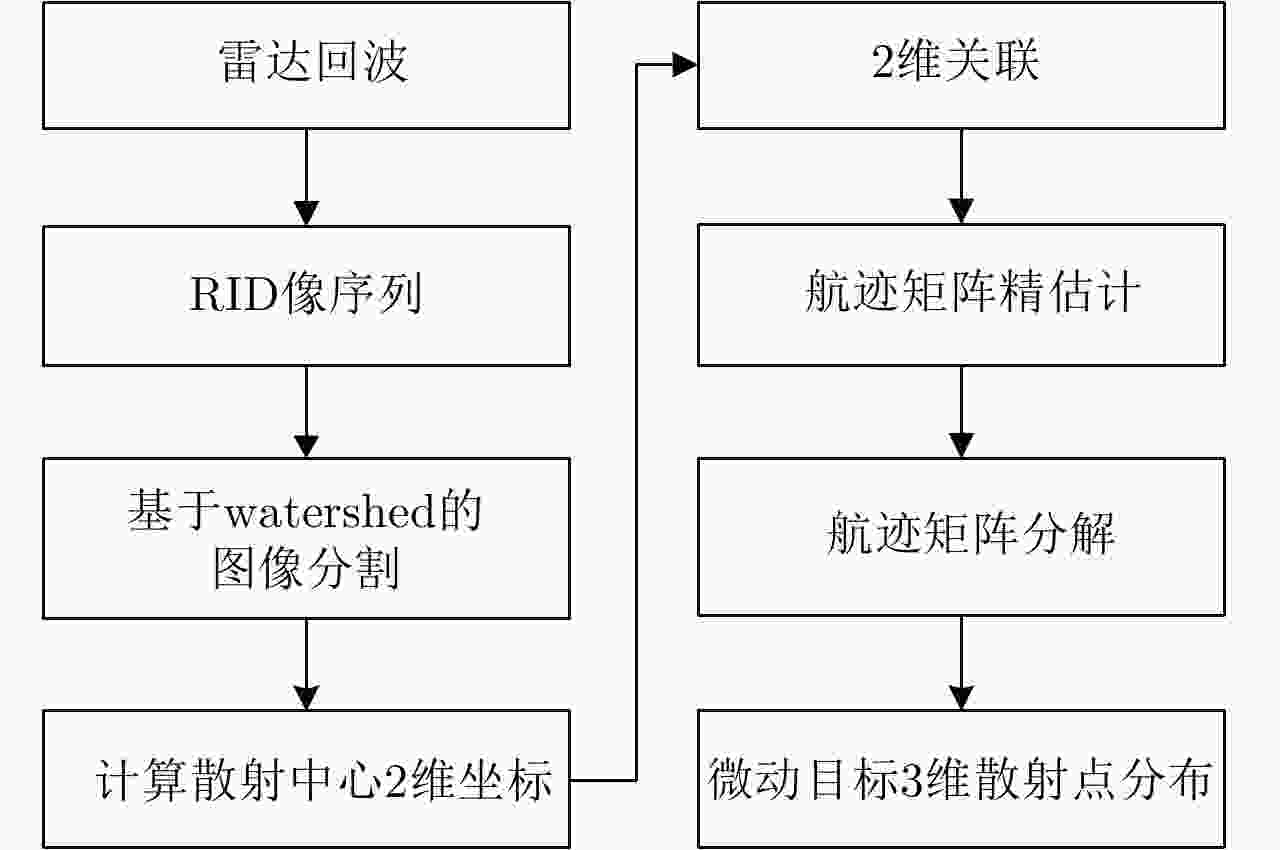
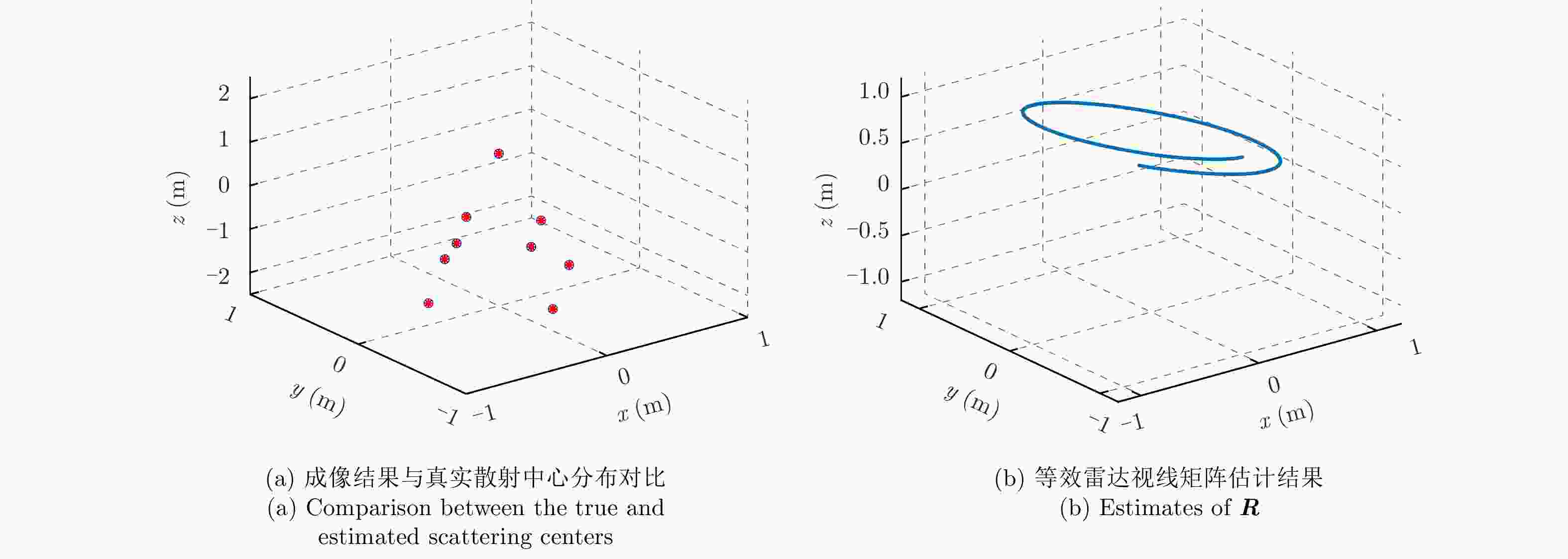
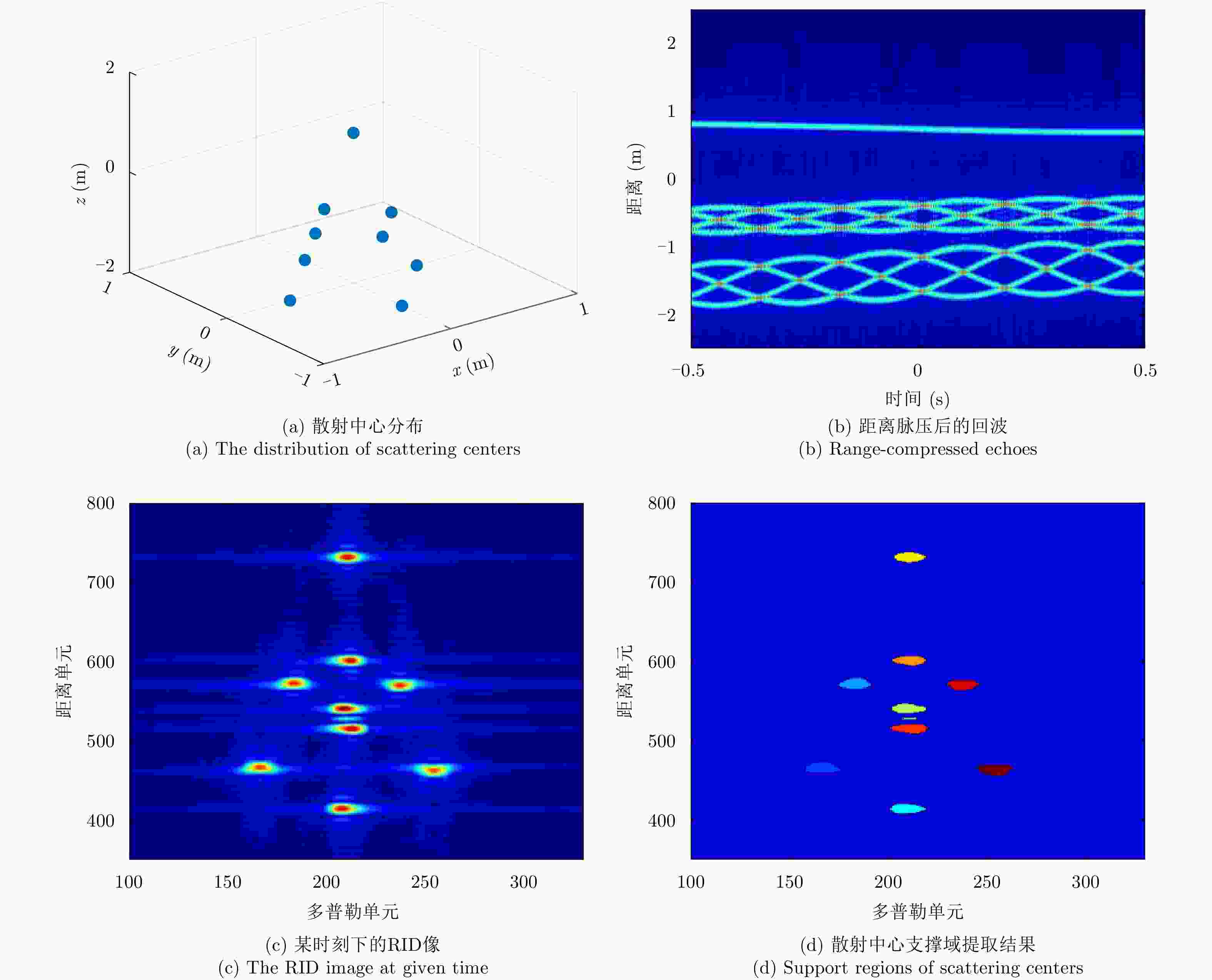
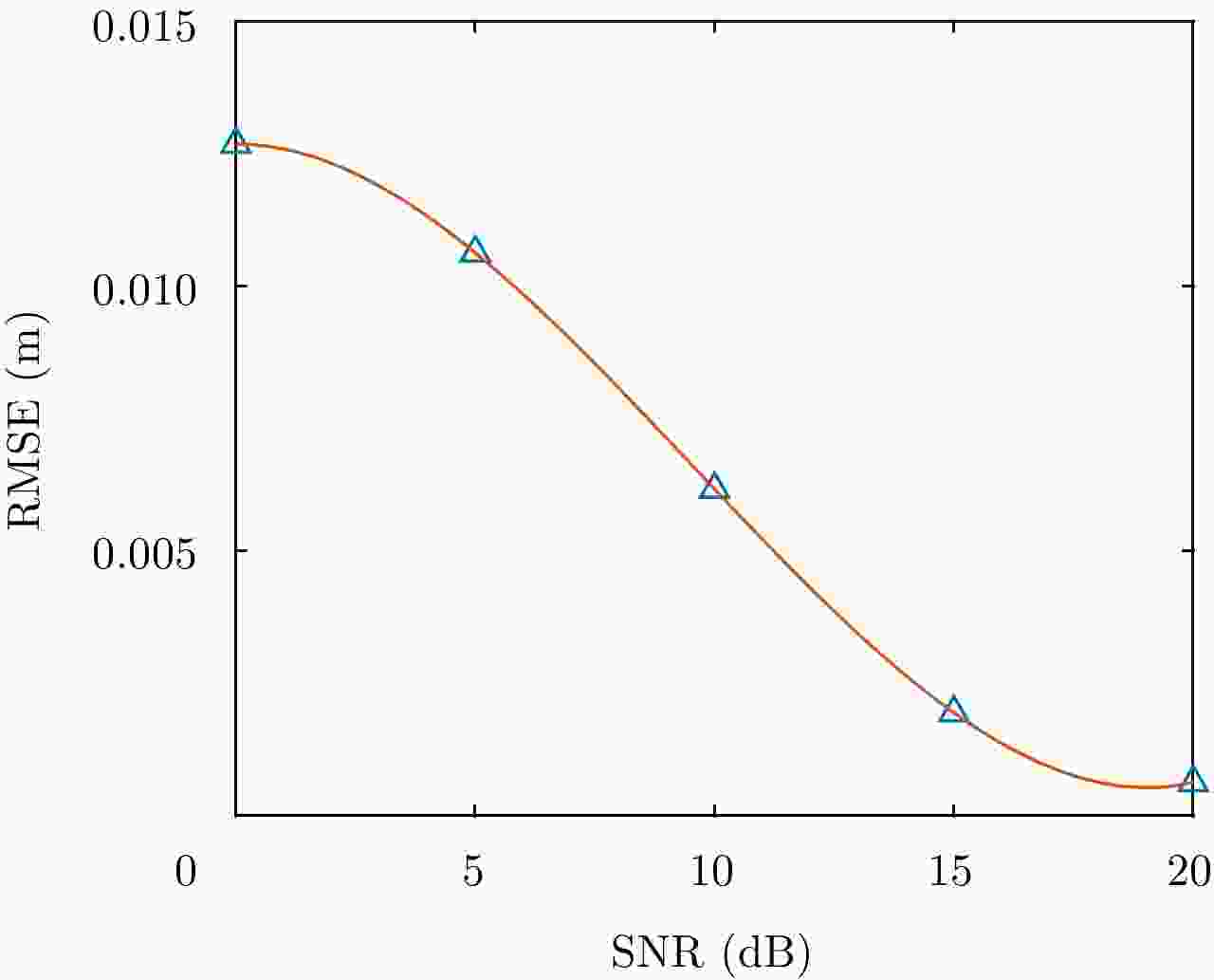
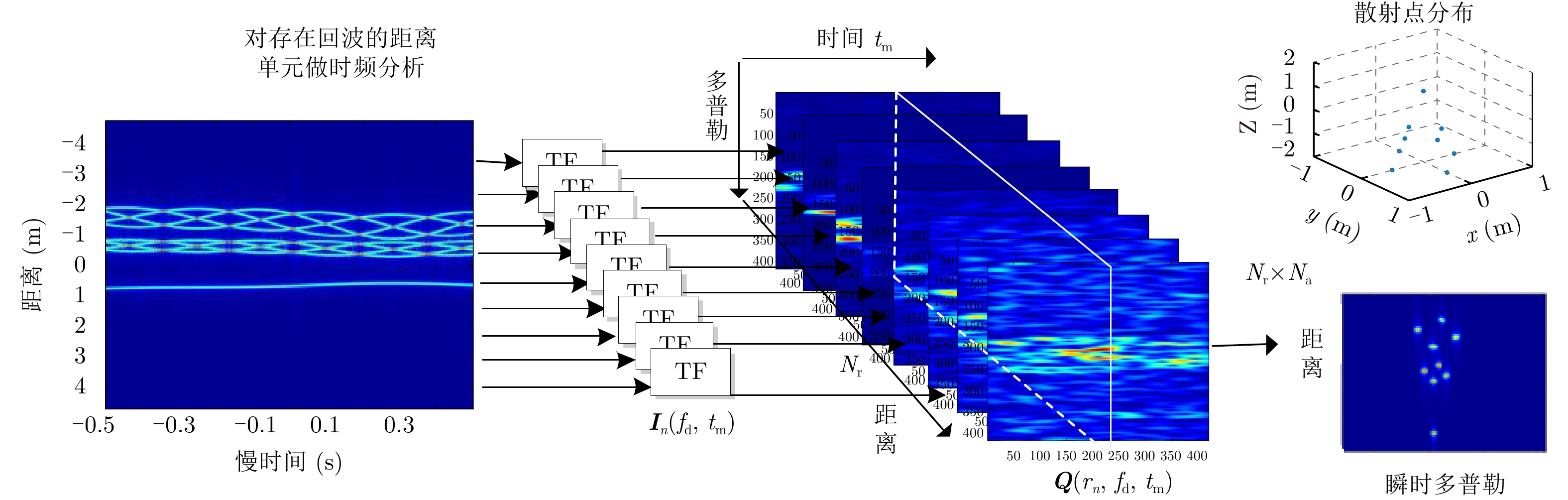
| [1] |
Chen V C, Li F Y, Ho S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402
|
| [2] |
Chen V C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2011.
|
| [3] |
Brown W M and Fredricks R J. Range-Doppler imaging with motion through resolution cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1969, AES-5(1): 98–102. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.1969.309826
|
| [4] |
Carrara W G, Goodman R S, and Majewski R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995.
|
| [5] |
张翼, 朱玉鹏, 黎湘. 基于微多普勒特征的目标微动参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022Zhang Yi, Zhu Yu-peng, and Li Xiang. Micro-motion parameter estimation of ballistic missile target based on micro-Doppler feature[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022
|
| [6] |
Wang T, Wang X S, Chang Y L, et al. Estimation of precession parameters and generation of ISAR images of ballistic missile targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(4): 1983–1995. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5595608
|
| [7] |
Luo Y, Zhang Q, Qiu C W, et al. Micro-Doppler effect analysis and feature extraction in ISAR imaging with stepped-frequency chirp signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2087–2098. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2034367
|
| [8] |
邹小海, 艾小锋, 李永祯, 等. 基于微多普勒的圆锥弹头进动与结构参数估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(10): 2413–2419. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00120Zou Xiao-hai, Ai Xiao-feng, Li Yong-zhen, et al. Precession and structural parameter estimation of the cone-shaped warhead based on the micro-Doppler[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2011, 33(10): 2413–2419. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00120
|
| [9] |
Luo Y, Zhang Q, Yuan N, et al. Three-dimensional precession feature extraction of space targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1313–1329. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.110545
|
| [10] |
Zhang Q, Yeo T S, Tan H S, et al. Imaging of a moving target with rotating parts based on the Hough transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 291–299. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907105
|
| [11] |
Gao H W, Xie L G, Wen S L, et al. Micro-Doppler signature extraction from ballistic target with micro-motions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(4): 1969–1982. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5595607
|
| [12] |
Bai X R and Bao Z. High-resolution 3D imaging of precession cone-shaped targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(8): 4209–4219. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2329004
|
| [13] |
Bai X R and Bao Z. Imaging of rotation-symmetric space targets based on electromagnetic modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 1680–1689. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120772
|
| [14] |
Bai X R and Bao Z. High-resolution radar imaging of aerospace targets with micromotion[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2014: 934–937. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946579.
|
| [15] |
Chen V C and Ling H. Time-Frequency Transforms for Radar Imaging and Signal Analysis[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2002.
|
| [16] |
Tomasi C and Kanade T. Shape and motion from image streams under orthography: A factorization method[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1992, 9(2): 137–154. DOI: 10.1007/BF00129684
|
| [17] |
Bai X R, Zhou F, and Bao Z. High-resolution radar imaging of space targets based on HRRP series[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2369–2381. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2260342
|
| [18] |
Chen V C and Qian S. Joint time-frequency transform for radar range-Doppler imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(2): 486–499. DOI: 10.1109/7.670330
|
| [19] |
Chen V C. Adaptive time-frequency ISAR processing[C]. Proceedings Volume 2845, Radar Processing, Technology, and Applications, Denver, CO, United States, 1996. DOI: 10.1117/12.257216.
|
| [20] |
Chen V C. Radar detection of multiple moving targets in clutter using time-frequency radon transform[C]. Proceedings Volume 4728, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2002, Orlando, FL, United States, 2002. DOI: 10.1117/12.478534.
|
| [21] |
Bai X R, Zhou F, and Bao Z. High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of space targets in micromotion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3428–3440. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2431119
|
| [22] |
Wang Q, Xing M D, Lu G Y, et al. SRMF-CLEAN imaging algorithm for space debris[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(12): 3524–3533. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2007.910343
|
| [23] |
Wang Q, Xing M D, Lu G Y, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional radar imaging for rapidly spinning targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 22–30. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909086
|
| [24] |
Bai X R, Xing M D, Zhou F, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of spinning space debris[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(4): 2352–2362. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010854
|
| [25] |
Chen V C. Reconstruction of inverse synthetic aperture radar image using adaptive time-frequency wavelet transform[C]. Proceedings Volume 2491, Wavelet Applications II, Orlando, FL, United States, 1995, DOI: 10.1117/12.205404.
|
| [26] |
Ferrara M, Arnold G, and Stuff M. Shape and motion reconstruction from 3D-to-1D orthographically projected data via object-image relations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(10): 1906–1912. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.294
|
| [27] |
Mayhan J T, Burrows M L, Cuomo K M, et al. High resolution 3D " Snapshot” ISAR imaging and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 630–642. DOI: 10.1109/7.937474
|
| [28] |
Burrows M L. Two-dimensional ESPRIT with tracking for radar imaging and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2004, 52(2): 524–532. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2003.822411
|
| [29] |
Grewal M S and Andrews A P. Kalman Filtering, Theory and Practice Using MATLAB[M]. New York, USA: Wiley, 2001.
|
| [30] |
Allen J. Short term spectral analysis, synthesis, and modification by discrete Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing, 1977, 25(3): 235–238. DOI: 10.1109/TASSP.1977.1162950
|
| [31] |
Vincent L and Soille P. Watersheds in digital spaces: An efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(6): 583–598. DOI: 10.1109/34.87344
|
| [32] |
Stoica P and Moses R L. Spectral Analysis of Signals[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2005.
|
| [33] |
Liu H C, Jiu B, Liu H W, et al. Superresolution ISAR imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 5005–5013. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2286402
|
| [34] |
Li H T, Wang C Y, Wang K, et al. High resolution range profile of compressive sensing radar with low computational complexity[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 984–990. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0454
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
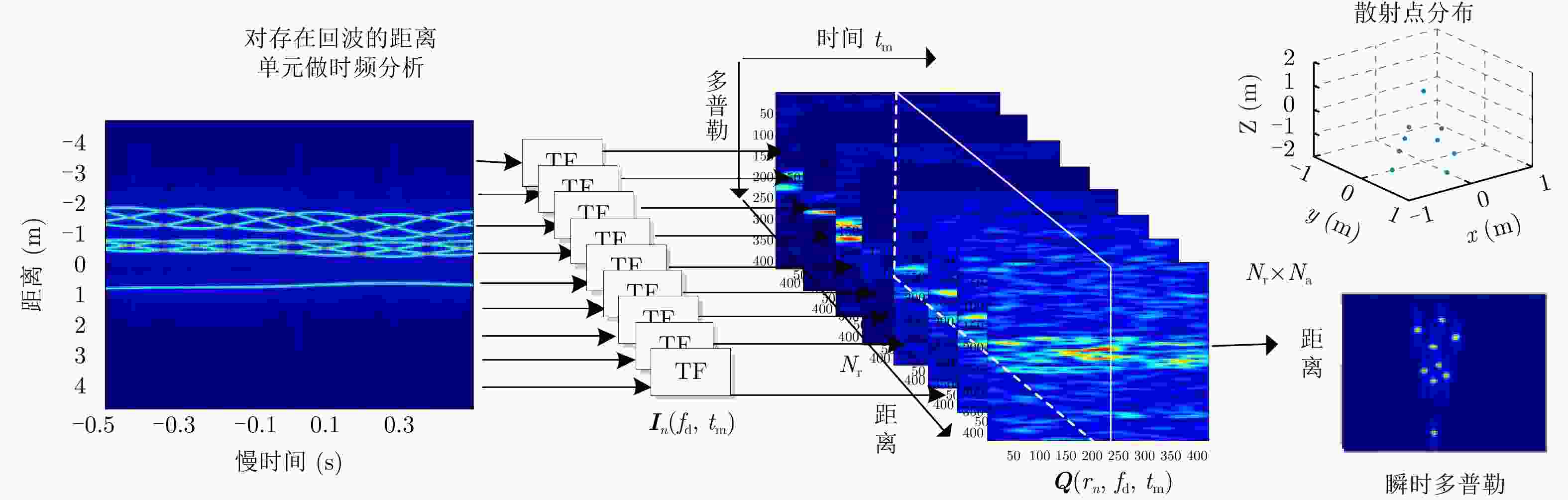
 下载:
下载: