A New Method of Target Detection for Passive Radar Based on Information Accumulation
-
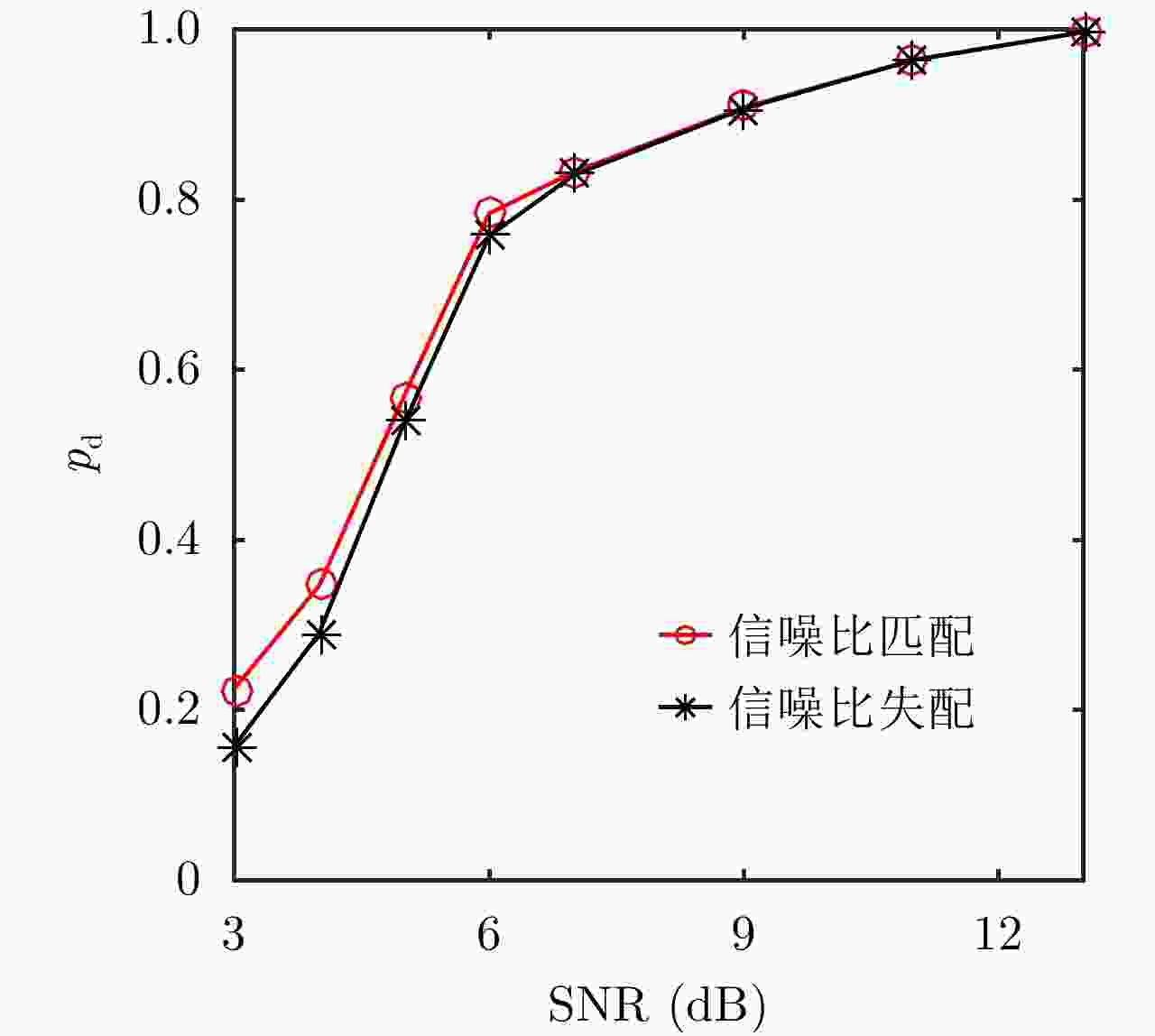
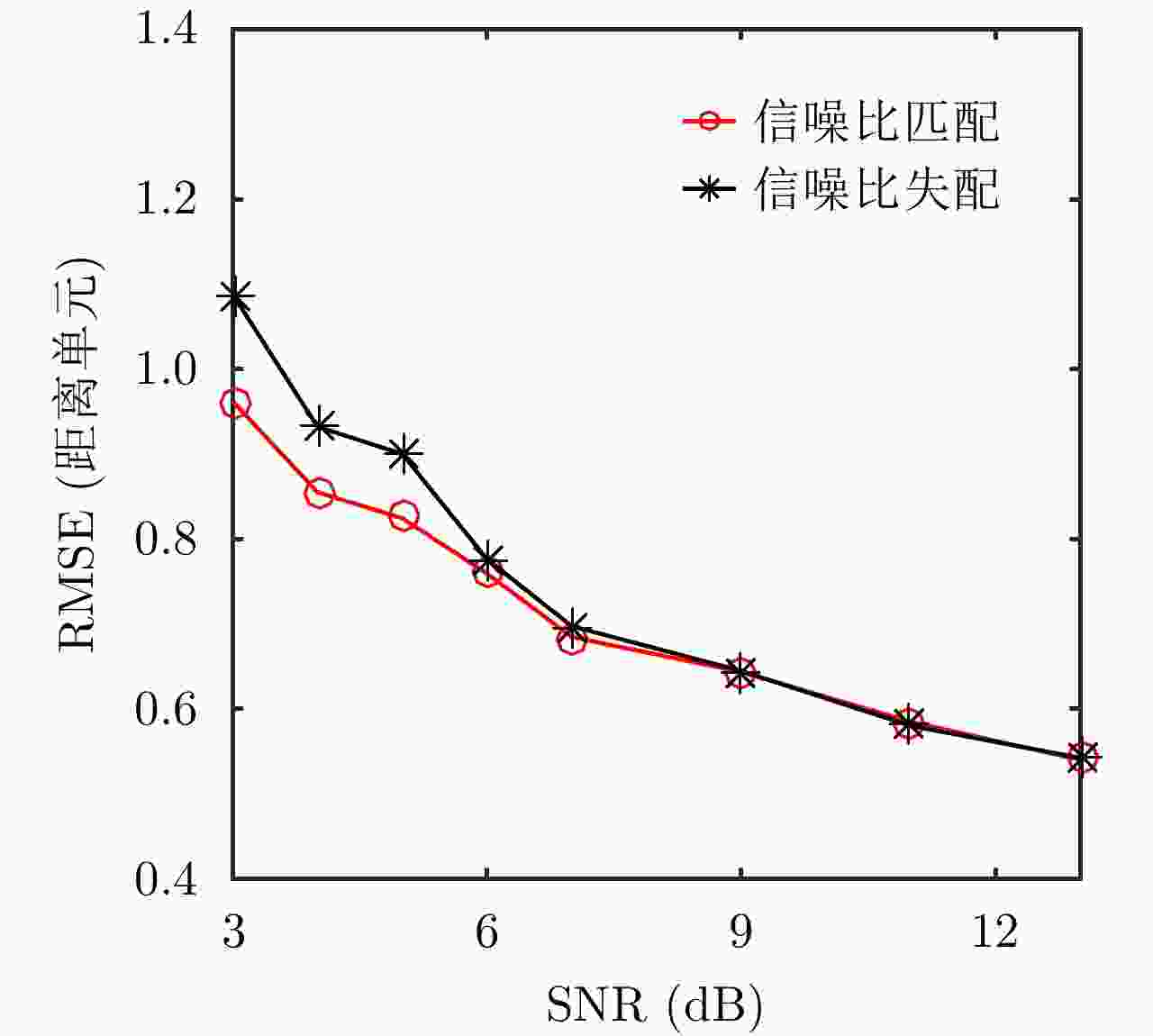
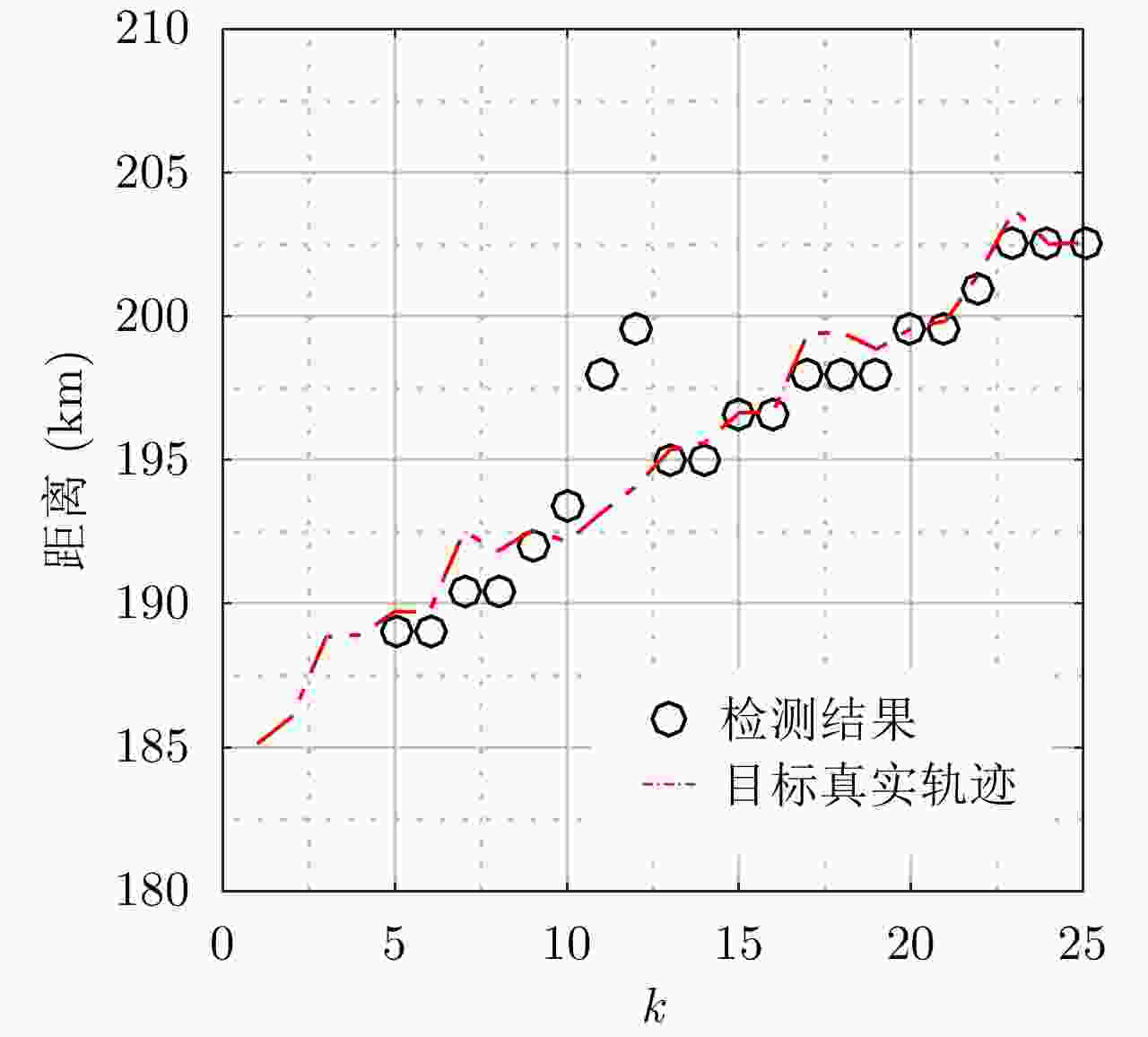
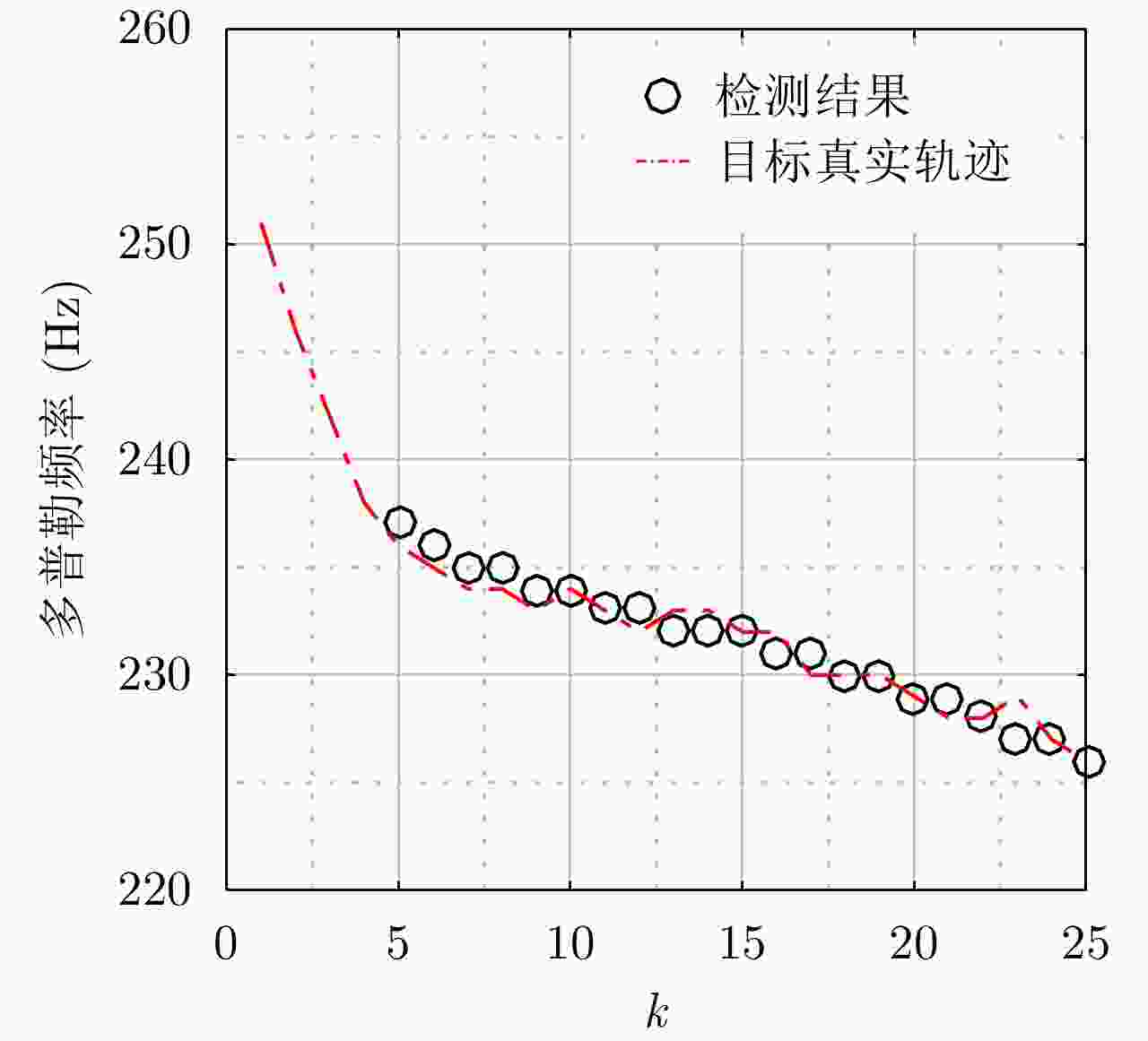
摘要: 外辐射源雷达系统反隐身性能强、隐蔽性好、生存能力强,在军用和民用领域都具有十分广阔的应用场景。为了有效地对低信噪比的弱目标进行检测,并且同时满足系统的实时性需求,该文针对外辐射源雷达系统的特点,依据检测前跟踪算法的思想,提出一种基于信息积累的外辐射源雷达系统目标检测方法。该方法首先将目标状态空间离散格点化,然后利用递推贝叶斯滤波的思想在多帧观测数据之间进行目标状态信息的传递和积累,最后利用信息熵作为判决目标是否存在的条件,避免了对目标存在和目标不存在两种状态之间转移概率模型的先验假设,是一种实现简单、计算复杂度低、可并行度高的目标检测方法。实验结果表明,该方法不仅运行时间短,实时性能强,而且具有良好的检测性能和一定的鲁棒性。Abstract: Owing to their strong anti-stealth performance, good concealment and strong survivability, passive radar systems have a wide range of applications in both military and civilian fields. We propose a method of target detection for passive radar systems which is based on the characteristics of these systems and the track-before-detect concept. This method accumulates information to effectively detect weak targets with low signal-to-noise ratios and meet real-time requirements. First, we discretize the state space, then perform recursive Bayesian filtering to transfer and accumulate target-state information between multiple frames. Lastly, the information entropy is used to determine whether the target exists, thereby avoiding reliance on a prior assumption about the transition probability model between the existence and the absence of the target. This method is simple to implement and has low computational complexity and high parallelism. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method has a short running time and strong real-time performance, as well as good detection performance and robustness.
-
Key words:
- Passive radar /
- Target detection /
- Track-Before-Detect (TBD) /
- Bayesian filtering /
- Information entropy
-
表 1 基于信息积累的目标检测方法
Table 1. The method of target detection based on information accumulation
初始化:
$p\left( { { {{x} }_0} } \right) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 0}^{I - 1} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 0}^{J - 1} {\frac{1}{ {IJ} } } } \delta \left( { { {{x} }_0} - {x^{i,j} } } \right) \qquad $
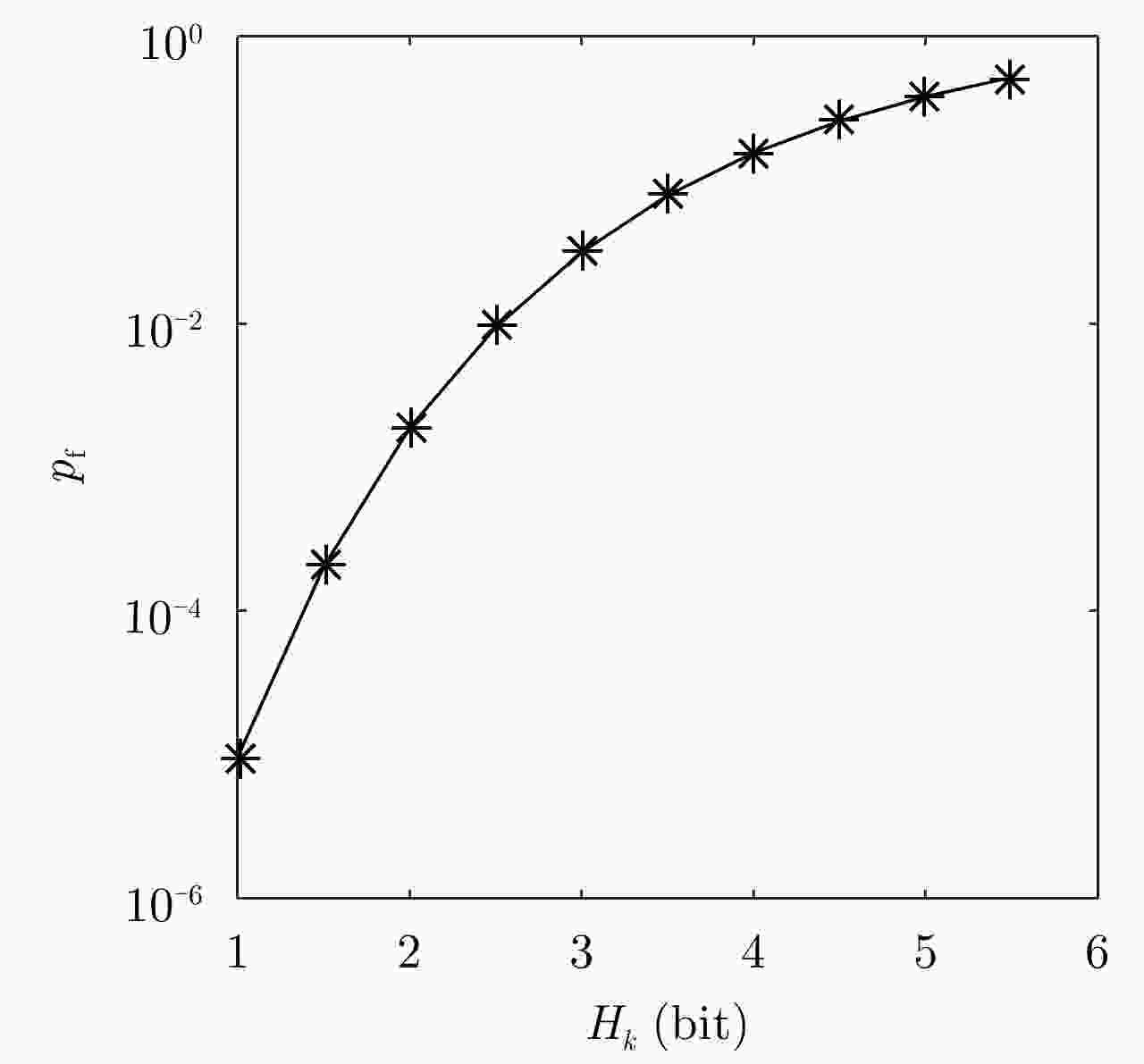
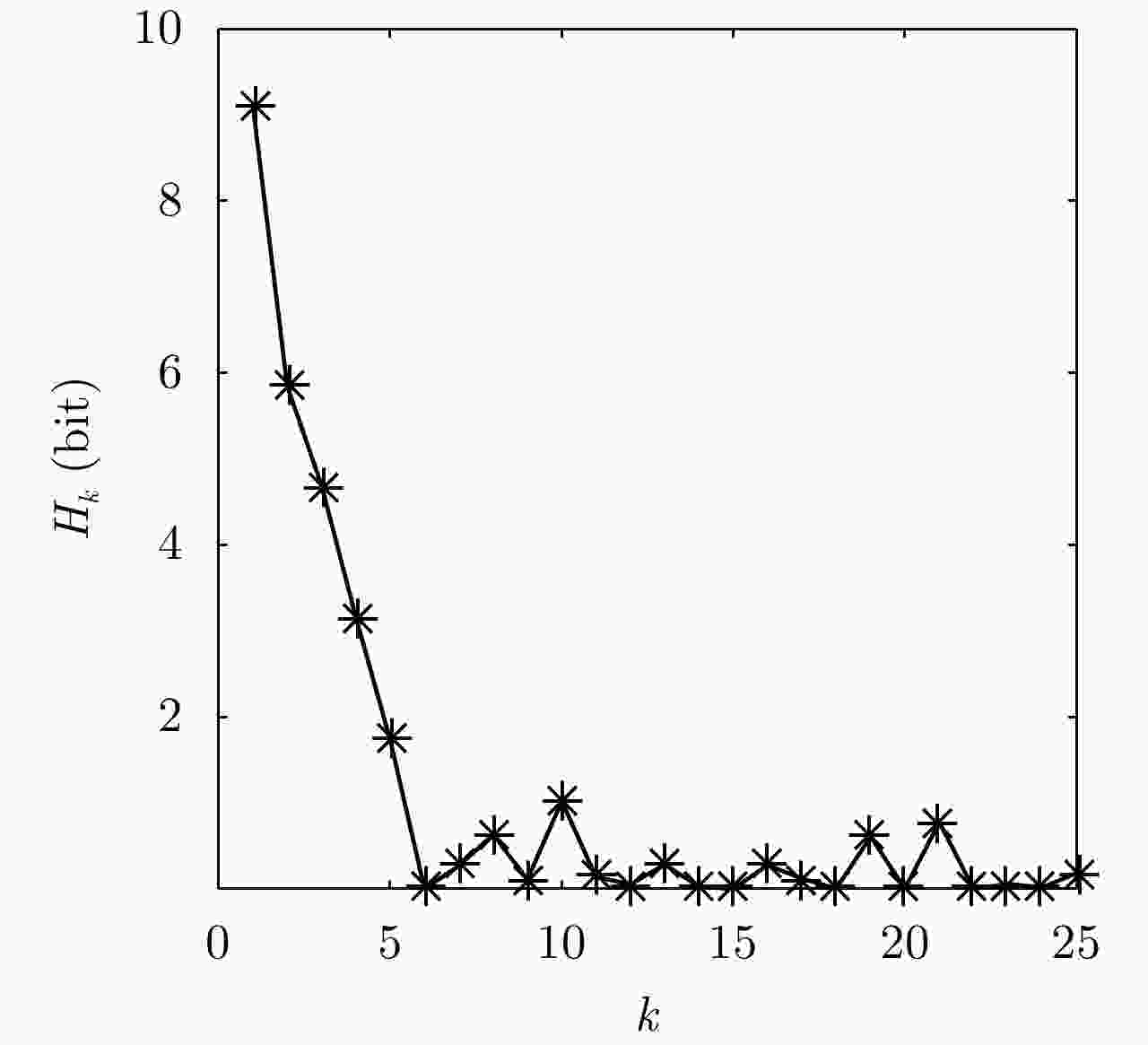
${H_0} = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 0}^{I - 1} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 0}^{J - 1} {w_{0|0}^{i,j} } } {\log _2}\left( {w_{0|0}^{i,j} } \right) = {\log _2}(IJ)$对于时刻$k = 1,2,3, ··· ,K$: 获得观测值${ {{z} }_k}$,信息传递矩阵${{ T}_k}$,似然函数$\mathcal{L}\left( {{{{z}}_k}|{{{x}}_k}} \right)$。 预测步,根据式(17)、式(18)预测概率密度函数$p\left( { { {{x} }_k}|{ {{z} }_{1:k - 1} } } \right)$。 更新步,根据式(24)、式(25)更新概率密度函数$p\left( {{{{x}}_k}|{{{z}}_{1:k}}} \right)$。 根据式(26)计算信息熵${H_k}$。 根据${H_k}$进行目标检测,如果${H_k} < {H_{{\rm{thr}}}}$,判定目标存在,目标
状态${{{x}}_k} = \arg {\max _{(i,j)}}w_{k|k}^{i,j}$;如果${H_k} \ge {H_{ {\rm{thr} } } }$,判定目标不存在。 表 2 多种目标检测算法的运行时间对比
Table 2. Comparison of running time among multiple target detection algorithms
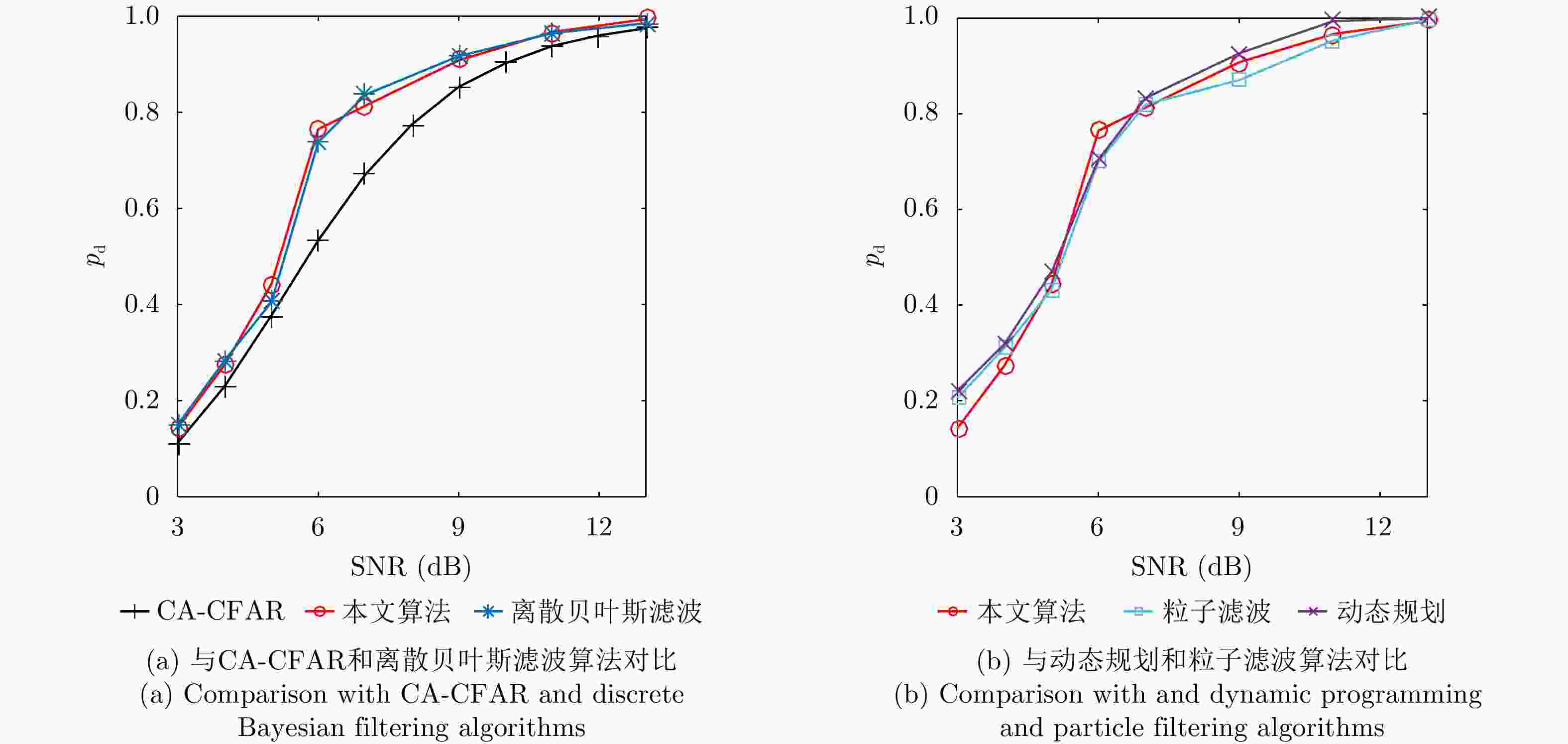
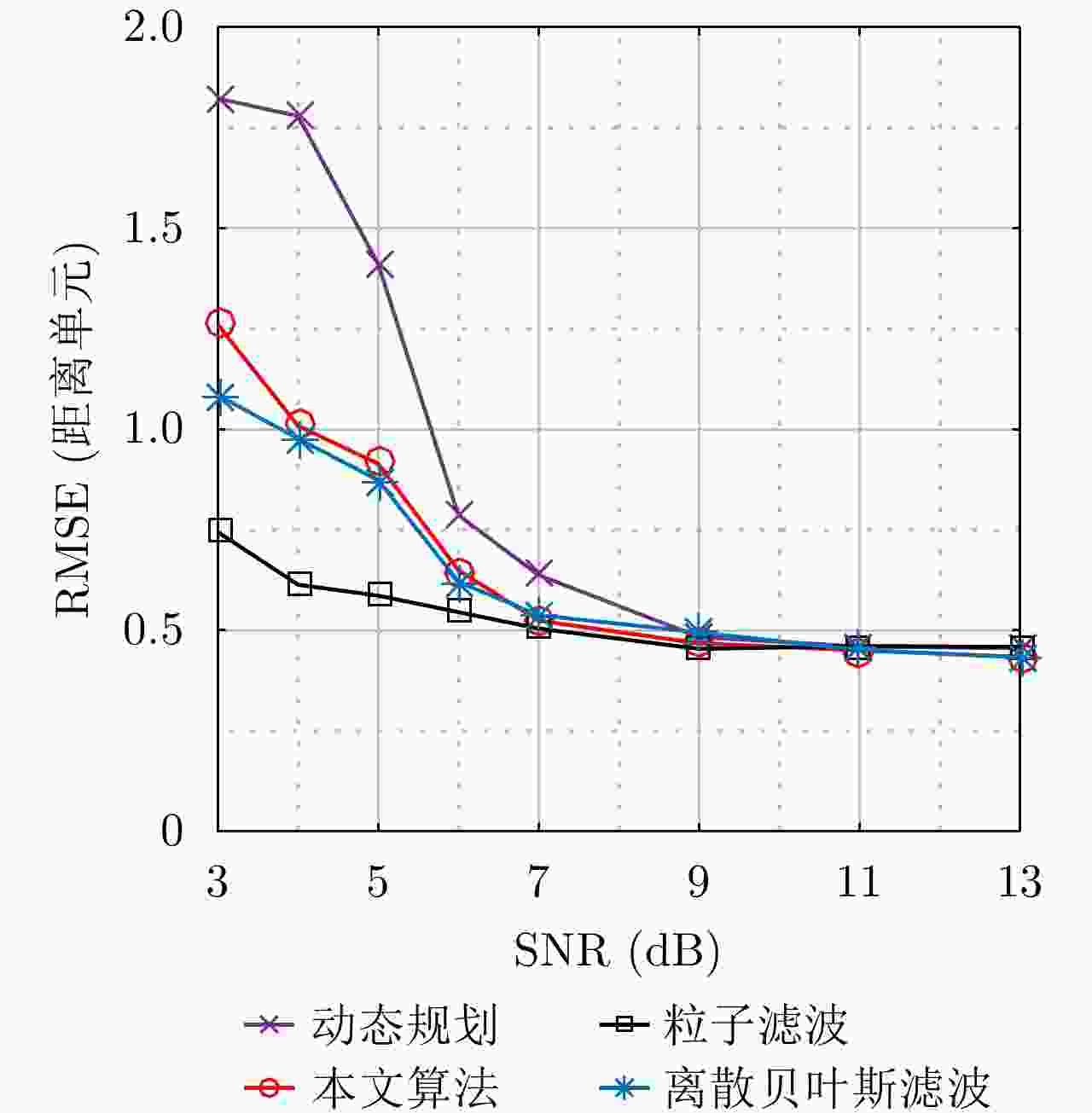
算法 本文算法 离散格点贝叶斯滤波 动态规划 粒子滤波 CA-CFAR 单帧运行时间(s) 0.016 0.018 1.200 1.102 0.003 -
[1] GRIFFITHS H D and BAKER C J. An Introduction to Passive Radar[M]. Boston, US: Artech House, 2017: 1–25. [2] WILLIS N J. Bistatic Radar[M]. Raleigh, US: SciTech Publishing, 2005: 15–57. [3] KULPA K and MALANOWSKI M. From Klein Heidelberg to modern multistatic passive radar[C]. The 2019 20th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Ulm, Germany, 2019: 1–9. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8768176. [4] 何友, 关键, 孟祥伟, 等. 雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011: 36–40.HE You, GUAN Jian, MENG Xiangwei, et al. Radar Target Detection and CFAR Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011: 36–40. [5] CARLSON B D, EVANS E D, and WILSON S L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. I. system concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(1): 102–108. doi: 10.1109/7.250410 [6] BARNIV Y. Dynamic programming solution for detecting dim moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES–21(1): 144–156. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310548 [7] YI Wei, JIANG Haichao, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Track-before-detect strategies for radar detection in G0-distributed clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(5): 2516–2533. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2702259 [8] SALMOND D J and BIRCH H. A particle filter for track-before-detect[C]. 2001 American Control Conference, Arlington, USA, 2001: 3755–3760. doi: 10.1109/ACC.2001.946220. [9] RUTTEN M G, GORDON N J, and MASKELL S. Recursive track-before-detect with target amplitude fluctuations[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(5): 345–352. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045041 [10] RUTTEN M G, GORDON N J, and MASKELL S. Efficient particle-based track-before-detect in Rayleigh noise[C]. The 7th International Conference on Information Fusion, Stockholm, Sweden, 2004: 693–700. [11] JISHY K and LEHMANN F. A Bayesian track-before-detect procedure for passive radars[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013(1): 45. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-45 [12] ROLLASON M and SALMOND D. Particle filter for track-before-detect of a target with unknown amplitude viewed against a structured scene[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(6): 603–609. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0483 [13] STONE L D, CORWIN T L, and BARLOW C A. Bayesian Multiple Target Tracking[M]. Boston, US: Artech House, 2013: 65–77. [14] ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374 [15] MAHAFZA B R. Introduction to Radar Analysis[M]. Boca Raton, US: CRC Press, 1998: 267–287. [16] DAVEY S J, RUTTEN M G, and CHEUNG B. A comparison of detection performance for several track-before-detect algorithms[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2007, 2008(1): 428036. doi: 10.1155/2008/428036 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: