Passive Direct Location Determination for Multiple Sources Based on FRFT
-
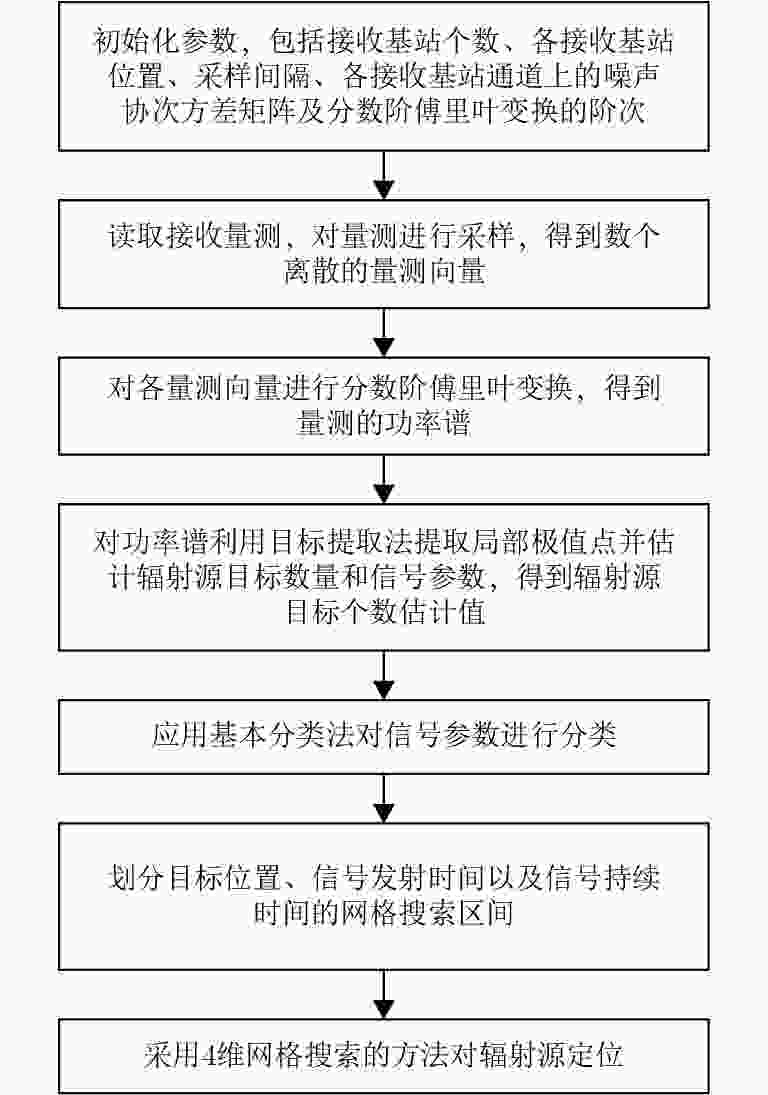
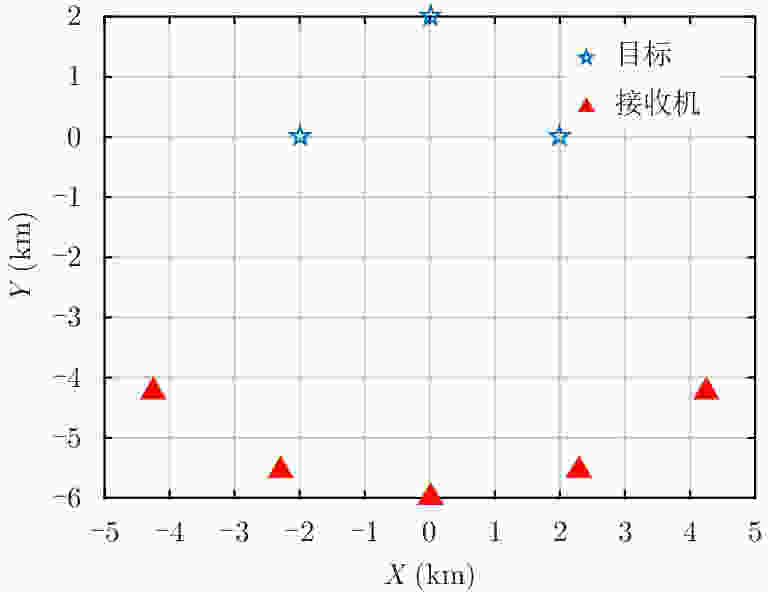
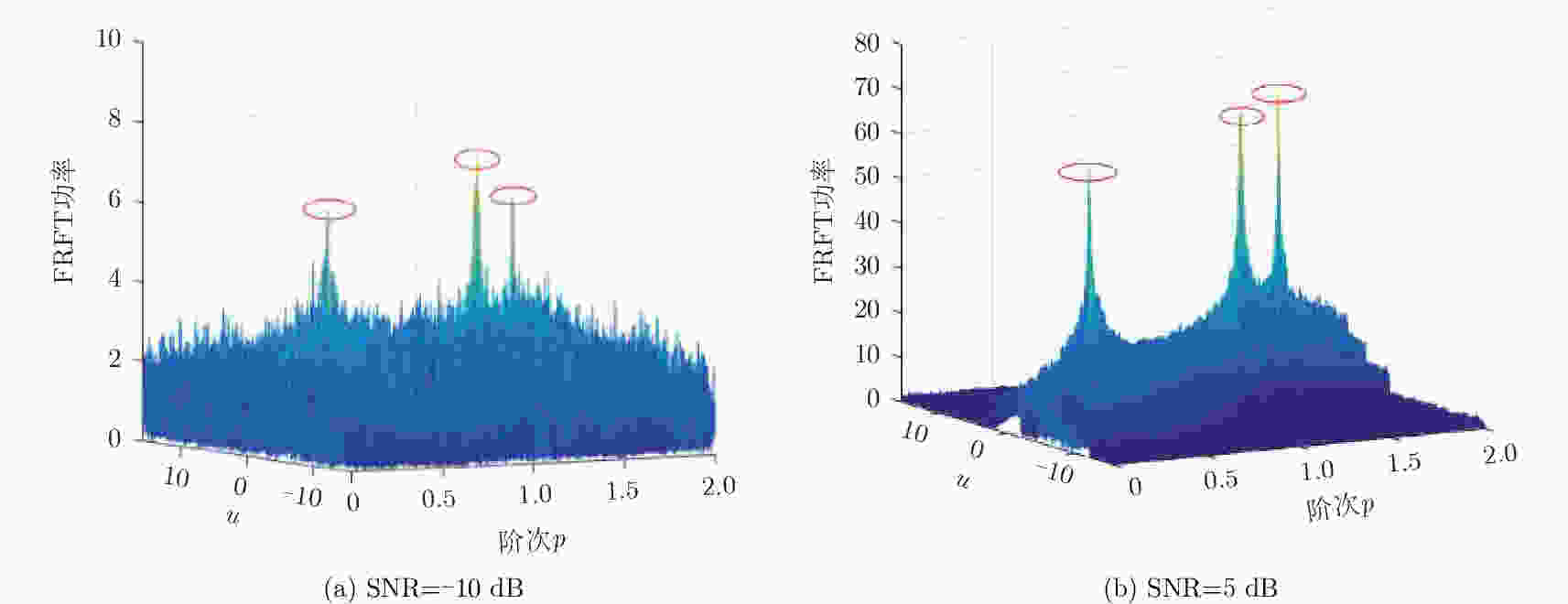
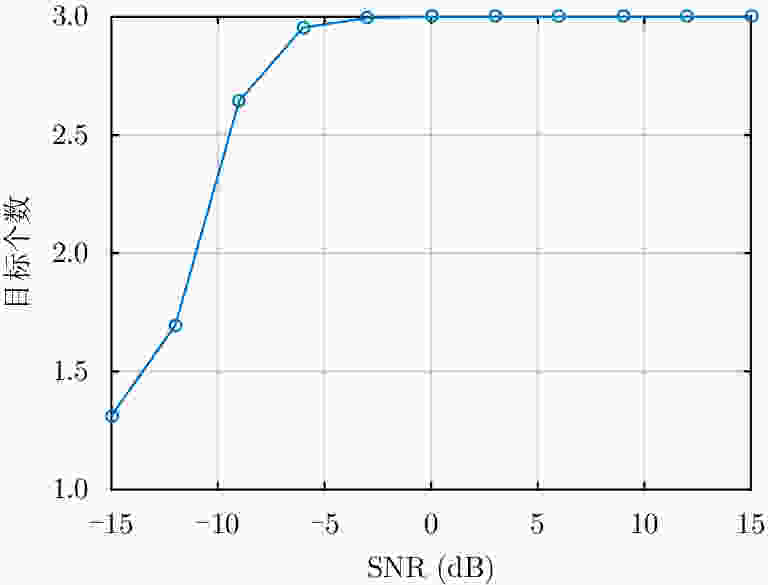
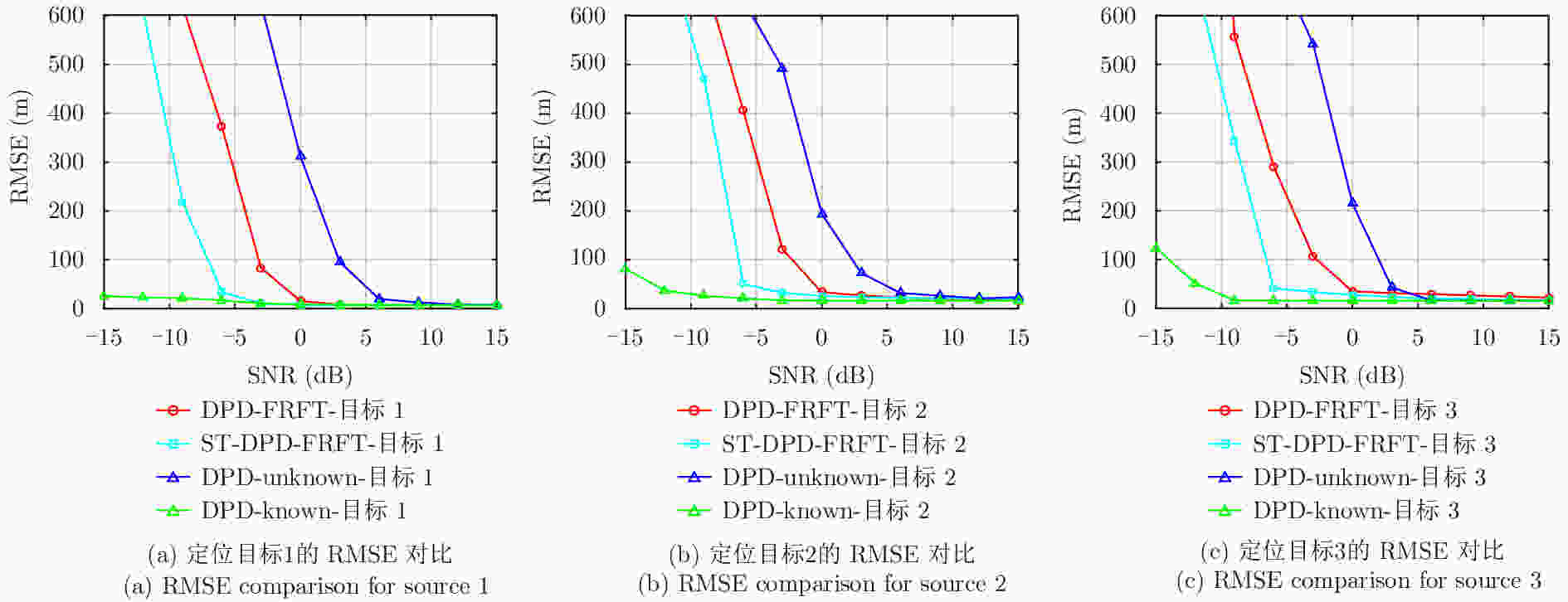
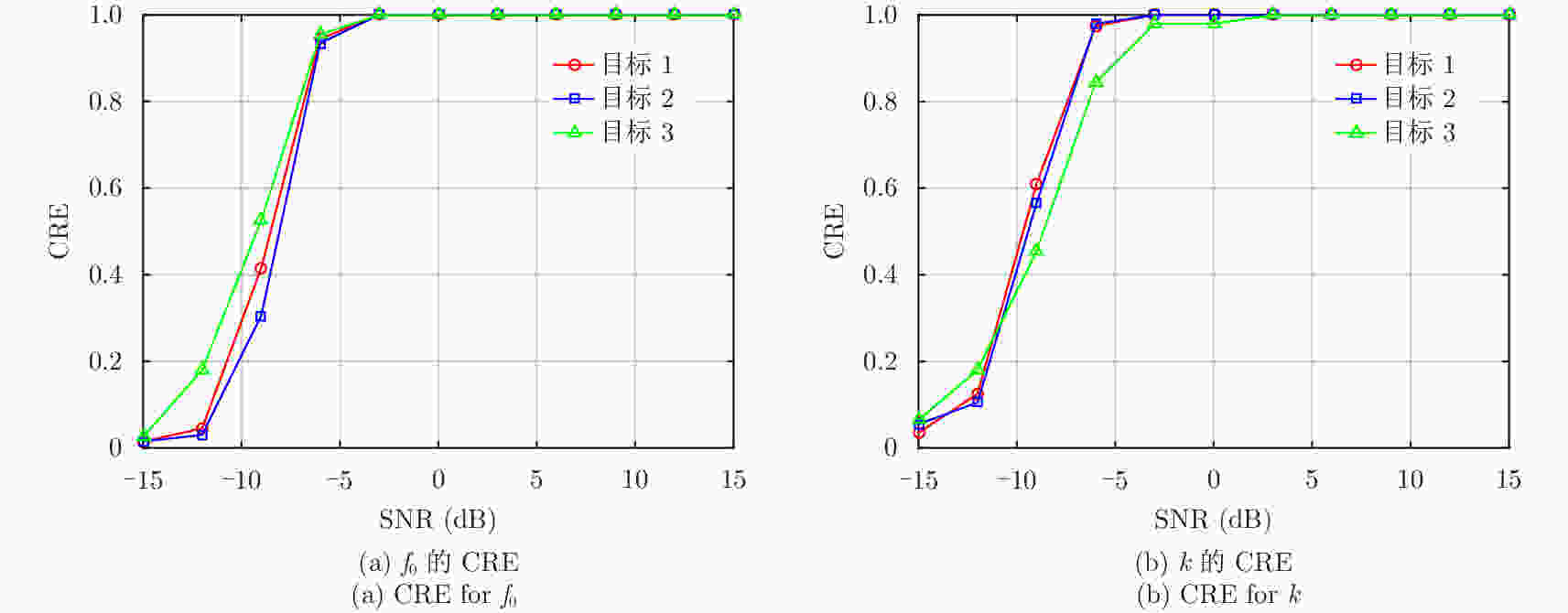
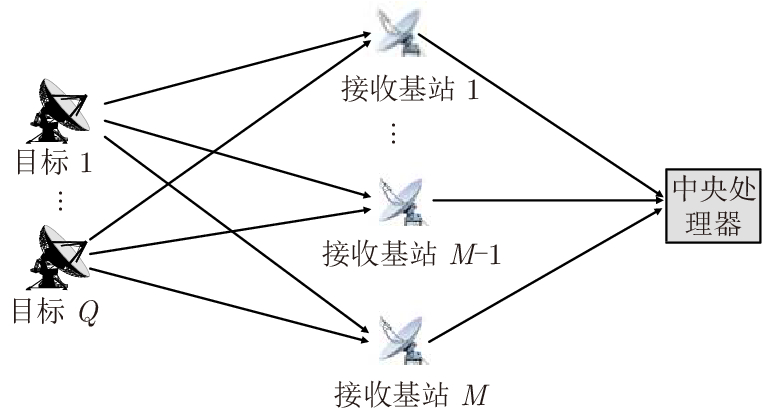
摘要: 直接定位(DPD)算法能充分利用观测回波信息,在低信噪比条件下其定位精度一般要高于传统的两步定位算法。为解决多基站无源雷达系统中多个未知线性调频(LFM)信号辐射源的定位问题,该文提出一种基于DPD算法和分数傅里叶变换(FRFT)相结合的多目标定位算法。首先,根据建立的信号模型推导了理论上最优的高维最大似然估计器;其次,由于高维信号参数和目标位置联合估计的计算复杂度限制,利用基于FRFT和基本分类算法的降维策略将多目标定位问题转化为多个单目标定位问题;最后,目标的位置及相应信号参数可通过4维网格搜索得到有效估计。仿真结果表明,相比于已存在的忽略发射信号的DPD算法,该文提出算法定位性能更优。Abstract: The Direct Position Determination (DPD) method can fully use the information of an observed signal, and it is known to outperform the traditional two-step methods at a low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). To solve the problem of localizing multiple transmitters with unknown Linear Frequency Modulation (LFM) signals in multi-static passive radar systems, a multi-target positioning algorithm based on DPD algorithm and FRactional Fourier Transform (FRFT) is proposed. First, according to the established signal model, the theoretically optimal high-dimensional maximum likelihood estimator is deduced; Then, to address the high computational complexity of the estimator in jointly estimating high-dimensional signal parameters and positions of sources, we propose a dimensionality reduction strategy based on the FRFT and some basic classification algorithms to transform the multi-target localizing problem to a multiple single-target localizing problem. Through this method, the position and the corresponding signal parameters of each source can be efficiently estimated by a four-dimensional grid search. Simulation results show that the proposed method outperforms the existing DPD algorithm, and it can determine the positions of sources without directly utilizing the transmitted signal information.
-
表 1 信号参数设置
Table 1. Signal parameter setting
目标信号 信号长度Tp
(μs)初始频率f0
(MHz)调频斜率k
(MHz/μs)目标1信号 20 2 0.10 目标2信号 25 6 –0.05 目标3信号 30 5 0.25 -
[1] Amar A and Weiss A J. Localization of narrowband radio emitters based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(11): 5500–5508. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2008.929655 [2] 贾兴江. 运动多站无源定位关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011: 3–42Jia Xing-jiang. Research on passive location technologies of multiple moving observers[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011: 3–42 [3] Tirer T and Weiss A J. High resolution localization of narrowband radio emitters based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 288–298. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.06.019 [4] 赵勇胜, 赵拥军, 赵闯. 联合角度和时差的单站无源相干定位加权最小二乘算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. DOI: 10.12000/JR15133Zhao Yong-sheng, Zhao Yong-jun, and Zhao Chuang. Weighted least squares algorithm for single-observer passive coherent location using DOA and TDOA measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. DOI: 10.12000/JR15133 [5] Weiss A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 [6] Yi W, Chen Z H, Hoseinnezhad R, et al. Joint estimation of location and signal parameters for an LFM emitter[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 134: 100–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.11.014 [7] Oispuu M and Nickel U. Direct detection and position determination of multiple sources with intermittent emission[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(12): 3056–3064. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.05.010 [8] Ozaktas H M, Arikan O, Kutay M A, et al. Digital computation of the fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(9): 2141–2150. DOI: 10.1109/78.536672 [9] Saxena R and Singh K. Fractional Fourier transform: A novel tool for signal processing[J]. Journal of the Indian Institute of Science, 2005, 85(1): 11–26. [10] Namias V. The fractional order Fourier transform and its application to quantum mechanics[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 1980, 25(3): 241–265. DOI: 10.1093/imamat/25.3.241 [11] 田瑞琦, 鲍庆龙, 王丁禾, 等. 基于FRFT与Keystone变换的运动目标参数估计算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(5): 511–517. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14058Tian Rui-qi, Bao Qing-long, Wang Ding-he, et al. An algorithm for target parameter estimation based on fractional Fourier and Keystone transforms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 511–517. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14058 [12] Almeida L B. The fractional Fourier transform and time-frequency representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3084–3091. DOI: 10.1109/78.330368 [13] 吴超楠. 基于分数阶傅里叶变换的高精度线性调频信号参数估计方法[D]. [硕士论文], 华南理工大学, 2014: 15–63Wu Chaonan. High-precision parameter estimation for LFM signal based on fractional Fourier transform[D]. [Master dissertation], South China University of Technology, 2014: 15–63 [14] Schonhoff T A and Giordano A A. Detection and Estimation Theory and its Applications[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2006 [15] 艾越. 分置MIMO雷达多目标信号级定位算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015: 19–23Ai Yue. Research of MIMO radar with widely separated antennas signal level multi-target localization[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015: 19–23 [16] Schultz R R and Stevenson R L. A Bayesian approach to image expansion for improved definition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, 3(3): 233–242. DOI: 10.1109/83.287017 [17] Sneath P H A and Sokal R R. Numerical taxonomy: The principles and practice of numerical classification[J]. Taxon, 1963, 12(5): 190–199. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: