-
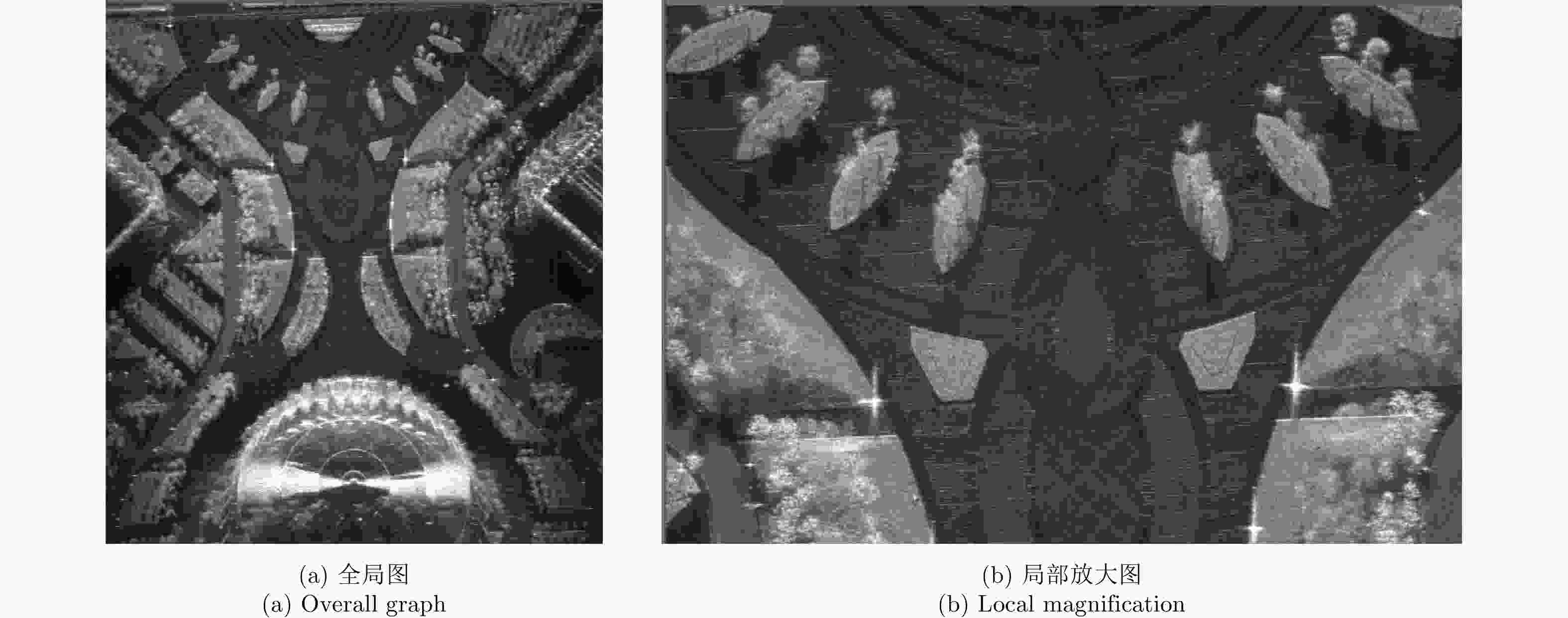
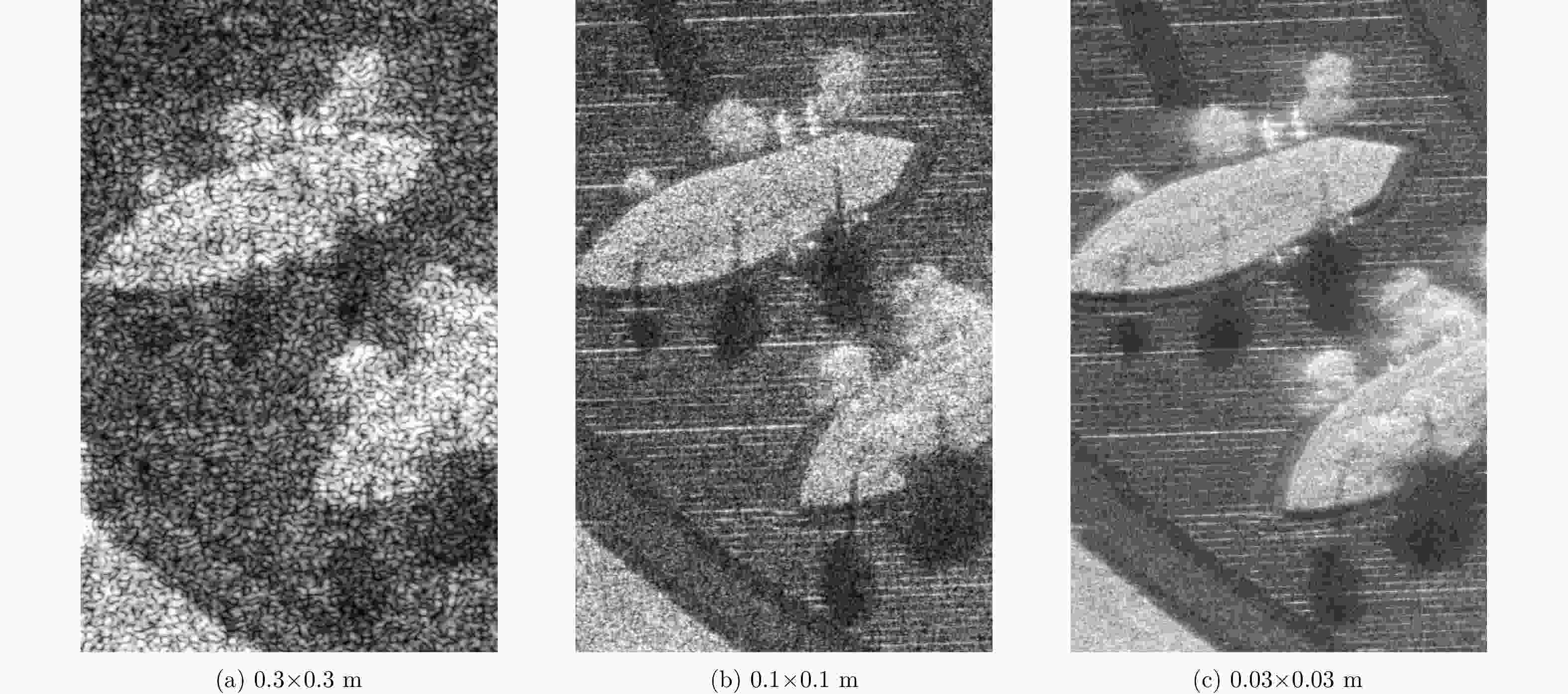
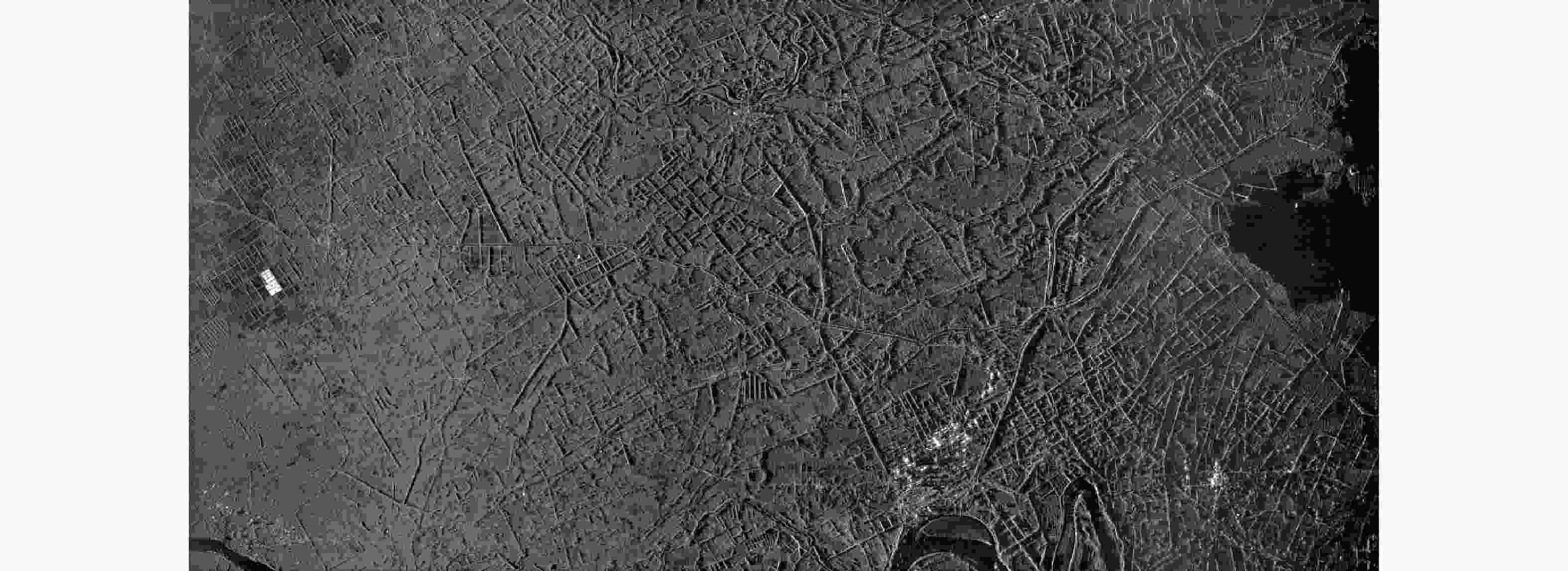
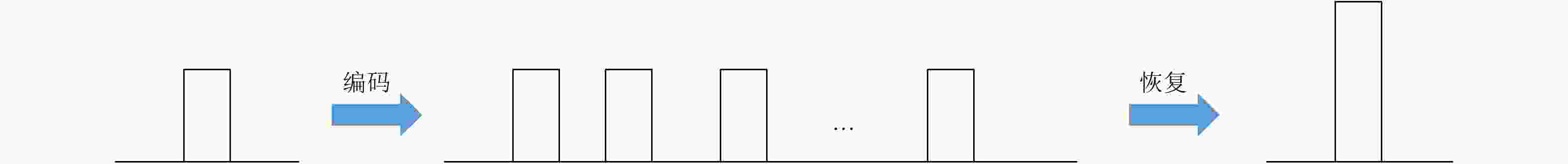
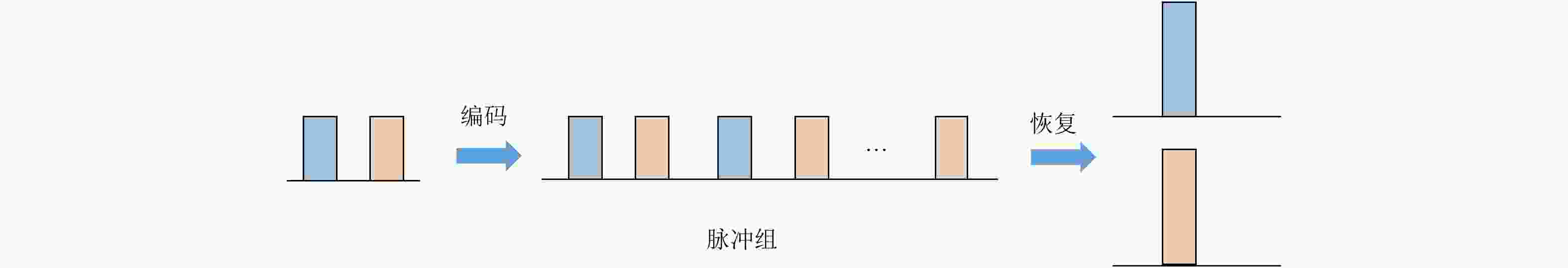
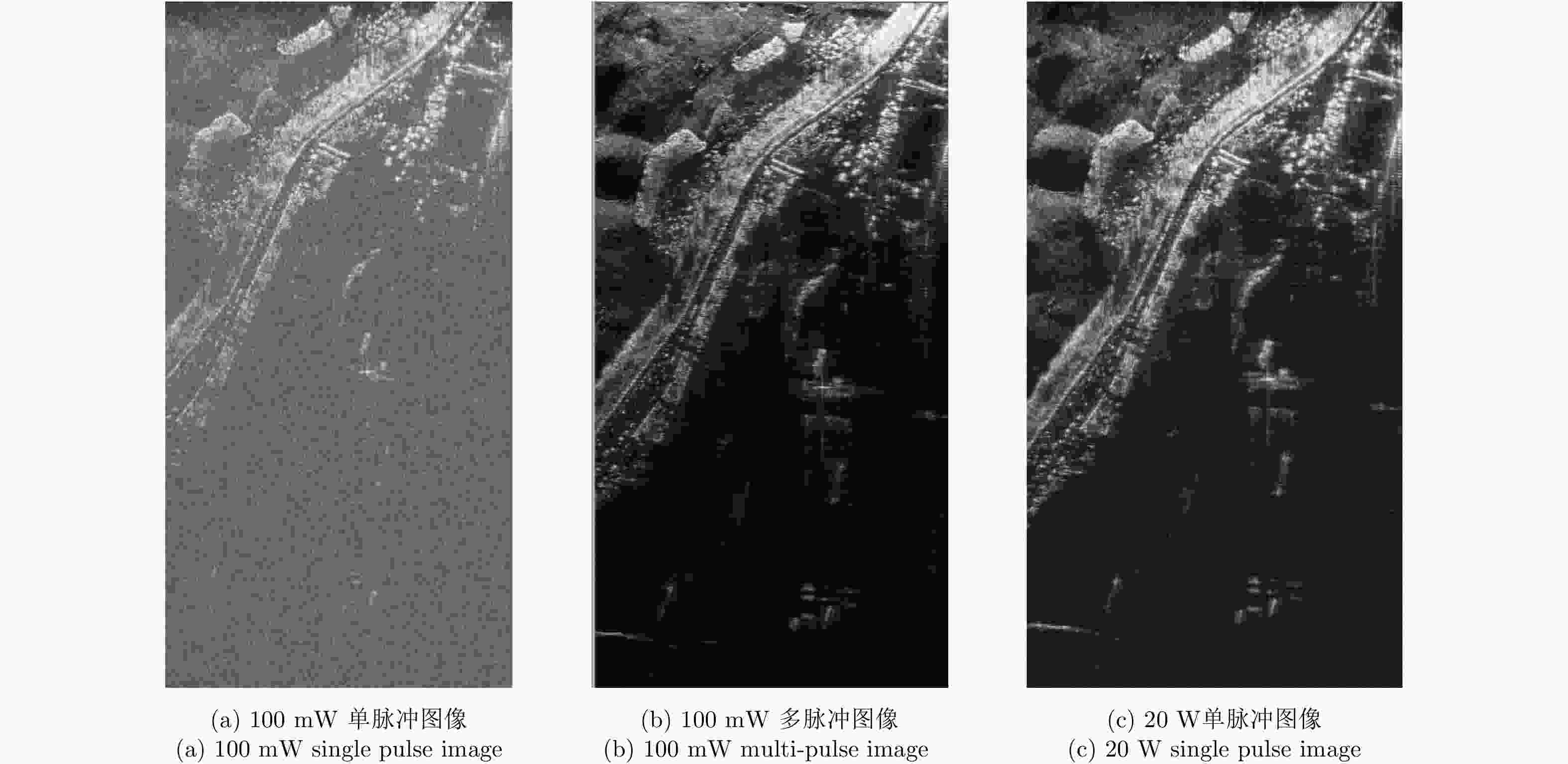
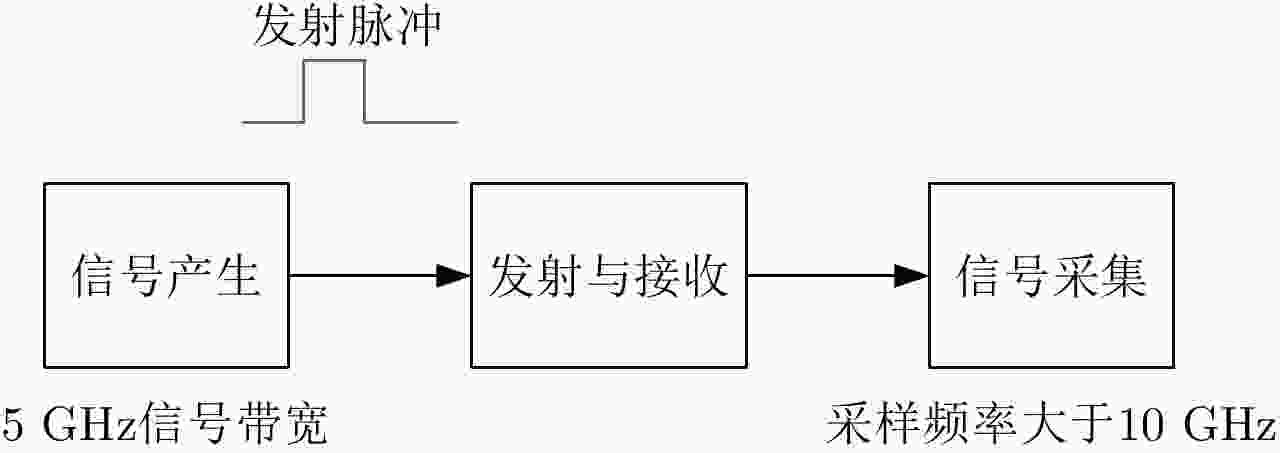
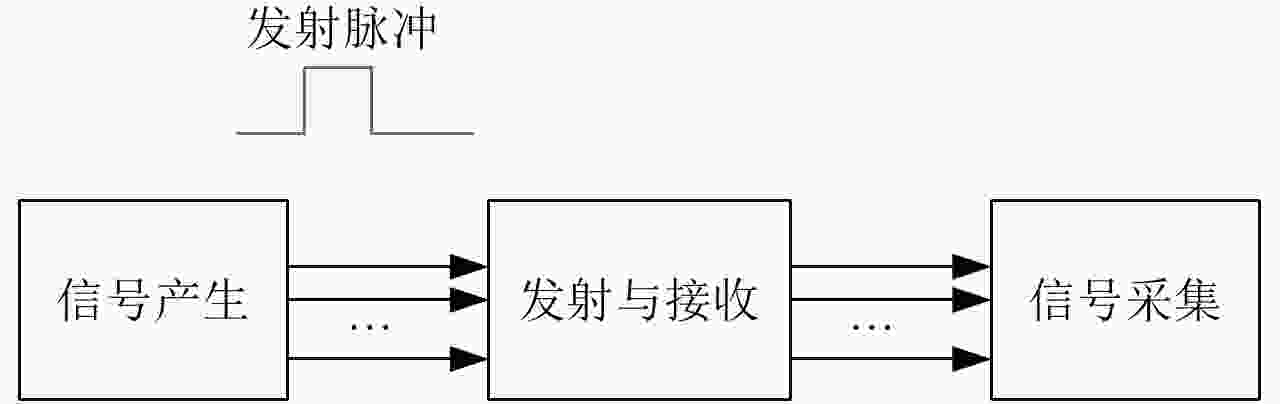
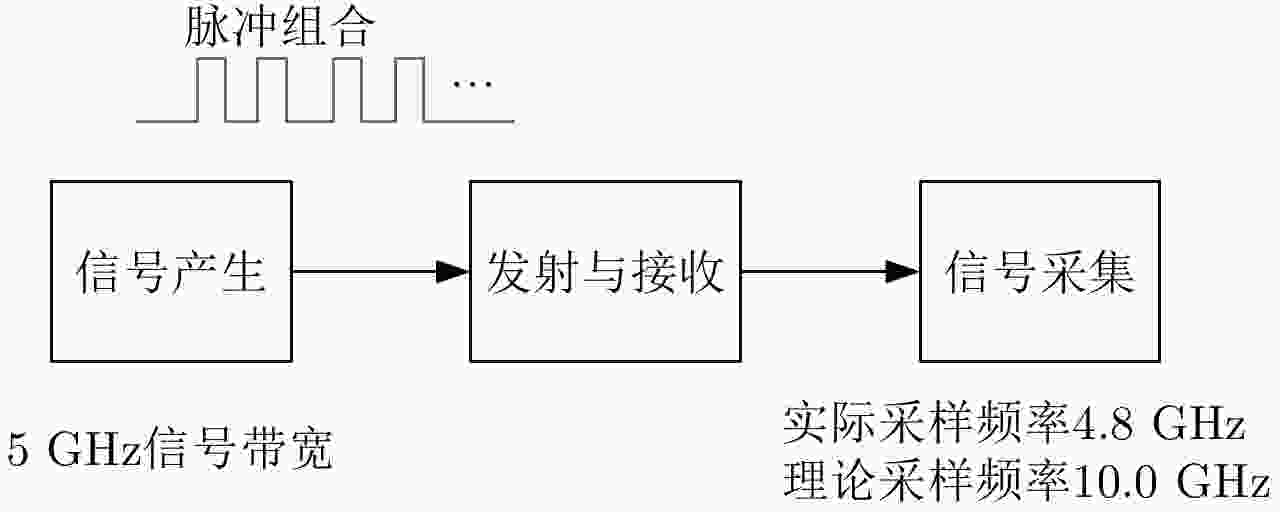
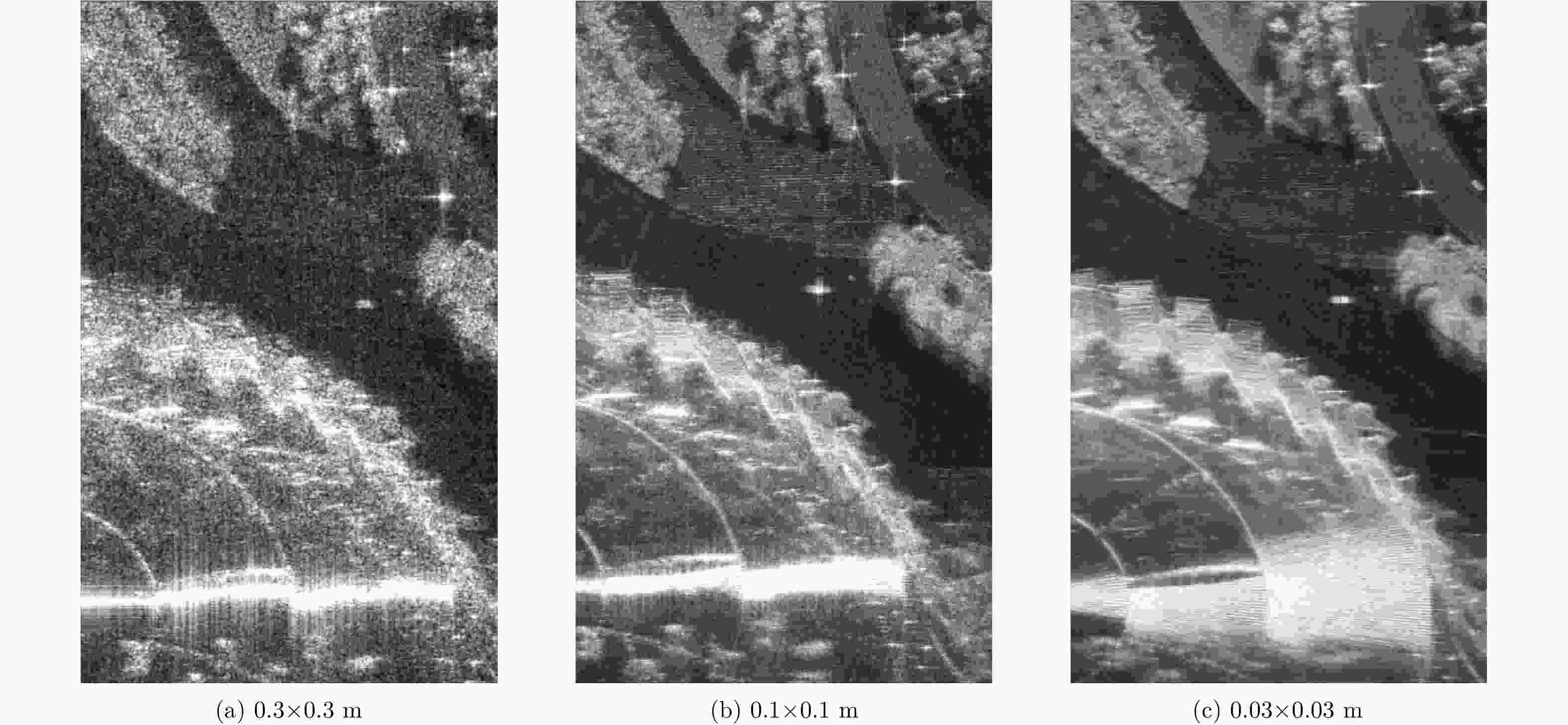
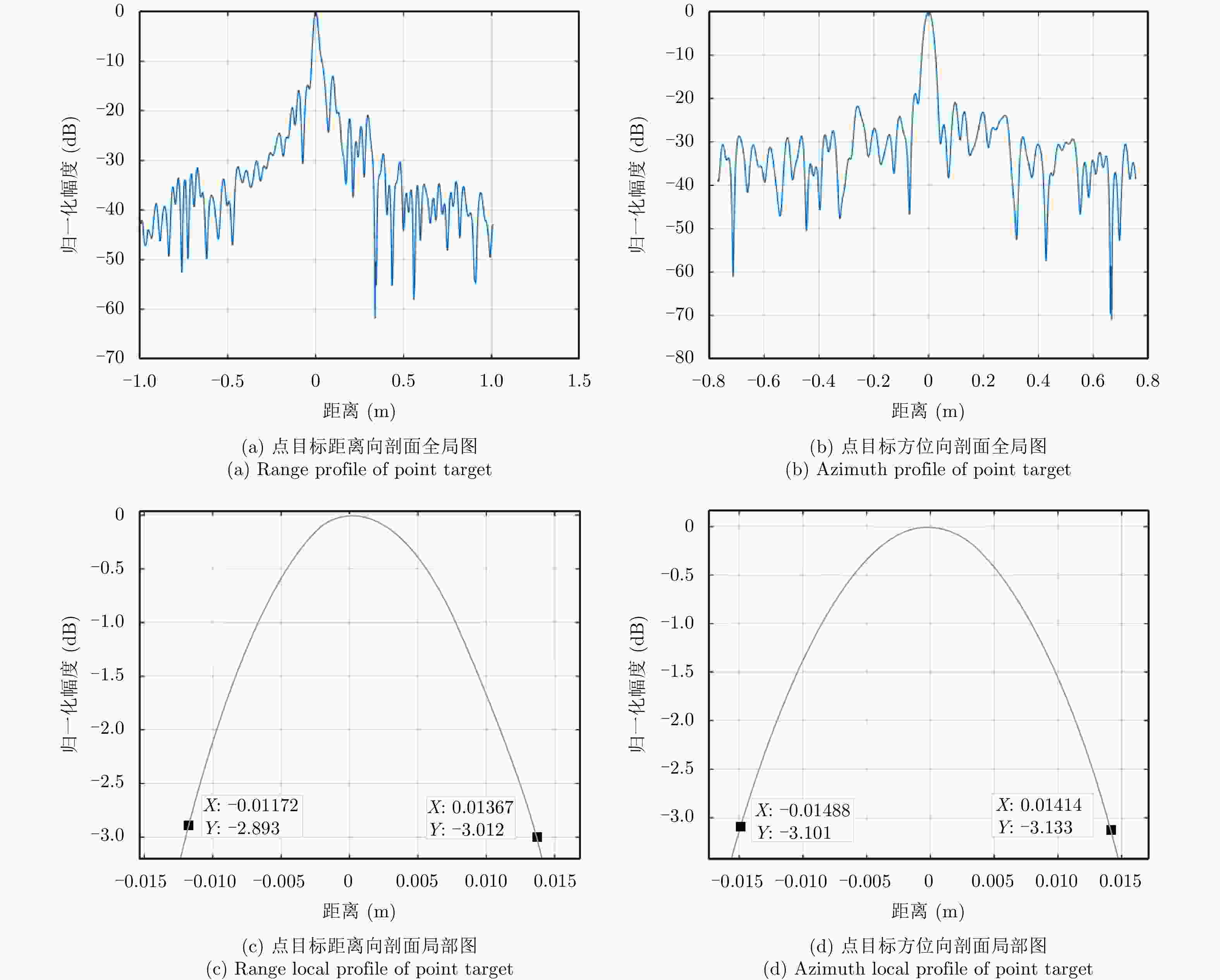
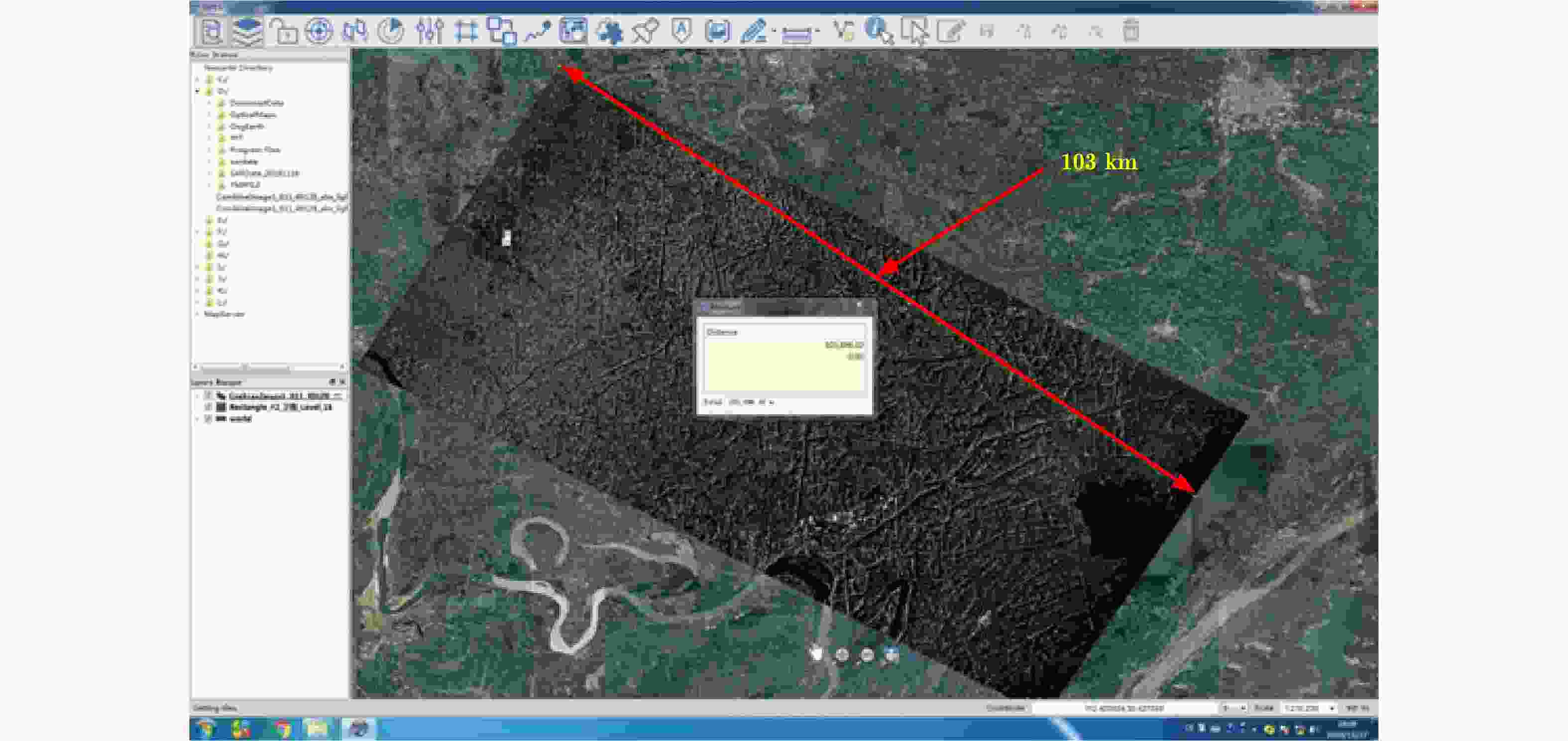
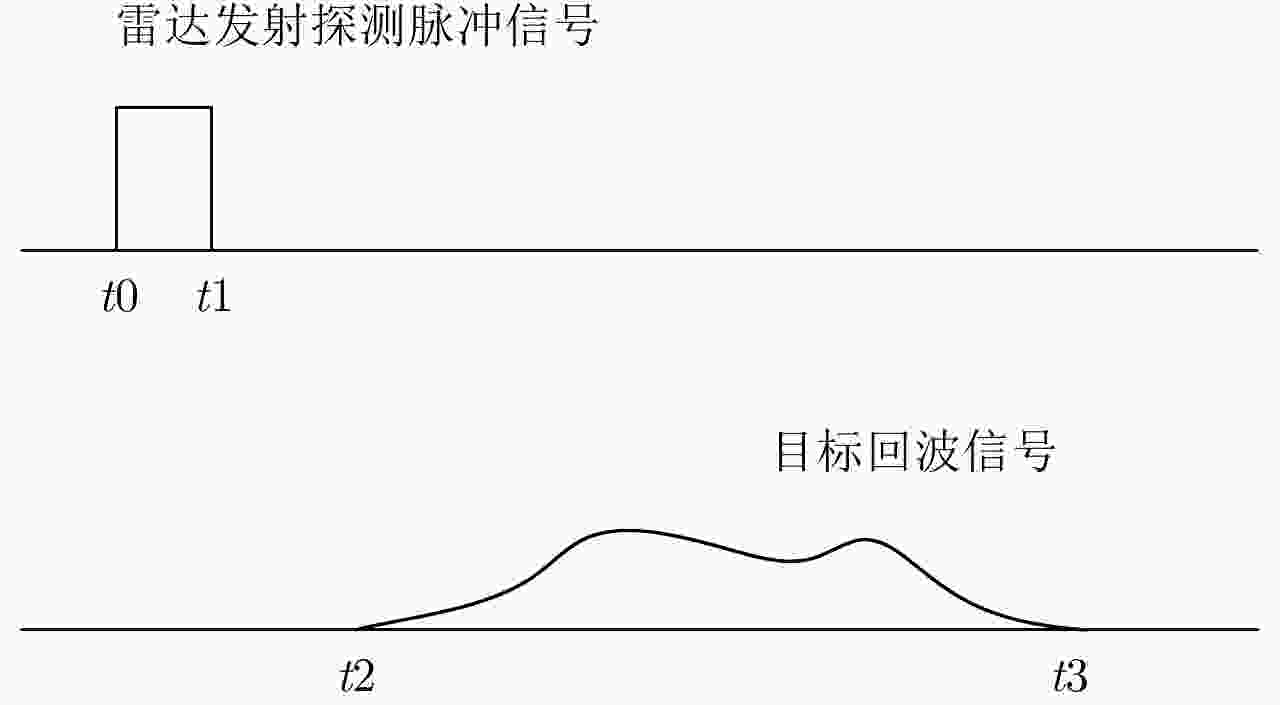
摘要: 该文提出了基于脉冲组合编码的雷达探测模式,建立了脉冲编码雷达的基本概念和理论模型。利用多脉冲组合及其时间、频率、相位参量的调制,实现脉冲信号在时间域、频率域、或者时频域结合的编码,为解决传统的脉冲及连续波雷达系统参数相互耦合约束、及其对雷达性能的限制问题,提供了基于多脉冲组合探测的新方法及理论基础。该文着重介绍了多脉冲组合探测的编码、目标信号恢复方法,以及结合研制的合成孔径雷达开展的编码方法、性能评估等实验研究。研究及实验表明,通过采用分频带脉冲编码方法,可使雷达信号采样率突破奈奎斯特采样定理限制,降低系统的实现难度,实验系统中实现了4.8 GHz采样率对5 GHz带宽信号的采样及无失真恢复,成像分辨率达到0.03×0.03 m;通过采用增加占空比的时域脉冲编码方法,实现了信噪比改善超过20 dB的大幅度提高;通过针对合成孔径雷达的成像特性进行2维编码,去除了信号模糊问题,实现了成像幅宽超过90 km等先进性能指标。理论及实验结果验证了脉冲编码方法在提高雷达核心性能方面的显著优势,为高性能雷达系统的实现建立了新的技术途径。Abstract: This paper presents a radar working mode based on multi-pulse combination and coding, and the basic concept and theoretical model of pulse-coded radar are established. Using multi-pulse combination and the modulation of the time, frequency, and phase parameters, the pulse signal is coded in time domain, frequency domain, or time-frequency domain. Based on multi-pulse combination and coding, a new working method and theoretical basis are provided to solve the problem of coupling constraints among parameters of traditional pulse and continuous wave radars, which limits the performance of the radar system. Based on the fabricated Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and its tests, the pulse coding, target signal recovery method, and pulse coding performance were studied. The study and test results show that the sampling rate of radar signals could be reduced to break through the limitation of Nyquist sampling theorem and simplify the difficulty of system implementation using frequency division pulse coding method. A 5 GHz bandwidth signal was sampled with 4.8 GHz and was recovered without distortion in the radar system, and an SAR imaging resolution of 0.03×0.03 m was realized. By using the time domain pulse coding method with an increase of duty cycle, the signal-to-noise ratio was improved by over 20 dB. By using the two-dimensional pulse coding method, the SAR signal ambiguity was removed, and the imaging swath of over 90 km was realized. The theoretical and test results verify the significant advantages of the pulse coding method in improving radar performance, by which a new technical approach for the realization of high performance radar system is provided.
-
表 1 多脉冲编码信噪比改善结果(与单脉冲比较)
Table 1. Improvement of signal-to-noise ratio of multi-pulse coding (Comparison with single pulse)
回波接收窗口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 SNR改善(dB) 13.59 9.61 11.37 11.37 11.37 11.37 11.37 11.37 11.37 9.61 13.59 表 2 多相编码
Table 2. Polyphase coding
编码方式 实现形式 2相编码 $0,{{π}} ,{{π}} ,0,0,{{π}} ,{{π}} ,0,0, ·\!·\!· $ 3相编码 $0,{{2{{π}} } / 3},0, ·\!·\!· $ 4相编码 $0,{{{π}} / 2}, - {{{π}} / 2},{{π}} ,{{π}} , - {{{π}} / 2},{{{π}} / 2},0, ·\!·\!· $ 5相编码 $0,{{2{{π}} } / 5}, - {{4{{π}} } / 5},{{2{{π}} } / 5},0,0,{{2{{π}} } / 5}, - {{4{{π}} } / 5},{{2{{π}} } / 5},0, ·\!·\!· $ 多相编码 ${\varphi _q} = {\varphi _{q - 1}} + q\frac{{2{{π}} }}{Q}$ -
[1] 丁鹭飞, 耿富录. 雷达原理[M]. 第3版, 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002: 1–22.DING Lufei and GENG Fulu. Principle of Radar[M]. 3rd ed, Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2002: 1–22. [2] WEHNER D R. High Resolution Radar[M]. Norwood, MA: Artech House, 1987: 9–42. [3] WILEY C A. Synthetic aperture radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1985, AES-21(3): 440–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1985.310578 [4] STIMSON G W. Introduction to Airborne Radar[M]. 2nd ed, Mendham, NJ: SciTech Publishing, Inc., 1998: 393–431. [5] CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873 [6] GRAHAM L C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(6): 763–768. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9516 [7] ZEBKER H A and GOLDSTEIN R M. Topographic mapping from interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1986, 91(B5): 4993–4999. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB05p04993 [8] VAN ZYL J J, ZEBKER H A, and ELACHI C. Imaging radar polarization signatures: Theory and observation[J]. Radio Science, 1987, 22(4): 529–543. doi: 10.1029/RS022i004p00529 [9] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995: 1–75. [10] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [11] BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2007: 128–133. [12] YOON Y S and AMIN M G. Compressed sensing technique for high-resolution radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 6968, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition XVII, Orlando, Florida, 2008: 69681A. [13] 刘记红, 徐少坤, 高勋章, 等. 压缩感知雷达成像技术综述[J]. 信号处理, 2011, 27(2): 251–260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.02.016LIU Jihong, XU Shaokun, GAO Xunzhang, et al. A review of radar imaging technique based on compressed sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 27(2): 251–260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.02.016 [14] 张弓, 杨萌, 张劲东, 等. 压缩感知在雷达目标探测与识别中的研究进展[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2012, 27(1): 1–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.01.001ZHANG Gong, YANG Meng, ZHANG Jindong, et al. Advances in theory and application of compressed sensing in radar target detection and recognition[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2012, 27(1): 1–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.01.001 [15] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMINI L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448 [16] WANG Wenqin. Large-area remote sensing in high-altitude high-speed platform using MIMO SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(5): 2146–2158. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2236301 [17] 武其松, 井伟, 邢孟道, 等. MIMO-SAR大测绘带成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(4): 772–775. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01959WU Qisong, JING Wei, XING Mengdao, et al. Wide swath imaging with MIMO-SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(4): 772–775. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01959 [18] 周伟, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. MIMO-SAR技术发展概况及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074ZHOU Wei, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Brief analysis on the development and application of multi-input multi-output synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 10–18. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13074 [19] 王怀军, 许红波, 陆珉, 等. MIMO雷达技术及其应用分析[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2009, 7(4): 245–249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.04.001WANG Huaijun, XU Hongbo, LU Min, et al. Technology and application analysis of MIMO radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2009, 7(4): 245–249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.04.001 [20] HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335 [21] ADVE R, HALE T, and WICKS M. Knowledge based adaptive processing for ground moving target indication[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2007, 17(2): 495–514. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2005.06.005 [22] GOODMAN N A, VENKATA P R, and NEIFELD M A. Adaptive waveform design and sequential hypothesis testing for target recognition with active sensors[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(1): 105–113. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2007.897053 [23] 黎湘, 范梅梅. 认知雷达及其关键技术研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025LI Xiang and FAN Meimei. Research advance on cognitive radar and its key technology[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.09.025 [24] 金林. 智能化认知雷达综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2013, 35(11): 6–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2013.11.002JIN Lin. Overview of cognitive radar with intelligence[J]. Modern Radar, 2013, 35(11): 6–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2013.11.002 [25] 王岩飞, 刘畅, 詹学丽, 等. 无人机载合成孔径雷达系统技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089WANG Yanfei, LIU Chang, ZHAN Xueli, et al. Technology and applications of UAV synthetic aperture radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089 [26] META A, DE WIT J J M, and HOOGEBOOM P. Development of a high resolution airborne millimeter wave FM-CW SAR[C]. 2004 First European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004: 209–212. [27] META A and HOOGEBOOM P. Development of signal processing algorithms for high resolution airborne millimeter wave FMCW SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2005: 326–331. [28] YAMAGUCHI Y, MITSUMOTO M, SENGOKU M, et al. Synthetic aperture FM-CW radar applied to the detection of objects buried in snowpack[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(1): 11–18. doi: 10.1109/36.285184 [29] CHARVAT G L and KEMPEL L C. Synthetic aperture radar imaging using a unique approach to frequency-modulated continuous-wave radar design[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2006, 48(1): 171–177. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2006.1645606 [30] 蔡永俊, 张祥坤, 姜景山. 毫米波FMCW SAR系统设计与成像研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2016, 38(2): 1–5. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.02.001CAI Yongjun, ZHANG Xiangkun, and JIANG Jingshan. A study on system design and imaging of millimeter wave FMCW SAR[J]. Modern Radar, 2016, 38(2): 1–5. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.02.001 [31] 耿淑敏, 江志红, 程翥, 等. FM-CW SAR距离-多普勒成像算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(10): 2346–2349. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00415GENG Shumin, JIANG Zhihong, CHENG Zhu, et al. Study on imaging algorithm of FM-CW SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(10): 2346–2349. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00415 [32] KHAN R H and MITCHELL D K. Waveform analysis for high-frequency FMICW radar[J]. IEE Proceedings F Radar and Signal Processing, 1991, 138(5): 411–419. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0054 [33] 朱天林, 金胜, 王海波. 准连续波体制雷达应用研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2012, 34(7): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2012.07.001ZHU Tianlin, JIN Sheng, and WANG Haibo. Application on quasi-continuous wave radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2012, 34(7): 1–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2012.07.001 [34] 王岩飞, 刘中梅. SAR分布目标多视图像分辨特性研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(10): 2294–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170118WANG Yanfei and LIU Zhongmei. Study on distributed targets resolution of multilook SAR image[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(10): 2294–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170118 [35] CANTALLOUBE H and DUBOIS-FERNANDEZ P. Airborne X-band SAR imaging with 10 cm resolution: Technical challenge and preliminary results[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 163–176. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045097 [36] REIGBER A, SCHEIBER R, JAGER M, et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: signal processing and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2013, 101(3): 759–783. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2220511 [37] ENDER J H G and BRENNER A R. PAMIR — a wideband phased array SAR/MTI system[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 165–172. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030445 [38] BRENNER A R. Ultra-high resolution airborne SAR imaging of vegetation and man-made objects based on 40% relative bandwidth in X-band[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 7397–7400. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351920. [39] BRENNER A R. Improved radar imaging by centimeter resolution capabilities of the airborne SAR sensor PAMIR[C]. Proceedings of the 2013 14th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 218–223. [40] TSUNODA S I, PACE F, STENCE J, et al. Lynx: A high-resolution synthetic aperture radar[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 3704, Radar Sensor Technology IV, Orlando, FL, 1999: 20–27. [41] 王岩飞, 刘畅, 李和平, 等. 基于多通道合成的优于0.1 m分辨率的机载SAR系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(1): 29–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01370WANG Yanfei, LIU Chang, LI Heping, et al. An airborne SAR with 0.1 m resolution using multi-channel synthetic bandwidth[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(1): 29–35. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01370 [42] CURRIE A and BROWN M A. Wide-swath SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings F - Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(2): 122–135. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0016 [43] CALLAGHAN G D and LONGSTAFF I D. Wide-swath space-borne SAR using a quad-element array[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1999, 146(3): 159–165. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19990126 [44] SUESS M, GRAFMUELLER B, and ZAHN R. A novel high resolution, wide swath SAR system[C]. Proceedings of Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future. Proceedings. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 2001, 3: 1013–1015. [45] 宋岳鹏, 杨汝良. 应用多收发孔径实现高分辨率宽测绘带的合成孔径雷达研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(9): 2110–2113. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00140SONG Yuepeng and YANG Ruliang. Study on high resolution, wide swath synthetic aperture radar using multiple transmit-receive apertures[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(9): 2110–2113. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00140 [46] 郭振永, 袁新哲, 张平. 一种多通道SAR高分辨率宽测绘带成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(2): 310–313. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00986GUO Zhenyong, YUAN Xinzhe, and ZHANG Ping. An algorithm of multichannel SAR high-resolution and wide-swath imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2008, 30(2): 310–313. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2006.00986 [47] BORDONI F, YOUNIS M, and KRIEGER G. Ambiguity suppression by azimuth phase coding in multichannel SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(2): 617–629. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2161672 [48] DALL J and KUSK A. Azimuth phase coding for range ambiguity suppression in SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2004, 3: 1734–1737. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2004.1370667. [49] 曾祥能, 刘宪勋, 白洁, 等. 基于方位向多波束-多相位中心的星载SAR多维波形编码技术研究[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 41(9): 1863–1868. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.032ZENG Xiangneng, LIU Xianxun, BAI Jie, et al. Study of space borne SAR multidimensional waveform encoding technology based on azimuth multi-beams multi-phase centers[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(9): 1863–1868. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.032 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: