Atmospheric Effects on the Performance of Geosynchronous Orbit SAR Systems
-
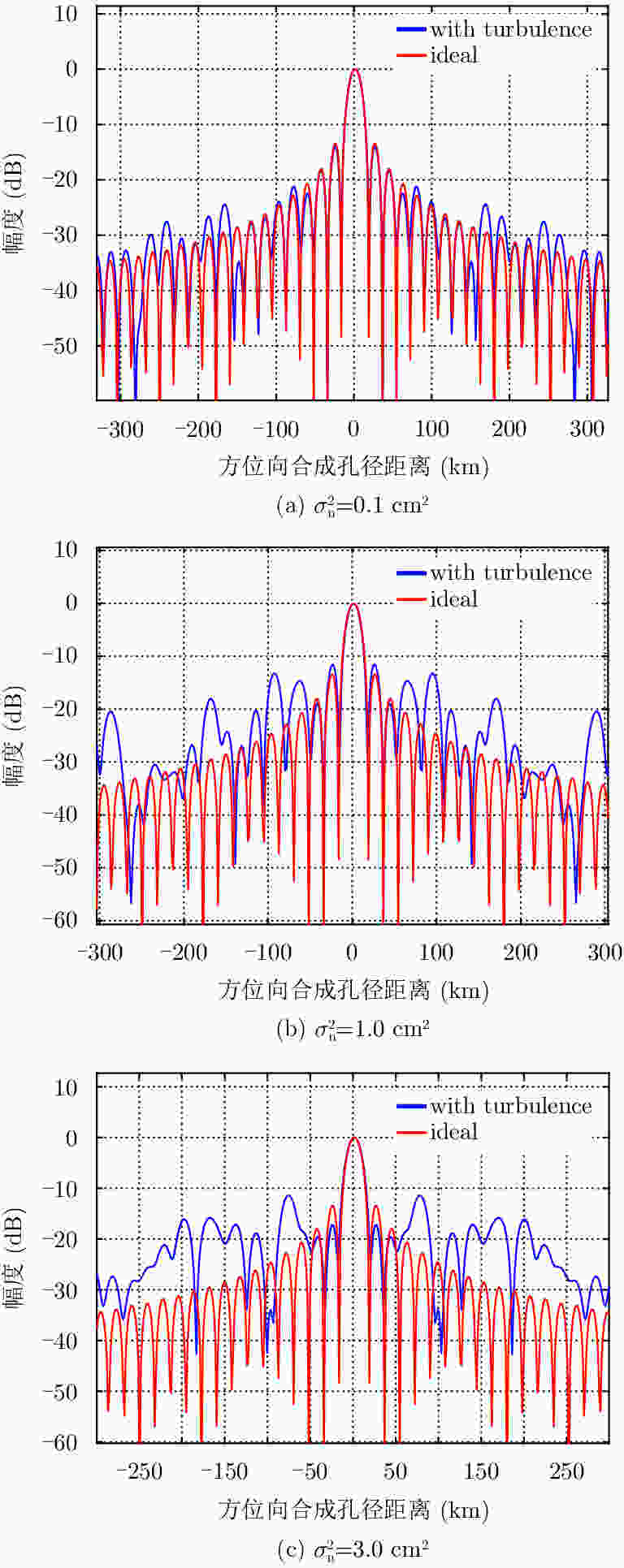
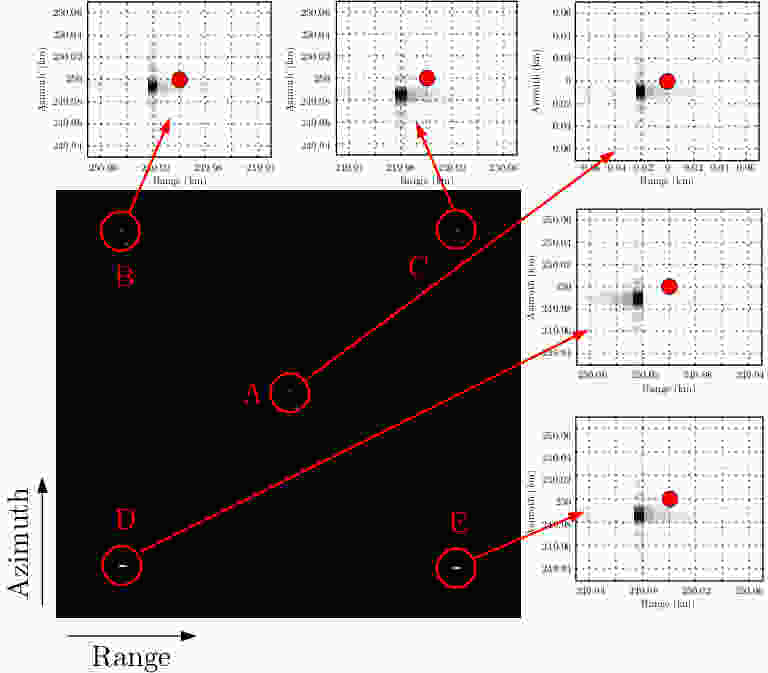
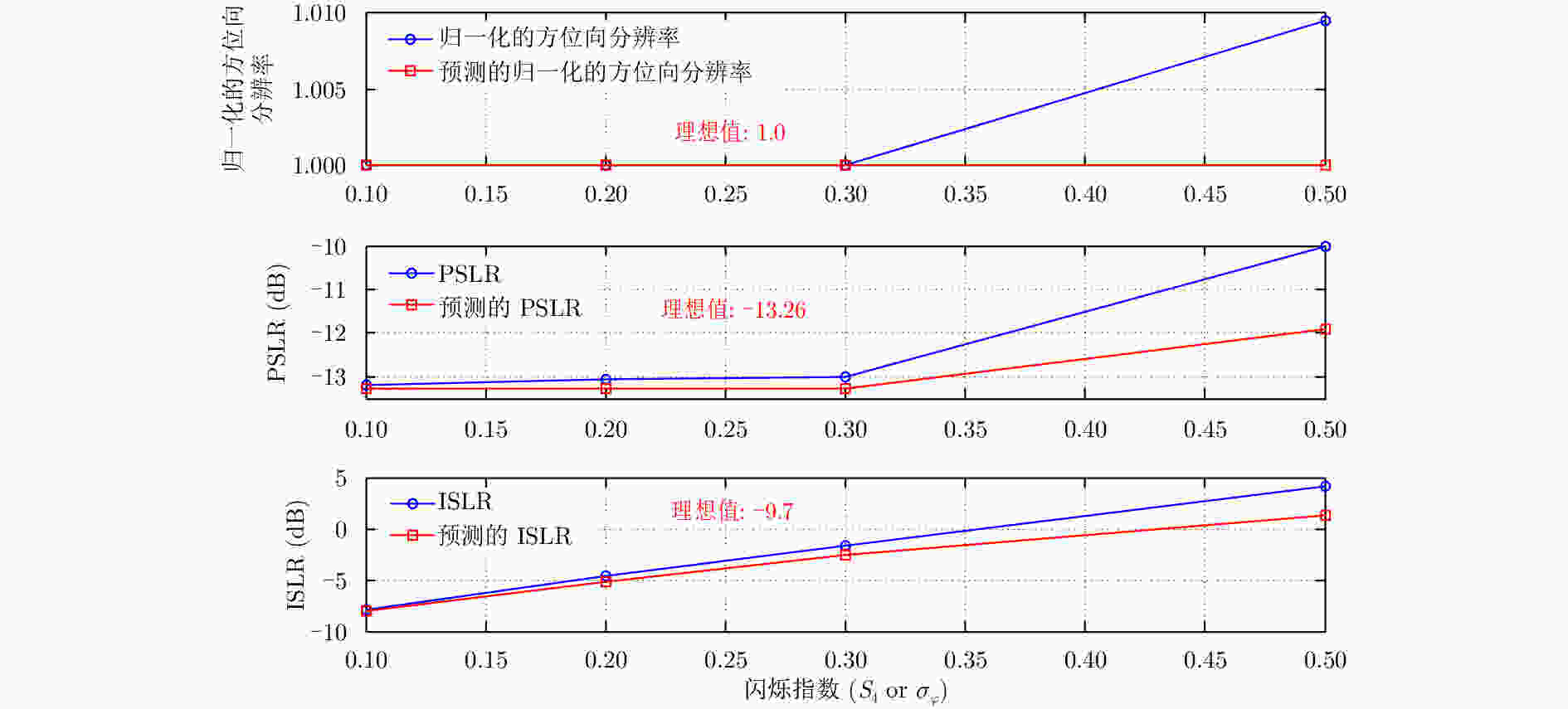
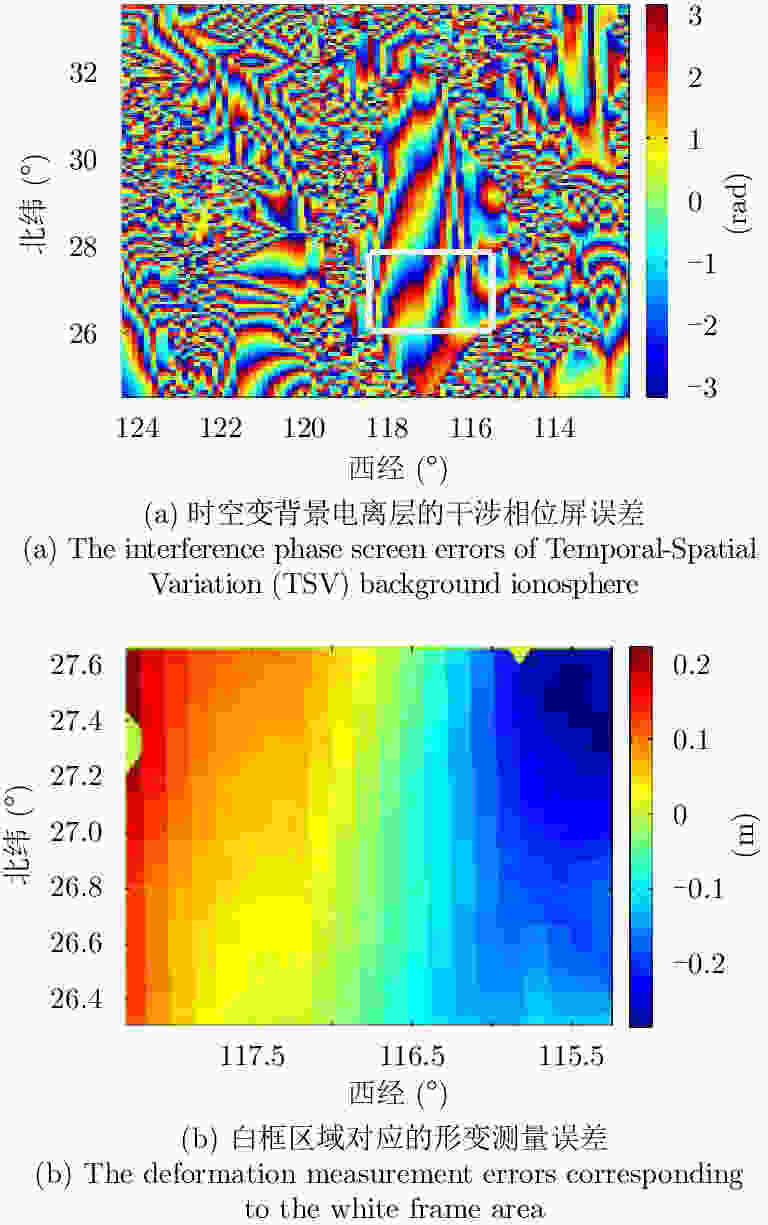
摘要: 地球同步轨道合成孔径雷达(GEO SAR)合成孔径时间长、观测范围大,易受到大气层效应时空变化的影响,使成像的聚焦质量和差分干涉处理精度严重下降。该文针对常规对流层和背景电离层等大气层缓变的干扰部分,建立了高精度时频混合GEO SAR信号模型,分析了不同大气层参数的时间变化率对成像质量和差分干涉处理精度的影响。针对大气层干扰中对流层湍流和电离层闪烁等随机扰动造成的影响,基于幂律功率谱模型,建立了大气扰动参数和成像质量的定量化分析模型,获得了大气层随机干扰的强度与成像评估指标间的关系。最后,通过仿真验证了模型的有效性,并分析了长孔径时间内缓变和随机扰动的大气层误差对成像和差分干涉处理质量的影响,仿真结果表明:L波段GEO SAR成像和差分干涉处理受时空变电离层干扰的影响十分严重,必须予以补偿;对流层干扰对其影响较小,仅当积累时间达到数百秒时才需要考虑它对成像性能的恶化。
-
关键词:
- 地球同步轨道合成孔径雷达 /
- 合成孔径雷达成像 /
- 对流层干扰影响 /
- 电离层干扰影响
Abstract: GEOsynchronous orbit Synthetic Aperture Radar (GEO SAR) has a long synthetic aperture and large observation region; therefore, it is easily affected by atmospheric spatial-temporal changes, which results in a serious degradation in the focusing quality and performance of differential interference processing. In this paper, a high-precision spatial-temporal hybrid GEO SAR signal model is established for the slowly disturbed parts of the atmosphere such as the background troposphere and the ionosphere. The effects of the time rate of different atmospheric parameters on the image quality and accuracy of differential interference processing are analyzed. Considering the influence of random disturbances such as tropospheric turbulence and ionospheric scintillation in atmosphere, a quantitative analysis model is established based on a power law power spectrum model using the atmospheric disturbance and imaging quality parameters. The relationships of the random disturbances intensity in the atmosphere and the imaging evaluation index are obtained. Finally, the model is verified by simulations, and the effects of slow-varying atmospheric errors in a long aperture time on the quality of imaging and differential interference processing are analyzed. Simulation results show that spatial-temporal variable ionospheric disturbances seriously affect L-band GEO SAR imaging and differential interference processing, which must be compensated, and they are slightly affected by tropospheric disturbances. Moreover, it is necessary to consider the tropospheric effects on imaging performance only when the integration time reaches several hundred seconds. -
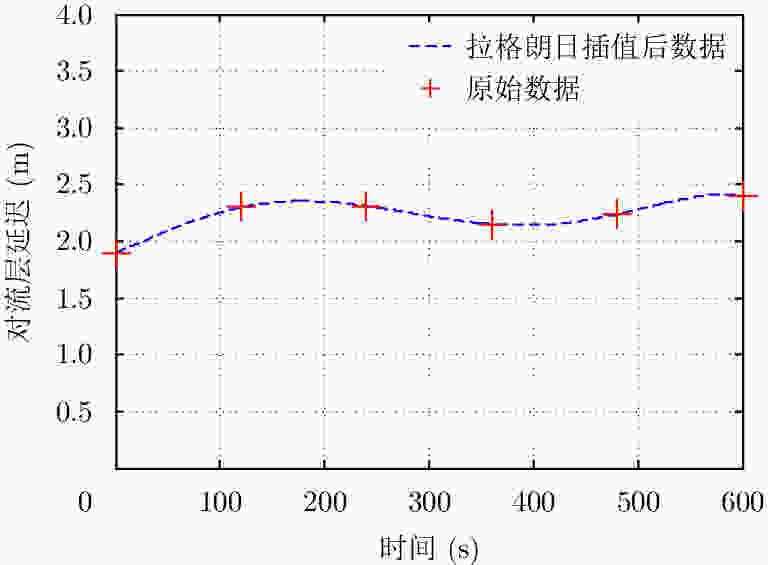
表 1 GEO SAR对流层延迟的各阶时间变化情况
Table 1. Temporal variability of each order of GEO SAR tropospheric delay
项目 数值 $\Delta \,{r_0}$ (m) 2.21 ${q_1}$ (m/s) 2.52×10–4 ${q_2}$ (m/s2) 2.71×10–7 ${q_3}$ (m/s3) 1.64×10–13 表 2 电离层TEC随时间变化情况
Table 2. Rate of ionospheric TEC changing with time
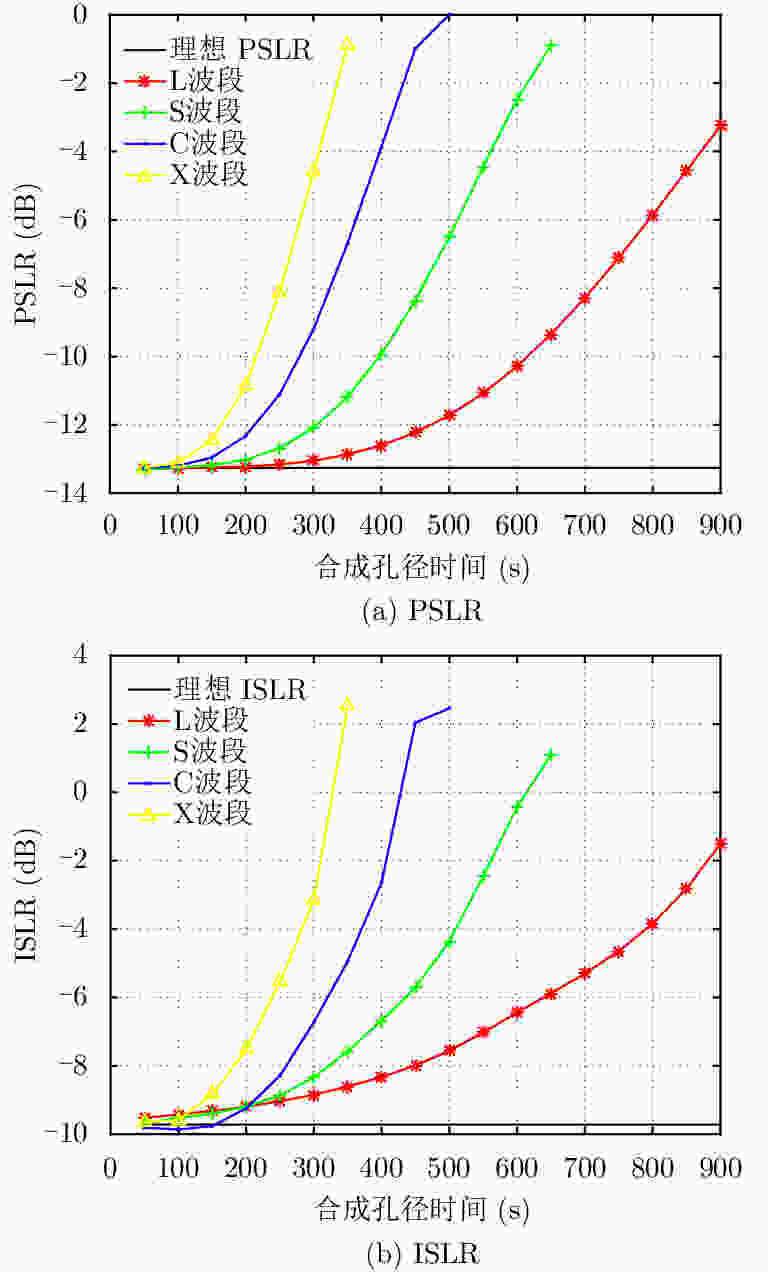
项目 数值 TEC0(TECU) 68.3 k1 (TECU/s) 0.0068 k2 (TECU/s2) 7.32×10–6 k3 (TECU/s3) 4.42×10–12 表 3 背景电离层对GEO SAR成像影响评估结果
Table 3. Results of GEO SAR imaging effected by background ionosphere
合成孔径时间(s) 距离向PSLR (dB) 方位向PSLR (dB) 方位向移位(m) 100 –13.23 –13.21 4.3 300 –13.25 –12.11 4.3 500 –13.22 –10.39 4.3 -
[1] Tomiyasu K. Synthetic aperture radar in geosynchronous orbit[C]. Proceedings of 1978 Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 1978: 42–45 [2] Tomiyasu K and Pacelli J L. Synthetic aperture radar imaging from an inclined geosynchronous orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1983, 21(3): 324–329. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.1983.350561 [3] NASA and JPL. Global earthquake satellite system: A 20-year plan to enable earthquake prediction[EB/OL]. http://solidearth.jpl.nasa.gov/GESS/3123_GESS_Rep_2003.pdf, 2015, 9 [4] Edelstein W N, Madsen S N, Moussessian A, et al.. Concepts and technologies for synthetic aperture radar from MEO and geosynchronous orbits[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 5659, Enabling Sensor and Platform Technologies for Spaceborne Remote Sensing, Honolulu, Hawaii, 2005: 195–203 [5] Laurence Gray A, Mattar K E, and Sofko G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(10): 1451–1454. DOI: 10.1029/2000GL000016 [6] Meyer F, Bamler R, Jakowski N, et al. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(4): 560–564. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.882148 [7] Meyer F J and Nicoll J. The impact of the ionosphere on interferometric SAR processing[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 2008: II-391–II-394 [8] Meyer F J. Performance requirements for ionospheric correction of low-frequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3694–3702. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2146786 [9] Sun J P, Bi Y K, Wang Y P, et al.. High resolution SAR performance limitation by the change of tropospheric refractivity[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011 [10] Zhang F, Li G J, Li W, et al. Multiband microwave imaging analysis of ionosphere and troposphere refraction for spaceborne SAR[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 2014: 913056. [11] Hanssen R F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2001 [12] Danklmayer A, Doring B J, Schwerdt M, et al. Assessment of atmospheric propagation effects in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(10): 3507–3518. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2022271 [13] Hobbs S, Mitchell C, Forte B, et al. System design for geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar missions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(12): 7750–7763. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2318171 [14] Bruno D and Hobbs S E. Radar imaging from geosynchronous orbit: Temporal decorrelation aspects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2924–2929. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2042062 [15] Bruno D, Hobbs S E, and Ottavianelli G. Geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar: Concept design, properties and possible applications[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2006, 59(1–5): 149–156. DOI: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.02.005 [16] Ruiz Rodon J, Broquetas A, Guarnieri A M, et al. Geosynchronous SAR focusing with atmospheric phase screen retrieval and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4397–4404. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242202 [17] Ruiz-Rodon J, Broquetas A, Makhoul E, et al. Nearly zero inclination geosynchronous SAR mission analysis with long integration time for earth observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6379–6391. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2296357 [18] Guarnieri A M, Rocca F, and Ibars A B. Impact of atmospheric water vapor on the design of a Ku band geosynchronous SAR system[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009 [19] Guarnieri A M, Tebaldini S, Rocca F, et al.. GEMINI: Geosynchronous SAR for earth monitoring by interferometry and imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012 [20] Monti Guarnieri A, Broquetas A, Recchia A, et al. Advanced radar geosynchronous observation system: ARGOS[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1406–1410. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2404214 [21] Monti Guarnieri A, Leanza A, Recchia A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen in GEO-SAR: Estimation and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(3): 1668–1679. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2766084 [22] Hu C, Long T, Zeng T, et al. The accurate focusing and resolution analysis method in geosynchronous SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3548–3563. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160402 [23] Hu C, Tian Y, Yang X P, et al. Background ionosphere effects on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Theoretical analysis and verification based on the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1143–1162. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2475283 [24] Dong X C, Hu C, Tian Y, et al. Experimental study of ionospheric impacts on geosynchronous SAR using GPS signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2171–2183. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2537401 [25] Tian Y, Hu C, Dong X C, et al.. Analysis of effects of time variant troposphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 5051–5054 [26] 田野, 董锡超, 胡程. 对流层对地球同步轨道SAR成像的影响研究[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(12): 1562–1567. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.12.003Tian Ye, Dong Xi-chao, and Hu Cheng. Analysis of troposphere impacts on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(12): 1562–1567. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.12.003 [27] Tian Y, Hu C, Dong X C, et al. Theoretical analysis and verification of time variation of background ionosphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 721–725. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2360235 [28] Wang R, et al. Joint amplitude-phase compensation for ionospheric scintillation in GEO SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3454–3465. [29] Hu C, Li Y H, Dong X C, et al. Performance analysis of L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging in the presence of ionospheric scintillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 3454–3465. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2602939 [30] Li Y H, Hu C, Dong X C, et al. Impacts of ionospheric scintillation on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Preliminary experiments and analysis[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(10): 1–3. [31] Hu C, Li Y H, Dong X C, et al. Impacts of temporal-spatial variant background ionosphere on repeat-track GEO D-InSAR system[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(11): 916. DOI: 10.3390/rs8110916 [32] Kou L L, Wang X Q, Xiang M S, et al. Effect of orbital errors on the geosynchronous circular synthetic aperture radar imaging and interferometric processing[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science C, 2011, 12(5): 404–416. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.C1000170 [33] Kou L L, Xiang M S, Wang X Q, et al. Tropospheric effects on L-band geosynchronous circular SAR imaging[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2013, 7(6): 693–701. [34] Ji Y F, Zhang Q L, Zhang Y S, et al. L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging degradations imposed by ionospheric irregularities[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 060308. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9064-1 [35] Li D X, Rodriguez-Cassola M, Prats-Iraola P, et al. Modelling of tropospheric delays in geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 060307. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9065-1 [36] Tofsted D H. Turbulence simulation: Outer scale effects on the refractive index spectrum[R]. Technical Report ARL-TR-548. US Army Research Lab. NM, 2000 [37] Von Kármán T. Progress in the statistical theory of turbulence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1948, 34(11): 530–539. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.34.11.530 [38] Tunick A D. The Refractive Index Structure Parameter/Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Model: CN2[M]. U.S. Adelphi: A.R. Laboratory, 1998 [39] Liu Z P, Hu C, Zeng T, et al. Improved secondary range compression focusing method in GEO SAR[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 1373–1376 [40] Long T, Hu C, Ding Z, et al.. Geosynchronous SAR: System and Signal Processing[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018 [41] Zhang D D, Chen Z Y, Dong X C, et al.. Simulating the impacts of ionospheric scintillation on geosynchronous SAR[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2017 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: