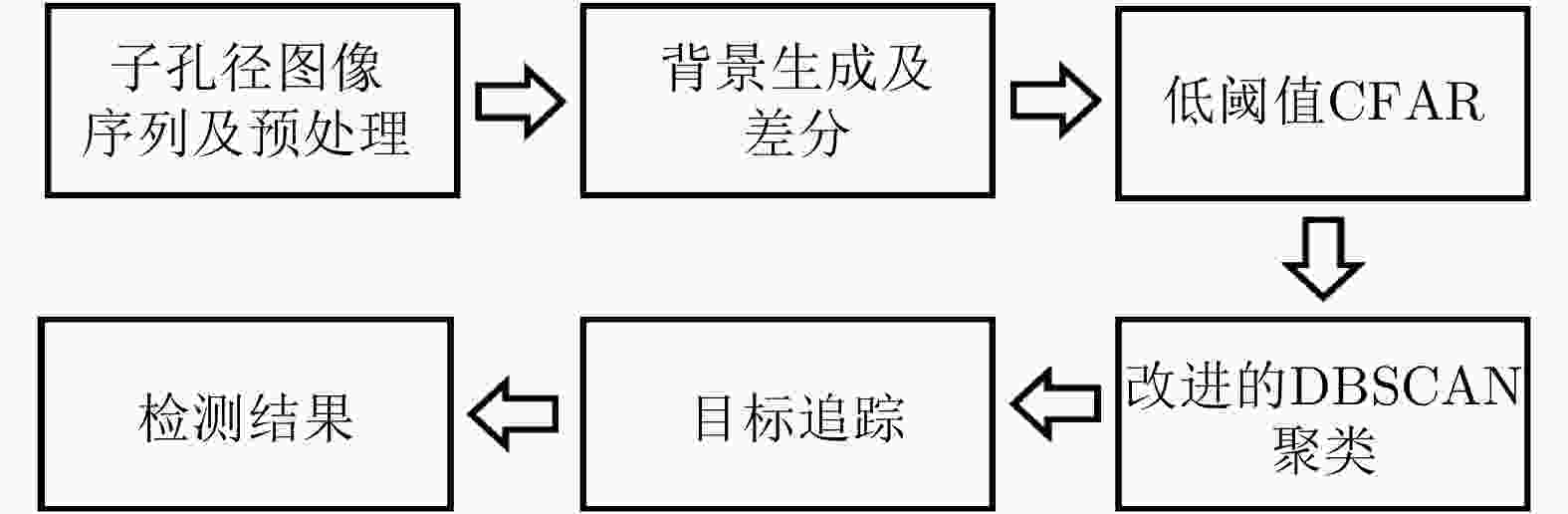
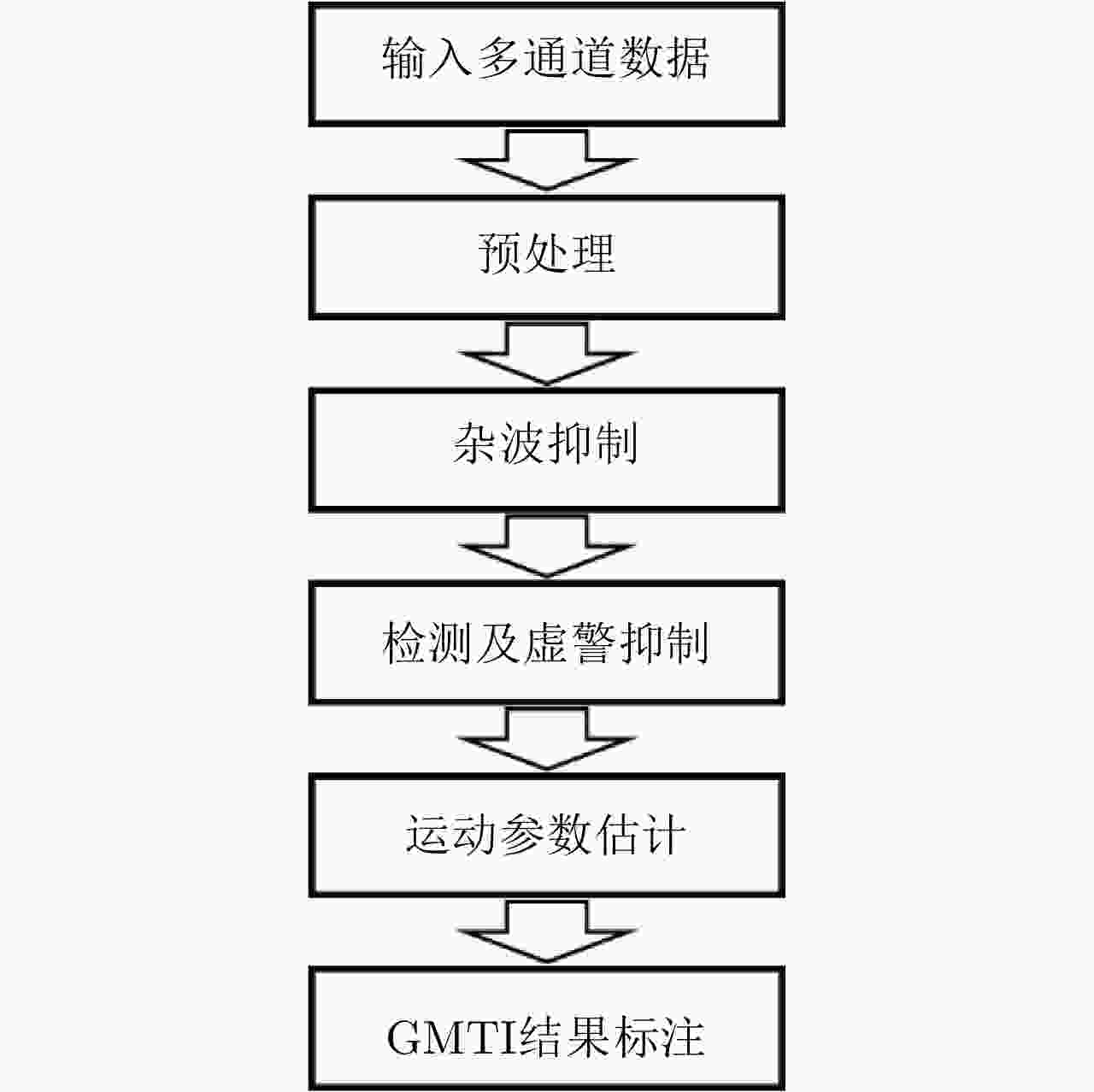
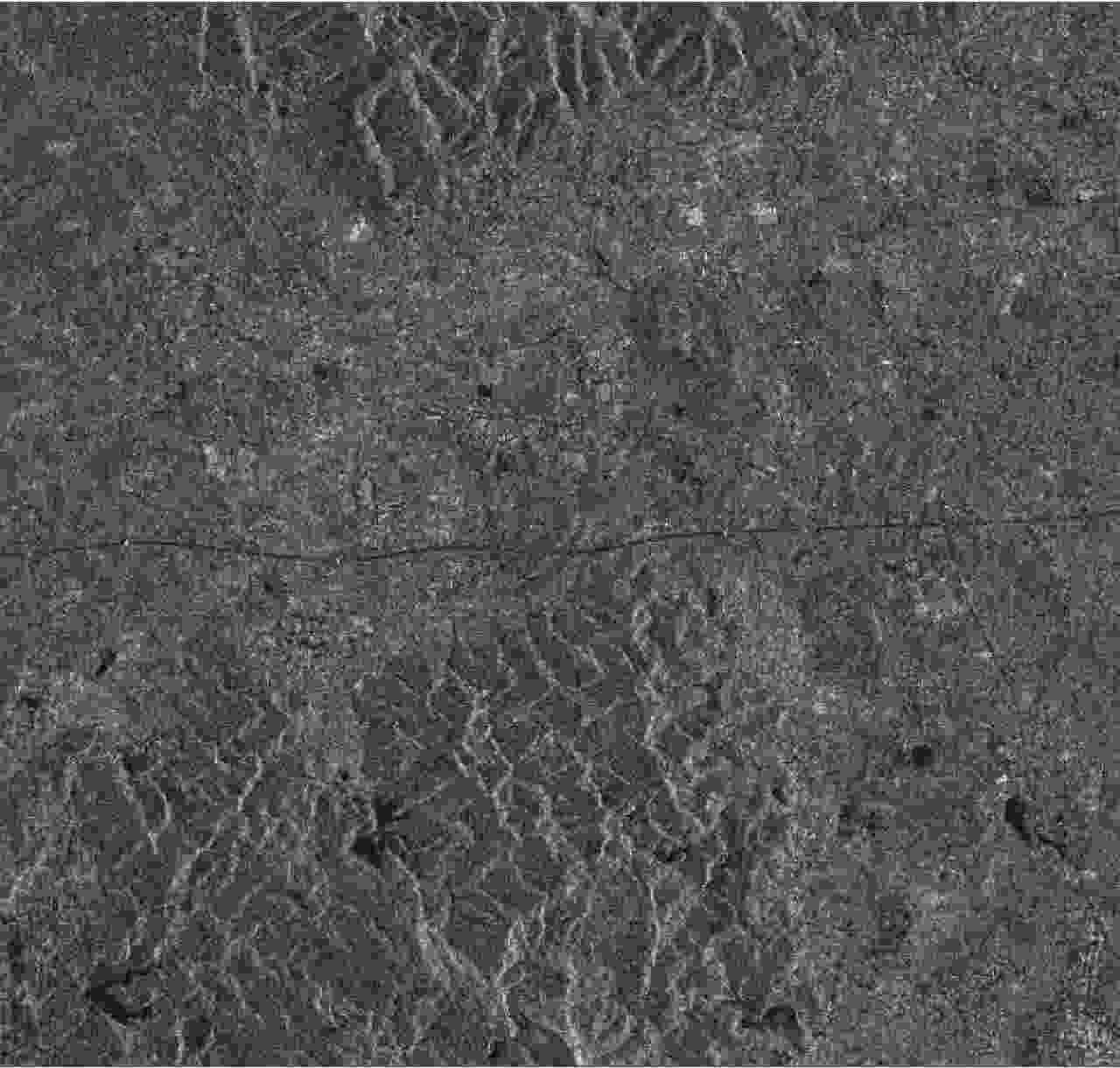
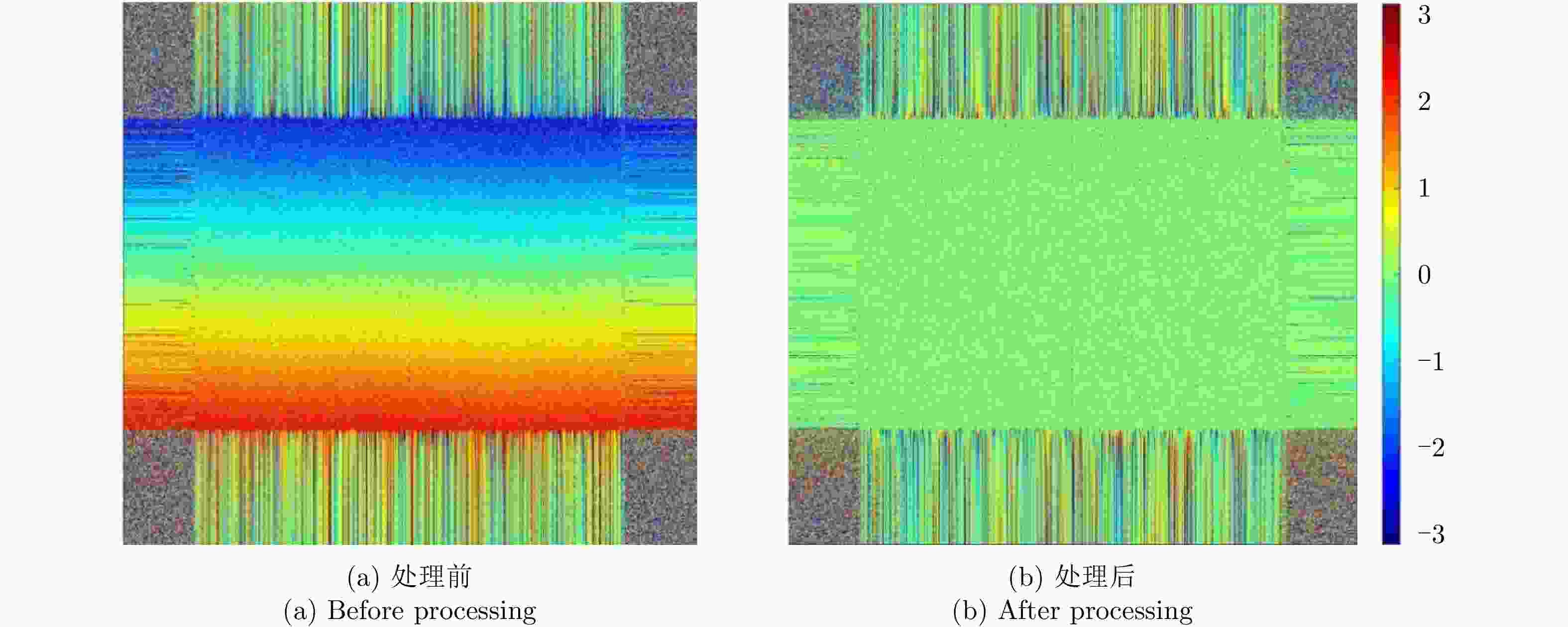
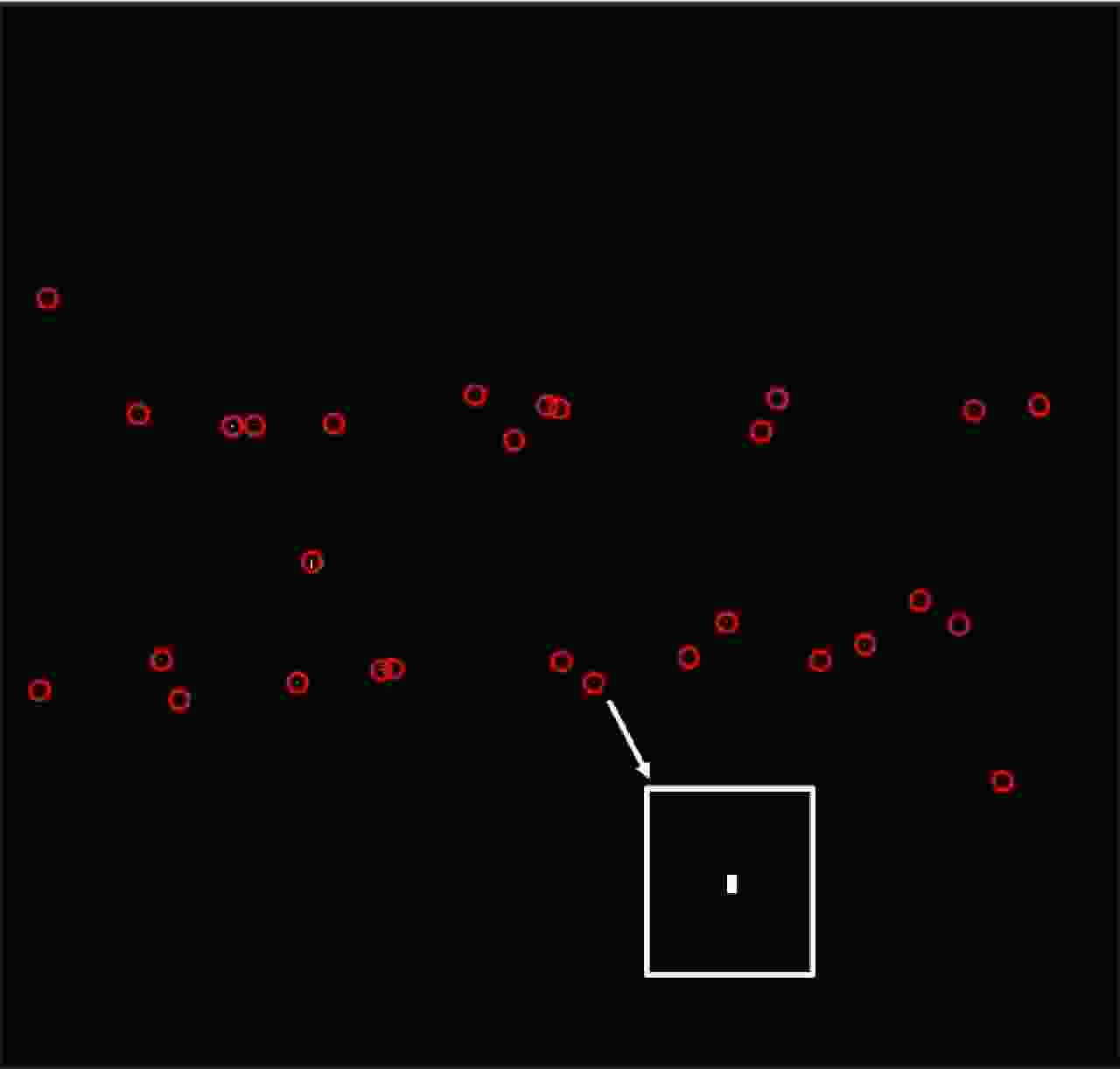
-
摘要: 多角度SAR作为一种新的SAR模式,它具备对场景的长时间观测以及大合成孔径角两个优势。已有研究表明,这两点区别于传统SAR模式的优势,使得单通道系统也可以具备较强的动目标检测能力,即,无需增加雷达系统的复杂度,就可以实现在轨星载SAR系统动目标检测能力的拓展和提升。这也使得多角度SAR动目标研究成为新的研究热点。在研讨近年来多角度SAR-GMTI研究基础及发展现状的基础上,该文重点介绍了研究团队围绕高分3号开展的原理性验证实验研究,包括凝视聚束模式动目标检测方法研究、双通道动目实验模式、双通道凝视聚束GMTI模式研究等。通过上述研究,以期为在轨及规划星载SAR单通道GMTI工程实现、未来星载多角度SAR时序动态观测新型工作模式设计等奠定可行性研究基础。Abstract: Multi-aspect SAR is a new SAR mode that has two advantages, i.e., long-term observations and a large synthetic-aperture azimuth angle. Previous studies have reported that these unique advantages enable even single-channel systems to have a relatively strong capability for detecting moving targets, i.e., multi-aspect SAR expands and improves the moving-target-related capabilities of the earlier SAR satellite system without increasing its complexity. As such, multi-aspect SAR-GMTI has become a trending topic for research. After reviewing the recent progress and research basis of multi-aspect SAR-GMTI, in this paper, we present our research on the Gaofen-3 SAR, which includes: moving-target detection methods that use the staring spotlight mode, dual-channels GMTI mode, and the dual-channel spotlight GMTI mode. With the results obtained by this research, we hope to establish a basis for the engineering implementation of current and future spaceborne single-channel SAR-GMTI modes and the design of a future spaceborne multi-aspect SAR mode capable of retrieving time-series and dynamic scene information.
-
表 1 数据参数
Table 1. Dataset parameters
符号 参数 参数值 符号 参数 参数值 $ \lambda $ 波长 $ 0.056\;\mathrm{m} $ $ {R}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 场景中心斜距 934.6 km $ {V}_{\mathrm{s}} $ 平台速度 7568 m/s $ {T}_{\mathrm{a}} $ 合成孔径时间 12.5 s $ {\theta }_{\mathrm{L}} $ 下视角 $ {33.7}^{\circ } $ $ {\theta }_{\mathrm{a}} $ 合成孔径角 $ -{1.78}^{\circ }\sim {1.78}^{\circ } $ $ {B}_{\mathrm{w}} $ 带宽 240 MHz $ {\Delta }_{\mathrm{r}} $ 距离向像素尺寸 0.56 m $ {f}_{\mathrm{P}\mathrm{R}\mathrm{F}} $ PRF 3742.7 Hz $ {\Delta }_{\mathrm{a}} $ 方位向像素尺寸 0.33 m 表 2 追踪结果
Table 2. Tracking results
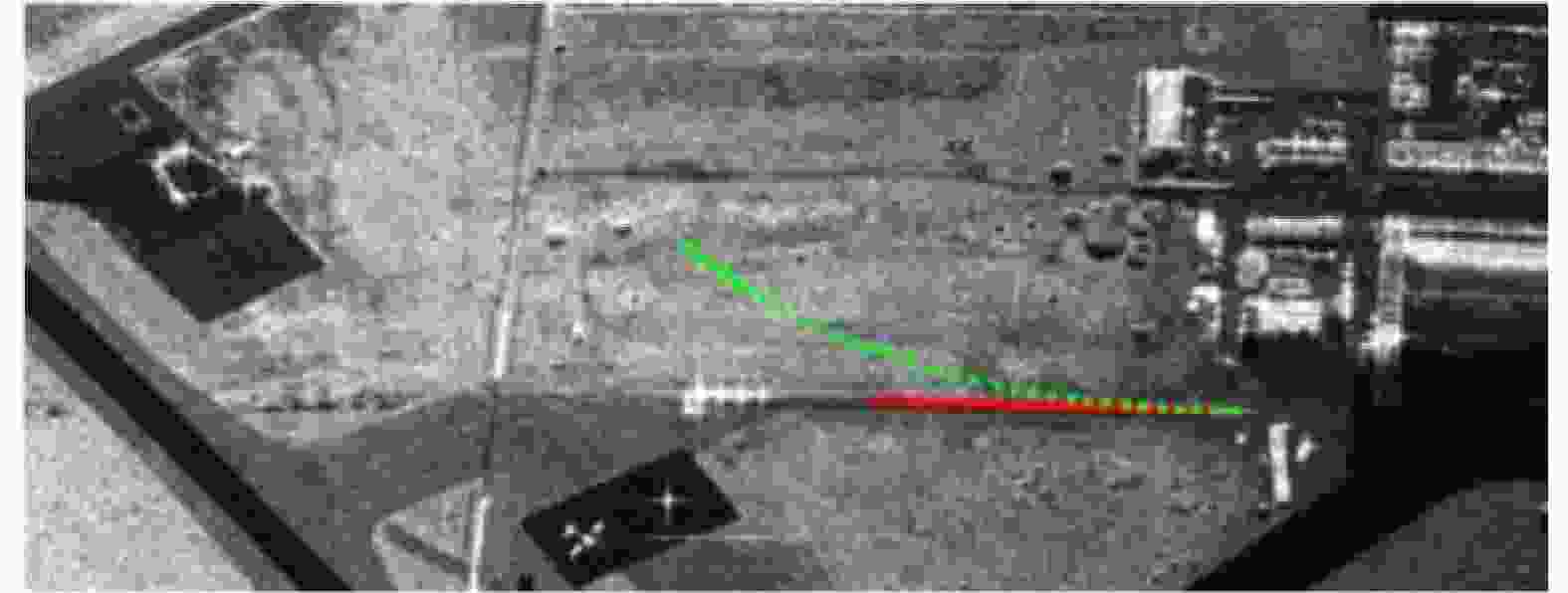
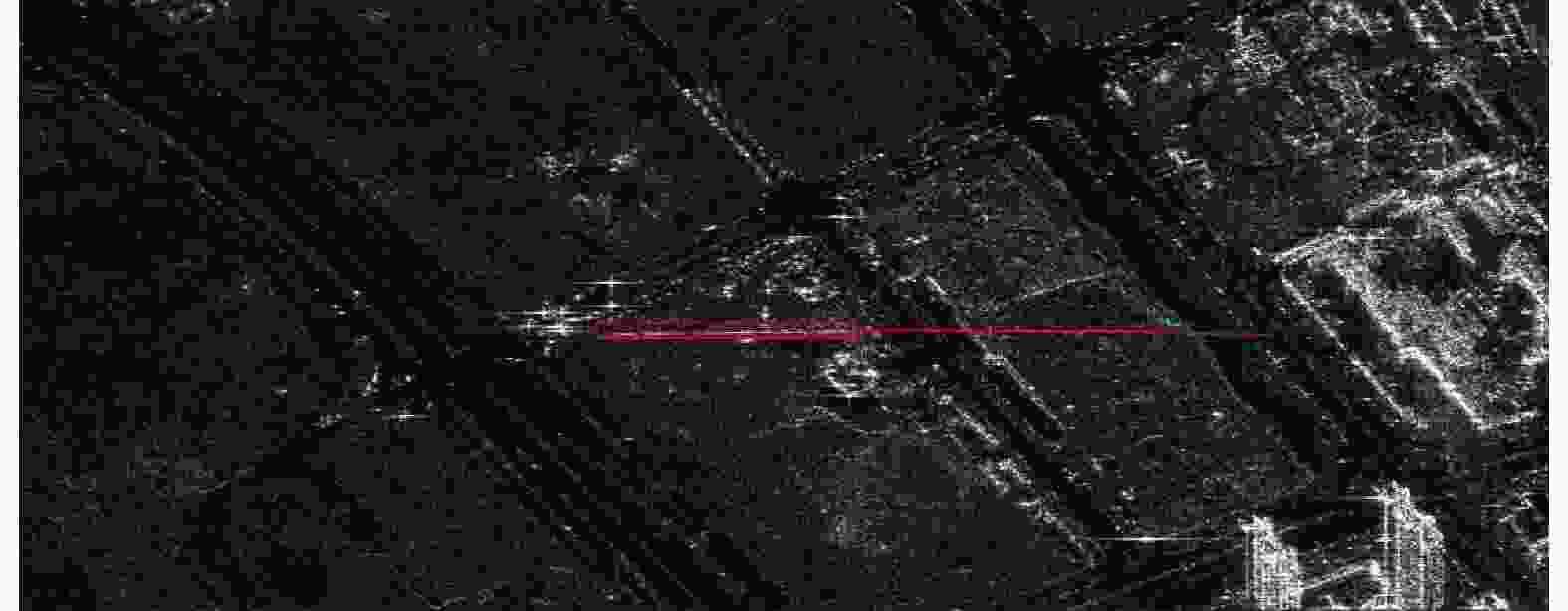
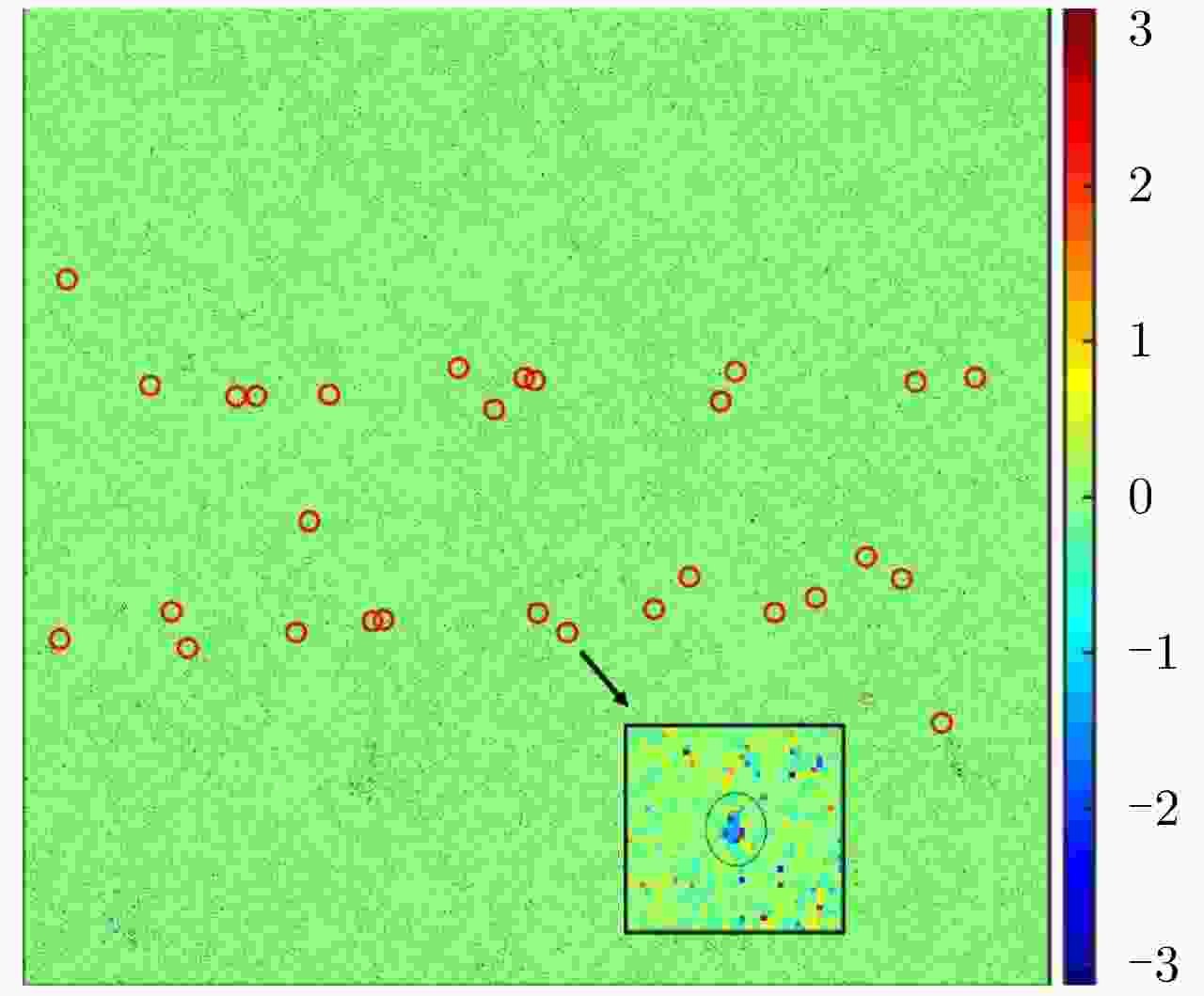
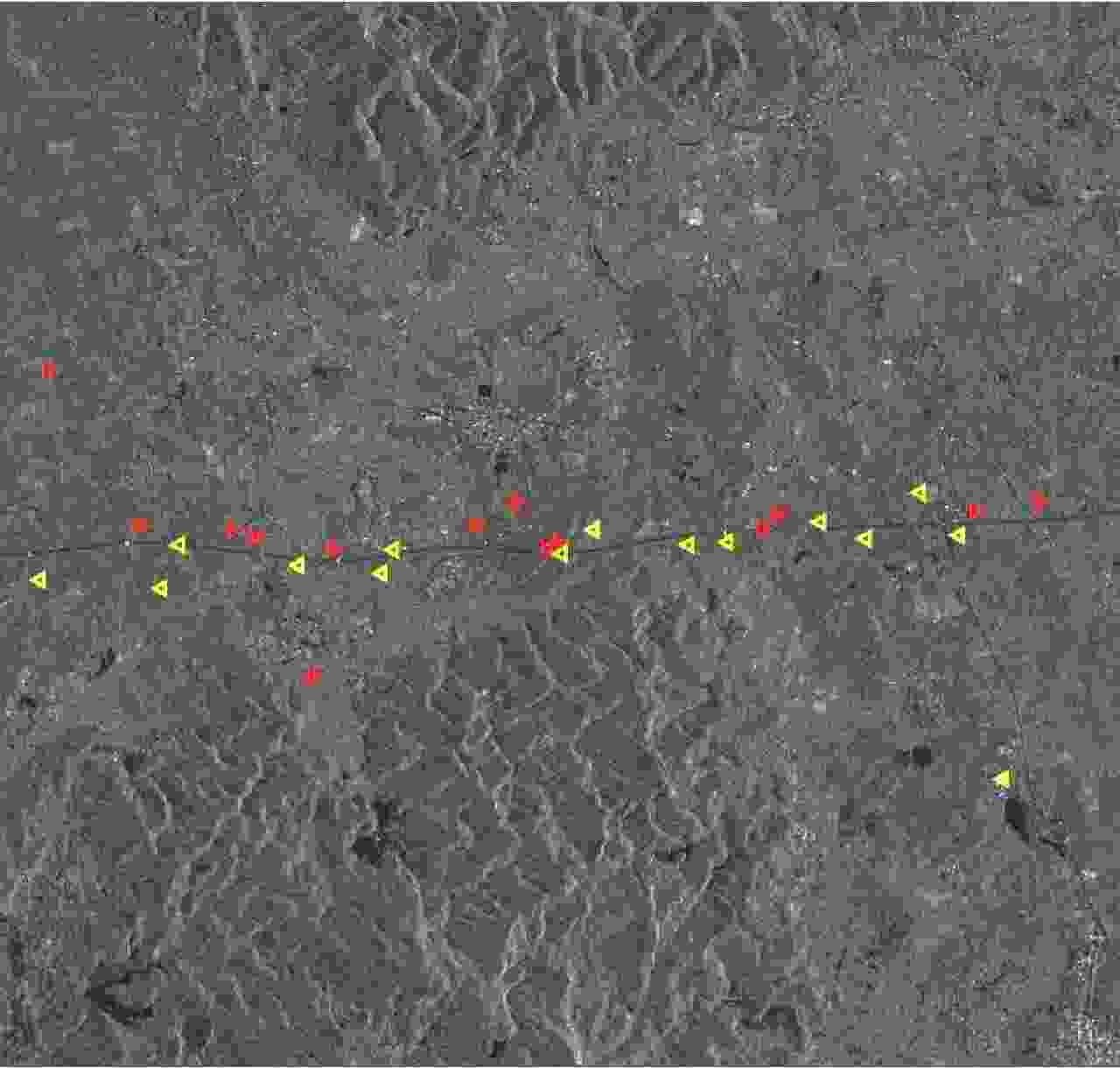
序号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 运动距离(m) 12.8 35.6 37.4 36.6 417.8 11.2 21.9 22.1 27.6 31.6 方位速度(m/s) 0.5 1.4 1.5 1.5 16.7 0.4 0.9 0.9 1.1 1.3 表 3 实验参数
Table 3. Experiment parameters
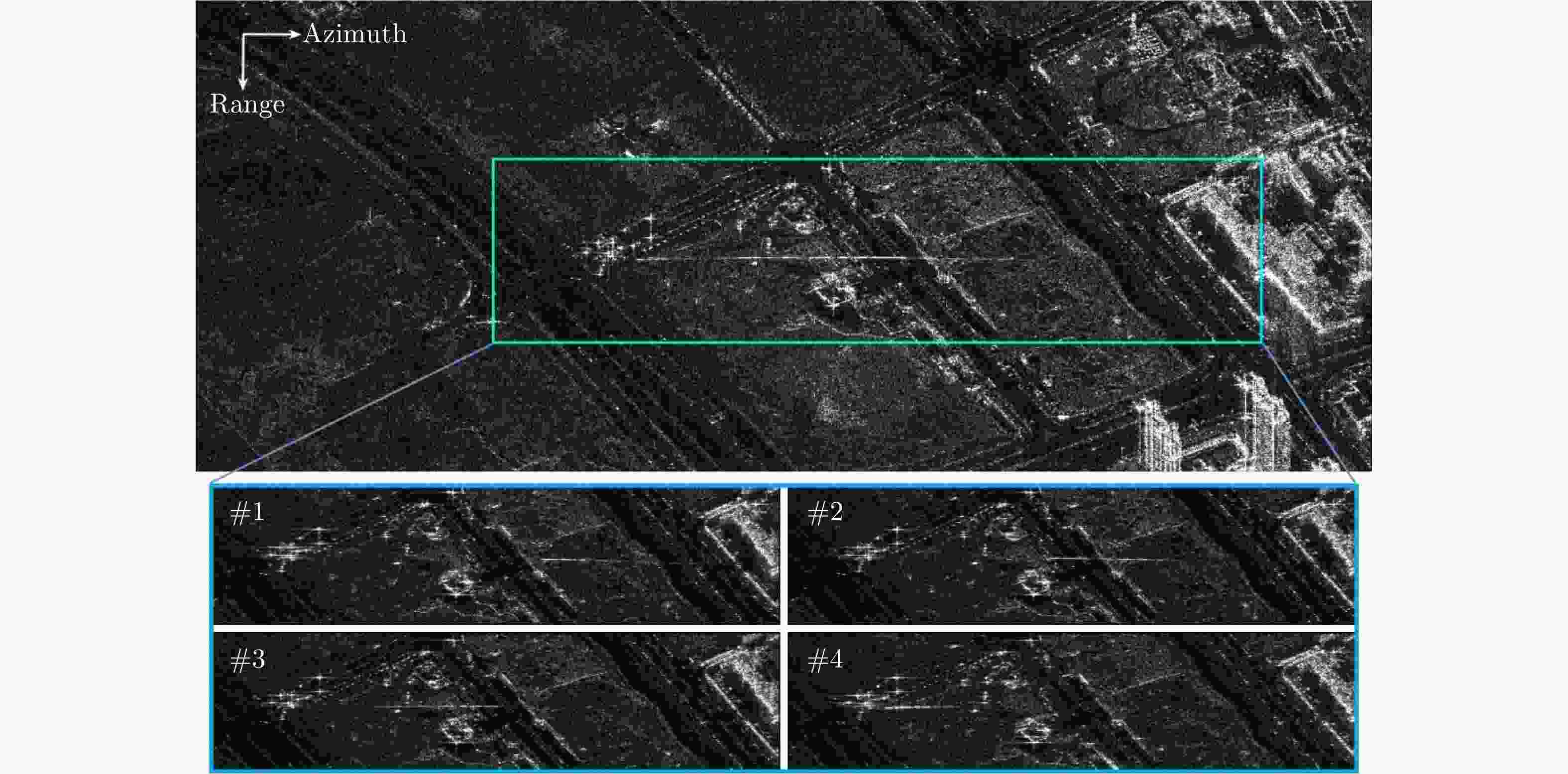
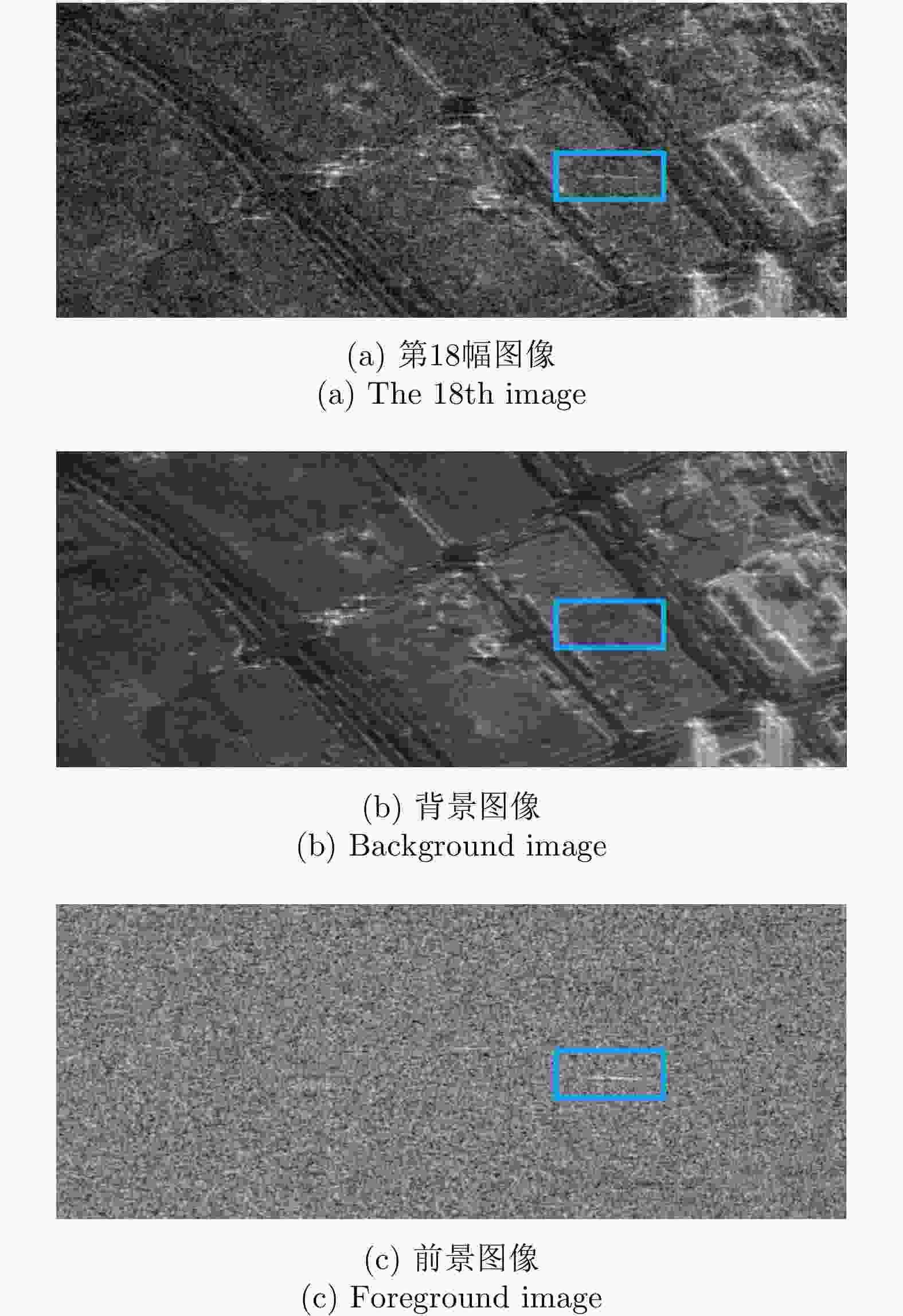
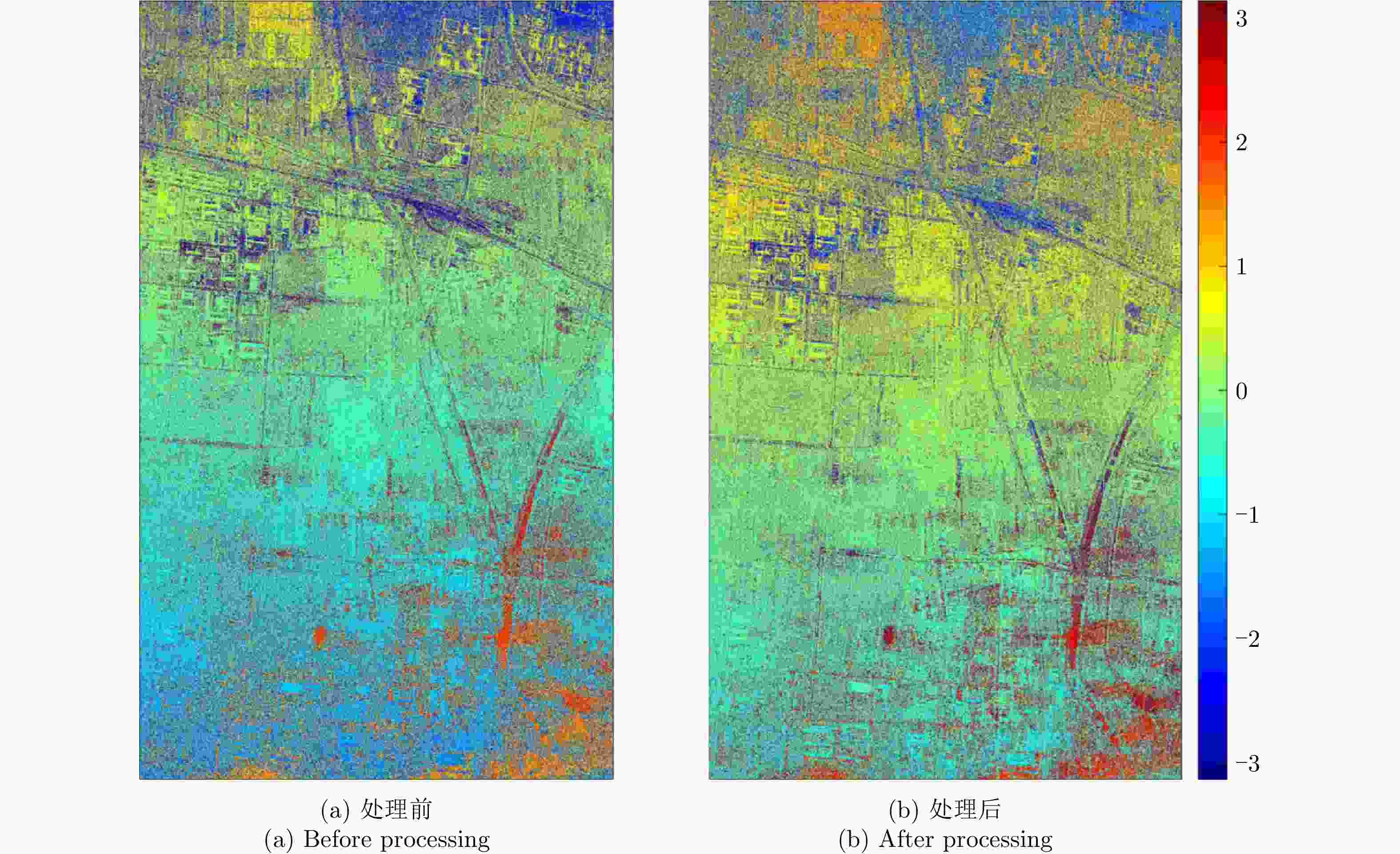
实验参数 参数值 中心频率$ {f}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 5.4 GHz 带宽 $ {B}_{\mathrm{d}} $ 100 MHz $ \mathrm{P}\mathrm{R}\mathrm{F} $ 1948 Hz 场景中心斜距 $ {r}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 974347 m 入射角 $ {\theta }_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{c}} $ $ {34.5}^{\circ } $ 平台速度 $ {v}_{\mathrm{s}} $ 7566 m/s 轨道类型 Descending 方位观测角 $ {\theta }_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{z}\mathrm{i}} $ $ -{1.7}^{\circ }\sim {1.7}^{\circ } $ 合成孔径时间 $ T $ $ 15\;\mathrm{s} $ -
[1] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047WU Yirong. Concept of multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047 [2] 洪文. 圆迹SAR成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046HONG Wen. Progress in circular SAR imaging technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046 [3] 洪文, 林赟, 谭维贤, 等. 地球同步轨道圆迹SAR研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(3): 241–253. doi: 10.12000/JR15062HONG Wen, LIN Yun, TAN Weixian, et al. Study on geosynchronous circular SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(3): 241–253. doi: 10.12000/JR15062 [4] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 [5] 王彦平, 韩阔业, 洪文, 等. 多角度合成孔径雷达数据获取的方法[P]. 中国, CN201410217041.6, 2014.WANG Yanping, HAN Kuoye, HONG Wen, et al. Multi-angle synthetic aperture radar data acquisition method[P]. CN, CN201410217041.6, 2014. [6] SOUMEKH M. Reconnaissance with slant plane circular SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1996, 5(8): 1252–1265. doi: 10.1109/83.506760 [7] 林赟, 谭维贤, 洪文, 等. 圆迹SAR极坐标格式算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(12): 2802–2807. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.0003LIN Yun, TAN Weixian, HONG Wen, et al. Polar format algorithm for circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(12): 2802–2807. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.0003 [8] 林赟. 圆迹合成孔径雷达成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2011.LIN Yun. Research on circular synthetic aperture radar imaging algorithm[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electrics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. [9] LIN Yun, HONG Wen, TAN Weixian, et al. Interferometric circular SAR method for three-dimensional imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(6): 1026–1030. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2150732 [10] HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, TAN Weixian, et al. Tomographic SAR and circular SAR experiments in anechoic chamber[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4. [11] ORIOT H and CANTALLOUBE H. Circular SAR imagery for urban remote sensing[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4. [12] 刘燕, 谭维贤, 林赟, 等. 基于圆迹SAR的建筑物轮廓信息提取[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 946–952. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140717LIU Yan, TAN Weixian, LIN Yun, et al. An approach of the outlines extraction of building footprints from the circular SAR data[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 946–952. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140717 [13] ZHAO Yue, LIN Yun, HONG Wen, et al. Adaptive imaging of anisotropic target based on circular-SAR[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(16): 1406–1408. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.1764 [14] GUO Bin, VU D, XU Luzhou, et al. Ground moving target indication via multichannel airborne SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3753–3764. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2143420 [15] DEMING R W. Along-track interferometry for simultaneous SAR and GMTI: Application to Gotcha challenge data[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVⅢ, Orlando, United States, 2011: 80510P. [16] DEMING R W, MACINTOSH S, and BEST M. Three-channel processing for improved geo-location performance in SAR-based GMTI interferometry[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIX, Baltimore, United States, 2012: 83940F. [17] DEMING R, BEST M, FARRELL S. Simultaneous SAR and GMTI using ATI/DPCA[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXI, Baltimore, United States, 2014: 90930U. [18] BARBER B and BARKER J. Indication of slowly moving ground targets in non-Gaussian clutter using multi-channel synthetic aperture radar[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2012, 6(5): 424–434. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2011.0157 [19] POISSON I P, ORIOT H M, and TUPIN. Ground moving target trajectory reconstruction in single-channel circular SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 1976–1984. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2351419 [20] SHEN Wenjie, LIN Yun, CHEN Shiqiang, et al. Apparent trace analysis of moving target with linear motion in circular SAR imagery[C]. The 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–4. [21] 洪文, 申文杰, 林赟, 等. 基于背景差分法的单通道圆迹SAR动目标检测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(9): 2182–2189. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161300HONG Wen, SHEN Wenjie, LIN Yun, et al. Single channel circular SAR moving targets detection based on background subtraction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(9): 2182–2189. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161300 [22] SHEN Wenjie, LIN Yun, YU Lingjuan, et al. Single channel circular SAR moving target detection based on logarithm background subtraction algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(5): 742. doi: 10.3390/rs10050742 [23] SHEN Wenjie, HONG Wen, HAN Bing, et al. Moving target detection with modified logarithm background subtraction and its application to the GF-3 spotlight mode[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(10): 1190. doi: 10.3390/rs11101190 [24] WANG Wu, AN Daoxiang, LUO Yuxiao, et al. The fundamental trajectory reconstruction results of ground moving target from single-channel CSAR geometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5647–5657. [25] LI Jianpeng, AN Daoxiang, WANG Wu, et al. A novel method for single-channel CSAR ground moving target imaging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(19): 8642–8649. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2912863 [26] AN Daoxiang, WANG Wu, and ZHOU Zhimin. Refocusing of ground moving target in circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(19): 8668–8674. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2922649 [27] SUN Jili, YU Weidong, and DENG Yunkai. The SAR payload design and performance for the GF-3 mission[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10): 2419. doi: 10.3390/s17102419 [28] GIERULL C H, SIKANETA I, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Two-step detector for RADARSAT-2’s experimental GMTI mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 436–454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201729 [29] ENDER J H G. Space-time adaptive processing for synthetic aperture radar[C]. IEE Colloquium on Space-Time Adaptive Processing, London, UK, 1998: 611–618. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: