Improved Change Detection Method for Flood Monitoring
-
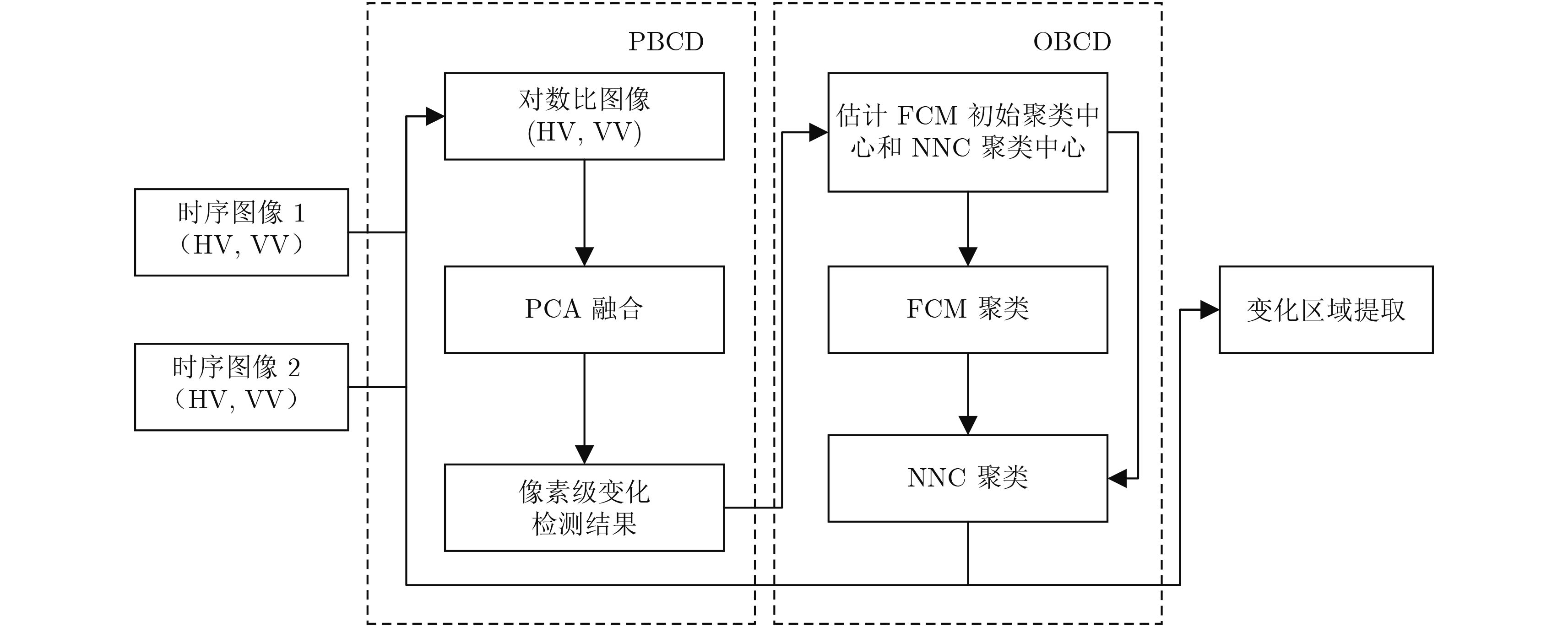
摘要: 针对多时相合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)图像的变化检测,该文提出一种改进的混合变化检测方法来提高检测精度。该方法首先采用基于像素级的变化检测方法提取初始变化区域,并以此估计初始聚类中心;然后采用模糊聚类(FCM)将变化前后SAR图像分为3类,即水体区域、背景区域、过渡区域;接着采用最近距离聚类(NNC)将过渡区域像素进一步划分为水体和背景两部分,合并所有水体像素,实现洪水区域的提取。最后得到的洪水区域差异图即为最终的变化检测结果。该文采用Sentinel-1A获取的淮河与鄱阳湖水域数据进行算法验证,实验表明,该文方法的检测率较高,且总体误差较低。
-
关键词:
- 变化检测 /
- SAR /
- 模糊聚类 /
- 混合变化检测 /
- Sentinel-1A
Abstract: An improved Hybrid Change Detection (HCD) method is proposed for multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. Firstly, a Pixel-Based Change Detection (PBCD) method is used to extract the initial change area, and the initial cluster center is estimated based on its results. Then, Fuzzy Clustering Method (FCM) is used to get three clusters, which including water, background, and the intermediate area. The Nearest Neighbor Clustering (NNC) is adopted as the second-level clustering to divide the pixels belonging to the intermediate area into water and background respectively, afterwards merge all pixels belonging to water. Finally, the difference map of flood region in the time series images is calculated to get the final change detection result. The algorithm is validated by the Sentinel-1A data obtained from Huaihe River and Poyang Lake. The results show that our proposed method can achieve better correctness and has lower total error compared to other methods. -
表 1 Sentinel-1A数据参数(干涉宽测绘带模式)
Table 1. Parameters of Sentinel-1A product (IW)
参数 数值 成像波段 C 载频 5.4 GHZ 幅宽 250 km 入射角 38.9° 极化 VV HV 地距分辨率 20×22 m 表 2 变化检测精度对比分析
Table 2. Quantitative evalutaions and comparison of change detection results
-
[1] Wang Y, Du L, and Dai H. Unsupervised SAR image change detection based on SIFT keypoints and region information[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(7): 931–935. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2554606. [2] Addabbo A D, Refice A, Pasquariello G, et al. A Bayesian network for flood detection combining SAR imagery and ancillary data[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(6): 3612–3625. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2520487. [3] Hussain M, Chen D, Cheng A, et al. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches[J].ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 80(2): 91–106. DOI: 10.1016/ j.isprsjprs.2013.03.006. [4] Chen G, Hay G, Carvalho L M T, et al. Object-based change detection[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2012, 33(14): 4434–4457. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2011.648285. [5] Ghofrani Z, Mokhtarzade M, Sahebi M R, et al. Evaluating coverage changes in national parks using a hybrid change detection algorithm and remote sensing[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2014, 8(1): 1–16. DOI: 10.1117/1.JRS.8.083646. [6] Huo C, Zhou Z, Lu H, et al. Fast object-level change detection for VHR images[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(1): 118–122. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2028438. [7] Hachicha S and Chaabane F. Comparison of change detection indicators in SAR images[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 109–112. [8] Lu J, Li J, Chen G, et al. Improving pixel-based change detection accuracy using an object-based approach in multitemporal SAR flood images[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3486–3496. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2416635. [9] Pulvirenti L, Chini M, Pierdicca N, et al. Flood monitoring using multi-temporal COSMO-SkyMed data: Image segmentation and signature interpretation[J].Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(1): 990–1002. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.12.002. [10] Avendano J, Mora S F, Vera J E, et al. Flood monitoring and change detection based on unsupervised image segmentation and fusion in multitemporal SAR imagery[C]. International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), Mexico, 2015: 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/ICEEE.2015.7357982. [11] Xiong B, Chen J M, and Kuang G. A change detection measure based on a likelihood ratio and the statistical properties of SAR intensity images[J].Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 3(3): 267–275. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2011.572093. [12] Lu J, Giustarini L, Xiong B, et al. Automated flood detection with improved robustness and efficiency using multi-temporal SAR data[J].Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 5(3): 240–248. DOI: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.898190. [13] Schmitt M and Stilla U. Adaptive multilooking of airborne single-pass multi-baseline InSAR stacks[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 51(1): 305–312. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2238947. [14] 浮瑶瑶, 柳彬, 张增辉, 等. 基于词包模型的高分辨SAR图像变化检测与分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 101–110. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13134.Fu Yaoyao, Liu Bin, Zhang Zenghui, et al. Change detection and analysis of high resolution synthetic aperture radar images based on bag-of-words model[J].Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 101–110. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13134. [15] Celik T and Ma K K. Multitemporal image change detection using undecimated discrete wavelet transform and active contours[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 706–716. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2066979. [16] Salehi S, Valadan Z, and Mohammad J. Unsupervised change detection based on improved Markov random field technique using multichannel synthetic aperture radar images[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2014, 8(1): 5230–5237. DOI: 10.1117/1.JRS.8.083591. [17] 安成锦, 牛照东, 李志军, 等. 典型Otsu算法阈值比较及其SAR图像水域分割性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426.An Chengjin, Niu Zhaodong, Li Zhijun, et al. Otsu threshold comparison and SAR water segmentation result analysis[J].Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426. [18] Liu Z L, Li N, WANG R, et al. A novel region-merging approach for coastline extraction from Sentinel-1A IW mode SAR imagery[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 324–328. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2510745. [19] Sheng G F, Yang W, Deng X P, et al. Coastline detection in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images by integrating watershed transformation and controllable gradient vector flow (GVF) snake model[J].IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2012, 37(3): 375–383. DOI: 10.1109/JOE.2012.2191998. [20] 张慧哲, 王坚. 基于初始聚类中心选取的改进FCM聚类算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2009, 36(6): 206–209. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002–137X.2009.06.055.Zhang Huizhe and Wang Jian. Improved fuzzy C means clustering algorithm based on selecting initial clustering centers[J].Computer Science, 2009, 36(6): 206–209. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002–137X.2009.06.055. [21] Li H C, Celik T, Longbotham N, et al. Gabor feature based unsupervised change detection of multitemporal SAR images based on two-level clustering[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(12): 2458–2462. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2484220. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: