High Resolution Microwave Photonics Radar Real-time Imaging Based on Generalized Keystone and Frequency Scaling
-
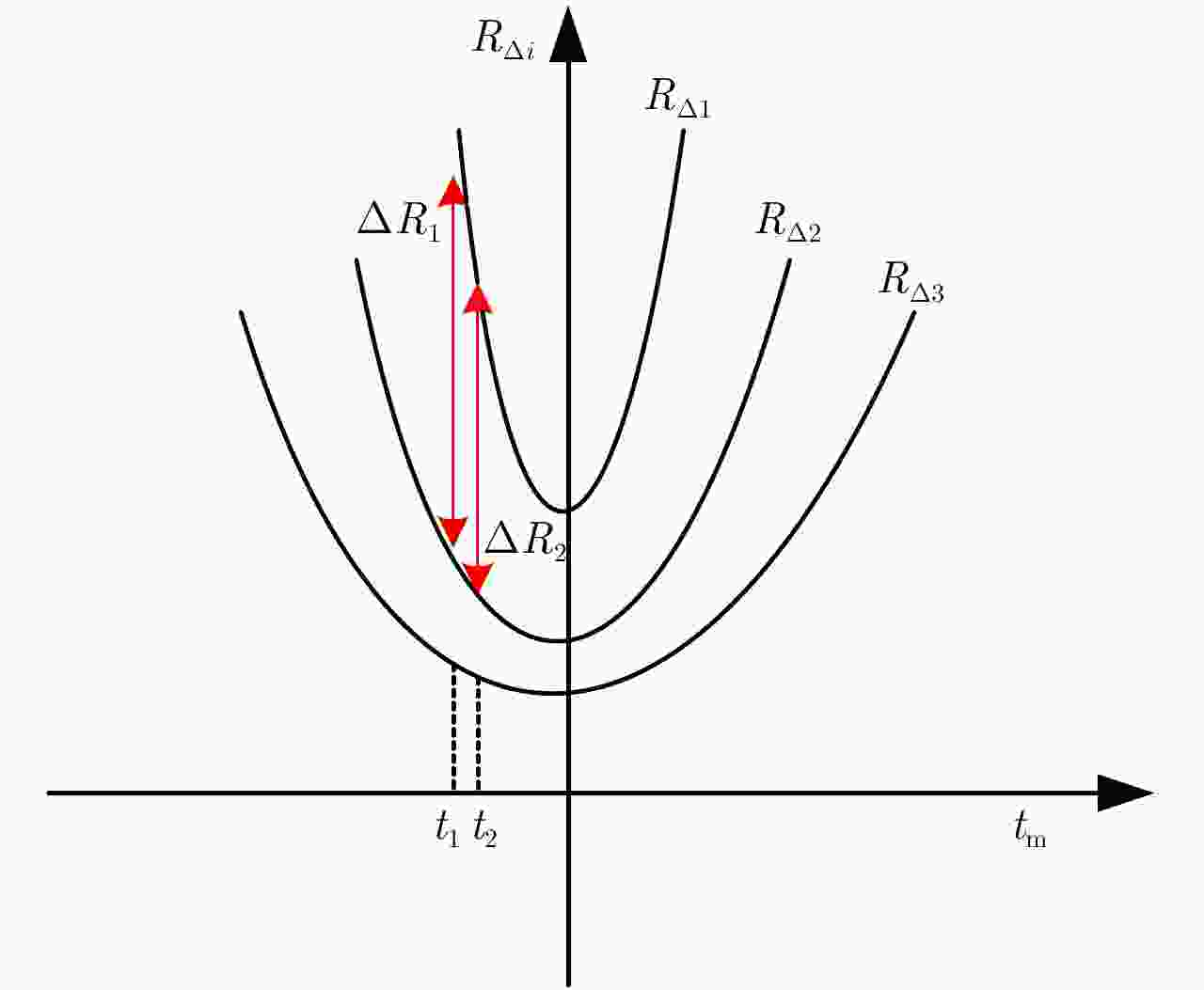
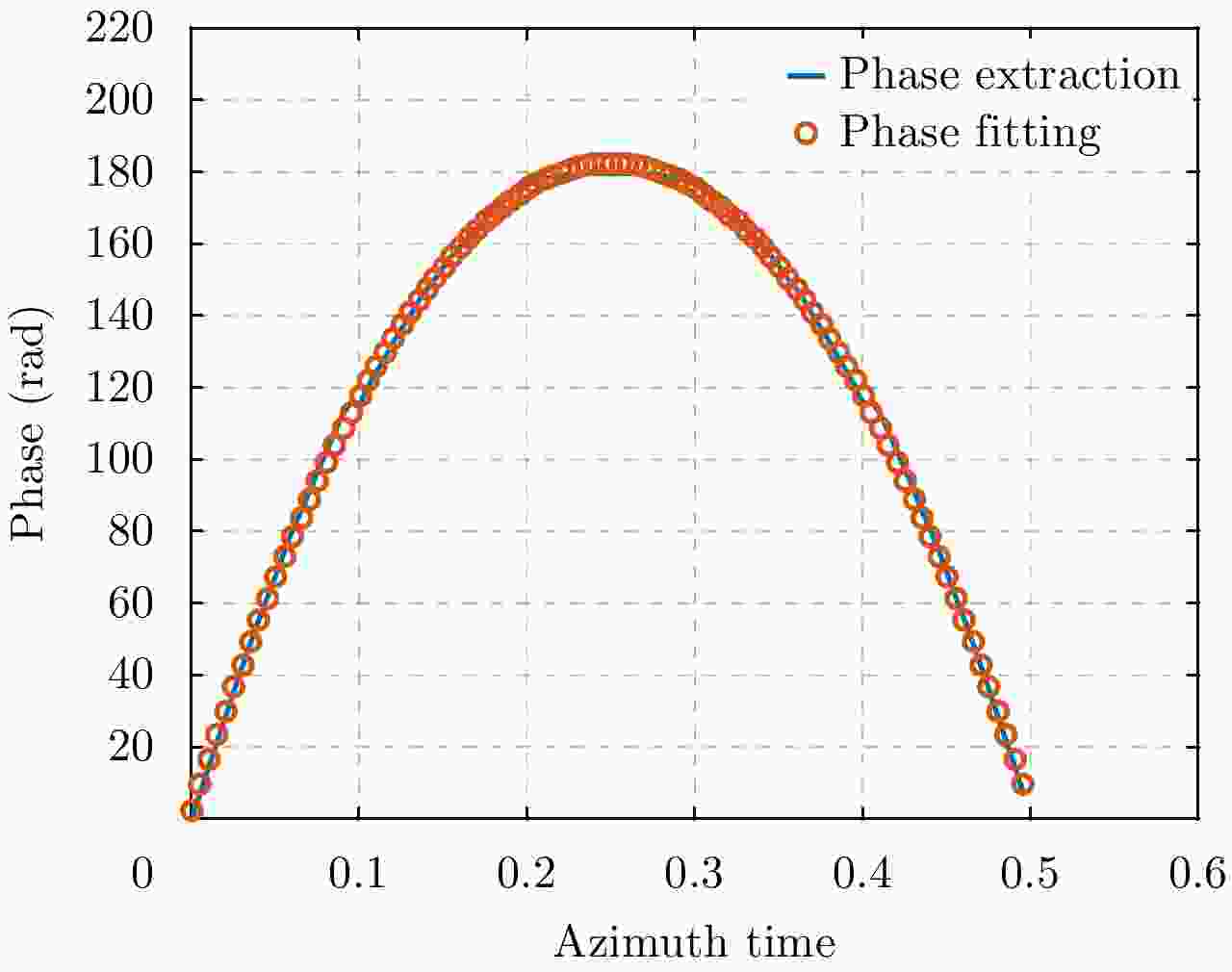
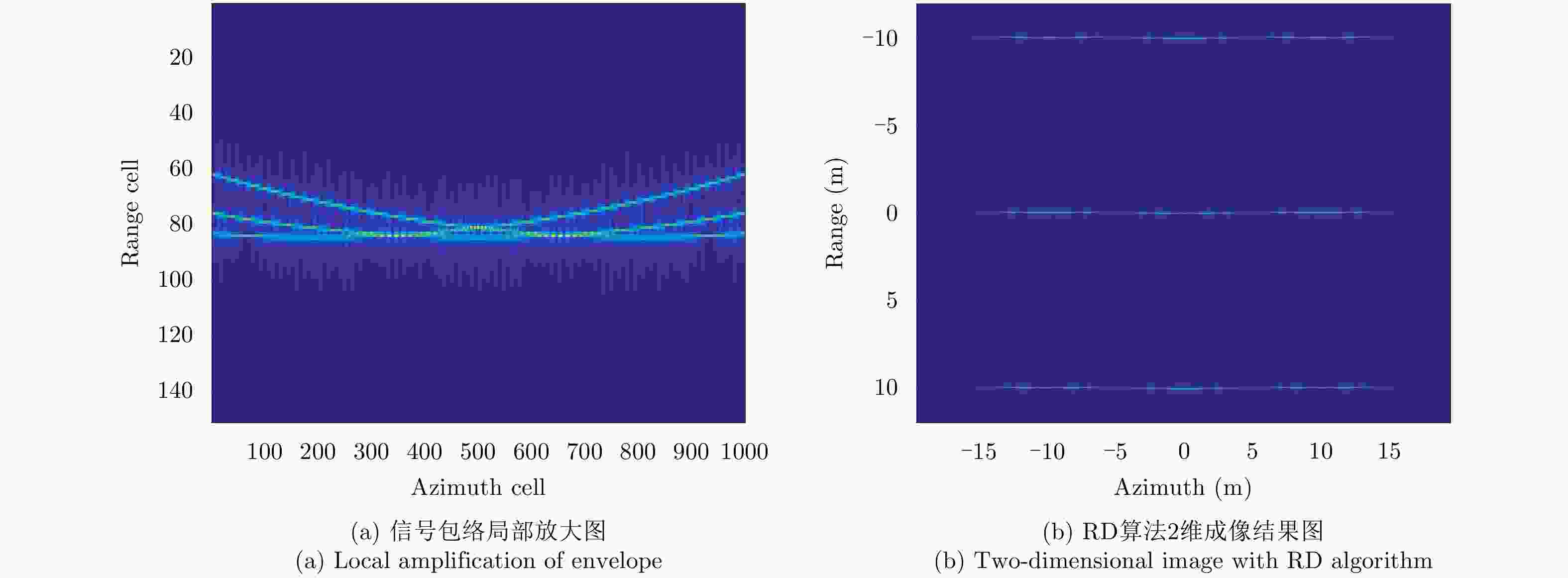
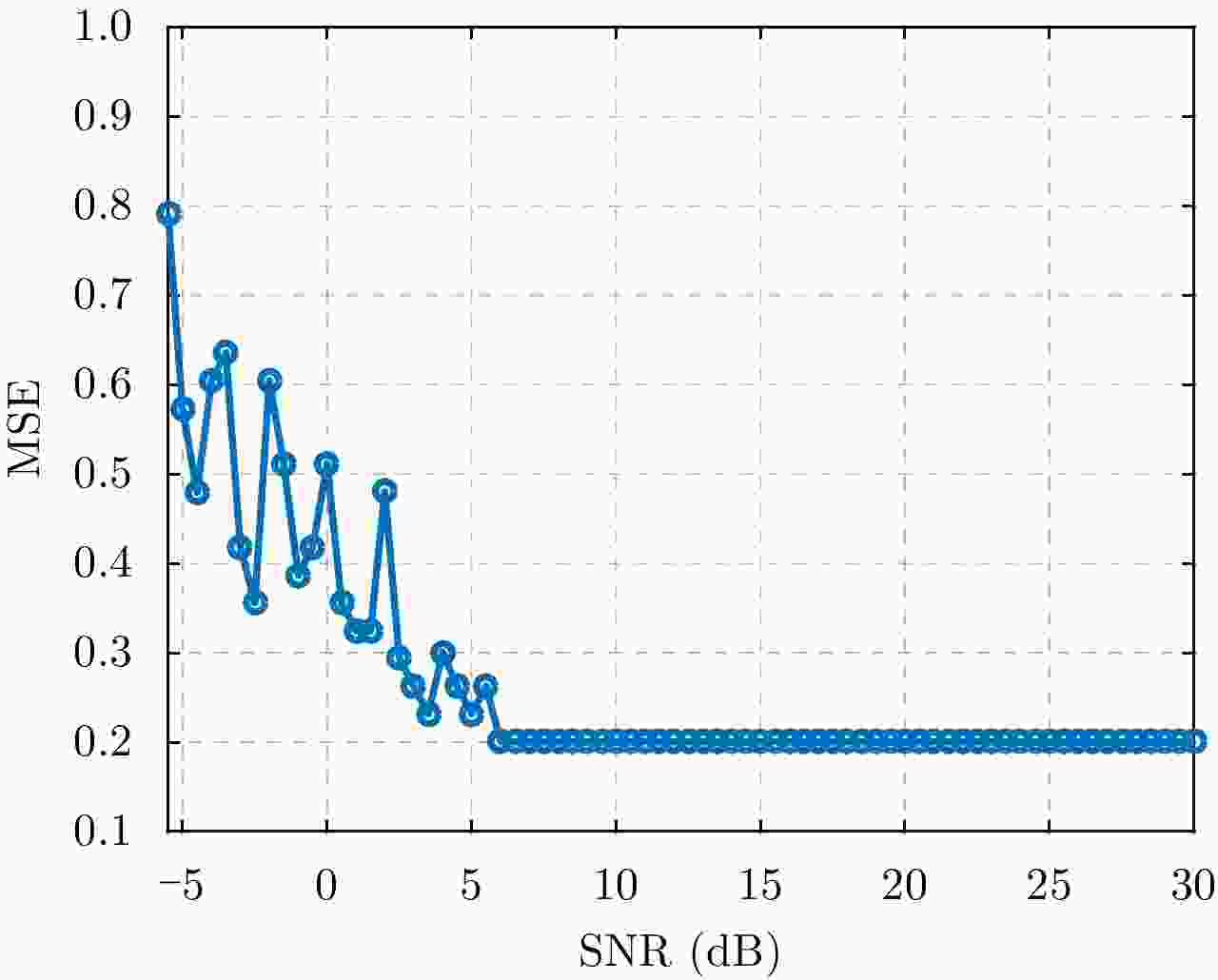
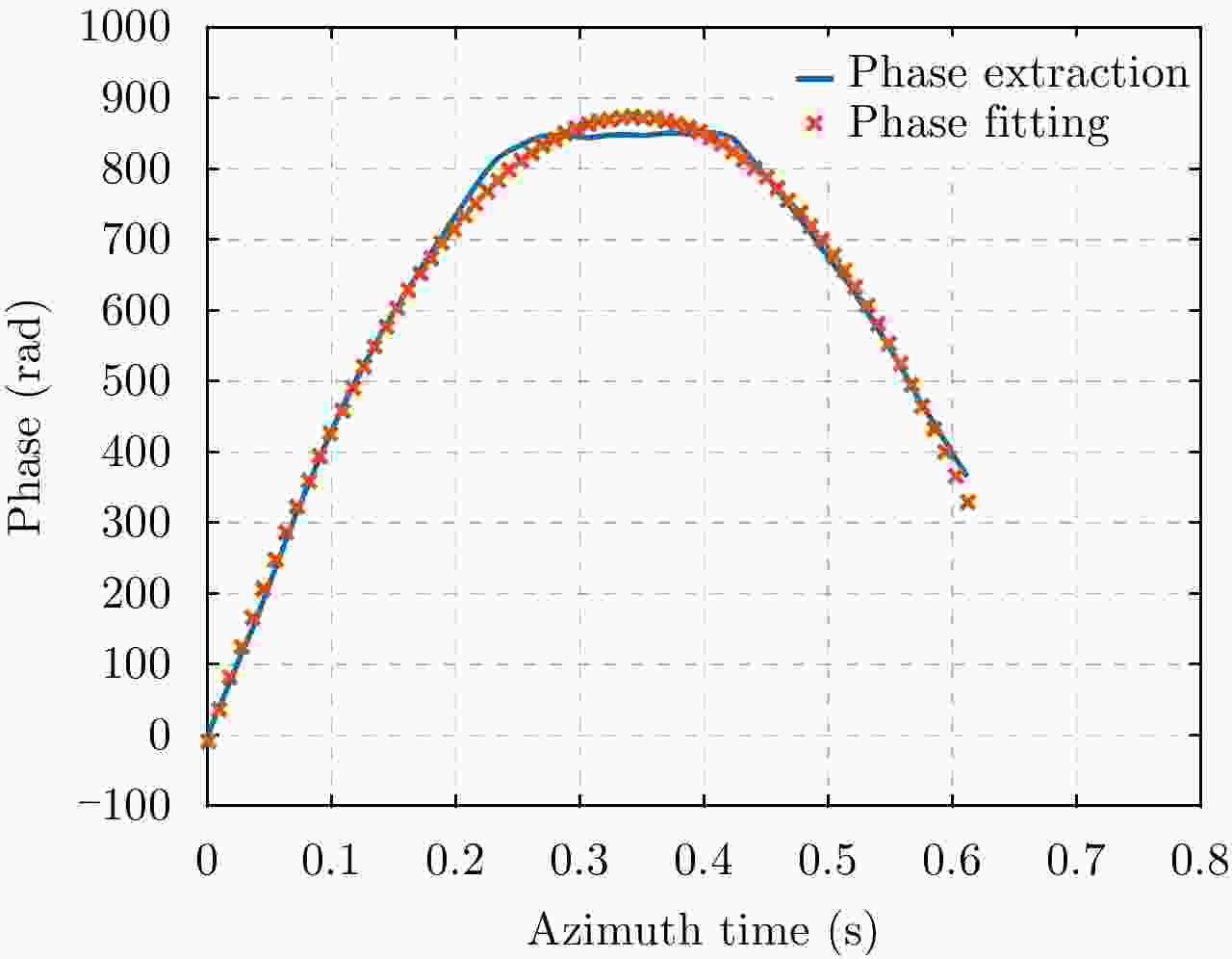
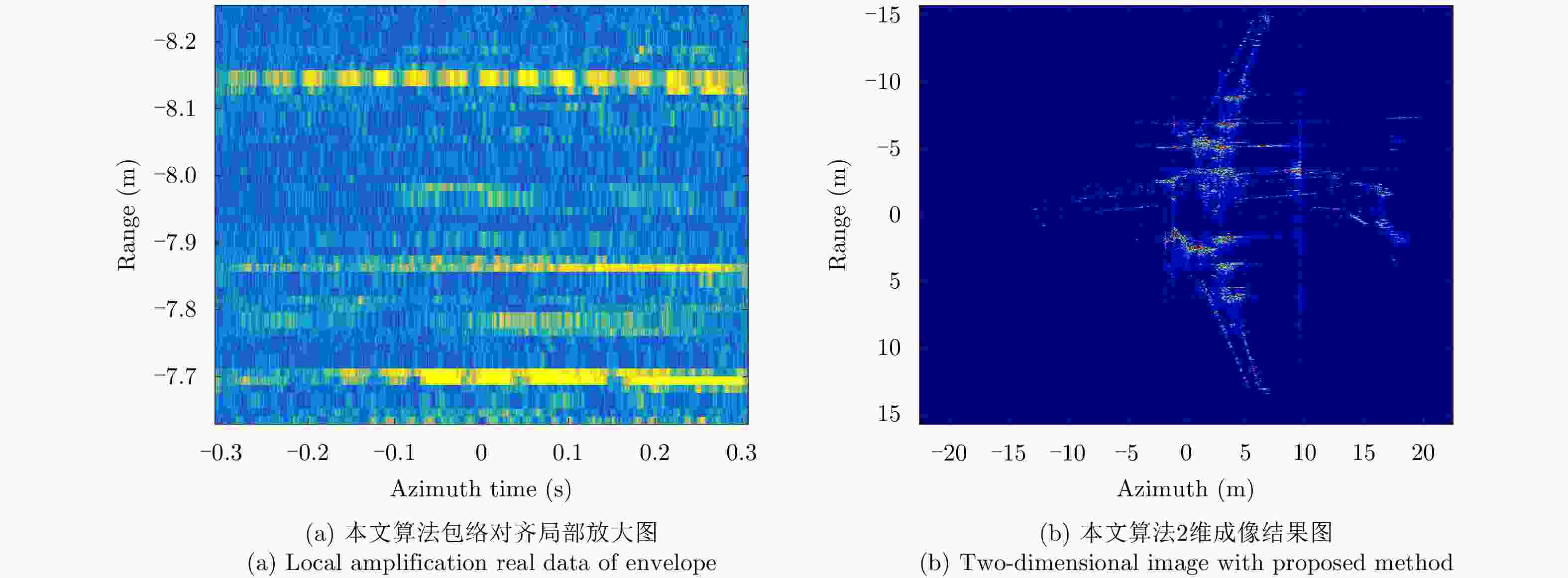
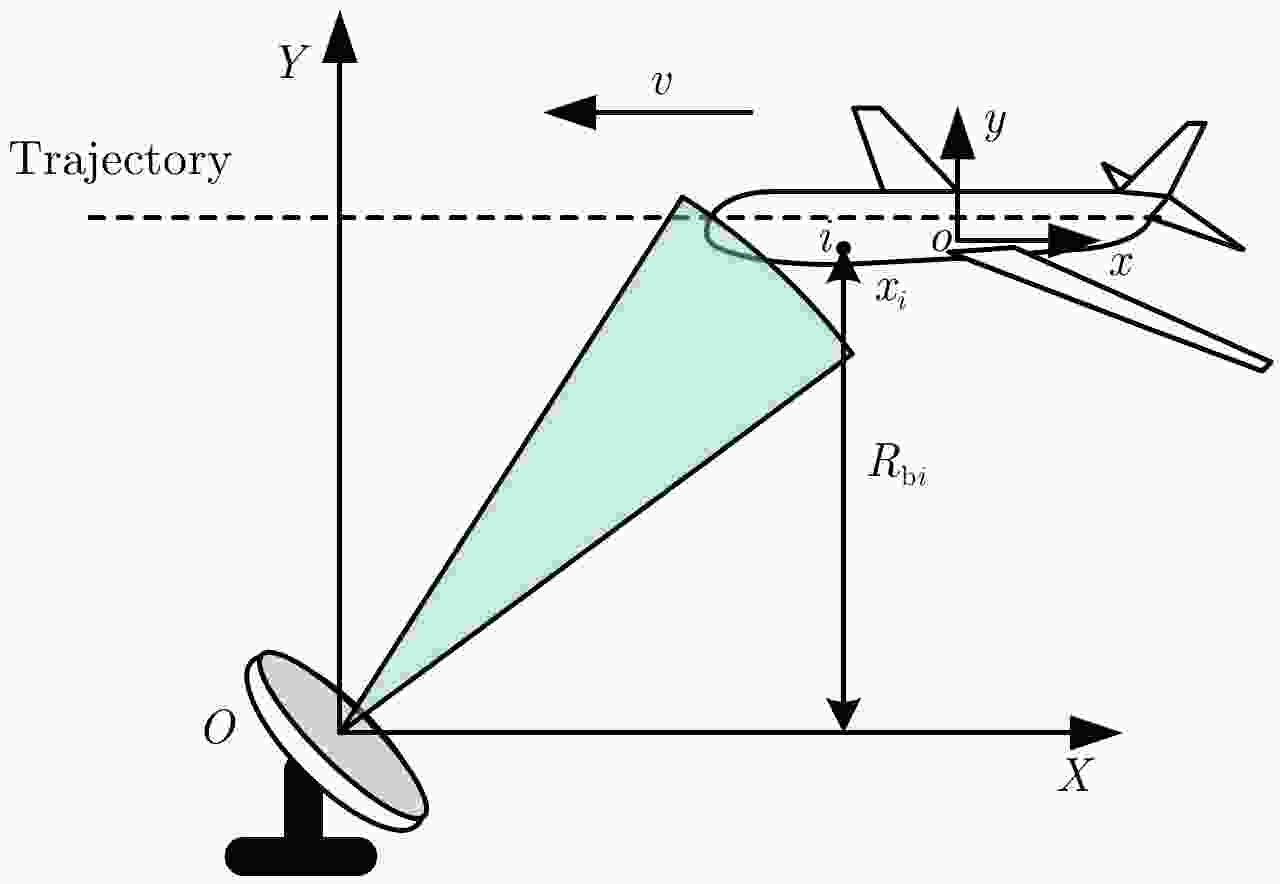
摘要: 微波光子雷达具有发射大带宽和高载频信号的能力,可实现2维高分辨的逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像。研究相应的实时成像算法具有重要意义。但信号的高距离分辨率特点使得距离弯曲的空变性无法忽略,高载频特性使得相位历程的空变性无法忽略,导致传统的多普勒域实时成像算法成像效果差。另外,计算量较大的波束域成像算法不适用于大数据量的微波光子雷达信号。因此该文提出一种高效率的微波光子ISAR高分辨实时成像算法,该算法首先利用广义楔石变换(GKT)提取特显点相位,进而由相位调频率反演目标横向速度,最后利用速度估计结果结合频率变标(FS)算法完成空变的距离弯曲校正和方位匹配滤波成像。仿真和实测数据的处理结果验证了该算法的有效性。Abstract: Microwave photonic radars can transmit large bandwidth and high carrier frequency signals, which makes two-dimensional high-resolution Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) imaging possible. It is important to study the corresponding real-time imaging algorithms. However, the high range resolution and high carrier frequency of the signal make the space curvature of the distance bend non-negligible. This is the reason for the poor imaging performance of the traditional Doppler real-time imaging algorithm. In addition, the computationally intensive beam domain imaging algorithm is not suitable for microwave photonic radar signals of large data volume. Therefore, a high-efficiency microwave photonic ISAR high-resolution real-time imaging algorithm is proposed in this paper. Firstly, this algorithm uses the Generalized Keystone Transform (GKT) to extract the phase of the special display point. Next, it inverts the target lateral velocity from phase modulation frequency. Finally, the result of velocity estimation and Frequency Scaling (FS) are used to correct the distance space-bending and conduct matched filtering imaging in azimuth. The simulation results and the measured data have been shown to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Microwave photonic radar /
- ISAR /
- Real-time imaging /
- Lateral speed estimate /
- Frequency Scaling (FS)
-
表 1 仿真数据参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
信号带宽(GHz) 载频(GHz) 脉冲宽度(μs) 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 采样率(MHz) 参考斜距(m) 目标速度(m/s) 观测时间(s) 10 35 150 2000 500 1000 65 0.5 表 2 实测数据参数
Table 2. Measured data parameters
信号带宽(GHz) 载频 脉冲宽度(μs) 数据采样率(MHz) 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 成像距离(m) 观测时间(s) 10 Ka波段 150 500 6670 750 0.6 -
[1] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 6–70.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 6–70. [2] 潘时龙, 张亚梅. 微波光子雷达及关键技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 36–52. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.004PAN Shilong and ZHANG Yamei. Microwave photonic radar and key technologies[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 36–52. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.004 [3] PÉREZ D, GASULLA I, CAPMANY J, et al. Integrated microwave photonics: The quest for the universal programmable processor[C]. 2016 IEEE Photonics Society Summer Topical Meeting Series, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 2016: 144–145. doi: 10.1109/PHOSST.2016.7548751. [4] WU Tingwei, ZHANG Chongfu, ZHOU Heng, et al. Photonic microwave waveforms generation based on frequency and time-domain synthesis[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 34372–34379. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2842250 [5] GRODENSKY D, KRAVITZ D, and ZADOK A. Ultra-wideband microwave-photonic noise radar based on optical waveform generation[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(10): 839–841. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2188889 [6] XIAO Xuedi, LI Shangyuan, CHEN Boyu, et al. A microwave photonics-based inverse synthetic aperture radar system[C]. 2017 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, San Jose, CA, USA, 2017: 1–2. [7] GUO Qingshui, ZHANG Fangzheng, WANG Ziqian, et al. High-resolution and real-time inverse synthetic aperture imaging based on a broadband microwave photonic radar[C]. 2017 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–3. [8] CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873 [9] ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562 [10] 徐刚, 杨磊, 张磊, 等. 一种加权最小熵的ISAR自聚焦算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(8): 1809–1815. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01153XU Gang, YANG Lei, ZHANG Lei, et al. Weighted minimum entropy autofocus algorithm for ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(8): 1809–1815. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01153 [11] 符吉祥, 孙光才, 邢孟道. 一种大转角ISAR两维自聚焦平动补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2889–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170303FU Jixiang, SUN Guangcai, and XING Mengdao. A two dimensional autofocus translation compensation method for wide-angle ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2889–2898. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170303 [12] HUANG Penghui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Ground maneuvering target imaging and high-order motion parameter estimation based on second-order keystone and generalized Hough-HAF transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 320–335. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606436 [13] LI Xiaolong, CUI Guolong, YI Wei, et al. Range migration correction for maneuvering target based on generalized keystone transform[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2015, 0095–0099. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130977. [14] MITTERMAYER J, MOREIRA A, and LOFFELD O. Spotlight SAR data processing using the frequency scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2198–2214. doi: 10.1109/36.789617 [15] ZHU Daiyin, SHEN Mingwei, and ZHU Zhaoda. Some aspects of improving the frequency scaling algorithm for dechirped SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(6): 1579–1588. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.916468 [16] 许志伟, 张磊, 邢孟道. 基于特征配准的ISAR图像方位定标方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2173–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01590XU Zhiwei, ZHANG Lei, and XING Mengdao. A novel cross-range scaling algorithm for ISAR images based on feature registration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2173–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01590 [17] LI Y, WU R, XING M, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of ship target with complex motion[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2008, 2(6): 395–403. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20070101 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: