Intelligent Suppression Method for Ionospheric Clutter Based on Clustering and Greedy Strategy
-
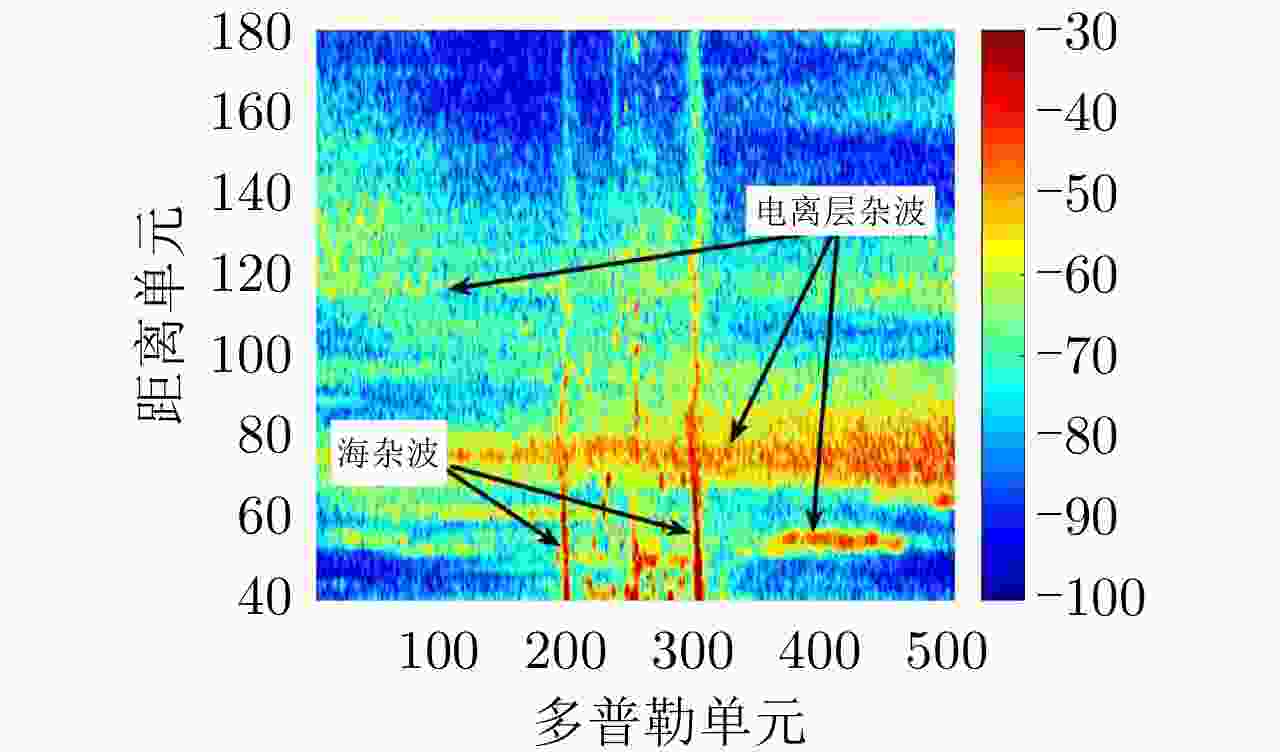
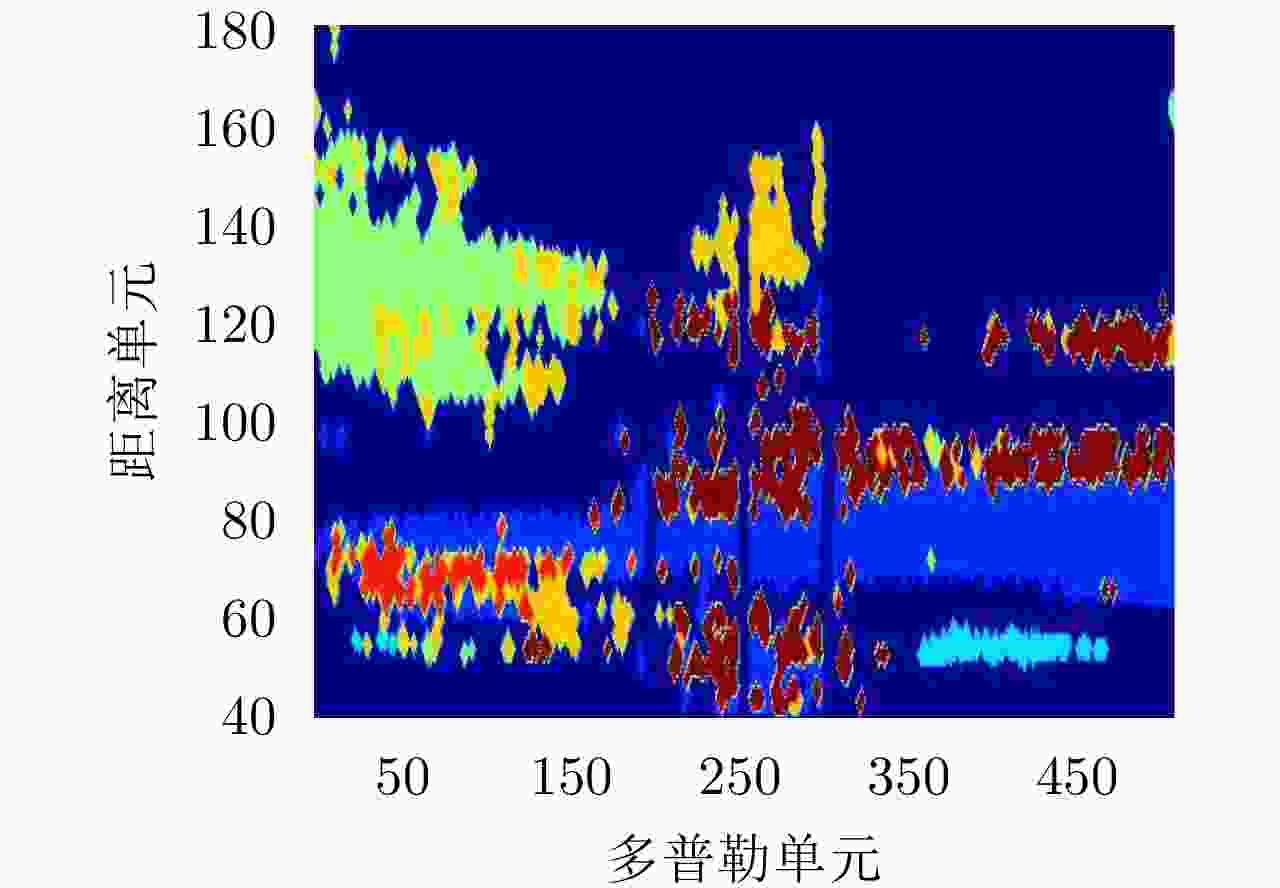
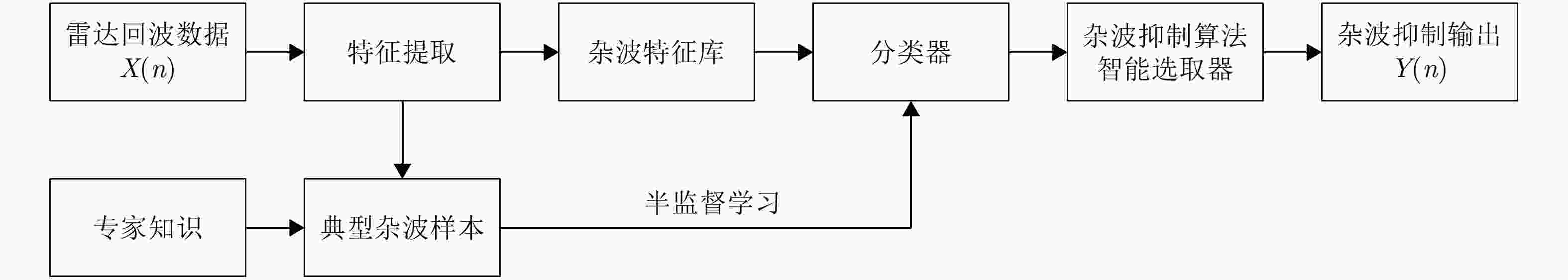
摘要: 在高频地波超视距雷达系统中,电离层杂波作为一种时变、非均匀、非高斯的复杂杂波,其抑制方法一直是困扰国内外的研究难点。针对传统杂波抑制方法对电离层杂波的处理能力单一、普适性差的问题,该文开展了杂波智能分类抑制处理方法的研究,通过对电离层杂波的成因与特性分析,提出了一种基于杂波聚类与贪婪策略的电离层杂波智能处理方法,对电离层杂波进行分类分情况处理。实验分析表明该方法对电离层杂波的抑制性能优于典型传统算法。Abstract: Clutter is a term used for unwanted echoes in electronic systems, particularly in reference to radars. Such echoes are typically returned from ground, sea, rain, animals/insects, chaff, and atmospheric turbulences, and can cause serious performance issues with radar systems. Ionospheric clutter is a time-varying, nonstationary, and non-Gaussian complex clutter in High-Frequency Surface-Wave Radar (HFSWR) system and its suppression is a daunting task. Extensive research on intelligent classification systems and suppression techniques of ionospheric clutter was conducted to solve the universal problem of single clutter suppression algorithm. After a complete analysis of the characteristics of ionospheric clutter, the present work proposes an intelligent ionospheric clutter processing method based on clustering and greedy algorithms for the classification and suppression of ionospheric clutter. Experimental results showed that the proposed method has a better performance than the traditional algorithm in suppressing ionospheric clutter.
-
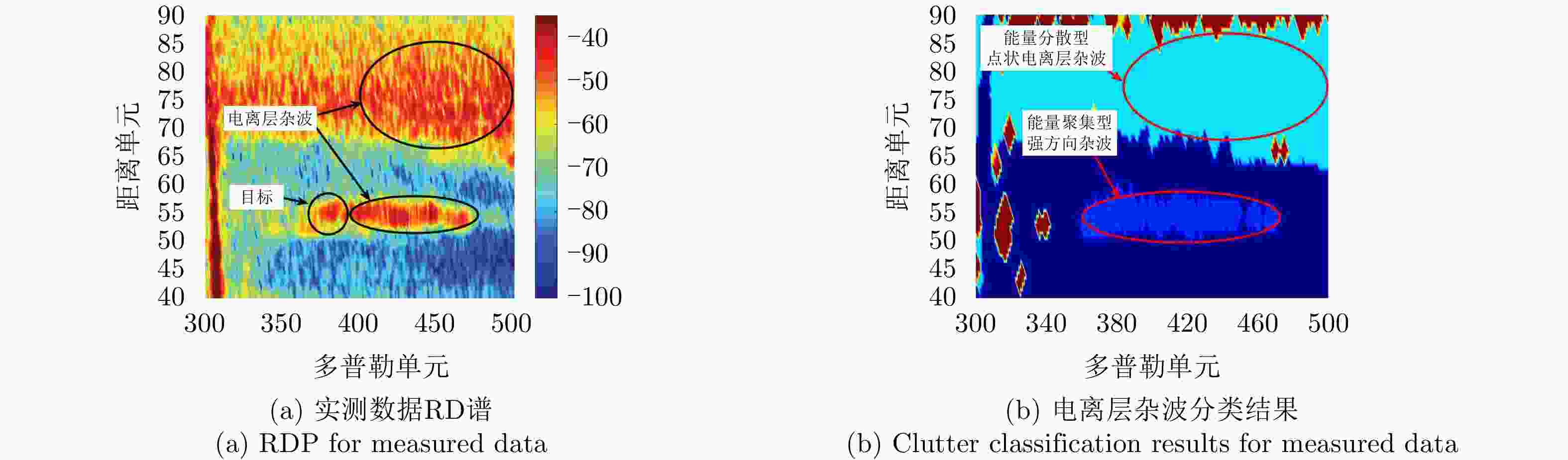
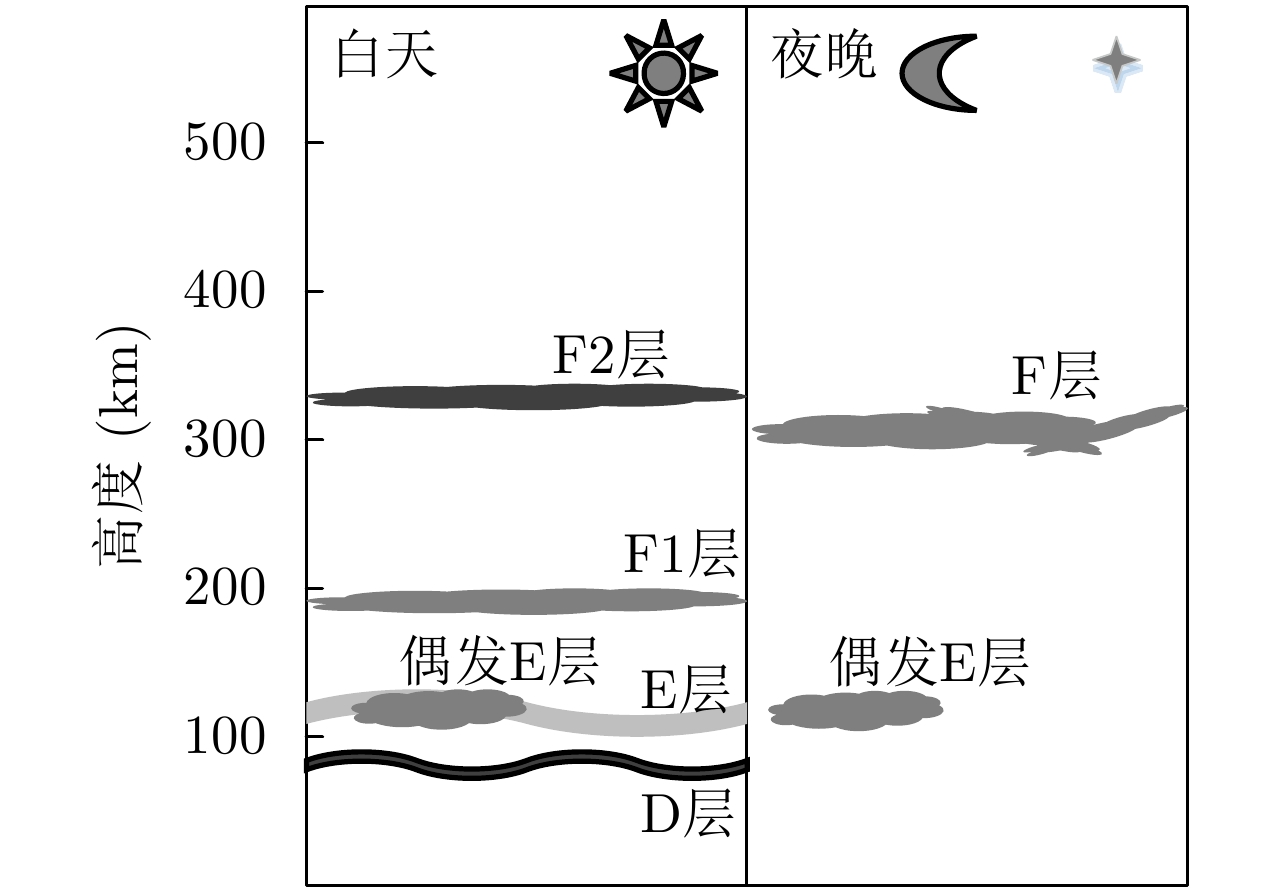
表 1 典型电离层杂波特性
Table 1. Characteristics of typical ionospheric clutter
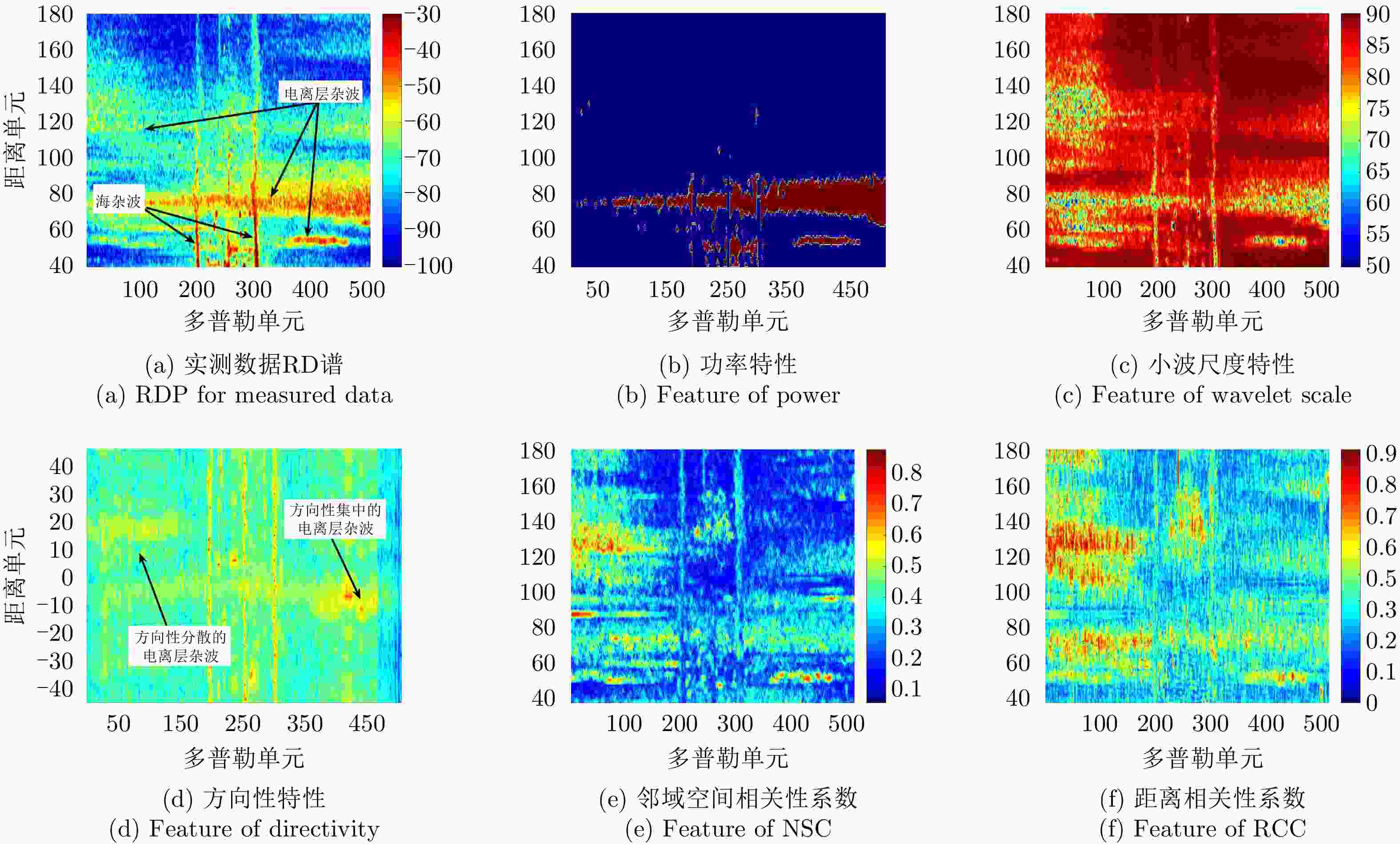
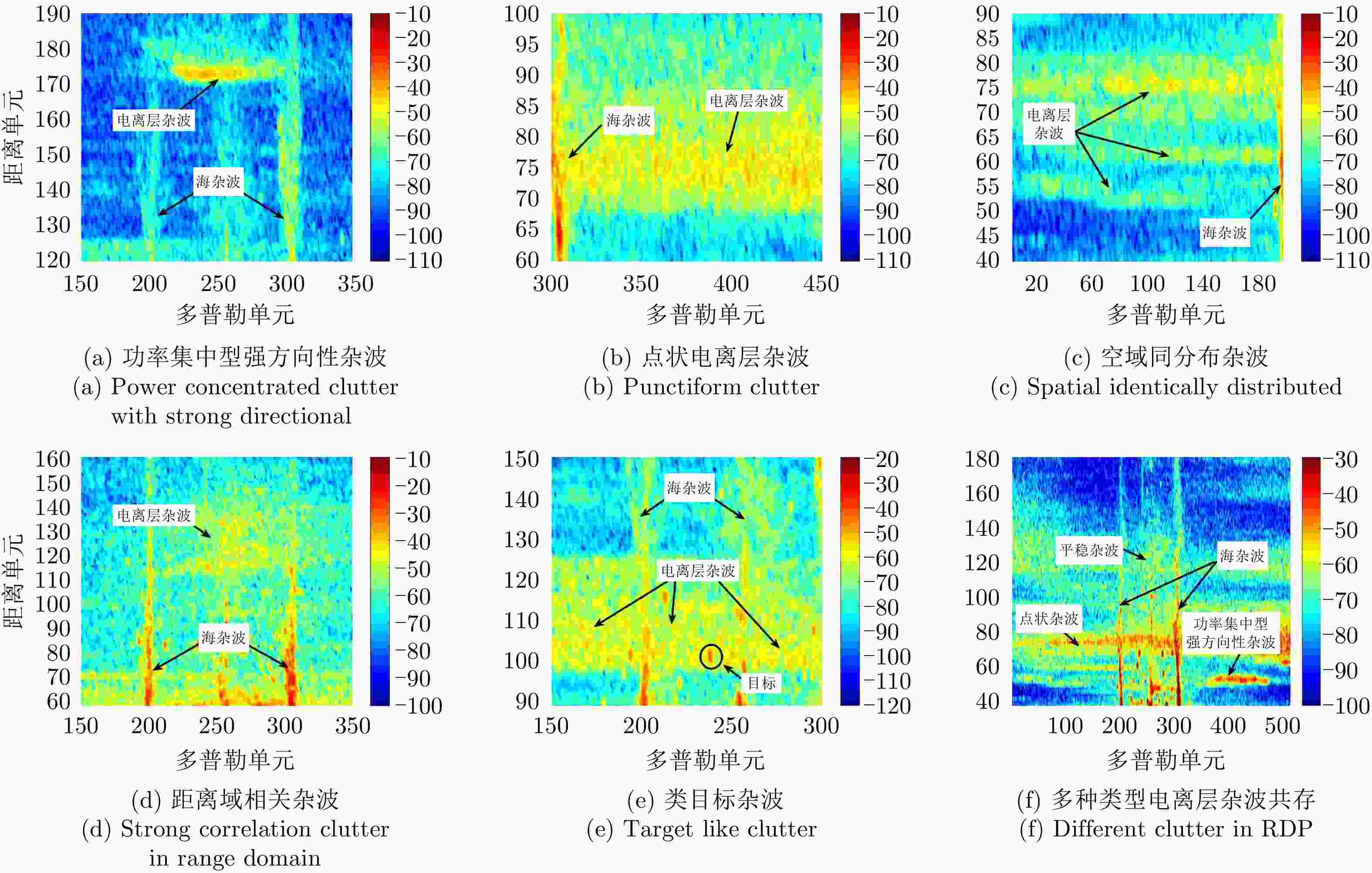
杂波类型 功率 小波尺度 方向性 空域同质性 距离域相关性 能量聚集型强方向性 聚集 与目标相异 集中 同质 相关 点状 聚集 与目标相似 分散 异质 非相关 空域同分布 分散 与目标相异 分散 同质 非相关 距离域相关 分散 与目标相异 分散 异质 相关 类目标 分散 与目标相似 集中 异质 非相关 表 2 K-means算法聚类后样本的特性统计
Table 2. Characteristic statistics after K-means algorithm clustering
类型 特性A 特性B 特性C 特性D 特性E A 0 0.26 0.21 0.29 0.25 B 0.44 0.85 0.15 0.41 1.00 C 0.29 0 0.23 1.00 1.00 D 1.00 0.02 0.88 0.04 0.03 E 1.00 0.60 0.09 0.79 0 F 0 0.64 1.00 0.81 0.22 表 3 CSKM算法聚类后样本的特性统计
Table 3. Characteristic statistics after CSKM algorithm clustering
类型 特性A 特性B 特性C 特性D 特性E A 1.00 0.07 0.90 1.00 0.86 B 0.99 1.00 0.11 0.18 0.14 C 0.15 0 0.11 1.00 0.30 D 0.09 0 0.08 0 1.00 E 0.13 1.00 1.00 0.07 0.06 F 0 0.04 0 0 0 表 4 聚类结果有效性指标
Table 4. Validity index of clustering results
算法 DBI DI K-means 0.9916 0.2500 CSKM 0.6336 0.3333 表 5 K-means算法聚类后样本的特性统计
Table 5. Characteristic statistics after K-means algorithm clustering
类型 功率聚集性 小波尺度相似性 方向集中性 空域同质性 距离域相关性 A 0.76 1.00 0.69 0.68 0.79 B 0.78 0.34 0.80 0 0 C 0 0.13 0 0.12 0.16 D 1.00 0 0 0.44 0.87 E 0.50 0 1.00 0.61 0.73 F 0 0.80 0 0.86 0.99 表 6 CSKM算法聚类后样本的特性统计
Table 6. Characteristic statistics after CSKM algorithm clustering
类型 功率聚集性 小波尺度相似性 方向集中性 空域同质性 距离域相关性 A 0.73 0 0.77 0.87 0.86 B 0.83 1.00 0.10 0.15 0.12 C 0.09 0.55 0.10 1.00 0.78 D 0.12 0 0.13 0 1.00 E 0.14 1.00 0.92 0.18 0.15 F 0.14 0.03 0 0 0.10 表 7 聚类结果有效性指标
Table 7. Validity index of clustering results
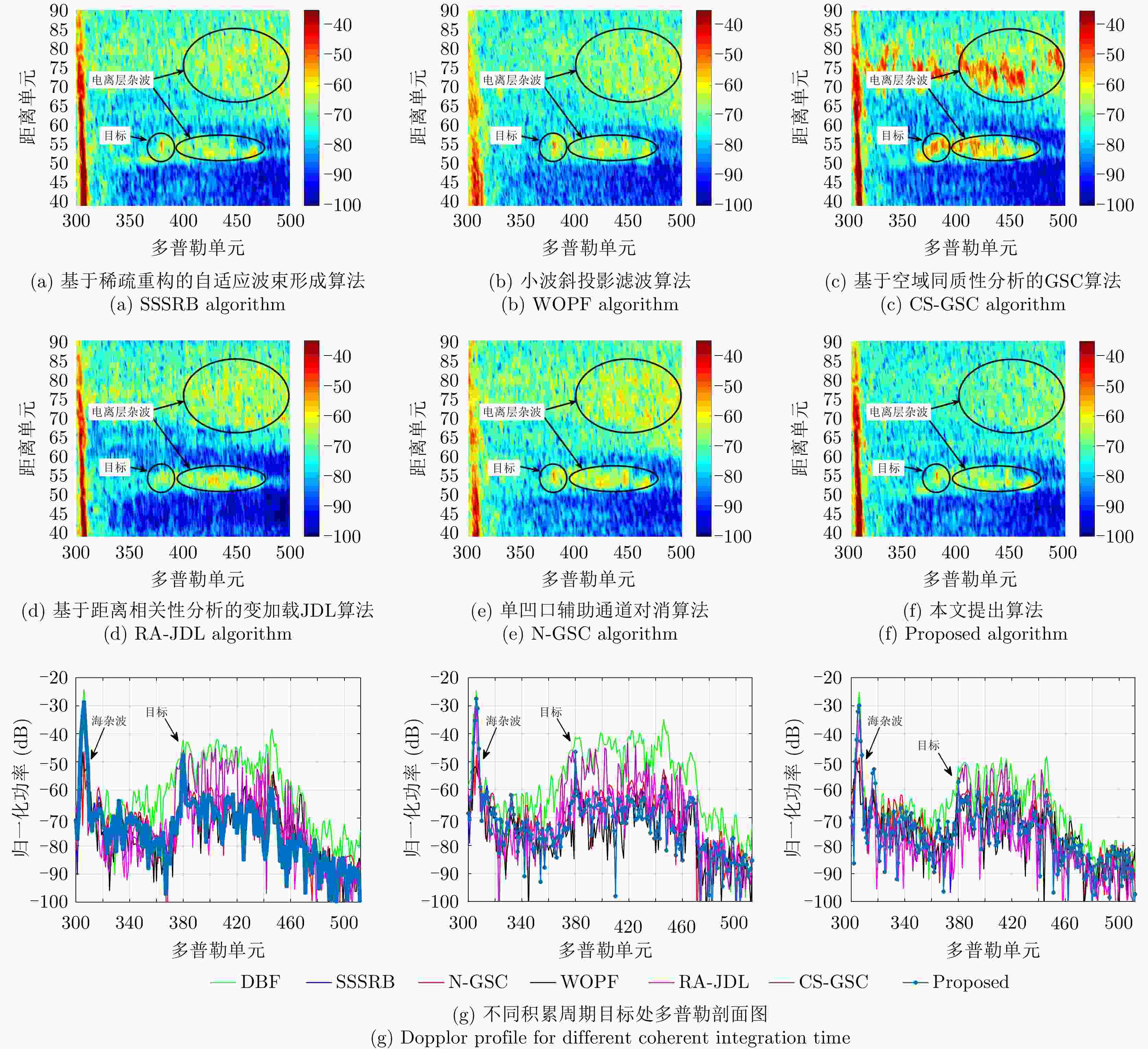
类型 DBI DI K-means 1.3976 0.2500 CSKM 0.8224 0.2500 表 8 目标在不同类型杂波处各算法处理后的信杂比
Table 8. Target SCR after different algorithms processed
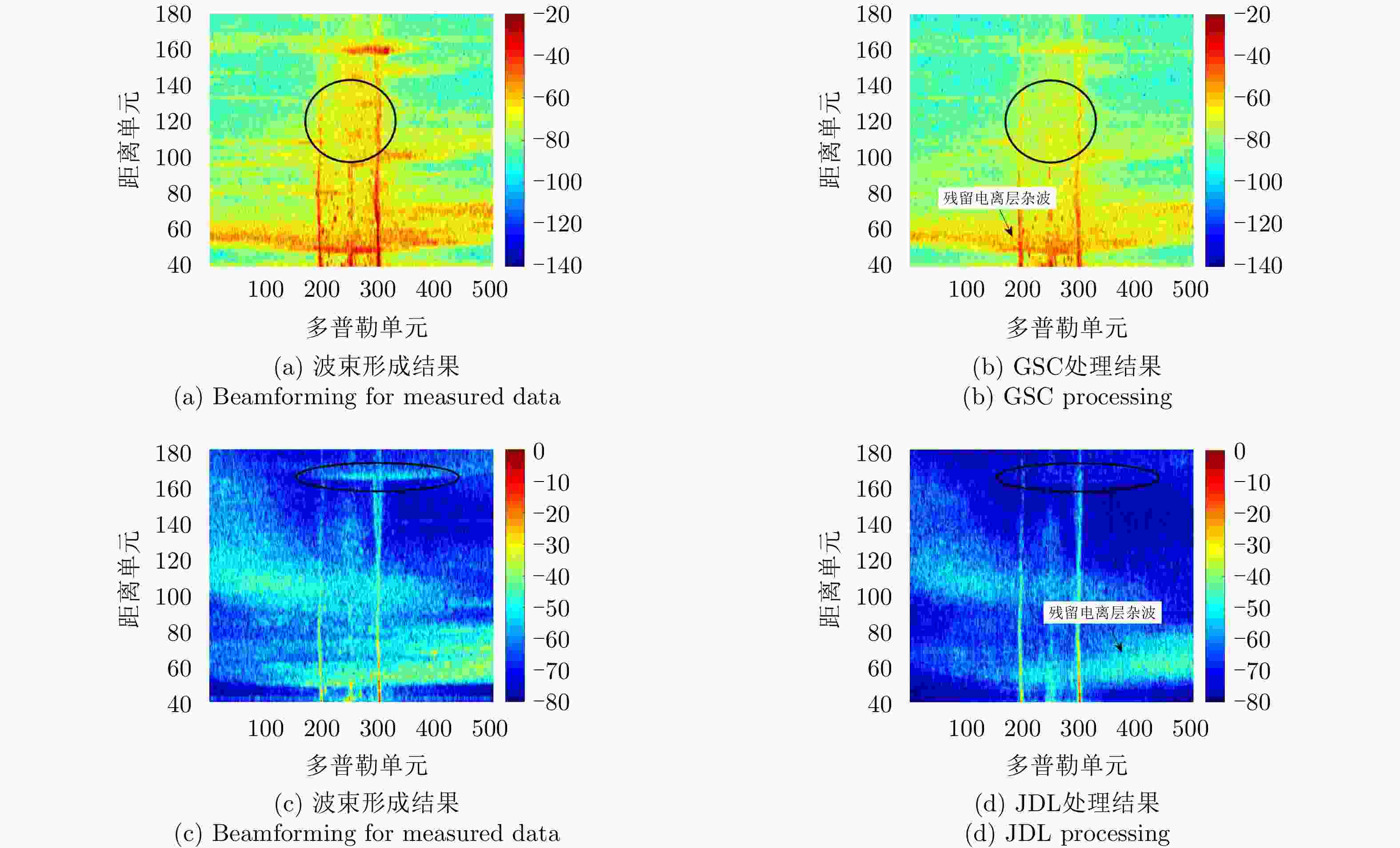
DBF SSSRB WOPF CS-GSC RA-JDL N-GSC 本文方法 类型A (dB) 5.00 18.03 14.46 5.84 3.51 14.74 18.40 类型B (dB) 5.00 16.46 19.71 4.67 13.20 15.90 19.55 类型C (dB) 5.00 10.12 9.65 16.93 7.30 9.20 16.64 类型D (dB) 5.00 7.31 1.70 10.25 14.10 6.20 14.07 类型E (dB) 5.00 15.90 13.78 12.12 12.41 17.46 18.01 平均SCR (dB) 5.00 13.56 11.86 9.96 10.10 12.70 17.33 -
[1] 王谦喆, 何召阳, 宋博文, 等. 射频隐身技术研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1505–1514. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170945WANG Qianzhe, HE Zhaoyang, SONG Bowen, et al. Overview on RF stealth technology research[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1505–1514. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170945 [2] CHAN H C and HUNG E K L. An investigation in interference suppression for HF surface wave radar[R]. DREO-TR-2000-028, 1999. [3] 康勇, 杨子杰, 田建生, 等. 高频地波超视距雷达干扰源及其抗干扰技术综述[C]. 第20届全国电磁兼容学术会议论文集, 无锡, 2010.KANG Yong, YANG Zijie, TIAN Jiansheng, et al. A survey of jamming sources and anti jamming techniques for HFSWR[C]. EMC2010, Wuxi, China, 2010. [4] 李雷. 高频雷达自适应抗干扰技术研究[D]. [博士论文]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008.LI Lei. Study on adaptive interference mitigation technique in HFSWR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin institute of technology, 2008. [5] 梁百先, 李钧, 马淑英. 我国的电离层研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 1994, 37(S1): 51–73.LIANG Baixian, LI Jun, and MA Shuying. Ionosphere research in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1994, 37(S1): 51–73. [6] 卢长建. 超视距雷达的发展现状[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2006, 29(5): 33–35, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2006.05.010LU Changjian. Development status of over-the-horizon radar[J]. Shipboard electronic countermeasure, 2006, 29(5): 33–35, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2006.05.010 [7] 杨旭光. 高频地波雷达电离层回波机理及应用研究[D]. [博士论文]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.YANG Xuguang. Research on ionospheric echo mechanism and application of HFSWR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin institute of technology, 2019. [8] 沈伟, 文必洋, 李自立, 等. 高频地波雷达的电离层杂波识别新试验[J]. 电波科学学报, 2008, 23(1): 1–5, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.01.001SHEN Wei, WEN Biyang, LI Zili, et al. Ionospheric measurement with HF ground wave radar system[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio ence, 2008, 23(1): 1–5, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2008.01.001 [9] KNIGHT M F. Ionospheric scintillation effects on global positioning system receivers[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation]. University of Adelaide, 2000: 9–10. [10] 吴敏. 高频地波雷达干扰与杂波抑制方法的研究[D]. [博士论文]. 武汉大学, 2011.WU Min. Research on interference and clutter suppression methods in HF ground wave radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Wuhan university, 2011. [11] JIANG Wei, DENG Weibo, and SHI Jialin. Characteristic study of ionospheric clutter in high-frequency over the horizon surface wave radar[C]. 2009 IEEE Youth Conference on Information, Computing and Telecommunication, Beijing, China, 2009, 154–157. doi: 10.1109/YCICT.2009.5382405. [12] RAVAN M, RIDDOLLS R J, and ADVE R S. Ionospheric and auroral clutter models for HF surface wave and over-the-horizon radar systems[J]. Radio Science, 2012, 47(3): RS3010. [13] 周浩, 文必洋, 吴世才. 高频地波雷达中电离层杂波的时频特征[J]. 电波科学学报, 2009, 24(3): 394–398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2009.03.003ZHOU Hao, WEN Biyang, and WU Shicai. Time-frequency characteristics of the ionospheric clutters in high-frequency surface wave radars[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2009, 24(3): 394–398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2009.03.003 [14] 周浩, 文必洋. 高频地波雷达中电离层ES层杂波分析及其抑制[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 39(4): 41–44.ZHOU Hao and WEN Biyang. Analysis and suppression of ionosphere Es layer clutters in high-frequency surface wave radars[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition) , 2011, 39(4): 41–44. [15] SU Yuan, WEI Yinsheng, XU Rongqing, et al. Ionospheric clutter suppression using wavelet oblique projecting filter[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017. [16] ZHOU Jianyu, LI Gaopeng, and XU Rongqing. Ionosphere clutter suppression based on sparse space spectrum rebuild beamforming[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059395. [17] ZHOU Jianyu, WEI Yinsheng, and XU Rongqing. A clutter sample selection-based generalized sidelobe canceller algorithm for ionosphere clutter suppression in HFSWR[C]. 2018 International Conference on Radar, Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8557332. [18] 张鑫. 基于多维联合的高频雷达杂波及干扰抑制方法研究[D]. [博士论文]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.ZHANG Xin. Research on clutter and interference suppression based on joint multi-dimension in HFSWR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin institute of technology, 2015. [19] 谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar:an overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073 [20] 同亚龙, 王彤, 文才, 等. 一种稳健的机载非正侧视阵雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(5): 1044–1050. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141222TONG Yalong, WANG Tong , WEN Cai, et al. A robust clutter suppression method for airborne non-sidelooking radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(5): 1044–1050. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141222 [21] 谢文冲, 王永良. 圆柱型阵机载雷达杂波抑制新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(10): 2371–2374. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00300XIE Wenchong and WANG Yongliang. New clutter suppression methods for airborne radar with cylindrical array antennas[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(10): 2371–2374. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00300 [22] 龚清勇, 朱兆达. 非正侧视阵机载雷达杂波抑制算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(4): 977–980. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01826GONG Qingyong and ZHU Zhaoda. Study on clutter suppression algorithm for airborne radar with non-sidelooking arrays[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(4): 977–980. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01826 [23] 陈洪猛, 刘京, 李明, 等. 一种新的无人机载雷达非均匀杂波抑制方法[J]. 深圳大学学报: 理工版, 2019, 36(5): 489–496.CHEN Hongmeng, LIU Jing, LI Ming, et al. A novel heterogeneous clutter suppression method for UAV airborne radar based on the CFAR strategy[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University(Science and Engineering) , 2019, 36(5): 489–496. [24] TIAN Wenlong, LI Gaopeng, and XU Rongqing. Ionospheric clutter mitigation for high-frequency surface-wave radar using two-dimensional array and beam space processing[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(3): 202–211. [25] RIDDOLLS R J and ADVE R S. Two-dimensional adaptive processing for ionospheric clutter mitigation in high frequency surface wave radar[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–4. [26] WAN X, XIONG X, CHENG F, et al. Experimental investigation of directional characteristics for ionospheric clutter in HF surface wave radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2007, 1(2): 124–130. [27] FABRIZIO G, COLONE F, LOMBARDO P, et al. Adaptive beamforming for high-frequency over-the-horizon passive radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2009, 3(4): 384–405. [28] LI Lei, XU Rongqing, and LI Gaopeng. Robust least squares method for sporadic E ionospheric clutter mitigation in high frequency surface wave radar[C]. 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006. [29] GREEN S D and KINGSLEY S P. Improving the range/time sidelobes of large bandwidth discontinuous spectra HF radar waveforms[C]. The 7th International Conference on HF Radio Systems and Techniques, Nottingham, UK, 1997: 246–250. [30] WANG Qin, YANG Zijie, WAN Xianrong, et al. Range sidelobes suppression for HF surface wave radar with discontinuous spectra[C]. The 2008 8th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Kunming, China, 2008: 645–648. [31] SELESNICK I W, PILLAI S U, and ZHENG Richeng. An iterative algorithm for the construction of notched chirp signals[C]. 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, USA, 2010: 200–203. [32] SELESNICK I W and PILLAI S U. Chirp-like transmit waveforms with multiple frequency-notches[C]. 2011 IEEE RadarCon, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 1106–1110. [33] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, PIEZZO M, et al. Radar waveform design in a spectrally crowded environment via nonconvex quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1138–1152. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120731 [34] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, HUANG Y, et al. A new radar waveform design algorithm with improved feasibility for spectral coexistence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1029–1038. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140093 [35] GERLACH K, FREY M R, STEINER M J, et al. Spectral nulling on transmit via nonlinear FM radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1507–1515. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751276 [36] LIU W X, LU Y L, and LESTURGIE M. Optimal sparse waveform design for HFSWR system[C]. 2007 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Pisa, Italy, 2007: 127–130. [37] MAO Zhineng and WEI Yinsheng. Waveform optimisation for unambiguous Doppler extension[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(2): 290–299. [38] MAO Zhineng and WEI Yinsheng. Interpulse-frequency-agile and intrapulse-phase-coded waveform optimisation for extend-range correlation sidelobe suppression[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1530–1539. [39] LEONG H and PONSFORD A. The advantage of dual-frequency operation in ship tracking by HF surface wave radar[C]. Radar 2004, International conference on Radar system, Toulouse, France, 2004: 233–237. [40] MAO Xingpeng, LIU Yongtan, DENG Weibo, et al. Sky wave interference of high-frequency surface wave radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2004, 40(15): 968–969. doi: 10.1049/el:20040594 [41] MAO Xingpeng and LIU Yongtan. Null phase-shift polarization filtering for high-frequency radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(4): 1397–1408. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4441747 [42] ADVE R S, HALE T B, and WICKS M C. Practical joint domain localised adaptive processing in homogeneous and nonhomogeneous environments. Part 1: Homogeneous environments[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2000, 147(2): 57–65. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20000035 [43] ADVE R S, HALE T B, and WICKS M C. Practical joint domain localised adaptive processing in homogeneous and nonhomogeneous environments. Part 2: Nonhomogeneous environments[J]. IEE proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2000, 147(2): 66–74. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20000085 [44] 熊新农, 万显荣, 柯亨玉, 等. 基于时频分析的高频地波雷达电离层杂波抑制[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(8): 1399–1402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.08.003XIONG Xinnong, WAN Xianrong, KE Hengyu, et al. Ionospheric clutter suppression in high frequency surface wave radar based on time-frequency analysis[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(8): 1399–1402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.08.003 [45] SU Yuan, WEI Yinsheng, and XU Rongqing. A novel ionospheric clutter mitigation method through time-frequency image processing based on ridgelet analysis[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059589. [46] HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335 [47] THAYAPARAN T and MACDOUGALL J. The role of ionospheric clutter in mid-latitude and arctic regions for assessment of HFSWR surveillance[R]. 2004. [48] 田文龙. 基于二维阵的高频地波雷达电离层杂波抑制[D]. [博士论文]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012.TIAN Wenlong. Ionospheric clutter mitigation for high frequency surface wave radar based on two-dimensional array[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin institute of technology, 2012. [49] 李迎春, 高红卫, 余继周. 智能雷达发展研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(11): 1–5.LI Yingchun, GAO Hongwei, and YU Jizhou. A study on development of intelligent radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(11): 1–5. [50] 姚迪, 张鑫, 杨强, 等. 基于空间多波束的高频地波雷达电离层杂波抑制算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2827–2833. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170477YAO Di, ZHANG Xin, YANG Qiang, et al. Ionospheric clutter suppression algorithm based on space multibeam for high frequency surface wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2827–2833. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170477 [51] KLEMM R. Applications of Space-Time Adaptive Processing[M]. London: Institution of Electrical Engineers, 2004. [52] 黄坚, 钟志峰. 高频地波雷达电离层杂波抑制研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2011, 36(2): 248–251.HUANG Jian and ZHONG Zhifeng. Ionospheric clutter suppression in high frequency ground wave rader[J]. Geomatics &Information ence of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(2): 248–251. [53] HAYKIN S and DENG C. Classification of radar clutter using neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1991, 2(6): 589–600. doi: 10.1109/72.97936 [54] HAYKIN S, KESLER S, and CURRIE B. An experimental classification of radar clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1979, 67(2): 332–333. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1979.11246 [55] STEHWIEN W and HAYKIN S. A statistical radar clutter classifier[C]. IEEE National Radar Conference, Dallas, USA, 1989: 164–169. [56] DARZIKOLAEI M A, EBRAHIMZADE A, and GHOLAMI E. Classification of radar clutters with artificial neural network[C]. The 2015 2nd International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation, Tehran, Iran, 2016. [57] FANG Xueli, LIANG Diannong, ZOU Kun, et al. A new method of radar clutter recognition based on multi-α truncation set[C]. IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Intelligent Systems and Signal Processing, Changsha, China, 2003: 858–862. [58] MA Xiaoyan, FANG Xueli, ZHANG Ronghua, et al. An approach of radar clutter recognition based on higher-order statistics combination[C]. The 2000 5th International Conference on Signal Processing Proceedings. 16th World Computer Congress 2000, Beijing, China, 2000: 1933–1937. [59] 李旭涛, 王首勇, 金连文. 应用Alpha稳定分布对雷达杂波的辨识[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(9): 2042–2045. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00853LI Xutao, WANG Shouyong, and JIN Linwen. Radar clutter recognition using alpha stable distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2008, 30(9): 2042–2045. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00853 [60] LI Yang, HE Mengke, and ZHANG Ning. An ionospheric clutter recognition method based on machine learning[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, USA, 2017: 1637–1638. doi: 10.1109/APUSNCURSINRSM.2017.8072861. [61] CHAN H C. Characterization of ionospheric clutter in HF surface-wave radar[R]. TR 2003–114, 2003. [62] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 197–198.ZHOU Zhihua. Machine Learning[M], Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 197–198. [63] LI Chaoqun, JIANG Liangxiao, LI Hongwei, et al. Attribute weighted value difference metric[C]. The 2013 IEEE 25th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Herndon, UK, 2013: 575–580. doi: 10.1109/ICTAI.2013.91. [64] DAVIES D L and BOULDIN D W. A cluster separation measure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1979, PAMI-1(2): 224–227. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1979.4766909 [65] DUNN J C. A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters[J]. Journal of Cybernetics, 1973, 3(3): 32–57. doi: 10.1080/01969727308546046 [66] 汪浩, 王峰. 强化学习算法在雷达智能抗干扰中的应用[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(3): 40–44, 48.WANG Hao and WANG Feng. Application of reinforcement learning algorithms in anti-jamming of Intelligent radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(3): 40–44, 48. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: