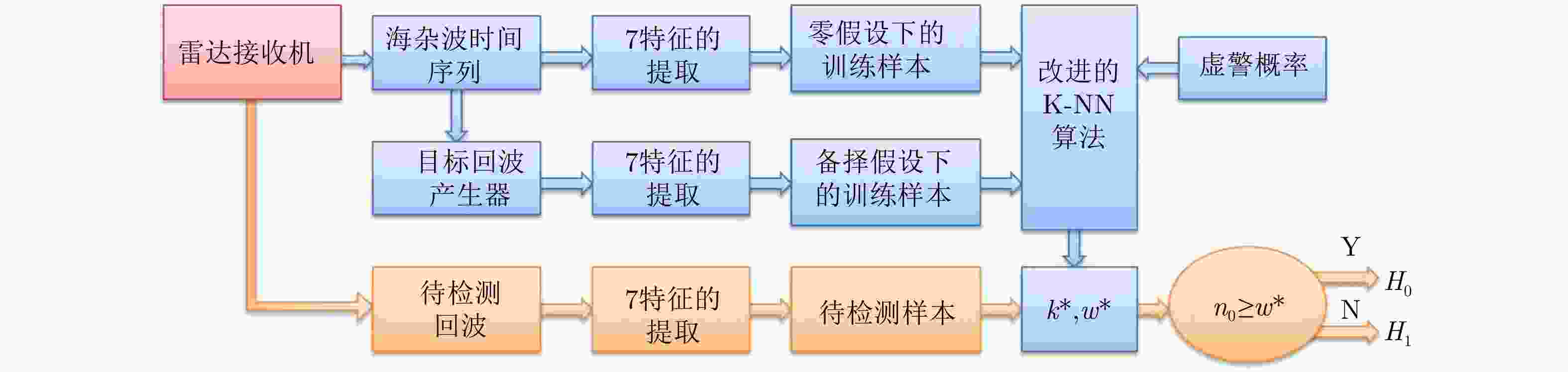
Sea-surface Small Target Detection Based on K-NN with Controlled False Alarm Rate in Sea Clutter
-
摘要: 由于高分辨海杂波具有复杂的特性以及海面小目标具有多样性,没有精确的简单统计模型可以较好地描述海杂波和目标回波时间序列,这导致目标检测遇到了很多阻碍。为了区分海杂波和目标回波,分别提取它们的特征将检测问题转化为特征空间中的分类问题是一种有效的方法。基于特征的检测可以归结为在特征空间中的一种2元假设检验问题,但是其有两个问题需要解决:一是目标回波数据远少于杂波数据;二是虚警概率不可控。为了解决第1个问题,一种典型小目标的仿真回波产生器被用于产生充足的典型目标回波数据,以辅佐后续检测器的设计。K近邻(K-NN)是一种简单有效的分类方法,但是因为无法精确地控制虚警率而不能直接在目标检测中使用。该文提出一种基于改进K-NN的海面小目标检测方法,可以很好地实现可控虚警。经IPIX雷达数据集验证,所提出的方法在观测时间分别为0.512 s和1.024 s时获得了85.1%和89.2%的检测概率,相比现有的检测器获得了7%和5%的提升,具有良好的检测效果和稳定性。Abstract: Owing to the complicated characteristics of high-resolution sea clutter and the diversity of sea-surface small targets, there is no precise parameter model to describe sea clutter and returns with targets. As a result, target detection faces many obstacles. To distinguish sea clutter and target returns, it is effective to extract their features to transform the detection problem into a classification problem in feature space. Feature-based detection is a binary hypothesis test in the feature space that encounters two intrinsic difficulties: one difficulty is insufficient target returns versus sufficient sea clutter; the other difficulty is an uncontrolled false alarm rate in detection. To solve the first difficulty, a generator of typical targets returns that can generate sufficient simulated targets returns is used to balance the number of samples between two classes and assist to design the detector. K Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) is the type of classification method that is simple and effective; however, it cannot be used to detect small targets directly because of the uncontrolled false alarm rate. This paper proposes a modified K-NN method with a controlled false alarm rate for detecting small targets. Experimental results on the IPIX radar database indicate that the proposed detector attains 85.1% and 89.2% rates of target detection for the observation time of 0.512 s and 1.024 s, respectively, compared with other existing feature-based detectors, the proposed detector exhibits 7% and 5% improvement, respectively. Thus, the proposed detector exhibits more stable and effective detection performance than other existing feature-based detectors.
-
序号 数据 WS(km/h) SWHs(m) Angle (degree) 目标单元 影响单元 1 19931107_135603_starea17 9 2.2 9 9 8,10,11 2 19931108_220902_starea26 9 1.1 97 7 6,8 3 19931109_191449_starea30 19 0.9 98 7 6,8 4 19931109_202217_starea31 19 0.9 98 7 6,8,9 5 19931110_001635_starea40 9 1.0 88 7 5,6,8 6 19931111_163625_starea54 20 0.7 8 8 7,9,10 7 19931118_023604_stareC0000280 10 1.6 130 8 7,9,10 8 19931118_162155_stareC0000310 33 0.9 30 7 6,8,9 9 19931118_162658_stareC0000311 33 0.9 40 7 6,8,9 10 19931118_174259_stareC0000320 28 0.9 30 7 6,8,9 11 19980204_202225_ANTSTEP – – 165 24 23,25,26 12 19980204_202525_ANTSTEP – – 180 7 6,8,9 13 19980204_163113_ANTSTEP – – 165 24 23,25,26 14 19980205_171437_ANTSTEP – – 180 7 6,8,9 15 19980205_180558_ANTSTEP – – 180 7 6,8,9 16 19980212_195704_ANTSTEP – – 180 7 6,8,9 17 19980223_164055_ANTSTEP – – 165 31 30,32,33 18 19980223_173317_ANTSTEP – – 165 32 31,33,34 19 19980223_173950_ANTSTEP – – 165 29 28,30–34 20 19980304_184537_ANTSTEP – – – 21 20,22 表 2 IPIX数据集上多种检测器的平均检测概率
Table 2. The average detection probabilities of detectors on IPIX radar database
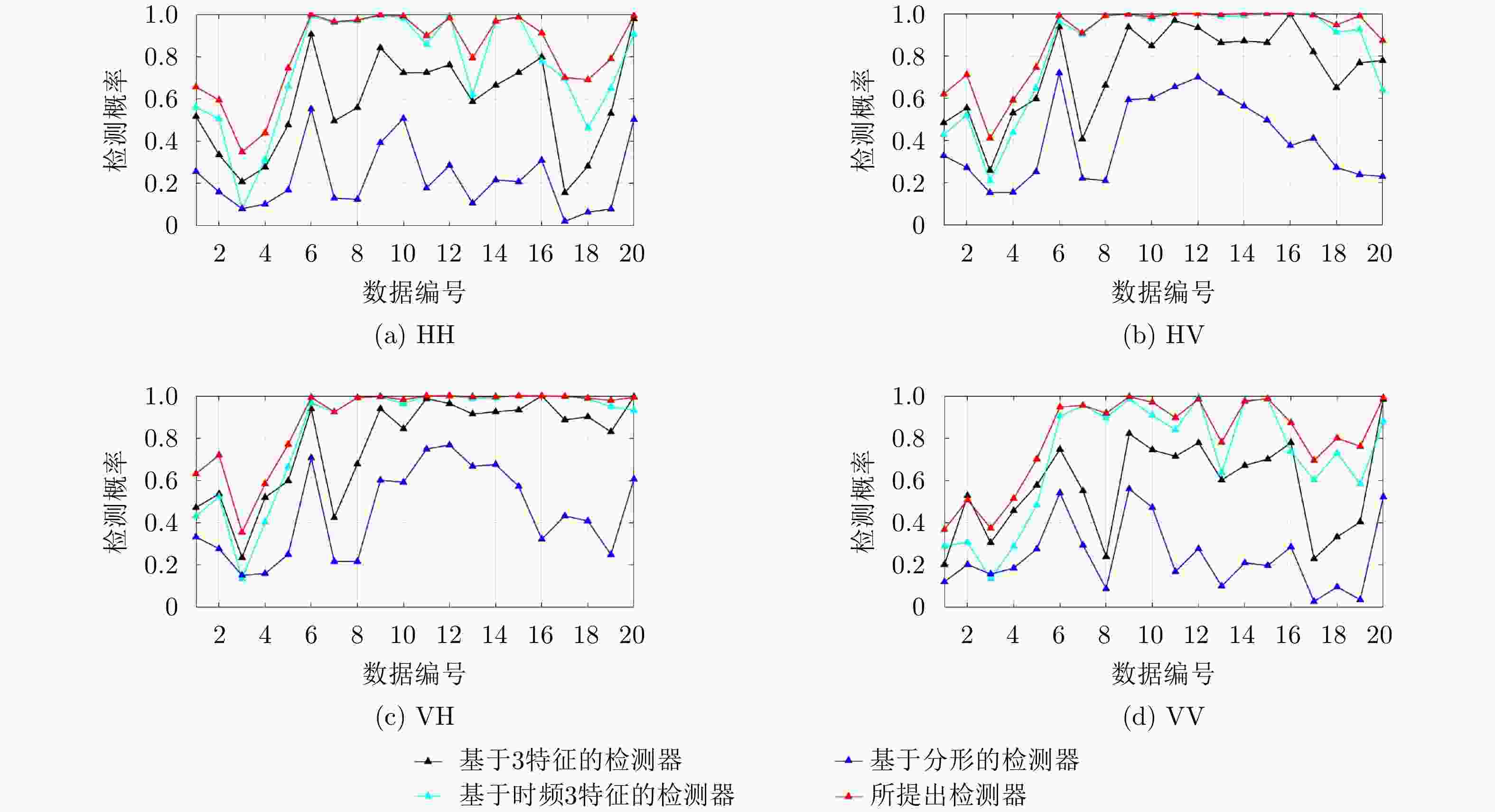
检测器 观测时间(s) HH HV VH VV 平均 基于分形的检测器[12] 0.512 0.223 0.404 0.448 0.241 0.329 1.024 0.301 0.536 0.576 0.328 0.435 基于3特征的检测器[9] 0.512 0.577 0.736 0.776 0.569 0.665 1.024 0.622 0.797 0.813 0.598 0.708 基于时频3特征的检测器[11] 0.512 0.747 0.826 0.842 0.706 0.780 1.024 0.821 0.882 0.877 0.789 0.842 所提检测器 0.512 0.821 0.887 0.895 0.800 0.851 1.024 0.868 0.922 0.921 0.858 0.892 表 3 IPIX数据库中20组数据的平均检测结果对比
Table 3. The comparisons of average detection results of 20 datasets on IPIX radar database
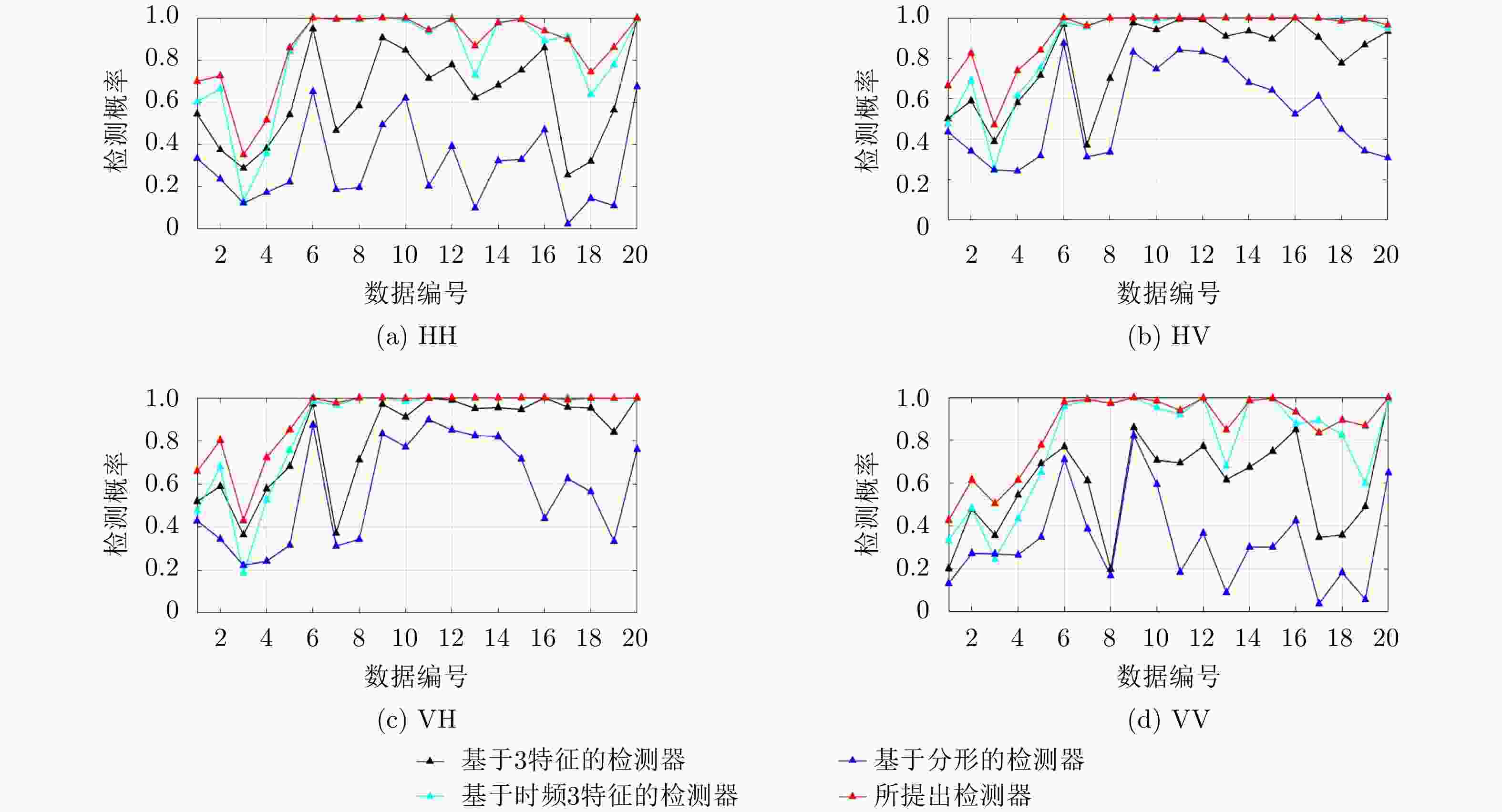
检测器 虚警概率 HH HV VH VV 平均 基于分形的检测器[12] 0.010 0.322 0.514 0.554 0.335 0.431 0.001 0.223 0.404 0.448 0.241 0.329 基于3特征的检测器[9] 0.010 0.673 0.812 0.841 0.657 0.745 0.001 0.577 0.736 0.776 0.569 0.665 基于时频3特征的检测器[11] 0.010 0.806 0.878 0.882 0.781 0.837 0.001 0.747 0.826 0.842 0.706 0.780 所提检测器 0.010 0.887 0.932 0.932 0.868 0.905 0.001 0.821 0.887 0.895 0.800 0.851 表 4 基于6特征的KNN检测器在IPIX数据库上20组数据的平均检测结果对比 (%)
Table 4. The average detection results comparisons of KNN-based detectors using six features at 20 datasets on IPIX radar database (%)
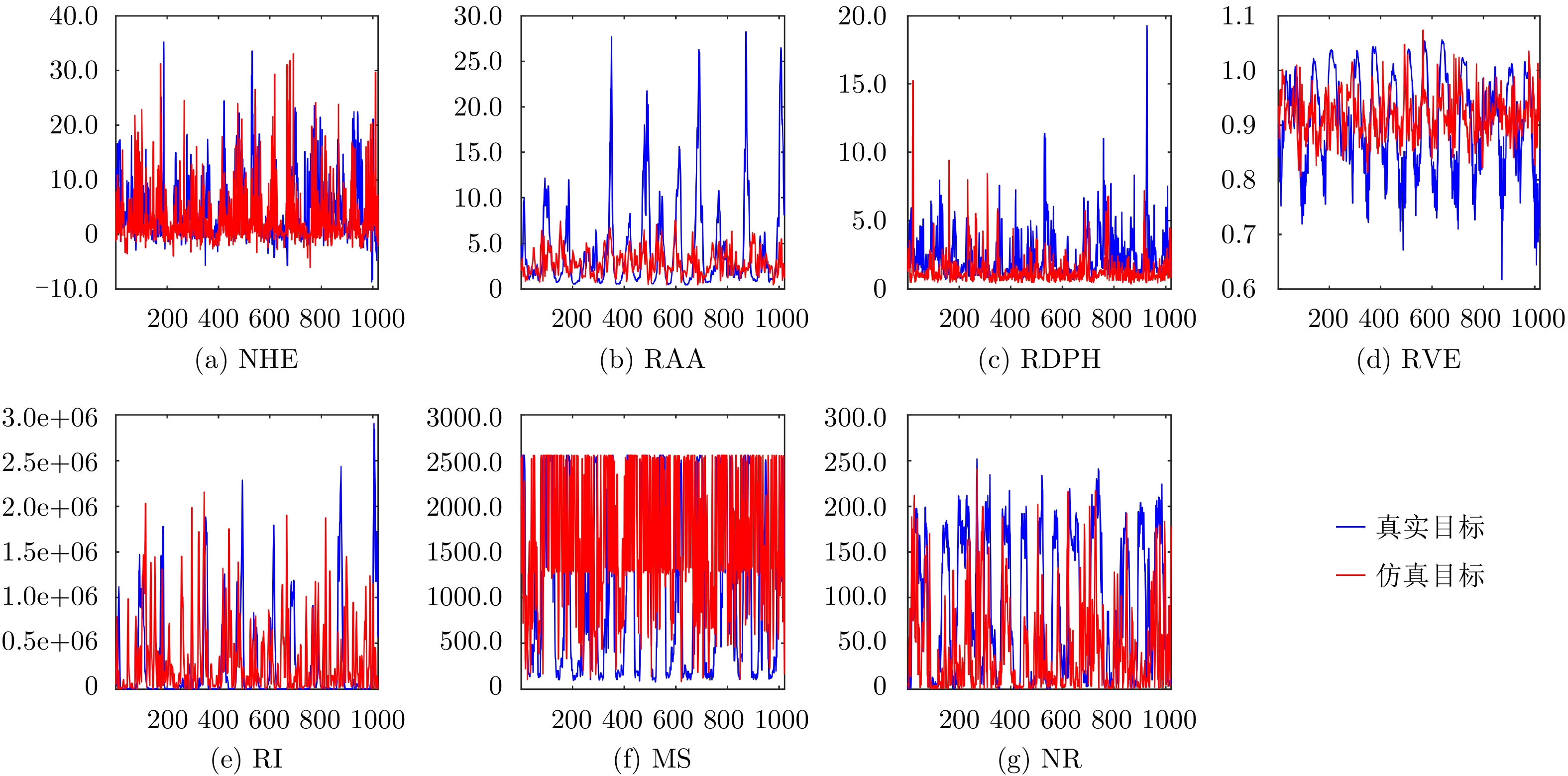
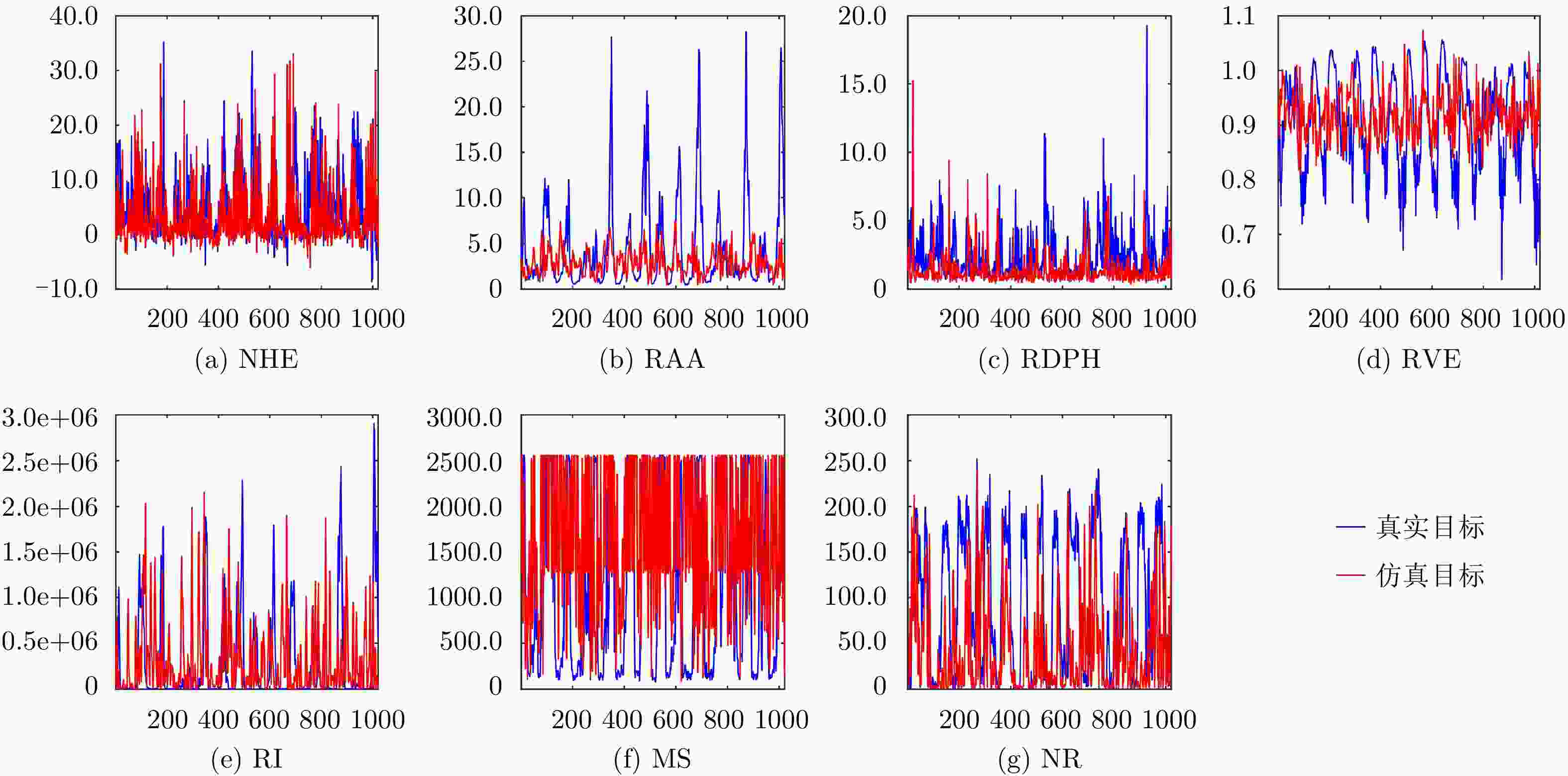
检测器所去掉的特征 NHE RAA RDPH RVE RI MS NR 性能损失 HH 0.01 0.79 5.14 0.50 3.01 1.46 0.20 HV 0.36 0.02 2.50 0.01 4.19 0.70 0.17 VH 0.67 0.21 2.68 0.08 5.45 1.31 0.12 VV 0.01 0.63 4.62 0.01 0.89 1.02 0.02 平均 0.26 0.41 3.74 0.15 3.38 1.12 0.13 表 5 所提检测器在20组IPIX雷达数据集上实现的虚警概率
Table 5. The realized false alarm rate of the proposed detector of 20 datasets on the IPIX radar database
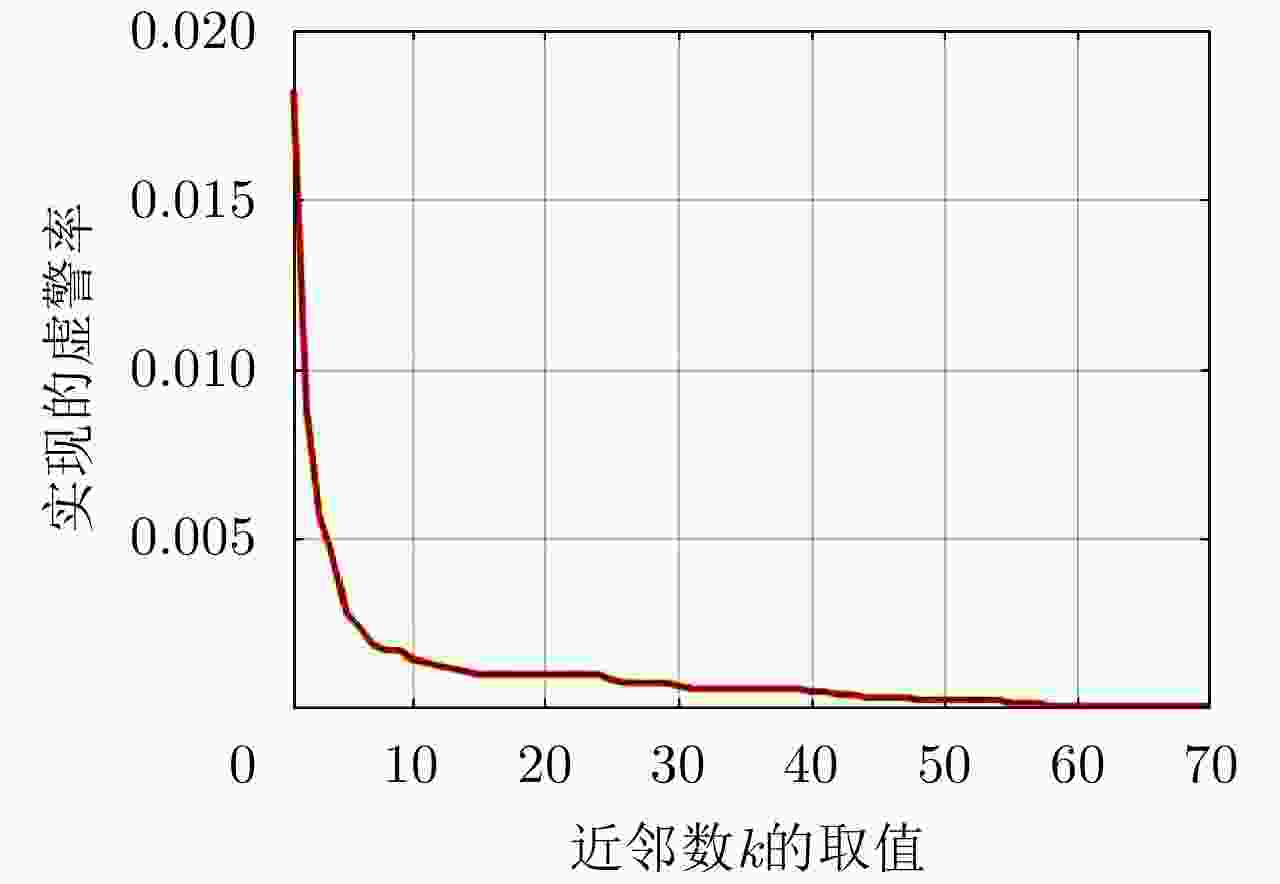
所需的虚警率 实现的虚警率 HH HV VH VV 平均 0.010 0.008774 0.009153 0.008776 0.008563 0.008816 0.001 0.001011 0.001028 0.001010 0.001015 0.001016 -
[1] WANG Shibin, CHEN Xufeng, WANG Yan, et al. Nonlinear squeezing time–frequency transform for weak signal detection[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 113: 195–210. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.01.022 [2] WARD K, TOUGH R, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013. doi: 10.1049/PBRA025E. [3] RABIDEAU D J and PARKER P. Ubiquitous MIMO multifunction digital array radar[C]. The 37th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2003: 1057–1064. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2003.1292087. [4] CARTA P, GALATI G, PIRACCI E G, et al. Implementation of the ubiquitous radar concept with a conformal array[C]. 2015 European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2015: 1463–1466. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD.2015.7346332. [5] SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Detection of low-velocity and floating small targets in sea clutter via income-reference particle filters[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 148: 78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.02.005 [6] 陈世超, 罗丰, 胡冲, 等. 基于多普勒谱非广延熵的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012CHEN Shichao, LUO Feng, HU Chong, et al. Small target detection in sea clutter background based on Tsallis entropy of Doppler spectrum[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012 [7] 左磊, 产秀秀, 禄晓飞, 等. 基于空域联合时频分解的海面微弱目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035ZUO Lei, CHAN Xiuxiu, LU Xiaofei, et al. A weak target detection method in sea clutter based on joint space-time-frequency decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035 [8] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077 [9] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/taes.2014.120657 [10] Cognitive Systems Laboratory. IPIX radar database[EB/OL]. http://soma.mcmaster.ca//ipix.php, 2012. [11] SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection by one-class classifier in time-frequency feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6395–6411. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838260 [12] HU Jing, TUNG W W, and GAO Jianbo. Detection of low observable targets within sea clutter by structure function based multifractal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2006, 54(1): 136–143. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.861541 [13] LI Dongchen and SHUI Penglang. Floating small target detection in sea clutter via normalised Hurst exponent[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(17): 1240–1242. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.1569 [14] GUO Zixun and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection based on feature compression[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 8160–8164. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0694 [15] SHUI Penglang, GUO Zixun, and SHI Sainan. Feature-compression-based detection of sea-surface small targets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 8: 8371–8385. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962793 [16] ZHANG Shichao, LI Xuelong, and ZONG Ming. Efficient kNN classification with different numbers of nearest neighbors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(5): 1774–1785. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2673241 [17] FAYED H A and ATIYA A F. A novel template reduction approach for the K-nearest neighbor method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(5): 890–896. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2018547 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: