-
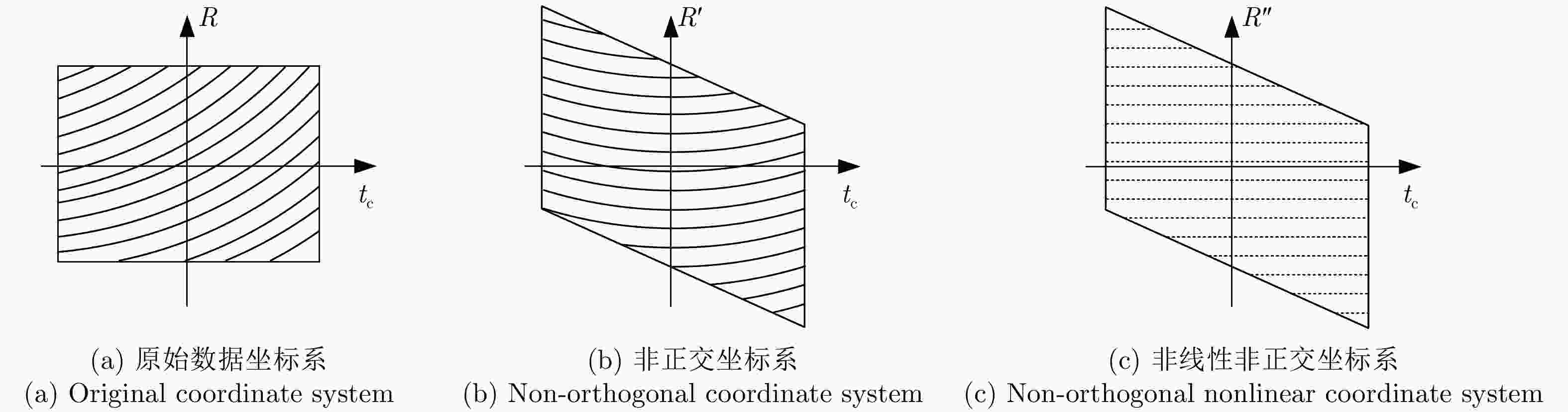
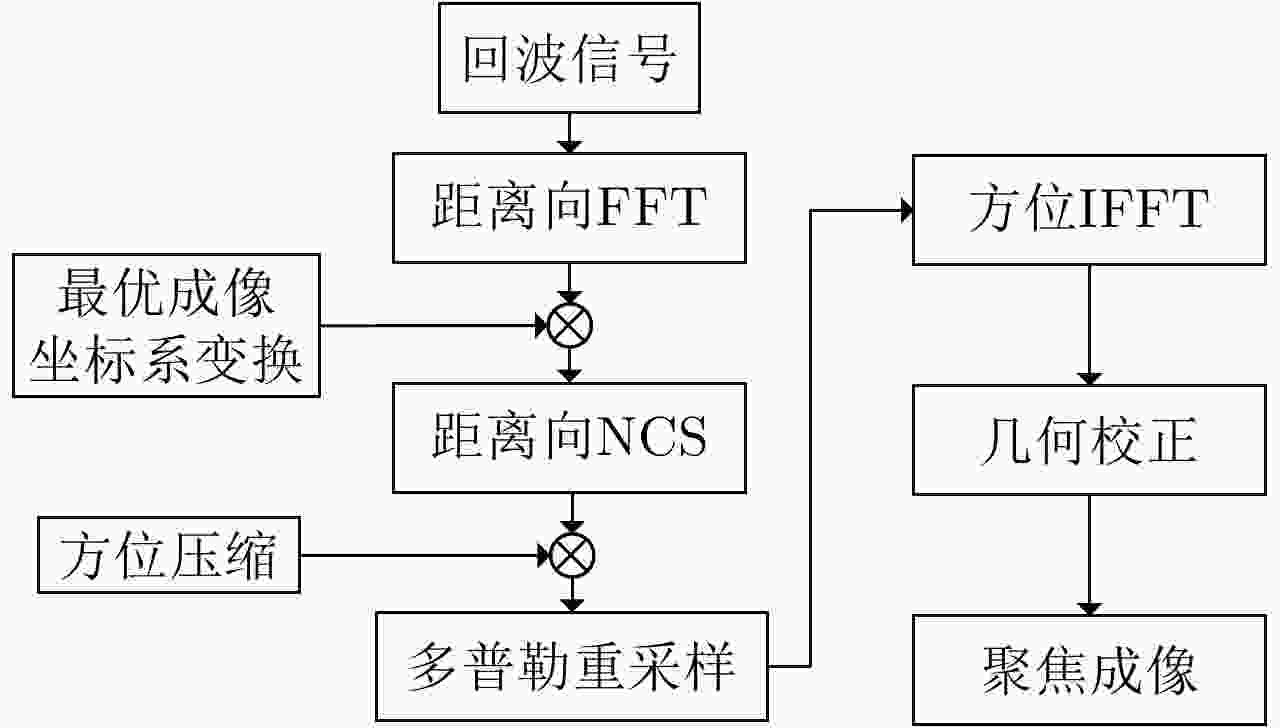
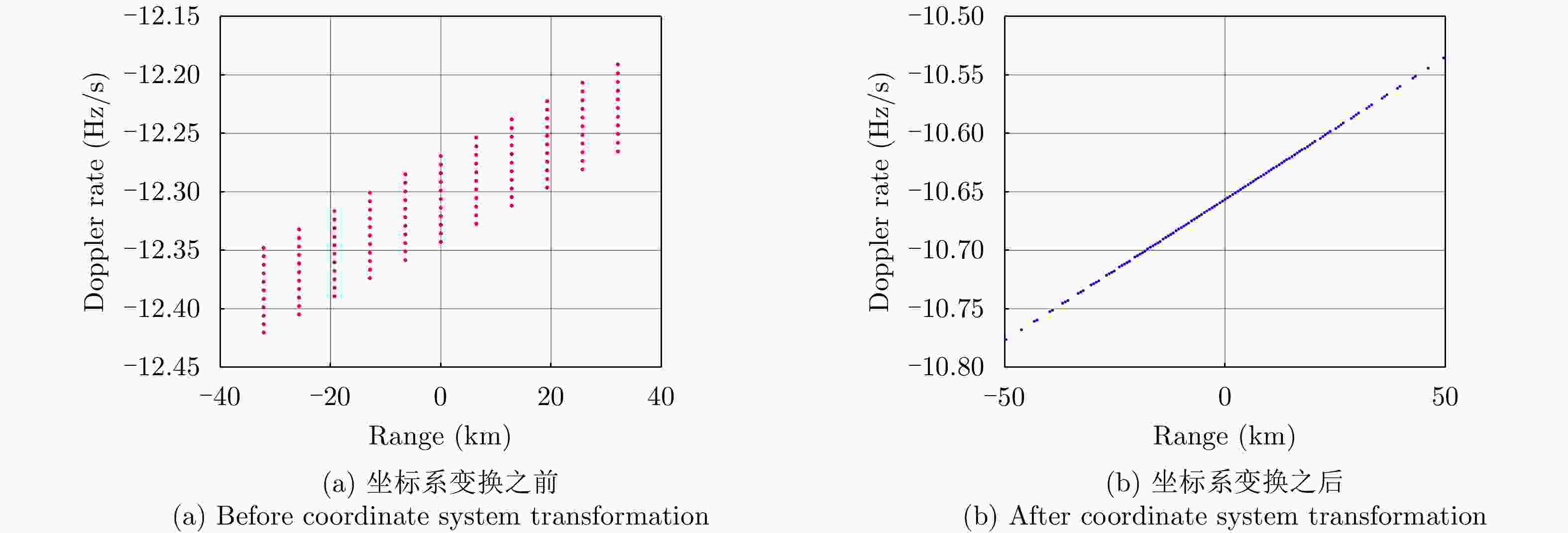
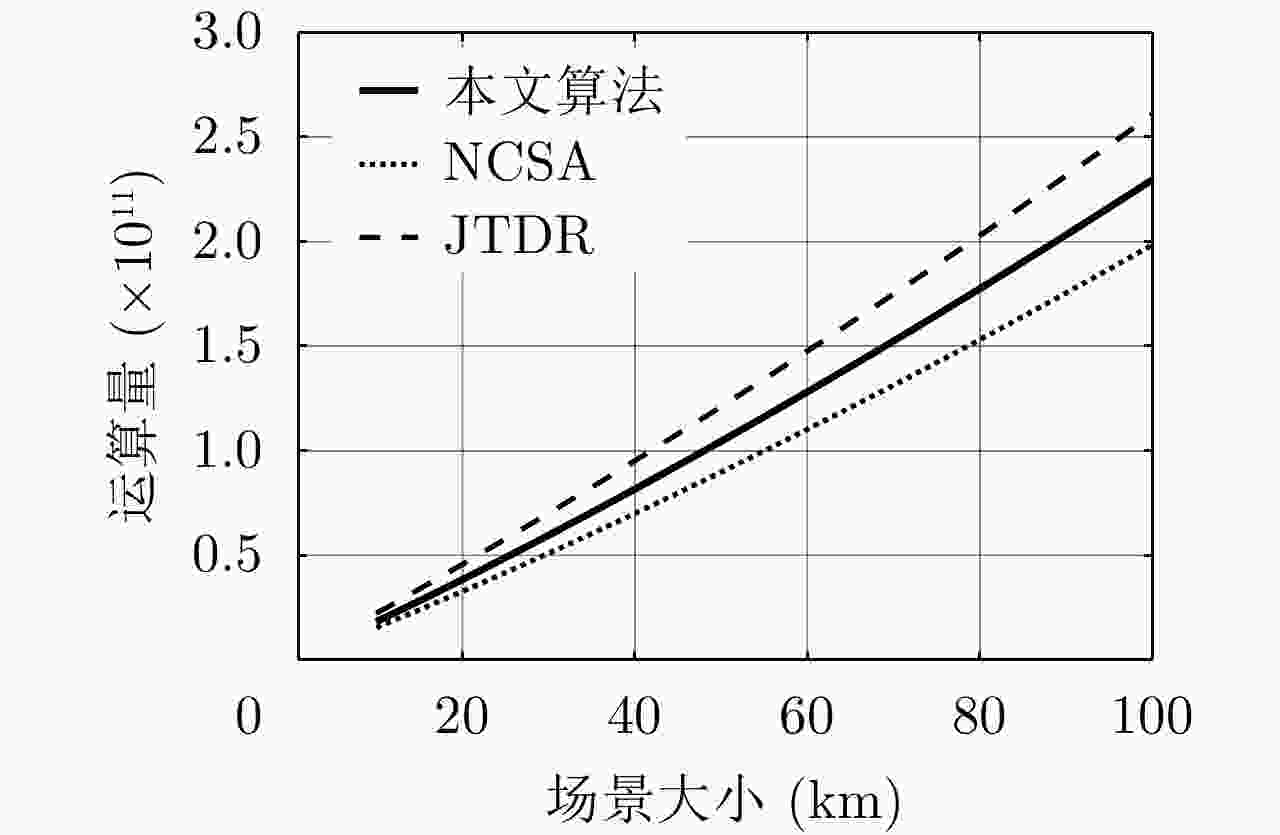
摘要: 在中轨合成孔径雷达(MEO SAR)成像中,大弯曲轨道以及长合成孔径时间会导致信号产生严重的两维空变。常规方法分别在距离和方位两个方向处理空变,计算复杂度通常比较高。该文研究了大场景中的多普勒调频率的空间分布,并提出将数据变换到一种非正交非线性成像坐标系中进行成像,使中轨SAR信号在该坐标系中满足方位平移不变性,由于不需要对方位空变做额外处理,该成像方法的运算量显著降低。最后通过多普勒线性化处理可以进一步补偿高阶多普勒参数的影响,以实现场景边缘点更精确的聚焦,并校正由非线性坐标系变换引入的方位聚焦位置偏移。最后,在条带模式下仿真2 m分辨率的数据,可以验证所提出算法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 中轨SAR /
- 两维空变 /
- 成像坐标系优化 /
- 非正交非线性成像坐标系
Abstract: In the Medium-Earth-Orbit Synthetic Aperture Radar (MEO SAR), the curved trajectory and long synthetic aperture time lead to a two-dimensional spatial variation in the signals. Traditional methods usually process the range and azimuth variations separately, and the computational complexities are high. Herein, we study the Doppler rate distribution across a large scene and propose a non-orthogonal and nonlinear coordinate system wherein the MEO SAR signals satisfy the azimuth-shift–invariant property. Thus, the efficiency of the image formation processor can be significantly improved. The higher-order Doppler parameters are addressed by the Doppler linearization. Then, more precise focusing can be achieved, and the azimuth time-shift caused by the changes in signal distribution is addressed. Finally, the processing results of simulated stripmap-mode data with a 2-m resolution are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. -
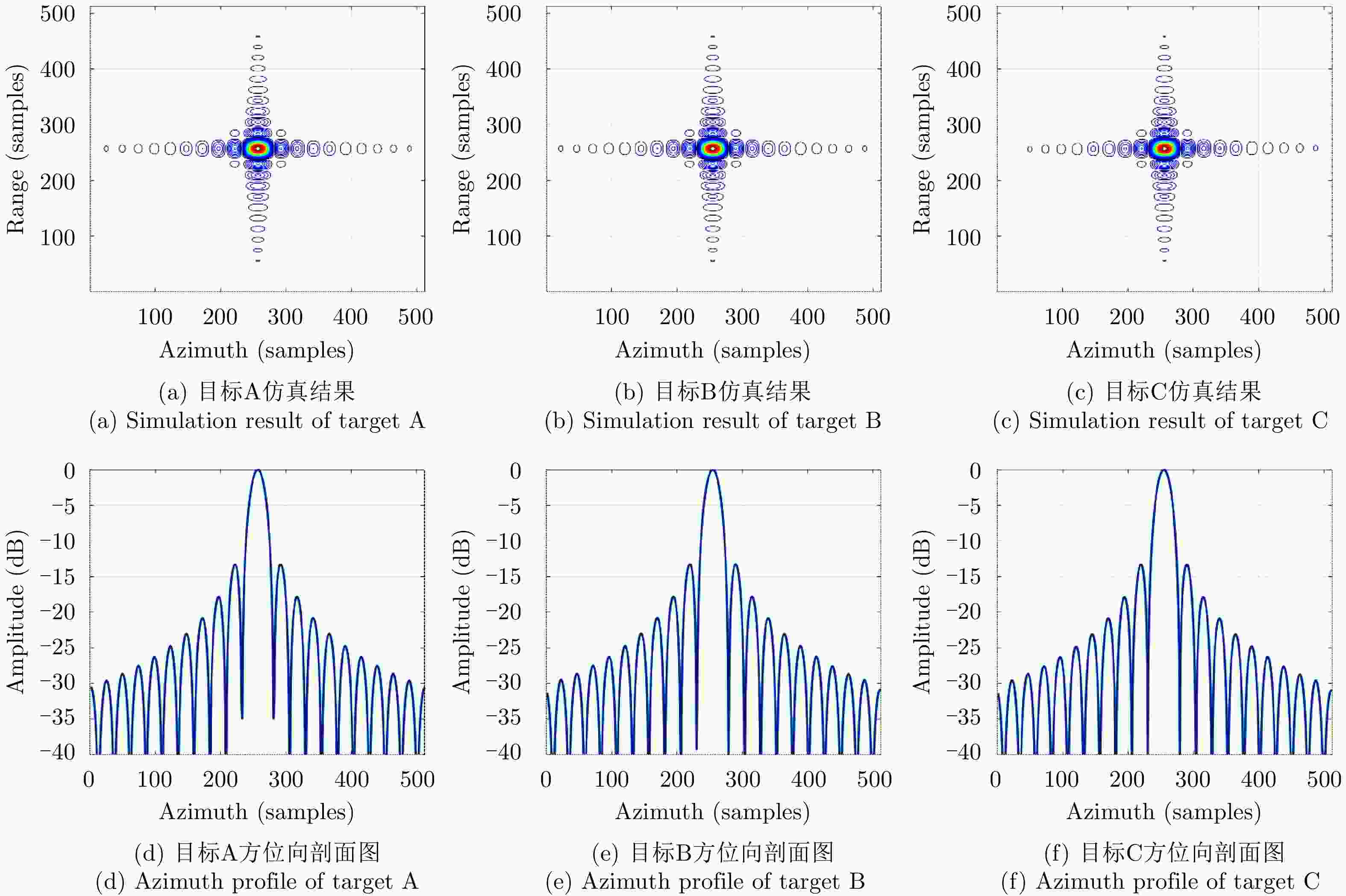
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
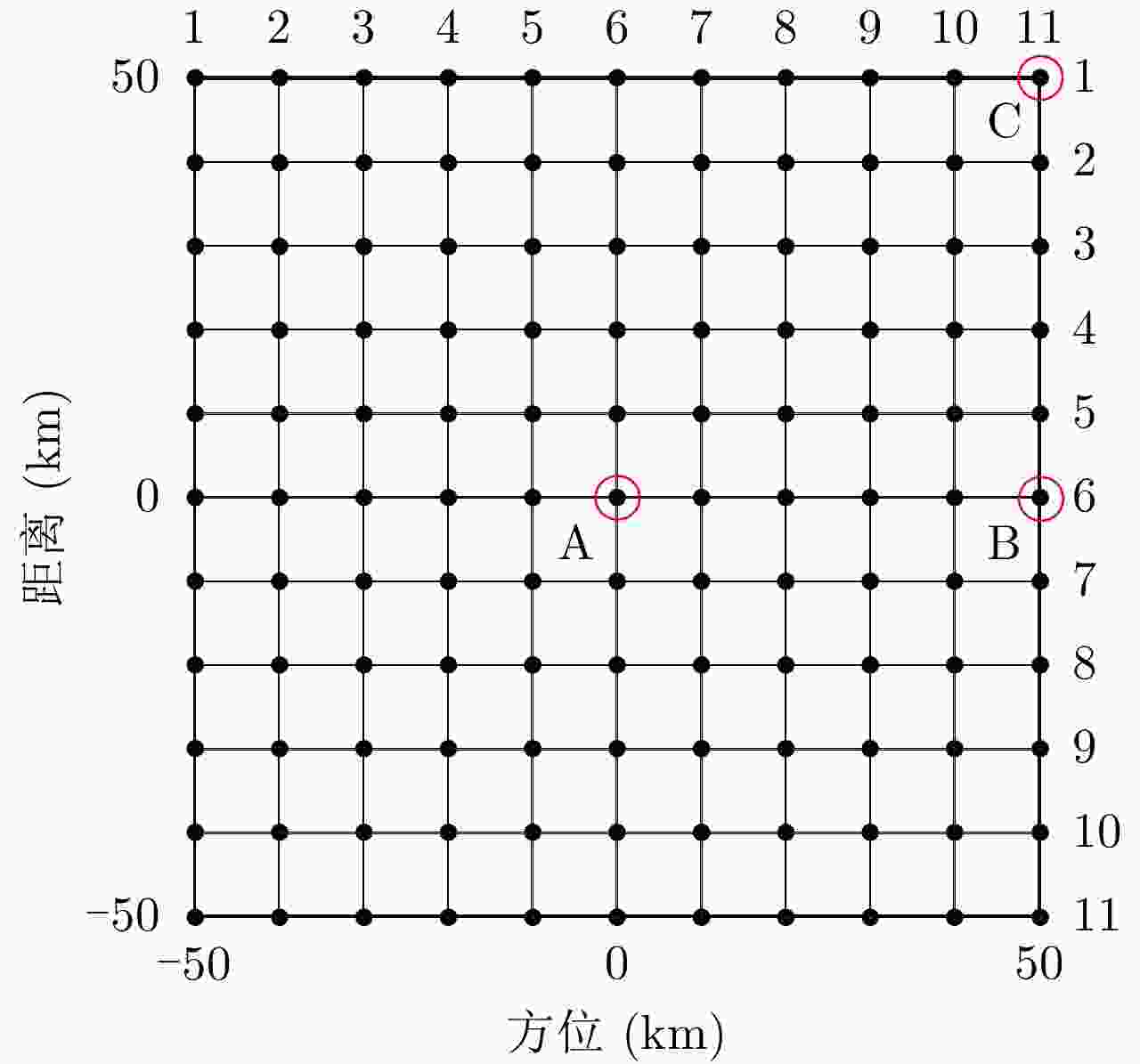
类型 名称 值 轨道参数 轨道高度(km) 13000 偏心率 0 倾角(°) 90 近地点幅角(°) 0 雷达参数 载频(GHz) 5.2 带宽(MHz) 105 PRF(Hz) 830 斜视角(°) 0 入射角(°) 40 合成孔径时间(s) 40.1 地面距离/方位分辨率(m) 2/2 场景参数 方位场景幅宽(km) 100 距离场景幅宽(km) 100 表 2 文献[21]中JTDR算法与本文所提算法仿真PSLR及ISLR数值
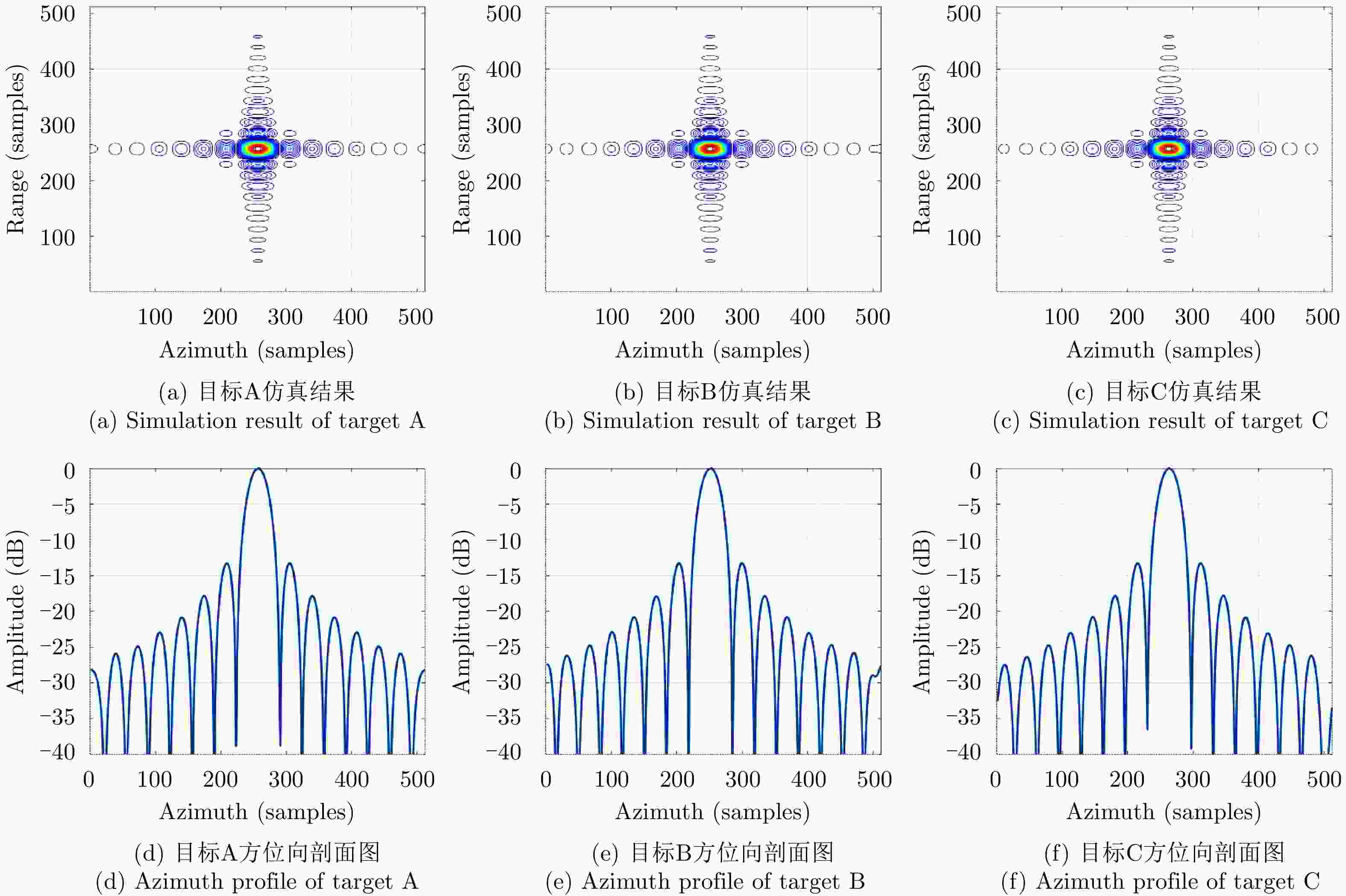
Table 2. Compare of simulated values of PSLR and ISLR using the JTDR algorithm in Ref. [21] and the proposed method
目标坐标 文献[21]中JTDR算法 本文所提算法 PSLR ISLR PSLR ISLR 方位 距离 方位 距离 方位 距离 方位 距离 A(6,6) –13.26 –13.28 –10.17 –10.06 –13.25 –13.28 –10.08 –10.02 B(6,11) –13.26 –13.29 –10.14 –10.07 –13.26 –13.28 –10.06 –10.03 C(1,11) –13.32 –13.28 –10.21 –10.06 –13.27 –13.28 –10.09 –10.02 -
[1] 李春升, 于泽, 陈杰. 高分辨率星载SAR成像与图像质量提升方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 717–731. doi: 10.12000/JR19085LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, and CHEN Jie. Overview of techniques for improving high-resolution spaceborne SAR imaging and image quality[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 717–731. doi: 10.12000/JR19085 [2] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. A 2-D space-variant chirp scaling algorithm based on the RCM equalization and subband synthesis to process geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4868–4880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2285721 [3] SUN Guangcai, JIANG Xiuwei, XING Mengdao, et al. Focus improvement of highly squinted data based on azimuth nonlinear scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2308–2322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2102040 [4] HU Bin, JIANG Yicheng, ZHANG Shunsheng, et al. Generalized omega-k algorithm for geosynchronous SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(11): 2286–2290. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2470516 [5] 李春升, 杨威, 王鹏波. 星载SAR成像处理算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071 [6] WONG F W and YEO T S. New applications of nonlinear chirp scaling in SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(5): 946–953. doi: 10.1109/36.921412 [7] RANEY R K, RUNGE H, BAMLER R, et al. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(4): 786–799. doi: 10.1109/36.298008 [8] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, LIU Yan, et al. Extended NCS based on method of series reversion for imaging of highly squinted SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 446–450. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2084562 [9] SHIN H S and LIM J T. Omega-K algorithm for spaceborne spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 343–347. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2168380 [10] SHIN H S and LIM L T. Omega-k algorithm for airborne spatial invariant bistatic spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 238–250. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002954 [11] ZHANG Tianyi, DING Zegang, TIAN Weiming, et al. A 2-D nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high squint GEO SAR imaging based on optimal azimuth polynomial compensation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(12): 5724–5735. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2765353 [12] HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Medium-earth-orbit SAR focusing using range doppler algorithm with integrated two-step azimuth perturbation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 626–630. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2353674 [13] LI Dong, LIN Huan, LIU Hongqing, et al. Focus improvement for high-resolution highly squinted SAR imaging based on 2-D spatial-variant linear and quadratic RCMs correction and azimuth-dependent Doppler equalization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(1): 168–183. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2569561 [14] LI Dexin, WU Manqing, SUN Zaoyu, et al. Modeling and processing of two-dimensional spatial-variant geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 3999–4009. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2418814 [15] 汪丙南, 向茂生. 地球同步轨道圆迹SAR三维分辨特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(3): 314–322. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20044WANG Bingnan and XIANG Maosheng. Three-dimensional resolution analysis for geosynchronous circular SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(3): 314–322. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20044 [16] CHEN Jianlai, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A TSVD-NCS algorithm in Range-Doppler domain for geosynchronous synthetic aperture Radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1631–1635. [17] TANG Shiyang, LIN Chunhui, ZHOU Yu, et al. Processing of long integration time spaceborne SAR data with curved orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 888–904. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2756109 [18] LI Zhuo, LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, et al. Back projection algorithm for high resolution GEO-SAR image formation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 336–339. [19] RAN Lei, LIU Zheng, LI Tao, et al. An adaptive fast factorized back-projection algorithm with integrated target detection technique for high-resolution and high-squint spotlight SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 171–183. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2771503 [20] ZHANG Lei, LI Haolin, QIAO Zhijun, et al. A fast BP algorithm with wavenumber spectrum fusion for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(9): 1460–1464. [21] LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. A modified CSA based on joint Time-Doppler resampling for MEO SAR stripmap mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3573–3586. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2802545 [22] HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Focusing of medium-earth-orbit SAR with advanced nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 500–508. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053211 [23] LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. Highly squinted MEO SAR focusing based on extended Omega-K algorithm and modified joint time and Doppler resampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9188–9200. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2925385 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: