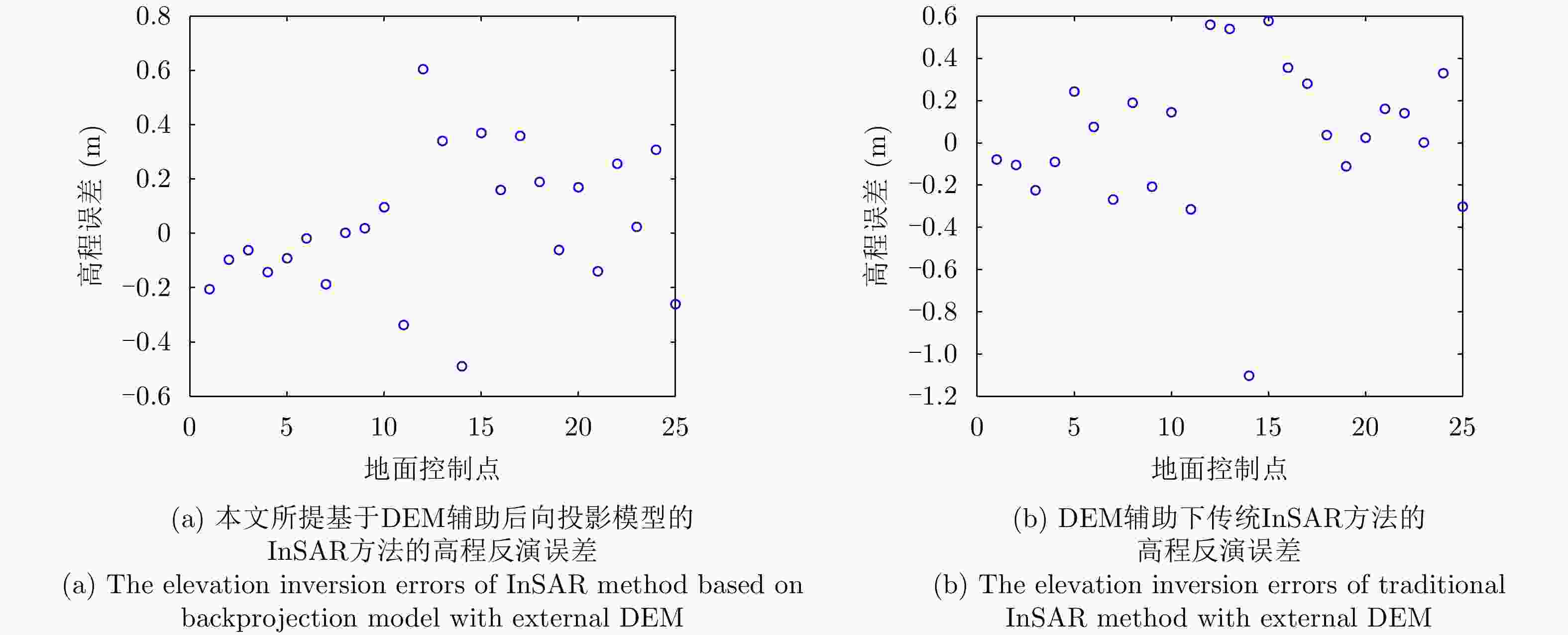
机载InSAR参数 数值 载频(GHz) 9.6 距离向带宽(MHz) 300 距离向采样率(MHz) 500 脉冲宽度(μs) 15 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1000 平台平均速度(m/s) 108 平台平均高度(m) 4874 中心下视角(rad) 0.7854 基线长度(m) 1.05 基线倾角(rad) –0.2358 表 3 地面检查点处高程反演误差
Table 3. The elevation inversion errors of ground detection points
地面检查点 本文方法(m) 传统InSAR方法(m) 1 –0.5765 –0.8017 2 –0.1310 –0.0824 3 0.7075 0.8840 标准差 0.6519 0.8459 -
[1] WECHSLER S P. Uncertainties associated with digital elevation models for hydrologic applications: A review[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2007, 11(4): 1481–1500. doi: 10.5194/hess-11-1481-2007 [2] YANG Kang, SMITH L C, CHU V W, et al. A caution on the use of surface digital elevation models to simulate supraglacial hydrology of the Greenland ice sheet[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 5212–5224. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2483483 [3] SHUKLA G, GARG R D, SRIVASTAVA H S, et al. Performance analysis of different predictive models for crop classification across an aridic to ustic area of Indian states[J]. Geocarto International, 2018, 33(3): 240–259. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2016.1240721 [4] RUFINO G, MOCCIA A, and ESPOSITO S. DEM generation by means of ERS tandem data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(6): 1905–1912. doi: 10.1109/36.729362 [5] 靳国旺, 徐青, 张红敏. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014: 169–183.JIN Guowang, XU Qing, and ZHANG Hongmin. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2014: 169–183. [6] SEYMOUR M S and CUMMING I G. InSAR terrain height estimation using low-quality sparse DEMs[C]. 3rd ERS Symposium, Florence, Italy, 1997: 421–426. [7] LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Teng, LU Lijun, et al. Reconstruction of DEMs from ERS-1/2 Tandem data in mountainous area facilitated by SRTM data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(7): 2325–2335. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.896546 [8] 刘辉, 靳国旺, 张红敏, 等. DEM辅助的山区InSAR相位解缠[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2017, 34(2): 215–220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.019LIU Hui, JIN Guowang, ZHANG Hongmin, et al. Phase unwrapping assisted by DEM of InSAR for mountainous terrain[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2017, 34(2): 215–220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2017.02.019 [9] FARR T G, ROSEN P A, CARO E, et al. The shuttle radar topography mission[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2007, 45(2): RG2004. doi: 10.1029/2005RG000183 [10] FUJISADA H, BAILEY G B, KELLY G G, et al. ASTER DEM performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(12): 2707–2714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.847924 [11] CRIPPEN R, BUCKLEY S, AGRAM P, et al. NASADEM global elevation model: Methods and progress[C]. XXIII ISPRS Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016: 125–128. doi: 10.5194/isprsarchives-XLI-B4-125-2016. [12] LIN Jianhe, LÜ Xiaolei, and LI Rui. Automatic registered back-projection approach based on object orientation for airborne repeat-track interferometric SAR[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 1066–1076. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5053 [13] DUERSCH M I. Backprojection for synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Brigham Young University, 2013. [14] 韦顺军, 师君, 张晓玲, 等. 基于曲面投影的毫米波InSAR数据成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 49–59. doi: 10.12000/JR14137WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, ZHANG Xiaoling, et al. Millimeter-wave interferometric synthetic aperture radar data imaging based on terrain surface projection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 49–59. doi: 10.12000/JR14137 [15] ZEBKER H. User-friendly InSAR products – do we need range-Doppler?[C]. 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–4. [16] 师君, 马龙, 韦顺军, 等. 基于导航数据的Ka波段InSAR成像处理与分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13142SHI Jun, MA Long, WEI Shunjun, et al. Ka-band InSAR imaging and analysis based on IMU data[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13142 [17] 潘舟浩, 李道京, 刘波, 等. 基于BP算法和时变基线的机载InSAR数据处理方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(7): 1585–1591. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00715PAN Zhouhao, LI Daojing, LIU Bo, et al. Processing of the airborne InSAR data based on the BP algorithm and the time-varying baseline[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(7): 1585–1591. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00715 [18] 韦顺军, 张晓玲, 师君, 等. 同空间后向投影InSAR成像及干涉相位提取方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2015, 36(3): 336–343. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2015.03.013WEI Shunjun, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. InSAR imaging and interferogram extraction-based the same space back-projection[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2015, 36(3): 336–343. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2015.03.013 [19] SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley. 1999. [20] 王超, 张红, 刘智. 星载合成孔径雷达干涉测量[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 33–37.WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, and LIU Zhi. Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 33–37. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: