Analysis of Crosstalk Impact on the Cloude-decomposition-based Scattering Characteristic
-
摘要: 串扰是极化SAR系统的主要误差源之一,也是用于衡量极化定标质量的参考指标。为研究系统串扰在具体地物分类应用中的影响,该文首先推导了串扰量作用于由Cloude分解获得的地物散射机制特征量的数学表达,并利用不同类型的实际Radarsat-2数据通过半物理仿真,验证理论分析结果。最后在实验数据上进行基于Cloude分解的H/a/Wishart非监督分类,从各类图像分类偏差比率随串扰的变化曲线中,获得满足应用需求的串扰量指标。
-
关键词:
- 极化合成孔径雷达 /
- 定标模型 /
- 串扰影响 /
- H/a/Wishart非监督分类
Abstract: Crosstalk is not only one of the main error sources in the polarimetric SAR system, but is also an indicator for evaluating calibration performance. In this paper, to determine the impact of crosstalk on land cover classification, we first retrieve the mathematical relation expressions between crosstalk and the Cloude-decomposition-based scattering characteristic. Then, we verify our theoretical conclusions in a semi-physical simulation based on Radarsat-2 polarimetric data for different land covers. Finally, we perform H/a/Wishart classification on the experimental data. From the ratio curve of pixels labeled differently under changing crosstalk, we can determine the crosstalk requirement that will meet the needs of specific applications.-
Key words:
- Polarimetric SAR /
- Calibration model /
- Crosstalk /
- H/a/Wishart classification
-
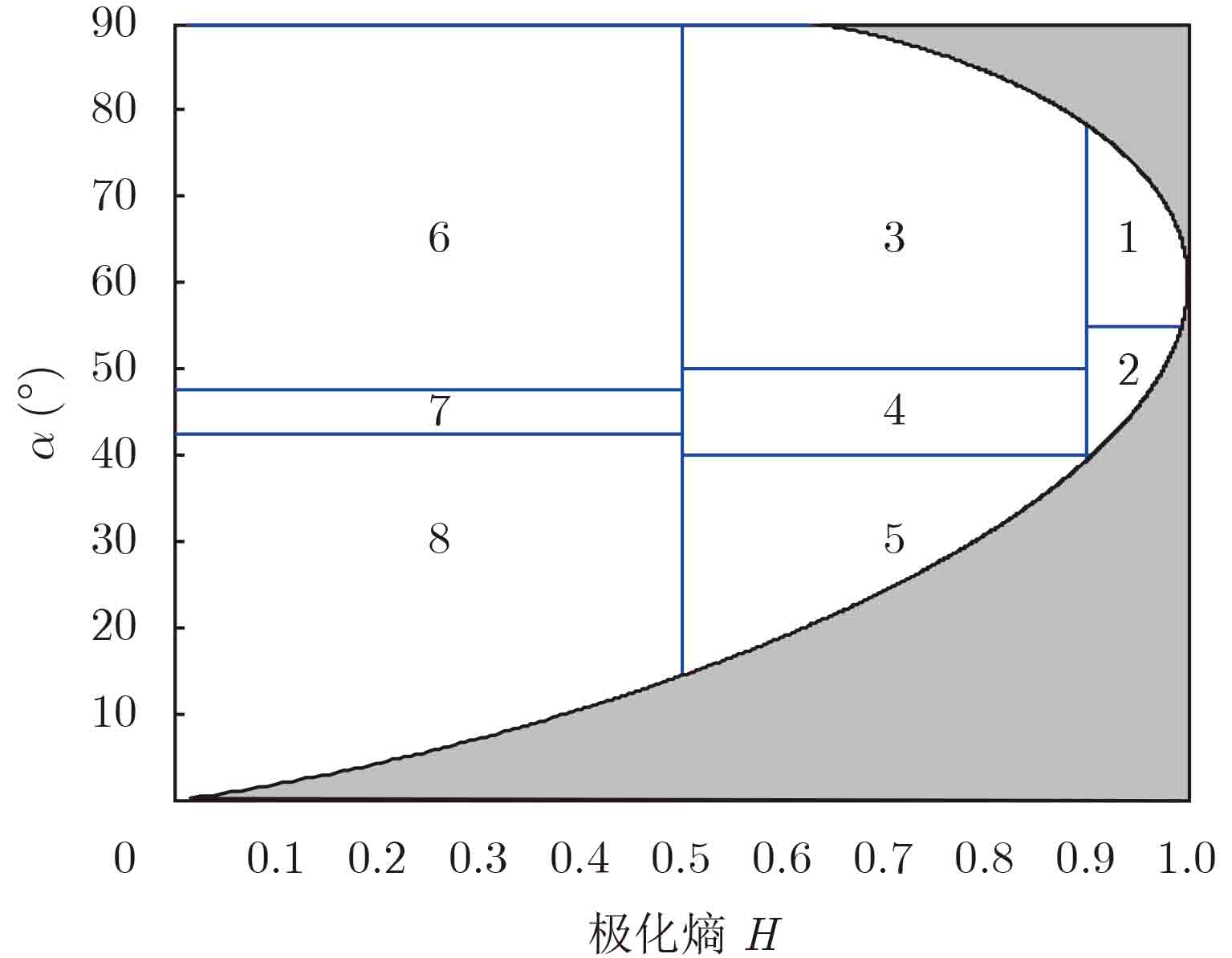
图 3 不同串扰下的中心散射机制在H-$\alpha $平面上变化,红色代表城区图像,黄色代表农田图像,蓝色代表入海口图像,绿色代表丛林图像
Figure 3. The changing of scattering center on the H-$\alpha $ plane under different crosstalk, red represents the urban area, yellow represents the agricultural field, blue represents the estuary scene, and green represents the forest area
图 5 不同串扰下的 $H/\alpha /{\rm{Wishart}}$分类结果偏差比例变化曲线,红色代表城区图像,黄色代表农田图像,蓝色代表入海口图像,绿色代表丛林图像,黑色虚线表示分类偏差率5%指标
Figure 5. The bias of $H/\alpha /{\rm{Wishart}}$ classification results under different crosstalk, red represents the urban area, yellow represents the agricultural field, blue represents the estuary scene, and green represents the forest area, the black dashed line denotes the bias less than 5%
表 1 数据情况说明
Table 1. The description of datasets
图像编号 尺寸(像素) 距离向分辨率(m) 方位向分辨率(m) 中心视角(°) 场景 1 512×512 4.76655 4.73308 34.2372 城区 2 512×512 5.46646 4.73308 37.1864 农田 3 512×512 4.81696 4.73308 35.2785 入海口 4 512×512 4.81687 4.73308 35.2859 丛林 -
[1] Akbari V, Anfinsen S, Doulgeris A, et al. Polarimetric SAR change detection with the complex Hotelling-Lawley trace statistic[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7): 3953–3966. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2532320 [2] Doulgeris A. An automatic U-distribution and Markov Random Field segmentation algorithm for PolSAR images[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 1819–1827. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2349575 [3] Tao D, Doulgeris A, and BrekkeC. A segmentation-based CFAR detection algorithm using truncated statistics[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 2887–2898. http://munin.uit.no/handle/10037/10602 [4] Whitt M, Ulaby F, Polatin P, et al. A general polarimetric radar calibration technique[J].IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1991, 39(1): 62–67. doi: 10.1109/8.64436 [5] Freeman A. SAR calibration: An overview[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(6): 1107–1121. doi: 10.1109/36.193786 [6] Quegan S. A unified algorithm for phase and cross-talk calibration of polarimetric data-theory and observations[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(1): 89–99. doi: 10.1109/36.285192 [7] Sarabandi K, Pierce L, Dobson M, et al. Polarimetric calibration of SIR-C using point and distributed target[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 858–866. doi: 10.1109/36.406672 [8] Freeman A. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to Faraday rotation[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(8): 1617–1624. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.830161 [9] Sabry R, Vachon P, and Cole M. Prediction of polarimetric-SAR field-orientation rotation due to topographical slope variation for squint operations[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 570–574. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2092410 [10] Hu Dingsheng, Qiu Xiaolan, Hu Donghui, et al. Improved airborne PolSAR calibration algorithm based on time-variant attitude compensation[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(12): 3184–3195. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2015.1054042 [11] Touzi R, Hawkins R, and Cote S. High-precision assessment and calibration of polarimetric RADARSAT-2 SAR using transponder measurements[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 487–503. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201946 [12] Azcueta M, d’Alessandro M, Zajc T, et al. ALOS-2 preliminary calibration assessment[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 2015: 4117–4120. [13] Geudtner D, Torres R, Snoeij P, et al. Sentinel-1 mission capabilities and SAR system calibration[C]. IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, Canada, 2013: 1–4. [14] Lee J, Grunes M, Ainsworth T, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621 [15] Benz U and Pottier E. Object based analysis of polarimetric SAR data in alpha-entropy-anisotropy decomposition using fuzzy classification by eCognition[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, Austrilia, 2001, 3: 1427–1429. [16] Cao F, Hong W, Wu Y, et al. An unsupervised segmentation with an adaptive number of clusters using the Span/H/alpha/A space and the complex Wishart clustering for fully polarimetric SAR data analysis[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3454–3467. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907601 [17] Yu P, Qin A, and Clausi D. Unsupervised polarimetric SAR image segmentation and classification using region growing with edge penalty[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1302–1317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164085 [18] Dabboor M, Collins M, Karathanassi V, et al. An unsupervised classification approach for polarimetric SAR data based on the Chernoff distance for complex Wishart distribution[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(7): 4200–4213. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2227755 [19] Correia A, Freitas C, and Mura J. Evaluation of the influence of the polarimetric calibration process on the H/A/alpha decomposition[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 2010: 2039–2042. [20] Wang Y, Ainsworth T, and Lee J. Assessment of system polarization quality for polarimetric SAR imagery and target decomposition[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1755–1771. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2087342 [21] Wang C, Yu W, Wang Y, et al. Polarimetric calibration requirements on several classification schemes for land application of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J].IET Radar, Sonar &Navigation, 2013, 7(2): 113–122. [22] Lee J and Potter E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging From Basic to Application[M]. New York: CSC Press, 2009: 53–84. [23] Cloude S and Pottier E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 [24] 数学手册编写组. 数学手册[M]. 北京: 人民教育出版社, 1979: 117–120.Mathematical Manual drafting group. Mathematical Manual[M]. Beijing: People’s Education Press, 1979: 117–120. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: