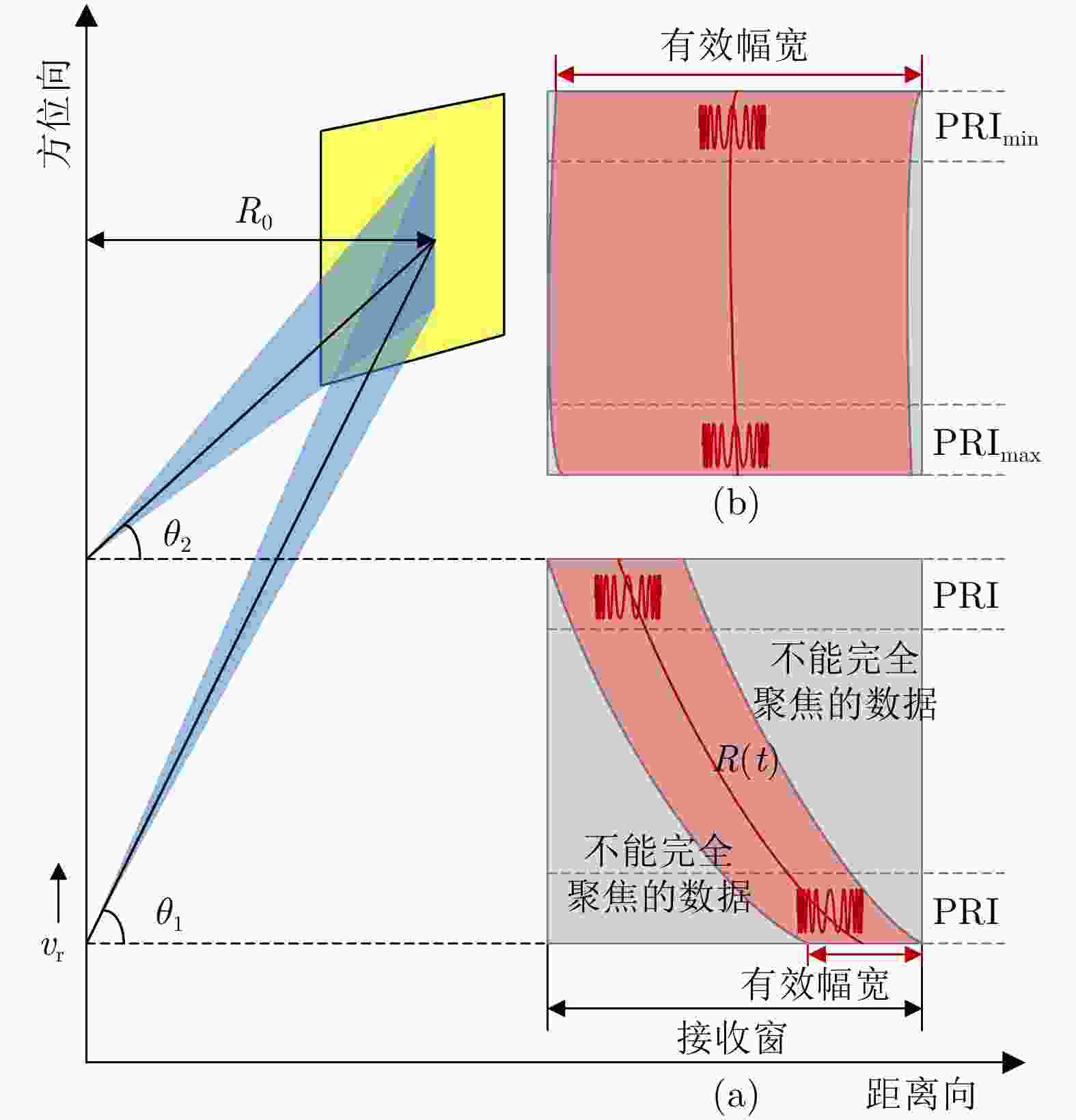
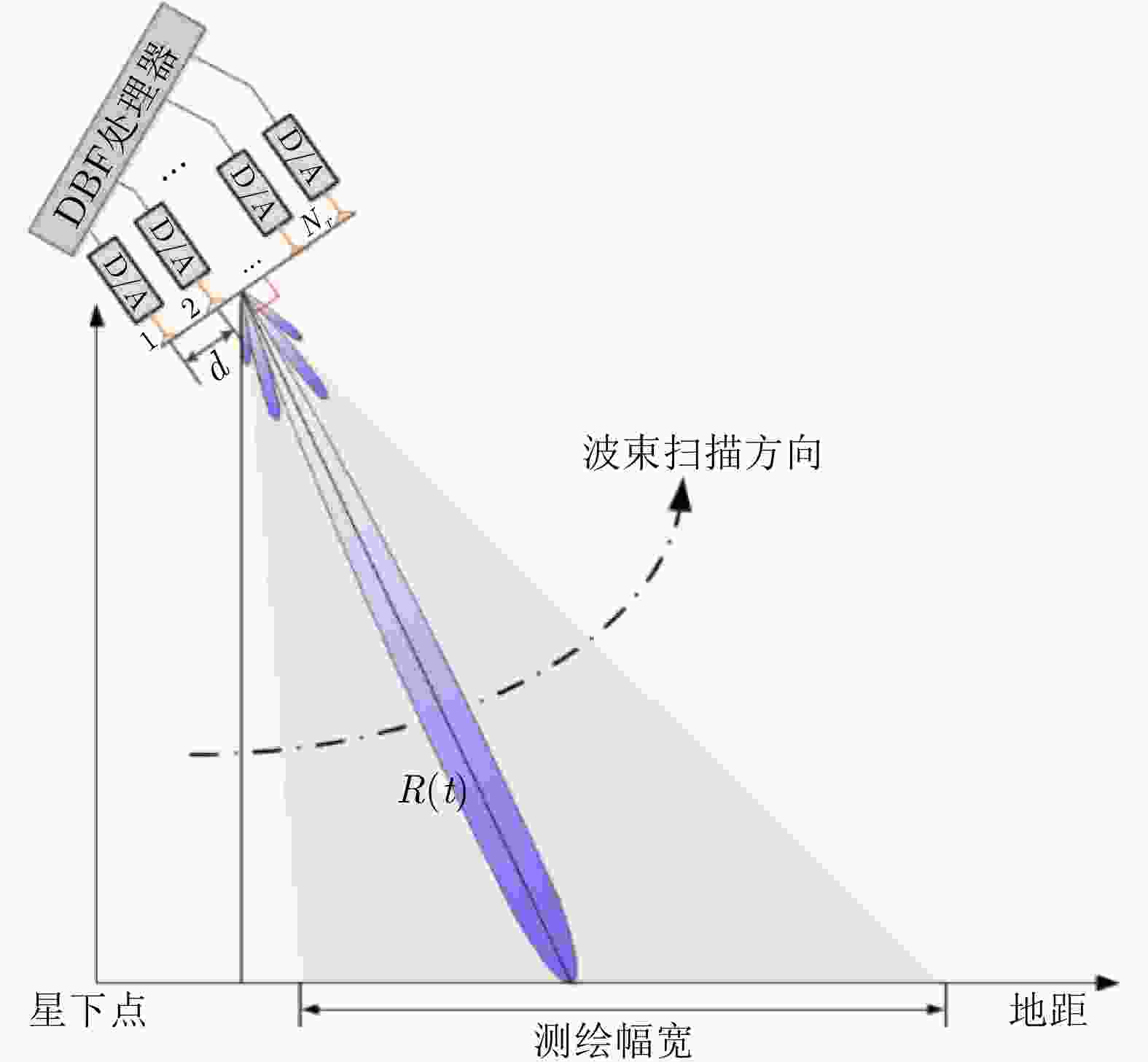
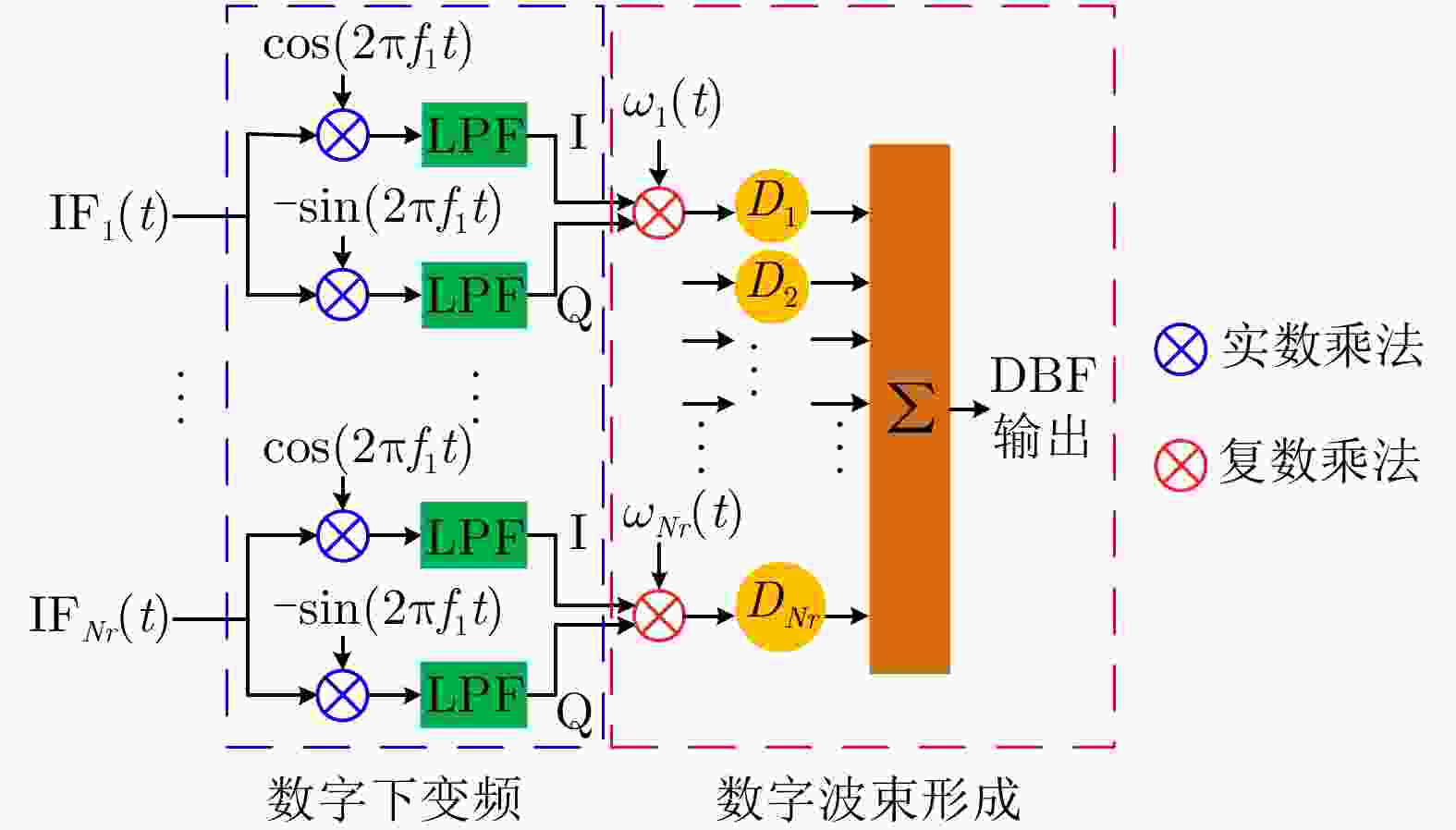
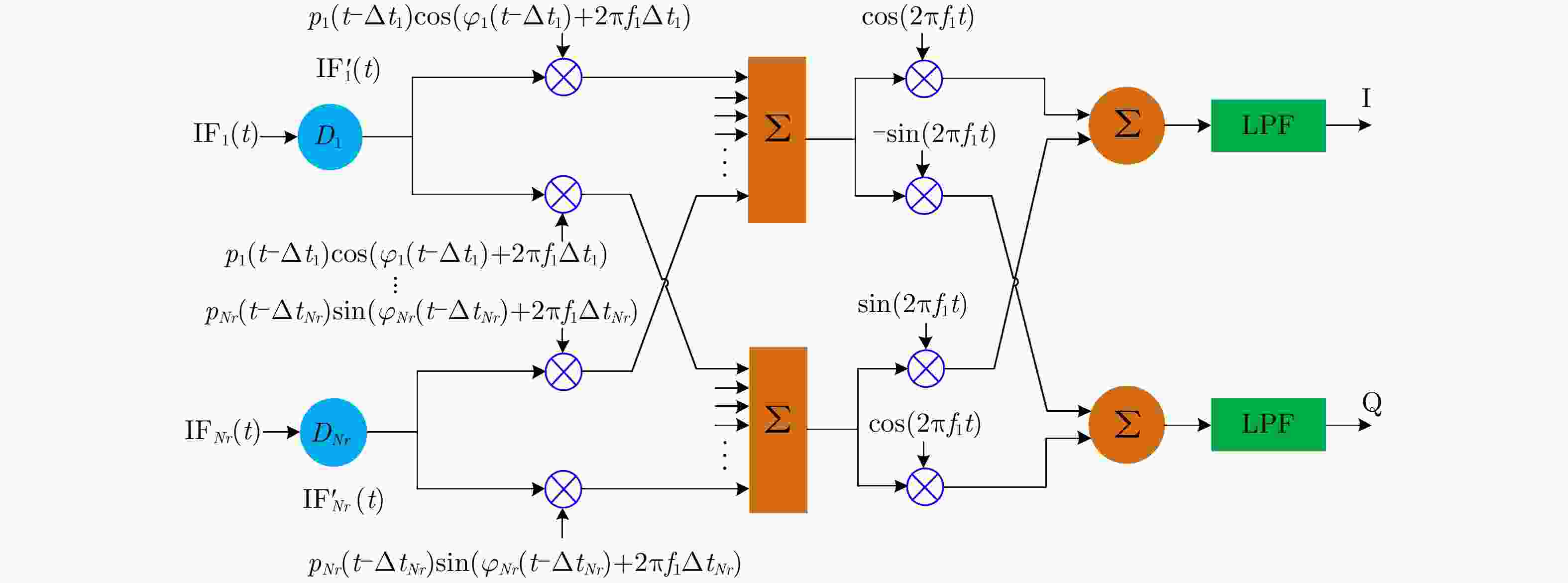
-
摘要: 星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)以卫星等空间飞行器为运动平台,具有全天时、全天候、全球观测能力,已成为一种不可或缺的对地观测手段。当前,我国星载SAR已实现分辨率从米级到亚米级、系统体制从正侧视条带向方位扫描聚束、从单通道向多通道、极化方式从单一极化到全极化的技术跨越。随着技术的不断进步,未来星载SAR将在体制、概念、技术、模式等方面取得突破,包括高分辨率宽幅成像、多基地、轻小型化、智能化等,从而不断拓展星载SAR的观测维度,实现多维度信息获取。该文将围绕星载SAR的技术发展趋势展开论述。Abstract: Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), which can be mounted on space vehicles to collect information of the entire planet with all-day and all-weather imaging capacity, has been an indispensable device for earth observation. Currently, the technology of our spaceborne SAR has achieved a considerable technological improvement, including the resolution change from meter to submeter, the imaging mode from stripmap to azimuth beam steering like the sliding spotlight, the practical application of the multichannel approach and the conversion of single polarization into full polarization. With the development of SAR techniques, forthcoming SAR will make breakthroughs in SAR architectures, concepts, technologies and modes, for example, high-resolution wide-swath imaging, multistatic SAR, payload miniaturization and intelligence. All of these will extend the observation dimensions and obtain multidimensional data. This study focuses on the forthcoming development of spaceborne SAR.
-
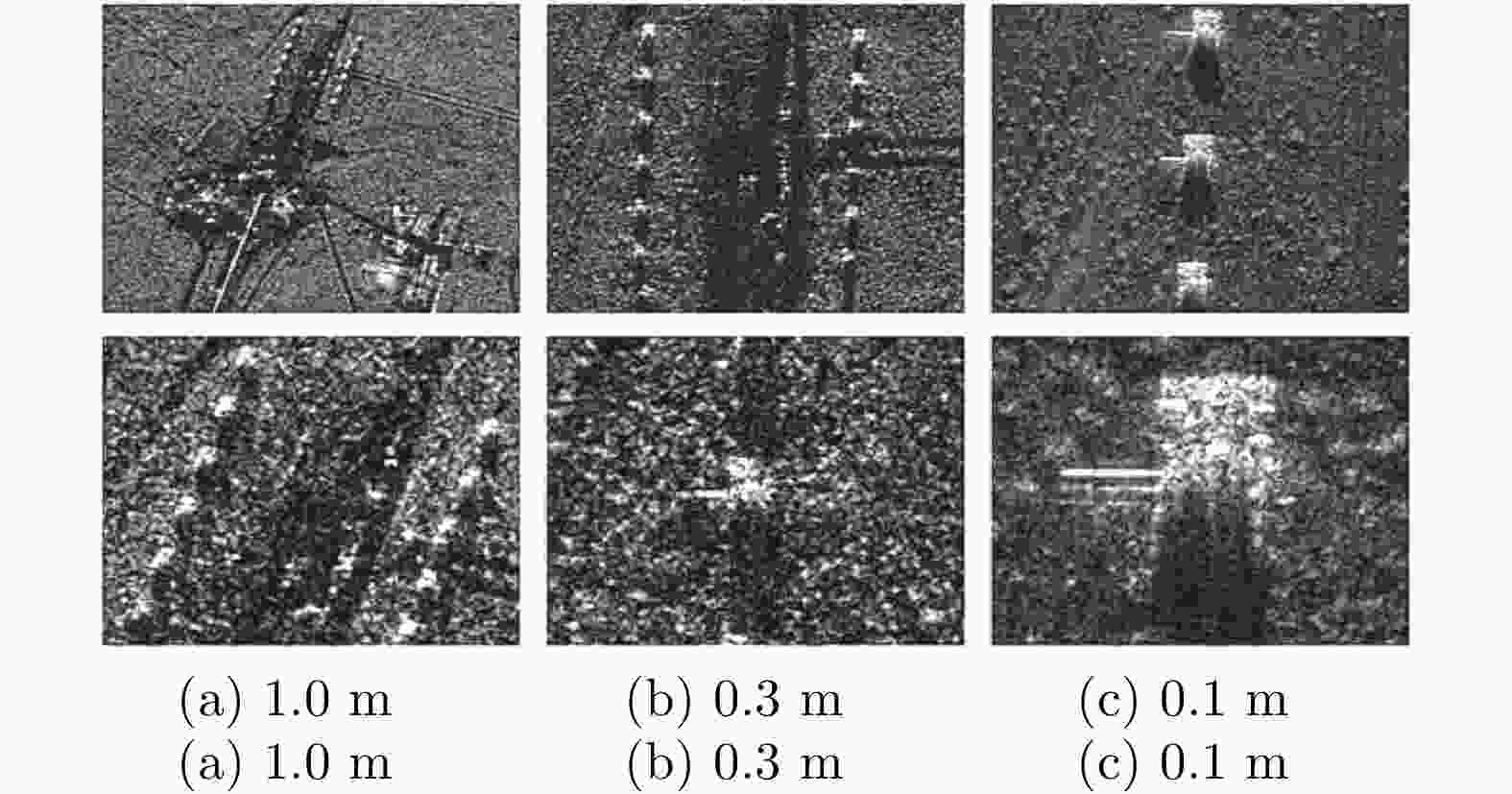
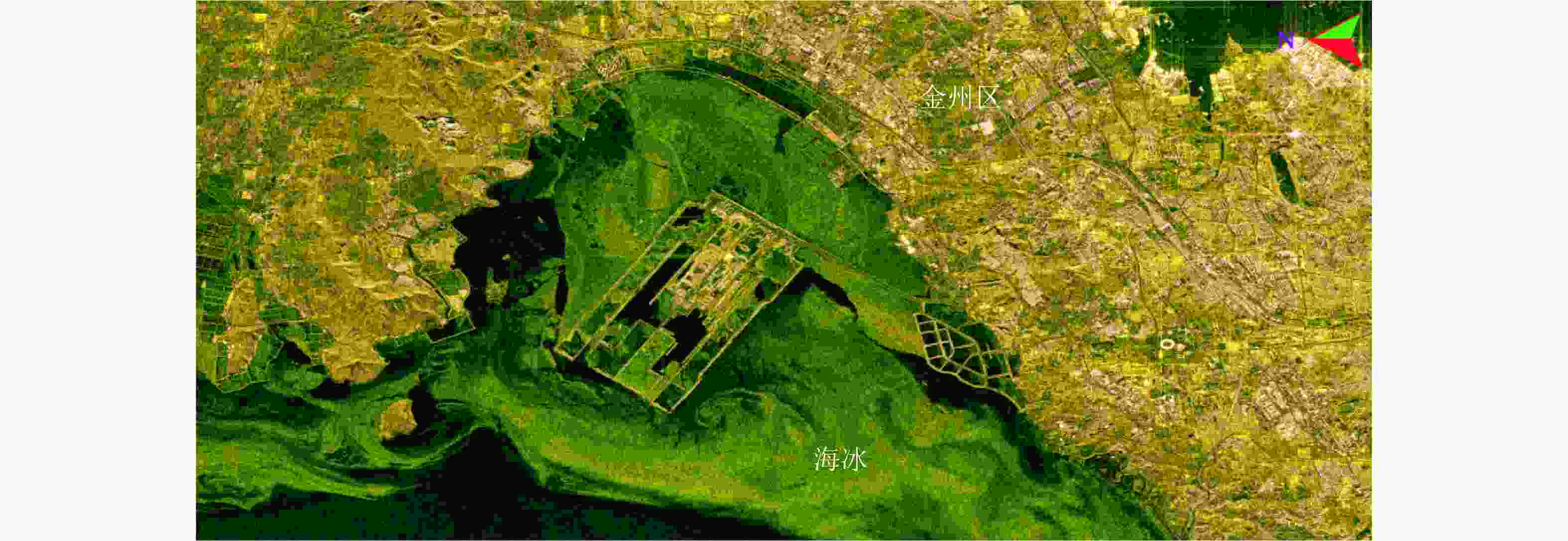
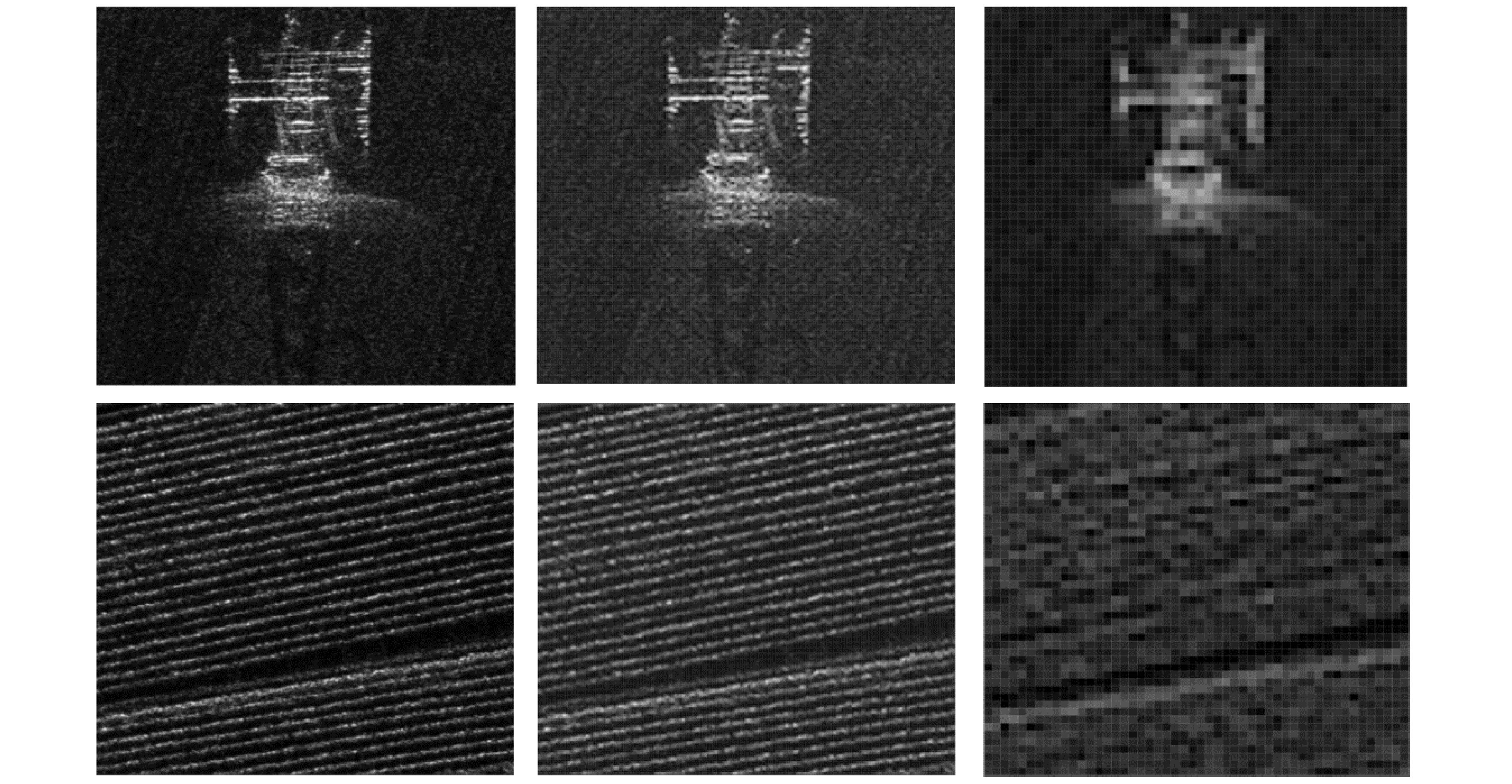
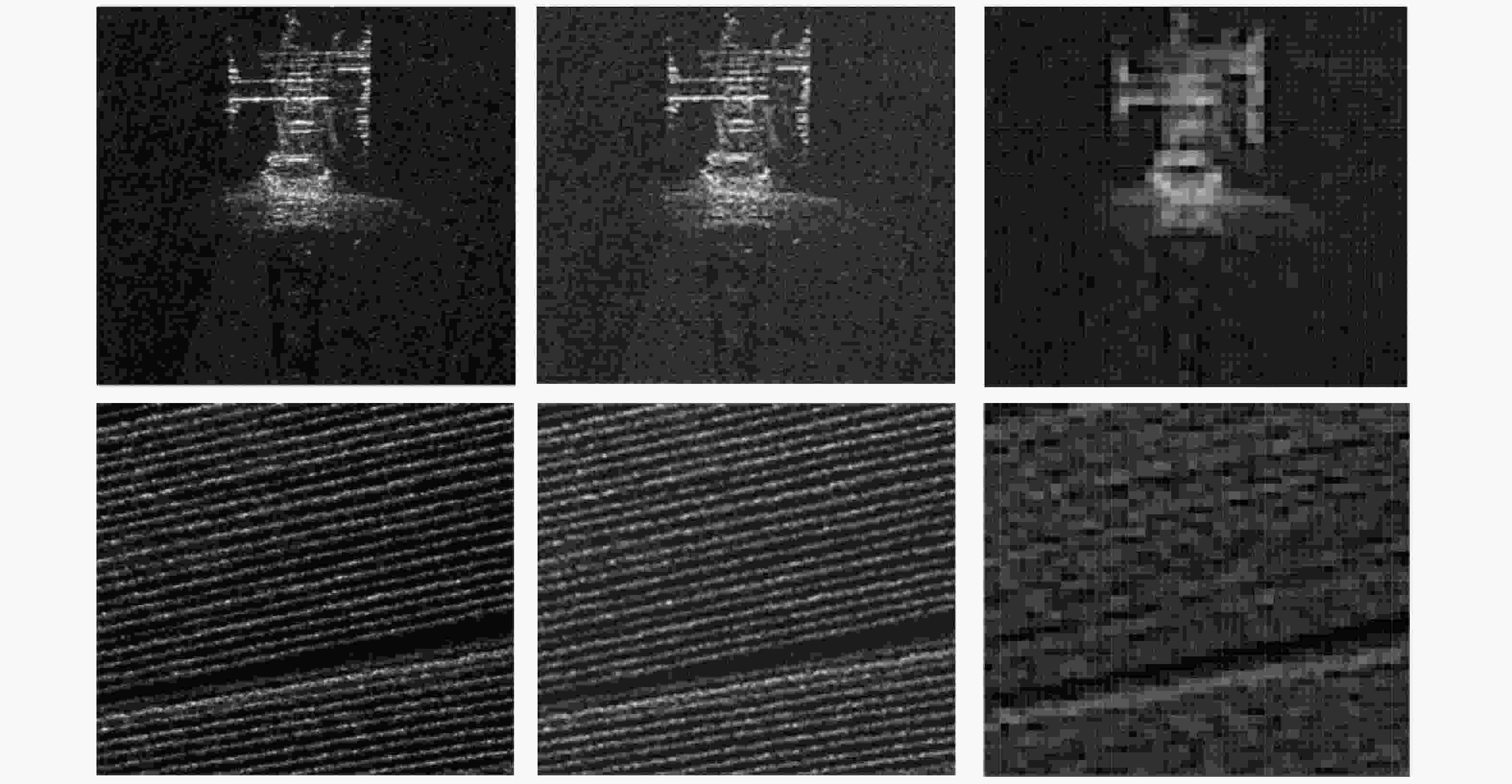
图 1 不同分辨率SAR图像对比(X波段,分辨率自左至右分别为0.1 m, 0.5 m和2.0 m,场景分别为电塔和农田,中国科学院空天信息创新研究院(下文简称AIR-CAS)航天微波遥感系统部供图)
Figure 1. SAR image comparison between different resolution (tower and farm at X band, the resolution are 0.1 m, 0.5 m and 2.0 m. Images are provided by the Department of Space Microwave Remote Sensing System, AIR-CAS)
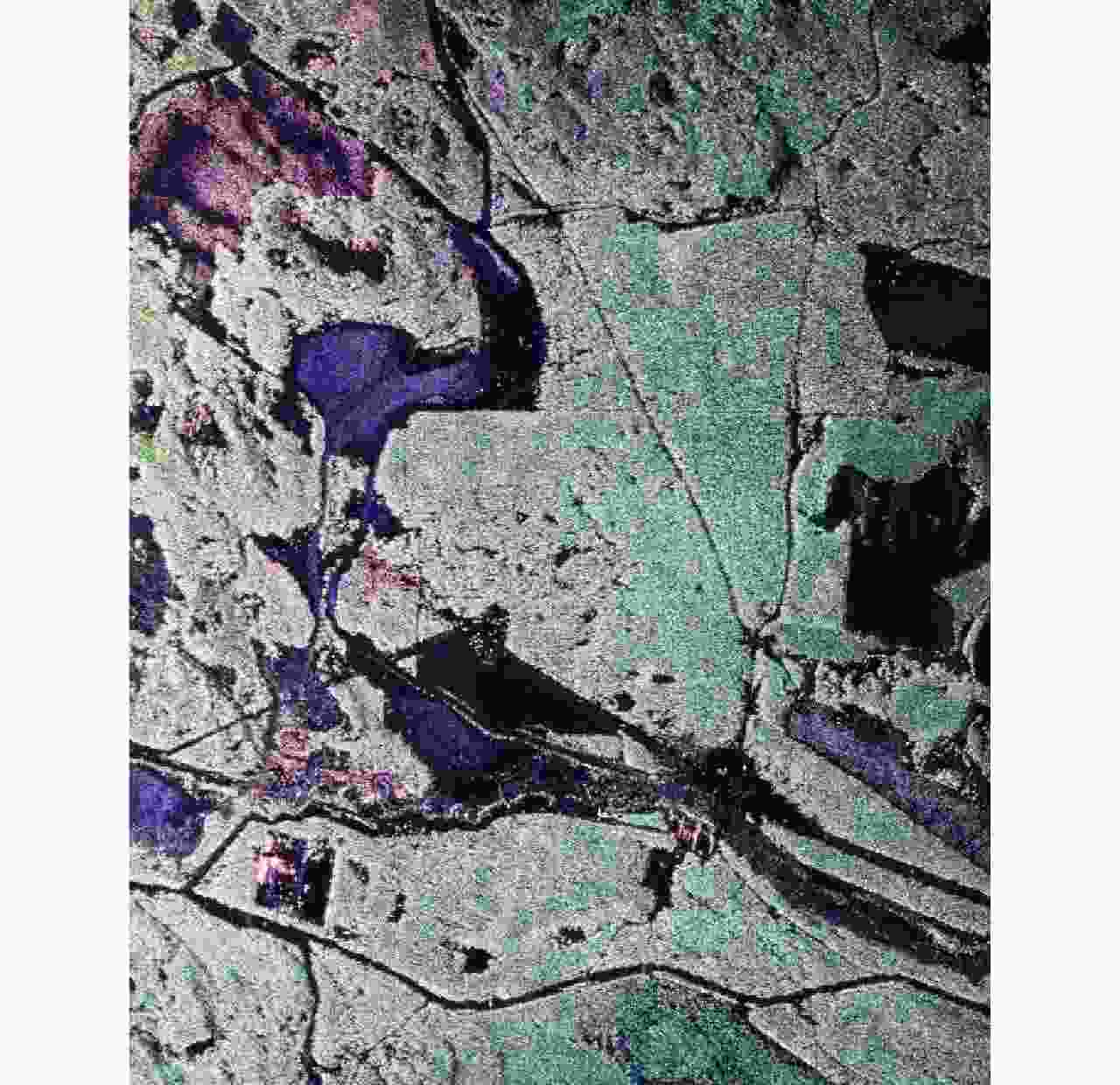
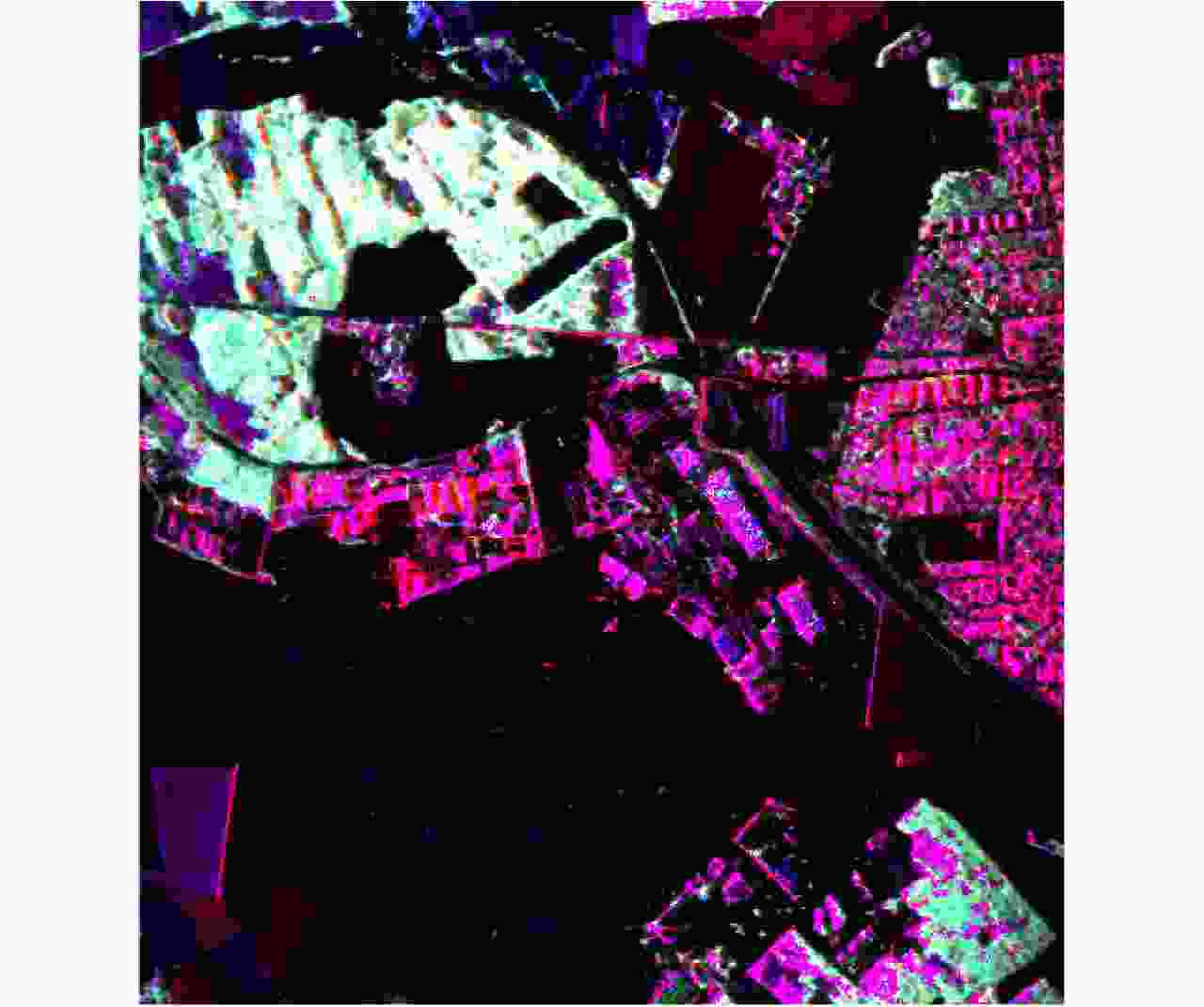
图 35 机载P波段混合极化SAR(圆极化发射/双线极化接收)极化分解图像:红色表示偶次散射,蓝色表示表面散射,绿色表示体散射(AIR-CAS供图)
Figure 35. Polarimetric decomposition image of airborne P-band hybrid polarimetric SAR (circularly polarized on transmit and dual-circularly polarized on receive) Red for double-bounce scattering, blue for single-bounce scattering and green for volume scattering (Image provided by AIR-CAS)
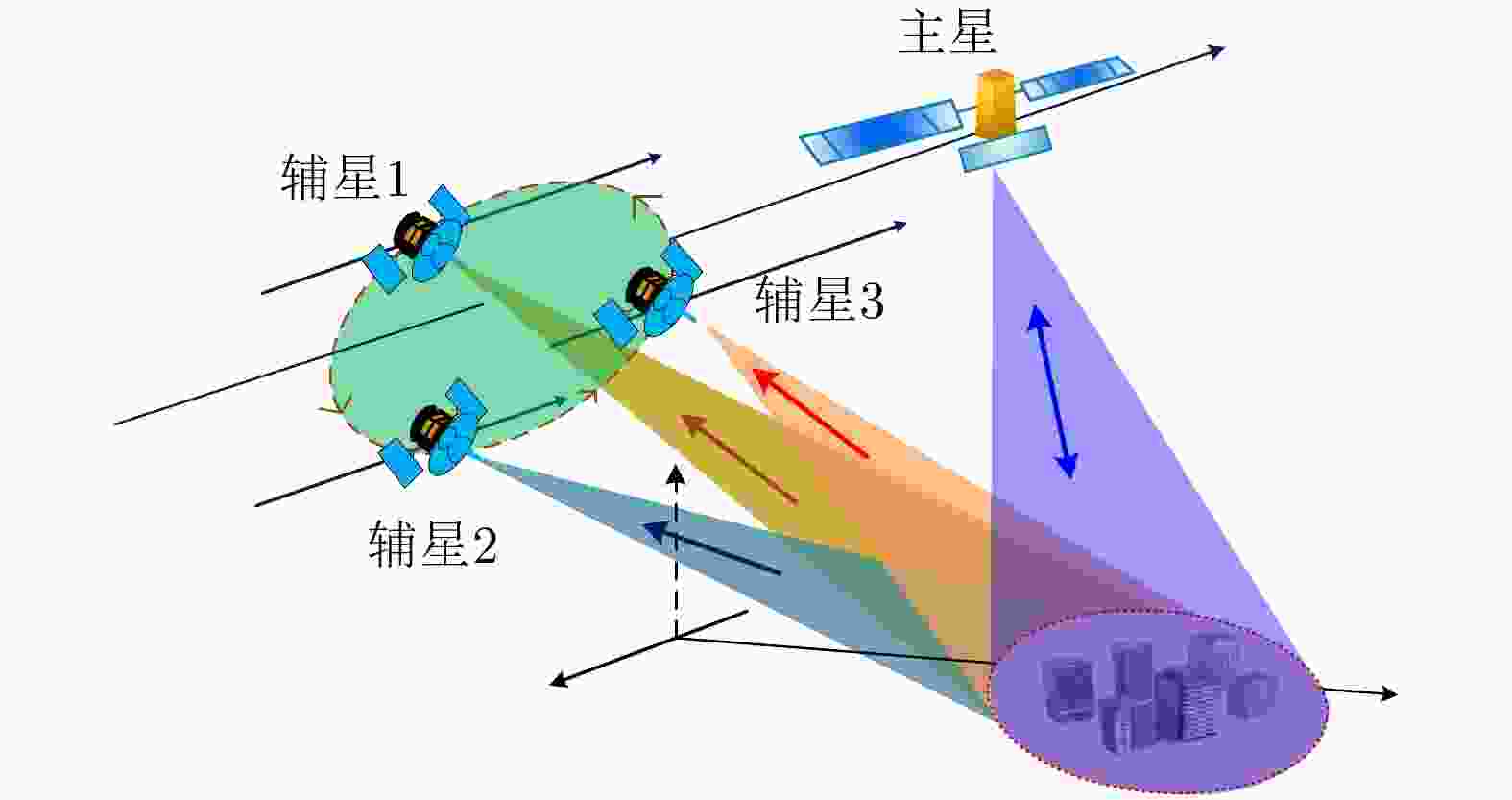
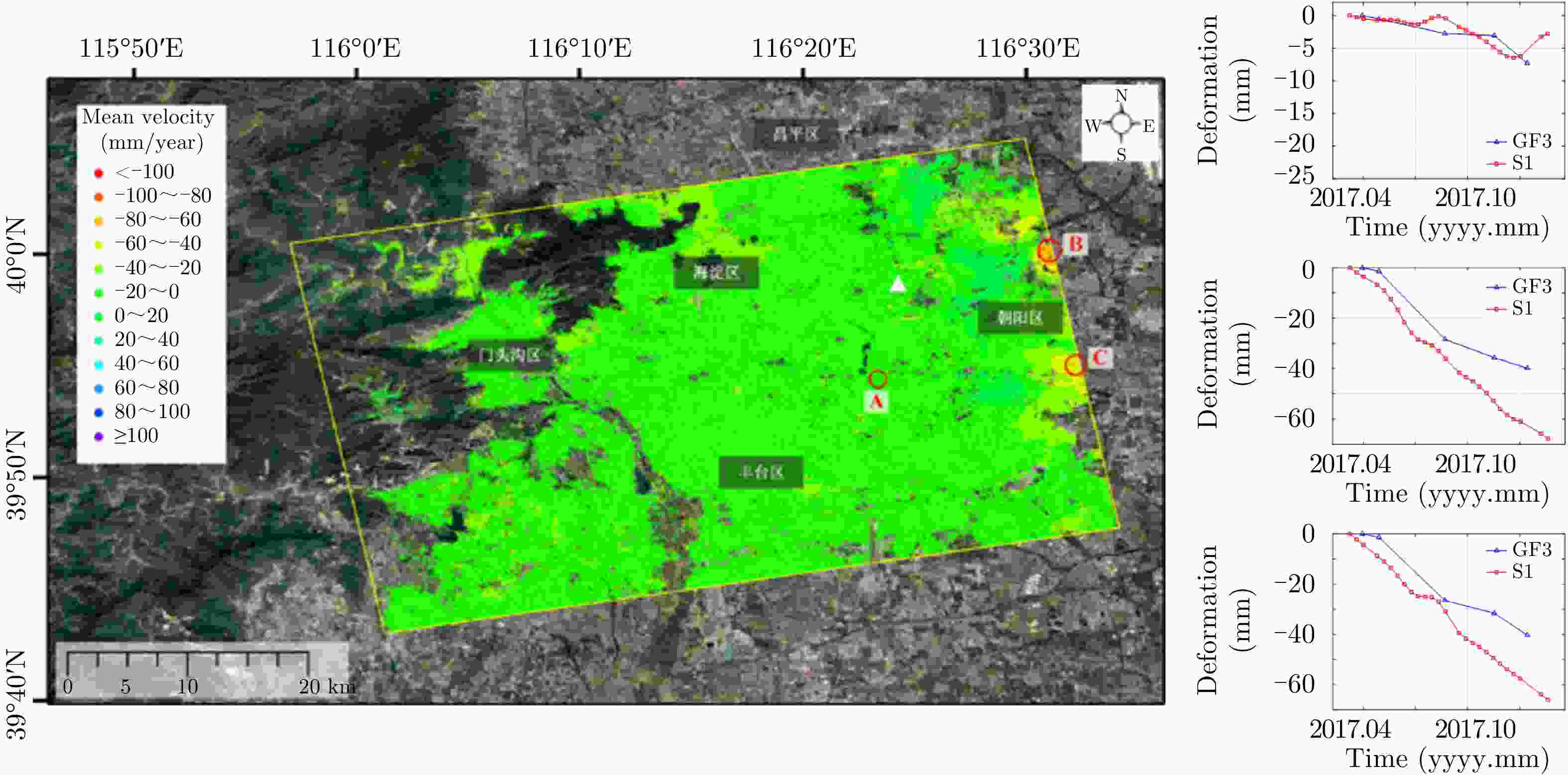
表 1 SAR图像分辨率与典型军事目标关系(m)
Table 1. The relationship between the resolution and typical military targets (m)
目标 发现 识别 确认 描述 雷达 3 0.9 0.3 0.15 无线通讯设施 3 1.5 0.3 0.15 部队单位或营地 3 3 1.2 0.3 机场设施 6 4.5 3 0.3 火炮兵器/火箭 0.9 0.6 0.15 0.05 飞机 4.5 1.5 0.9 0.15 司令部 3 1.5 0.9 0.15 导弹阵地 3 1.5 0.6 0.3 中小型船只 7.5 4.5 0.6 0.3 车辆 1.5 0.6 0.3 0.05 表 2 DEM指标划分标准(m)
Table 2. Index classification criteria of DEM(m)
空间分辨率 绝对高程精度 相对高程精度 HRTI-1 90 ×90 < 30 < 20 HRTI-2 30 ×30 < 18 < 12 HRTI-3 12 ×12 < 10 < 2 HRTI-4 6 ×6 < 5 < 0.8 HRE-4 4 ×4 < 5 < 0.8 表 3 不同体制的优缺点对比
Table 3. Advantages and disadvantages comparison between different systems
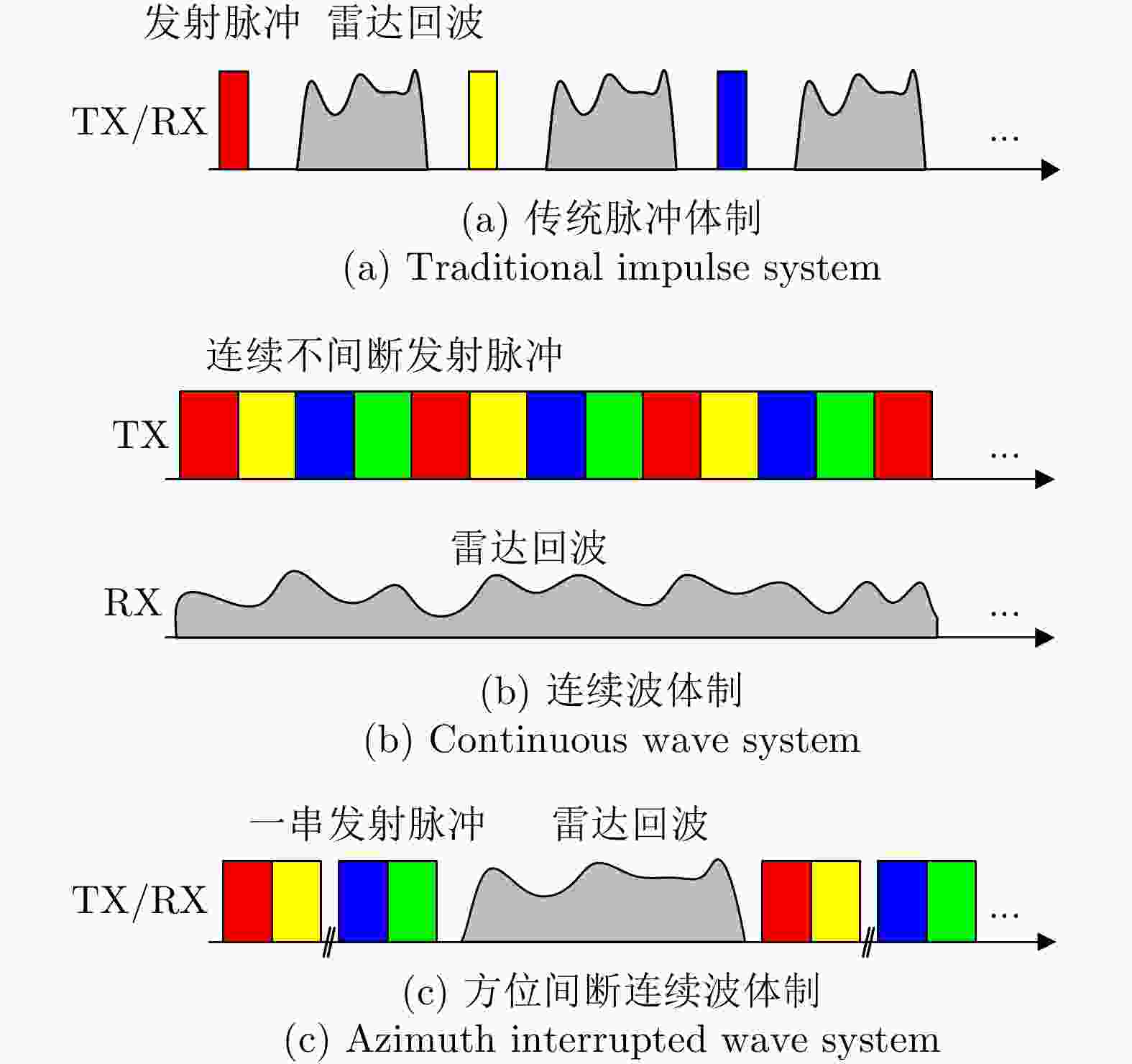
信号体制 优点 缺点 传统脉冲体制 收发天线共用 占空比低,发射功率大 连续波体制 占空比~100%,峰值功率低 收发天线无法共用 间断连续波体制 占空比90~100%,结合脉冲与连续波的优势 回波信号部分缺失,需要估计重构 -
[1] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [2] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [3] 魏钟铨. 合成孔径雷达卫星[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.WEI Zhongquan. Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. [4] REIGBER A, SCHEIBER R, JAGER M, et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2013, 101(3): 759–783. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2220511 [5] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 260–264. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.832700 [6] 范剑超, 王德毅, 赵建华, 等. 高分三号SAR影像在国家海域使用动态监测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 456–472. doi: 10.12000/JR17080FAN Jianchao, WANG Deyi, ZHAO Jianhua, et al. National sea area use dynamic monitoring based on GF-3 SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 456–472. doi: 10.12000/JR17080 [7] KRIEGER G and MOREIRA A. Spaceborne Bi- and multistatic SAR: Potential and challenges[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(3): 184–198. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045111 [8] KRIEGER G, MOREIRA A, FIEDLER H, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3317–3341. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900693 [9] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [10] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston, MA: Artech House, 1995. [11] 王伟. 新体制星载SAR成像模型与二维多通道技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2016.WANG Wei. Study on new imaging model and two-dimensional multi-channel techniques for spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], UCAS, 2016. [12] WANG Xiangyu, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Precise calibration of channel imbalance for very high resolution SAR with stepped frequency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4252–4261. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2688728 [13] GEBERT N, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Digital beamforming on receive: Techniques and optimization strategies for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 564–592. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089542 [14] YOUNIS M, ROMMEL T, BORDONI F, et al. On the pulse extension loss in digital beamforming SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1436–1440. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2406815 [15] WANG Wei, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. An improved processing scheme of digital beam-forming in elevation for reducing resource occupation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 309–313. [16] WANG Hui, ZHANG Hui, DAI Shoulun, et al. Azimuth multichannel GMTI based on Ka-band DBF-SCORE SAR system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(3): 419–423. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2791622 [17] ZHAO Qingchao, ZHANG Yi, WANG Wei, et al. On the frequency dispersion in DBF SAR and digital scalloped beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958863 [18] RINCON R F, VEGA M A, BUENFIL M, et al. NASA’s L-band digital beamforming synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3622–3628. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2157971 [19] BERGER M, MORENO J, JOHANNESSEN J A, et al. ESA’s sentinel missions in support of Earth system science[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 120: 84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.023 [20] LUO Xiulian, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Image formation processing for sliding spotlight SAR with stepped frequency chirps[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1692–1696. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2306206 [21] 罗秀莲. 新体制星载聚束/滑动聚束SAR信号处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015.LUO Xiulian. Study on signal processing of novel spaceborne spotlight/sliding spotlight SAR data[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], UCAS, 2015. [22] RANEY R K and PRINCZ G J. Reconsideration of azimuth ambiguities in SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1987. [23] YOUNIS M. General formulation of NESZ[R]. Technical Note TN-SAR-Tech-001, 2008. [24] CURRIE A and BROWN M A. Wide-swath SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings F - Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(2): 122–135. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0016 [25] ZHAO Shuo, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Modifications on multichannel reconstruction algorithm for SAR processing based on periodic nonuniform sampling theory and nonuniform fast fourier transform[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 4998–5006. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2421303 [26] CERUTTI-MAORI D, SIKANETA I, KLARE J, et al. MIMO SAR processing for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 5034–5055. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2286520 [27] LIU Baochang and HE Yijun. Improved DBF algorithm for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2476496 [28] WANG Wei, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Azimuth ambiguity suppression with an improved reconstruction method based on antenna pattern for multichannel synthetic aperture radar systems[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(5): 492–500. [29] LIU Na, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Modified multichannel reconstruction method of SAR with highly nonuniform spatial sampling[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(2): 617–627. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2630048 [30] ZHANG Yongwei, WANG Wei, DENG Yunkai, et al. Signal reconstruction algorithm for azimuth multichannel SAR system based on a multiobjective optimization model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2959217 [31] CHENG Pu, WAN Jianwei, XIN Qin, et al. An improved azimuth reconstruction method for multichannel SAR using Vandermonde matrix[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 67–71. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2626309 [32] CHEN Renyuan, JIANG Kai, YONG Yanmei, et al. High resolution dual channel receiving SAR compensation technique[C]. 2007 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 2007: 713–717. [33] GIERULL C H. Digital channel balancing of along-track interferometric SAR data[R]. Technical Memorandum TM 2003-024, 2003. [34] LIU Aifei, LIAO Guisheng, MA Lun, et al. An array error estimation method for constellation SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(4): 731–735. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2046878 [35] YANG Taoli, LI Zhenfang, LIU Yanyang, et al. Channel error estimation methods for multichannel SAR systems in azimuth[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 548–552. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2212873 [36] LIU Yanyang, LI Zhenfang, YANG Taoli, et al. An adaptively weighted least square estimation method of channel mismatches in phase for multichannel SAR systems in azimuth[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(2): 439–443. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2264771 [37] 郜参观. 高分辨率宽测绘带合成孔径雷达的新体制研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2012.GAO Canguan. Study on the new concept of high-resolution and wide-swath synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], UCAS, 2012. [38] FENG Jin, GAO Canguan, ZHANG Yi, et al. Phase mismatch calibration of the multichannel SAR based on azimuth cross correlation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 903–907. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2227107 [39] 陈倩, 邓云凯, 刘亚东, 等. 基于自适应滤波的DPC-MAB SAR方位向信号重建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(6): 1331–1336. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01074CHEN Qian, DENG Yunkai, LIU Yadong, et al. SAR azimuth signal reconstruction based on adaptive filtering for the DPC-MAB SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(6): 1331–1336. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01074 [40] ZHANG Lei, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. Channel error compensation for multi-channel SAR based on cost function[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 556–564. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14052 [41] MOREIRA A, KRIEGER G, HAJNSEK I, et al. Tandem-L: A highly innovative bistatic SAR mission for global observation of dynamic processes on the earth’s surface[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2015, 3(2): 8–23. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2015.2437353 [42] GEBERT N and KRIEGER G. Ultra-wide swath SAR imaging with continuous PRF variation[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [43] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered-SAR for high-resolution wide-swath imaging[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012: 1–6. [44] LUO Xiulian, WANG R, XU Wei, et al. Modification of multichannel reconstruction algorithm on the SAR with linear variation of PRI[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(7): 3050–3059. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2298242 [45] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Staggered SAR: High-resolution wide-swath imaging by continuous PRI variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4462–4479. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282192 [46] VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Onboard processing for data volume reduction in high-resolution wide-swath SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(8): 1173–1177. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2574886 [47] WANG Xiangyu, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. SAR signal recovery and reconstruction in staggered mode with low oversampling factors[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 704–708. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2805311 [48] PINHEIRO M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, et al. Combining spectral estimation and blu interpolation for the reconstruction of low-oversampled staggered SAR data[C]. 2018 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018. [49] ZENG Hongcheng, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. Modified omega-k algorithm for high-speed platform highly-squint staggered SAR based on azimuth non-uniform interpolation[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(2): 3750–3765. doi: 10.3390/s150203750 [50] 罗绣莲, 徐伟, 郭磊. 捷变PRF技术在斜视聚束SAR中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 70–77. doi: 10.12000/JR14149LUO Xiulian, XU Wei, and GUO Lei. The application of PRF variation to squint spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 70–77. doi: 10.12000/JR14149 [51] MEN Zhirong, WANG Pengbo, LI Chunsheng, et al. High-temporal-resolution high-spatial-resolution spaceborne SAR based on continuously varying PRF[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): 1700. doi: 10.3390/s17081700 [52] 王沛, 徐伟, 李宁, 等. 星载大斜视聚束SAR变PRI成像技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2470–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180049WANG Pei, XU Wei, LI Ning, et al. Investigation on PRI variation for high squint spaceborn spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2470–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180049 [53] YOUNIS M, FISCHER C, and WIESBECK W. Digital beamforming in SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(7): 1735–1739. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.815662 [54] HUBER S, YOUNIS M, PATYUCHENKO A, et al. Digital beam forming techniques for spaceborne reflector SAR systems[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [55] YOUNIS M. Digital beam-forming for high resolution wide swath real and synthetic aperture radar[D]. Universität Karlsruhe, 2004. [56] SCHAEFER C, HEER C, LUDWIG M. X-band demonstrator for receive-only frontend with digital beamforming[C]. 2010 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [57] SADOWY G, GHAEMI H, HEAVEY B, et al. Ka-band Digital Beamforming and SweepSAR Demonstration for Ice and Solid Earth Topography[C]. 2010 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [58] KRIEGER G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2628–2645. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2263934 [59] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO Radar Signal Processing[M]. New Jersey: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2009: 787–788. [60] ROMMEL T, RINCON R, YOUNIS M, et al. Implementation of a MIMO SAR imaging mode for NASA’s next generation airborne L-band SAR[C]. EUSAR 2018; 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–5. [61] MARTIN M, KLUPAR P, KILBERG S, et al. TECHSAT 21 and revolutionizing space missions using microsatellites[C]. The 15th AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Reston, USA, 2001. [62] CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. doi: 10.1109/36.718859 [63] KLARE J, WEISS M, PETERS O, et al. ARTINO: A new high resolution 3D imaging radar system on an autonomous airborne platform[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 3842–3845. [64] 周高杯, 宋红军, 邓云凯. MIMO-SAR中虚拟孔径相位校正与子带合成方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(2): 484–488. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00435ZHOU Gaobei, SONG Hongjun, and DENG Yunkai. Investigation of virtual aperture phase correction and sub band synthesis algorithms in MIMO-SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(2): 484–488. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00435 [65] ENDER J H G and BRENNER A R. PAMIR—a wideband phased array SAR/MTI system[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 165–172. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030445 [66] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, MOREIRA A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 31–46. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.905974 [67] WANG Wei, WANG R, ZHANG Zhimin, et al. First demonstration of airborne SAR with nonlinear FM chirp waveforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 247–251. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2508102 [68] JIN Guodong, LIU Kaiyu, DENG Yunkai, et al. Nonlinear frequency modulation signal generator in LT-1[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1570–1574. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2905359 [69] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. An advanced nonlinear frequency modulation waveform for radar imaging with low sidelobe[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6155–6168. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904627 [70] ENDER J H G. Signal theoretical aspects of bistatic SAR[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1438–1441. [71] ENDER J H G, WALTERSCHEID I, and BRENNER A R. New aspects of bistatic SAR: Processing and experiments[C]. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 1758–1762. [72] PRATS-IRAOLA P, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, and MOREIRA A. Investigations on bistatic SAR image formation for the SAOCOM-CS mission[C]. EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016. [73] KRIEGER G, ZONNO M, MITTERMAYER J, et al. MirrorSAR: A fractionated space transponder concept for the implementation of low-cost multistatic SAR missions[C]. EUSAR 2018: 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018. [74] KRIGER G, ZINK M, BACHMANN, et al. TanDEM-X:A radar interferometer with two formation-flying satellites[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2013, 89: 83–98. [75] HUBER S, DE ALMEIDA F Q, VILLANO M, et al. Tandem-L: A technical perspective on future spaceborne SAR sensors for earth observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4792–4807. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2837673 [76] EINEDER M. Ocillator clock drift compensation in bistatic interferometric SAR[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1449–1451. [77] ROTT H, LÓPEZ-DEKKER P, SOLBERG S, et al. SESAME: A single-pass interferometric Sentinel-1 companion SAR mission for monitoring GEO- and biosphere dynamics[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 107–110. [78] D’ERRICO M. Distributed Space Missions for Earth System Monitoring[M]. Springer New York, 2013. [79] SAKAR N, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. Azimuth reconstruction algorithm for multistatic SAR formations with large along-track baselines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2950963 [80] WANG R and DENG Yunkai. Bistatic SAR System and Signal Processing Technology[M]. Singapore: Springer Press, 2018. [81] ZHANG Heng, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator in staring-spotlight mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5203–5216. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2558294 [82] YOUNIS M, METZIG R, and KRIEGER G. Performance prediction of a phase synchronization link for bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(3): 429–433. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.874163 [83] HE Zhihua, HE Feng, CHEN Junli, et al. Echo-domain phase synchronization algorithm for bistatic SAR in alternating bistatic/ping–pong mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 604–608. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2176714 [84] ZHANG Mingmin, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. A synchronization algorithm for spaceborne/stationary BiSAR imaging based on contrast optimization with direct signal from radar satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 1977–1989. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2493078 [85] PINHEIRO M, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. Reconstruction of coherent pairs of synthetic aperture radar data acquired in interrupted mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 1876–1893. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2350255 [86] Liang Da, Liu Kaiyu, Yue Haixia, et al. An advanced non-interrupted synchronization scheme for bistatic synthetic aperture radar[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1116–1119. [87] LIANG Da, LIU Kaiyu, ZHANG Heng, et al. A High-accuracy synchronization phase-compensation method based on Kalman filter for bistatic synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2952475 [88] ZHANG Yanyan, ZHANG Heng, OU Naiming, et al. First demonstration of multipath effects on phase synchronization scheme for LT-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2952471 [89] JIN Guodong, LIU Kaiyu, LIU Dacheng, et al. An advanced phase synchronization scheme for LT-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2948219 [90] KRAUS T, KRIEGER G, BACHMANN M, et al. Spaceborne demonstration of distributed SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(11): 1731–1735. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2907371 [91] KRAUS T, BRAEUTIGAM B, BACHMANN M, et al. Multistatic SAR imaging: First results of a four phase center experiment with TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X[C]. EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1–5. [92] ZHAO Qingchao, ZHANG Yi, WANG R, et al. Estimation and removal of strong range ambiguities in multistatic synthetic aperture radar with multiple elevation beams[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 407–411. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2875434 [93] JOCHUM M. HRWS: X-Band-SAR[R]. Airbus Report, 2018. [94] SCIPAL K and DAVIDSON M. The SAOCOM-CS mission: ESA’s first bistatic and tomographic L-band mission[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 123–124. [95] DHINGRA S and BHATTACHARYA A. A modified m-χ decomposition for compact polarimetric SAR data[C]. Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, USA, 2015. [96] ATTEIA G E and COLLINS M J. On the use of compact polarimetry SAR for ship detection[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 80: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.01.009 [97] CHARBONNEAU F J, BRISCO B, RANEY R K, et al. Compact polarimetry overview and applications assessment[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 36(S2): S298–S315. [98] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Mitigating range ambiguities with advanced nonlinear frequency modulation waveform[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1230–1234. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2895111 [99] YANG Rong, HU Zhentao, LIU Yiming, et al. A novel polarimetric SAR classification method integrating pixel-based and patch-based classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2923403 [100] HAJNSEK I, BUSCHE T, MOREIRA A, et al. Mission status and data availability: Tandem-X[C]. The 4th International Polinsar 2009 Workshop, Wessling, Germany, 2009. [101] ZINK M, BACHMANN M, BRAUTIGAM B, et al. TanDEM-X: The new global DEM takes shape[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2014, 2(2): 8–23. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2014.2318895 [102] RIZZOLI P, MARTONE M, GONZALEZ C, et al. Generation and performance assessment of the global TanDEM-X digital elevation model[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 132: 119–139. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.08.008 [103] ZHU Xiaoxiang, BAIER G, LACHAISE M, et al. Potential and limits of non-local means InSAR filtering for TanDEM-X high-resolution DEM generation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 218: 148–161. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.09.012 [104] LACHAISE M, FRITZ T, and BREIT H. InSAR processing and dual-baseline phase unwrapping for global TanDEM-X DEM generation[C]. 2014 Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec, Canada, 2014: 2229–2232. [105] DING Zegang, WANG Zhen, LIN Sheng, et al. Local fringe frequency estimation based on multifrequency InSAR for phase-noise reduction in highly sloped terrain[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1527–1531. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2720695 [106] TANDEM-L: A satellite mission for monitoring dynamic processes on the earth’s surface[R]. DLR Report, 2014. [107] CRIPPEN R E and BLOM R G. Concept for the subresolution measurement of earthquake strain fields using SPOT panchromatic imagery[C]. Earth and Atmospheric Remote Sensing, Orlando, USA, 1991. doi: 10.1117/12.45870. [108] OSMANOĞLU B, SUNAR F, WDOWINSKI S, et al. Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 115: 90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.003 [109] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [110] BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2375–2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792 [111] ZHANG Bowen, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Mapping the Yellow River Delta land subsidence with multitemporal SAR interferometry by exploiting both persistent and distributed scatterers[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 148: 157–173. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.12.008 [112] WANG Jili, YU Weidong, DENG Yunkai, et al. Demonstration of time-series INSAR processing in Beijing using a small stack of gaofen-3 differential Interferograms[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2019, 2019: 4204580. [113] MICHEL R, AVOUAC J P, and TABOURY J. Measuring ground displacements from SAR amplitude images: Application to the Landers Earthquake[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1999, 26(7): 875–878. doi: 10.1029/1999GL900138 [114] WANG Changcheng, MAO Xiaokang, and WANG Qijie. Landslide displacement monitoring by a fully polarimetric SAR offset tracking method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(8): 624. doi: 10.3390/rs8080624 [115] HU Xie, WANG Teng, and LIAO Mingsheng. Measuring coseismic displacements with point-like targets offset tracking[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 283–287. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2256104 [116] SINGLETON A, LI Z, HOEY T, et al. Evaluating sub-pixel offset techniques as an alternative to D-InSAR for monitoring episodic landslide movements in vegetated terrain[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 147: 133–144. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.03.003 [117] LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M, BALLESTER-BERMAN J D, and MARQUEZ-MORENO Y. Model limitations and parameter-estimation methods for agricultural applications of polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3481–3493. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900690 [118] NEUMANN M, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Estimation of forest structure, ground, and canopy layer characteristics from multibaseline polarimetric interferometric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1086–1104. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2031101 [119] WANG Yu, YU Weidong, LIU Xiuqing, et al. A hierarchical extended multiple-component scattering decomposition of polarimetric sar interferometry[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2942090 [120] CARREIRAS J M B, QUEGAN S, LE TOAN T, et al. Coverage of high biomass forests by the ESA BIOMASS mission under defense restrictions[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 196: 154–162. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.05.003 [121] KNAELL K. Three-dimensional SAR from practical apertures[C]. SPIE Radar/Ladar Processing and Applications, San Diego, USA, 1995: 31–41. [122] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(9): 2142–2152. [123] TEBALDINI S. Single and multipolarimetric SAR tomography of forested areas: A parametric approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(5): 2375–2387. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037748 [124] LU Hongliang, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Heng, et al. SAR tomographic imaging demonstration using GF-3 data[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 3645–3648. [125] LUO Hui, LI Zhenhong, DONG Zhen, et al. A new baseline linear combination algorithm for generating urban digital elevation models with multitemporal InSAR observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(2): 1120–1133. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943919 [126] ROMEISER R and THOMPSON D R. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 446–458. doi: 10.1109/36.823940 [127] CERUTTI-MAORI D, BÜRGER W, ENDER J H G, et al. Wide area surveillance of moving targets with the SAR/GMTI system PAMIR[C]. EUSAR 2006 - 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Dresden, Germany, 2006. [128] ENDER J H G. Space-time processing for multichannel synthetic aperture radar[J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1999, 11(1): 29–38. [129] ENDER J H G, GIERULL C H, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Improved space-based moving target indication via alternate transmission and receiver switching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(12): 3960–3974. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002266 [130] SUCHANDT S, RUNGE H, BREIT H, et al. Automatic extraction of traffic flows using TerraSAR-X along-track interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 807–819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037919 [131] CERUTTI-MAORI D and SIKANETA I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 560–572. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201260 [132] LIU Yue, DENG Yunkai, WANG R. Focus squint FMCW SAR data using inverse chirp-Z transform based on an analytical point target reference spectrum[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(5): 866–870. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2184833 [133] SAR-Lupe[EB/OL]. https://www.ohb-system.de/sar-lupe-english.html. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: