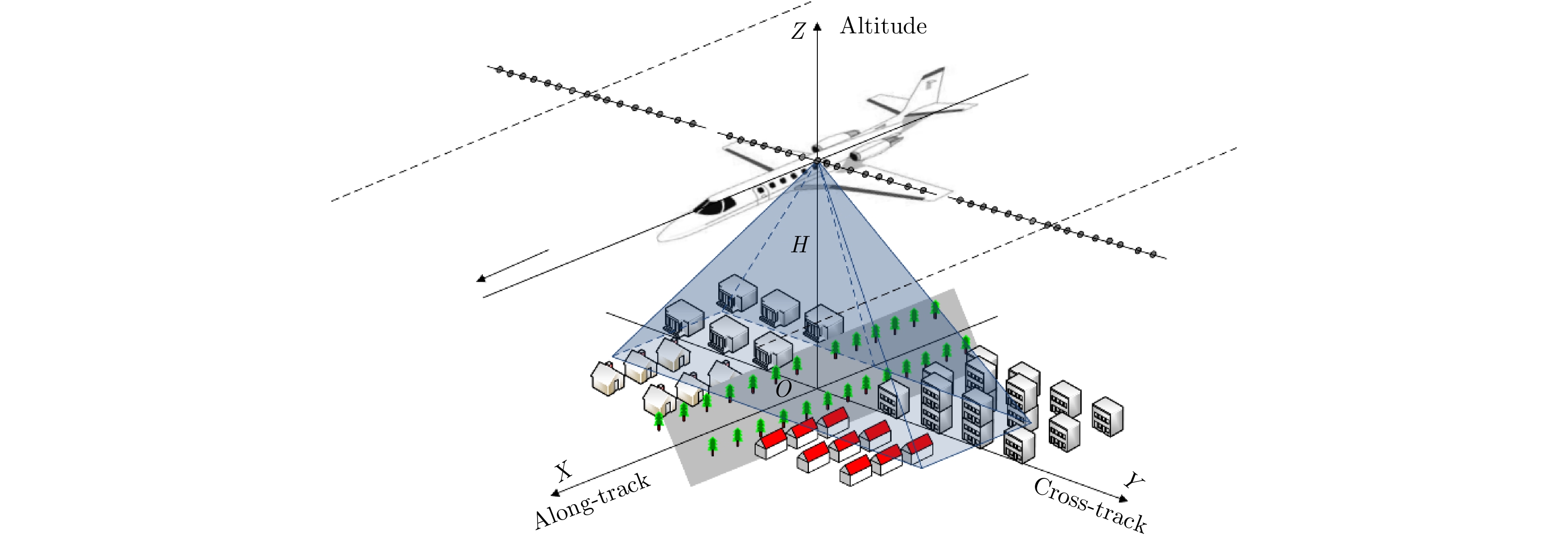
Motion Compensation and 3-D Imaging Algorithm in Sparse Flight Based Airborne Array SAR
-
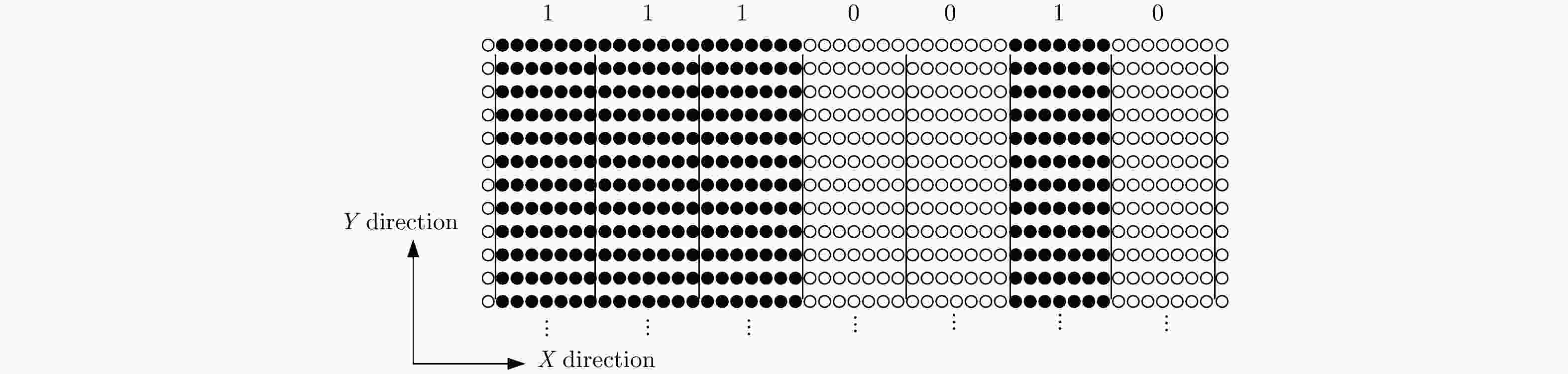
摘要: 该文针对机载交轨阵列SAR下视3维成像模型,采用以巴克码伪随机序列为准则的稀疏重航过采样方式,利用较少飞行次数提高交轨向分辨率。针对重航过采样方式存在的运动误差,利用修正均匀冗余阵列(Modified Uniformly Redundant Arrays, MURA)编码空间调制和3维后向投影(Back Projection, BP)算法获得各航过3维复图像对,基于干涉处理和频域压缩感知(Compressed Sensing, CS)等效实现各航过阵列形变误差补偿。将MURA反码对应回波形成的3维复图像相位作为参考,对各单航过复图像进行相位补偿,以恢复各航过间复图像相位关系。根据单航过阵列SAR3维复图像具备频域稀疏的性质,对各个复图像相干累加,实现稀疏重航过阵列SAR高分辨率下视3维成像。仿真和暗室试验数据处理结果验证了方法的有效性。Abstract: In this study, we adopt a criterion of Barker code to generate a high-resolution image from sparse flight samples to establish a three-dimensional (3-D) imaging model of airborne array SAR. Under the condition of motion error, we utilize the Modified Uniformly Redundant Arrays (MURA) modulation and 3-D Back Projection (BP) algorithm to obtain 3-D complex image pairs under each flight. Based on interferometry and Compressed Sensing (CS) in frequency domain, the array deformation error compensation is realized. The phases of 3-D complex image formed by the echo corresponding to negative MURA modulation are referred to perform phase compensation on each single-pass complex image to restore the image phase relation of each flight. Coherent accumulation of each complex image is implemented to realize high-resolution 3-D imaging under sparse flight sampling. Simulation analysis and experimental data verify the feasibility of the proposed method.
-
表 1 机载交轨向稀疏重航过阵列SAR仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of airborne sparse flight array SAR
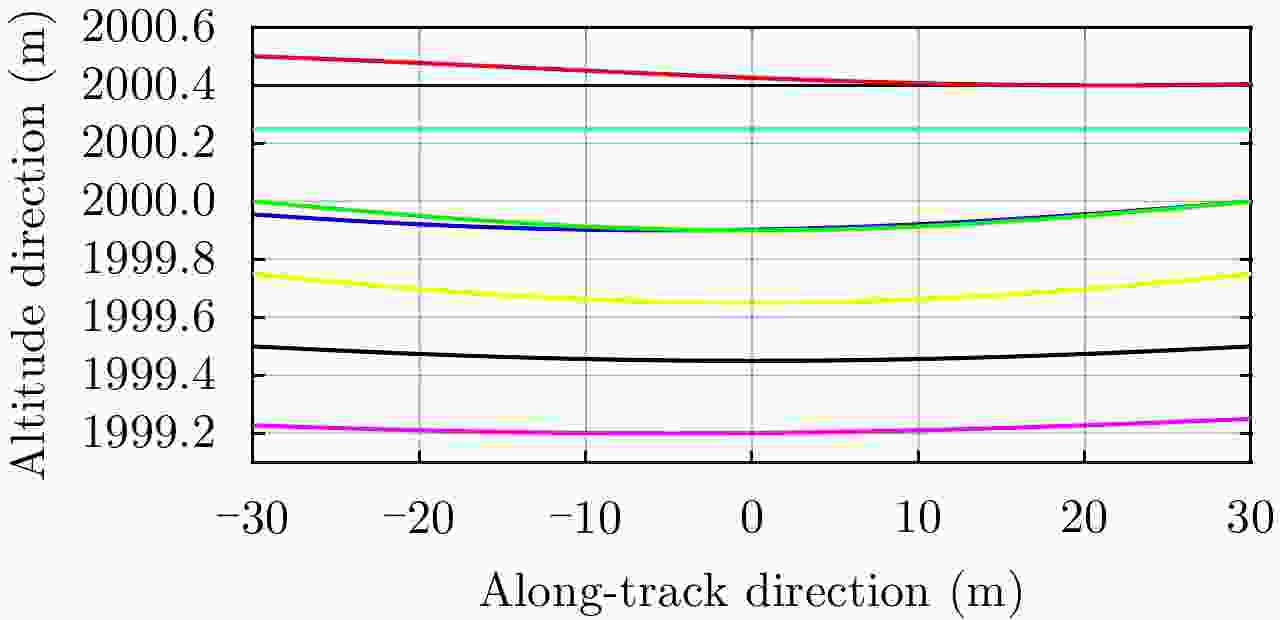
参数 数值 参数 数值 飞行高度 2000 m 顺轨向天线子阵尺寸 1.0 m 信号带宽 300 MHz 交轨向阵列天线长度 9 m 雷达工作波长 0.03 m 各航过飞行间隔 9.15 m 脉冲重复频率 400 Hz 顺轨向分辨率 0.50 m 载机飞行速度 75 m/s 高程向分辨率 0.5 m 交轨向等效相位中心数量 61 单航过交轨分辨率 3.33 m 交轨向等效相位中心间隔 0.15 m 7次重航过交轨分辨率 0.47 m 交轨向幅宽 200 m 稀疏重航过交轨分辨率 0.55 m 表 2 运动误差条件下的3维成像结果误差分析
Table 2. 3-D imaging performance analysis under motion error
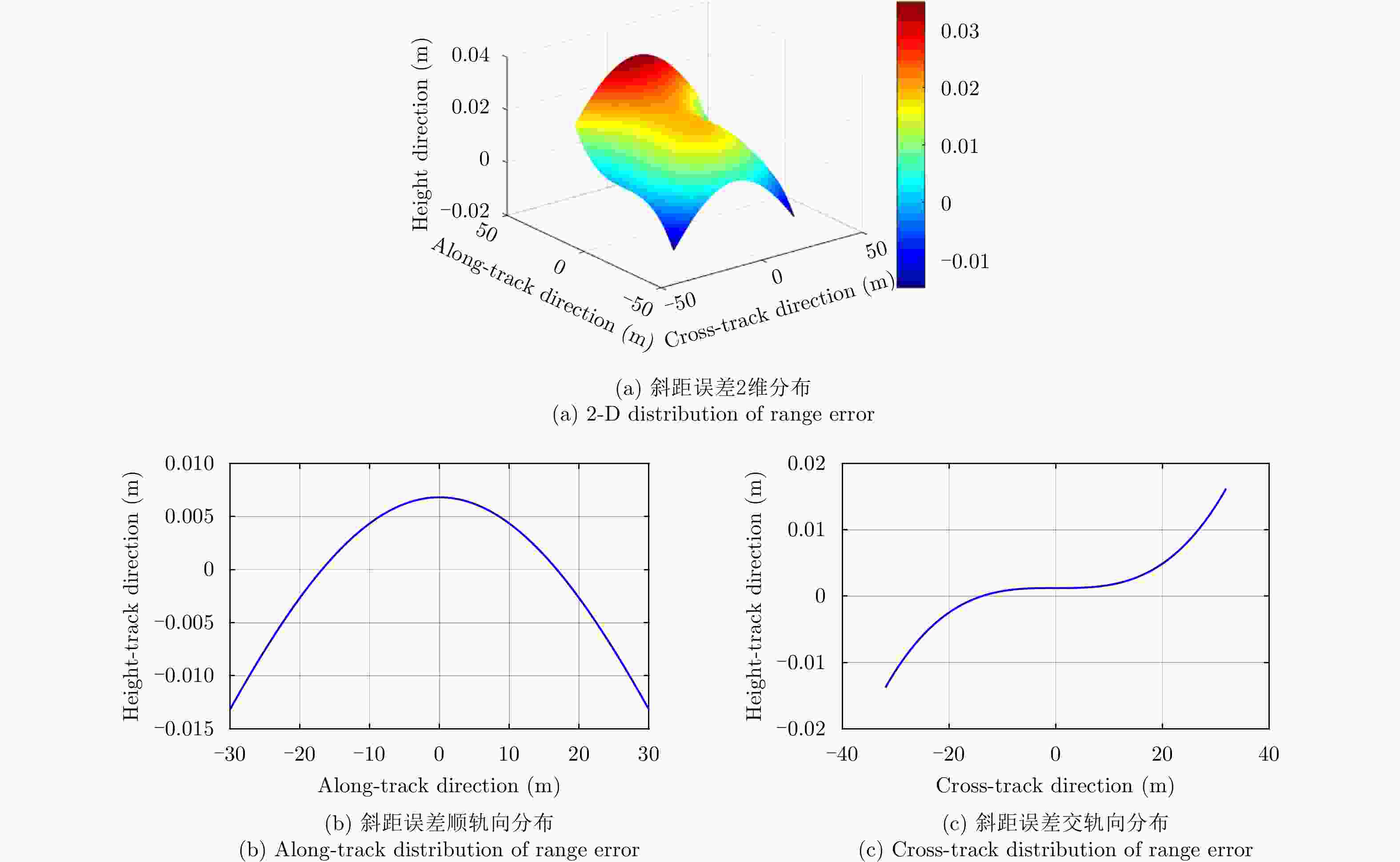
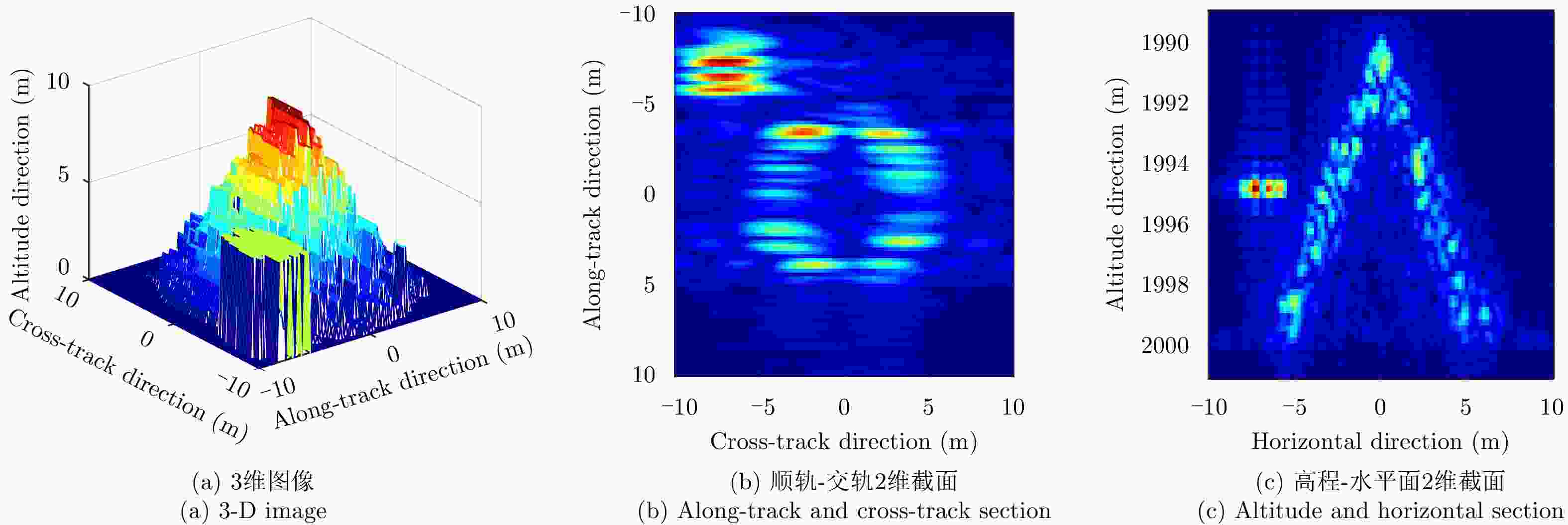
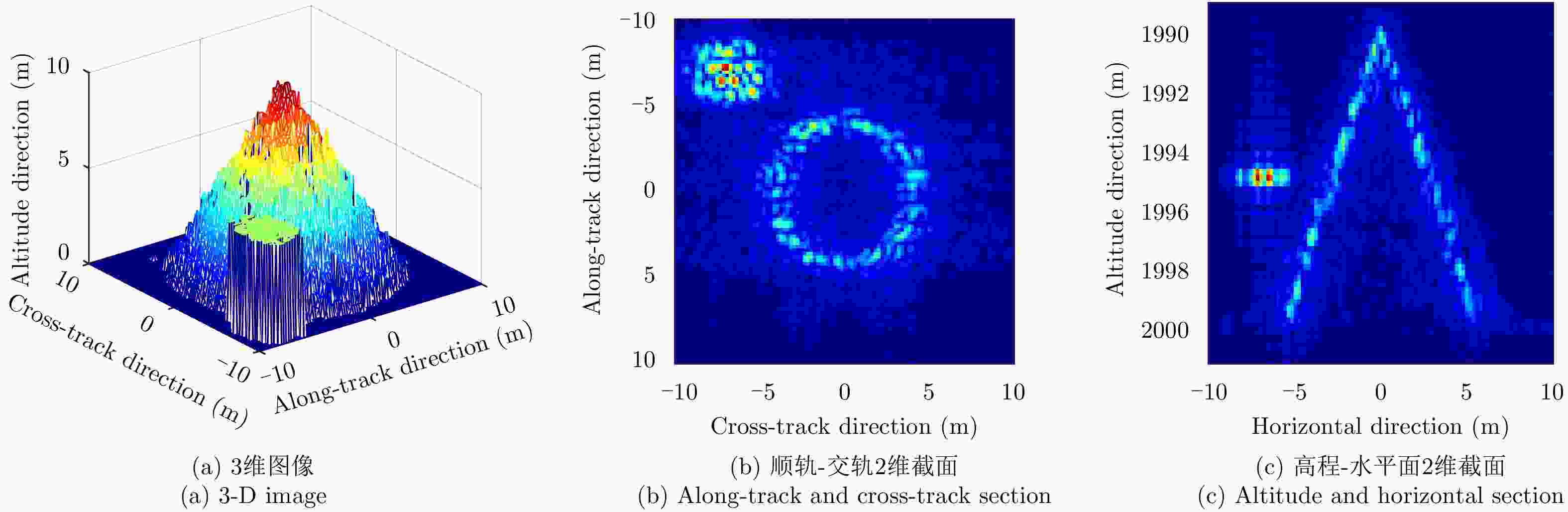
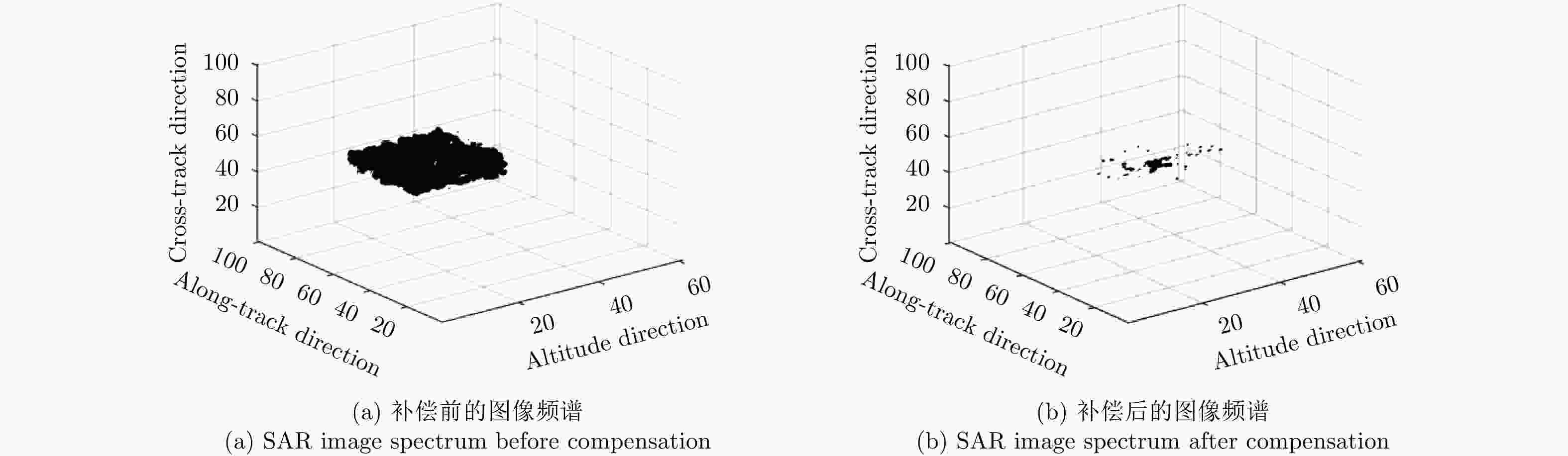
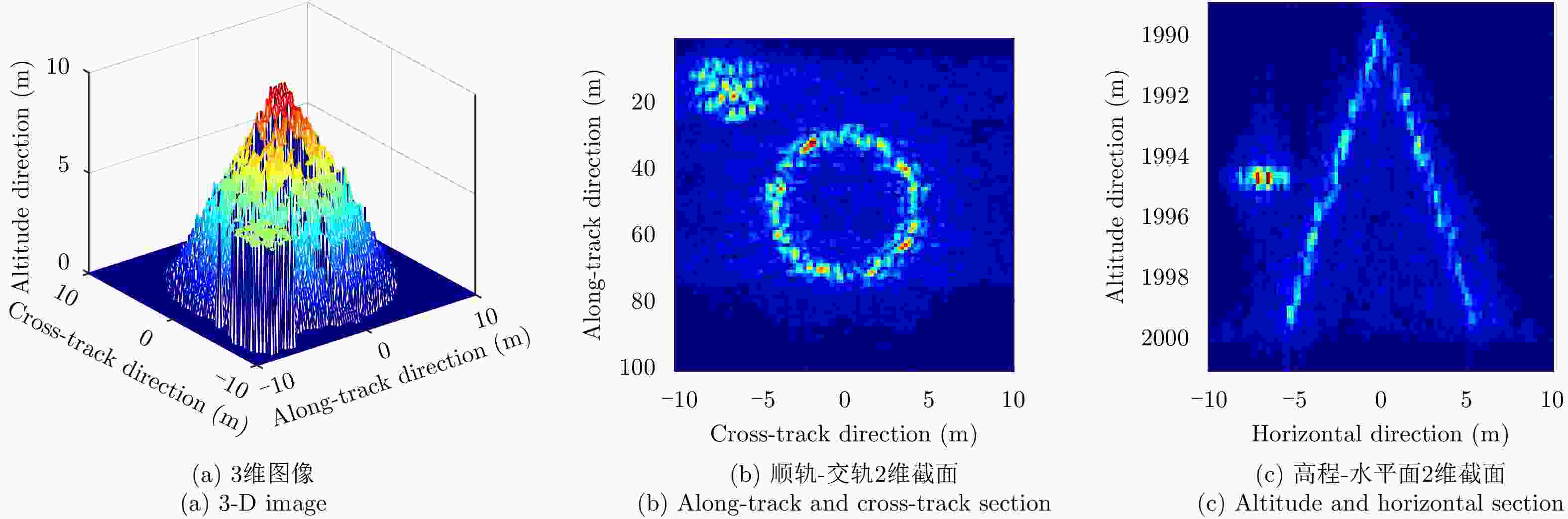
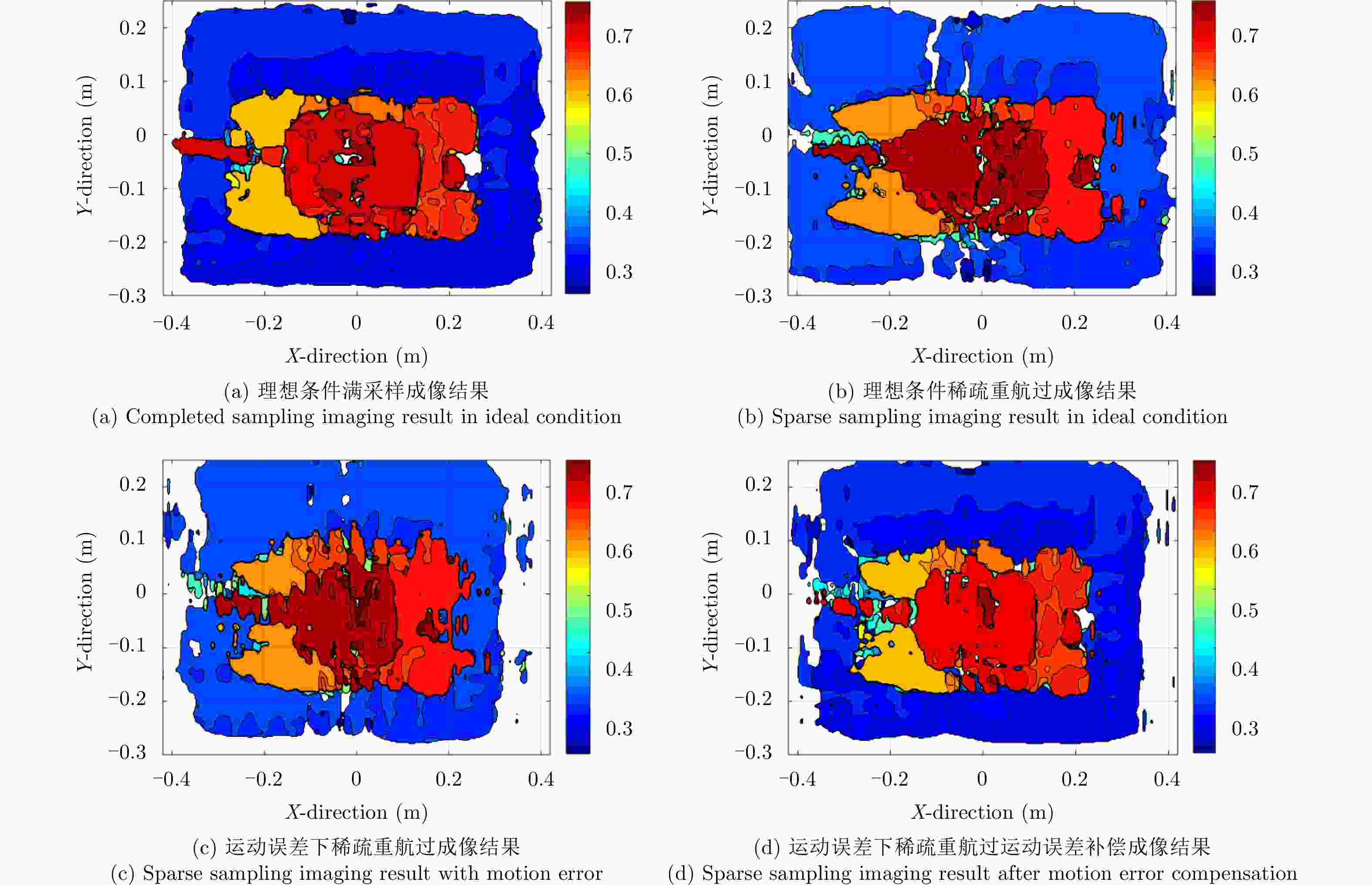
成像方法 相关系数 RMSE(m) SSIM 理想条件单航过阵列SAR 3维BP成像 0.7378 0.1083 0.7936 理想条件未稀疏重航过阵列SAR 3维BP成像 0.9216 0.0111 0.9532 理想条件巴克码稀疏重航过阵列SAR 3维BP成像 0.8718 0.0146 0.9079 运动误差下巴克码稀疏重航过阵列SAR 3维BP成像 0.8205 0.0276 0.8908 运动误差下巴克码稀疏重航过阵列SAR运动误差补偿和3维成像 0.8904 0.0151 0.9312 表 3 试验参数
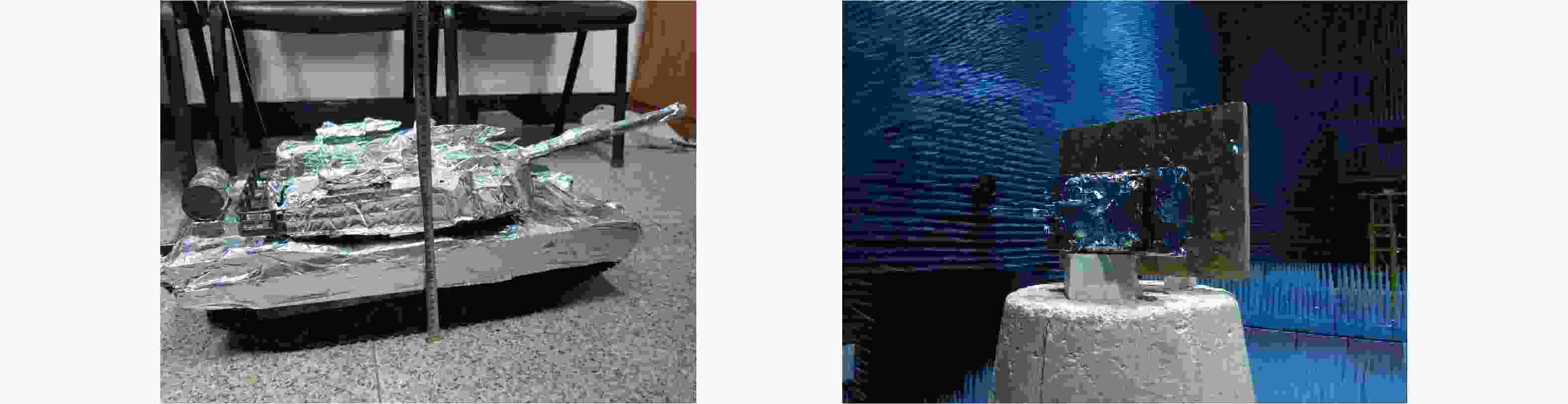
Table 3. Experimental parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 测试距离R0 1.60 m 顺轨向采样点数 51 雷达工作波长 $\lambda$ 0.03 m 高程向采样点数 201 信号总带宽B 4 GHz 交轨向分辨率 0.027 m 天线扫描面大小 1.00 m×1.00 m 顺轨向分辨率 0.027 m 交轨向采样点数 51 高程向全带宽分辨率 0.0375 m 表 4 运动误差条件下的3维成像结果误差分析
Table 4. 3-D imaging performance analysis under motion error
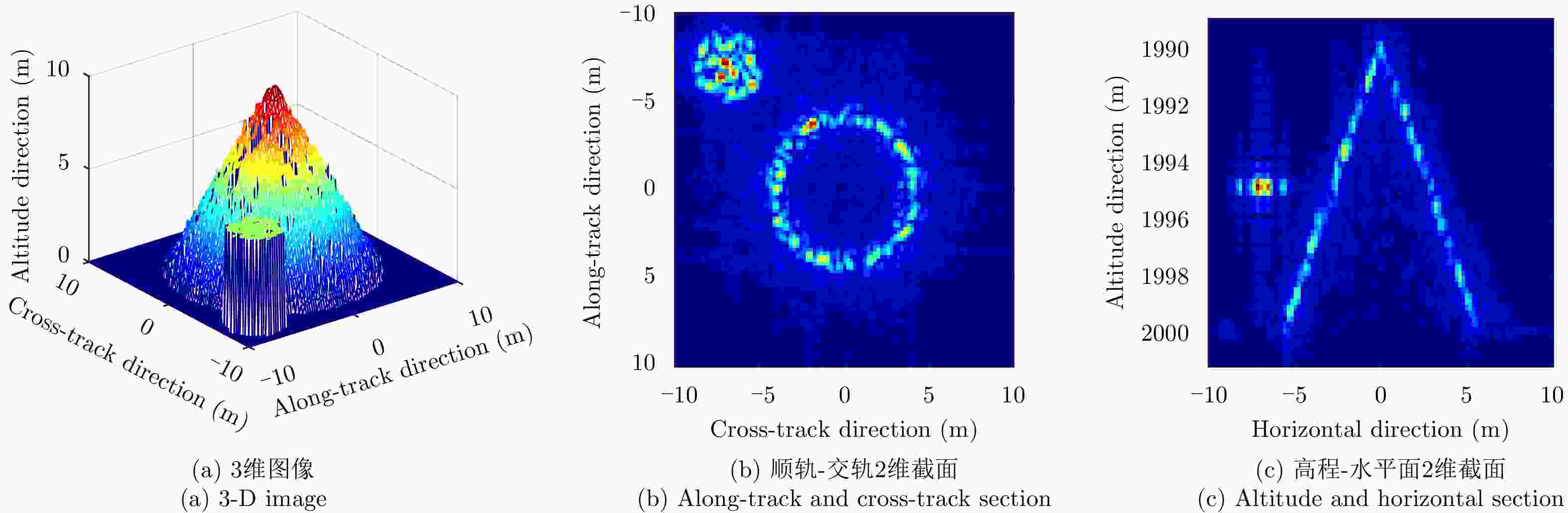
成像方法 相关系数 RMSE (m) SSIM 理想条件下巴克码稀疏重航过直接成像结果 0.8759 0.0104 0.9535 运动误差下稀疏重航过直接成像结果 0.8329 0.0204 0.9133 运动误差下稀疏重航过运动误差补偿和3维成像结果 0.8781 0.0115 0.9647 -
[1] 吴一戎, 洪文, 张冰尘, 等. 稀疏微波成像研究进展(科普类)[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(4): 383–396. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14105Wu Yi-rong, Hong Wen, Zhang Bing-chen, et al. Current developments of sparse microwave imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(4): 383–396. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14105 [2] Peng X M, Tan W X, Hong W, et al. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR image reconstruction by combination of polar formatting and L1 regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 213–226. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2453202 [3] Li D J and Teng X M. Cross-track sparse flight simulation analysis for airborne sparse array downward-looking 3D imaging Radar[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2011: 1686–1688. [4] 张清娟, 李道京, 李烈辰. 连续场景的稀疏阵列SAR侧视三维成像研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136Zhang Qing-juan, Li Dao-jing, and Li Lie-chen. Research on continuous scene side-looking 3D imaging based on sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136 [5] 李烈辰, 李道京. 基于压缩感知的连续场景稀疏阵列SAR三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645Li Lie-chen and Li Dao-jing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 [6] Tian H and Li D J. Sparse flight array SAR downward-looking 3-D imaging based on compressed sensing[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1395–1399. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2560238 [7] Candès E and Romberg J. Sparsity and incoherence in compressive sampling[J]. Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(3): 969–985. DOI: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/3/008 [8] Candes E J, Romberg J, and Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489–509. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 [9] Candes E J and Tao T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(12): 5406–5425. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.885507 [10] Candes E J and Wakin M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 [11] Candès E. Compressive sampling[C]. Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, Madrid, Spain, 2006: 1–20. [12] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [13] 李学仕. 高分辨率宽测绘带SAR动目标处理方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015: 21–81.Li Xue-shi. Study on high-resolution wide-swath SAR moving target processing method[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2015: 21–81. [14] 韦顺军. 线阵三维合成孔径雷达稀疏成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013: 16–55.Wei Shun-jun. Research on linear array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar sparse imaging technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013: 16–55. [15] 李道京, 滕秀敏, 潘舟浩. 分布式位置和姿态测量系统的概念与应用方向[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(4): 400–405. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13094Li Dao-jing, Teng Xiu-min, and Pan Zhou-hao. The concept and applications of distributed POS[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(4): 400–405. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13094 [16] 尹建凤, 张庆君, 刘杰, 等. 国外编队飞行干涉SAR卫星系统发展综述[J]. 航天器工程, 2018, 27(1): 116–122. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2018.01.016Yin Jian-feng, Zhang Qing-jun, Liu Jie, et al. A review on development of formation flying interferometric SAR satellite system[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2018, 27(1): 116–122. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2018.01.016 [17] Peterman D, James K, and Glavac V. Distortion measurement and compensation in a synthetic aperture radar phased-array antenna[C]. Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics & the American Electromagnetics Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2010: 1–5. [18] 田鹤, 李道京, 潘洁, 等. 基于修正均匀冗余阵列正反编码的稀疏阵列SAR下视三维成像处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209Tian He, Li Dao-jing, Pan Jie, et al. Downward-looking 3D imaging processing of sparse array SAR based on modified uniformly redundant arrays positive and negative coding[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209 [19] Tian H, Li D J, and Hu X. Microwave three-dimensional imaging under sparse sampling based on MURA code[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 7411–7414. [20] Golomb S and Scholtz R. Generalized Barker sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1965, 11(4): 533–537. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.1965.1053828 [21] Ulander L M H, Hellsten H, and Stenstrom G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 [22] Teixeira R M A and Aizawa K. Noise attenuation performance of mura apertures in photographic cameras[C]. Proceedings of the 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 2012: 361–364. [23] Candes E J and Tao T. Decoding by linear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(12): 4203–4215. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2005.858979 [24] 周建卫, 李道京, 田鹤, 等. 基于共形稀疏阵列的艇载外辐射源雷达性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1058–1063. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160846Zhou Jian-wei, Li Dao-jing, Tian He, et al. Performance analysis on airship-borne passive radar based on conformal sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1058–1063. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160846 [25] Lucido M, Meglio F, Pascazio V, et al. Closed-form evaluation of the second-order statistical distribution of the interferometric phases in dual-Baseline SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1698–1707. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2037849 [26] Rousseau D, Delahaies A, and Chapeau-Blondeau F. Structural similarity measure to assess improvement by noise in nonlinear image transmission[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(1): 36–39. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2009.2031734 [27] Hu C F, Xu J D, Li N J, et al.. Hard-in-loop polarization linear SAR imaging system[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xian, Shanxi, China, 2009: 64–66. [28] 陈弓, 戴晨光, 刘航冶. 雷达阵地场景三维可视化系统的实现[J]. 空军雷达学院学报, 2007, 21(4): 248–251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8691.2007.04.005Chen Gong, Dai Chen-guang, and Liu Hang-zhi. Implementation on radar site 3D visualization simulation system[J]. Journal of Air Force Radar Academy, 2007, 21(4): 248–251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8691.2007.04.005 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: