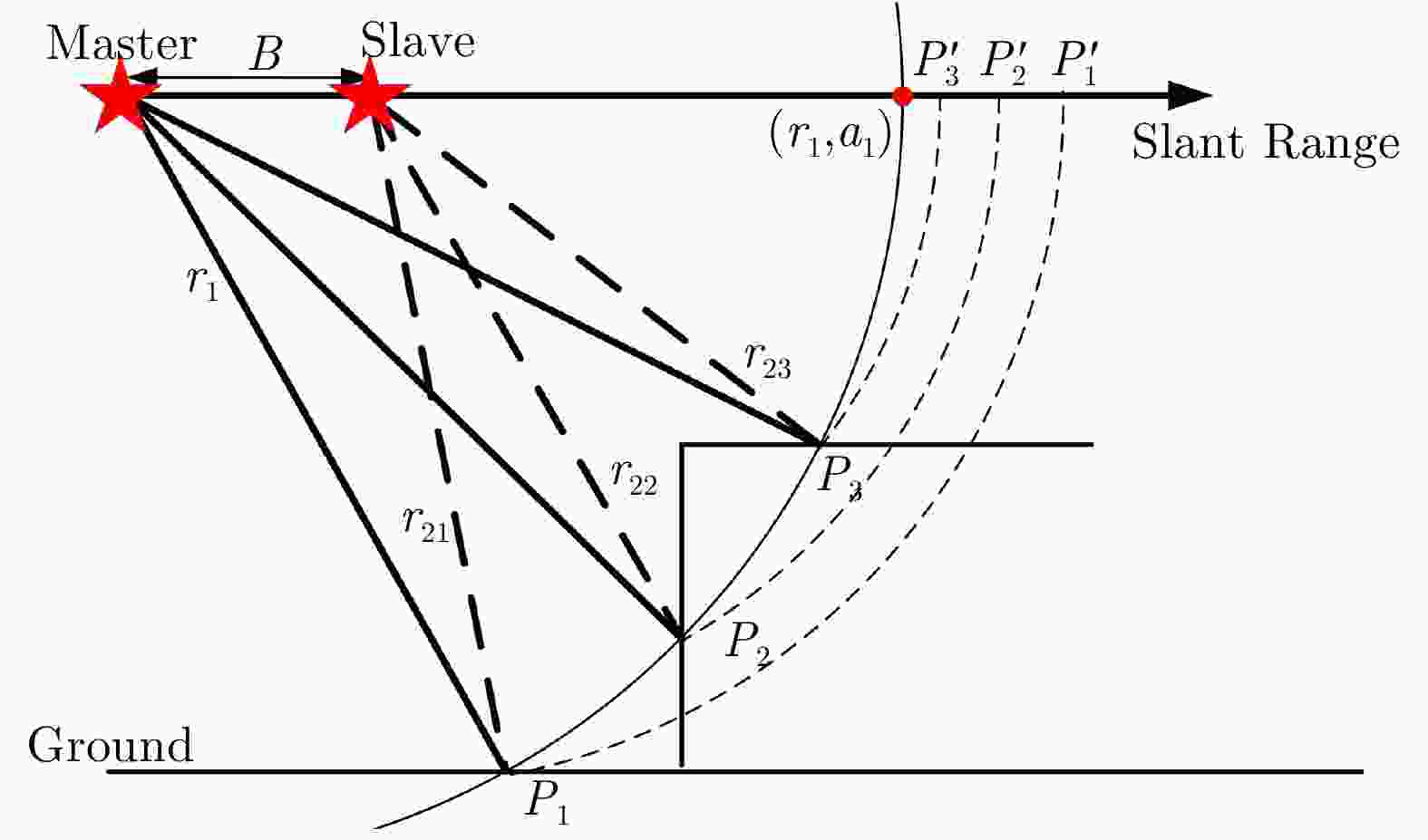
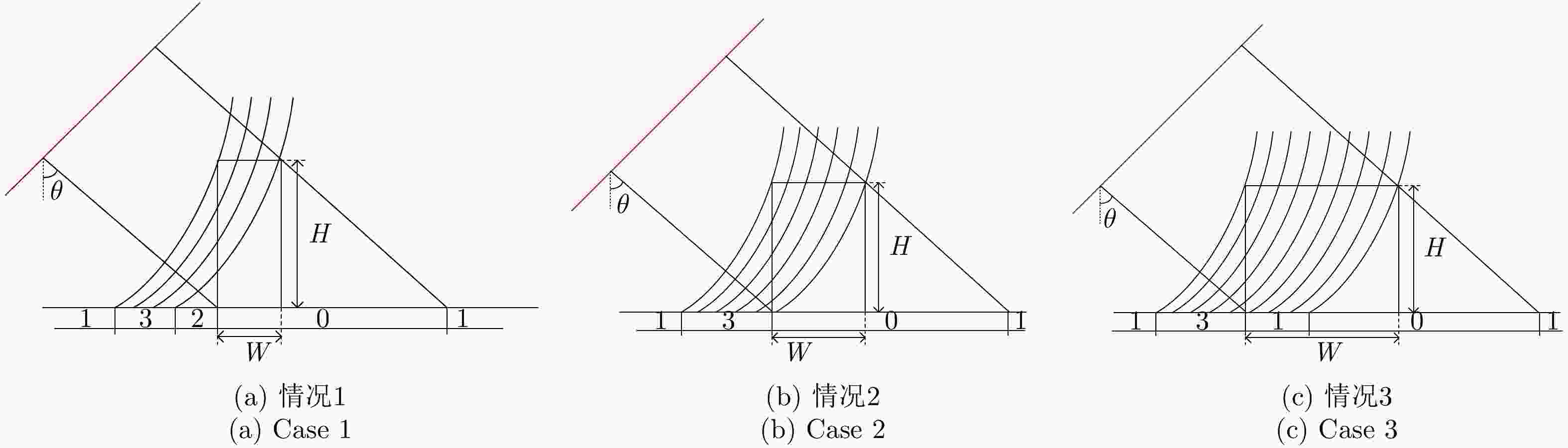
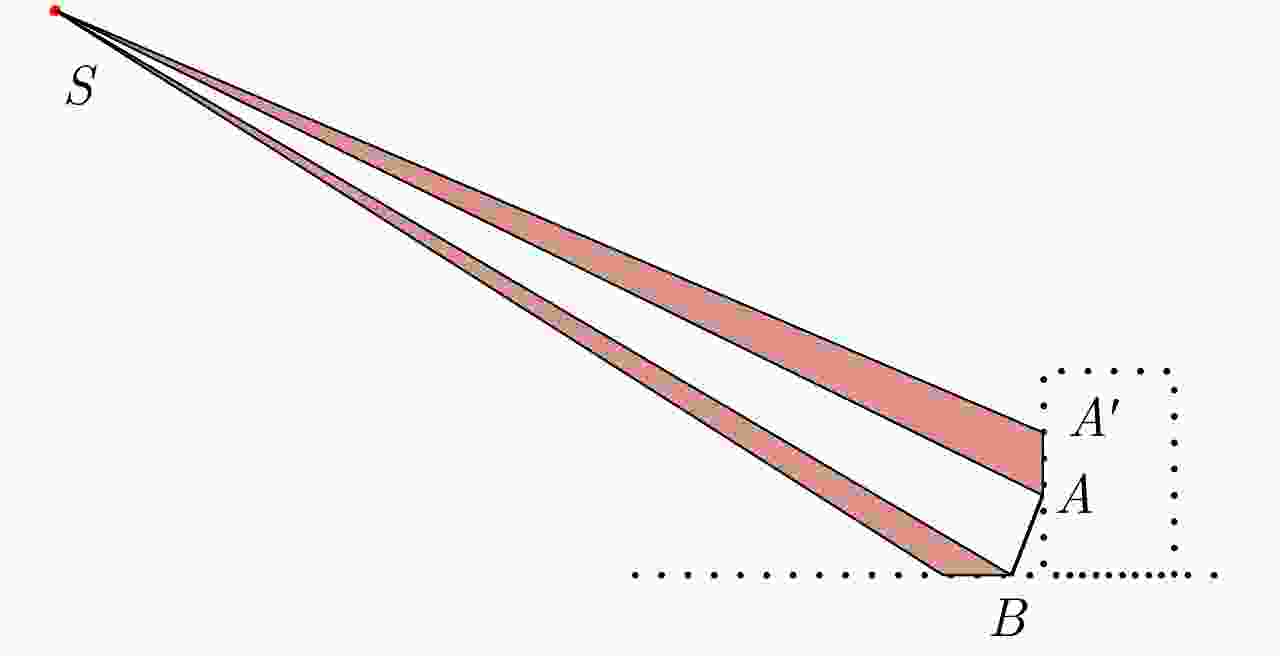
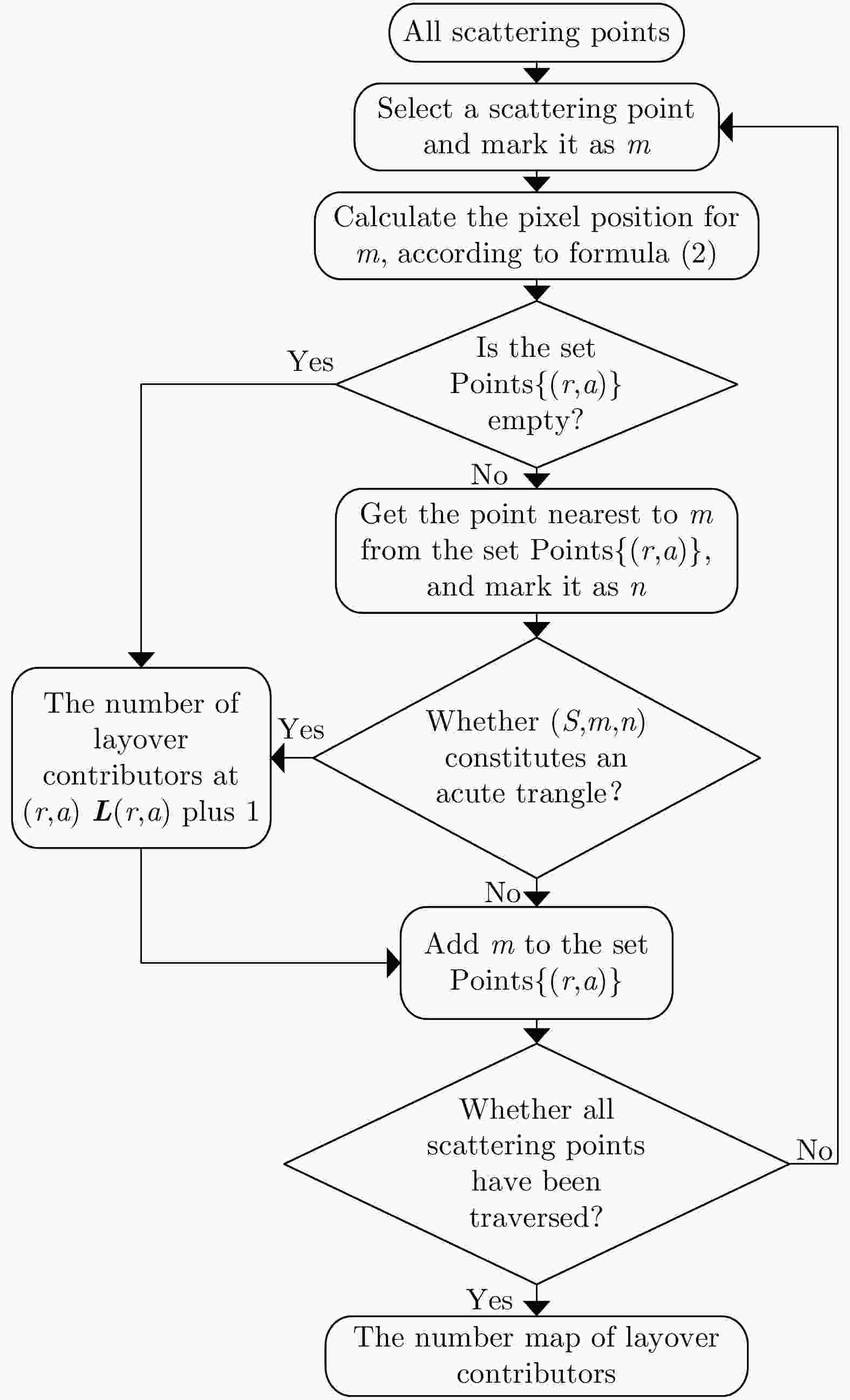
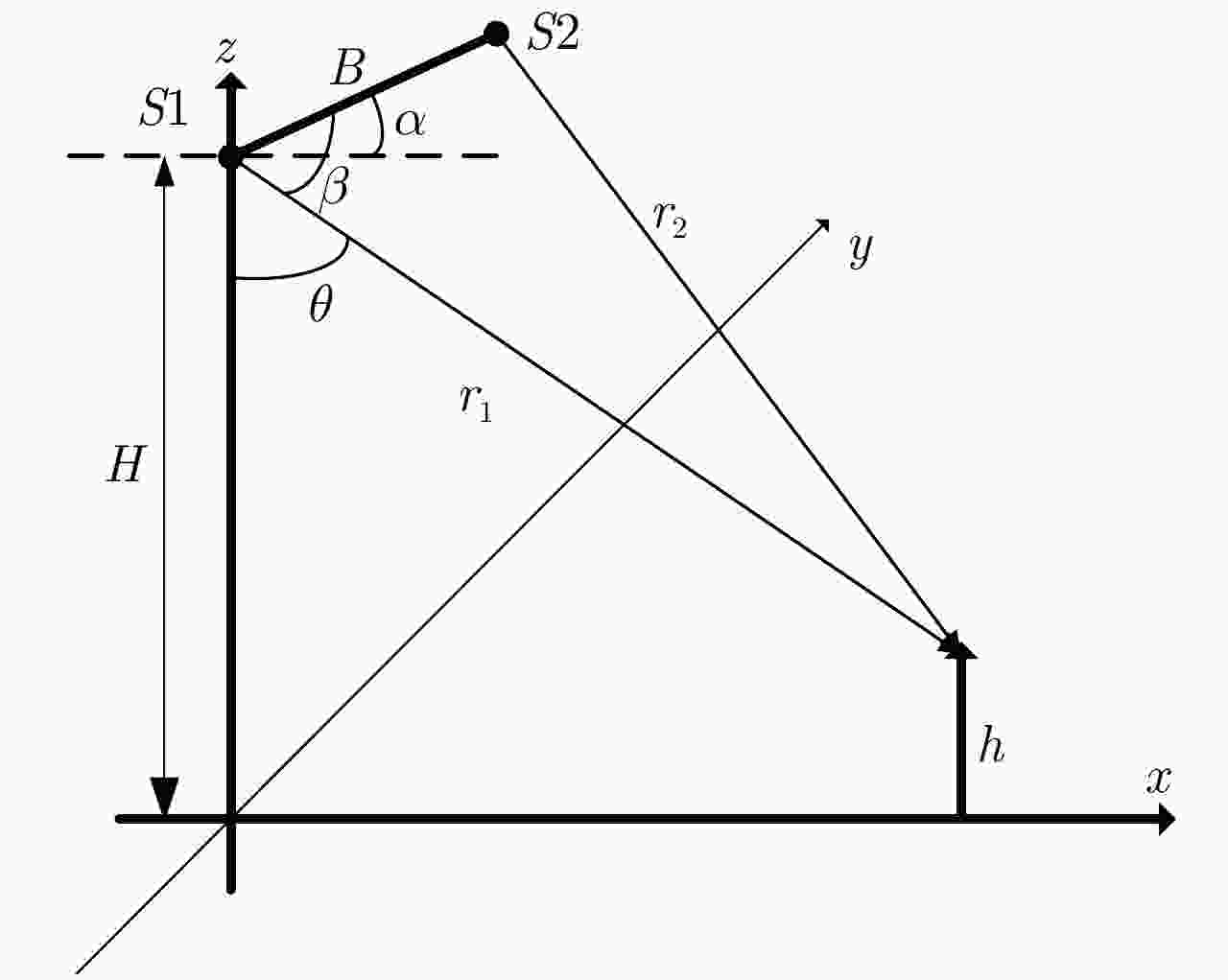
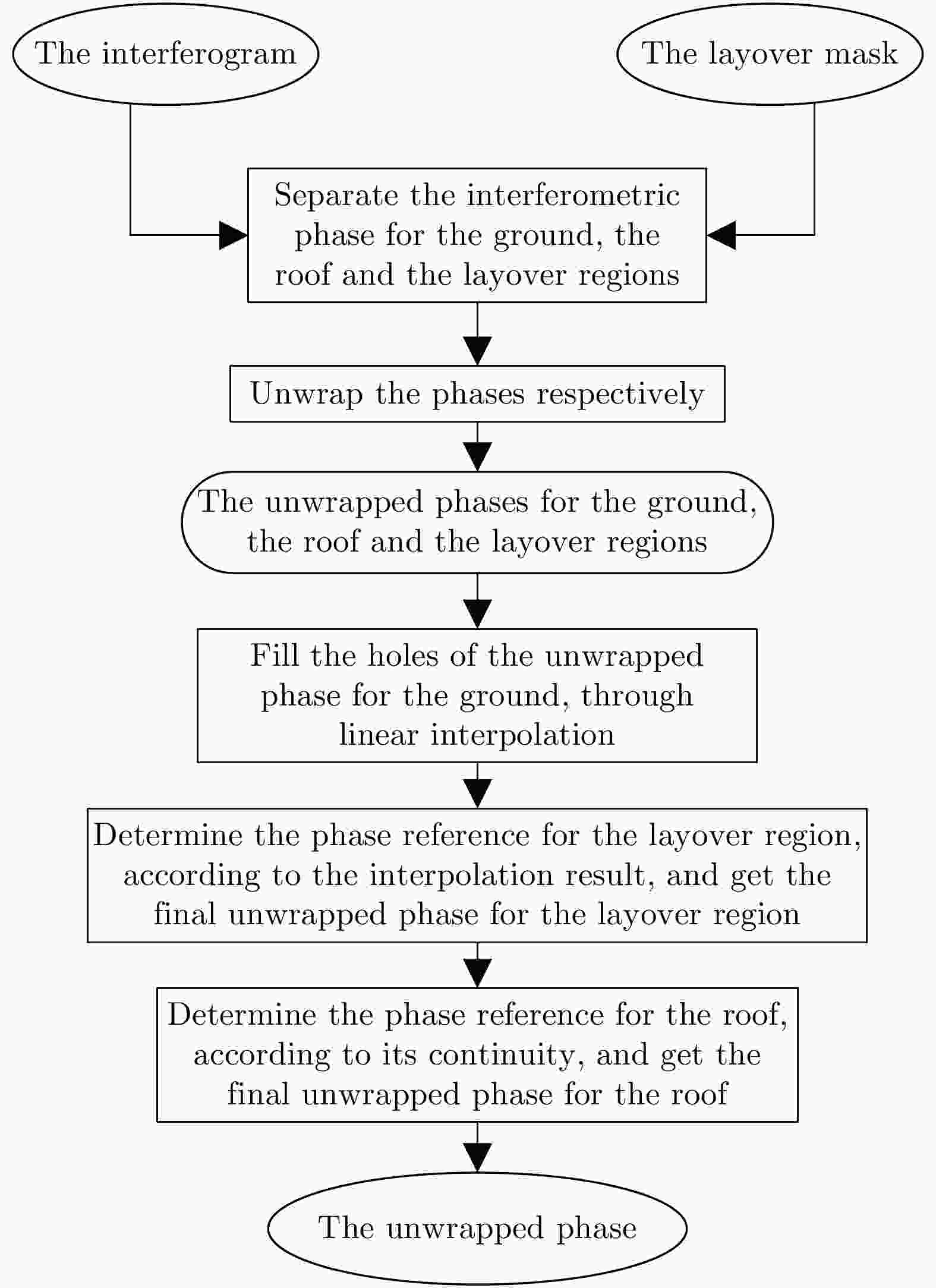
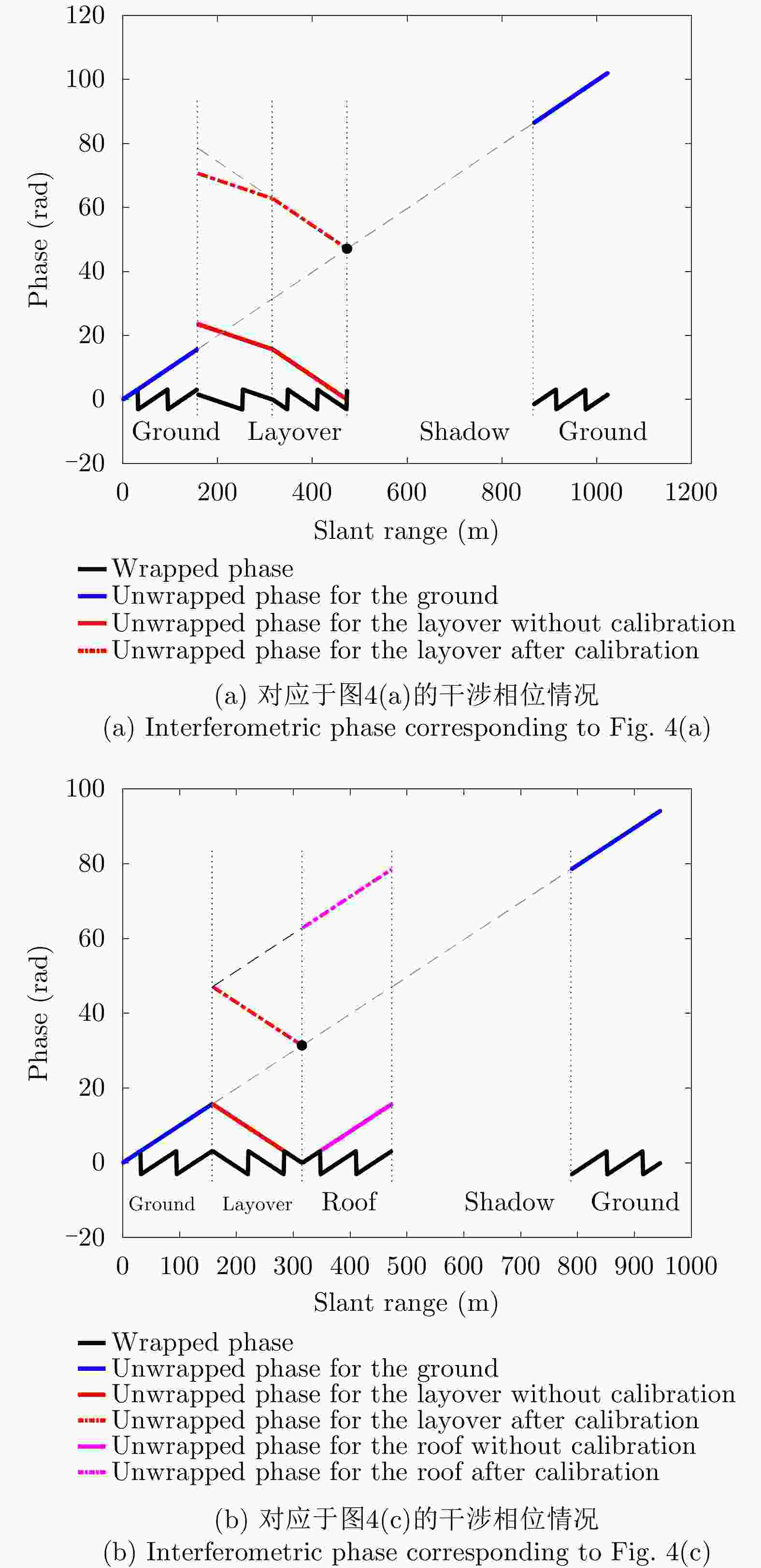
-
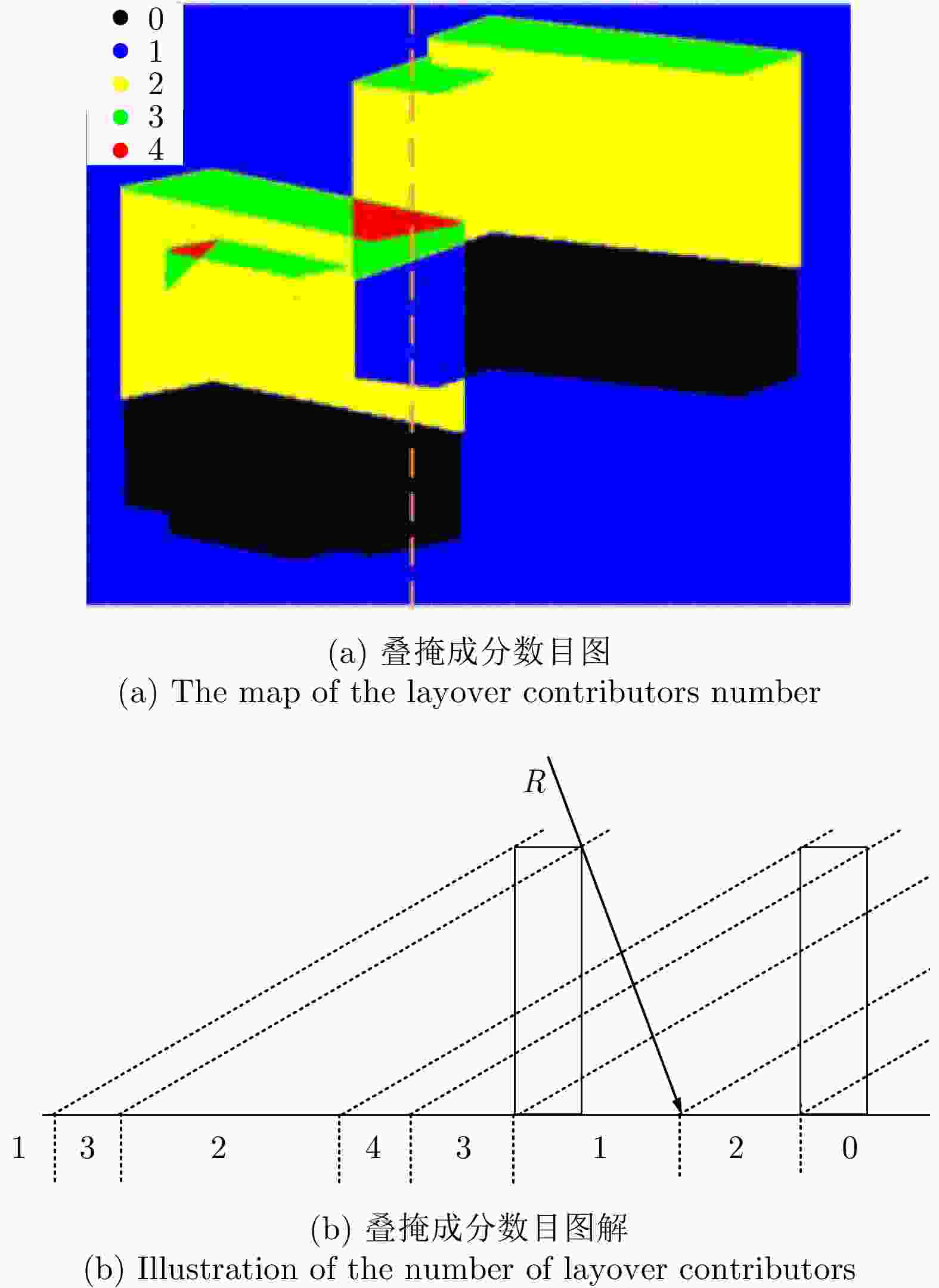
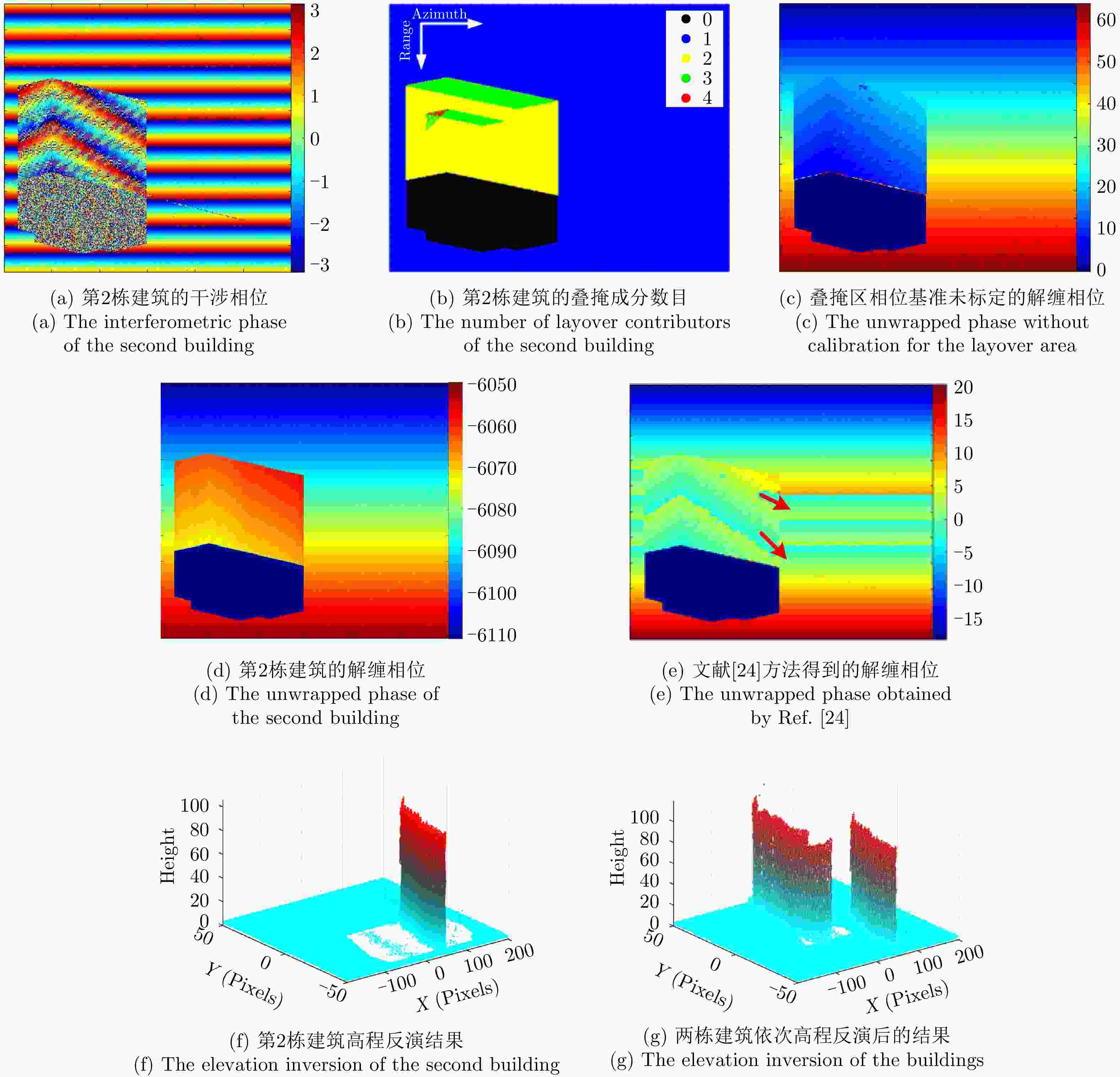
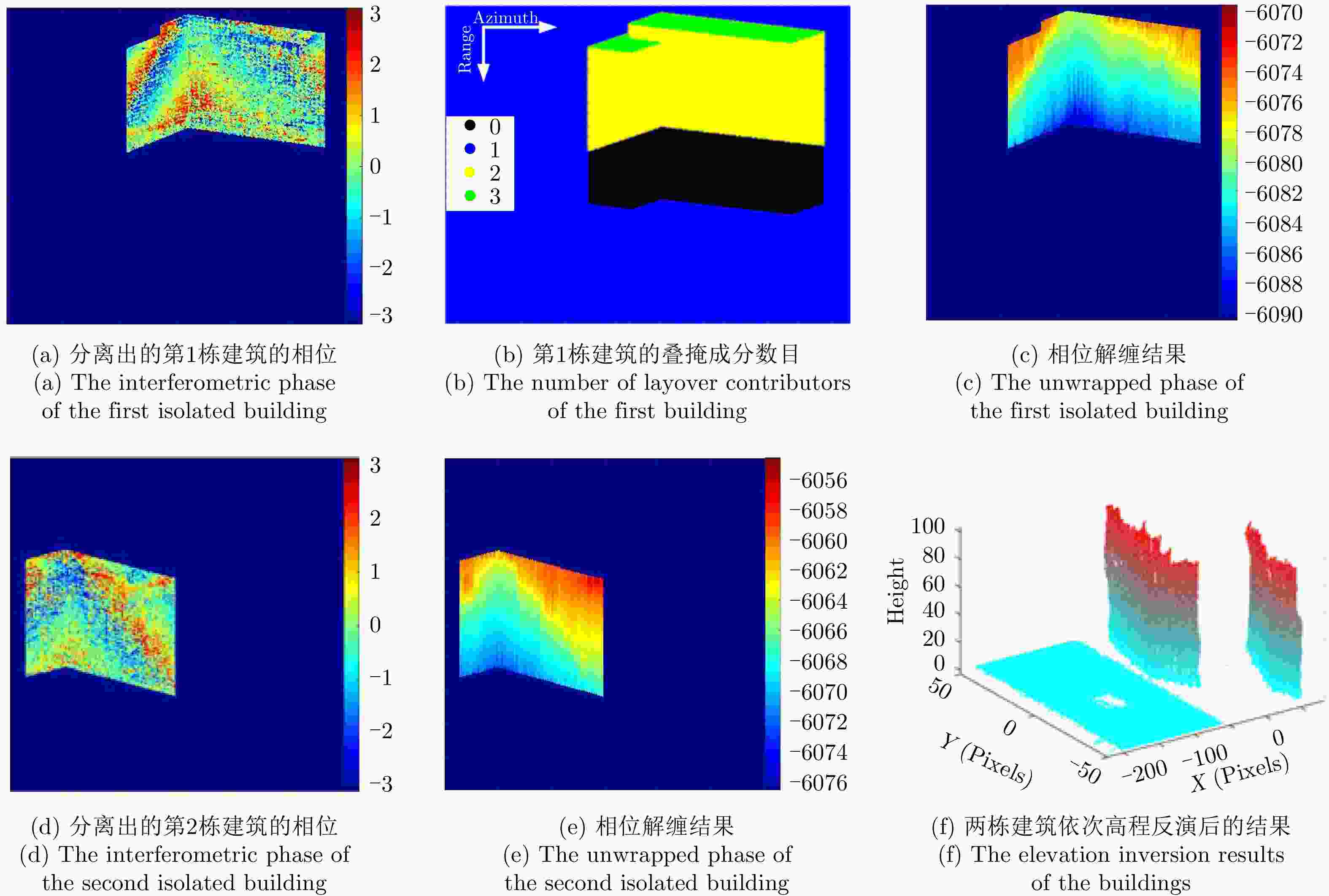
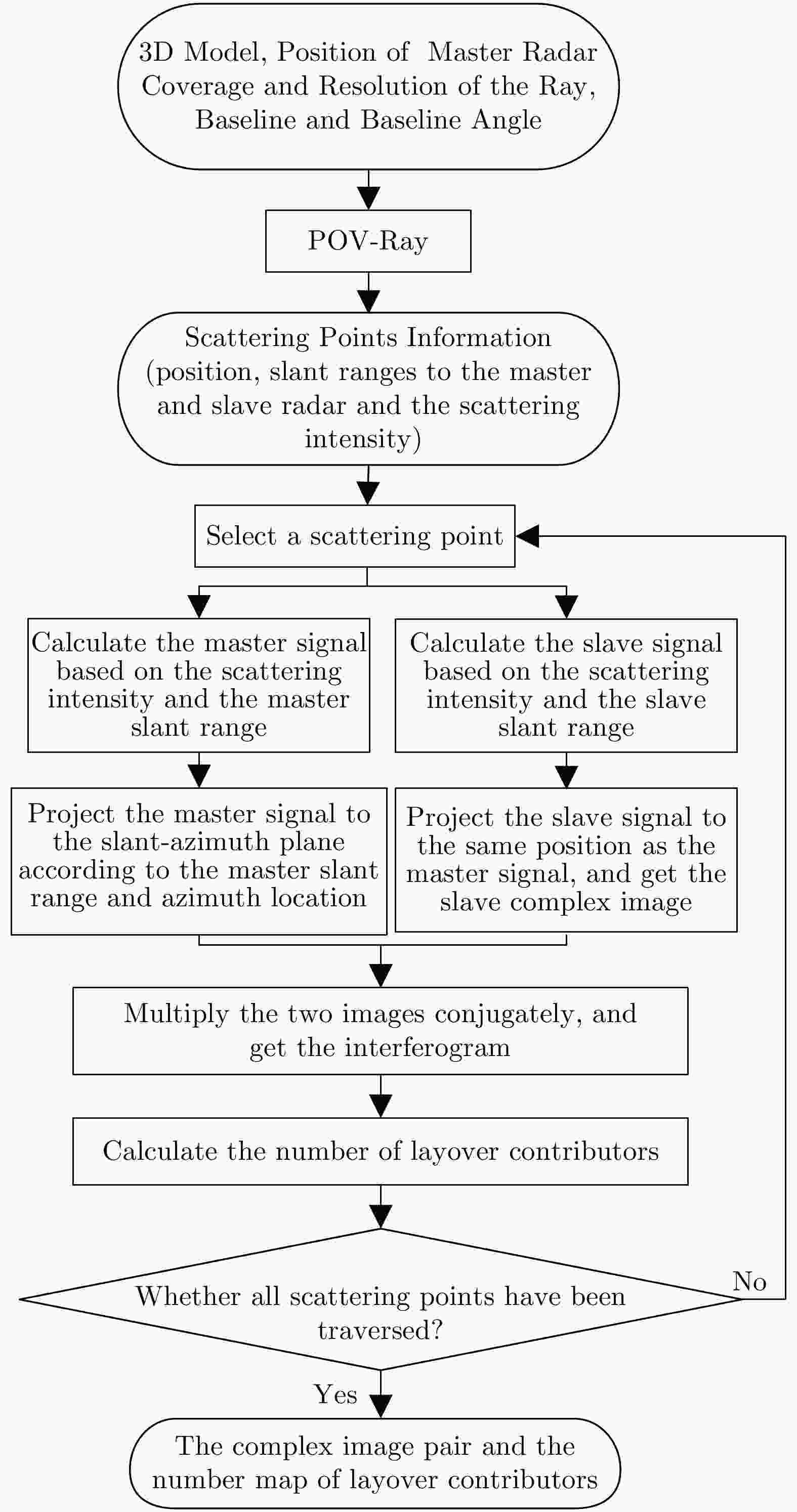
摘要: 城市建筑区域叠掩、阴影严重,图像理解困难且干涉相位变化复杂紊乱,一直是InSAR处理的困难区域。SAR图像仿真能为图像理解和处理方法研究提供数据支撑,然而现有建筑区域SAR图像仿真方法大多无法获得具有相干性的干涉SAR图像对。该文提出了一种面向建筑区域的干涉SAR复图像对仿真方法,能够获得建筑的复数图像对、干涉相位图以及叠掩成分数目等信息,为城区干涉SAR处理及信息提取研究提供仿真数据支撑。同时,基于仿真中对相位变化规律的分析,提出叠掩区相位解缠时的基准确定方法,解决传统解缠方法面临的叠掩区域干涉相位不连续问题,进而反演建筑高程信息。最后,通过建模仿真结果与实际SAR图像和干涉相位的对比,验证了仿真方法的正确性,并对仿真及实际干涉相位进行解缠和高程反演处理,验证了该文高程反演方法的有效性。Abstract: The layover and shadow phenomenon is serious in urban areas, where the interferometric phase is complex and disordered and interpretation of an image is difficult. Therefore, it is always a hot and difficult problem for InSAR processing. SAR image simulation can provide data support for the study of image processing and understanding methods. However, most existing SAR image simulation methods for construction areas cannot obtain coherent interferometric SAR image pairs. This article proposes an InSAR simulation method for buildings. It can simulate complex images, interferograms, and the number of layover components of the construction areas. In addition, based on the analysis of the phase variation characteristics of the simulation, a reference determination method for the unwrapped phase in the layover area is proposed. It solves the problem of discontinuity of the interferometric phase in the construction areas, with which the traditional method of unwrapping cannot deal effectively. We compared the simulated results using the actual SAR images and interferometric phase and verified the correctness of our simulation method. Moreover, we carry out phase unwrapping and elevation inversion experiments using the simulated and real images and verified the effectiveness of our phase unwrapping method in applying the InSAR elevation inversion.
-
表 1 TerraSAR参数及仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of TerraSAR images and simulation
图像 参数 取值 TerraSAR
及仿真距离向分辨率(m) 0.4547 方位向分辨率(m) 0.1670 主图像下视角(°) 54.52 辅图像下视角(°) 54.49 仿真 图像大小(距离,方位) (500, 600) 主雷达位置(m) (0, 500160.3, –356368.6) 基线向量(m) (51.52, –188.1, –238.0) 相位噪声模型 标准差为π/4的高斯随机噪声 表 2 建筑物高程反演结果
Table 2. The elevation inversion results of the buildings
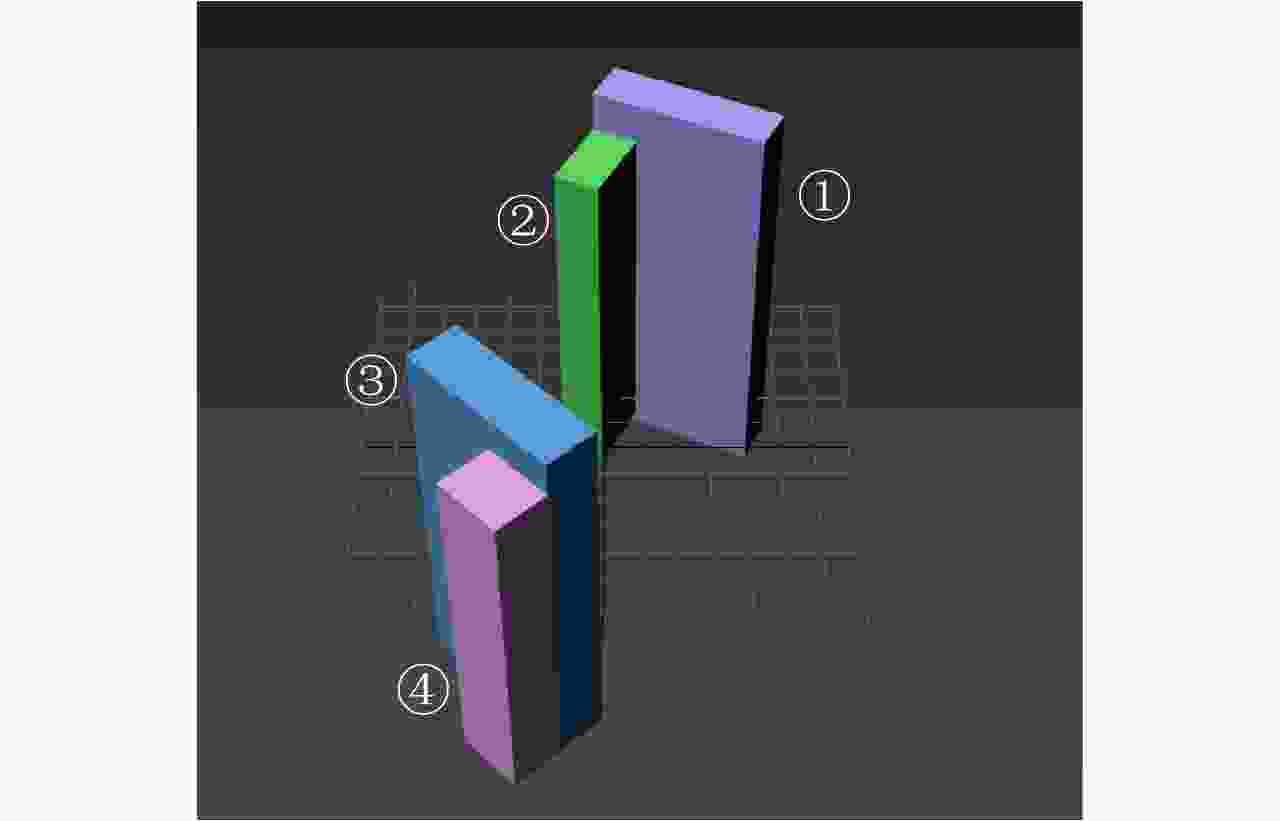
建筑序号 三维模型建筑
高度(m)仿真图像重建高度 真实图像重建高度 均值(m) 标准差(m) 均值(m) 标准差(m) 1 100.5 101.39 1.20 99.75 4.48 2 91.6 92.84 2.56 93.69 2.31 3 98.4 99.90 2.35 99.10 3.17 4 88.3 \ \ \ \ -
[1] LIU Dawei, SUN Guoqing, GUO Zhifeng, et al. Three-dimensional coherent radar backscatter model and simulations of scattering phase center of forest canopies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(1): 349–357. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2024301 [2] LIU Dawei, DU Yang, SUN Guoqing, et al. Analysis of InSAR sensitivity to forest structure based on radar scattering model[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2008, 84: 149–171. doi: 10.2528/PIER08071802 [3] XUE Fengli and XU Feng. Scattering verification and imaging of vegetation and its components[C]. The 2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Hangzhou, China, 2018: 1–4. [4] XUE Fengli and XU Feng. Coherent scattering and PolinSAR imaging simulation of fractal trees[C]. 2018 China International SAR Symposium, Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–4. [5] XU Feng, JIN Yaqiu, and MOREIRA A. A preliminary study on SAR advanced information retrieval and scene reconstruction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1443–1447. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2590878 [6] 张红敏, 靳国旺, 徐青, 等. 多基线InSAR干涉图的直接法仿真[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2010, 27(2): 127–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2010.02.014ZHANG Hongmin, JIN Guowang, XU Qing, et al. Direct algorithm for simulation of multi-baseline InSAR interferograms[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2010, 27(2): 127–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2010.02.014 [7] 靳国旺, 徐青, 张红敏. 合成孔径雷达干涉测量[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014: 176–179.JIN Guowang, XU Qing, and ZHANG Hongmin. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2014: 176–179. [8] AUER S, HINZ S, BAMLER R, et al. Ray-tracing simulation techniques for understanding high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1445–1456. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2029339 [9] AUER S. 3D synthetic aperture radar simulation for interpreting complex urban reflection scenarios[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2011: 62–76. [10] HAMMER H and SCHULZ K. SAR-simulation of large urban scenes using an extended ray tracing approach[C]. 2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Munich, Germany, 2011: 289–292. [11] 孙造宇, 梁甸农, 张永胜. 星载InSAR系统DEM重建及其误差分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(6): 1336–1340. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.01735SUN Zaoyu, LIANG Diannong, and ZHANG Yongsheng. Method and error analysis of DEM reconstruction for spaceborne InSAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2008, 30(6): 1336–1340. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.01735 [12] 林雪, 李曾玺, 李芳芳, 等. 一种自适应迭代的非局部干涉相位滤波方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 166–175. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13123LIN Xue, LI Zengxi, LI Fangfang, et al. An adaptive iterated nonlocal interferometry filtering method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 166–175. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13123 [13] 靳国旺. InSAR获取高精度DEM关键处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 解放军信息工程大学, 2007: 141–146.JIN Guowang. Research on key processing techniques for deriving accurate DEM from InSAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Information Engineering University, 2007: 141–146. [14] 王彦兵, 洪伟, 李小娟, 等. 基于D-InSAR技术的北京城区地面沉降监测[J]. 测绘通报, 2016(5): 66–68, 79.WANG Yanbing, HONG Wei, LI Xiaojuan, et al. Monitoring of land subsidence in Beijing based on D-InSAR[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2016(5): 66–68, 79. [15] 王青松, 时信华, 黄海风, 等. 星载干涉SAR阴影及叠掩区域相位重构方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(4): 699–702.WANG Qingsong, SHI Xinhua, HUANG Haifeng, et al. Method of spaceborne InSAR shadow and layover phase reconstruction[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(4): 699–702. [16] CELLIER F and COLIN E. Building height estimation using fine analysis of altimetric mixtures in layover areas on polarimetric interferometric X-band SAR images[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 4004–4007. [17] LIU Bin, TUPIN F, LIU Xingzhao, et al. Characterization and extraction of building layovers in urban areas using high resolution SAR imagery[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium - IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 895–898. [18] 张同同, 杨红磊, 李东明, 等. SAR影像中叠掩与阴影区域的识别——以湖北巴东为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2019(11): 85–88.ZHANG Tongtong, YANG Honglei, LI Dongming, et al. Identification of layover and shadows regions in SAR images——Taking Badong as an example[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(11): 85–88. [19] ROSSI C and EINEDER M. High-resolution InSAR building layovers detection and exploitation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6457–6468. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2440913 [20] YU Hanwen, LAN Yang, YUAN Zhihui, et al. Phase unwrapping in InSAR: A review[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2019, 7(1): 40–58. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2018.2873644 [21] POV-Ray 3.6.1 documentation[EB/OL]. http://www.povray.org/documentation/index-3.6.php. [22] CHEN Jiankun, PENG Lingxiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. A 3D building reconstruction method for SAR images based on deep neural network[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2019, 49(12): 1606–1625. [23] SUN Y, HUA Y, MOU L, et al. Large-scale building height estimation from single VHR SAR image using fully convolutional network and GIS building footprints[C]. 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Vannes, France, 2019: 1–4. [24] HERRÁEZ M A, BURTON D R, LALOR M J, et al. Fast two-dimensional phase-unwrapping algorithm based on sorting by reliability following a noncontinuous path[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 41(35): 7437–7444. [25] NIU Shengren, QIU Xiaolan, LEI Bin, et al. Parameter prediction method of SAR target simulation based on convolutional neural networks[C]. The 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–5. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: