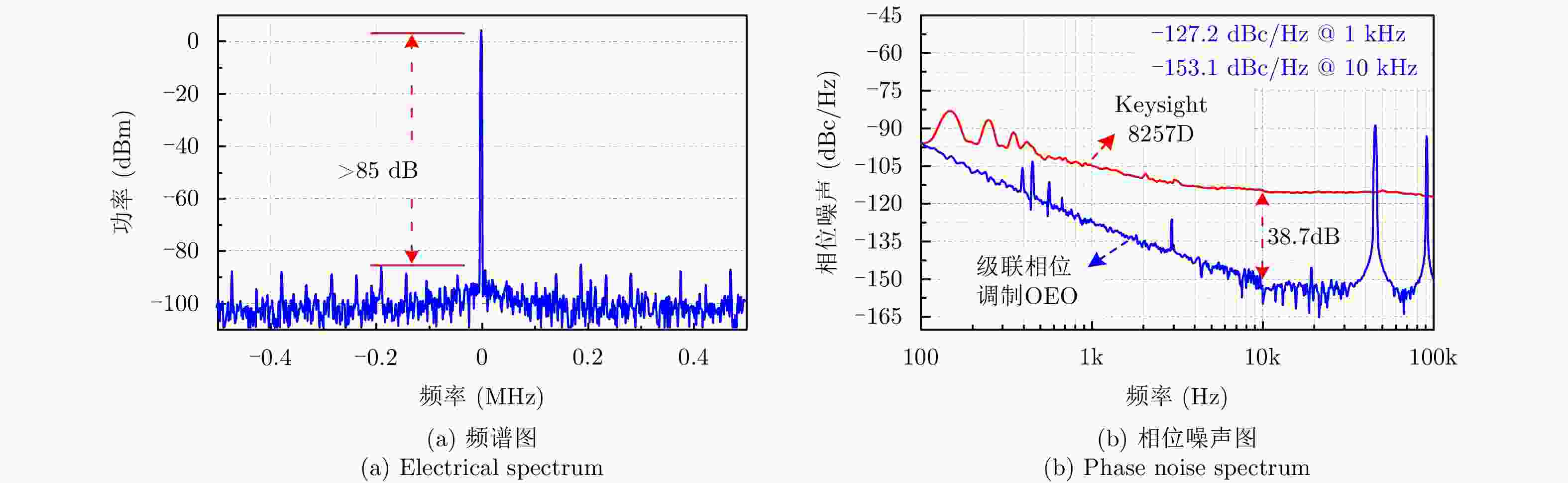
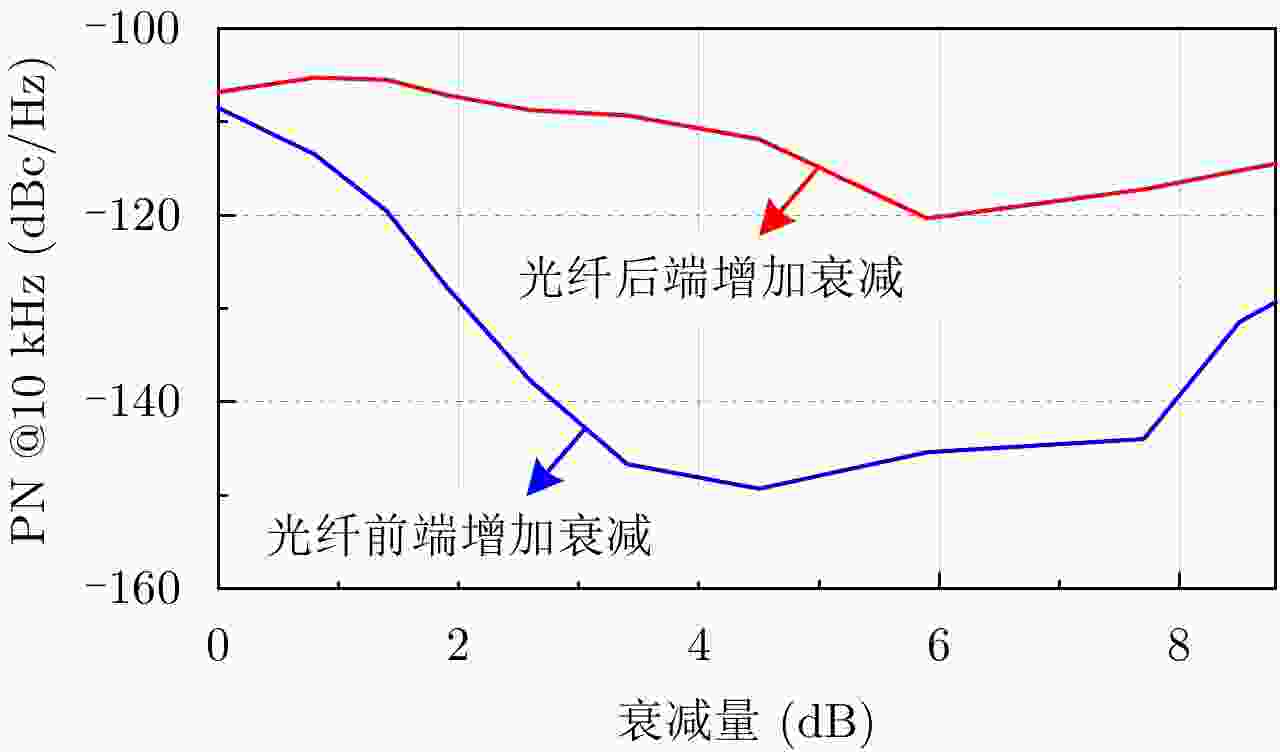
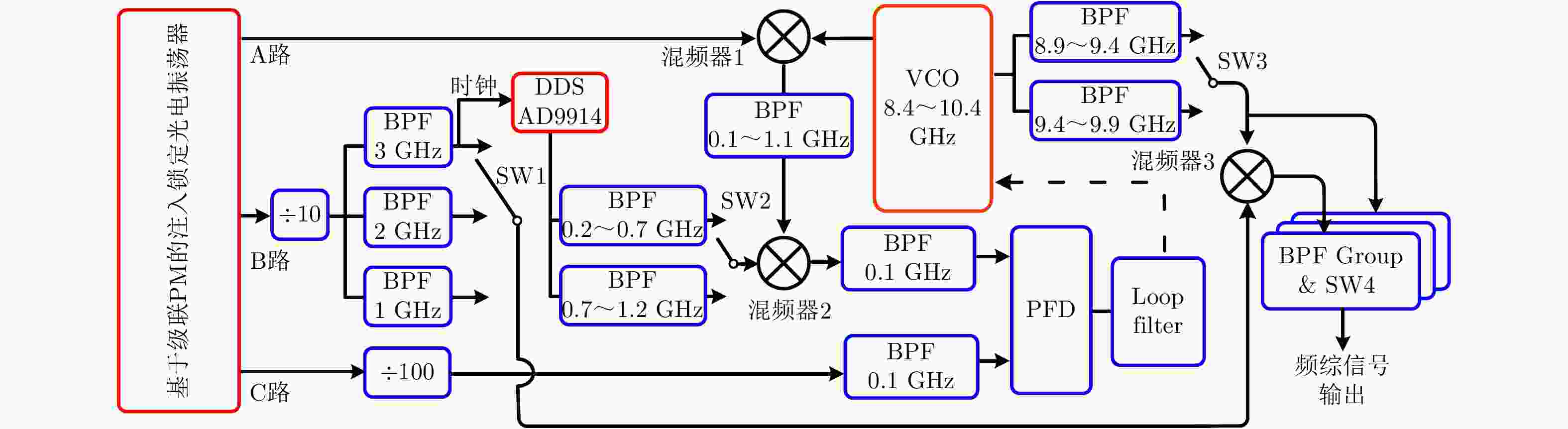
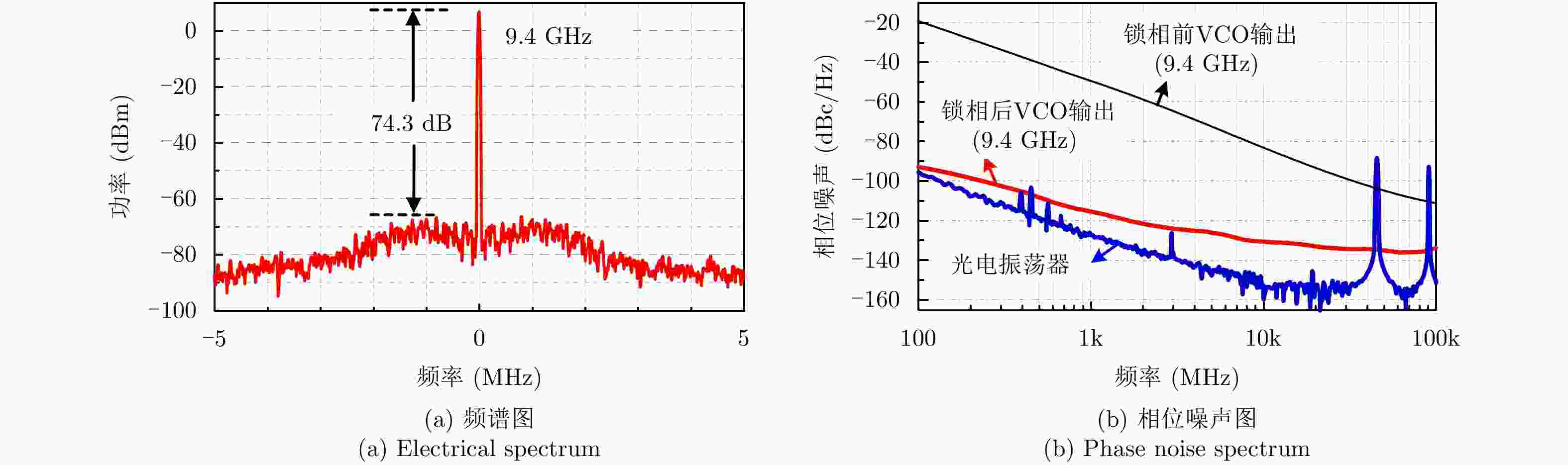
| [1] |
LI Yongke. The design of wide BW frequency synthesizer based on the DDS&PLL hybrid method[C]. 2009 9th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, Beijing, China, 2009: 2-689–2-692. doi: 10.1109/ICEMI.2009.5274484.
|
| [2] |
CHENAKIN A. Frequency synthesis: Current solutions and new trends[J]. Microwave Journal, 2007, 50(5): 256–260.
|
| [3] |
Zhao Z Y, Li X Y, and Chang W G. LFM-CW signal generator based on hybrid DDS-PLL structure[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(6): 391–393. doi: 10.1049/el.2012.2852
|
| [4] |
ROMASHOV V V, ROMASHOVA L V, KHRAMOV K K, et al. Wide-band hybrid frequency synthesizer with improved noise performance[C]. 2018 Moscow Workshop on Electronic and Networking Technologies (MWENT), Moscow, Russia, 2018: 1–4.
|
| [5] |
LI J, YI X, LEE H, et al. Electro-optical frequency division and stable microwave synthesis[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6194): 309–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1252909
|
| [6] |
WEI J, KWON D, ZHANG S, et al. All-fiber-photonics-based ultralow-noise agile frequency synthesizer for X-band radars[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(1): 12–17. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000012
|
| [7] |
ZHOU P, ZHANG F, GUO Q, et al. Linearly chirped microwave waveform generation with large time-bandwidth product by optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 18460–18467. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.018460
|
| [8] |
PENG H, XU Y, GUO R, et al. High frequency resolution X-Band frequency synthesizer based on a Phase-Locked optoelectronic oscillator[C]. 2018 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP), Hangzhou, China, 2018: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ACP.2018.8596011.
|
| [9] |
BELTCHICOV S, DZISIAK A, and GULETSKIY I. A low phase noise octave band synthesizer using an X-Band frequency reference[J]. Mirowave Journal, 2014, 57(5): 104–112.
|
| [10] |
ZHOU W M and BLASCHE G. Injection-locked dual opto-electronic oscillator with ultra-low phase noise and ultra-low spurious level[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(3): 929–933. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.842489
|
| [11] |
LELIÈVRE O, CROZATIER V, BERGER P, et al. A model for designing ultralow noise single- and dual-loop 10-GHz optoelectronic oscillators[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(20): 4366–4374. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2729018
|
| [12] |
ELIYAHU D, SEIDEL D, and MALEKI L. RF amplitude and phase-noise reduction of an optical link and an opto-electronic oscillator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(2): 449–456. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.914640
|
| [13] |
HOROWITZ M, CHRAPLYVY A R, TKACH R W, et al. Broad-band transmitted intensity noise induced by stokes and anti-stokes brillouin scattering in single-mode fibers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 1997, 9(1): 124–126. doi: 10.1109/68.554530
|
| [14] |
VASSILIEVA O, KIM I, and IKEUCHI T. Enabling technologies for fiber nonlinearity mitigation in high capacity transmission systems[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(1): 50–60. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2877310
|
| [15] |
YANG T, DONG J, LIAO S, et al. Comparison analysis of optical frequency comb generation with nonlinear effects in highly nonlinear fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(7): 8508–8520. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.008508
|
| [16] |
YAO X S and MALEKI L. Optoelectronic microwave oscillator[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B (Optical Physics) , 1996, 13(8): 1725–1735. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.13.001725
|
| [17] |
LIU Y, LV Z, DONG Y, et al. Research on stimulated Brillouin scattering suppression based on multi-frequency phase modulation[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2009, 7(1): 29–31. doi: 10.3788/COL20090701.0029
|
| [18] |
CALLAHAN P T, DENNIS M L, and CLARK T R. Experimental demonstration of a phase-modulated optoelectronic oscillator using balanced detection[C]. 2011 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control and the European Frequency and Time Forum (FCS) Proceedings, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/FCS.2011.5977742.
|
| [19] |
ZHU Y, ZHANG H, and HONG W. A frequency agile synthesizer using DDS and PLL techniques for FMCW radar[C]. 2015 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Nanjing, China, 2015, 2: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/APMC.2015.7413219.
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: