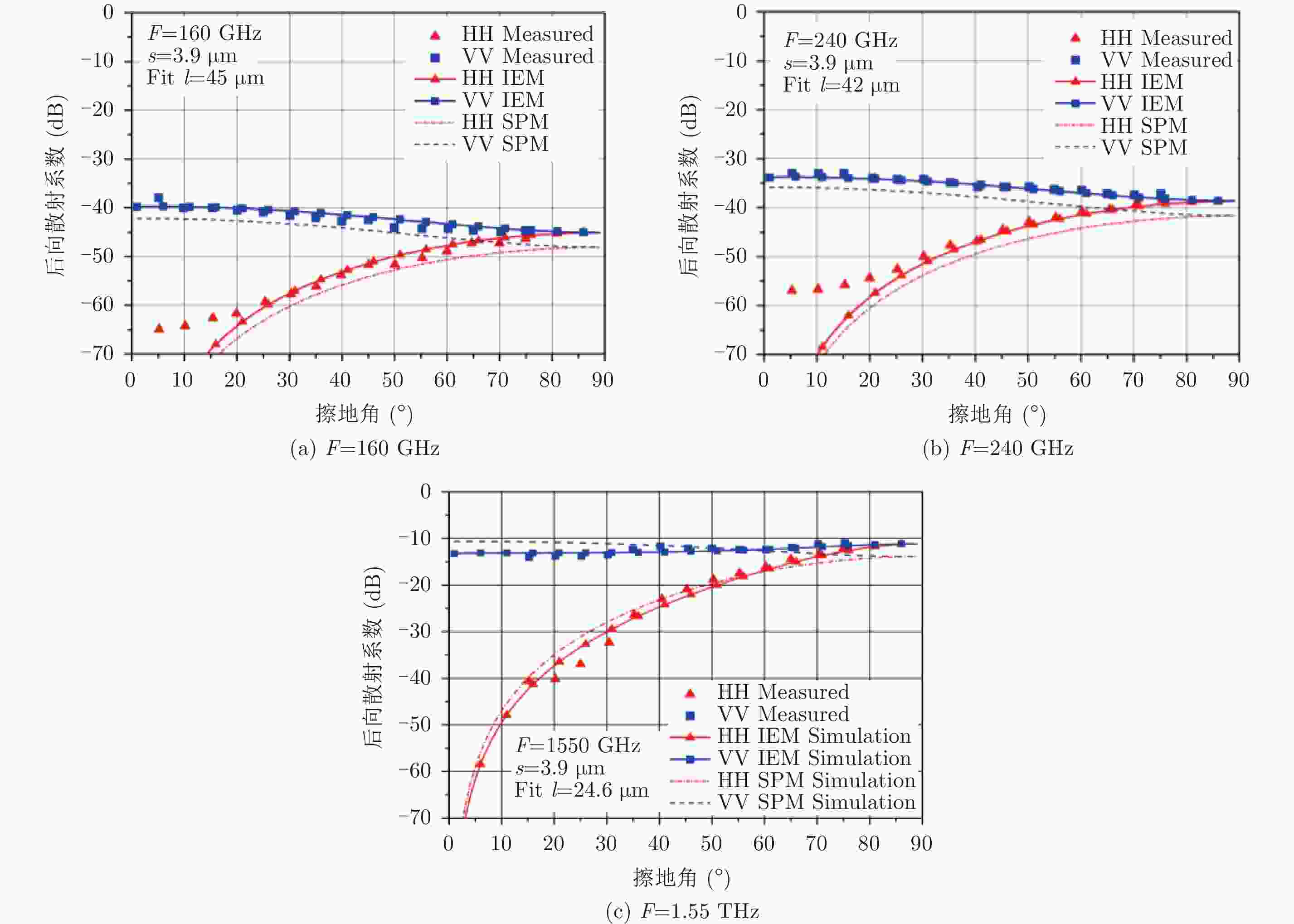
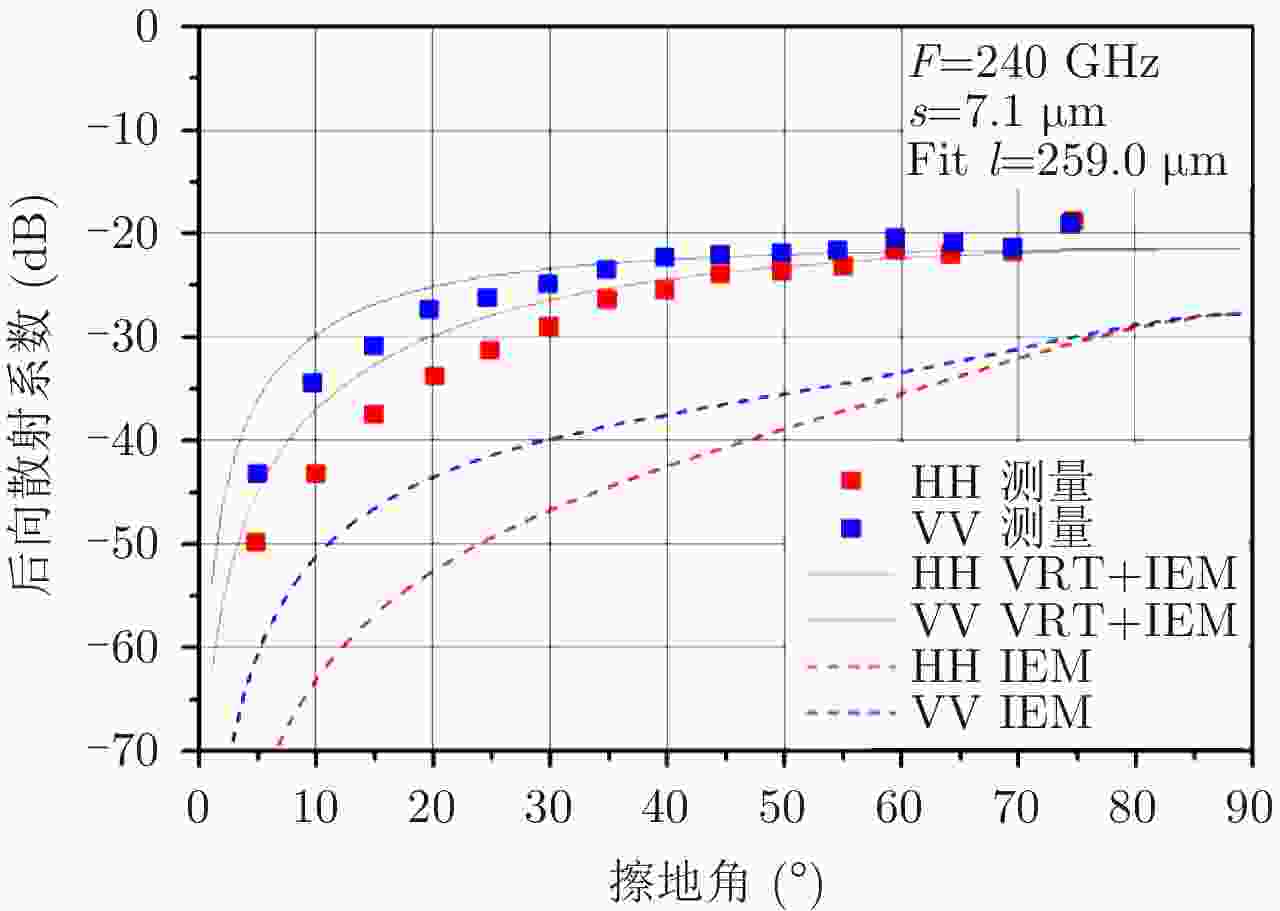
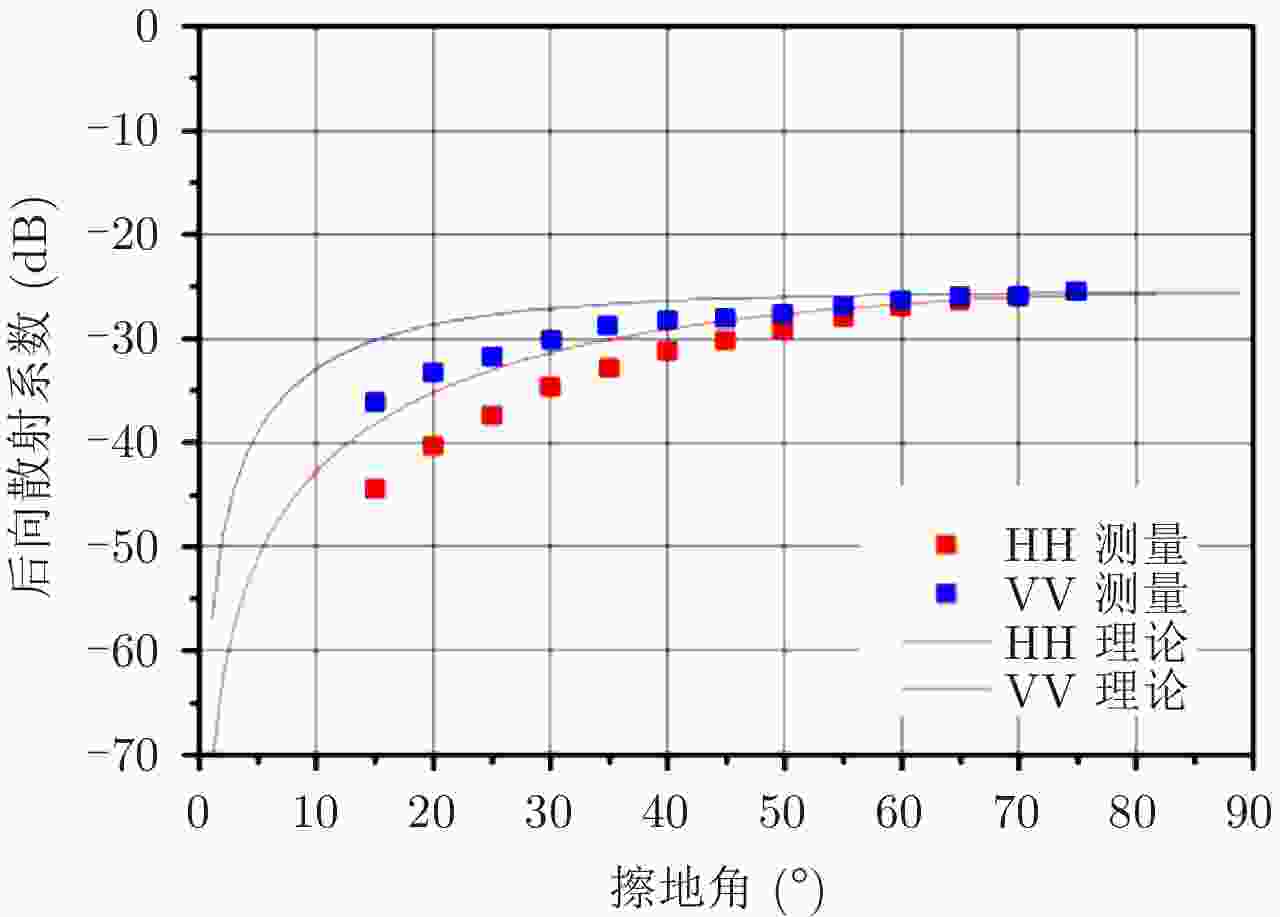
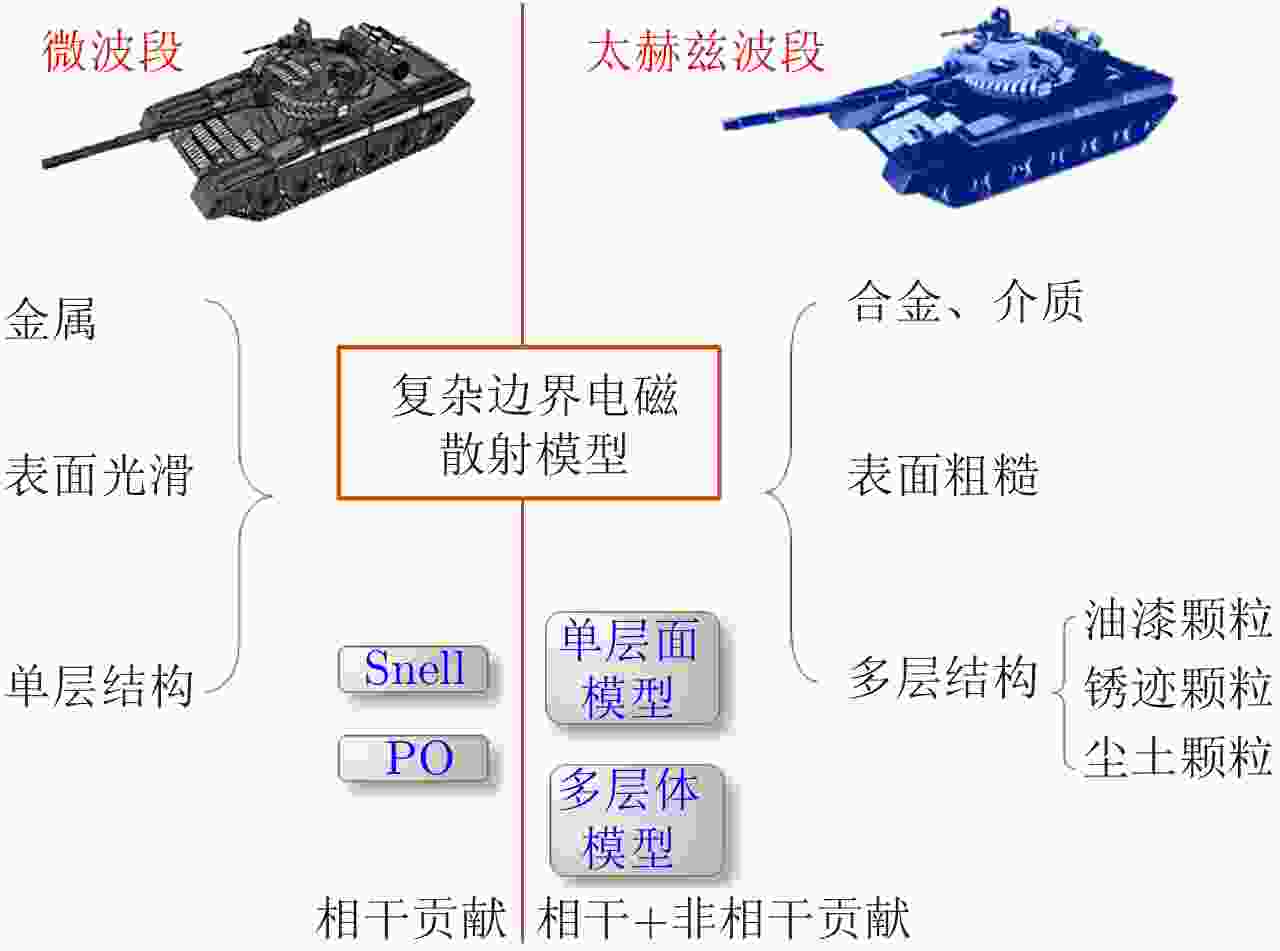
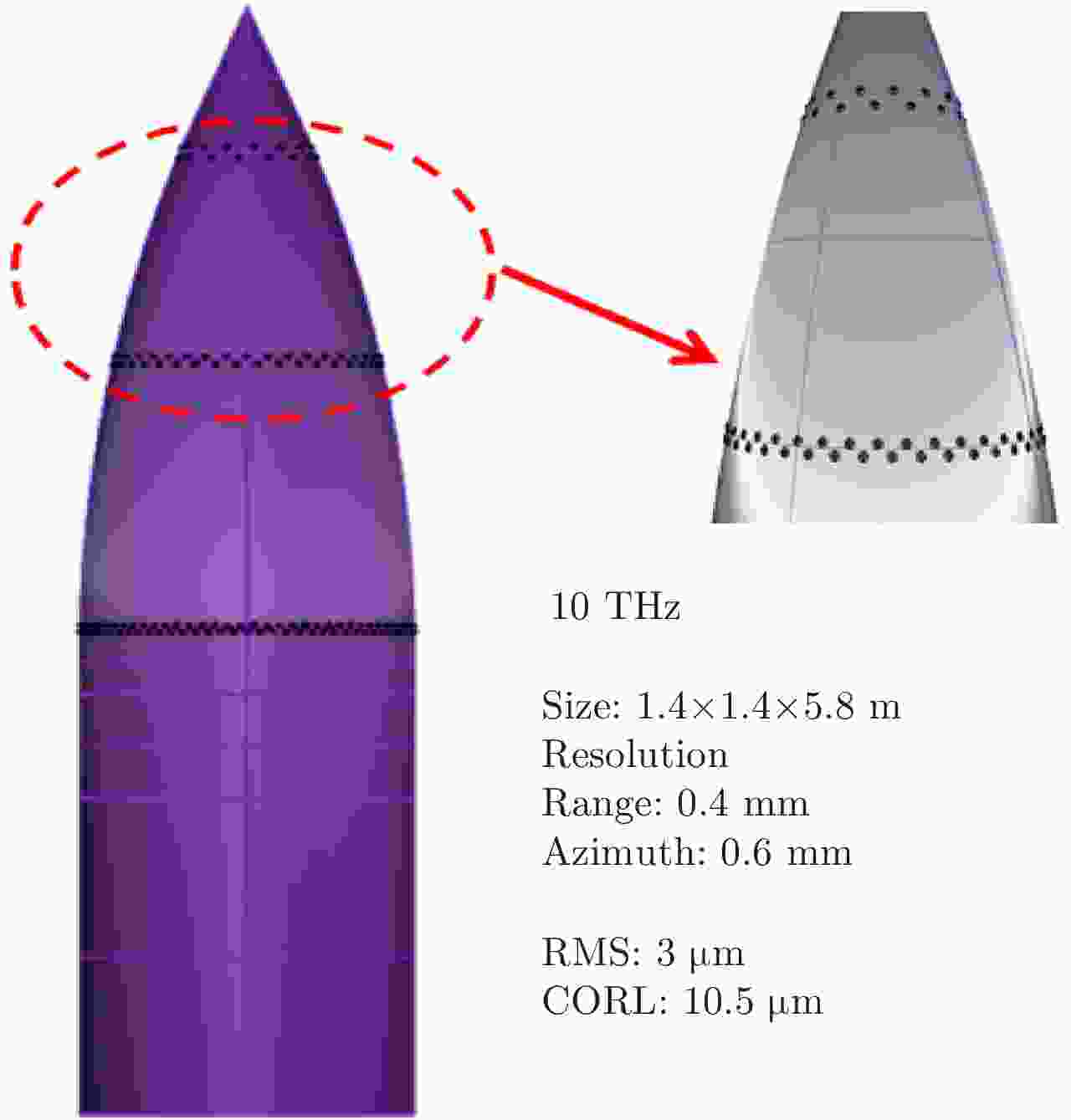
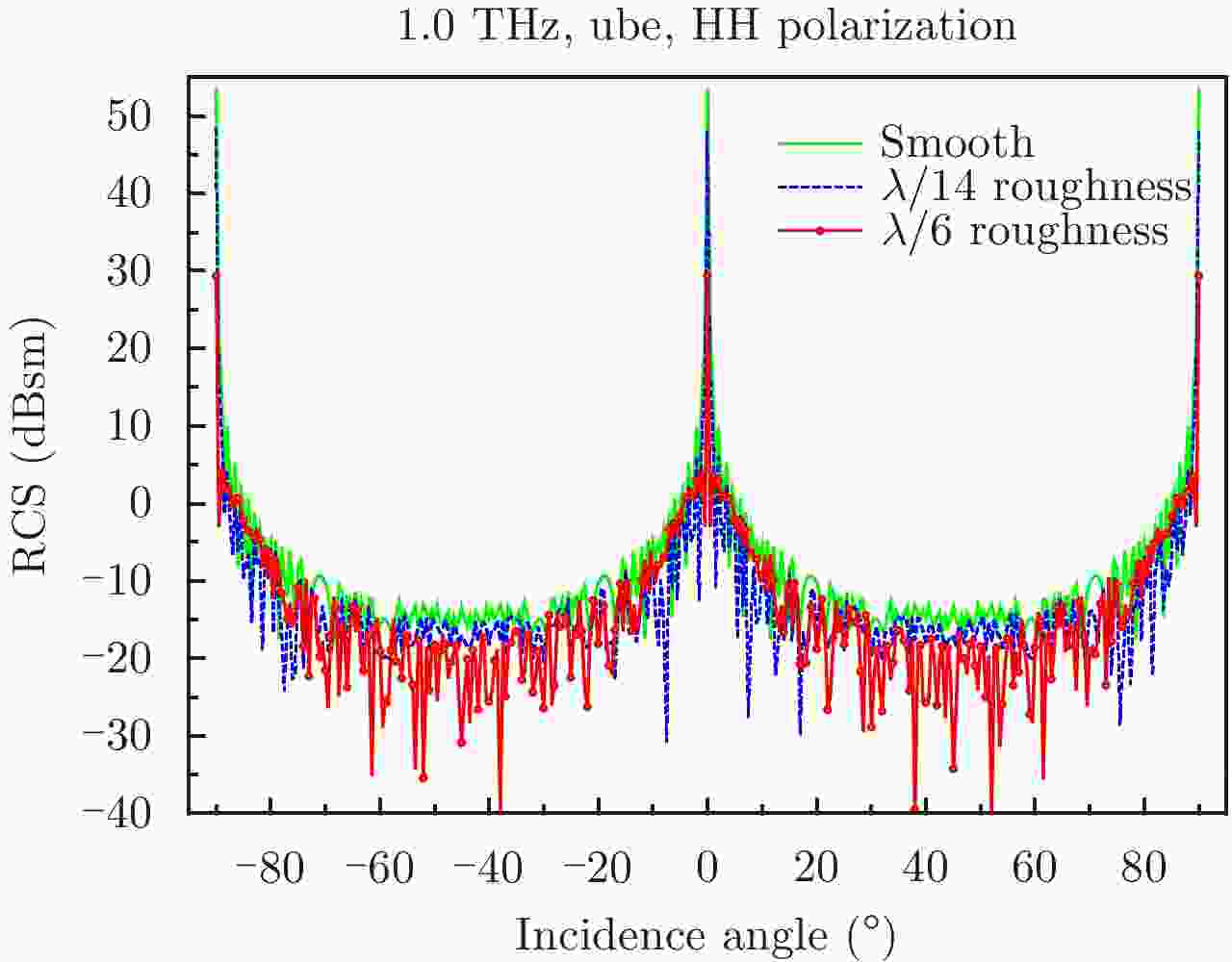
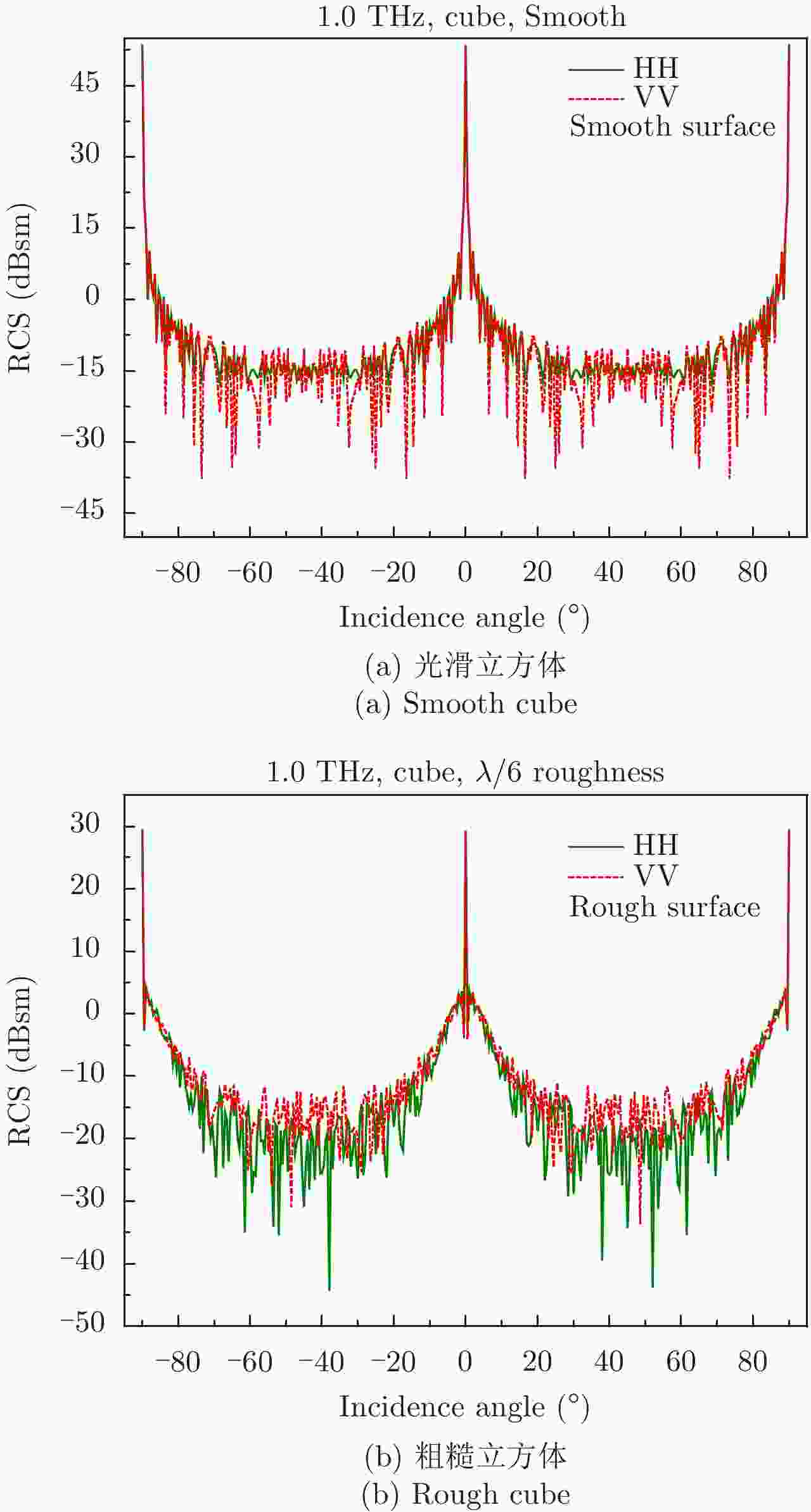
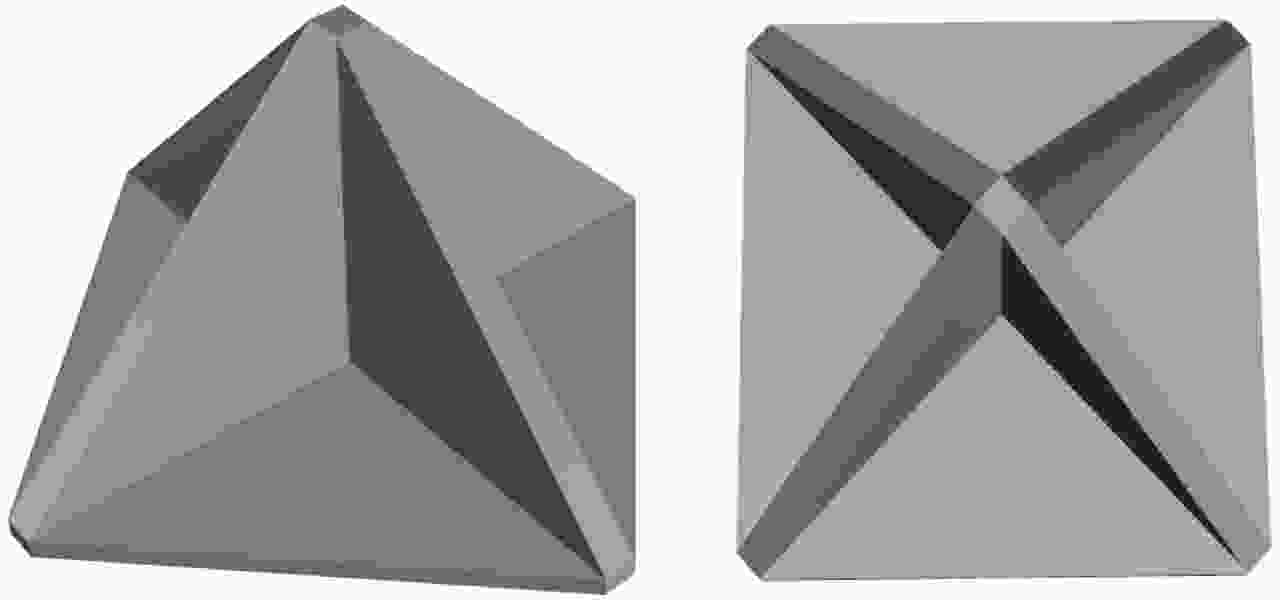
| [1] |
Siegel P H. Terahertz technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 910–928. DOI: 10.1109/22.989974
|
| [2] |
许景周, 张希成. 太赫兹科学技术和应用[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2007.Xu Jing-zhou and Zhang Xicheng. Terahertz Science and Technology and its Application[M]. Beijing: Beijing University Press, 2007.
|
| [3] |
刘盛纲. 太赫兹科学技术的新发展[J]. 中国基础科学科学前沿, 2006, 8(1): 7–12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2006.01.003Liu Sheng-gang. Recent development of terahertz science and technology[J]. China Basic Science, 2006, 8(1): 7–12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2006.01.003
|
| [4] |
Ferguson B and Zhang X C. Materials for terahertz science and technology[J]. Nature Materials, 2002, 1(1): 26–33. DOI: 10.1038/nmat708
|
| [5] |
Goyette T M, Gatesman A, Horgan T M, et al.. THz compact range radar systems[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Microwave Symposium, Philadelphia, 2003.
|
| [6] |
Goyette T M, Dickinson J C, Waldman J, et al.. Three-dimensional fully polarimetric W-band ISAR imagery of scale-model tactical targets using a 1.56-THz compact range[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 5095, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery X, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2003.
|
| [7] |
Digiovanni D A, Gatesman A J, and Giles R H. Backscattering of ground terrain and building materials at submillimeter-wave and terahertz frequencies[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 8715, Passive and Active Millimeter-Wave Imaging XVI, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, 2013, 8715: 871507.
|
| [8] |
Tamminen A, Ala-Laurinaho J, and Räisänen A V. Indirect holographic imaging: Evaluation of image quality at 310 GHz[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 7670, Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technology XIII, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2010, 7670: 76700A.
|
| [9] |
Tamminen A, Lonnqvist A, Mallat J, et al. Monostatic reflectivity and transmittance of radar absorbing materials at 650 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(3): 632–637. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.916881
|
| [10] |
Iwaszczuk K, Heiselberg H, and Jepsen P U. Terahertz radar cross section measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(25): 26399–26408. DOI: 10.1364/OE.18.026399
|
| [11] |
Iwaszczuk K, Strikwerda A C, Fan K B, et al. Flexible metamaterial absorbers for stealth applications at terahertz frequencies[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(1): 635–643. DOI: 10.1364/OE.20.000635
|
| [12] |
Gente R, Jansen C, Geise R, et al. Scaled bistatic radar cross section measurements of aircraft with a fiber-coupled THz time-domain spectrometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2012, 2(4): 424–431. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2012.2192929
|
| [13] |
王瑞君, 王宏强, 庄钊文, 等. 太赫兹雷达技术研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2013, 50(4): 040001Wang Rui-jun, Wang Hong-qiang, Zhuang Zhao-wen, et al. Research progress of Terahertz radar technology[J]. Laser&Optoelectronics Progress, 2013, 50(4): 040001
|
| [14] |
武亚君, 黄欣, 徐秀丽, 等. 太赫兹目标RCS缩比测量技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(6): 1541–1544. DOI: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1541Wu Ya-jun, Huang Xin, Xu Xiu-li, et al. Radar cross section measurement technique of scale-model targets at terahertz[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(6): 1541–1544. DOI: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1541
|
| [15] |
梁达川, 谷建强, 韩家广, 等. 宽频太赫兹时域雷达系统[J]. 空间电子技术, 2013(4): 99–103. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.04.023Liang Da-chuan, Gu Jian-qiang, Han Jia-guang, et al. Terahertz time-domain radar system[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2013(4): 99–103. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.04.023
|
| [16] |
江舸, 成彬彬, 张健. 基于0.14 THz成像雷达的RCS测量[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2014, 12(1): 19–23. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201401.0019Jiang Ge, Cheng Bin-bin, and Zhang Jian. 0.14 THz radar imaging based Radar Cross Section measurement[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2014, 12(1): 19–23. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201401.0019
|
| [17] |
DiGiovanni D A, Gatesman A J, Giles R H, et al.. Electromagnetic scattering from dielectric surfaces at millimeter wave and terahertz frequencies[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 9462, Passive and Active Millimeter-Wave Imaging XVIII, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, 2015, 9462: 94620H.
|
| [18] |
DiGiovanni D A, Gatesman A J, Goyette T M, et al.. Surface and volumetric backscattering between 100 GHz and 1.6 THz[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 9078, Passive and Active Millimeter-Wave Imaging XVII, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, 2014, 9078: 90780A.
|
| [19] |
Soto-Crespo J M, Nieto-Vesperinas M, and Friberg A T. Scattering from slightly rough random surfaces: A detailed study on the validity of the small perturbation method[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(7): 1185–1201. DOI: 10.1364/JOSAA.7.001185
|
| [20] |
Hsieh C Y, Fung A K, Nesti G, et al. A further study of the IEM surface scattering model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(4): 901–909. DOI: 10.1109/36.602532
|
| [21] |
Jin Y Q. Electromagnetic Scattering Modelling for Quantitative Remote Sensing[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 1993.
|
| [22] |
金亚秋. 矢量辐射传输理论和参数反演[M]. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 1994.Jin Ya-qiu. Theory of Vector Radiation Transmission and Parameter Inversion[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press, 1994.
|
| [23] |
金亚秋. 电磁散射和热辐射的遥感理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993.Jin Ya-qiu. Remote Sensing Theory of Electromagnetic Scattering and Thermal Radiation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993.
|
| [24] |
Kozlov A I, Ligthart L P, Logvin A I, et al.. Mathematical and Physical Modelling of Microwave Scattering and Polarimetric Remote Sensing: Monitoring the Earth’s Environment Using Polarimetric Radar: Formulation and Potential Applications[M]. New York: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2001: 43–65.
|
| [25] |
Xu F and Jin Y Q. Bidirectional analytic ray tracing for fast computation of composite scattering from electric-large target over a randomly rough surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 57(5): 1495–1505. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2016691
|
| [26] |
Chen H, Zhang M, Zhao Y W, et al. An efficient slope-deterministic facet model for SAR imagery simulation of marine scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(11): 3751–3756. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2071349
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: