Vibration-parameters Estimation Method for Airplane Wings Based on Microwave-photonics Ultrahigh-resolution Radar
-
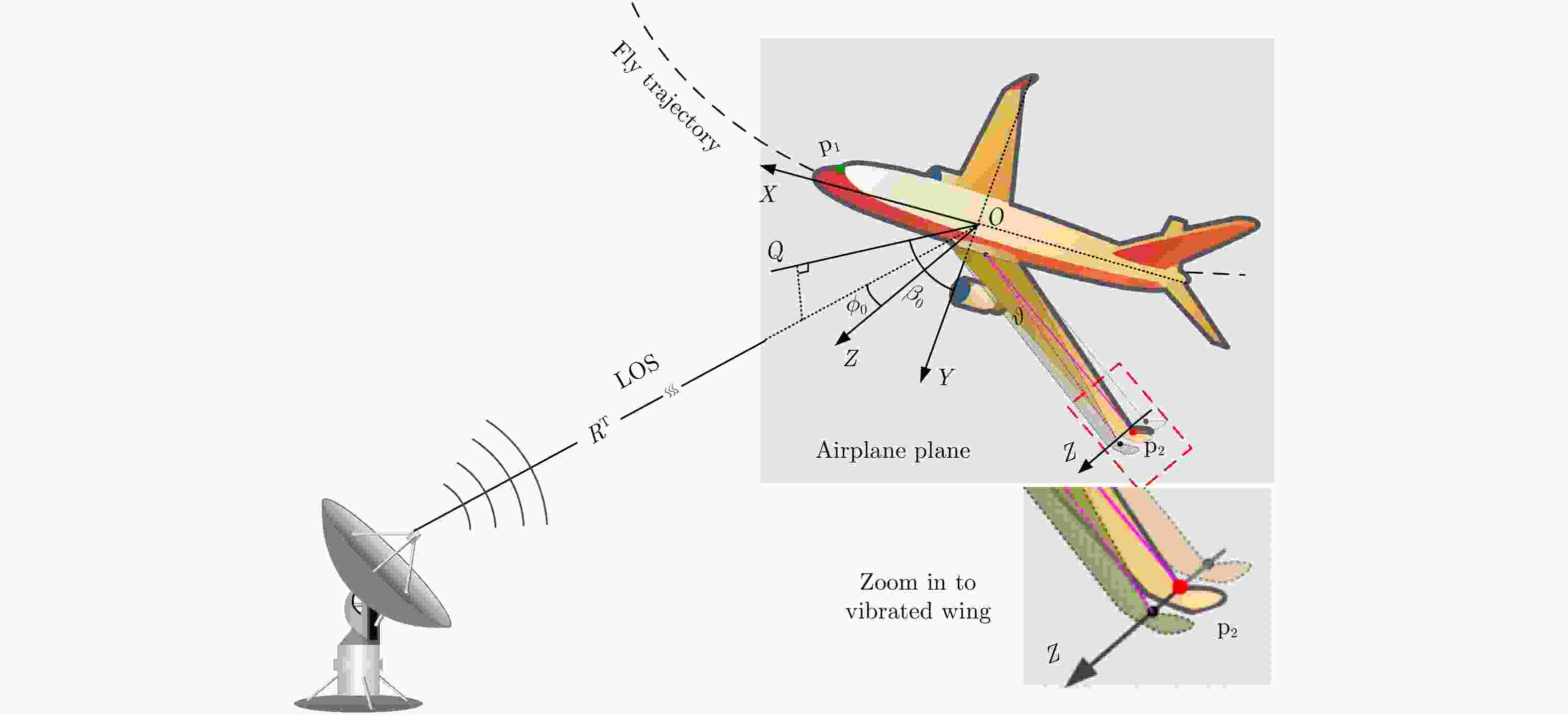
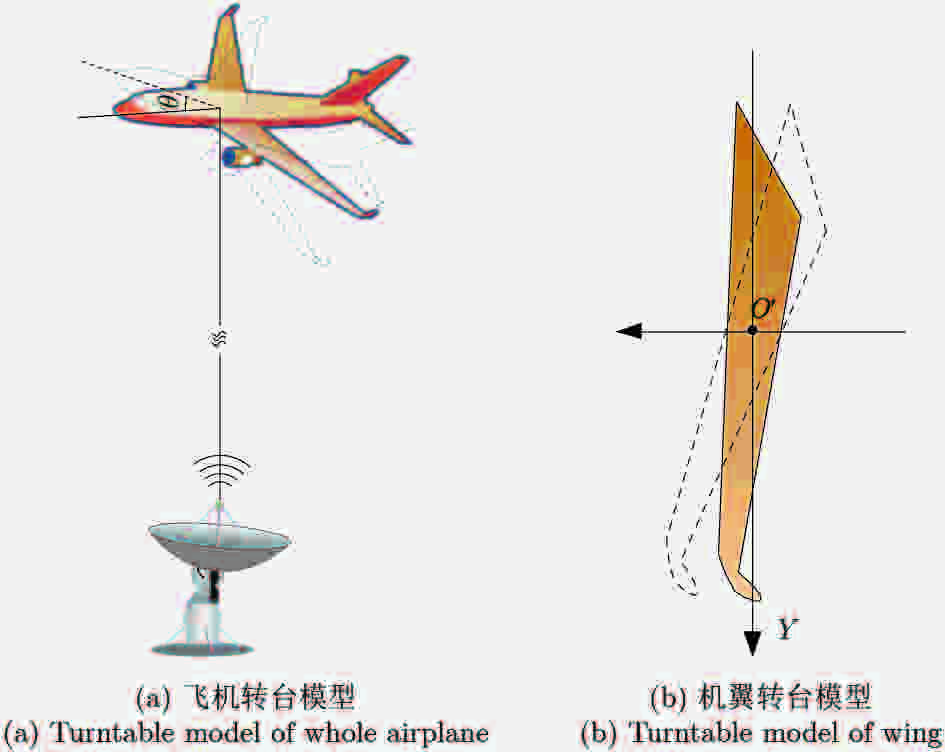
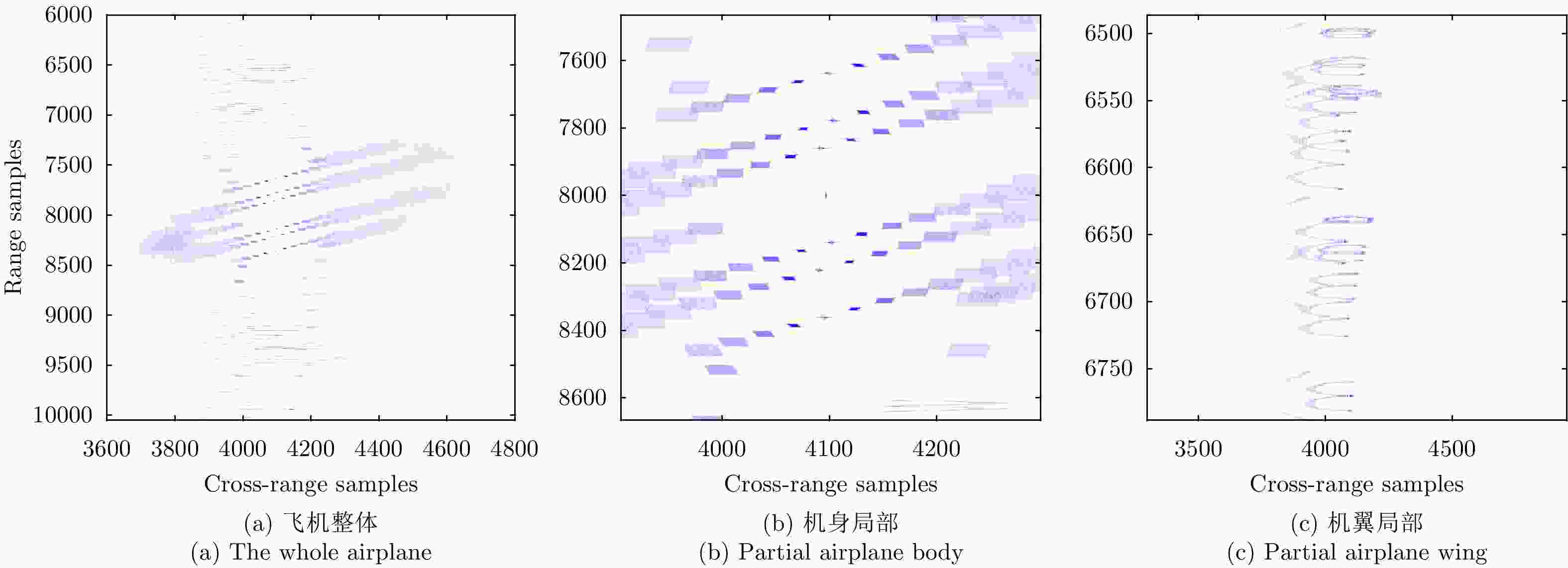
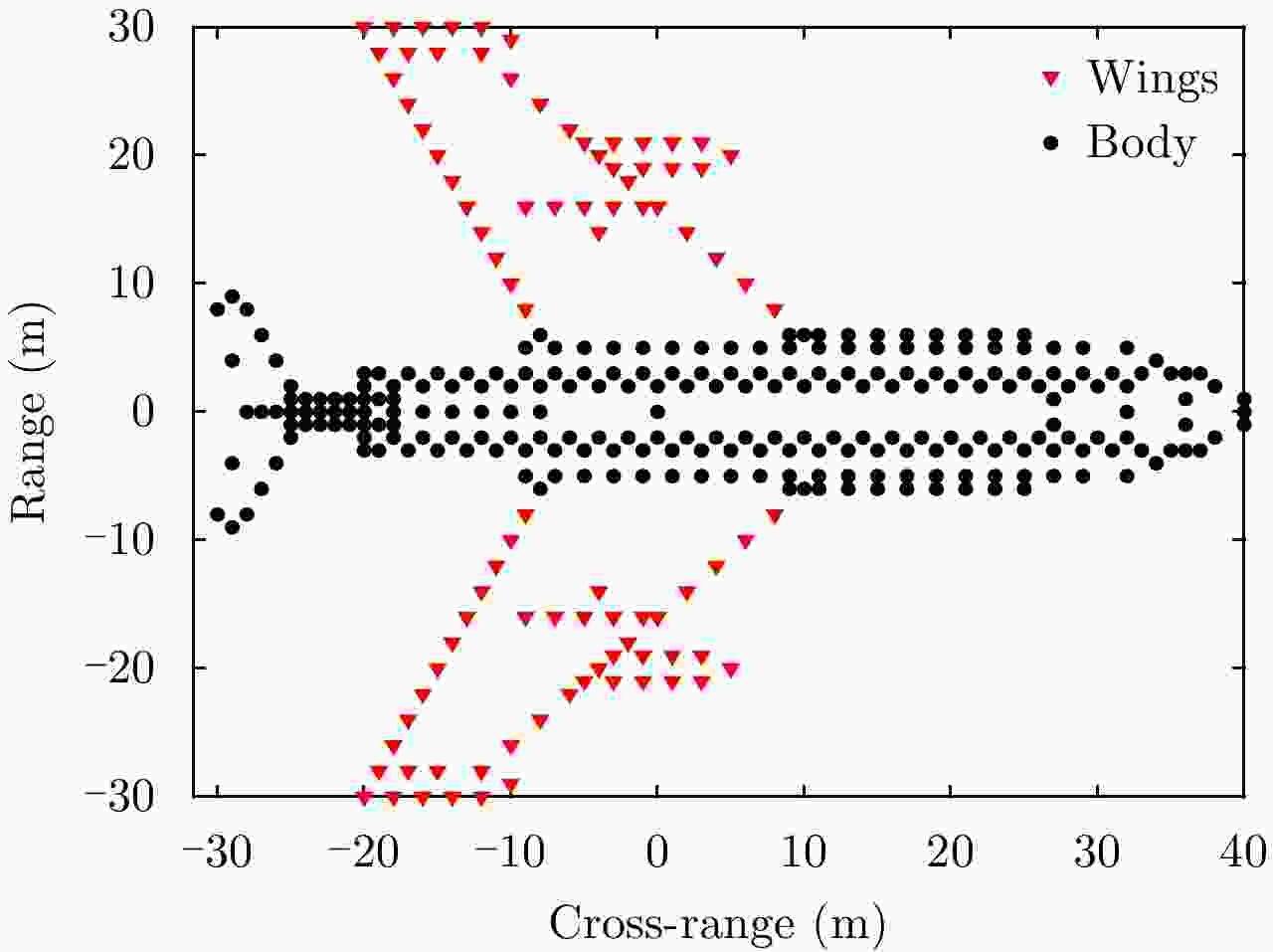
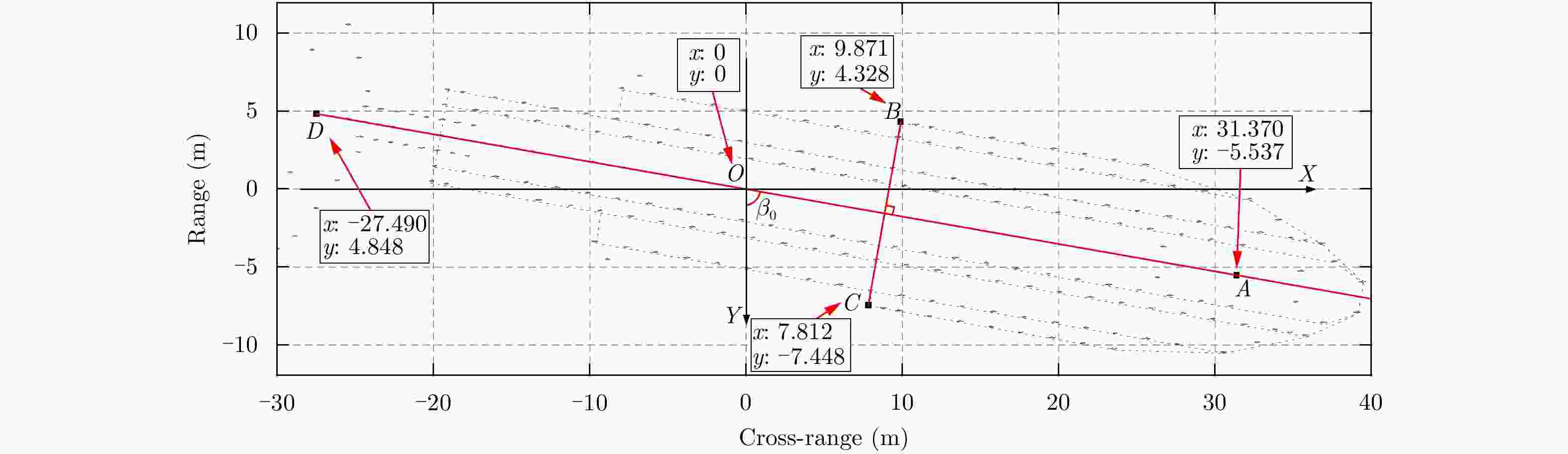
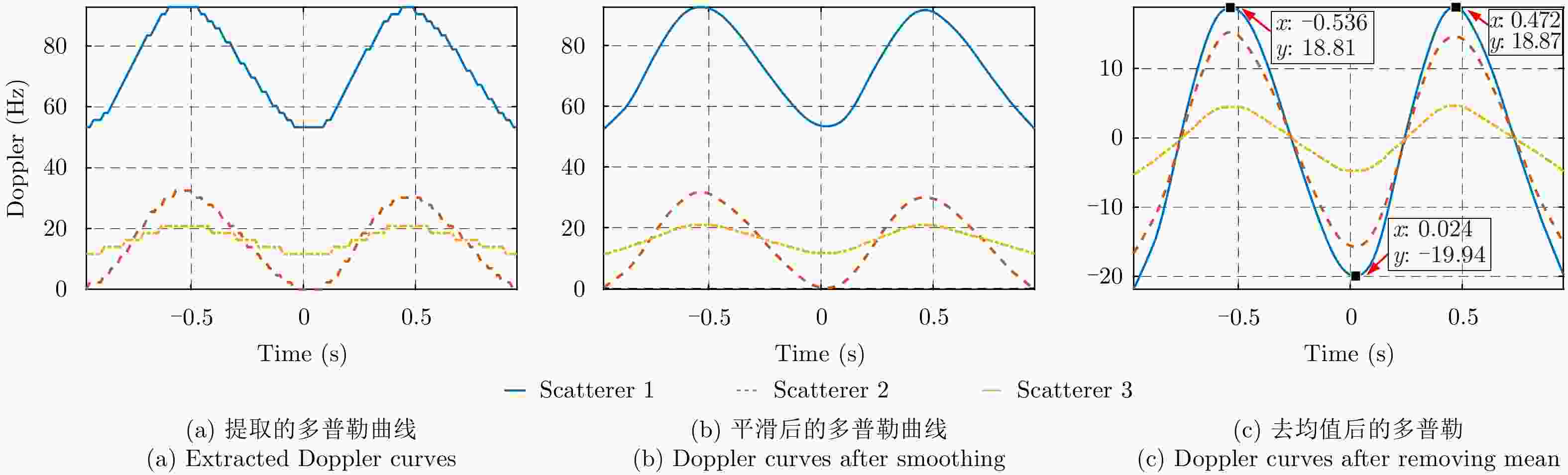
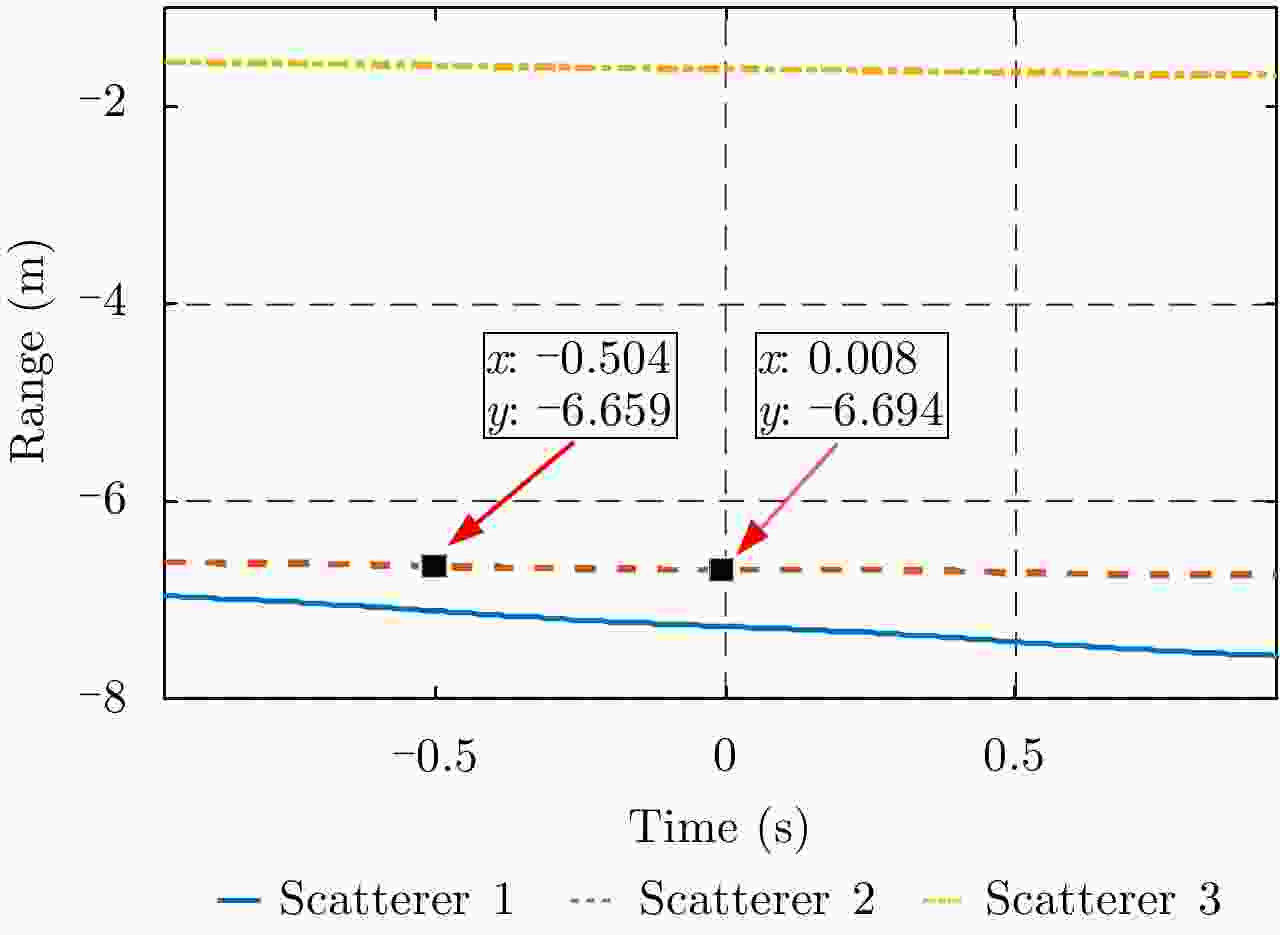
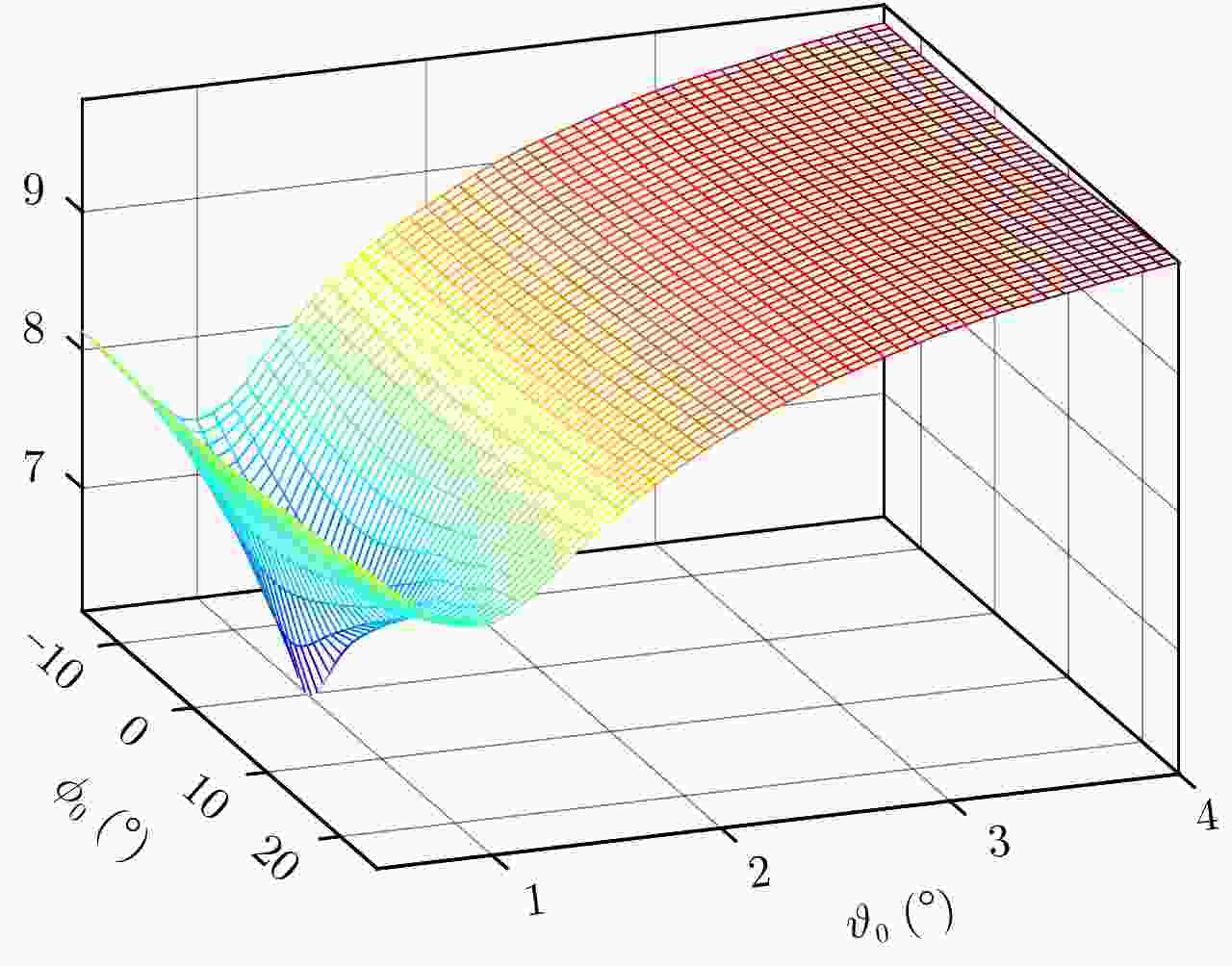
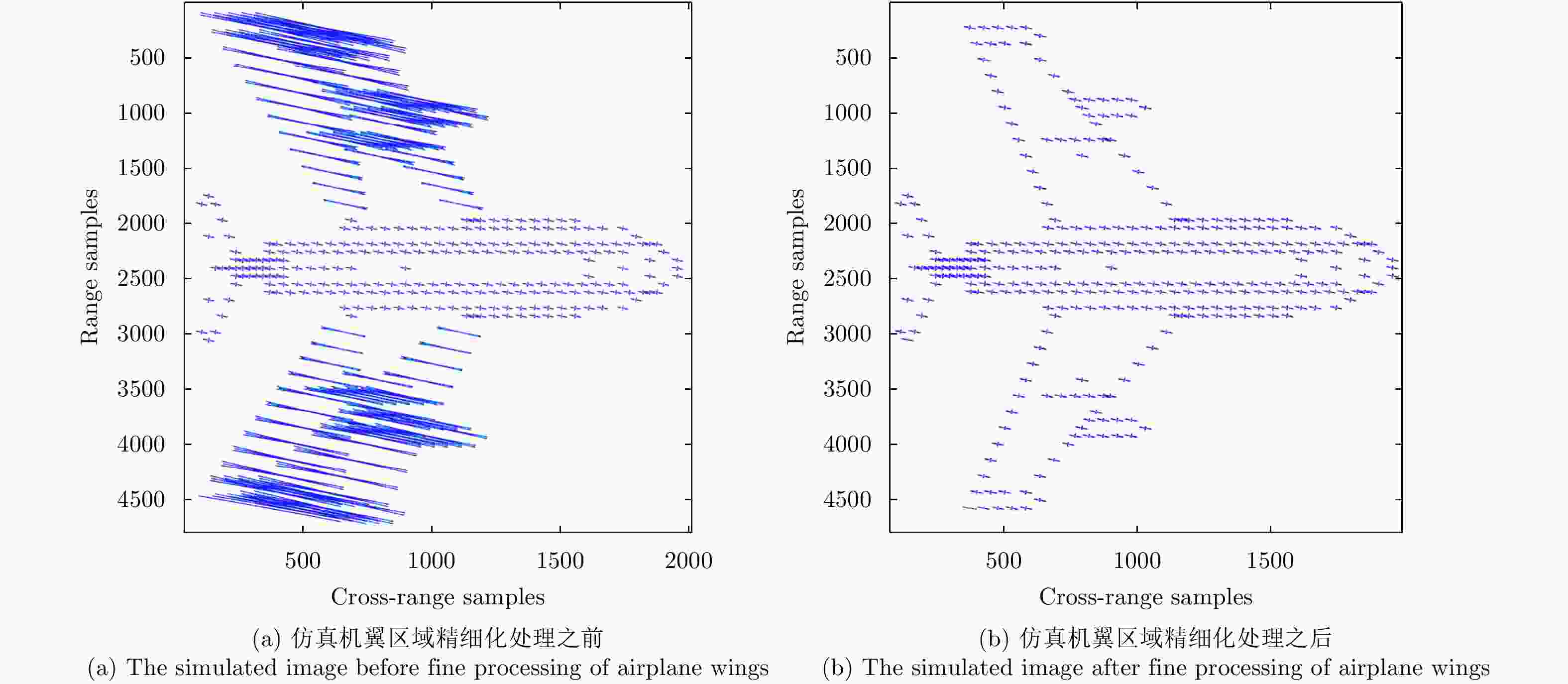
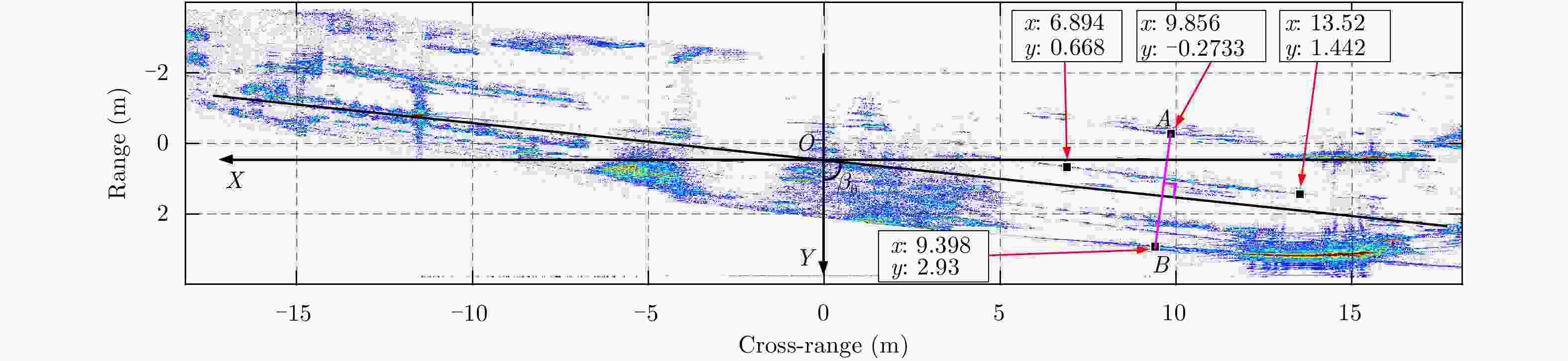
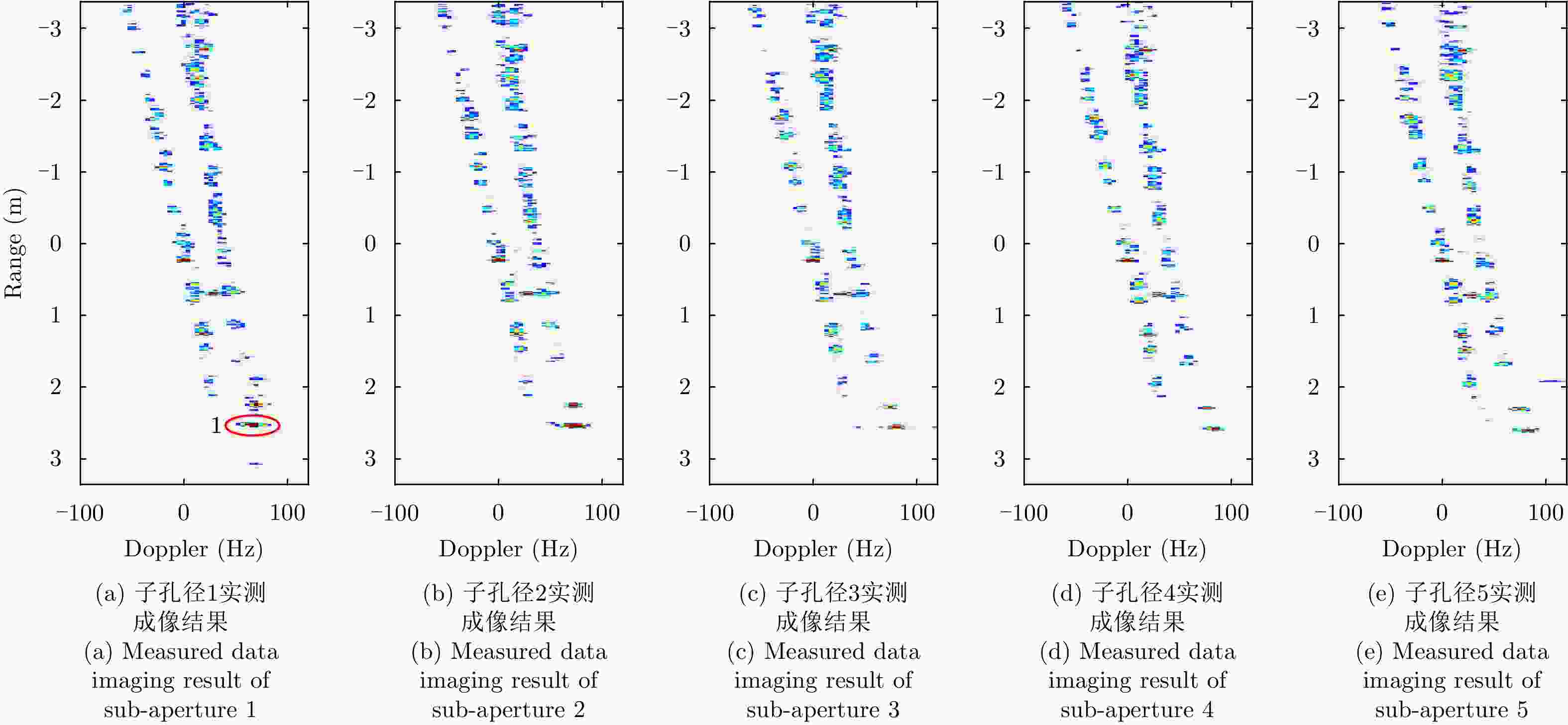
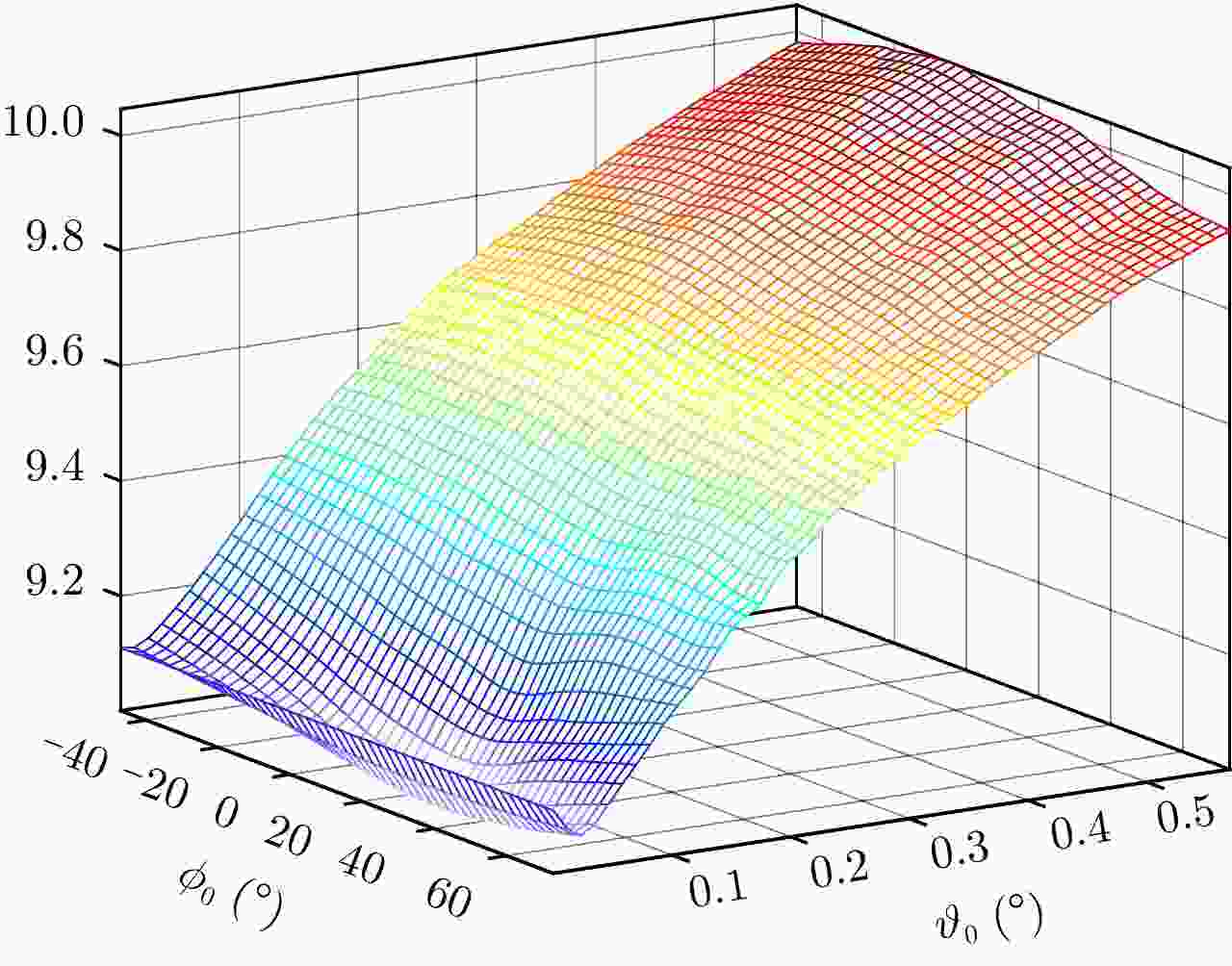
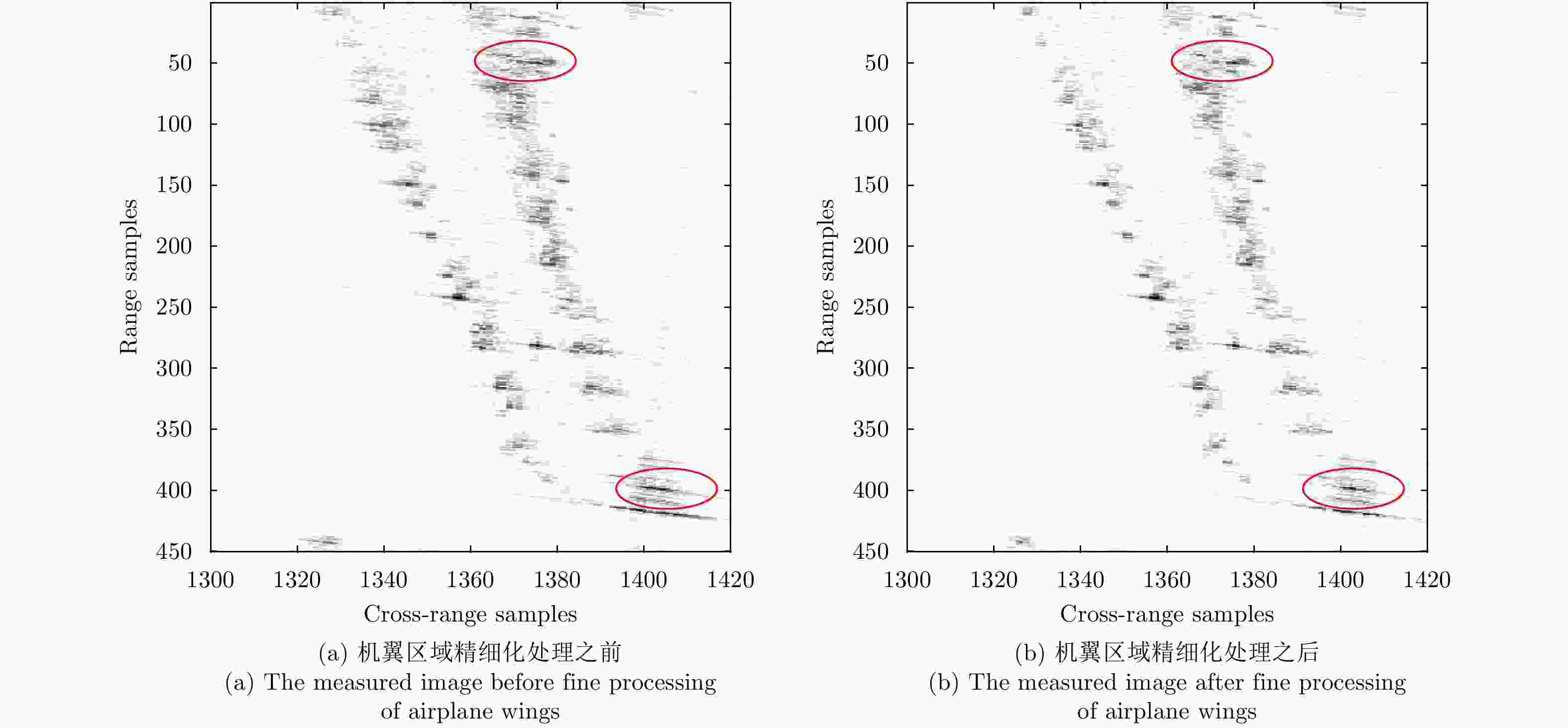
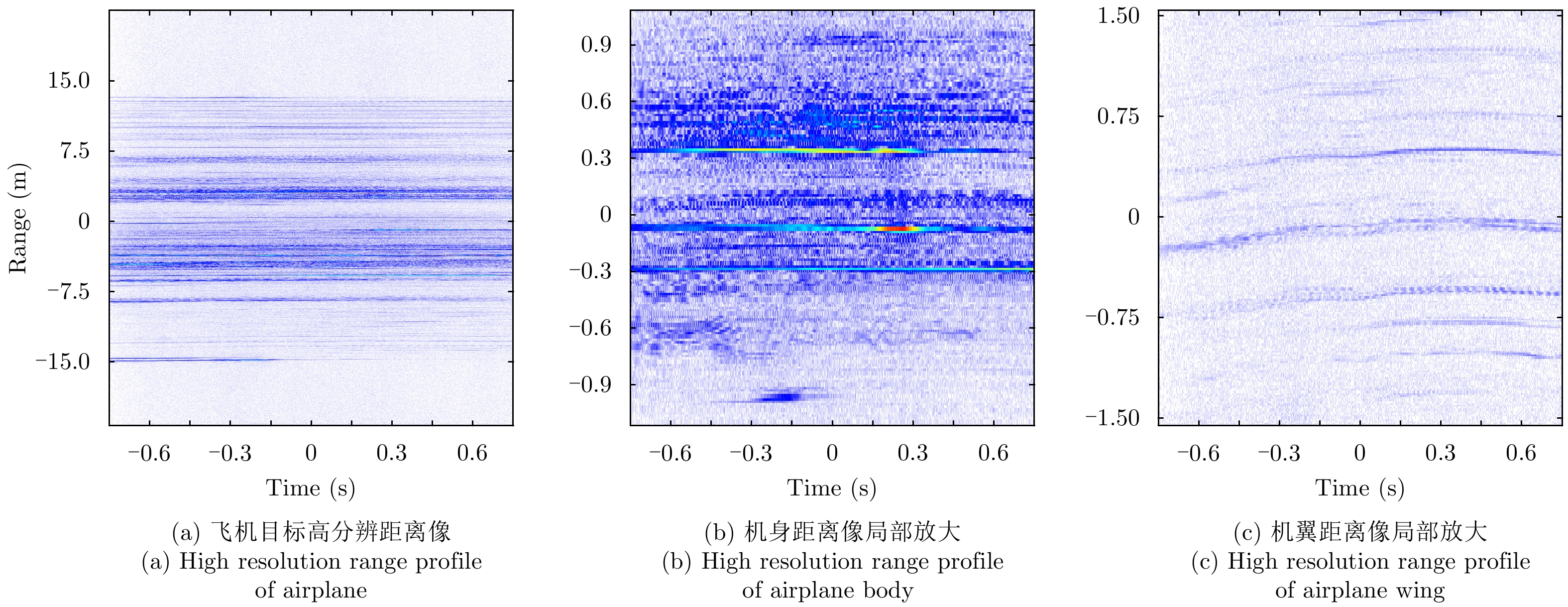
摘要: 机翼在飞机运动不平稳状态下存在振动,在微波光子超高分辨雷达观测下,这种振动会造成机翼难以聚焦,针对这一难题,该文提出一种基于微波光子超高分辨雷达的机翼振动参数估计方法。首先通过粗成像将机身和机翼回波进行分离,再通过对机身成像和定标结果估计雷达视线角(LOS)。然后对机翼进行子孔径序列成像,提取散射点的距离和多普勒变化曲线,再联合雷达LOS以及距离和多普勒曲线对振动参数进行粗估计,最后通过修正的极坐标格式算法(MPFA)以及构造最小熵优化函数对振动参数进行精估计。该文首次提出了修正的极坐标格式算法,其能够对复杂运动的目标进行距离和方位向的解耦,如震动的机翼和摇摆的舰船等。仿真和实测数据的处理结果验证了该方法的有效性和实用性。
-
关键词:
- 振动 /
- 子孔径 /
- 修正的极坐标格式算法 /
- 最小熵 /
- 优化
Abstract: The wings of an airplane vibrate when it is nonstationary. When an airplane is observed using a microwave photonics-based ultrahigh-resolution radar, and this vibration will cause defocusing of the wings. To address this problem, we propose a vibration-parameter estimation method for airplane wings based on microwave-photonics ultrahigh-resolution radar. In this method, we first coarsely separate images of the wings and body of the airplane, and estimate the Light-Of-Sight (LOS) of the radar from a focused and scaled image of the airplane body. Next, we apply sub-aperture imaging to the wings and extract the range and Doppler curves from a sequence of sub-aperture images. By combining the range and Doppler curves with the LOS, we can obtain a preliminary estimation of the vibration parameters. Finally, by Modifying the Polar Format Algorithm (MPFA) and constructing an optimization function that minimizes image entropy, we can obtain accurate vibration parameters. This novel modified polar format algorithm can be applied to complex motion targets, such as an airplane with vibrating wings, swinging ships to effectively decouple range and cross-range dimensional coupling. Experimental results using both simulated and measured data confirm the validity and practicality of the proposed algorithm.-
Key words:
- Vibration /
- Sub-aperture /
- Modified Polar Format Algorithm (MPFA) /
- Entropy minimization /
- Optimization
-
表 1 仿真雷达参数
Table 1. Simulation radar parameters
信号带宽(GHz) 脉冲宽度(μs) 载频(GHz) PRF (Hz) 采样率(Hz) 脉冲数 振动角(°) 振动频率(Hz) 初相(°) 10 150 35 666.66 500 8192 1 1 0 表 2 仿真数据机翼振动参数估计结果
Table 2. Vibration parameters estimation result of simulation data
振动频率(Hz) 振动角(°) 振动初相(°) 实际值 估计值 实际值 估计值 实际值 估计值 1 0.99 1 0.98 0 –0.18 表 3 实测数据机翼振动参数估计结果
Table 3. Vibration parameters estimation result of measured data
振动频率(Hz) 振动角(°) 振动初相(°) 2.48 0.07 12.93 -
[1] 潘时龙, 张亚梅. 微波光子雷达及关键技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 36–52.PAN Shilong and ZHANG Yamei. Microwave photonic radar and key technologies[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 36–52. [2] MCKINNEY J D. Technology: Photonics illuminates the future of radar[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7492): 310–311. doi: 10.1038/507310a [3] CAPMANY J and NOVAK D. Microwave photonics combines two worlds[J]. Nature Photonics, 2007, 1(6): 319–330. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.89 [4] YAO Yao, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHANG Ying, et al. Demonstration of ultra-high-resolution photonics-based Ka-band inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging[C]. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, San Diego, California, USA, 2018: Th3G.5. doi: 10.1364/OFC.2018.Th3G.5. [5] CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873 [6] 李彦兵, 张曦文, 李飞, 等. 一种大加速度机动目标微动参数估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(1): 82–87. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160261LI Yanbing, ZHANG Xiwen, LI Fei, et al. Estimation of micro-motion feature for large accelerated target[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(1): 82–87. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160261 [7] 张翼, 朱玉鹏, 黎湘. 基于微多普勒特征的目标微动参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022ZHANG Yi, ZHU Yupeng, and LI Xiang. Micro-motion parameter estimation of ballistic missile target based on micro-Doppler feature[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022 [8] ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letter, 2009, 6(4): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562 [9] PENG Shibao, XU Jia, WANG Libao, et al. A new ISAR range alignment method based on particle swarm optimizer[C]. Proceedings of 2009 Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China, 2009: 618–621. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2009.5374278. [10] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 1–336.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 1–336. [11] ZHANG Lei, SHENG Jialian, DUAN Jia, et al. Translational motion compensation for ISAR imaging under low SNR by minimum entropy[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013(1): 33. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-33 [12] 符吉祥, 孙光才, 邢孟道. 一种大转角ISAR两维自聚焦平动补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2889–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170303FU Jixiang, SUN Guangcai, and XING Mengdao. A two dimensional autofocus translation compensation method for wide-angle ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2889–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170303 [13] LI Xiaolong, CUI Guolong, YI Wei, et al. Range migration correction for maneuvering target based on generalized keystone transform[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2015: 95–99. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130977. [14] GAO Jingkun, DENG Bin, QIN Yuliang, et al. Efficient terahertz wide-angle NUFFT-based inverse synthetic aperture imaging considering spherical wavefront[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(12): E2120. doi: 10.3390/s16122120 [15] MA Zheng, ZHANG Yong, and ZHOU Zhennan. An improved semi-Lagrangian time splitting spectral method for the semi-classical Schrödinger equation with vector potentials using NUFFT[J]. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2017, 111: 144–159. doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2016.08.015 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: