DLSLA 3D SAR Motion Error Compensation and Imaging Method Based on Parameter Estimation
-
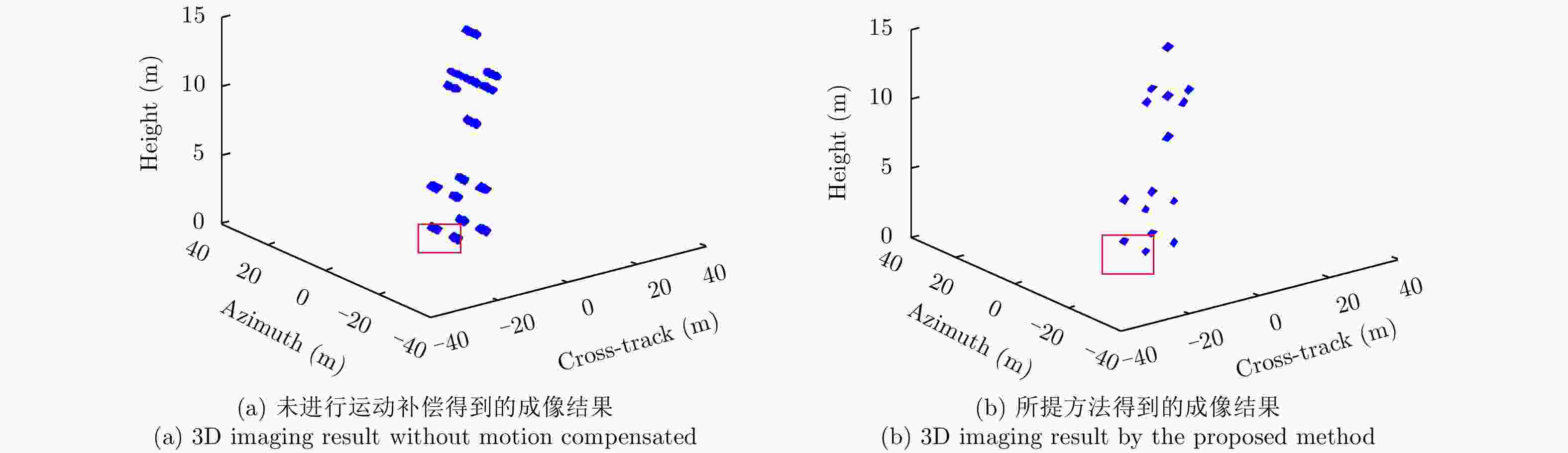
摘要: 当载机存在偏航角速度时,载机航线会偏离理想航线,对稀疏阵列下视3维合成孔径雷达(DLSLA 3D SAR)成像产生影响。该文建立了载机在飞行过程中存在偏航角速度下的DLSLA 3D SAR成像模型,通过理论推导得到了信号的多普勒调频率表达式,多普勒调频率与目标被调制后的跨航向坐标有关,而与被调制后的方位向坐标无关。进一步,完成跨航向信号处理之后,在平台的速度和偏航角速度不准的情况下,利用参数化稀疏表征方法实现了平台的速度和偏航角速度的估计,并完成了方位向稀疏场景的重构,最后提出了一种形变校正方法。仿真实验验证了该算法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 稀疏阵列下视3维合成孔径雷达 /
- 运动误差 /
- 多普勒调频率 /
- 参数化稀疏表征
Abstract: In the presence of yaw angular velocity, a body will deviate from its ideal flight path, which will affect imaging of Downward-Looking Sparse Linear Array 3D Synthetic Aperture Radar (DLSLA 3D SAR). In this paper, an imaging model including yaw rate is established. Furthermore, Doppler frequency modulation, which is related to cross-track coordinates and not azimuth coordinates, was theoretically calculated. Thus, a cross-track signal could be reconstructed to obtain the cross-track coordinates before azimuth signal compression. Based on the parametric sparse representation, the velocity and yaw rate of the platform were estimated, and the azimuth signal was compressed. Moreover, a deformation correction method is proposed to correct image deformation. The simulation results demonstrate the validity of the proposed method. -
表 1 平台和天线的参数
Table 1. Parameters of platform and antenna
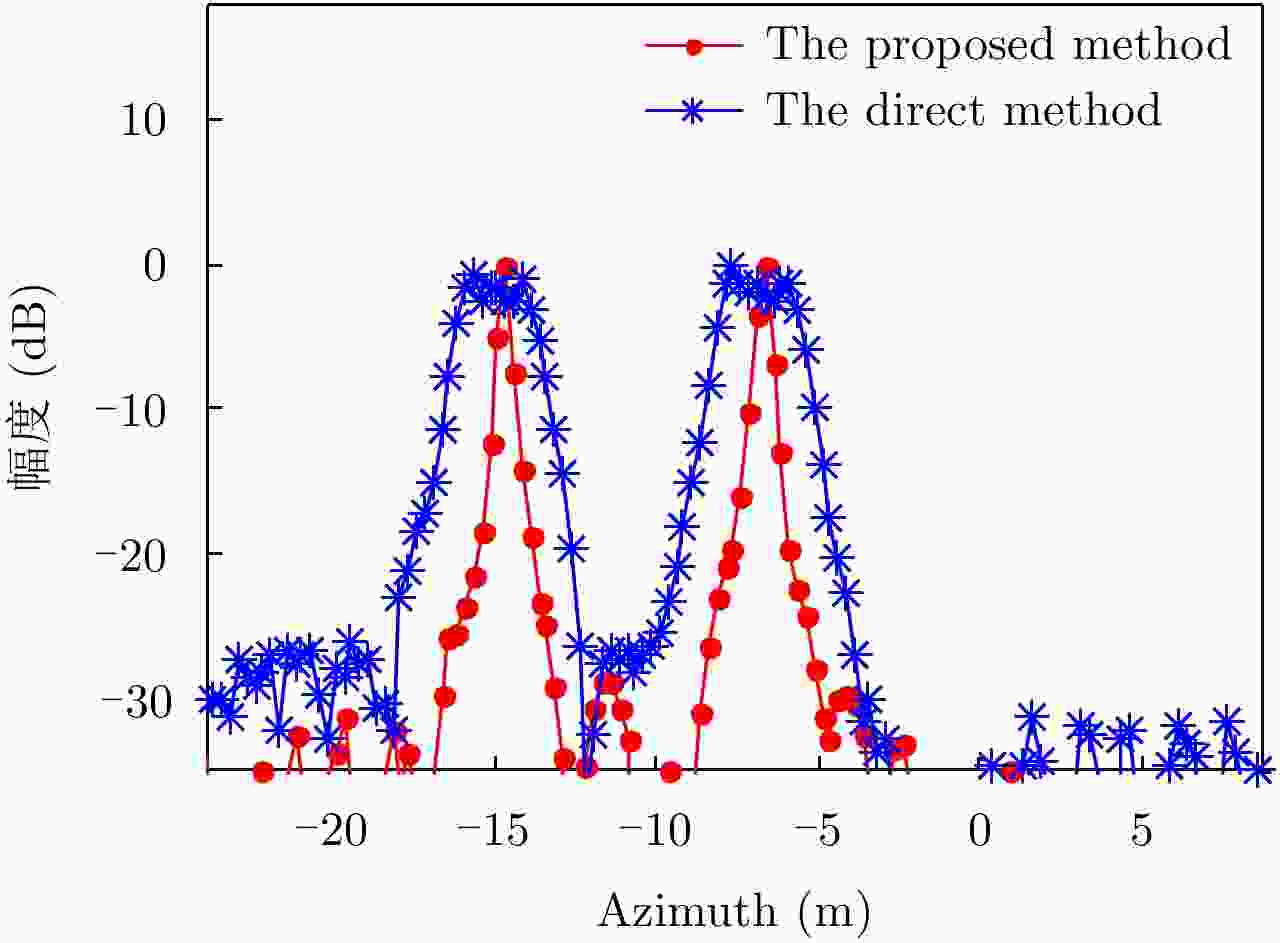
参数 值 参数 值 载频fc (GHz) 17 脉冲重复频率PRF (Hz) 5000 带宽Br (MHz) 200 发射天线数量Nt 16 平台高度H (m) 1300 接收天线数量Nr 15 平台速度v (m/s) 60 跨航向分辨率(m) 5.42 脉冲持续时间Tr (μs) 0.1 方位向分辨率(m) 0.5 偏航角速度(°/s) 2 初始偏航角(°) 3 目标 直接法 参数化稀疏表征法 提升倍数 1 2.26 m 0.41 m 5.51 2 2.51 m 0.36 m 6.97 表 3 形变校正前后的方位向、跨航向坐标
Table 3. The azimuth and cross-track coordinates before and after deformation correction
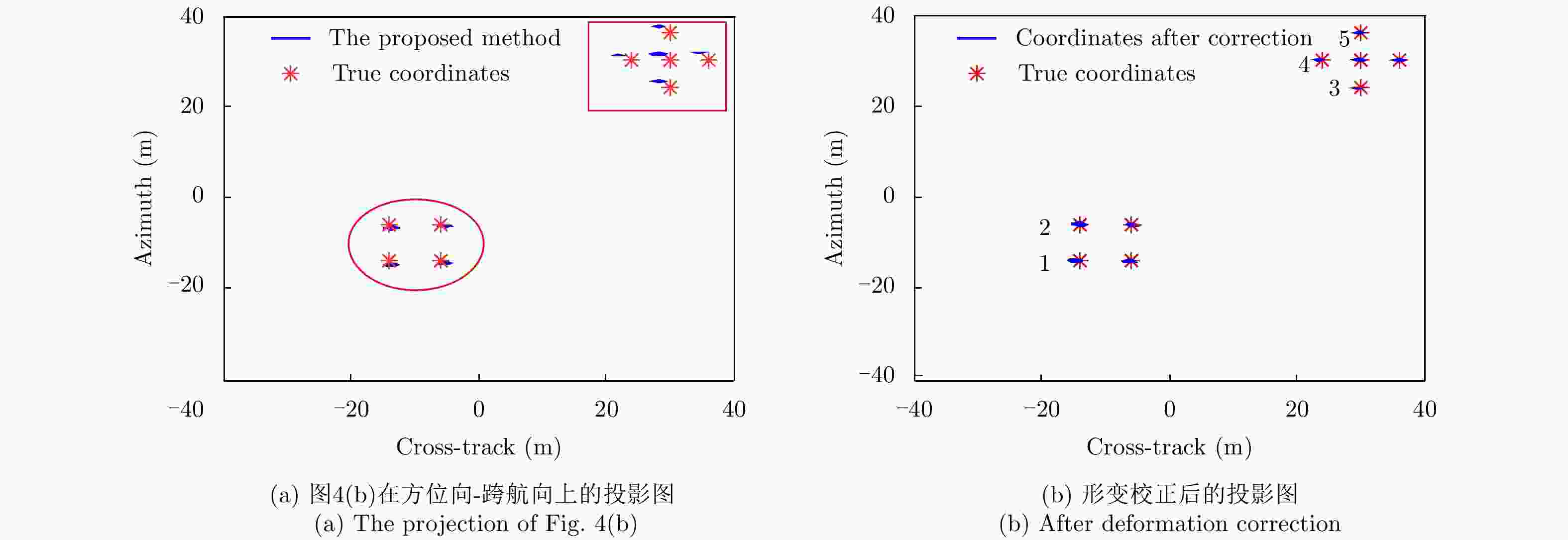
目标 实际坐标(m) 校正前的坐标(m) 校正后的坐标(m) 提升倍数 1 (–14, –14) (–14.92, –13.13) (–13.95, –14.49) (18.40, 1.77) 2 (–6, –14) (–6.64, –13.60) (–6.09, –14.02) (7.10, 20.00) 3 (24, 30) (25.45, 28.26) (24.01, 29.49) (145.00, 3.41) 4 (30, 24) (30.96, 21.98) (29.89, 23.41) (8.72, 3.42) 5 (36, 30) (37.48, 28.26) (36.19, 29.89) (7.79, 15.81) 表 4 形变校正前后的方位向、跨航向坐标
Table 4. The azimuth and cross-track coordinates before and after deformation correction
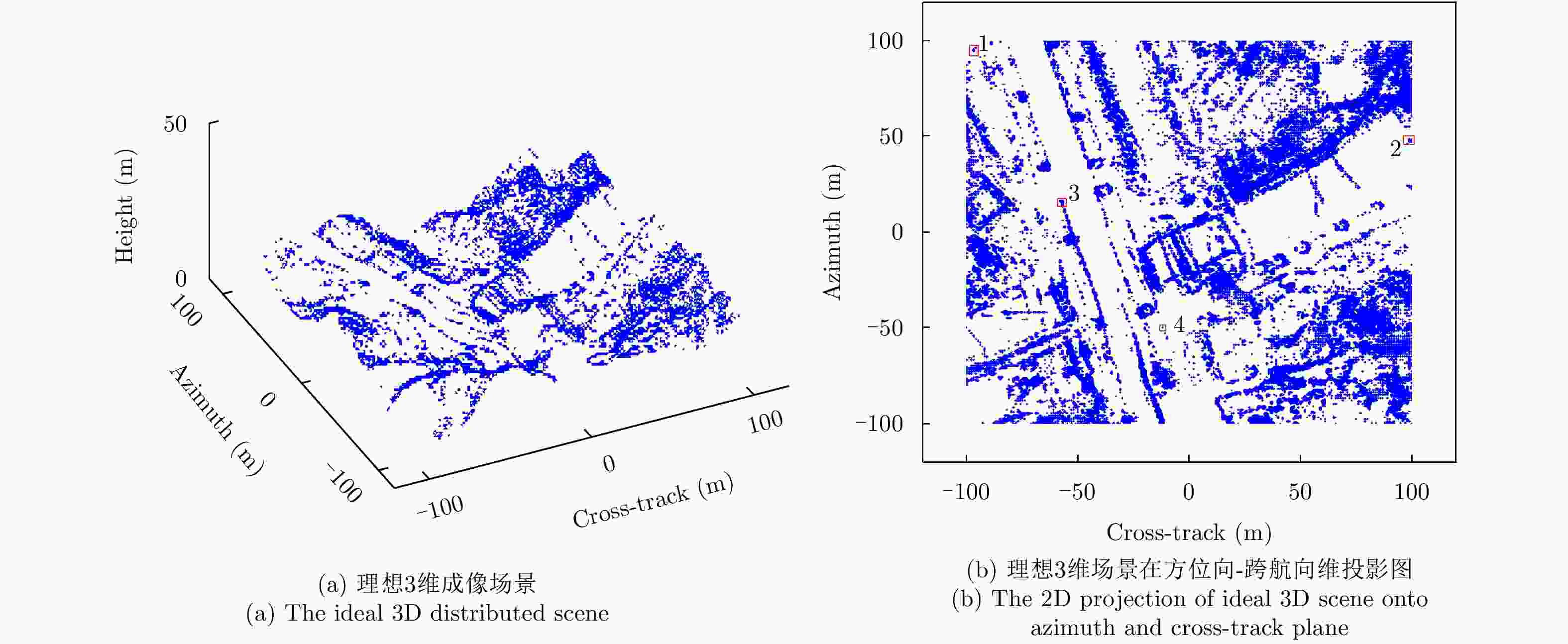
目标 实际坐标(m) 校正前的坐标(m) 校正后的坐标(m) 提升倍数 1 (95, –97) (81.72, –105.10) (95.32, –99.31) (41.50, 3.50) 2 (48, 100) (60.12, 97.15) (48.23, 100.92) (52.69, 3.09) 3 (16, –57) (12.68, –59.62) (16.30, –58.53) (11.06, 1.71) 4 (–50, –12) (–49.32, –11.56) (–49.91, –11.58) (7.55, 1.04) -
[1] Budillon A, Evangelista A, and Schirinzi G. Three-dimensional SAR focusing from multipass signals using compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 488–499. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2054099 [2] Zhu X X and Bamler R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487 [3] Peng X M, Tan W X, Hong W, et al. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR image reconstruction by combination of polar formatting and L1 regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 213–226. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2453202 [4] 徐宗本, 吴一戎, 张冰尘, 等. 基于L1/2正则化理论的稀疏雷达成像[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. DOI: 10.1360/N972018-00372Xu Zong-ben, Wu Yi-rong, Zhang Bing-chen, et al. Sparse radar imaging based on L1/2 regularization theory[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. DOI: 10.1360/N972018-00372 [5] 毕辉, 张冰尘, 洪文. 基于RIPless理论的层析SAR成像航迹分布优化方法[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(2): 680–687. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2015.0131Bi Hui, Zhang Bingchen, and Hong Wen. Track distribution optimization method based on TomoSAR via RIPless theory[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 680–687. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2015.0131 [6] 侯丽英, 林赟, 洪文. 干涉圆迹SAR的目标三维重建方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 538–547. DOI: 10.12000/JR16009Hou Li-ying, Lin Yun, and Hong Wen. Three-dimensional reconstruction method study based on interferometric circular SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 538–547. DOI: 10.12000/JR16009 [7] 李烈辰, 李道京, 张清娟. 基于压缩感知的三孔径毫米波合成孔径雷达侧视三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(3): 552–558. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01016Li Lie-chen, Li Dao-jing, and Zhang Qing-juan. Three-aperture millimeter-wave SAR side-looking three-dimensional imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 552–558. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01016 [8] 张清娟, 李道京, 李烈辰. 连续场景的稀疏阵列SAR侧视三维成像研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136Zhang Qing-juan, Li Dao-jing, and Li Lie-chen. Research on continuous scene side-looking 3D imaging based on sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136 [9] 田鹤, 李道京, 潘洁, 等. 基于修正均匀冗余阵列正反编码的稀疏阵列SAR下视三维成像处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209Tian He, Li Dao-jing, Pan Jie, et al. Downward-looking 3D imaging processing of sparse array SAR based on modified uniformly redundant arrays positive and negative coding[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209 [10] 李道京, 侯颖妮, 滕秀敏, 等. 稀疏阵列天线雷达技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.Li Dao-jing, Hou Ying-ni, Teng Xiu-min, et al.. Sparse Array Antenna Radar Imaging Technology and Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [11] Bao Q, Han K Y, Peng X M, et al. DLSLA 3-D SAR imaging algorithm for off-grid targets based on pseudo-polar formatting and atomic norm minimization[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(6): 062310. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-015-5477-5 [12] Liu Q Y, Zhang Q, Luo Y, et al. Fast algorithm for sparse signal reconstruction based on off-grid model[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2018, 12(4): 390–397. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0319 [13] 丁振宇, 谭维贤, 王彦平, 等. 基于波数域子孔径的机载三维SAR偏航角运动误差补偿[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(4): 467–473. DOI: 10.12000/JR15016Ding Zhen-yu, Tan Wei-xian, Wang Yan-ping, et al. Yaw angle error compensation for airborne 3-D SAR based on wavenumber-domain subblock[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(4): 467–473. DOI: 10.12000/JR15016 [14] 杨泽民, 孙光才, 邢孟道, 等. 基于多通道联合自聚焦技术的机载三维SAR运动补偿[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(7): 1581–1588. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01365Yang Ze-min, Sun Guang-cai, Xing Meng-dao, et al. Motion compensation for airborne 3-D SAR based on joint multi-channel auto-focusing technology[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(7): 1581–1588. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01365 [15] Chen Y C, Li G, Zhang Q, et al. Motion compensation for airborne SAR via parametric sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 551–562. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2611522 [16] 刘云龙, 李焱磊, 周良将, 等. 一种机载SAR快速几何精校正算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 419–424. DOI: 10.12000/JR16064Liu Yun-long, Li Yan-lei, Zhou Liang-jiang, et al. A fast precise geometric calibration method for airborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 419–424. DOI: 10.12000/JR16064 [17] 王力宝, 许稼, 皇甫堪, 等. MIMO-SAR等效相位中心误差分析与补偿[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(12): 2688–2693. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.015Wang Li-bao, Xu Jia, Huangfu Kan, et al. Analysis and compensation of equivalent phase center error in MIMO-SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(12): 2688–2693. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.015 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: