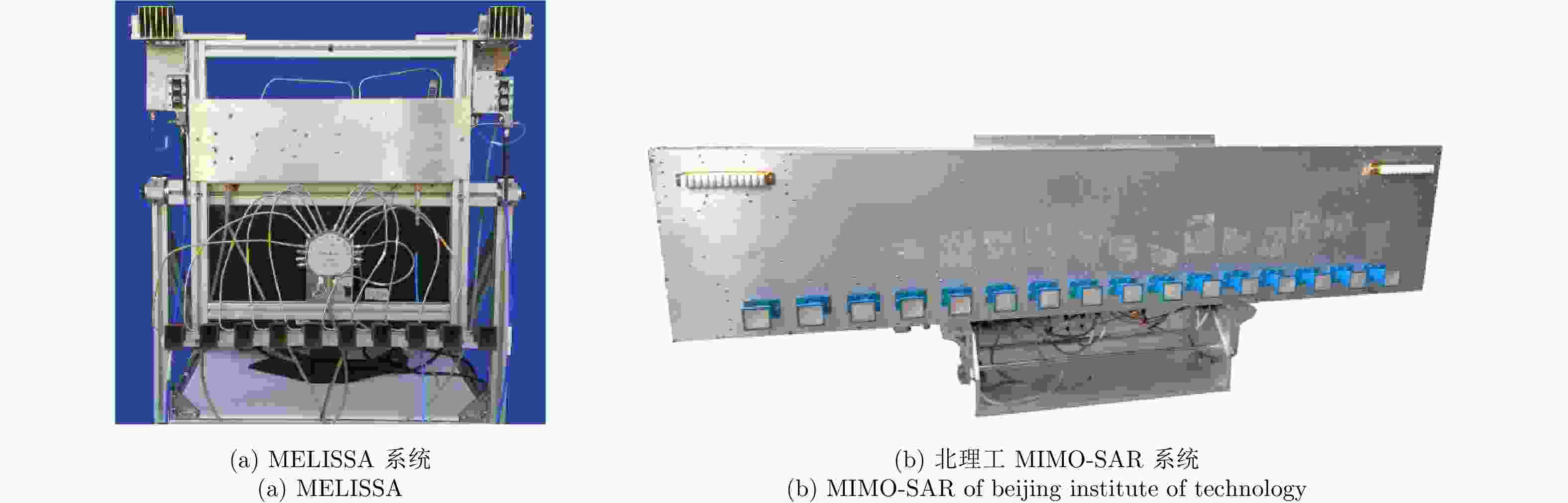
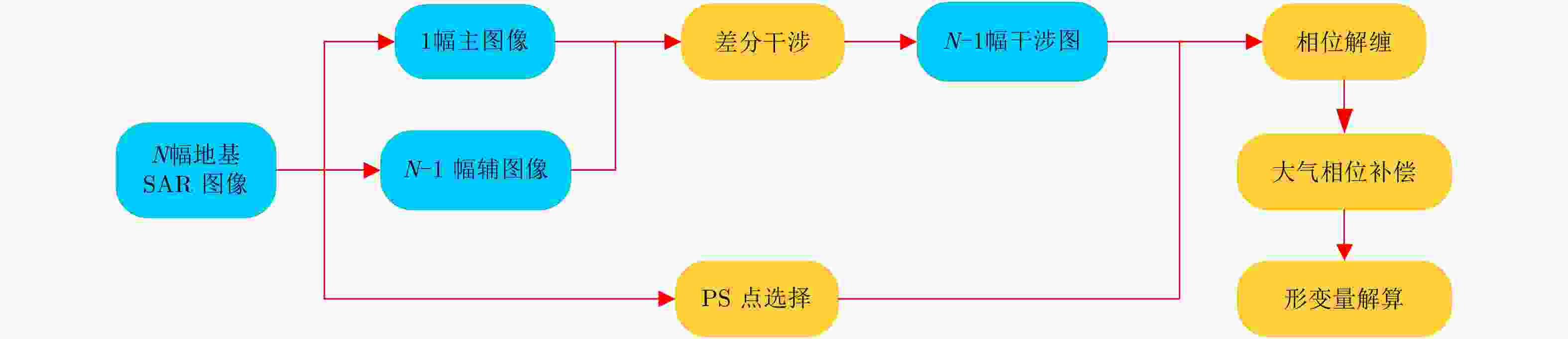
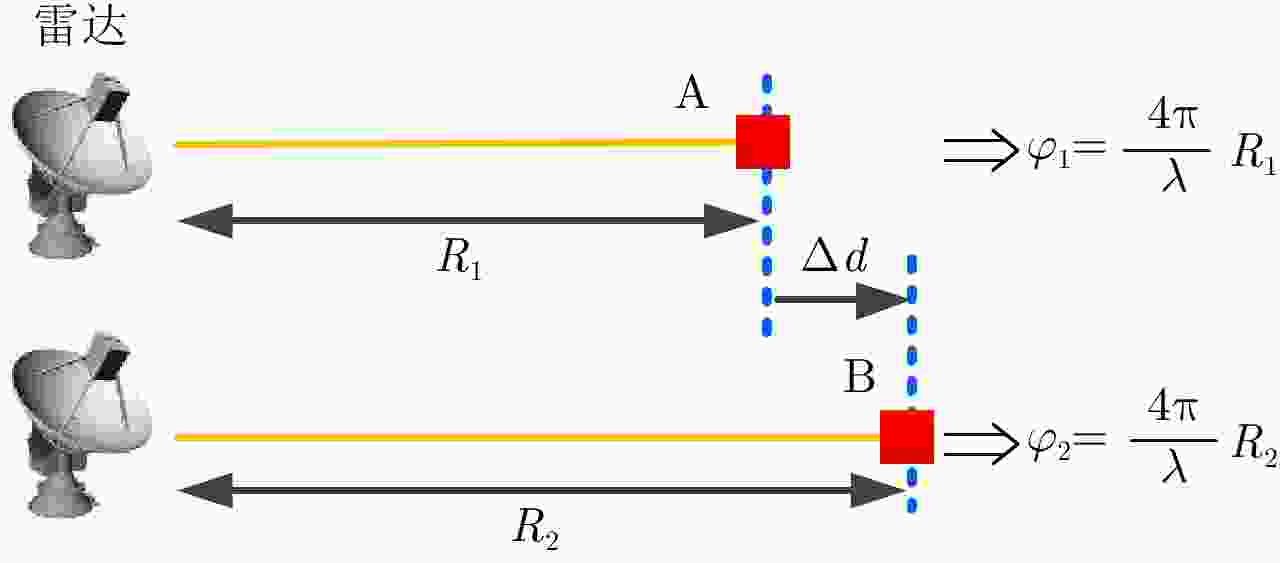
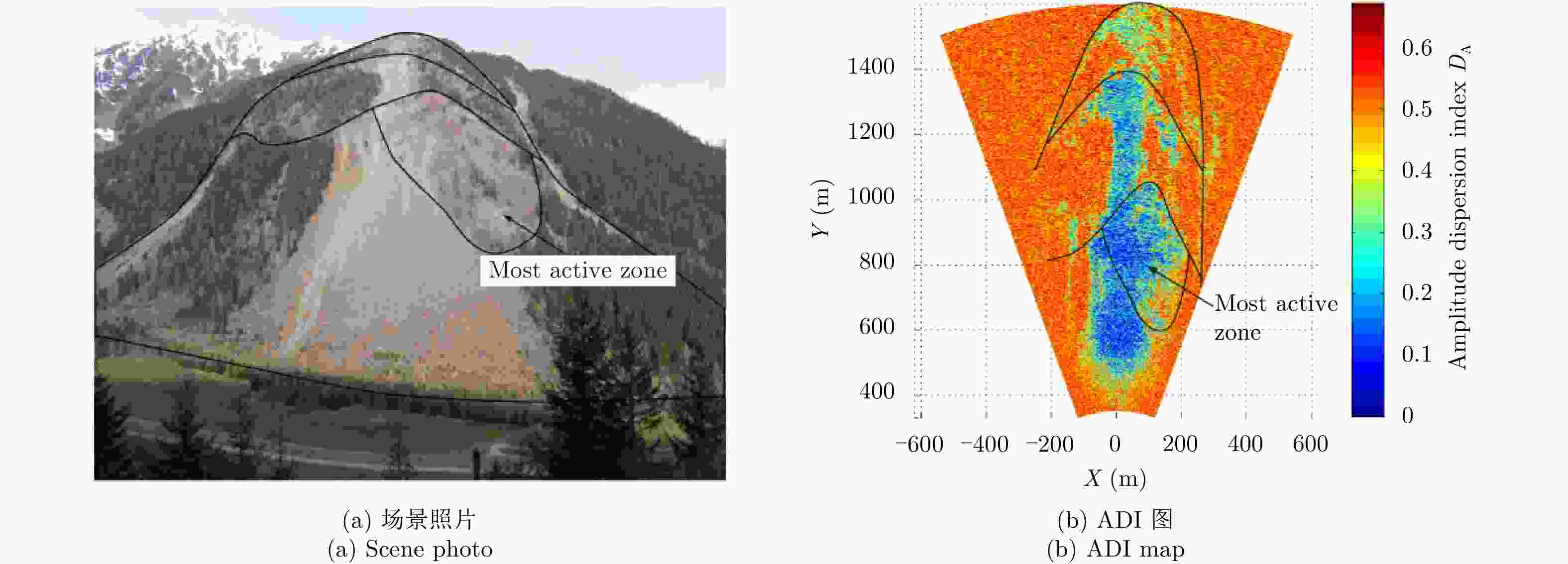
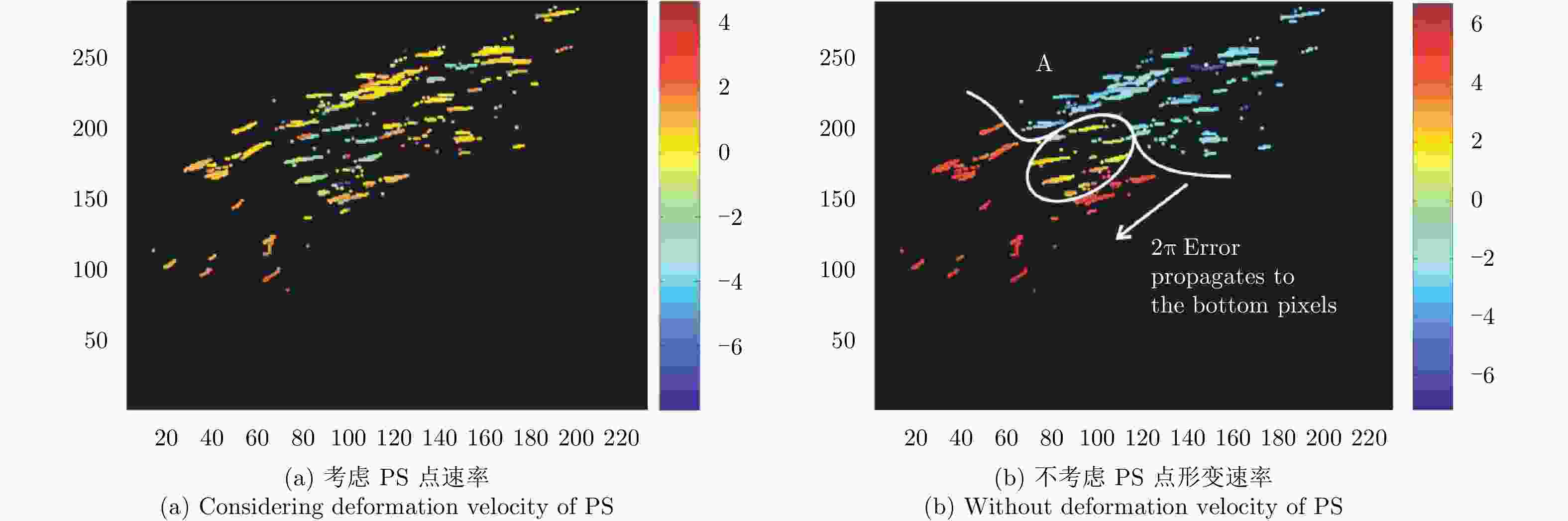
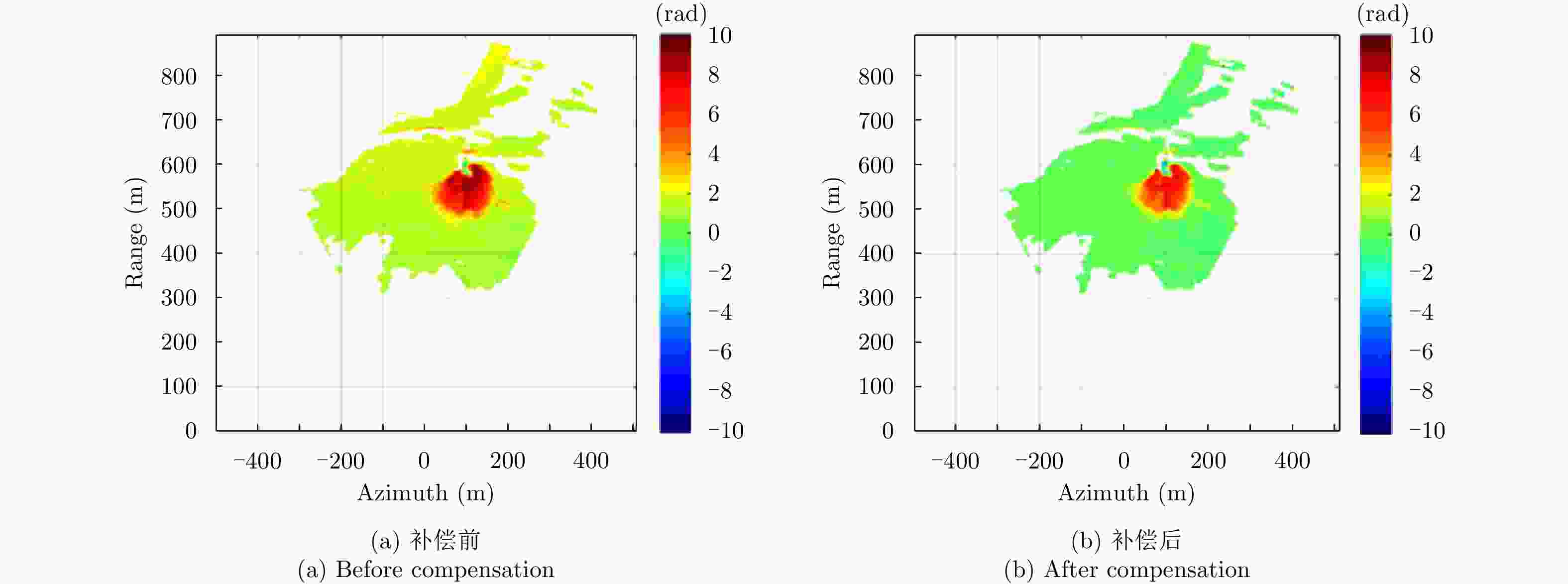
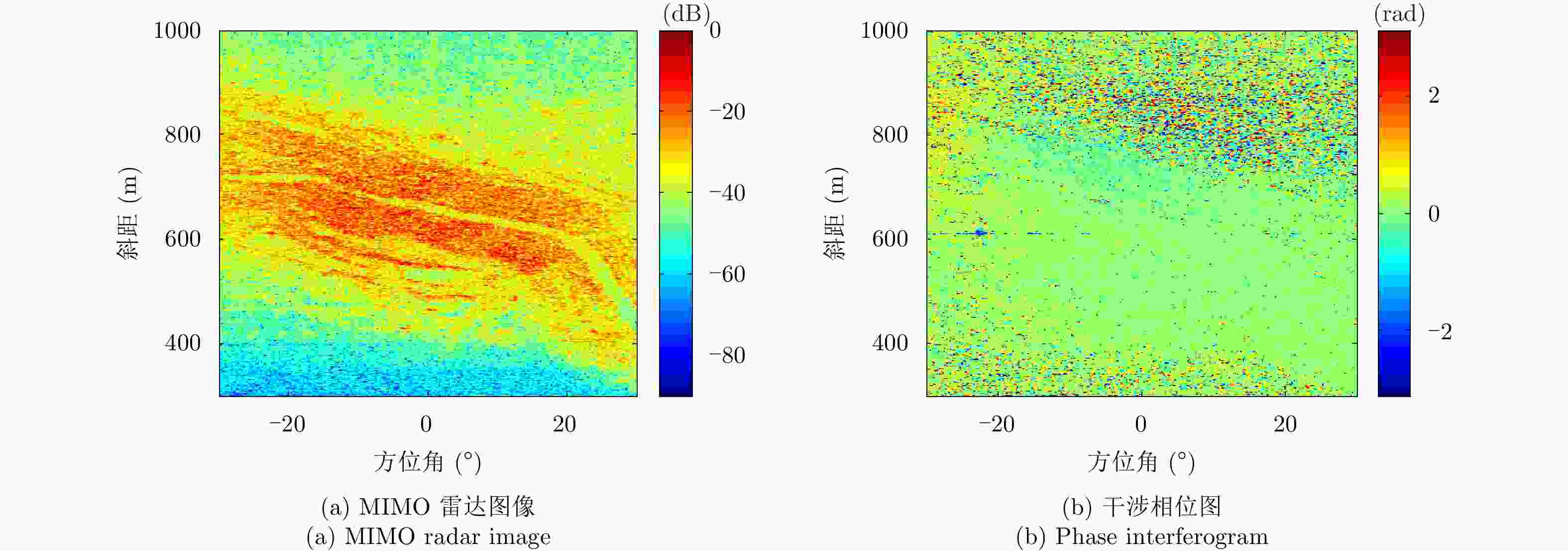
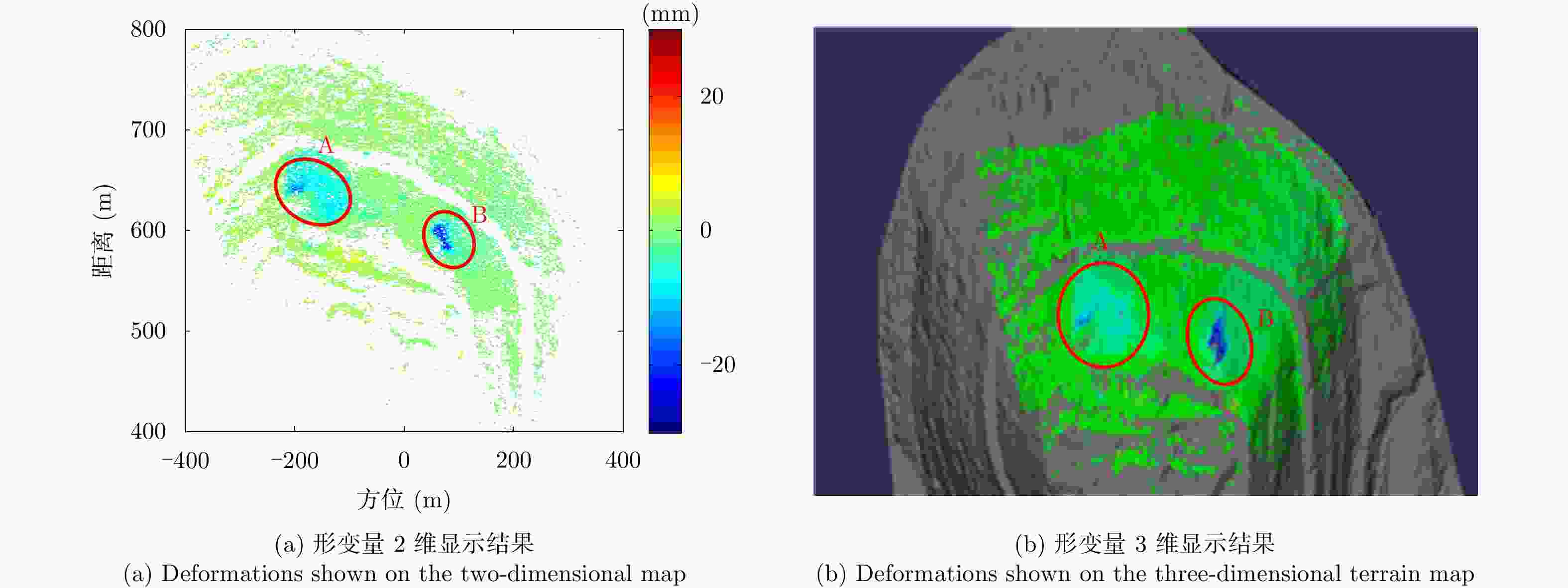
Development State and Application Examples of Ground-based Differential Interferometric Radar
-
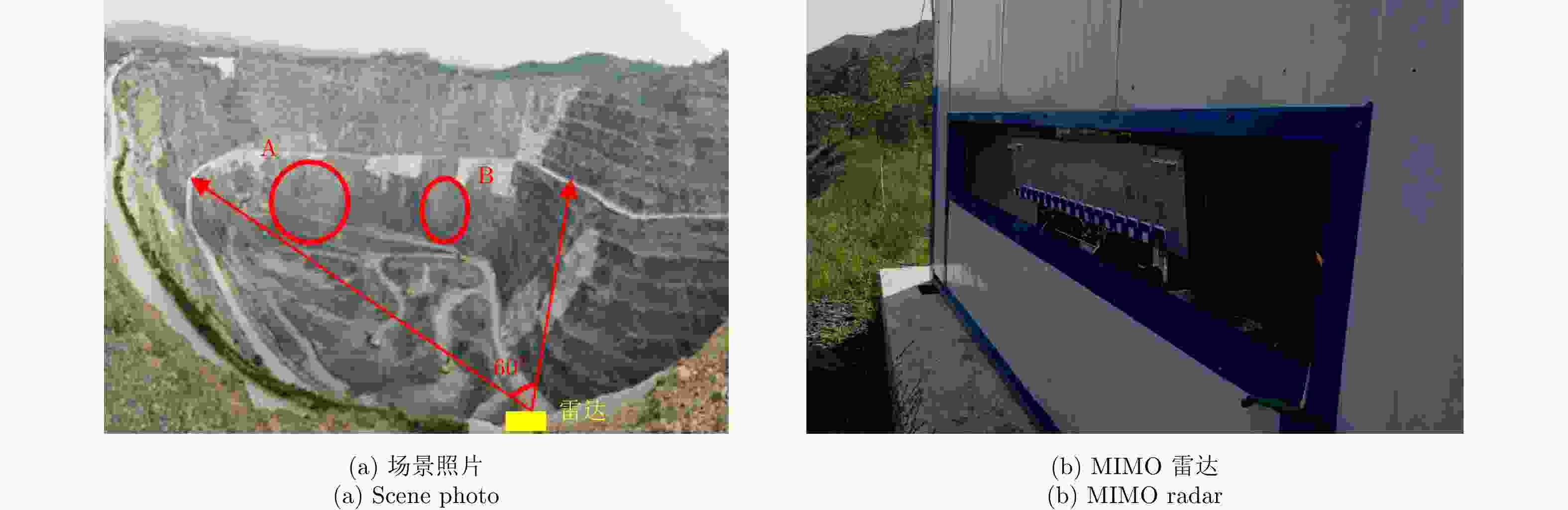
摘要: 地基差分干涉雷达在形变监测领域已经得到了广泛的应用。该文首先概述了地基差分干涉雷达的主要类型,分为地基实孔径雷达和地基合成孔径雷达两类,并选择代表性系统介绍了工作原理及重要参数。然后以地基合成孔径雷达为例,介绍了现阶段差分干涉处理中的重要技术,包括差分干涉、PS点选择、大气相位补偿等。最后以3个应用实例,展现了地基差分干涉雷达,在露天开采边坡监测、山体滑坡监测和桥梁振动测量方面的应用。Abstract: Ground-Based Differential Interferometric Radars (GB-DInRads) have been widely applied to measure deformations. In this paper, the main types of GB-DInRads are summarized, including ground-based real aperture radar and Ground-Based Synthetic Aperture Radar (GB-SAR). The working principles and important parameters of some representative systems are introduced. Then, taking the GB-SAR as an example, the current key processing techniques are introduced, which mainly include differential interferometry, permanent scatterer selection, and atmospheric phase compensation. Lastly, three examples are presented to show the applications of GB-DInRad in deformation measurements. A Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar was utilized to monitor an open-pit mine for about 11 days, and two regions with obvious deformation were found. In addition, a linear-scanning GB-SAR was utilized to monitor a mountain slope after severe landslide. The analysis result proved that rainfall could accelerate deformation. The feasibility of vibration measurement with the MIMO radar was also discussed in this paper.
-
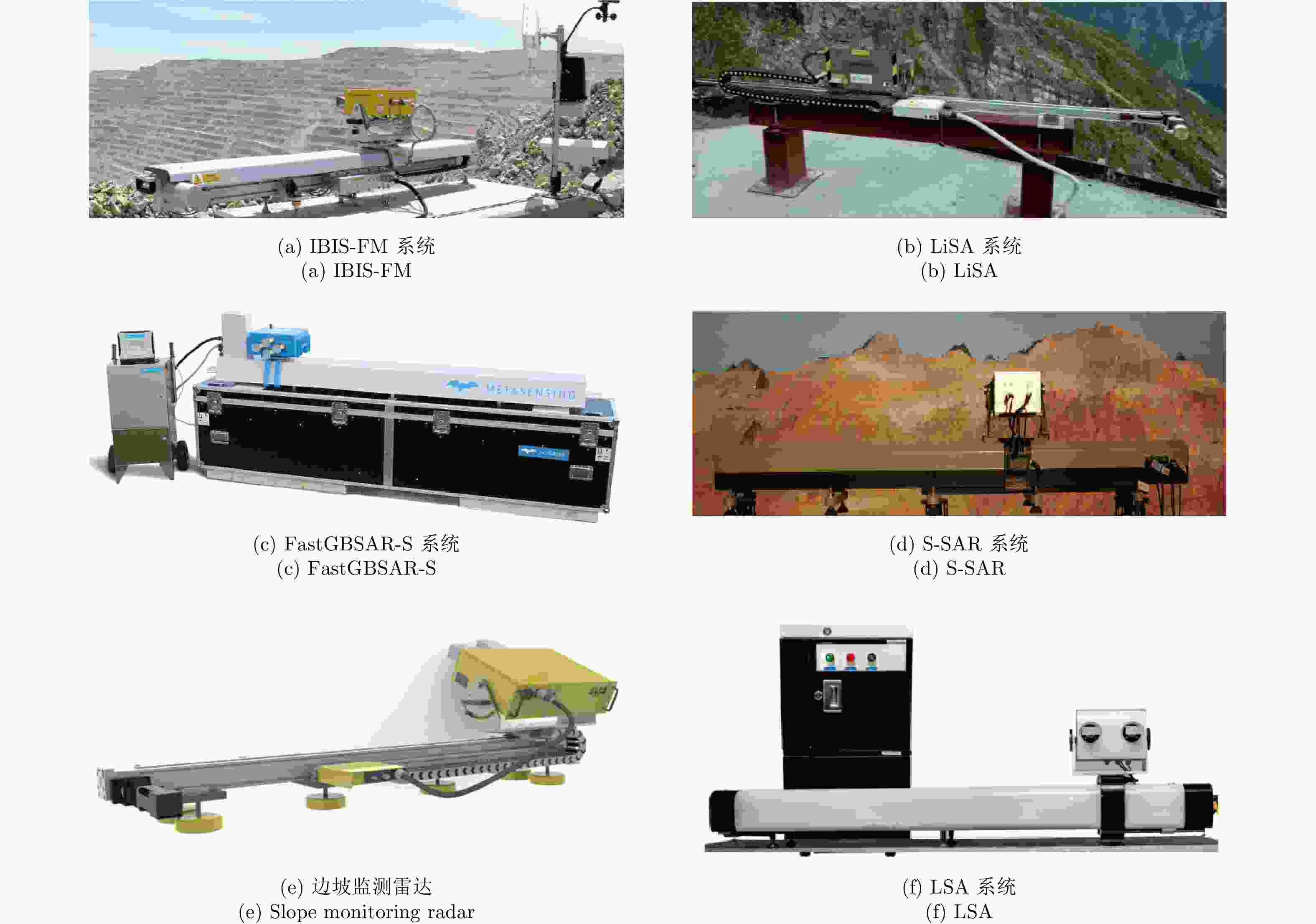
表 1 直线扫描地基SAR参数表
Table 1. Parameters of linear-scanning GB-SAR
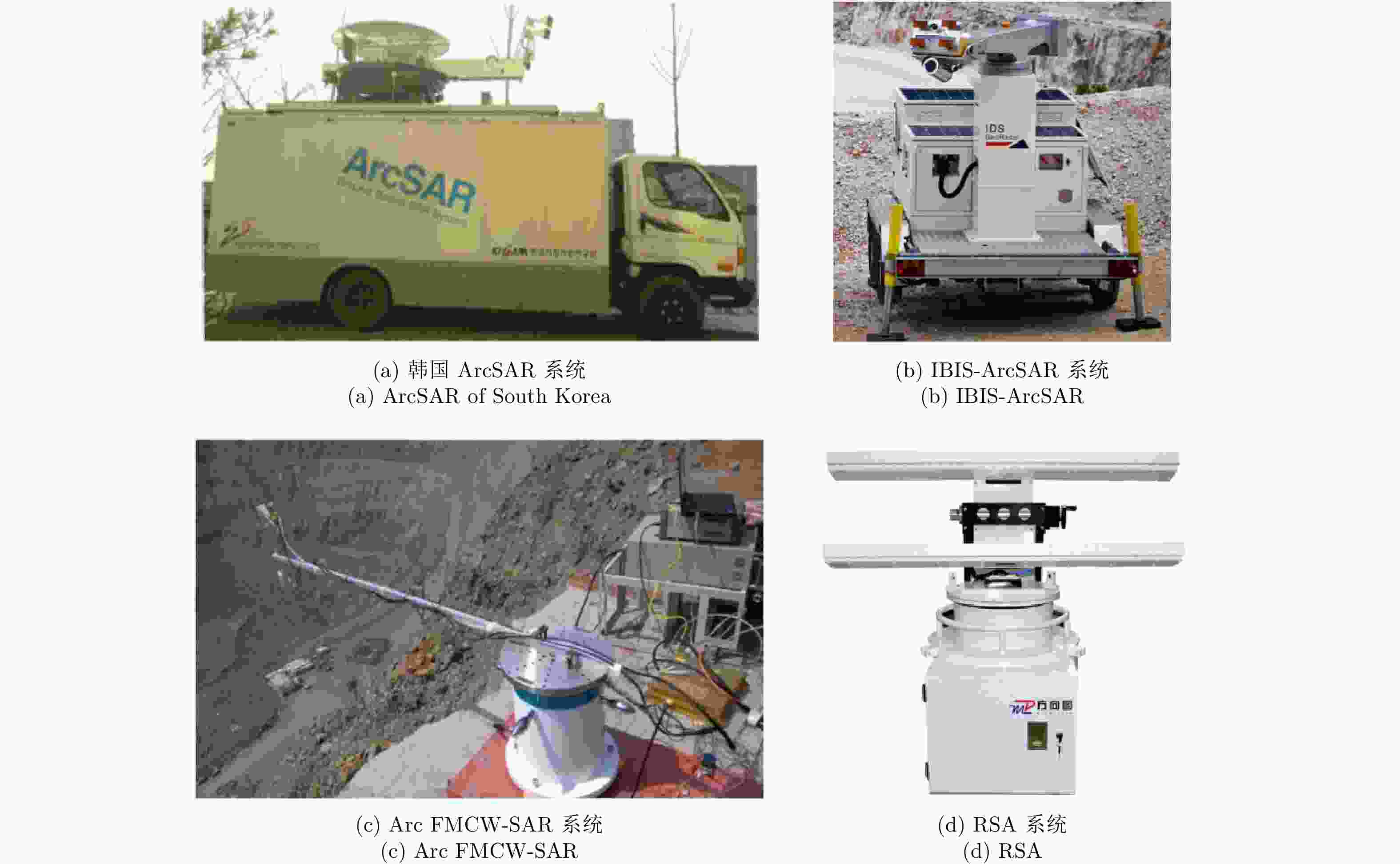
研究机构/公司 系统 波段 测量周期 空间分辨率(1 km处) 最远探测距离(km) IDS公司 (意大利) IBIS-FM Ku 约3 min 0.5 m×4.4 m 4.5 JRC组织 (欧盟) LiSA Ku 约12 min 0.5 m×3.0 m 3 MetaSensing公司(荷兰) FastGBSAR-S Ku 10 s 0.5 m×4.8 m 4 UPC大学 (西班牙) RiskSAR X 约20 min 1.5 m×7.7 m 10 安科院 (中国) S-SAR Ku <10 min 0.5 m×3.0 m 5 理工雷科公司 (中国) 边坡雷达 Ku 3~10 min 0.3 m×4.0 m 5 方向图公司 (中国) LSA Ku 4~10 min 0.2 m×5.4 m 5 表 2 MIMO雷达参数表
Table 2. Parameters of the MIMO radar system
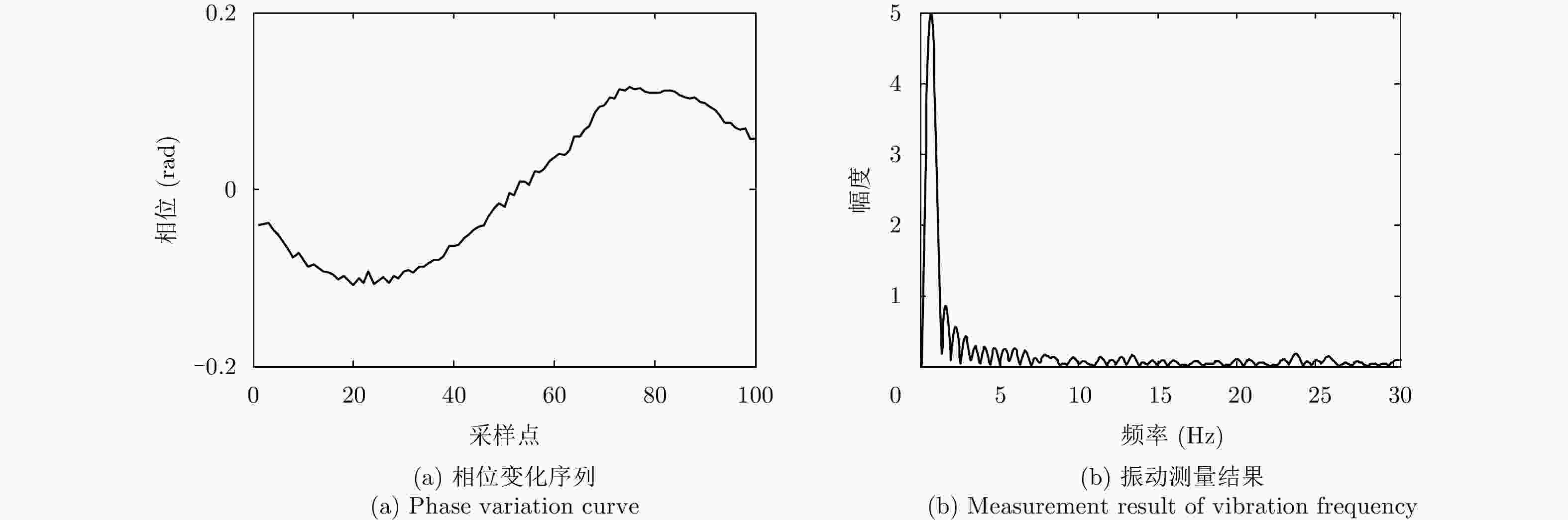
参数 数值 参数 数值 载频 16.2 GHz 发射信号时宽 0.1~0.5 ms 发射天线 16 发射信号带宽 400 MHz/1 GHz 接收天线 16 发射信号采样率 12.5 MHz/25.0 MHz 合成孔径长度 1.138 m 合成孔径采样点 256 表 3 振动测量结果
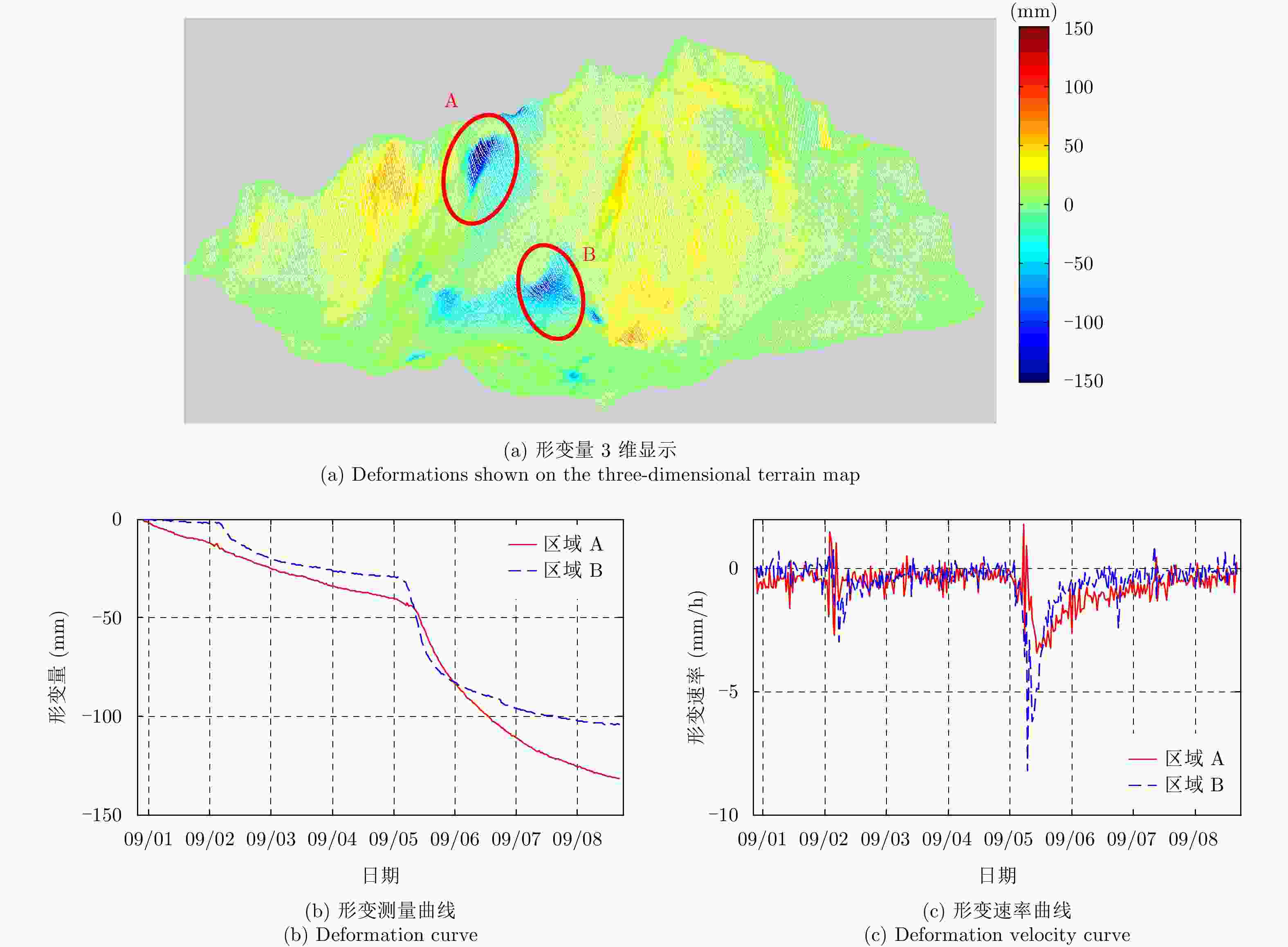
Table 3. Vibrating measurement results
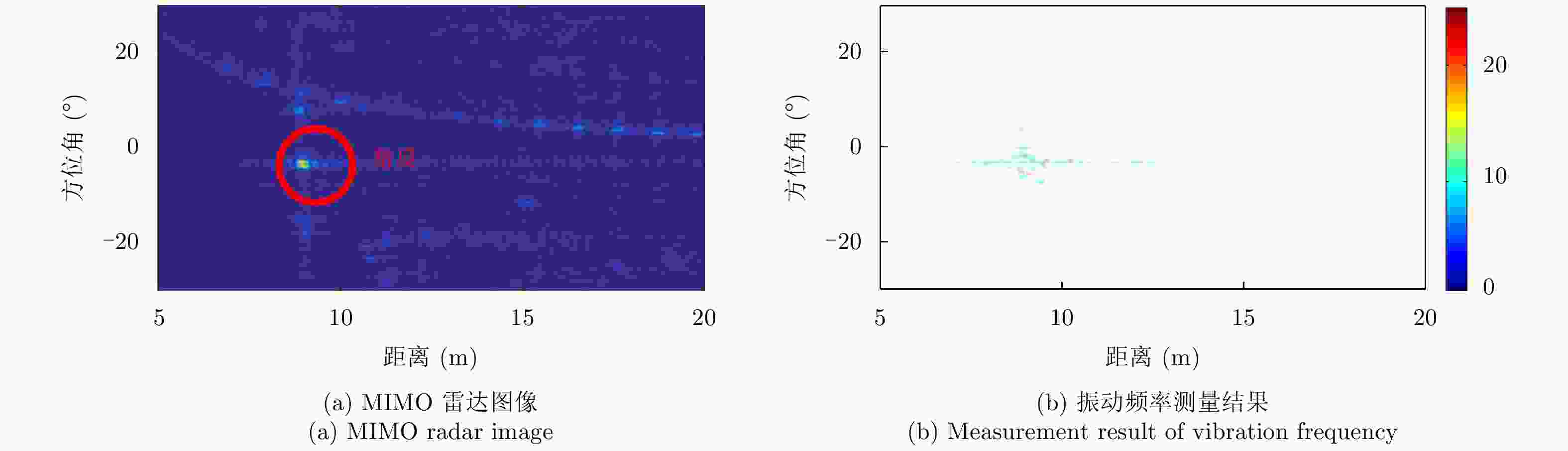
组号 振幅设定值(μm) 频率设定值(Hz) 频率测量值(Hz) 测量误差(Hz) 偏差比(%) 1 260 10 10.13 0.13 1.3 2 500 10 10.35 0.35 3.5 3 750 10 10.22 0.22 2.2 4 510 15 15.08 0.08 0.6 5 500 20 20.06 0.06 0.3 6 750 10 10.41 0.41 4.1 7 750 10 10.07 0.07 0.7 -
[1] 刘传正. 中国崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害成因类型[J]. 地质评论, 2014, 60(4): 858–868. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2014.04.015LIU Chuanzheng. Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(4): 858–868. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2014.04.015 [2] 杨光华, 钟志辉, 张玉成, 等. 滑坡灾害的机制与力学特性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(S2): 4009–4017. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0804YANG Guanghua, ZHONG Zhihui, ZHANG Yucheng, et al. Analysis of mechanism and mechanical characteristics of landslide disaster[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 4009–4017. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2016.0804 [3] 张德辉, 卢晓辉, 李天龙. GNSS实时形变监测系统在岩质高边坡中的应用[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2008(1): 36–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2018.01.009ZHANG Dehui, LU Xiaohui, and LI Tianlong. Application of GNSS surface displacement monitoring system in high rock slope[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2008(1): 36–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2018.01.009 [4] 于欢欢, 徐亚富, 谢洪波. 基于三维激光扫描技术的边坡变形监测应用研究[J]. 中州煤炭, 2015(12): 111–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0506.2015.12.035YU Huanhuan, XU Yafu, and XIE Hongbo. Application of slope deformation monitoring based on three-dimensional laser scanning technology[J]. Zhongzhou Coal, 2015(12): 111–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0506.2015.12.035 [5] 陈怡曲. 基于InSAR的形变监测技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.CHEN Yiqu. Deformation measurement techniques based on InSAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013. [6] 刘斌, 葛大庆, 李曼, 等. 地基合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术及其应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2017, 29(1): 1–6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.01LIU Bin, GE Daqing, LI Man, et al. Ground-based interferometric synthetic aperture radar and its applications[J]. Remote Sensing for Land &Resources, 2017, 29(1): 1–6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.01 [7] 孙建勋, 郑会歌. 关于地基InSAR新技术及水利工程变形监测应用的研究[J]. 水利建设与管理, 2017, 37(11): 7–10. doi: 10.16616/j.cnki.11-4446/TV.2017.011.002SUN Jianxun and ZHENG Huige. Research on application of foundation InSAR new technology and water conservancy engineering deformation monitoring[J]. Water Resources Development &Management, 2017, 37(11): 7–10. doi: 10.16616/j.cnki.11-4446/TV.2017.011.002 [8] REEVES B, NOON D A, STICKLEY G F, et al. Slope stability radar for monitoring mine walls[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 4491, Subsurface and Surface Sensing Technologies and Applications III, San Diego, CA, United States, 2001: 57–67. doi: 10.1117/12.450188. [9] 章亮, 任奋华, 王培涛, 等. 基于MSR300雷达监测的凹山采场降雨条件下的边坡变形及滑坡[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(4): 407–415. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2018.04.003ZHANG Liang, REN Fenhua, WANG Peitao, et al. Investigation of deformation and failure in washan slope considering rainfall conditions based on MSR300 radar monitoring[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(4): 407–415. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2018.04.003 [10] WERNER C, WIESMANN A, STROZZI T, et al. The GPRI multi-mode differential interferometric radar for ground-based observations[C]. Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 304–307. [11] ZENG Tao, MAO Cong, HU Cheng, et al. Ground-based SAR wide view angle full-field imaging algorithm based on keystone formatting[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2160–2170. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2558578 [12] RÖDELSPERGER S, LÄUFER G, GERSTENECKER C, et al. Monitoring of displacements with ground-based microwave interferometry: IBIS-S and IBIS-L[J]. Journal of Applied Geodesy, 2010, 4(1): 41–54. doi: 10.1515/JAG.2010.005 [13] LEVA D, NICO G, TARCHI D, et al. Temporal analysis of a landslide by means of a ground-based SAR Interferometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(4): 745–752. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.808902 [14] RÖDELSPERGER S and META A. MetaSensing’s FastGBSAR: Ground based radar for deformation monitoring[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 9243, SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XIV, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2014. doi: 10.1117/12.2067243. [15] AGUASCA A, BROQUETAS A, MALLORQUI J, et al. A solid state L to X-band flexible ground-based SAR system for continuous monitoring applications[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 2014. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2004.1368512. [16] 林德才, 马海涛, 宋宝宏. 边坡雷达在滑坡应急救援行动中的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2016, 12(S1): 284–289. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2016.S1.050LIN Decai, MA Haitao, and SONG Baohong. Application of slope radar in emergency rescue of landslide[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2016, 12(S1): 284–289. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2016.S1.050 [17] HU Cheng, ZHU Mao, ZENG Tao, et al. High-precision deformation monitoring algorithm for GBSAR system: Rail determination phase error compensation[J]. Science China Information Science, 2016, 59(8): 082307. doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5446-z [18] 路满, 宋红军, 罗运华. 基于调频连续波信号的圆弧式合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 425–433. doi: 10.12000/JR16007LU Man, SONG Hongjun, and LUO Yunhua. Imaging algorithm for Arc synthetic aperture radar using frequency modulated continuous wave[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 425–433. doi: 10.12000/JR16007 [19] 林赟, 谭维贤, 洪文, 等. 圆迹SAR极坐标格式算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(12): 2802–2807. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00003LIN Yun, TAN Weixian, HONG Wen, et al. Polar format algorithm for circular synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(12): 2802–2807. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00003 [20] LEE H, LEE J H, KIM K E, et al. Development of a truck-mounted arc-scanning synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2773–2779. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2265700 [21] VIVIANI F, MICHELINI A, MAYER L, et al. IBIS-ArcSAR: An innovative ground-based SAR system for slope monitoring[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8517702. [22] LUO Yunhua, SONG Hongjun, WANG R, et al. Arc FMCW SAR and applications in ground monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5989–5998. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2325905 [23] TARCHI D, OLIVERI F, and SAMMARTINO P F. MIMO radar and ground-based SAR imaging systems: Equivalent approaches for remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 425–435. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2199120 [24] HU C, WANG J, TIAN W, et al. Design and imaging of ground-based multiple-input multiple-output synthetic aperture radar (MIMO SAR) with non-collinear arrays[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17: 598. doi: 10.3390/s17030598 [25] BROUSSOLLE J, KYOVTOROV V, BASSO M, et al. MELISSA, a new class of ground based InSAR system. An example of application in support to the Costa Concordia emergency[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 91: 50–58. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.02.003 [26] 乞耀龙, 王彦平, 李湖生, 等. 一种用于地基雷达数据成像处理的数字波束形成算法[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(10): 1313–1317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.10.014QI Yaolong, WANG Yanping, LI Husheng, et al. Digital beam forming algorithm for ground-based radar imaging processing[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(10): 1313–1317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.10.014 [27] MONSERRAT O, CROSETTO M, and LUZI G. A review of ground-based SAR interferometry for deformation measurement[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 93: 40–48. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.04.001 [28] CADUFF R, SCHLUNEGGER F, KOS A, et al. A review of terrestrial radar interferometry for measuring surface change in the geosciences[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2015, 40(2): 208–228. doi: 10.1002/esp.3656 [29] 朱茂. 基于动态PS的地基合成孔径雷达高精度形变测量技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京理工大学, 2016.ZHU Mao. High Precision Deformation measurement using ground based synthetic aperture radar (GBSAR) based on dynamic persistent scatter (PS) technique[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. [30] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [31] RÖDELSPERGER S. Real-time processing of ground based synthetic aperture radar (GB-SAR) measurements[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Technische Universitat Darmstadt, 2011. [32] 周伟, 黄其欢, 张顺迎. 基于PS方法的地基SAR在大坝变形监测中的应用[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2016(1): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2016.01.005ZHOU Wei, HUANG Qihuan, and ZHANG Shunying. Application of ground-based SAR in dam deformation monitoring based on PS method[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2016(1): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2016.01.005 [33] CROSETTO M, MONSERRAT O, CUEVAS-GONZÁLEZ M, et al. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 115: 78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.011 [34] 韩洁, 赖涛, 赵拥军, 等. 小数据集PS-DInSAR的PS点探测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(6): 679–685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.06.007HAN Jie, LAI Tao, ZHAO Yongjun, et al. Method on PS detection of small dataset PS-DInSAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(6): 679–685. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.06.007 [35] COSTANTINI M and ROSEN P A. A generalized phase unwrapping approach for sparse data[C]. IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 1999, 1: 267–269. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1999.773467. [36] OJHA C, MANUNTA M, PEPE A, et al. An innovative region growing algorithm based on Minimum Cost Flow approach for Phase Unwrapping of full-resolution differential interferograms[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 5582–5585. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352054. [37] NOFERINI L, TAKAYAMA T, PIERACCINI M, et al. Analysis of ground-based SAR data with diverse temporal baselines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(6): 1614–1623. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.916216 [38] OSMANOĞLU B, DIXON T H, and WDOWINSKI S. Three-dimensional phase unwrapping for satellite radar interferometry, I: DEM generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1059–1075. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2247043 [39] 张祥, 陆必应, 宋千. 地基SAR差分干涉测量大气扰动误差校正[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2011, 9(6): 502–506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.06.004ZHANG Xiang, LU Biying, and SONG Qian. Atmospheric disturbance correction in ground-based SAR differential interferometry[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2011, 9(6): 502–506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.06.004 [40] NOFERINI L, PIERACCINI M, MECATTI D, et al. Permanent scatterers analysis for atmospheric correction in ground-based SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(7): 1459–1471. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.848707 [41] HUANG Zengshu, SUN Jinping, LI Qing, et al. Time- and space-varying atmospheric phase correction in discontinuous ground-based synthetic aperture radar deformation monitoring[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3883. doi: 10.3390/s18113883 [42] IGLESIAS R, FABREGAS X, AGUASCA A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen compensation in ground-based SAR with a multiple-regression model over mountainous regions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2436–2449. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2261077 [43] TAPETE D, CASAGLI N, LUZI G, et al. Integrating radar and laser-based remote sensing techniques for monitoring structural deformation of archaeological monuments[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2013, 40(1): 176–189. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2012.07.024 [44] KOS A, STROZZI T, STOCKMANN R, et al. Detection and Characterization of Rock Slope Instabilities Using a Portable Radar Interferometer (GPRI)[M]. MARGOTTINI C, CANUTI P, SASSA K. Landslide Science and Practice. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-31445-2_42. [45] 刘作利, 刘景玉, 申修强, 等. 唐山马兰庄铁矿露天开采边坡变形监测的GB-InSAR技术[J]. 现代矿业, 2018(4): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2018.04.047LIU Zuoli, LIU Jingyu, SHEN Xiuqiang, et al. Deformation monitoring of the open-pit slope of Malanshan iron mine in Tangshan City based on GB-InSAR[J]. Modern Mining, 2018(4): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2018.04.047 [46] 毛聪, 胡程, 曾涛, 等. 地基SAR子图相干合成快速成像算法[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(11): 1396–1403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.11.002MAO Cong, HU Cheng, ZENG Tao, et al. Ground-based SAR fast imaging algorithm based on sub-image combination[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(11): 1396–1403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.11.002 [47] HU C, DENG Y, TIAN W, et al. A novel MIMO-SAR system applied for high-speed and high accuracy deformation measurement[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2018, Nanjing, China, 2018. [48] ZHU Mao, HU Cheng, ZENG Tao, et al. Experimental results and analysis for GBSAR deformation measurement[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–4. doi: 10.1049/cp.2015.1332. [49] MARCHISIO M, PIRODDI L, RANIERI G, et al. Comparison of natural and artificial forcing to study the dynamic behaviour of Bell Towers in low wind context by means of ground-based radar interferometry: The case of the Leaning Tower in Pisa[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2014, 11(5): 055004. doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/11/5/055004 [50] LI Y, TIAN W, MEI H, et al. Weak vibration measurement technology and application based on FMCW radar system[C]. 2018 IET International Radar Conference, Nanjing, China, 2018. [51] MEI Hongyan, LI Yuqi, TIAN Weiming, et al. Weak vibration measurement based on MIMO imaging radar system[C]. Proceedings of 2018 China International SAR Symposium, Shanghai, China, 2018. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: