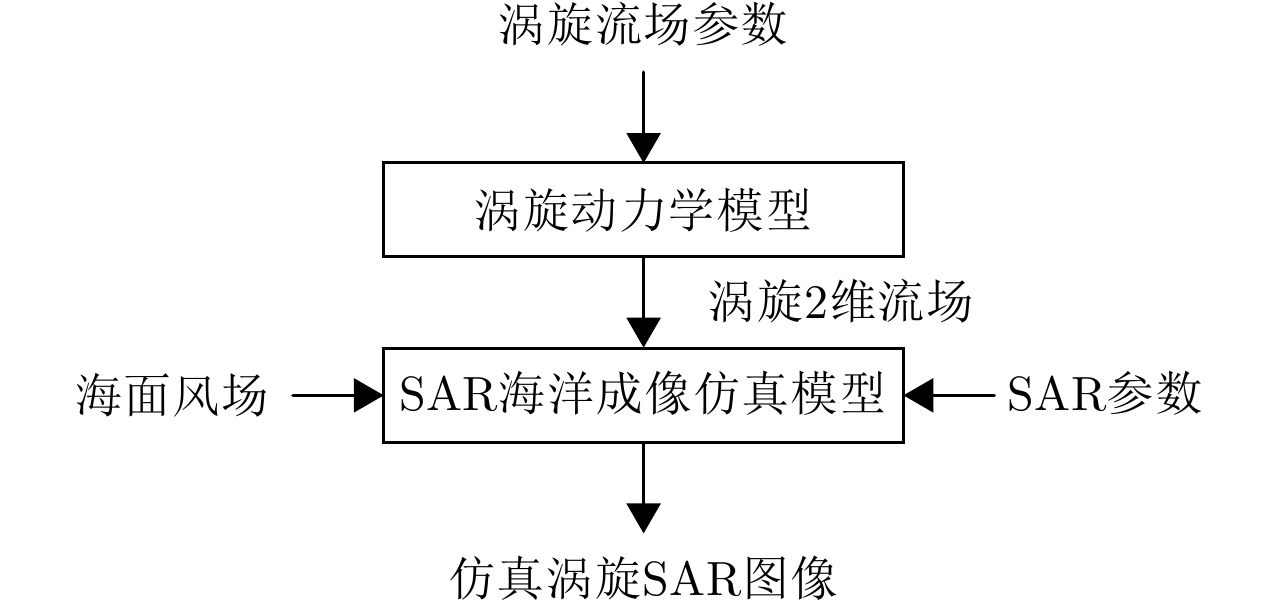
-
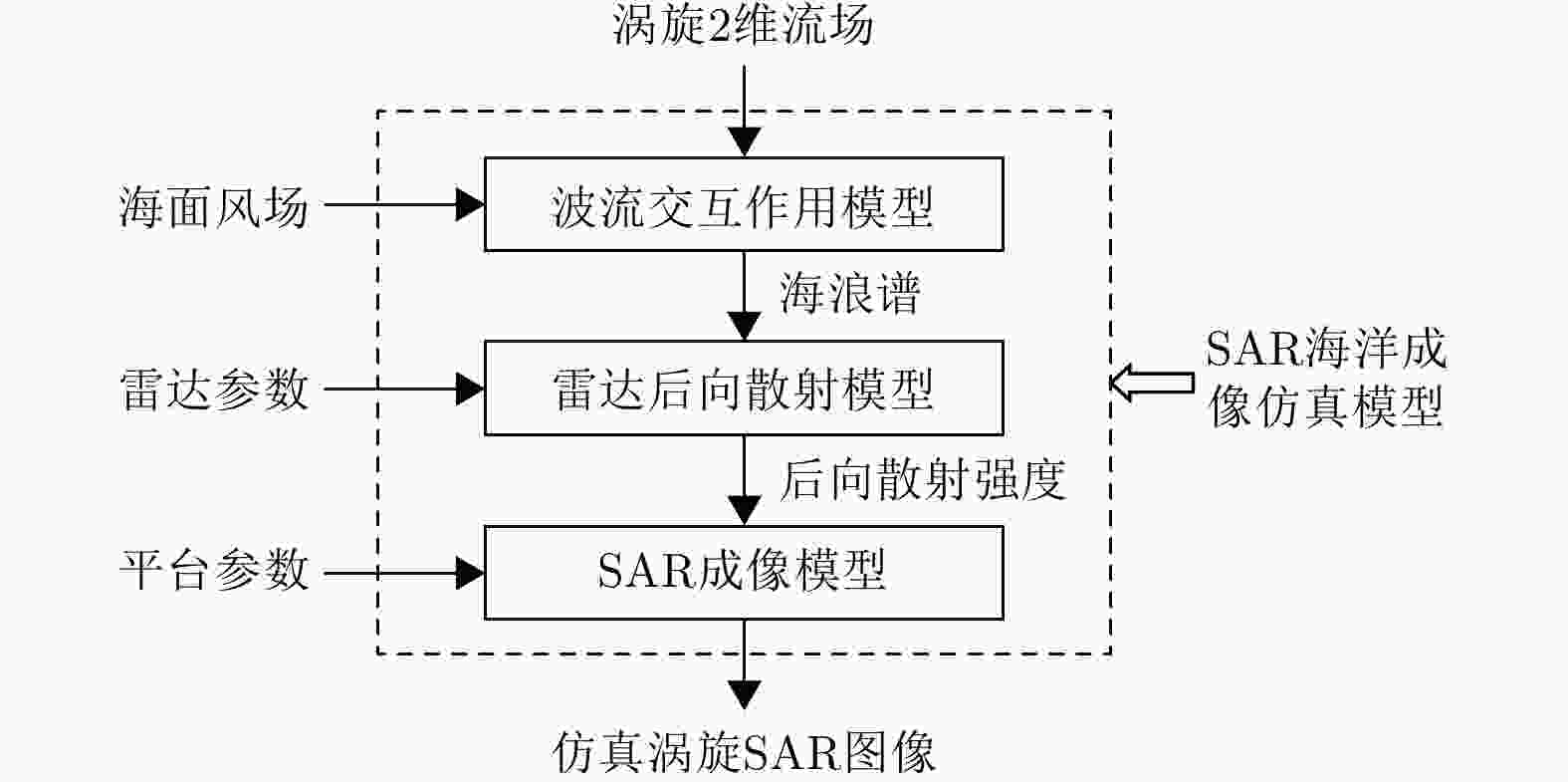
摘要: 海洋涡旋对海洋热循环起着关键作用,是海洋科学研究中的一个重要分支。合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)为海洋涡旋的观测和研究提供了大量的图像数据,但是涡旋在SAR成像时会受到各种海洋环境因素的影响,难以解译涡旋SAR图像特征。仿真SAR图像可以用于研究涡旋的特征,但是目前极少有关于涡旋SAR图像仿真方法的研究。为了更好地解译SAR图像中的涡旋特征,该文提出了一种涡旋SAR图像仿真方法。首先,基于流体力学中典型的Burgers-Rott涡旋模型,建立涡旋2维表面流场;然后,利用SAR海洋成像仿真模型,仿真给定涡旋2维流场、海面风场以及雷达系统参数下的涡旋SAR图像。该文针对气旋式涡旋与反气旋式涡旋进行了仿真实验,并建立了仿真涡旋SAR图像的相似度评价标准。实验结果表明,仿真的涡旋SAR图像与真实星载涡旋SAR图像能够较好地吻合,验证了方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 海洋涡旋 /
- SAR图像 /
- Burgers-Rott涡旋模型 /
- 图像仿真
Abstract: Oceanic eddies, which play an important role in ocean thermal cycling, is a significant branch of oceanic scientific research. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) provides a large number of images for the observation and investigation of oceanic eddies. However, SAR imagery of oceanic eddies is affected by various environmental factors; as such, it is difficult to interpret eddy features from SAR images. Alternatively, simulated SAR images can be used to investigate eddy features; however, few methods have been established for simulating SAR images for oceanic eddies. To better interpret the eddy features in real SAR images, an SAR image simulation method for oceanic eddies is proposed in this paper. First, a two-dimensional eddy surface current field was built based on the Burgers-Rott vortex model in hydrodynamics; SAR eddy images were then simulated according to the given eddy current field, wind field, and radar parameters. Images of cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies were simulated and evaluated. In addition, a standard for evaluating the similarity between real and simulated SAR eddy images was established. The features of the simulated SAR eddy images show good similarity with the real SAR eddy images, which validates the effectiveness of the proposed simulation method. -
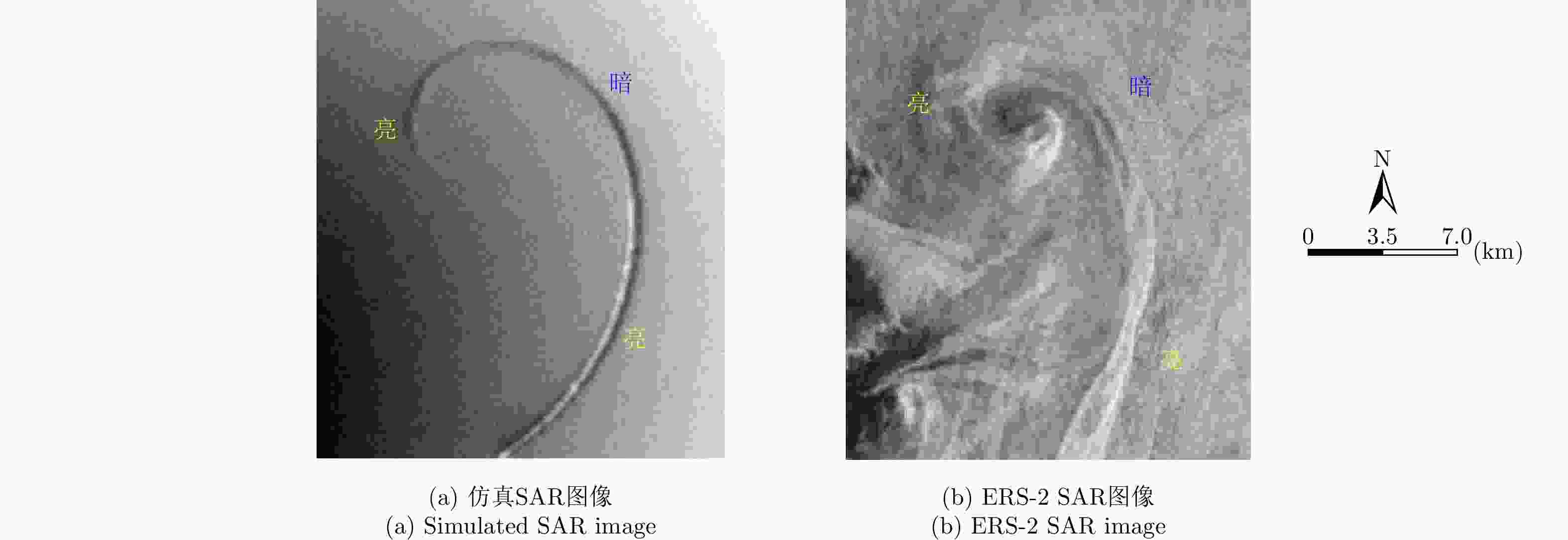
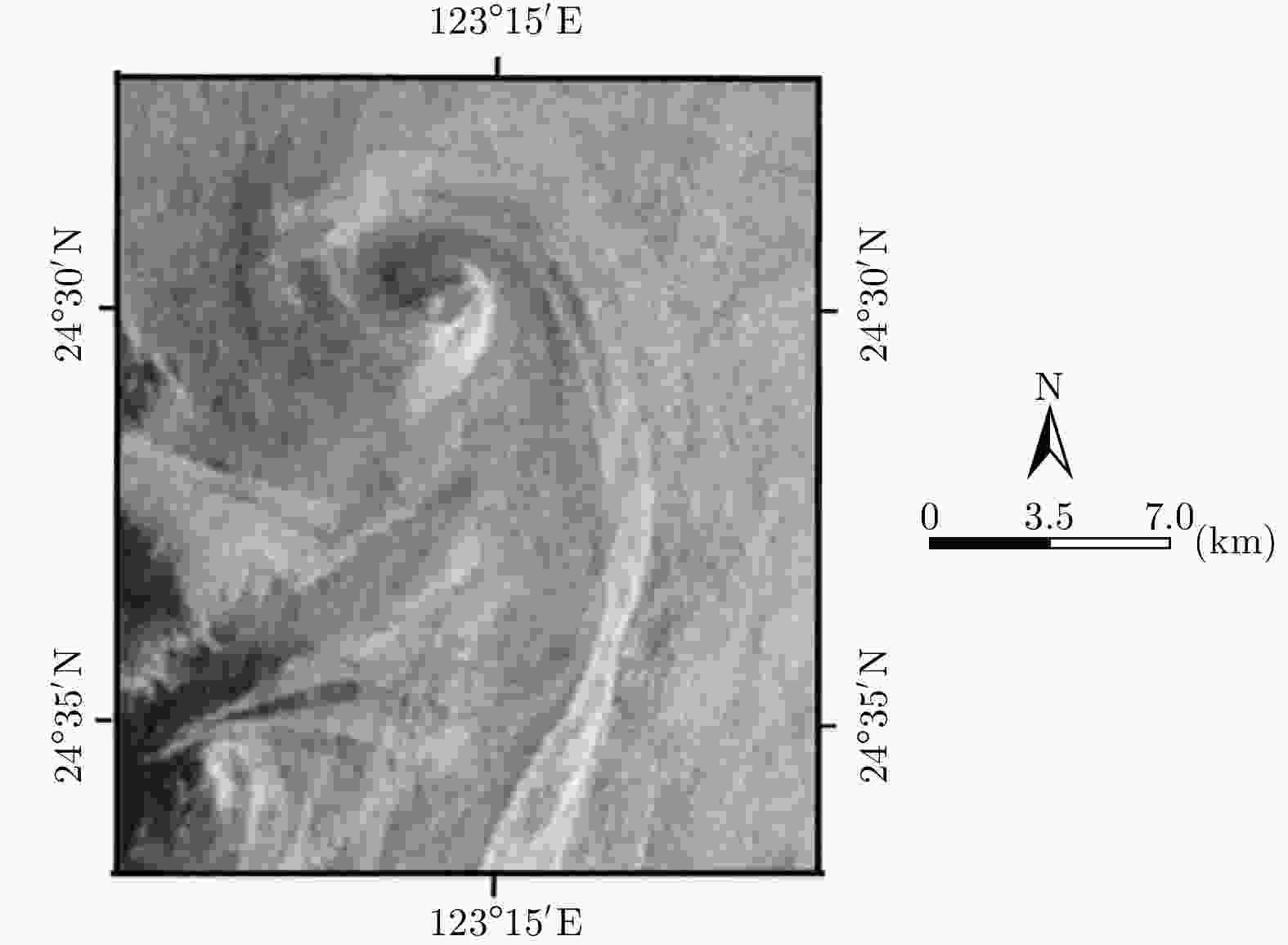
表 1 ERS-2 SAR参数
Table 1. SAR parameters of ERS-2
参数 数值 极化方式 VV 波段 C 入射角 23.0° 平台高度 780 km 平台速度 7500 m/s 表 2 涡旋信息提取结果
Table 2. Results of eddy information extraction
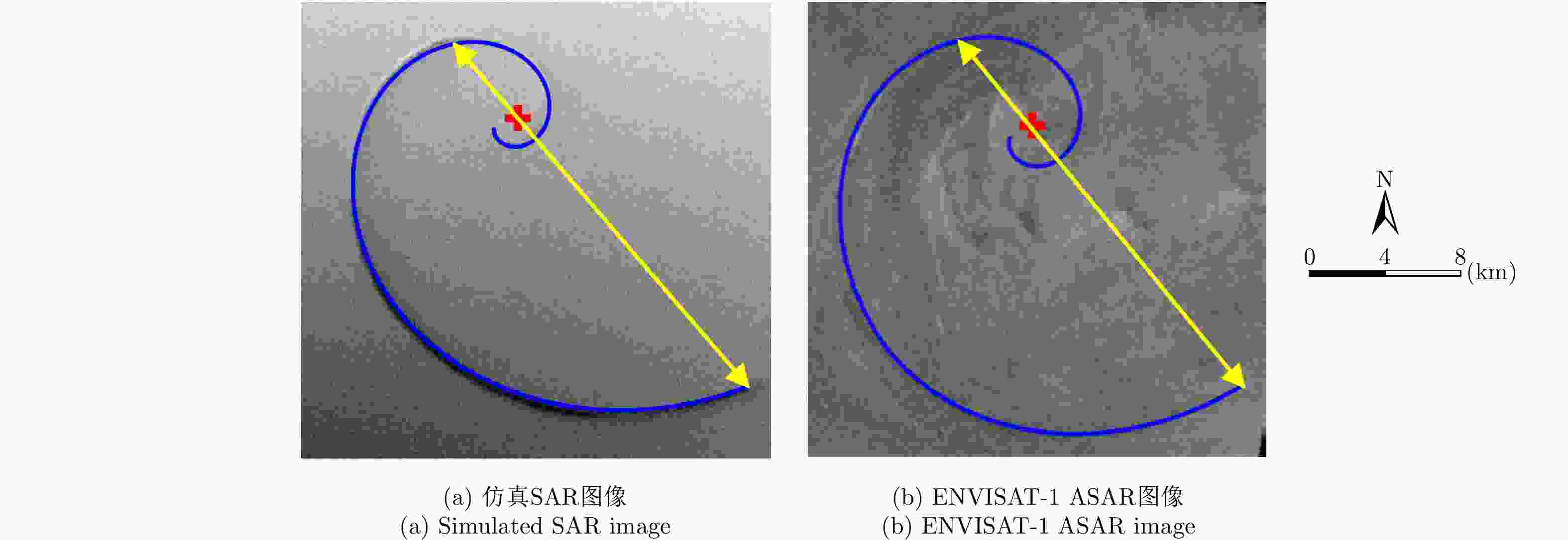
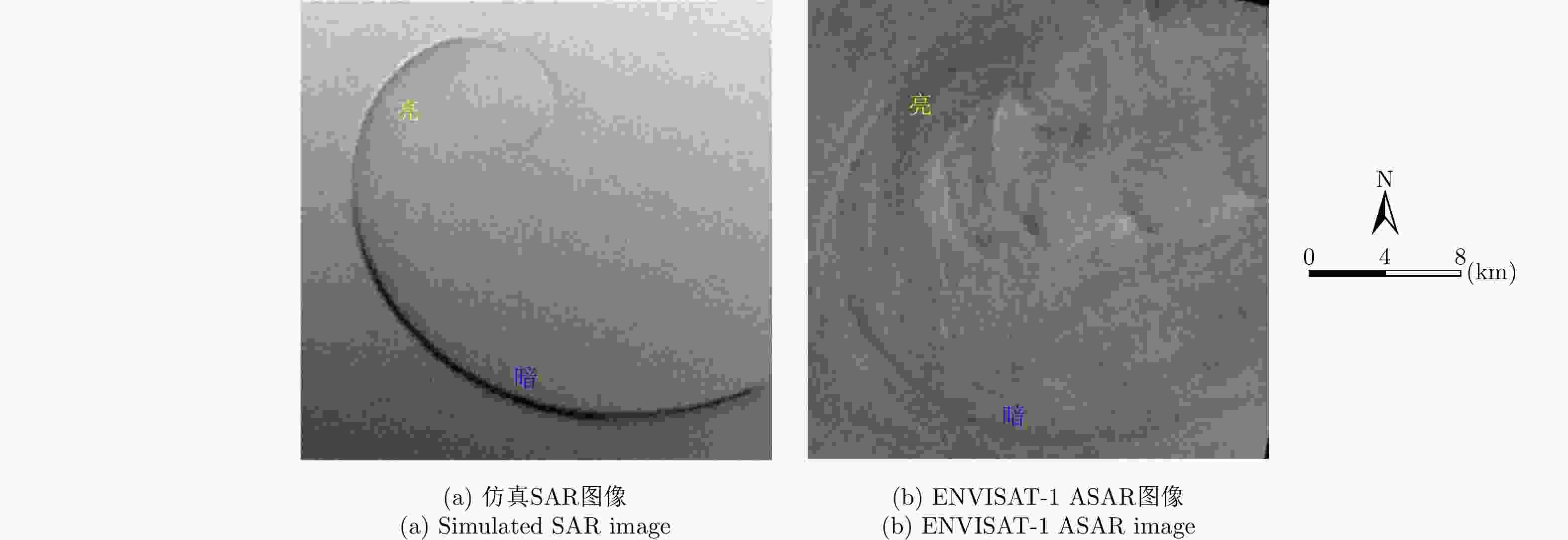
SAR图像 涡旋中心位置 涡旋直径 涡旋边缘长度 仿真SAR图像 (116,75) 18.9 km 35.7 km 真实SAR图像 (113,71) 18.7 km 35.4 km 绝对/相对误差 (3,4)/— 0.2 km/0.011 0.3 km/0.008 表 3 ENVISAT-1 ASAR参数
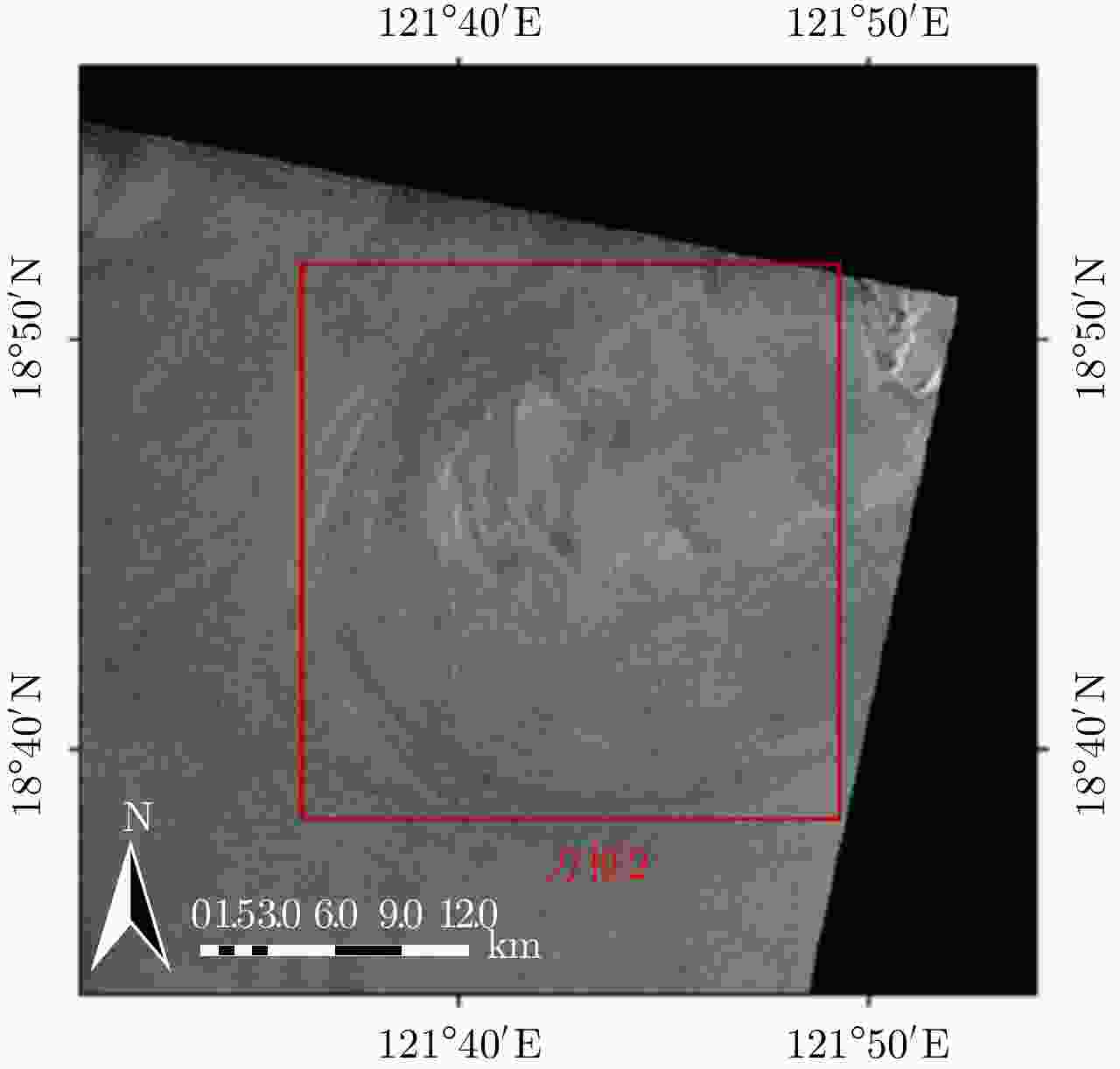
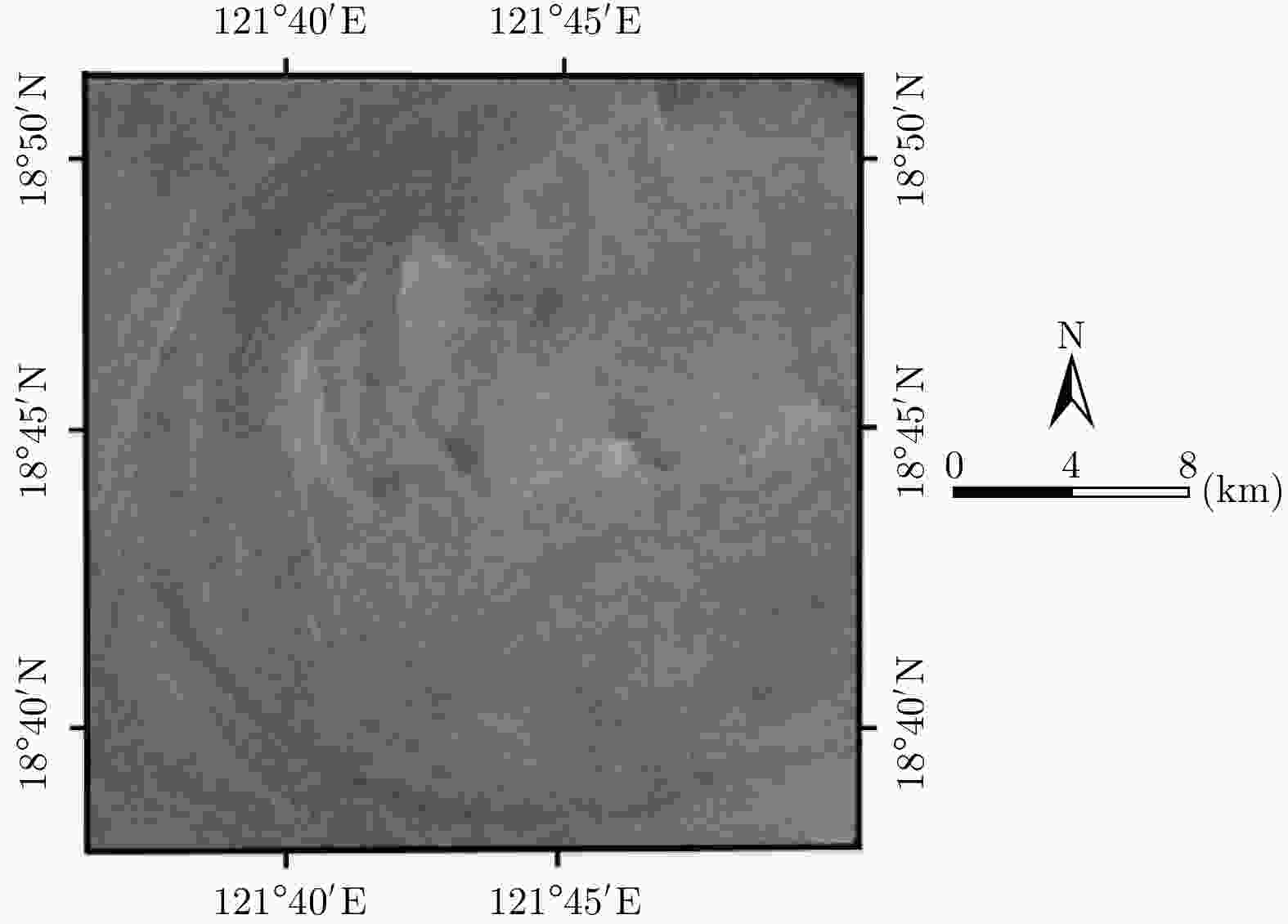
Table 3. ASAR parameters of ENVISAT-1
参数 数值 极化方式 HH 波段 C 入射角 26.7° 平台高度 800 km 平台速度 7455 m/s 表 4 涡旋信息提取结果
Table 4. Results of eddy information extraction
SAR图像 涡旋中心位置 涡旋直径 涡旋边缘尺寸 仿真SAR图像 (144,78) 24.0 km 49.4 km 真实SAR图像 (147,81) 23.9 km 49.7 km 绝对/相对误差 (3,3)/— 0.1 km/0.004 0.3 km/0.006 -
[1] KARIMOVA S. Spiral eddies in the Baltic, Black and Caspian seas as seen by satellite radar data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 50(8): 1107–1124. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2011.10.027 [2] IVANOV A Y and GINZBURG A I. Oceanic eddies in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2002, 111(3): 281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF02701974 [3] KARIMOVA S and GADE M. Improved statistics of sub-mesoscale eddies in the Baltic Sea retrieved from SAR imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 37(10): 2394–2414. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2016.1145367 [4] XU G J, YANG J S, DONG C M, et al. Statistical study of submesoscale eddies identified from synthetic aperture radar images in the Luzon Strait and adjacent seas[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(18): 4621–4631. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1084431 [5] TAVRI A, SINGHA S, LEHNER S, et al. Observation of sub-mesoscale eddies over Baltic Sea using TerraSAR-X and Oceanographic data[C]. Proceedings of Living Planet Symposium 2016, Prague, Czech Republic, 2016. [6] LYZENGA D and WACKERMAN C. Detection and classification of ocean eddies using ERS-1 and aircraft SAR images[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd ERS Symposium on Space at the Service of our Environment, Florence, Italy, 1997: 1267–1271. [7] MITNIK L, DUBINA V, and LOBANOV V. Cold season features of the Japan Sea coastal zone revealed by ERS SAR[C]. Proceedings of ERS-Envisat Symposium " Looking Down to Earth in the New Millennium”, Noordwijk, Netherlands, 2000: 4232–4242. [8] LAVROVA O Y and MITYAGINA M I. Manifestation specifics of hydrodynamic processes in satellite images of intense phytoplankton bloom areas[J]. Izvestiya Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 2016, 52(9): 974–987. doi: 10.1134/S0001433816090176 [9] 杨敏, 种劲松. 基于对数螺旋线边缘拟合的SAR图像漩涡信息提取方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 226–233. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13004YANG Min and CHONG Jing-song. A method based on logarithmic spiral edge fitting for information extraction of eddy in the SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 226–233. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13004 [10] DRESCHLER-FISCHER L, LAVROVA O, SEPPKE B, et al. Detecting and tracking small scale eddies in the black sea and the Baltic Sea using high-resolution Radarsat-2 and TerraSAR-X imagery (DTeddie)[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1214–1217. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946650. [11] KARIMOVA S. An approach to automated spiral eddy detection in SAR images[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, Texas, USA, 2017: 743–746. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8127059. [12] HUANG D M, DU Y L, HE Q, et al. DeepEddy: A simple deep architecture for mesoscale oceanic eddy detection in SAR images[C]. Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Calabria, Italy, 2017: 673–678. DOI: 10.1109/ICNSC.2017.8000171. [13] 于祥祯. 顺轨干涉SAR对海洋表面流场监测的若干问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院研究生院, 2012: 30–34.YU Xiang-zhen. Study on some problems of ocean surface current detection by along-track interferometric SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 30–34. [14] ROMEISER R, ALPERS W, and WISMANN V. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 1. Theory of the model and optimization/validation by scatterometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C11): 25237–25250. doi: 10.1029/97JC00190 [15] ROMEISER R and ALPERS W. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 2. Model response to surface roughness variations and the radar imaging of underwater bottom topography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C11): 25251–25267. doi: 10.1029/97JC00191 [16] ROMEISER R, SEIBT-WINCKLER A, HEINEKE M, et al. Validation of current and bathymetry measurements in the German Bight by airborne along-track interferometric SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2002 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 1822–1824. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1026266. [17] OUYANG Y, CHONG J S, WU Y R, et al. Simulation studies of internal waves in SAR images under different SAR and wind field conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1734–1743. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2087384 [18] 朱克勤, 彭杰. 高等流体力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 132–138.ZHU Ke-qin and PENG Jie. Advanced Fluid Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 132–138. [19] BURGERS J M. A mathematical model illustrating the theory of turbulence[J]. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1948, 1: 171–199. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2156(08)70100-5 [20] ROTT N. On the viscous core of a line vortex[J]. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP, 1958, 9(5/6): 543–553. doi: 10.1007/BF02424773 [21] LONGUET-HIGGINS M S and STEWART R W. Radiation stresses in water waves; a physical discussion, with applications[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1964, 11(4): 529–562. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(64)90001-4 [22] 余颖, 王小青, 朱敏慧, 等. 基于二阶散射的海面三尺度雷达后向散射模型[J]. 电子学报, 2008, 36(9): 1771–1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.09.022YU Ying, WANG Xiao-qing, ZHU Min-hui, et al. Three-scale radar backscattering model of the ocean surface based on second-order scattering[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(9): 1771–1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.09.022 [23] WHITHAM G B. A general approach to linear and non-linear dispersive waves using a Lagrangian[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1965, 22(2): 273–283. doi: 10.1017/S0022112065000745 [24] ALPERS W R, ROSS D B, and RUFENACH C L. On the detectability of ocean surface waves by real and synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C7): 6481–6498. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC07p06481 [25] ROMEISER R and THOMPSON D R. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 446–458. doi: 10.1109/36.823940 [26] ROBINSON I S. Discovering the Ocean from Space: The Unique Applications of Satellite Oceanography[M]. Chichester, UK: Springer-Praxis, 2010: 76–78. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: