Intra-pulse Spotlight SAR Imaging Method Based on Azimuth Phase Coding
-
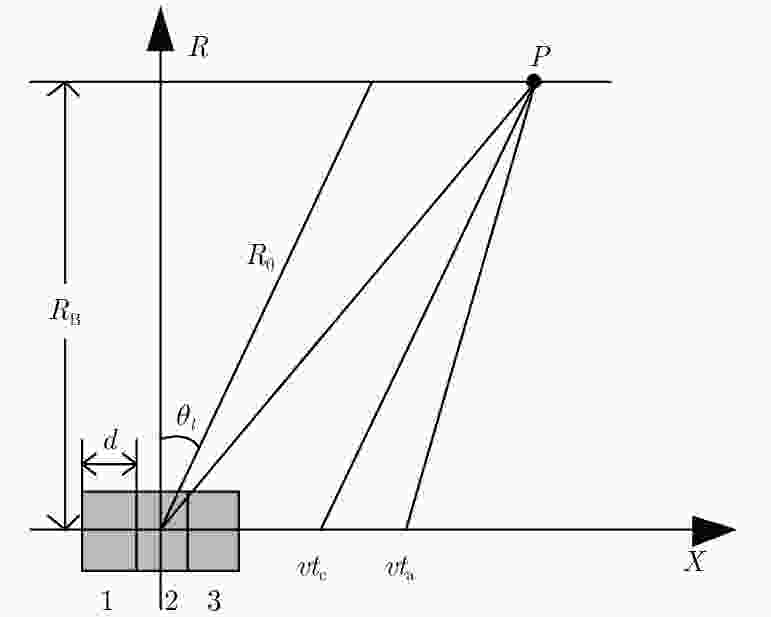
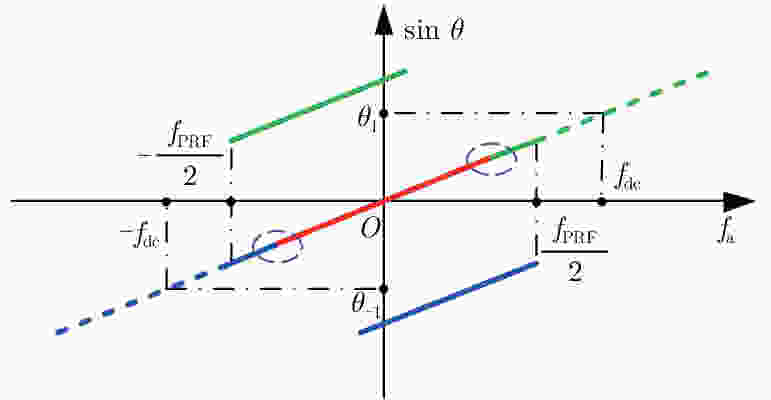
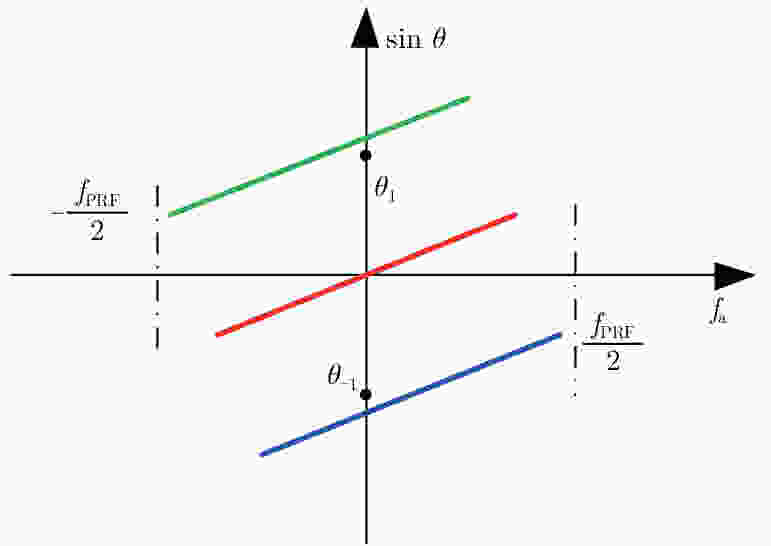
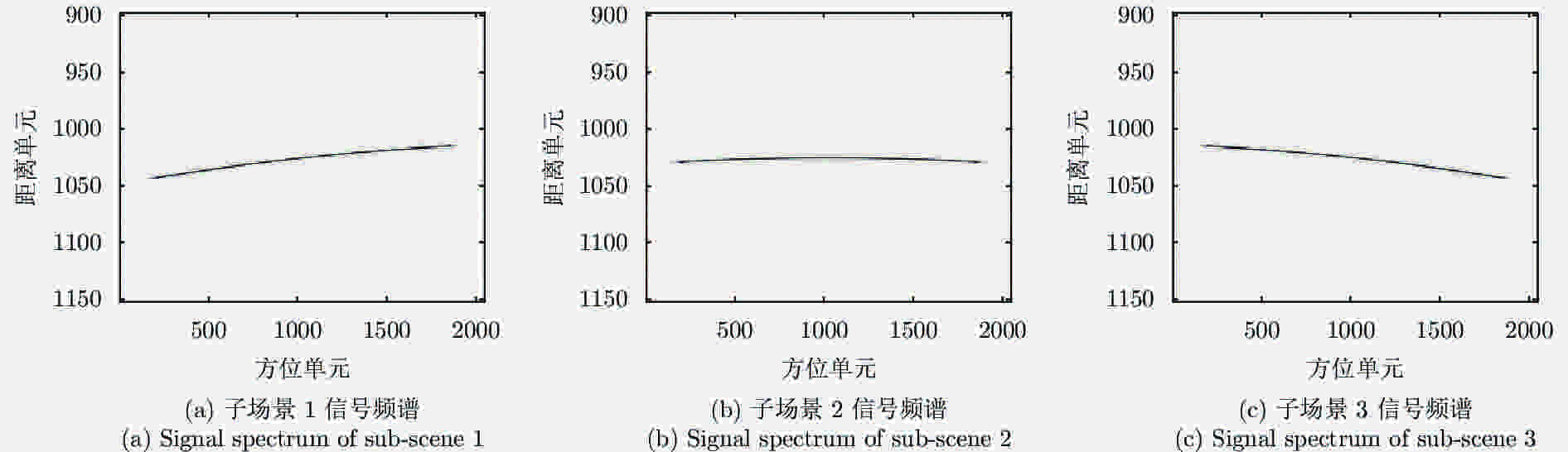
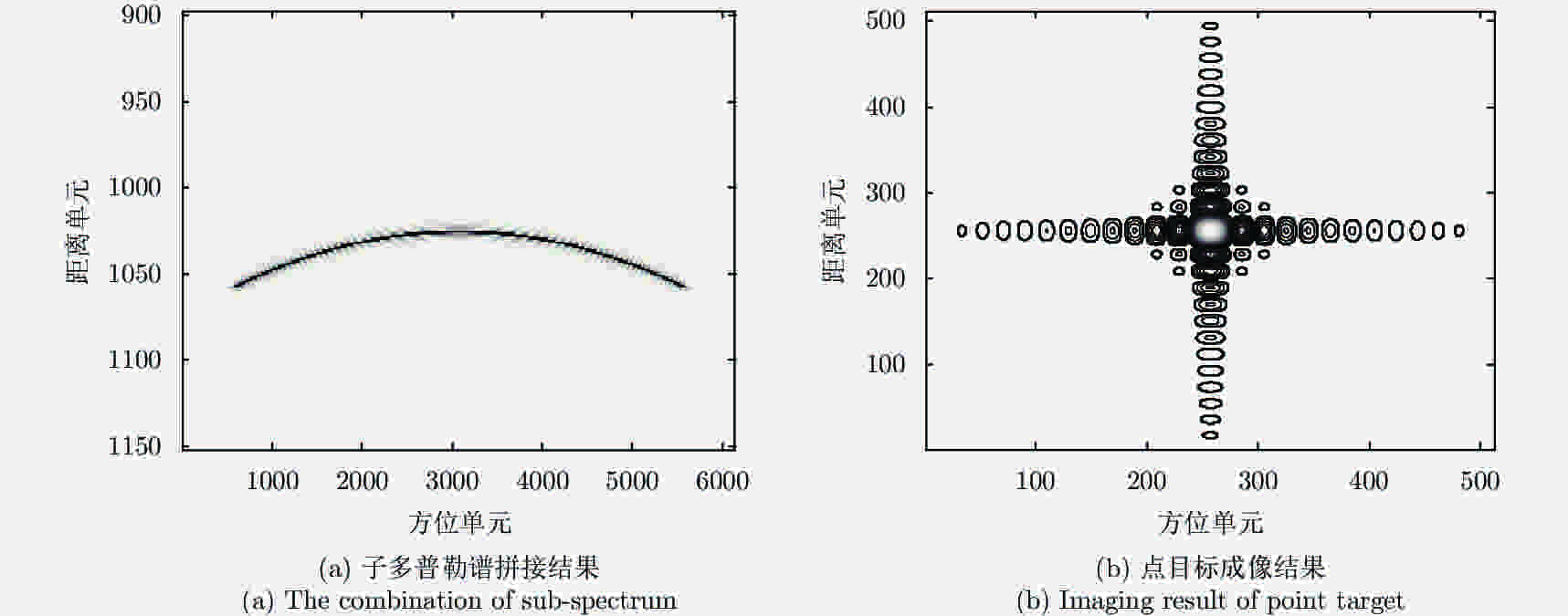
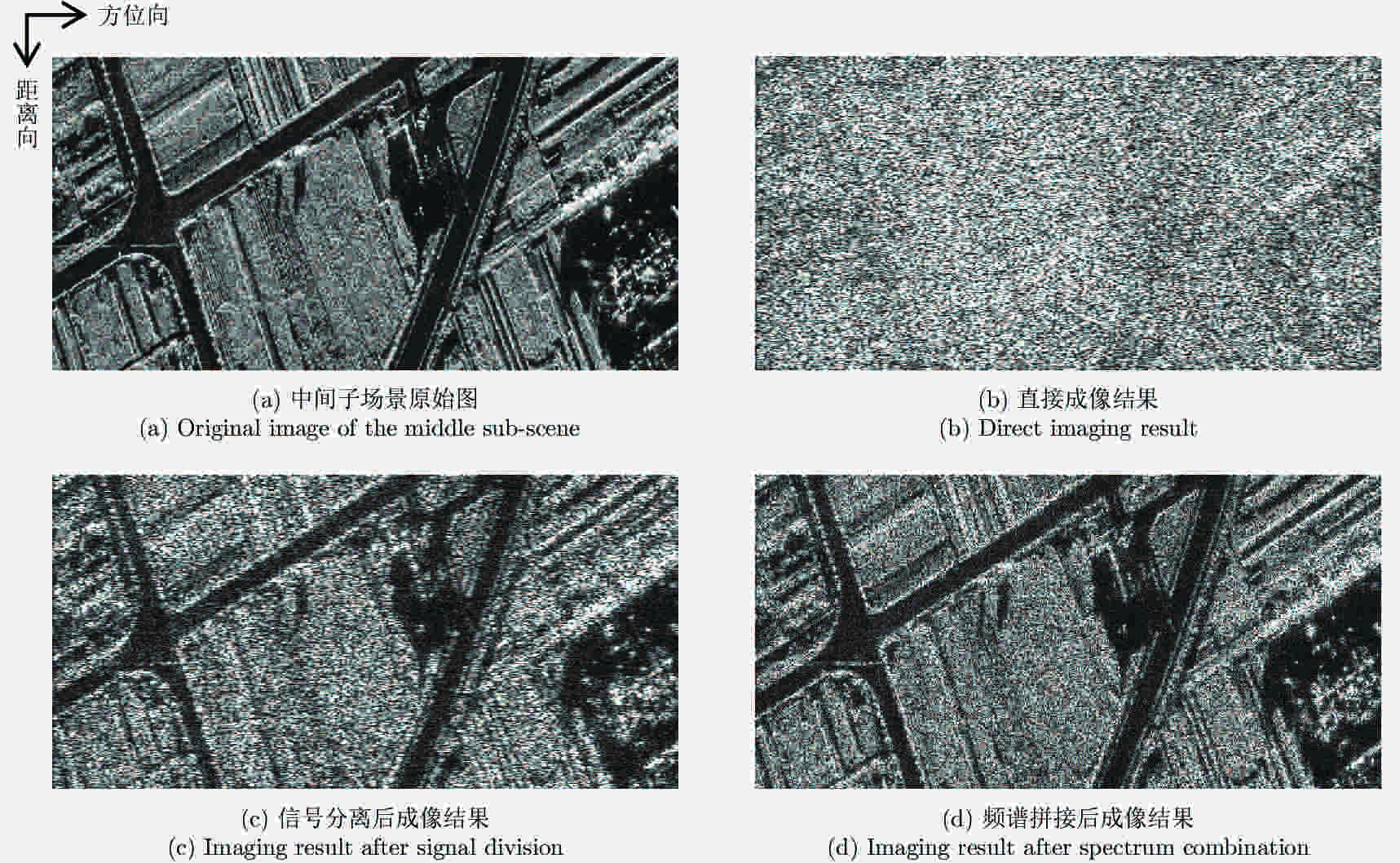
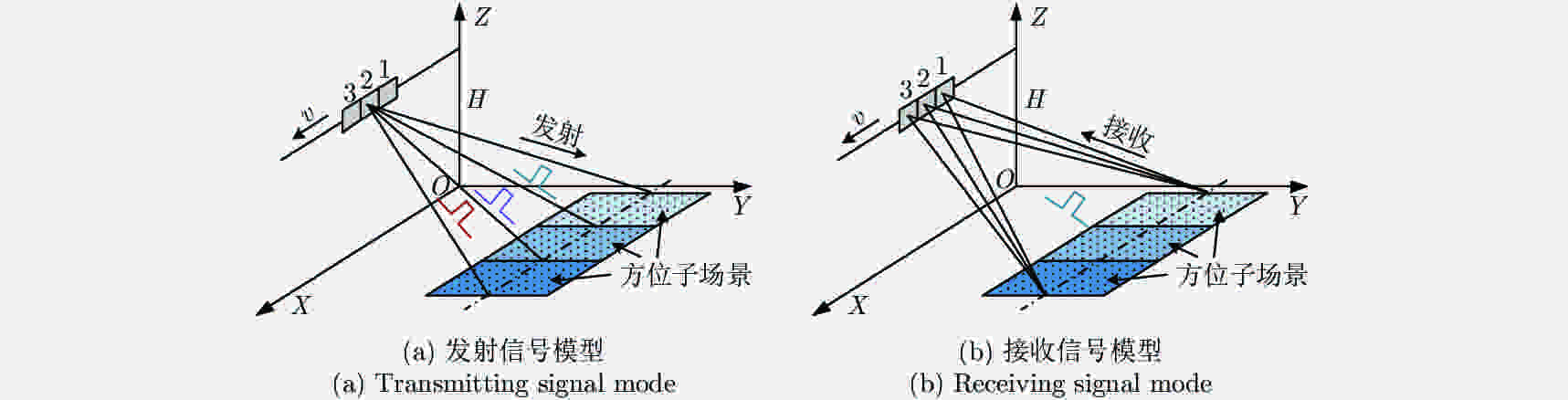
摘要: 脉内聚束模式有效克服了星载合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)高分辨率与宽测绘带之间的矛盾,同时可以兼顾回波的信噪比。然而距离维空域滤波的信号分离方法容易受地形起伏的影响,甚至失效。针对此,该文提出了一种结合方位相位编码(Azimuth Phase Coding, APC)的脉内聚束SAR成像方法,利用APC技术使不同子脉冲回波的方位频谱处在不同的脉冲重复频率(Pulse Repetition Frequencies, PRF)范围,然后利用方位自适应波束形成技术来分离回波信号。文中对信号分离方法以及频移因子的选择进行了详细的讨论。最后仿真实验结果验证了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: The intra-pulse spotlight imaging mode can effectively overcome the contradiction between high resolution and wide swath in spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), and considers the echo’s signal-to-noise ratio. However, signal division by spatial filtering along the range direction may be impacted by fluctuating terrain. To solve this problem, a novel intra-pulse spotlight imaging method based on Azimuth Phase Coding (APC) is proposed in this paper. Using APC, the azimuth spectrum of echo data from different sub-pulses will locate in different Pulse Repetition Frequencies (PRF). As such, the signal can be divided using an azimuth adaptive beamforming technique. The signal separation method and selection of the shift factor are discussed in detail. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
参数 值 参数 值 雷达载频(GHz) 9.65 方位孔径(m) 4.8 脉冲总时宽(μs) 30 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 3600 子脉冲信号带宽(MHz) 150 场景中心距离(km) 596 采样频率(MHz) 180 子脉冲个数 3 平台速度(m/s) 7200 方位通道数 3 表 2 成像性能参数统计
Table 2. Parameters of the focused targets
距离向 方位向 PSLR (dB) –13.28 PSLR (dB) –13.28 ISLR (dB) –9.67 ISLR (dB) –9.81 分辨率 (m) 1.0087 分辨率 (m) 0.8157 -
[1] Freeman A, Johnson W T K, Huneycutt B, et al. The " Myth” of the minimum SAR antenna area constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 320–324. DOI: 10.1109/36.823926 [2] Fan B, Qin Y L, You P, et al. An improved PFA with aperture accommodation for widefield spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 3–7. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2322858 [3] Wu Y, Sun G C, Yang C, et al. Processing of very high resolution spaceborne sliding spotlight SAR data using velocity scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1505–1518. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2481923 [4] Li N, Wang R, Deng Y K, et al. Improved full-aperture ScanSAR imaging algorithm based on aperture interpolation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(5): 1101–1105. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2384594 [5] Meta A, Mittermayer J, Prats P, et al. TOPS imaging with TerraSAR-X: Mode design and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 759–769. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2026743 [6] Callaghan G D and Longstaff I D. Wide-swath space-borne SAR and range ambiguity[C]. Radar 97, Edinburgh, UK, 1997: 248–252 [7] 李杨, 黄杰文, 禹卫东. 高分辨率宽测绘带星载SAR距离向DBF处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(6): 1510–1514. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01157Li Yang, Huang Jie-wen, and Yu Wei-dong. Range DBF processing for high-resolution wide-swath spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2011, 33(6): 1510–1514. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01157 [8] Wang W, Wang R, Deng Y K, et al. Improved digital beam-forming approach with scaling function for range multi-channel synthetic aperture radar system[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2016, 10(2): 379–385. [9] Currie A and Brown M A. Wide-swath SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(2): 122–135. DOI: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0016 [10] Liu B C and He Y J. Improved DBF algorithm for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 1209–1225. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2476496 [11] Li X S, Xing M D, Xia X G, et al. Simultaneous stationary scene imaging and ground moving target indication for high-resolution wide-swath SAR system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7): 4224–4239. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2538564 [12] Krieger G, Gebert N, and Moreira A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 31–46. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.905974 [13] 武其松, 邢孟道, 刘保昌, 等. 脉内聚束SAR方位高分辨率宽测绘带成像[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(4): 676–682, 699. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2010.04.017Wu Qi-song, Xing Meng-dao, Liu Bao-chang, et al. High azimuth resolution wide swath imaging based on the intrapulse spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2010, 37(4): 676–682, 699. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2010.04.017 [14] Dall J and Kusk A. Azimuth phase coding for range ambiguity suppression in SAR[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004, 3: 1734–1737 [15] 郭磊, 王宇, 邓云凯, 等. 基于方位向相位编码技术的方位向多通道SAR距离模糊抑制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(3): 601–606. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT140707Guo Lei, Wang Yu, Deng Yun-kai, et al. Range ambiguity suppression for multi-channel SAR system using azimuth phase coding technique[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2015, 37(3): 601–606. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT140707 [16] 邢孟道, 李真芳, 保铮, 等. 分布式小卫星雷达空时频成像方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2005, 26(S1): 70–76, 82. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.z1.014Xing Meng-dao, Li Zhen-fang, Bao Zheng, et al. Study of distributed microsatellites radar space-time-frequency imaging method[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2005, 26(S1): 70–76, 82. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.z1.014 [17] Cumming I G and Wong F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005 [18] Zhang S X, Xing M D, Xia X G, et al. Multichannel HRWS SAR imaging based on range-variant channel calibration and multi-Doppler-direction restriction ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4306–4327. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281329 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: