Feature Enhancement of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Formation Using Sparse Bayesian Learning in Joint Sparsity Approach
-
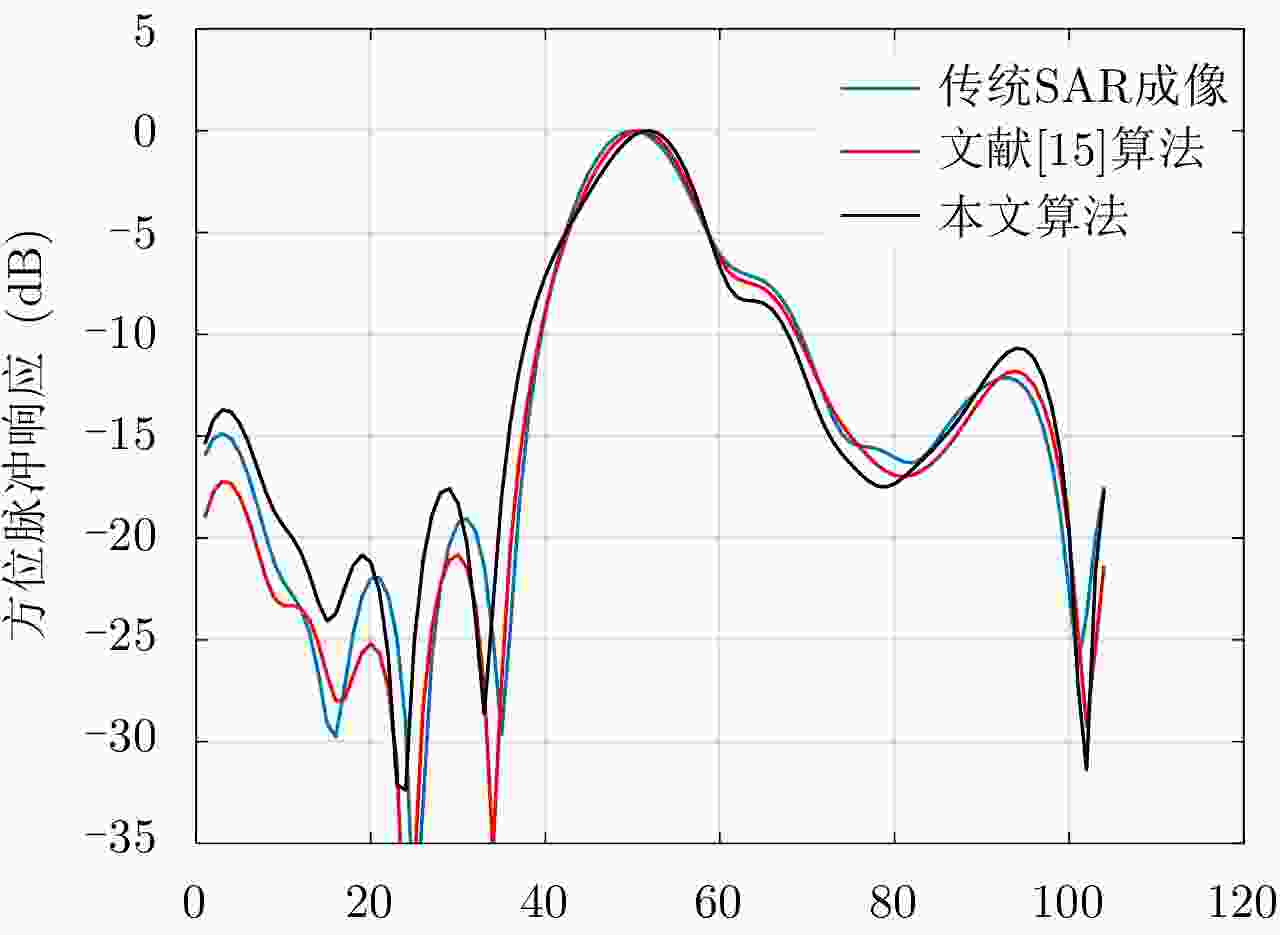
摘要: 针对干涉合成孔径雷达(InSAR)成像,该文提出了一种通道联合结构化稀疏的贝叶斯成像算法,可实现图像稀疏特征化增强,以提升干涉相位噪声滤波和相干斑抑制性能。基于贝叶斯准则,利用多层级统计模型建立稀疏成像模型,结构化稀疏表示InSAR图像。在稀疏成像求解中,利用最大期望(EM)算法进行图像重构和多层级统计参数估计。由于能够联合利用通道稀疏统计特性,所提算法能够有效提升InSAR幅度和相位噪声滤波性能。最后,通过实验分析进一步验证该文算法的有效性。Abstract: A novel sparse Bayesian learning approach with a joint sparsity model is proposed for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) image formation to realize the feature enhancements of interferometric phase denoising and speckle reduction. Using Bayesian rules, sparse image formation is achieved using a hierarchical statistical model. In particular, structured sparsity with joint channels is imposed on the InSAR images. During sparse imaging, an Expectation-Maximization (EM) method is employed for image formation and hyper-parameter estimation. Using joint sparsity statistics, the performance of the noise reduction on the magnitude and phase of InSAR images can be improved. Finally, experimental analysis is performed using simulated and measured data to confirm the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 本文算法流程框图
Table 1. Algorithm flow chart in this paper
InSAR稀疏贝叶斯特征化成像算法 输入:预处理多通道数据 ${{{{s}}}_l}$和观测矩阵 ${{{T}}_l}$ WHILE循环(符合迭代条件时) (1) 稀疏成像 (a) 利用式(3)更新自适应表征字典 ${{{Φ}}_l}$中的 ${{{P}}_l}$部分; (b) 利用式(10)和式(11)更新 ${{{μ}}_l}$和 ${{{Σ}}_l}$。 (2) 参数估计 (a) 利用式(16)估计 ${\gamma _{mn}}$和 $r$,更新协方差矩阵 ${{{Σ}}_b}$; (b) 利用式(17)更新噪声参数 $\alpha $。 END 输出: 特征化重构图像 ${\hat {{b}}_l}{\rm{ = }}{{{μ}}_l}$. 表 2 ENL估计
Table 2. ENL estimates
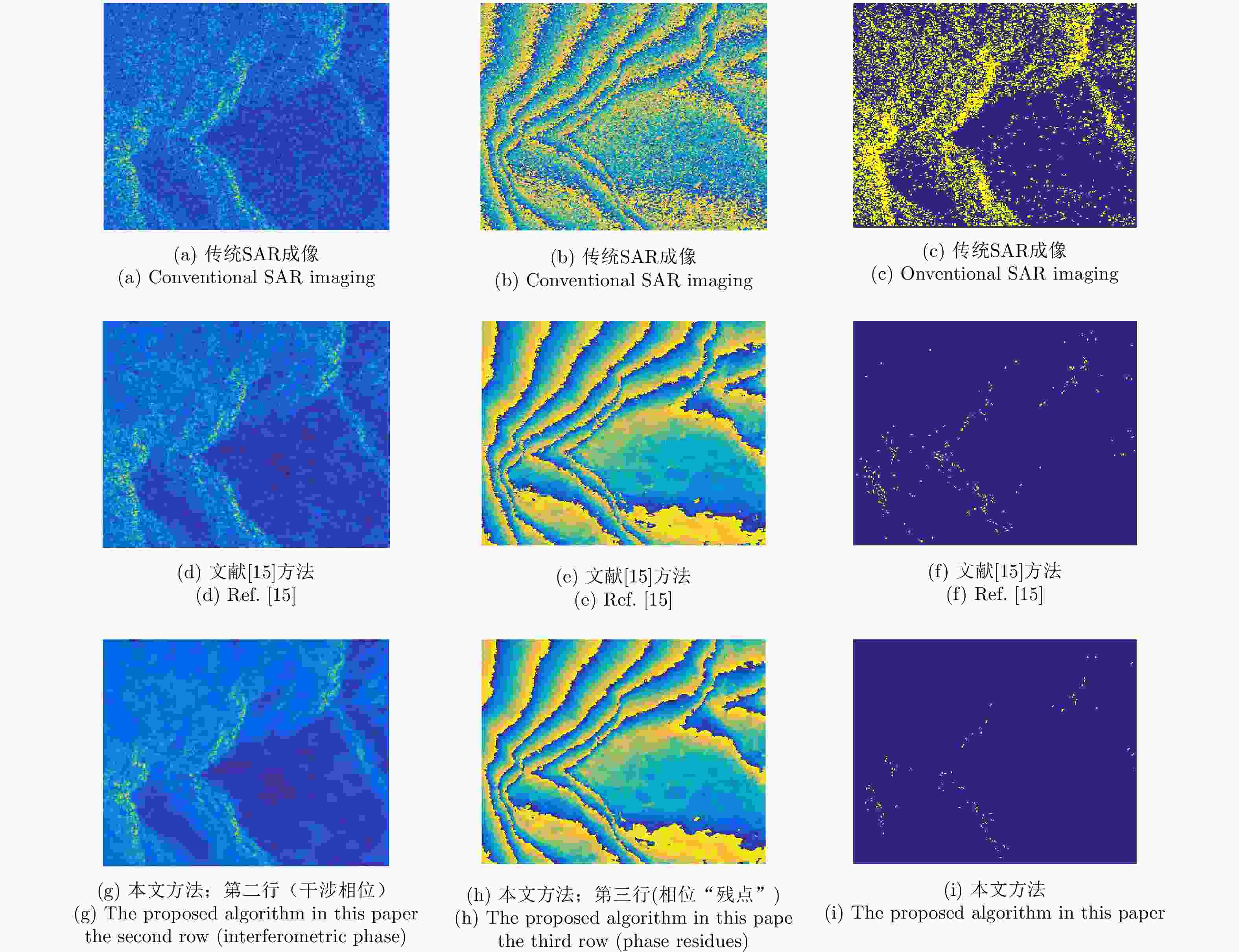
不同成像算法 区域1 区域2 传统SAR成像 0.8978 0.9742 文献[15]的方法 24.9886 96.2014 本文方法 30.1216 102.3843 -
[1] Goldstein R M, Zebker H A, and Werner C L. Satellite radar interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping[J]. Radio Science, 1988, 23(4): 713–720. DOI: 10.1029/RS023i004p00713 [2] 斯奇, 王宇, 邓云凯, 等. 一种基于最大后验框架的聚类分析多基线干涉SAR高度重建算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 640–652. DOI: 10.12000/JR17043Si Qi, Wang Yu, Deng Yun-kai, et al. A novel cluster-analysis algorithm based on MAP framework for multi-baseline InSAR height reconstruction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 640–652. DOI: 10.12000/JR17043 [3] 邓云凯, 王宇. 先进双基SAR技术研究(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13089Deng Yun-kai and Wang R. Exploration of advanced bistatic SAR experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13089 [4] Kwok R and Fahnestock M A. Ice sheet motion and topography from radar interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(1): 189–200. DOI: 10.1109/36.481903 [5] Cloude S R and Papathanassiou K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. DOI: 10.1109/36.718859 [6] López-Martínez C and Fàbregas X. Modeling and reduction of SAR interferometric phase noise in the wavelet domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(12): 2553–2566. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.806997 [7] Kuan D T, Sawchuk A A, Strand T C, et al. Adaptive noise smoothing filter for images with signal-dependent noise[J]. Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1985, PAMI-7(2): 165–177. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.1985.4767641 [8] Wu N, Feng D Z, and Li J X. A locally adaptive filter of interferometric phase images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(1): 73–77. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.856703 [9] 李杭, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 基于高斯混合聚类的阵列干涉SAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020Li Hang, Liang Xing-dong, Zhang Fu-bo, et al. 3D imaging for array InSAR based on Gaussian mixture model clustering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020 [10] 丁斌, 向茂生, 梁兴东. 射频干扰对机载P波段重复轨道InSAR系统的影响分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 82–90. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10062Ding Bin, Xiang Mao-sheng, and Liang Xing-dong. Analysis of the effect of radio frequency interference on repeat track airborne InSAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 82–90. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.10062 [11] Meng D, Sethu V, Ambikairajah E, et al. A novel technique for noise reduction in InSAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(2): 226–230. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.888845 [12] Zha X J, Fu R S, Dai Z Y, et al. Noise reduction in interferograms using the wavelet packet transform and wiener filtering[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 404–408. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.916066 [13] Denis L, Tupin F, Darbon J, et al. Joint regularization of phase and amplitude of InSAR data: application to 3-D reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11): 3774–3785. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2023668 [14] Shabou A, Baselice F, and Ferraioli G. Urban digital elevation model reconstruction using very high resolution multichannel InSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(11): 4748–4758. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2191155 [15] Xu G, Xing M D, Xia X G, et al. Sparse regularization of interferometric phase and amplitude for InSAR image formation based on Bayesian representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2123–2136. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2355592 [16] Li L C, Li D J J, and Pan Z H. Compressed sensing application in interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(10): 102305. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9017-6 [17] Wang L, Zhao L F, Bi G A, et al. Enhanced ISAR imaging by exploiting the continuity of the target scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5736–5750. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2292074 [18] Duan H P, Zhang L Z, Fang J, et al. Pattern-coupled sparse Bayesian learning for inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(11): 1995–1999. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2452412 [19] Xu G, Yang L, Bi G A, et al. Enhanced ISAR imaging and motion estimation with parametric and dynamic sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(4): 940–952. DOI: 10.1109/TCI.2017.2750330 [20] Xu G, Sheng J L, Zhang L, et al. Performance improvement in multi-ship imaging for ScanSAR based on sparse representation[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 1860–1875. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-012-4626-3 [21] López-Martínez C and Fàbregas X. Modeling and reduction of SAR interferometric phase noise in the wavelet domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(12): 2553–2566. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.806997 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: