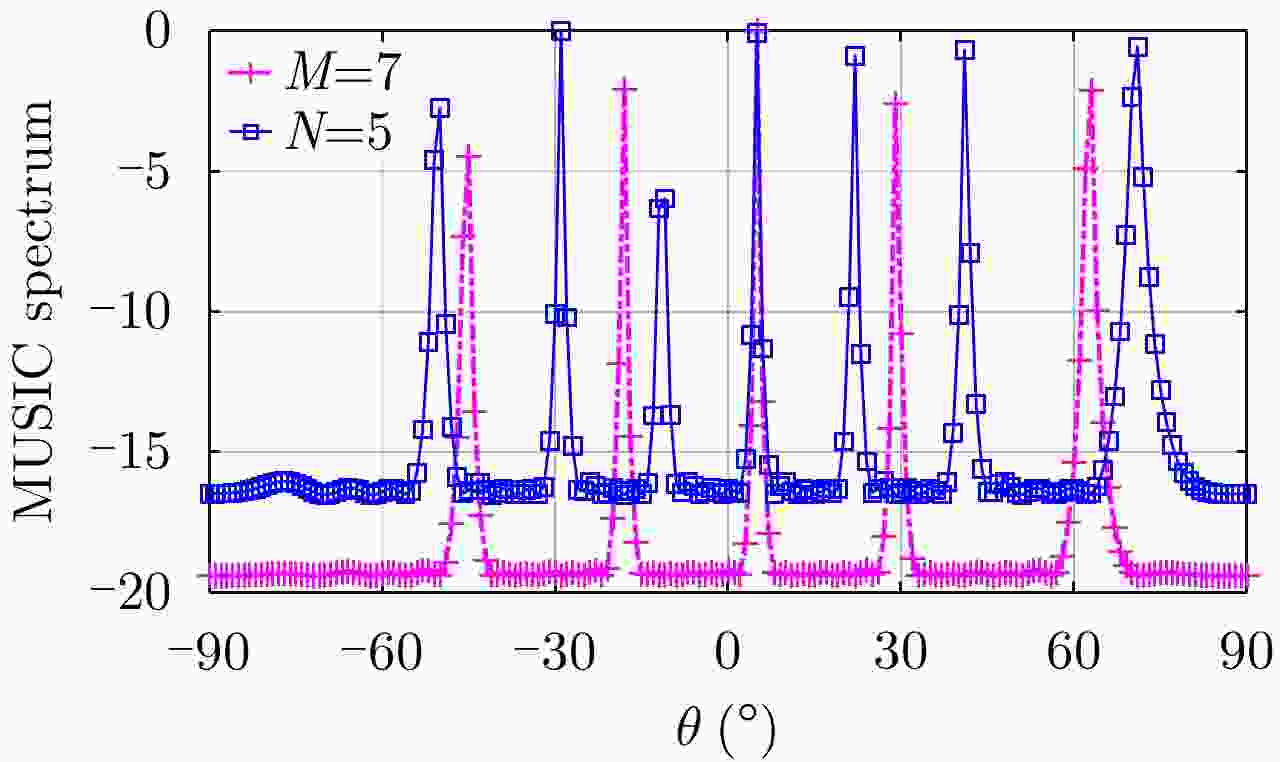
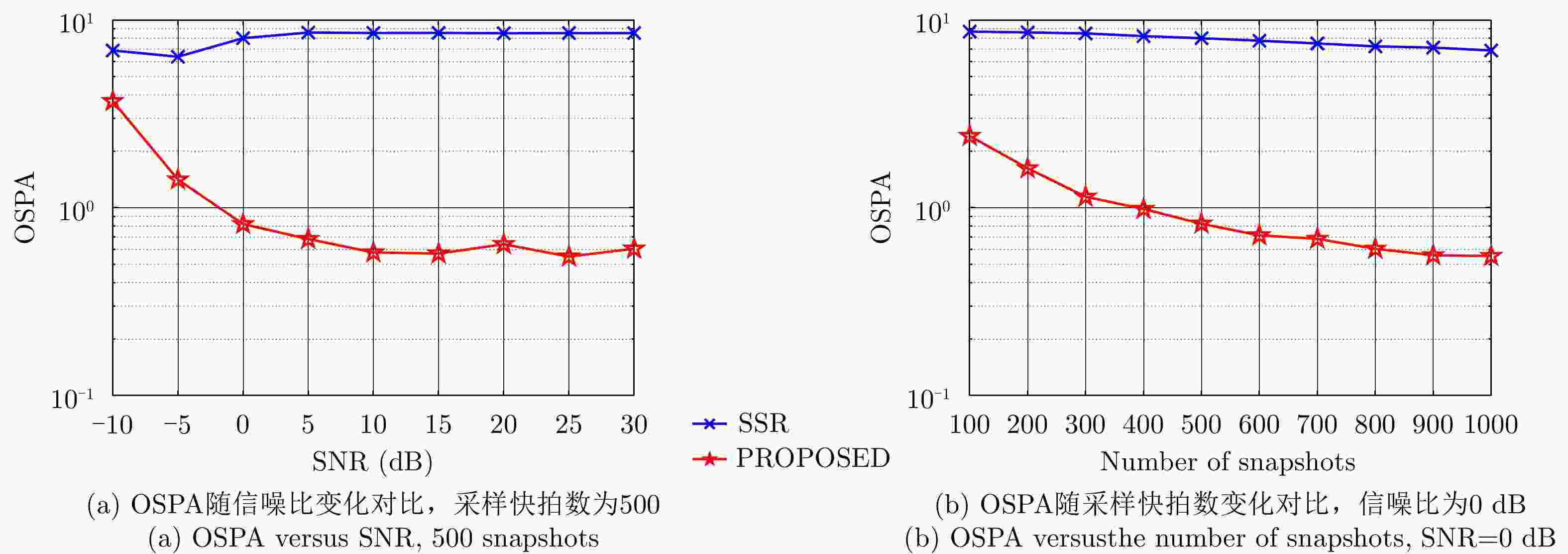
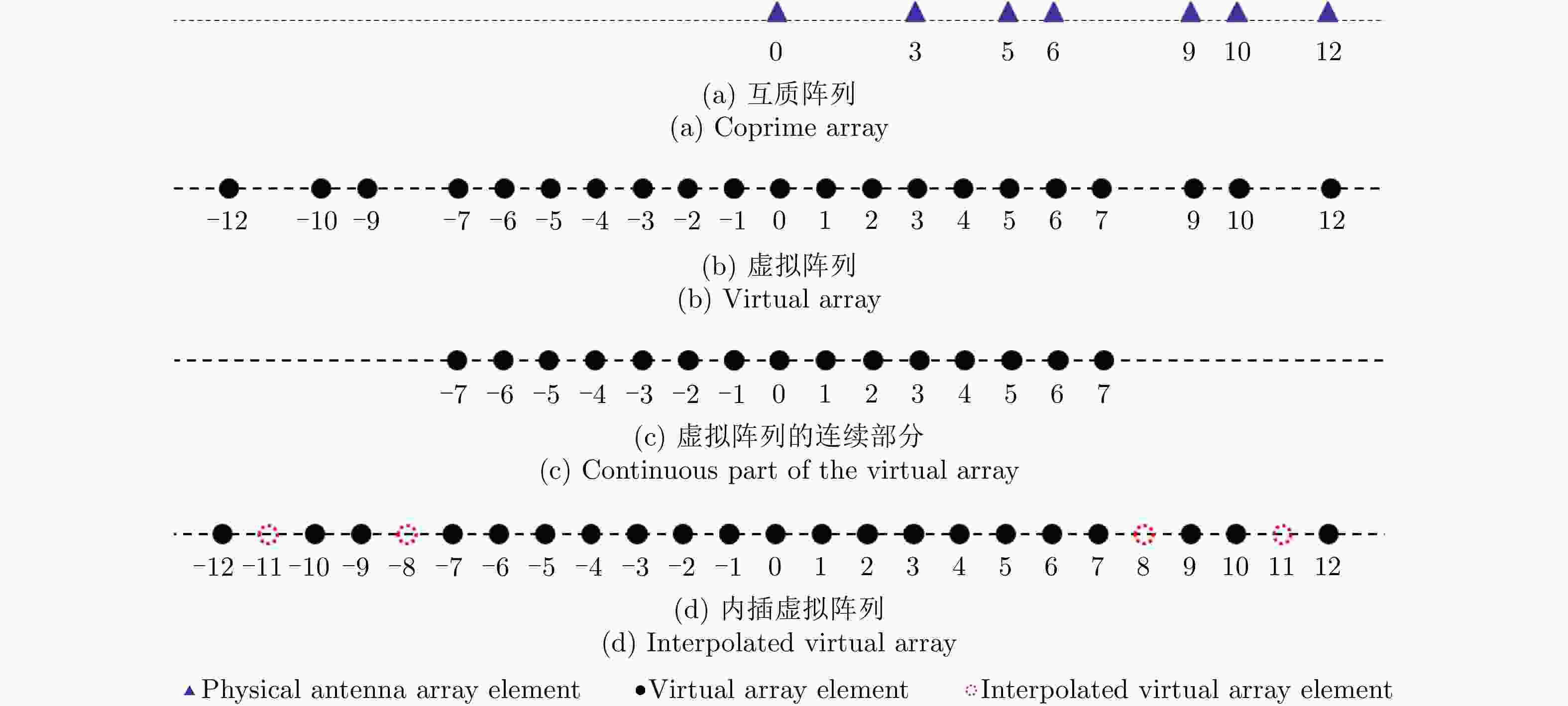
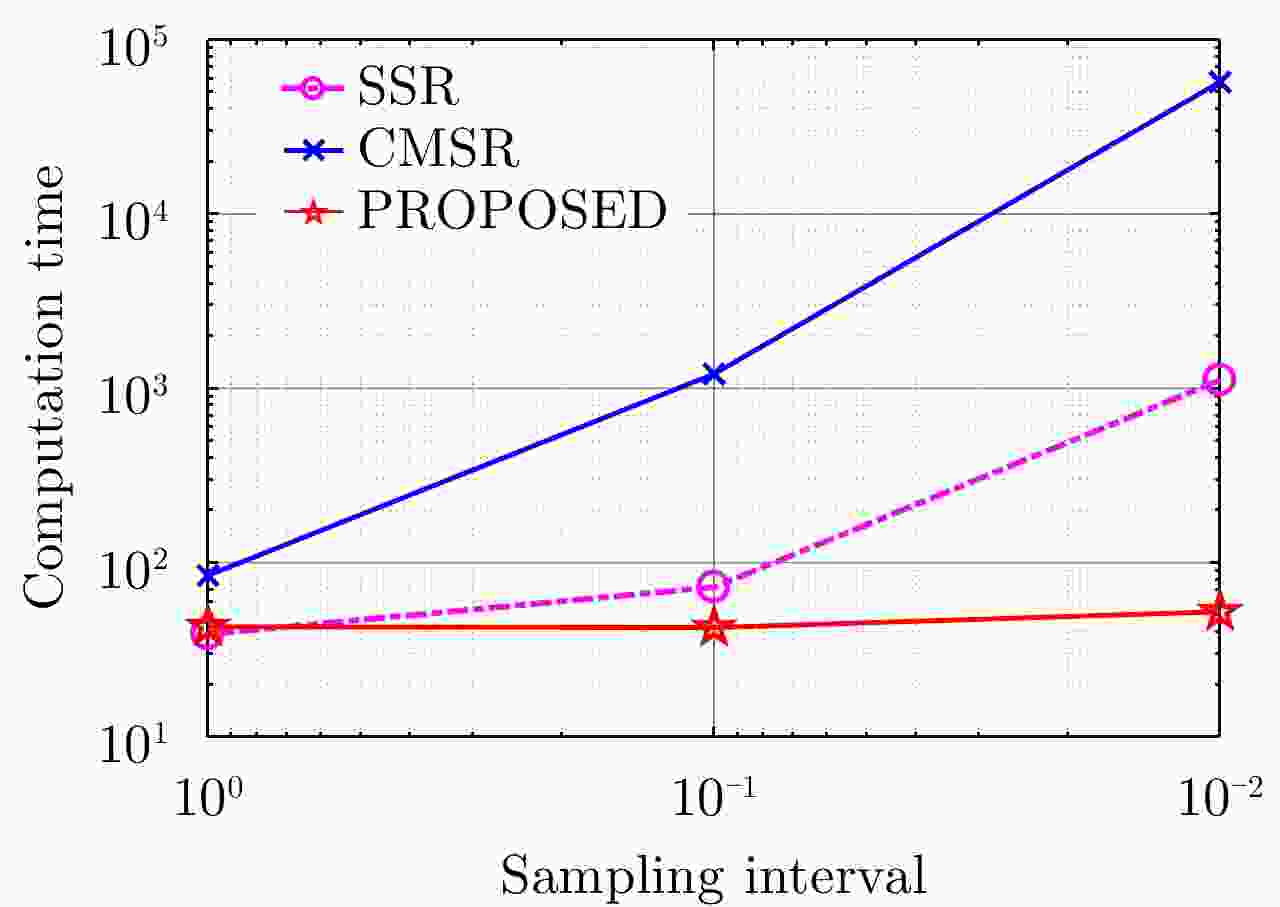
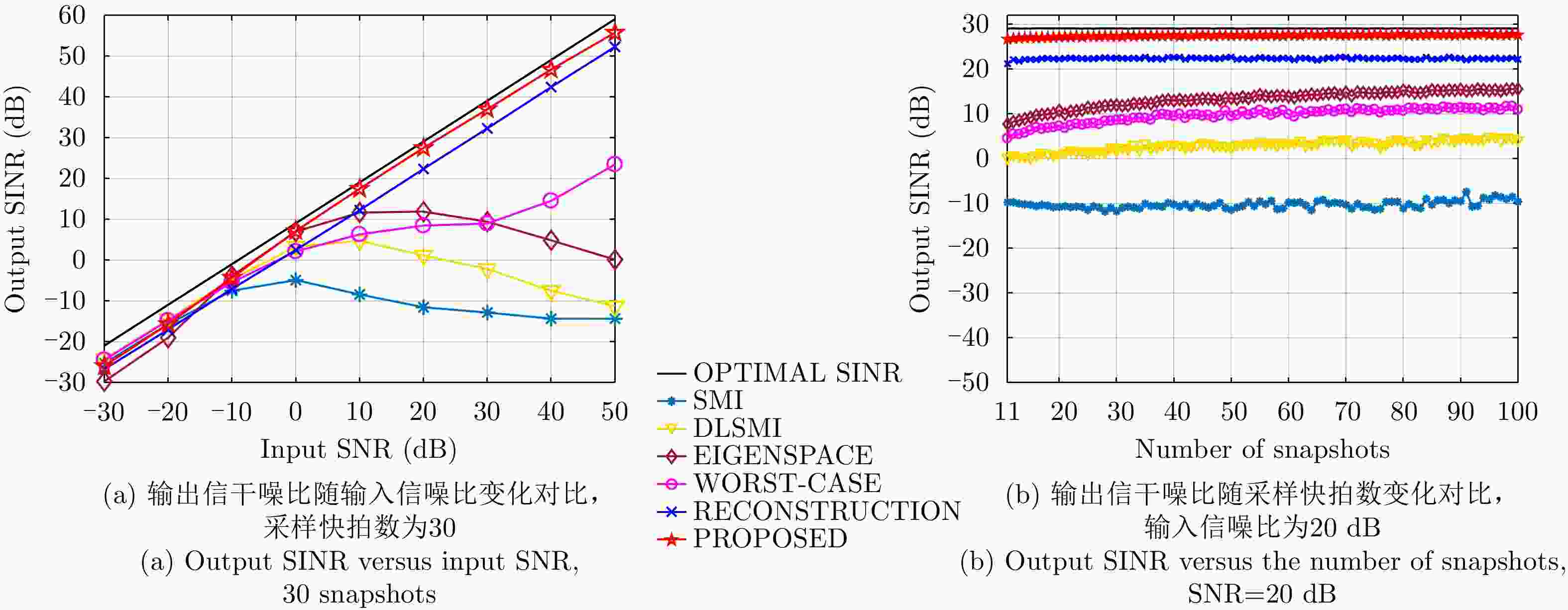
| [1] |
VON AULOCK W H. Properties of phased arrays[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1960, 48(10): 1715–1727. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1960.287523
|
| [2] |
MAILLOUX R J. Phased array theory and technology[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1982, 70(3): 246–291. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1982.12285
|
| [3] |
WARD C, HARGRAVE P, and MCWHIRTER J. A novel algorithm and architecture for adaptive digital beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 338–346. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143818
|
| [4] |
TALISA S H, O’HAVER K W, COMBERIATE T M, et al. Benefits of digital phased array radars[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(3): 530–543. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2515842
|
| [5] |
CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278
|
| [6] |
FROST O and SULLIVAN T. High-resolution two-dimensional spectral analysis[C]. 1979 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Washington, USA, 1979: 673–676.
|
| [7] |
WAX M, SHAN T J, and KAILATH T. Spatio-temporal spectral analysis by eigenstructure methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1984, 32(4): 817–827. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1984.1164400
|
| [8] |
LEMMA A N, VAN DER VEEN A J, and DEPRETTERE E F. Joint angle-frequency estimation using multi-resolution ESPRIT[C]. 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, USA, 1998: 1957–1960.
|
| [9] |
TSAKALIDES P, RASPANTI R, and NIKIAS C L. Angle/Doppler estimation in heavy-tailed clutter backgrounds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(2): 419–436. doi: 10.1109/7.766926
|
| [10] |
LU Lu, LI G Y, LEE SWINDLEHURST A, et al. An overview of massive MIMO: Benefits and challenges[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(5): 742–758. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2317671
|
| [11] |
LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO Radar Signal Processing[M]. Hoboken: Wiley & Sons, 2009.
|
| [12] |
LI Jian, BLUM R S, STOICA P, et al. Introduction to the issue on MIMO radar and its applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(1): 2–4. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2040416
|
| [13] |
周伟, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. MIMO-SAR技术发展概况及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074ZHOU Wei, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Brief analysis on the development and application of Multi-Input Multi-Output synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074
|
| [14] |
高敬坤, 邓彬, 秦玉亮, 等. 扫描MIMO阵列近场三维成像技术[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 676–684. doi: 10.12000/JR18102GAO Jingkun, DENG Bin, QIN Yuliang, et al. Near-field 3D SAR imaging techniques using a scanning MIMO array[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 676–684. doi: 10.12000/JR18102
|
| [15] |
CHEN Jinli, GU Hong, and SU Weimin. A new method for joint DOD and DOA estimation in bistatic MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(2): 714–718. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.08.003
|
| [16] |
WEN Fangqing, ZHANG Zijing, WANG Ke, et al. Angle estimation and mutual coupling self-calibration for ULA-based bistatic MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 144: 61–67. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.09.021
|
| [17] |
WEN Fangqing, XIONG Xiaodong, and ZHANG Zijing. Angle and mutual coupling estimation in bistatic MIMO radar based on PARAFAC decomposition[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 65: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.02.011
|
| [18] |
LIN Y C, LEE T S, PAN Yunhan, et al. Low-complexity high-resolution parameter estimation for automotive MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Access, 2019. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2926413
|
| [19] |
AMIRI R, BEHNIA F, and NOROOZI A. Efficient joint moving target and antenna localization in distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(9): 4425–4435. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2924626
|
| [20] |
MAO Chenxing, WEN Fangqing, ZHANG Zijing, et al. New approach for DOA estimation in MIMO radar with nonorthogonal waveforms[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2019, 3(7): 7001104.
|
| [21] |
WEN Fangqing. Computationally efficient DOA estimation algorithm for MIMO radar with imperfect waveforms[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(6): 1037–1040. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2911285
|
| [22] |
WEN Fangqing, XIONG Xiaodong, SU Jian, et al. Angle estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of spatial colored noise[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 134: 261–267. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.12.017
|
| [23] |
FU Xiuwen, CAO Renzheng, and WEN Fangqing. A de-noising 2-D-DOA estimation method for uniform rectangle array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(9): 1854–1857. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2849724
|
| [24] |
WEN Fangqing, ZHANG Xinyu, and ZHANG Zijing. CRBs for direction-of-departure and direction-of-arrival estimation in collocated MIMO radar in the presence of unknown spatially coloured noise[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(4): 530–537.
|
| [25] |
WEN Fangqing, WU Lei, CAI Changxin, et al. Joint DOD and DOA estimation for bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of combined array errors[C]. The 2018 IEEE 10th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Sheffield, UK, 2018: 174–178.
|
| [26] |
KLEMM R. Introduction to space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1999, 11(1): 5–12.
|
| [27] |
王珽, 赵拥军, 胡涛. 机载MIMO雷达空时自适应处理技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR14091WANG Ting, ZHAO Yongjun, and HU Tao. Overview of space-time adaptive processing for airborne Multiple-Input Multiple-Output radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR14091
|
| [28] |
谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar: An overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073
|
| [29] |
FU Dongning, WEN Jun, XU Jingwei, et al. STAP-based airborne radar system for maneuvering target detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 62071–62079. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914224
|
| [30] |
HE Tuan and ZHANG Yu. A MIMO radar STAP method based on sparse dictionary atomic selection[C]. The 2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chengdu, China, 2019: 433–436.
|
| [31] |
JIA Fengde, SUN Guohao, HE Zishu, et al. Grating-lobe clutter suppression in uniform subarray for airborne radar STAP[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(16): 6956–6965. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2912827
|
| [32] |
LU Lei, ZHOU Chengwei, SHI Zhiguo, et al. Off-grid angle-Doppler estimation for space-time adaptive processing: A sequential approach[C]. 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Changchun, China, 2019: 231–236.
|
| [33] |
VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 573–586. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2089682
|
| [34] |
WANG Huafei, WAN Liangtian, DONG Mianxiong, et al. Assistant vehicle localization based on three collaborative base stations via SBL-based robust DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 5766–5777. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2905788
|
| [35] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A high-resolution DOA estimation method with a family of nonconvex penalties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 4925–4938. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2817638
|
| [36] |
周超伟, 李真芳, 王跃锟, 等. 联合多方位角调频率估计的星载SAR三维成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 696–704. doi: 10.12000/JR18094ZHOU Chaowei, LI Zhenfang, WANG Yuekun, et al. Space-borne SAR three-dimensional imaging by joint multiple azimuth angle Doppler frequency rate estimation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 696–704. doi: 10.12000/JR18094
|
| [37] |
ZHOU Chengwei, SHI Zhiguo, GU Yujie, et al. DECOM: DOA estimation with combined MUSIC for coprime array[C]. 2013 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2013: 1–5.
|
| [38] |
SUN Fenggang, GAO Bin, CHEN Lizhen, et al. A low-complexity ESPRIT-based DOA estimation method for co-prime linear arrays[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(9): 1367. doi: 10.3390/s16091367
|
| [39] |
ZHANG Dong, ZHANG Yongshun, ZHENG Guimei, et al. Improved DOA estimation algorithm for co-prime linear arrays using root-MUSIC algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(18): 1277–1279. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2292
|
| [40] |
YAN Fenggang, LIU Shuai, WANG Jun, et al. Fast DOA estimation using co-prime array[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(7): 409–410. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2491
|
| [41] |
LI Jianfeng, SHEN Mingwei, and JIANG Defu. Fast direction of arrival estimation using a sensor-saving coprime array with enlarged inter-element spacing[C]. The 2018 IEEE 10th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Sheffield, UK, 2018: 179–183.
|
| [42] |
ZHENG Wang, ZHANG Xiaofei, GONG Pan, et al. DOA estimation for coprime linear arrays: An ambiguity-free method involving full DOFs[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(3): 562–565. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2787698
|
| [43] |
LI Jianfeng and ZHANG Xiaofei. Direction of arrival estimation of Quasi-Stationary signals using unfolded coprime array[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 6538–6545. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2695581
|
| [44] |
PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Coprime sampling and the MUSIC algorithm[C]. Proceedings of 2011 Digital Signal Processing and Signal Processing Education Meeting, Sedona, USA, 2011: 289–294.
|
| [45] |
LIU Chunlin and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Coprime arrays and samplers for space-time adaptive processing[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 2364–2368.
|
| [46] |
ZHOU Chengwei and ZHOU Jinfang. Direction-of-arrival estimation with coarray ESPRIT for coprime array[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): 1779. doi: 10.3390/s17081779
|
| [47] |
TAN Zhao, ELDAR Y C, and NEHORAI A. Direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays: A super resolution viewpoint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5565–5576. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354316
|
| [48] |
PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. On application of LASSO for sparse support recovery with imperfect correlation awareness[C]. 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2012: 958–962.
|
| [49] |
PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Correlation-aware techniques for sparse support recovery[C]. 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Ann Arbor, USA, 2012: 53–56.
|
| [50] |
LV Wanghan and WANG Huali. Joint DOA and frequency estimation based on spatio-temporal co-prime sampling[C]. 2015 International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 2015: 1–5.
|
| [51] |
QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, and AMIN M G. Multi-target localization using frequency diverse coprime arrays with coprime frequency offsets[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [52] |
ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, and HIMED B. Sparsity-based DOA estimation using co-prime arrays[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 3967–3971.
|
| [53] |
QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, et al. Generalized coprime sampling of Toeplitz matrices for spectrum estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(1): 81–94. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2614799
|
| [54] |
QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, and AMIN M G. Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(6): 1377–1390. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2393838
|
| [55] |
SHI Junpeng, HU Guoping, ZHANG Xiaofei, et al. Sparsity-based two-dimensional DOA estimation for coprime array: From sum-difference coarray viewpoint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(21): 5591–5604. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2739105
|
| [56] |
SHI Junpeng, HU Guoping, ZHANG Xiaofei, et al. Sparsity-based DOA estimation of coherent and uncorrelated targets with flexible MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5835–5848. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2913437
|
| [57] |
ZHOU Chengwei, SHI Zhiguo, GU Yujie, et al. DOA estimation by covariance matrix sparse reconstruction of coprime array[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 2369–2373.
|
| [58] |
SHI Zhiguo, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al. Source estimation using coprime array: A sparse reconstruction perspective[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(3): 755–765. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2637059
|
| [59] |
ZHENG Yunmei, SHI Zhiguo, LU Rongxing, et al. An efficient data-driven particle PHD filter for multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 2318–2326. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2228875
|
| [60] |
GU Yujie, GOODMAN N A, HONG Shaohua, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix sparse reconstruction[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 96: 375–381. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.10.009
|
| [61] |
GU Yujie and GOODMAN N A. Information-theoretic compressive sensing kernel optimization and Bayesian Cramér-Rao bound for time delay estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4525–4537. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2706187
|
| [62] |
YU Wenbin, CHEN Cailian, HE Tian, et al. Adaptive compressive engine for real-time electrocardiogram monitoring under unreliable wireless channels[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(6): 607–615. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.0882
|
| [63] |
DING Wenbo, YANG Fang, LIU Sicong, et al. Structured compressive sensing-based non-orthogonal time-domain training channel state information acquisition for multiple input multiple output systems[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(6): 685–690. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.0697
|
| [64] |
ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, ZHANG Y D, et al. Compressive sensing-based coprime array direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(11): 1719–1724. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2016.1048
|
| [65] |
GUO Muran, ZHANG Y D, and CHEN Tao. DOA estimation using compressed sparse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(15): 4133–4146. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2847645
|
| [66] |
GU Yujie, ZHANG Y D, and GOODMAN N A. Optimized compressive sensing-based direction-of-arrival estimation in massive MIMO[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, USA, 2017: 3181–3185.
|
| [67] |
BOUDAHER E, JIA Yong, AHMAD F, et al. Multi-frequency co-prime arrays for high-resolution direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(14): 3797–3808. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2432734
|
| [68] |
LIU Chunlin, VAIDYANATHAN P P, and PAL P. Coprime coarray interpolation for DOA estimation via nuclear norm minimization[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2016: 2639–2642.
|
| [69] |
HOSSEINI S M and SEBT M A. Array interpolation using covariance matrix completion of minimum-size virtual array[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(7): 1063–1067. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2708750
|
| [70] |
YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3139–3153. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2420541
|
| [71] |
CANDÈS E J and FERNANDEZ-GRANDA C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution[J]. Communications on Pure and applied Mathematics, 2014, 67(6): 906–956. doi: 10.1002/cpa.21455
|
| [72] |
YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(19): 4959–4973. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2339792
|
| [73] |
YANG Zai, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Sparse methods for direction-of-arrival estimation[M]. CHELLAPPA R and THEODORIDIS S. Academic Press Library in Signal Processing, Volume 7: Array, Radar and Communications Engineering. Amsterdam: Academic Press, 2018: 509–581.
|
| [74] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, YAN Jun, et al. Two sparse-based methods for off-grid direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 87–95. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.07.004
|
| [75] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. Direction of arrival estimation for off-grid signals based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(7): 2004–2016. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2508059
|
| [76] |
LI Jianfeng, LI Yunxiang, and ZHANG Xiaofei. Two-dimensional off-grid DOA estimation using unfolded parallel coprime array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(12): 2495–2498. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2872955
|
| [77] |
PAN Jie, ZHOU Changling, LIU Bo, et al. Joint DOA and Doppler frequency estimation for coprime arrays and samplers based on continuous compressed sensing[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [78] |
FAN Xing, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al. Toeplitz matrix reconstruction of interpolated coprime virtual array for DOA estimation[C]. The 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1–5.
|
| [79] |
ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, FAN Xing, et al. Direction-of-arrival estimation for coprime array via virtual array interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(22): 5956–5971. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2872012
|
| [80] |
ZHOU Chengwei, SHI Zhiguo, GU Yujie, et al. Coarray interpolation-based coprime array DOA estimation via covariance matrix reconstruction[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 3479–3483.
|
| [81] |
ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, SHI Zhiguo, et al. Off-grid direction-of-arrival estimation using coprime array interpolation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(11): 1710–1714. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2872400
|
| [82] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A Toeplitz covariance matrix reconstruction approach for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 8223–8237. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2695226
|
| [83] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A fast gridless covariance matrix reconstruction method for one- and two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(15): 4916–4927. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2709329
|
| [84] |
SHEN Yifan, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al.. Vandermonde decomposition of coprime coarray covariance matrix for DOA estimation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan, 2017: 1–5.
|
| [85] |
DU Lin, YARDIBI T, LI Jian, et al. Review of user parameter-free robust adaptive beamforming algorithms[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2009, 19(4): 567–582. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2009.02.001
|
| [86] |
CHOI Y H. Subspace based adaptive beamforming method with low complexity[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(9): 529–530. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.0512
|
| [87] |
FELDMAN D D and GRIFFITHS L J. A projection approach for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(4): 867–876. doi: 10.1109/78.285650
|
| [88] |
LI Jian, STOICA P, and WANG Zhisong. On robust capon beamforming and diagonal loading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(7): 1702–1715. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2003.812831
|
| [89] |
BELL K L, EPHRAIM Y, and VAN TREES H L. A Bayesian approach to robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2000, 48(2): 386–398. doi: 10.1109/78.823966
|
| [90] |
VOROBYOV S A, GERSHMAN A B, and LUO Zhiquan. Robust adaptive beamforming using worst-case performance optimization: A solution to the signal mismatch problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(2): 313–324. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.806865
|
| [91] |
GU Yujie and LESHEM A. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3881–3885. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2194289
|
| [92] |
ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, SONG Wenzhan, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming based on DOA support using decomposed coprime subarrays[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 2986–2990.
|
| [93] |
ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, HE Shibo, et al. A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1099–1112. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2704610
|
| [94] |
REED I S, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893
|
| [95] |
ZHOU Chengwei, SHI Zhiguo, and GU Yujie. Coprime array adaptive beamforming with enhanced degrees-of-freedom capability[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 1357–1361.
|
| [96] |
HUANG Jiyan, WANG Peng, and WAN Qun. Sidelobe suppression for blind adaptive beamforming with sparse constraint[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(3): 343–345. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.012511.102215
|
| [97] |
GU Yujie, ZHOU Chengwei, GOODMAN N A, et al. Coprime array adaptive beamforming based on compressive sensing virtual array signal[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 2981–2985.
|
| [98] |
LIU Jianyan, ZHANG Yanmei, LU Yilong, et al. Augmented nested arrays with enhanced DOF and reduced mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(21): 5549–5563. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2736493
|
| [99] |
ZHENG Wang, ZHANG Xiaofei, and ZHAI Hui. Generalized coprime planar array geometry for 2-D DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(5): 1075–1078. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2664809
|
| [100] |
YANG M, HAIMOVICH A M, CHEN Baixiao, et al. A new array geometry for DOA estimation with enhanced degrees of freedom[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 3041–3045.
|
| [101] |
RAZA A, LIU Wei, and SHEN Qing. Thinned coprime arrays for DOA estimation[C]. The 2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference, Kos, Greece, 2017: 395–399.
|
| [102] |
XU Haiyun, ZHANG Yankui, and BA Bin. Direction finding using coprime array with sensor gain and phase errors[C]. 2017 International Conference on Computer Technology, Electronics and Communication, Dalian, China, 2017: 880–885.
|
| [103] |
TIAN Ye, SHI Hongyin, and XU He. DOA estimation in the presence of unknown non-uniform noise with coprime array[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(2): 113–115. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.3944
|
| [104] |
LI Conghui, GAN Lu, and LING Cong. 2D MIMO radar with coprime arrays[C]. The 2018 IEEE 10th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Sheffield, UK, 2018: 612-616.
|
| [105] |
王龙刚, 李廉林. 基于互质阵列雷达技术的近距离目标探测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 244–253. doi: 10.12000/JR16022WANG Longgang and LI Lianlin. Short-range radar detection with (M, N)-coprime array configurations[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 244–253. doi: 10.12000/JR16022
|
| [106] |
SHI Junpeng, HU Guoping, ZHANG Xiaofei, et al. Generalized co-prime MIMO radar for DOA estimation with enhanced degrees of freedom[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(3): 1203–1212. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2782746
|
| [107] |
YANG Minglei, SUN Lei, YUAN Xin, et al. A new nested MIMO array with increased degrees of freedom and hole-free difference coarray[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(1): 40–44. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2766294
|
| [108] |
LI Jianfeng, ZHANG Xiaofei, and JIANG Defu. DOD and DOA estimation for bistatic coprime MIMO radar based on combined ESPRIT[C]. Proceedings of 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4.
|
| [109] |
ZHANG Zongyu, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al. FFT-based DOA estimation for coprime MIMO radar: A Hardware-Friendly approach[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–5.
|
| [110] |
TAO Yu, ZHANG Gong, and LI Daren. Coprime sampling with deterministic digital filters in compressive sensing radar[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4.
|
| [111] |
ZHANG Zongyu, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al. An IDFT approach for coprime array direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.05.006
|
| [112] |
LI Jianfeng, SHEN Mingwei, and DING Ji. Direction of arrival estimation for co-prime MIMO radar based on unitary root-MUSIC[C]. The 2015 2nd International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor Network, Changsha, China, 2016: 307–315.
|
| [113] |
LI Jianfeng, JIANG Defu, and ZHANG Xiaofei. DOA estimation based on combined unitary ESPRIT for coprime MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(1): 96–99. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2618789
|
| [114] |
JIA Yong, ZHONG Xiaoling, GUO Yong, et al. DOA and DOD estimation based on bistatic MIMO radar with co-prime array[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 394–397.
|
| [115] |
ZHANG Zongyu, ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, et al. Efficient DOA estimation for coprime array via inverse discrete Fourier transform[C]. The 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–5.
|
| [116] |
LI Jianfeng and JIANG Defu. Low-complexity propagator based two dimensional angle estimation for coprime MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 13931–13938. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2813014
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
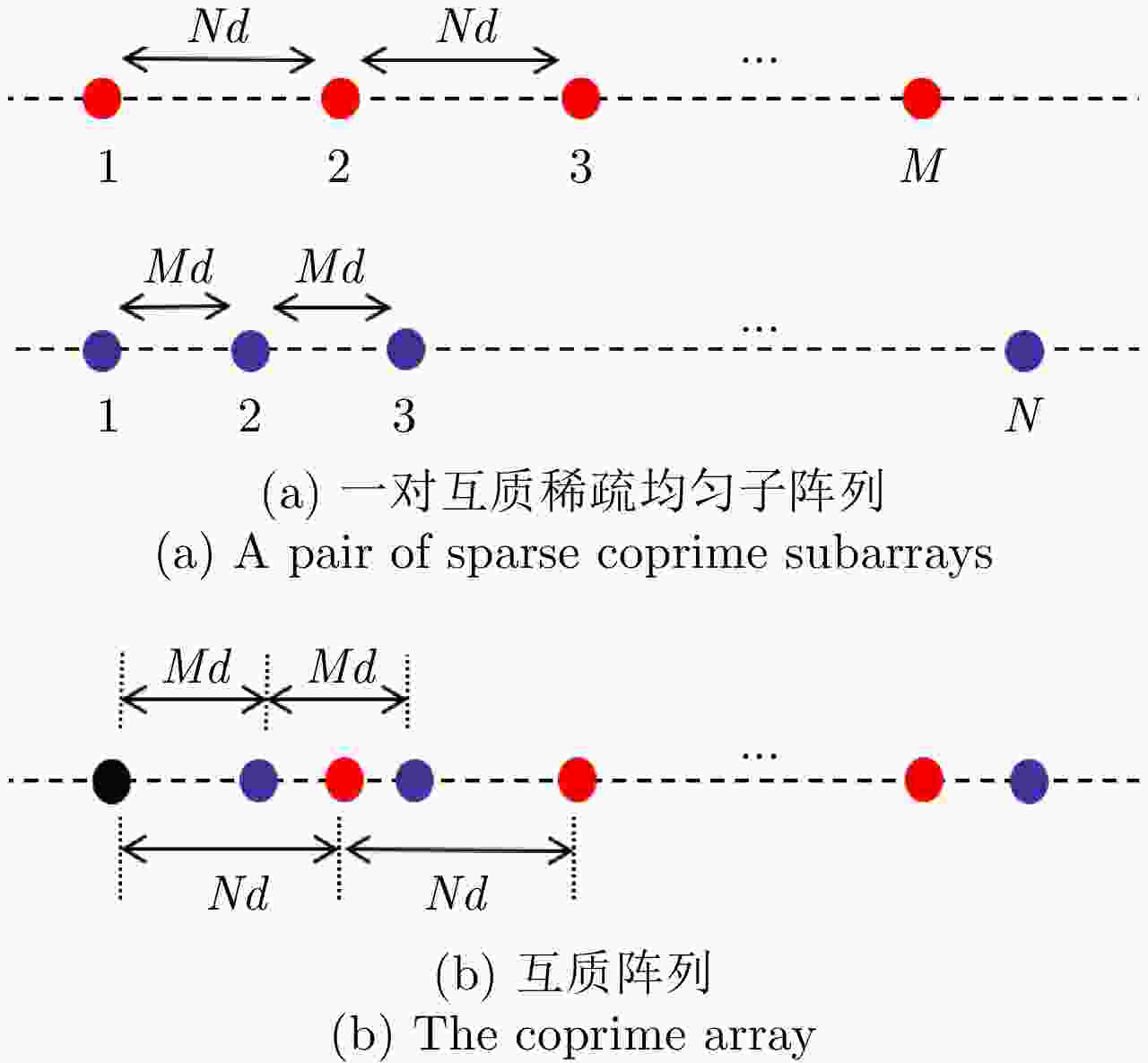
 下载:
下载: