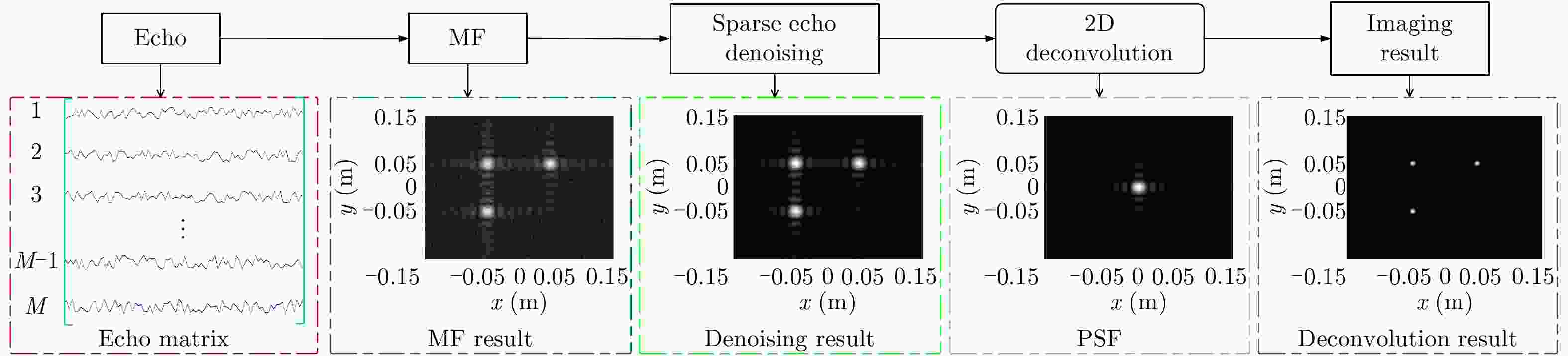
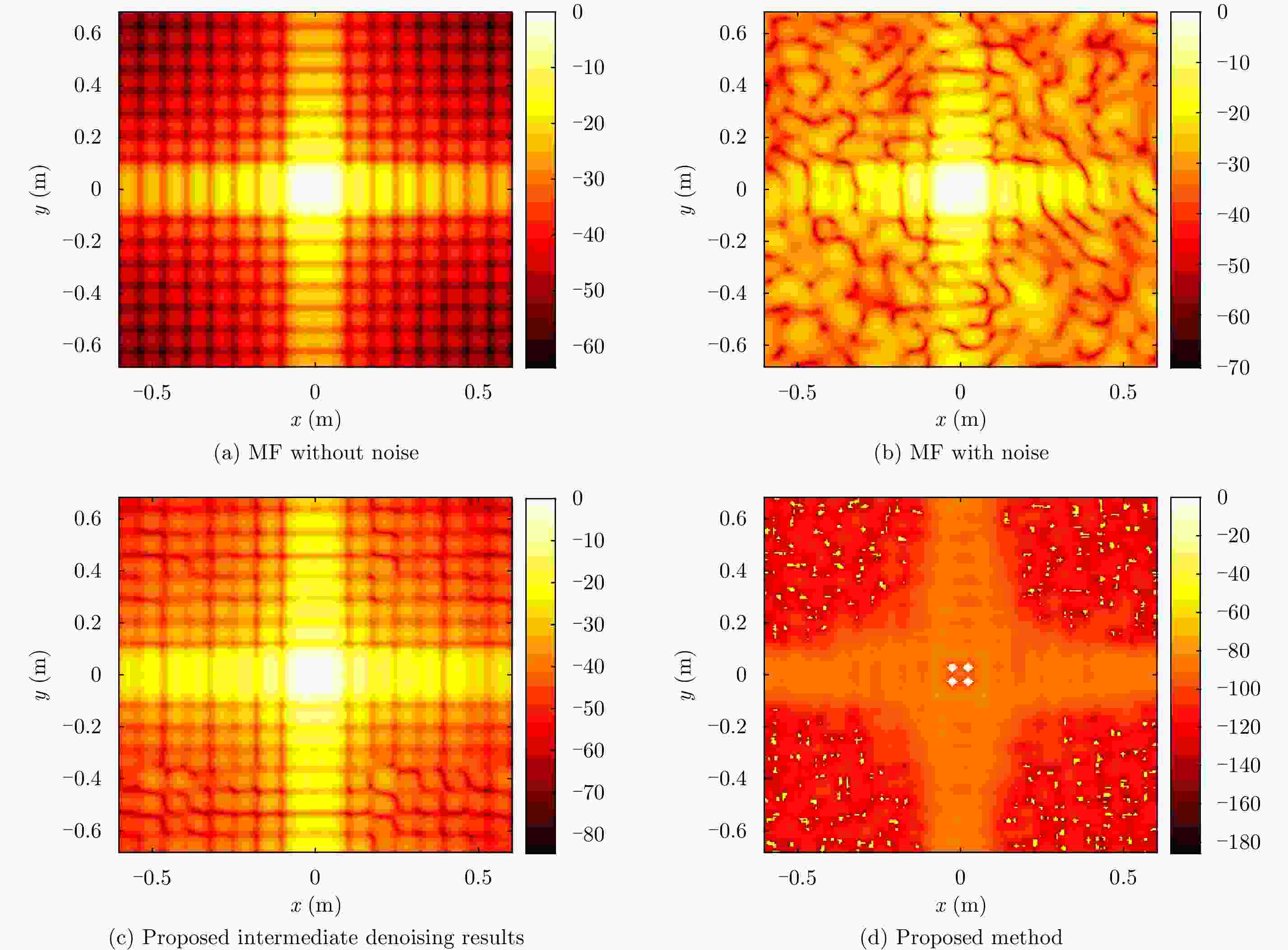
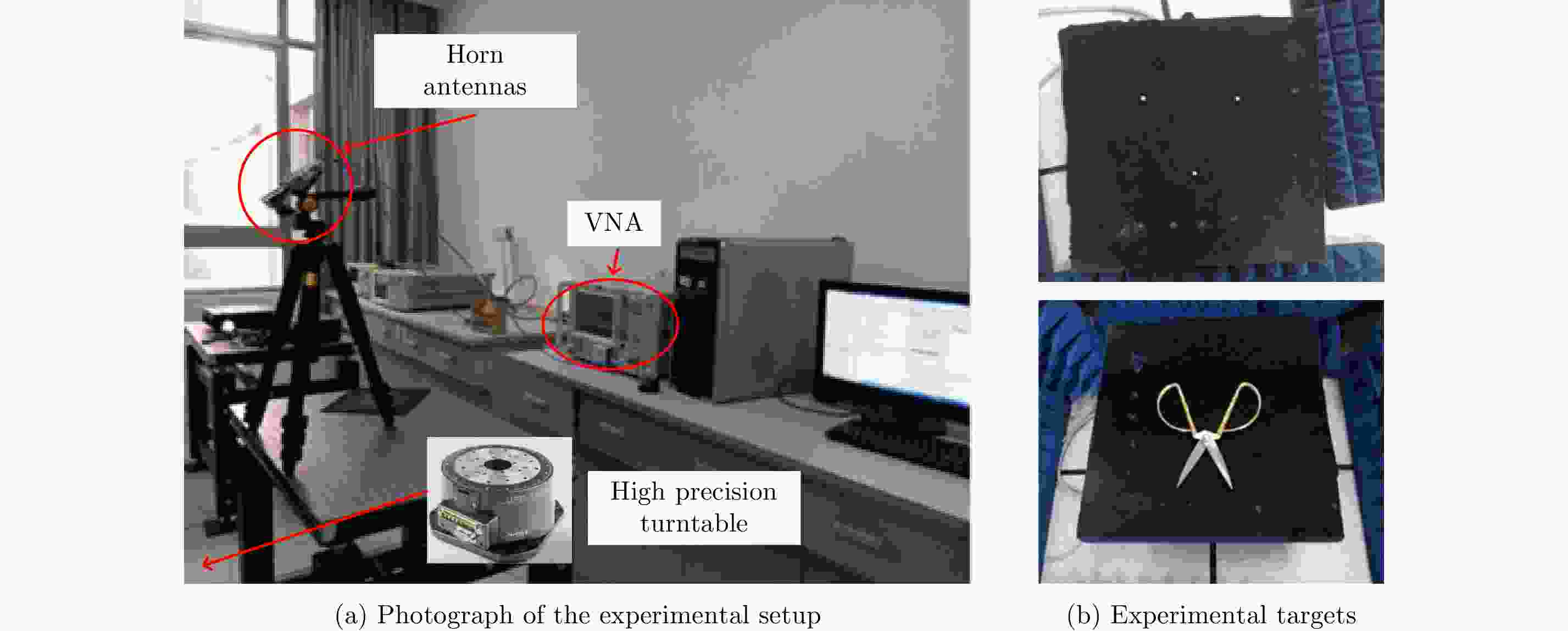
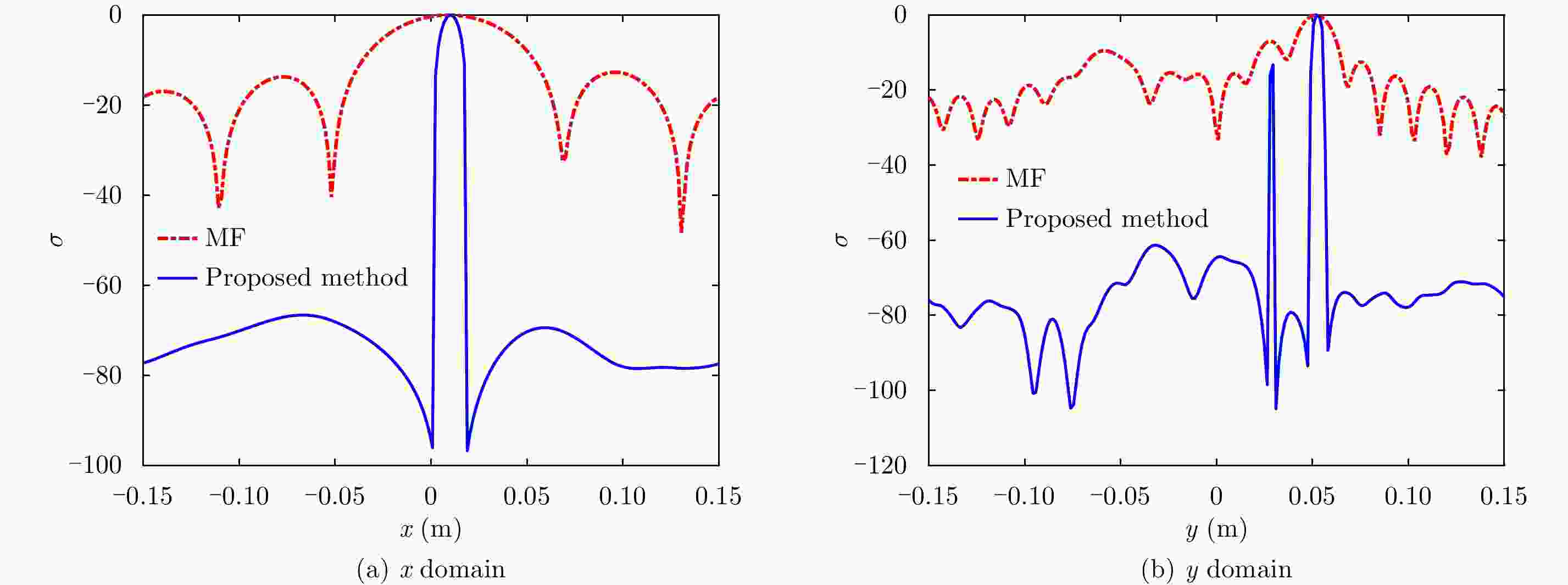
High-resolution Radar Imaging Using 2D Deconvolution with Sparse Echo Denoising
DOI: 10.12000/JR17108 cstr: 32380.14.JR17108
-
摘要: 该文提出了一种结合稀疏低秩矩阵恢复技术以及基于匹配滤波结果的反卷积算法的高分辨率雷达成像方法。对雷达回波信号进行匹配滤波操作可以最大化回波信噪比,通过推导发现经过匹配滤波操作后的回波信号可以建模为两维卷积的形式,对该结果做维纳滤波解卷积可以获得较高的分辨率。然而典型的解卷积算法面临着病态性问题,该问题会放大解卷积后的噪声、限制解卷积后的成像分辨率。文中证明了在目标稀疏分布的先验下,经过匹配滤波后的回波矩阵满足稀疏低秩的特性。在这种情况下,利用回波矩阵的稀疏低秩矩阵特征可以进一步提高信噪比,以减轻解卷积的病态性问题以及点扩散函数的平滑卷积造成目标散射低分辨率的影响。仿真实验以及实测数据证明了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: This study proposes a high-resolution radar imaging method combined with the sparse low-rank matrix recovery technique and the deconvolution algorithm based on the matched filtering result. We establish a two-Dimensional (2D) convolution model for the radar signal after the Matched Filter (MF) to maximize the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and use the 2D deconvolution algorithm of the Wiener filter to obtain a high resolution. However, representative deconvolution algorithms are confronted with an ill-posed problem, which magnifies the noise while influencing the imaging resolution. Prior to this study, the echo matrix after the MF was proven to be sparse and low rank under the constraint of a sparsely distributed target. The target distribution is smoothed by the influence of the point spread function. Hence, inspired by these points, we further enhance the SNR of the echo matrix based on the sparse and low-rank characteristics to alleviate the ill-posed problem of deconvolution and the poor resolution of the Wiener filter. The performance of the proposed method is demonstrated by the real experimental data.
-
Table 1. Simulation parameters
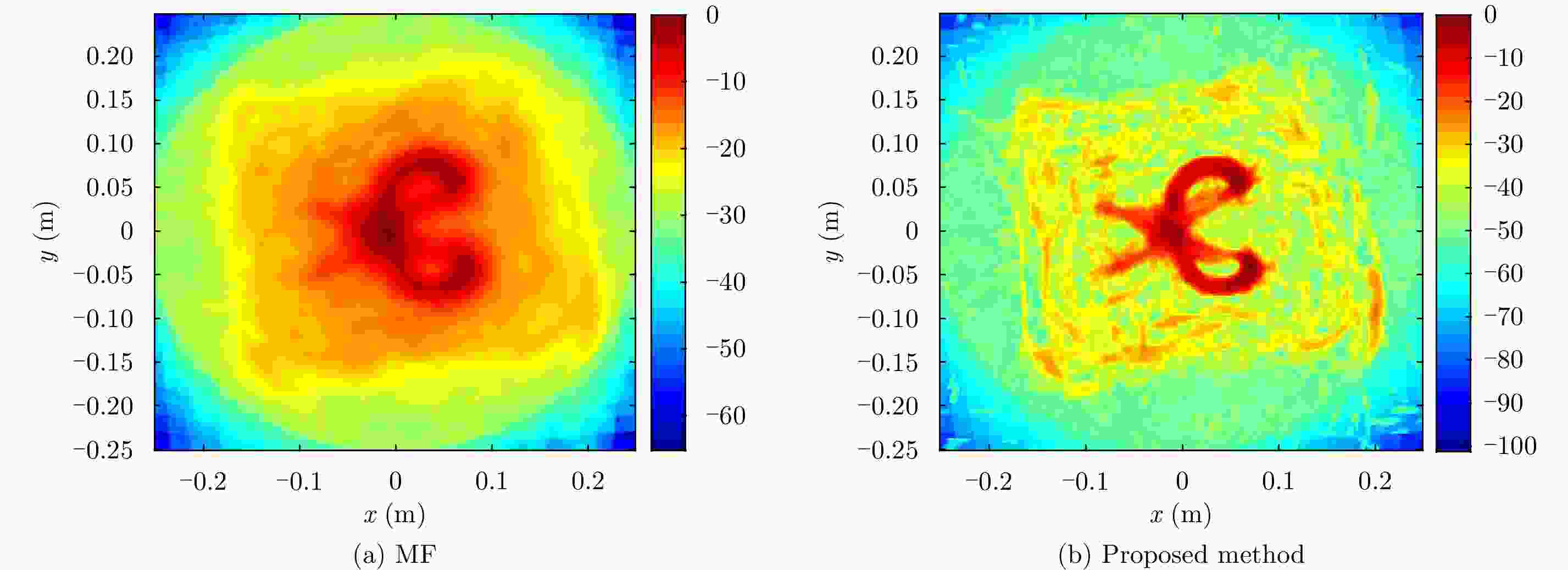
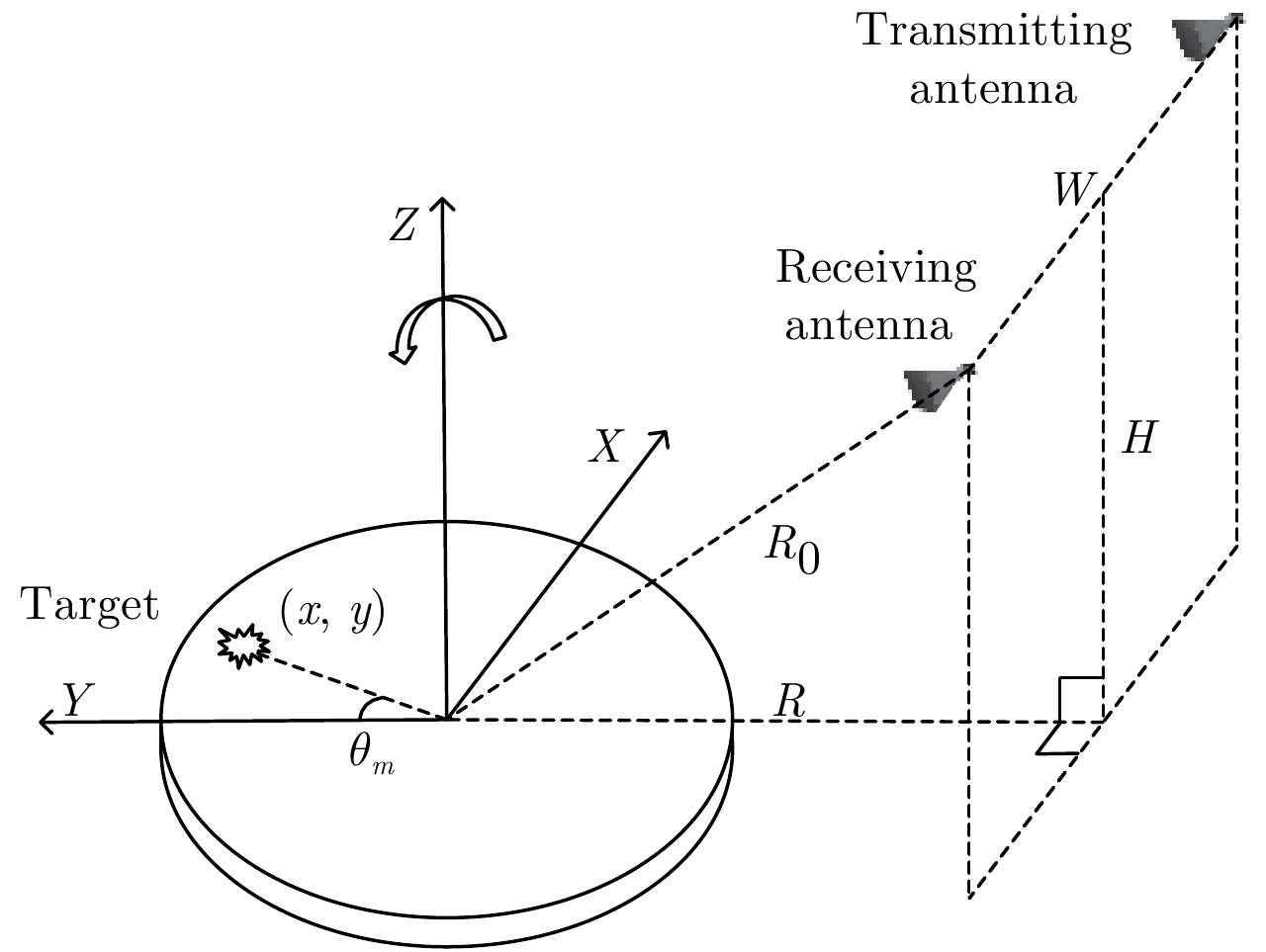
Parameter Value Parameter Value ${{M}}$ 256 $R$ 1 m ${{N}}$ 500 $H$ 0.7 m $\Delta f$ 10 MHz W 0.04 m $\Delta \theta $ 0.009° SNR –15 dB Table 2. Entropies of imaging results
Target MF Our proposed method Mental spheres 8.7282 4.8429 Scissors 8.9433 7.0454 -
[1] Hu K B, Zhang X L, Shi J, et al. A novel synthetic bandwidth method based on BP imaging for stepped-frequency SAR[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(8): 741–750. [2] Yiğit E. Compressed sensing for millimeter-wave ground based SAR/ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2014, 35(11): 932–948. [3] Zhang S S, Zhang W, Zong Z L, et al. High-resolution bistatic ISAR imaging based on two-dimensional compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(5): 2098–2111. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2408337. [4] Kreucher C and Brennan M. A compressive sensing approach to multistatic radar change imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1107–1112. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2247408. [5] Wang T Y, Lu X F, Yu X F, et al. A fast and accurate sparse continuous signal reconstruction by homotopy DCD with non-convex regularization[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(4): 5929–5951. DOI: 10.3390/s140405929. [6] Ding L and Chen W D. MIMO radar sparse imaging with phase mismatch[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 816–820. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2363110. [7] Ding L, Chen W D, Zhang W Y, et al. MIMO radar imaging with imperfect carrier synchronization: A point spread function analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 2236–2247. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140428. [8] Liu C C and Chen W D. Sparse self-calibration imaging via iterative MAP in FM-based distributed passive radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 538–542. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2212272. [9] Wang X, Zhang M, and Zhao J. Efficient cross-range scaling method via two-dimensional unitary ESPRIT scattering center extraction algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(5): 928–932. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2367521. [10] Yang L, Zhou J X, Xiao H T, et al.. Two-dimensional radar imaging based on continuous compressed sensing[C]. Proceedings of the 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 2015: 710–713. DOI: 10.1109/APSAR.2015.730630. [11] Guan J C, Yang J Y, Huang Y L, et al. Maximum a posteriori-based angular superresolution for scanning radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 2389–2398. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120555. [12] Parekh A and Selesnick I W. Enhanced low-rank matrix approximation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(4): 493–497. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2535227. [13] Lin Z C, Chen M M, and Ma Y. The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices[R]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1009.5055, 2010. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.10.010. [14] Pedone M, Bayro-Corrochano E, Flusser J, et al. Quaternion wiener deconvolution for noise robust color image registration[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(9): 1278–1282. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2398033. [15] Zhu J, Zhu S Q, and Liao G S. High-resolution radar imaging of space debris based on sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(10): 2090–2094. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2449861. [16] Horn R A and Johnson C R. Matrix Analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990. [17] Donoho D L. De-noising by soft-thresholding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1995, 41(3): 613–627. DOI: 10.1109/18.382009. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: