Track-MT3: A Novel Multitarget Tracking Algorithm Based on Transformer Network(in English)
-
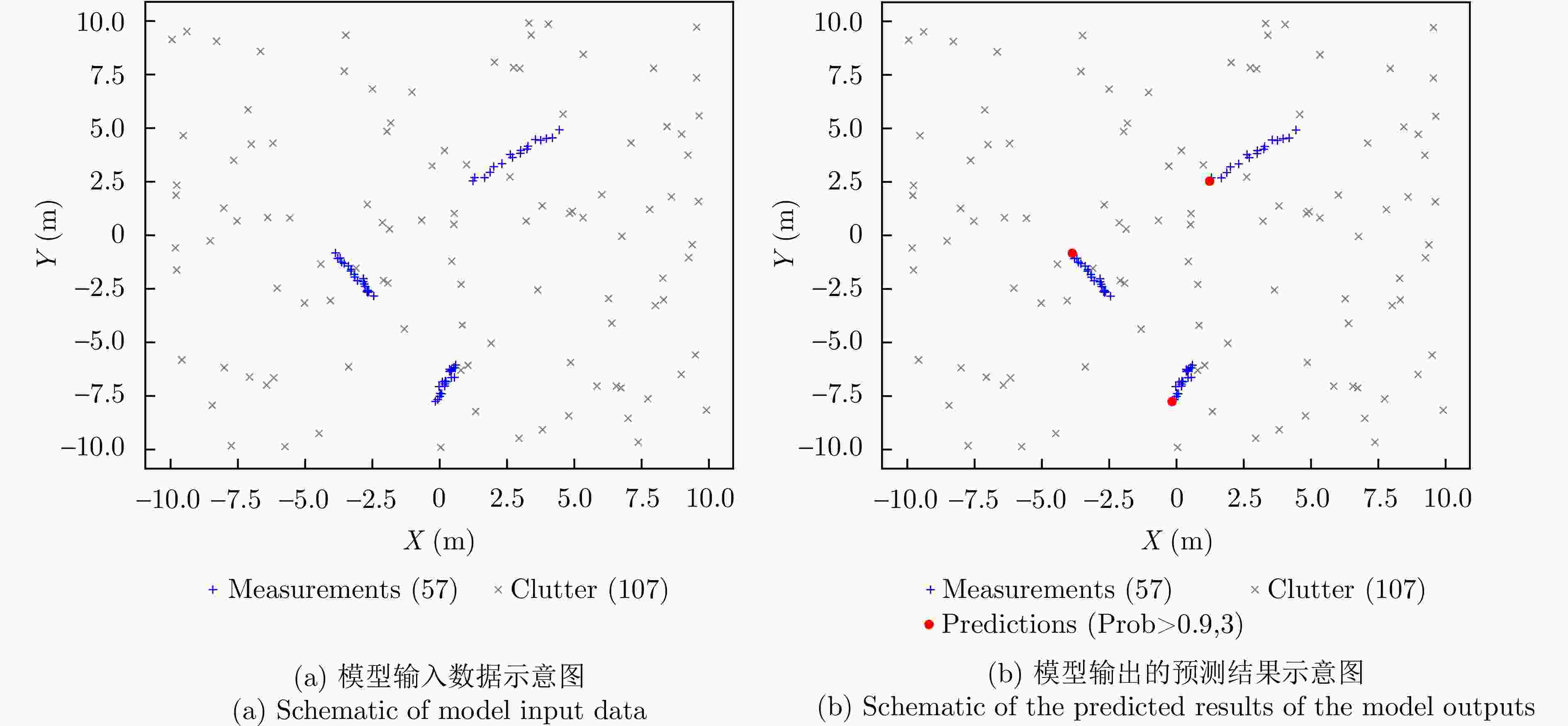
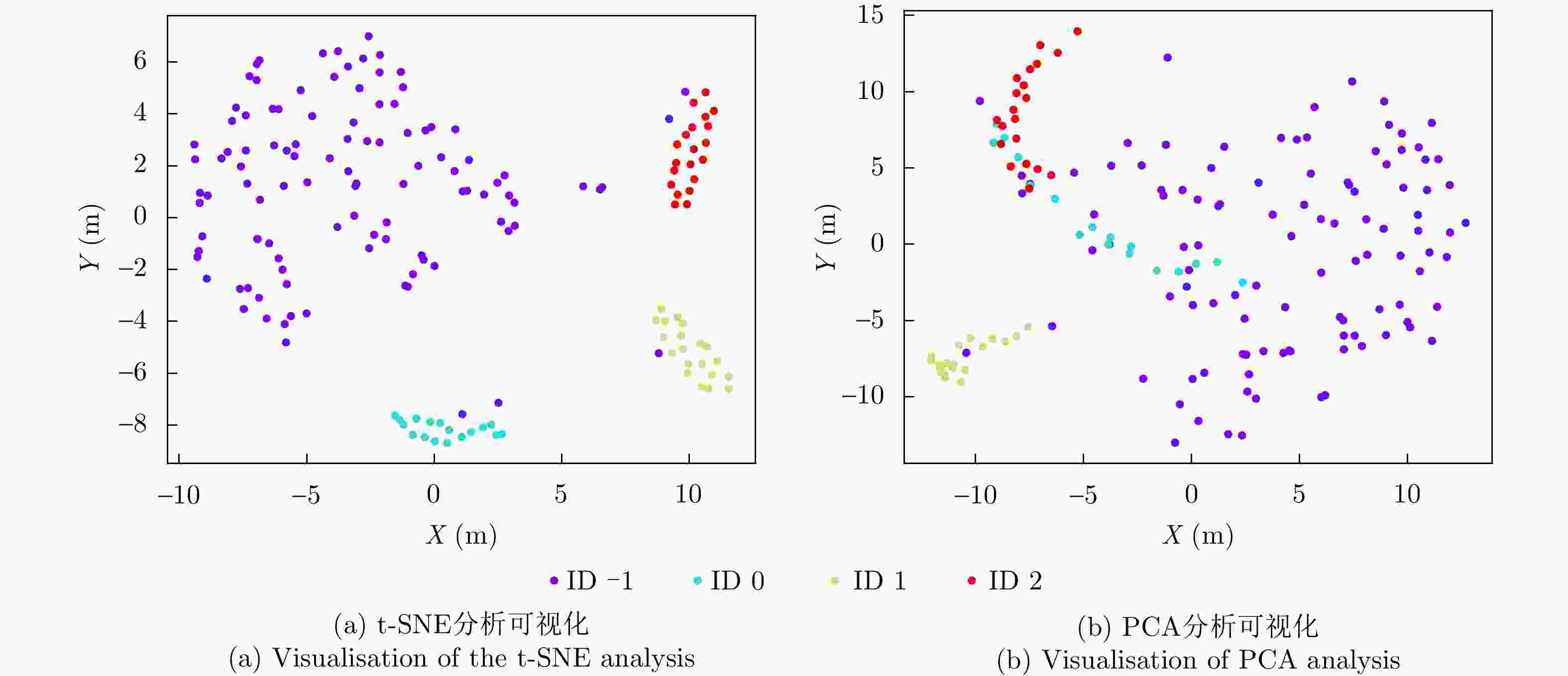
摘要: 针对复杂环境中多目标跟踪数据关联难度大、难以实现目标长时间稳定跟踪的问题,该文创新性地提出了一种基于Transformer网络的端到端多目标跟踪模型Track-MT3。首先,引入了检测查询和跟踪查询机制,隐式地执行量测-目标的数据关联并且实现了目标的状态估计任务。然后,采用跨帧目标对齐策略增强跟踪轨迹的时间连续性。同时,设计了查询变换与时间特征编码模块强化目标运动建模能力。最后,在模型训练中采用了集体平均损失函数,实现了模型性能的全局优化。通过构造多种复杂的多目标跟踪场景,并利用多重性能指标进行评估,Track-MT3展现了优于MT3等基线方法的长时跟踪性能,与JPDA和MHT方法相比整体性能分别提高了6%和20%,能够有效挖掘时序信息,在复杂动态环境下实现稳定、鲁棒的多目标跟踪。
-
关键词:
- 多目标跟踪 /
- 数据关联 /
- Transformer /
- 长时跟踪 /
- 注意力机制
Abstract: To address the challenges associated with the data association and stable long-term tracking of multiple targets in complex environments, this study proposes an innovative end-to-end multitarget tracking model called Track-MT3 based on a transformer network. First, a dual-query mechanism comprising detection and tracking queries is introduced to implicitly perform measurement-to-target data association and enable accurate target state estimation. Subsequently, a cross-frame target alignment strategy is employed to enhance the temporal continuity of tracking trajectories, ensuring consistent target identities across frames. In addition, a query transformation and temporal feature encoding module is designed to improve target motion pattern modeling by adaptively combining target dynamics information at different time scales. During model training, a collective average loss function is adopted to achieve the global optimization of tracking performance, considering the entire tracking process in an end-to-end manner. Finally, the performance of Track-MT3 is extensively evaluated under various complex multitarget tracking scenarios using multiple metrics. Experimental results demonstrate that Track-MT3 exhibits superior long-term tracking performance than baseline methods such as MT3. Specifically, Track-MT3 achieves overall performance improvements of 6% and 20% against JPDA and MHT, respectively. By effectively exploiting temporal information, Track-MT3 ensures stable and robust multitarget tracking in complex dynamic environments. -
表 1 训练样本信息
Table 1. Training sample information
参数 数值 总的样本数(有效量测点数) 401651991 真实目标量测点数 81664937 杂波量测点数 319987054 平均每个批次样本总数 8034 平均每个时间窗口样本总数 252 表 2 实验环境
Table 2. Experimental environment
项目 版本 CPU 12th Gen Intel(R) Core i5- 12400 GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 TiPython 3.7.4 Pytorch 1.6.0 Torchvision 0.7.0 CUDA 4.14.0 表 3 Track-MT3网络参数
Table 3. Track-MT3 network parameters
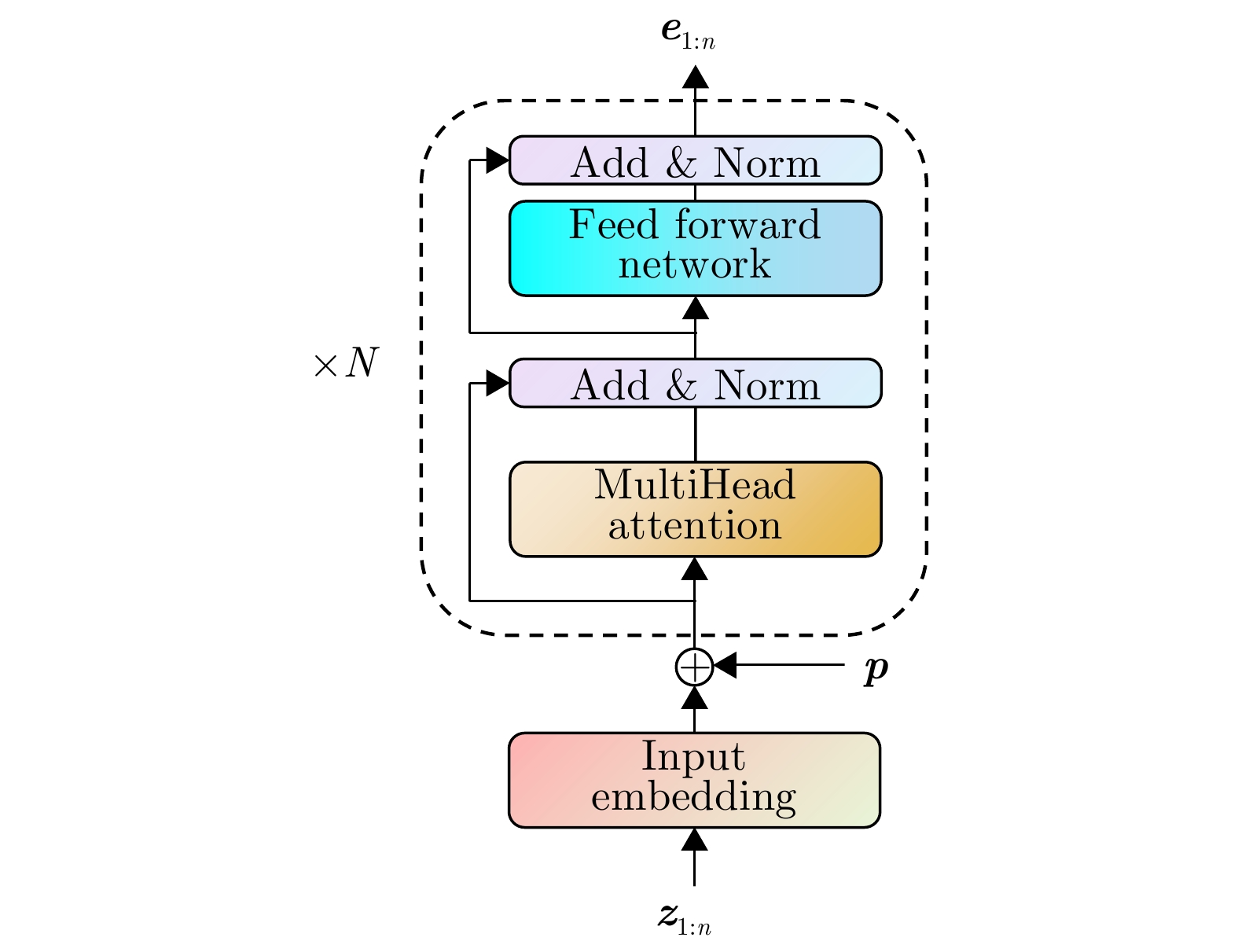
参数 取值 编码器层数 6 解码器层数 6 编码器输入数据维度 256 解码器输入数据层数 256 多头注意力头数 8 查询向量数量 16 前馈网络隐藏层维度 2048 神经元Dropout 0.1 预测器MLP层数 3 预测器隐藏层维度 128 表 4 模型训练参数
Table 4. Model training parameters
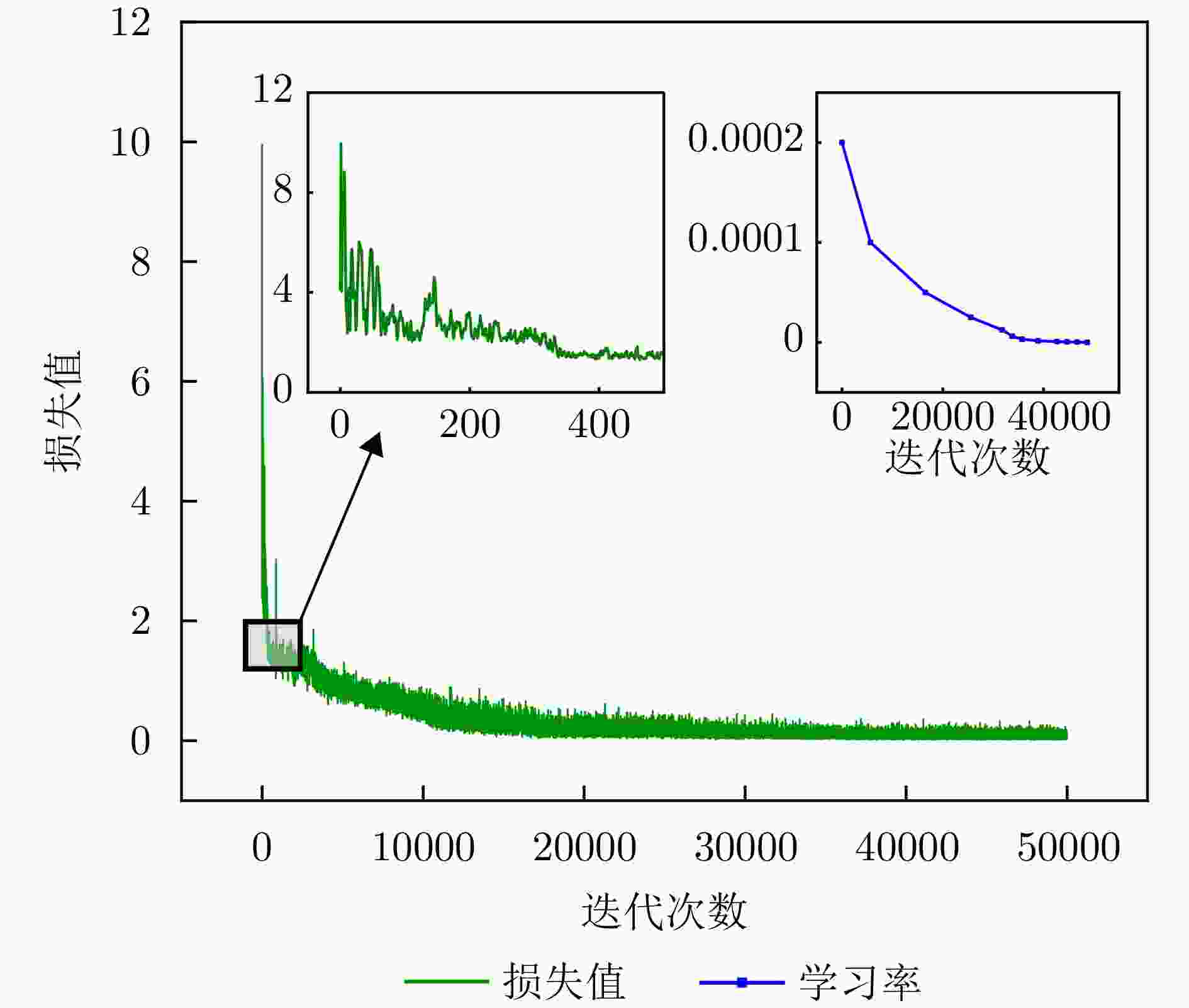
参数 取值 优化器 Adam Epoch数 50000 Batch Size 32 初始学习率 0.0002 学习率衰减容忍度 5000 学习率衰减因子 0.5 表 5 不同仿真场景参数设置
Table 5. Parameter settings for different simulation scenarios
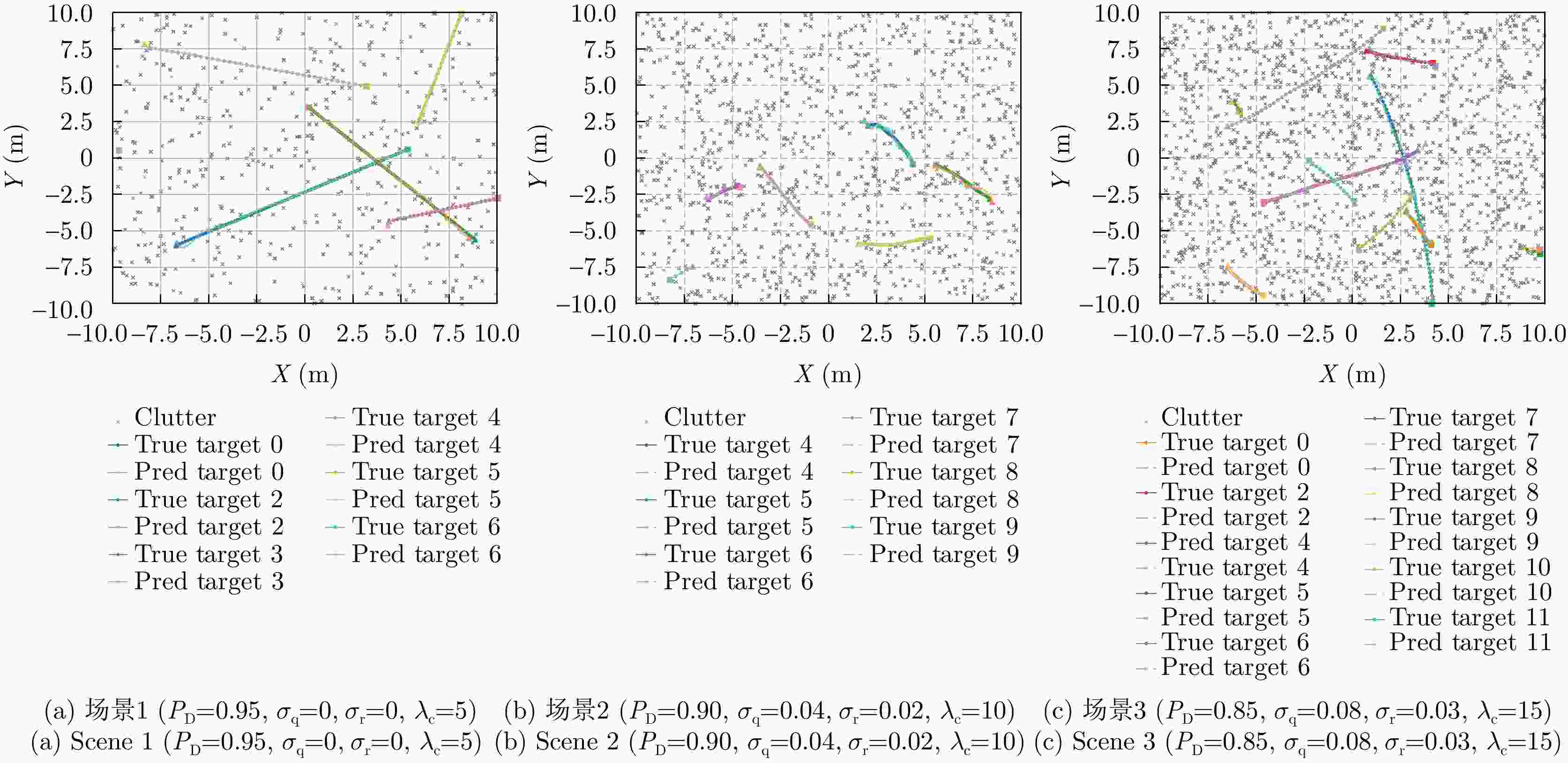
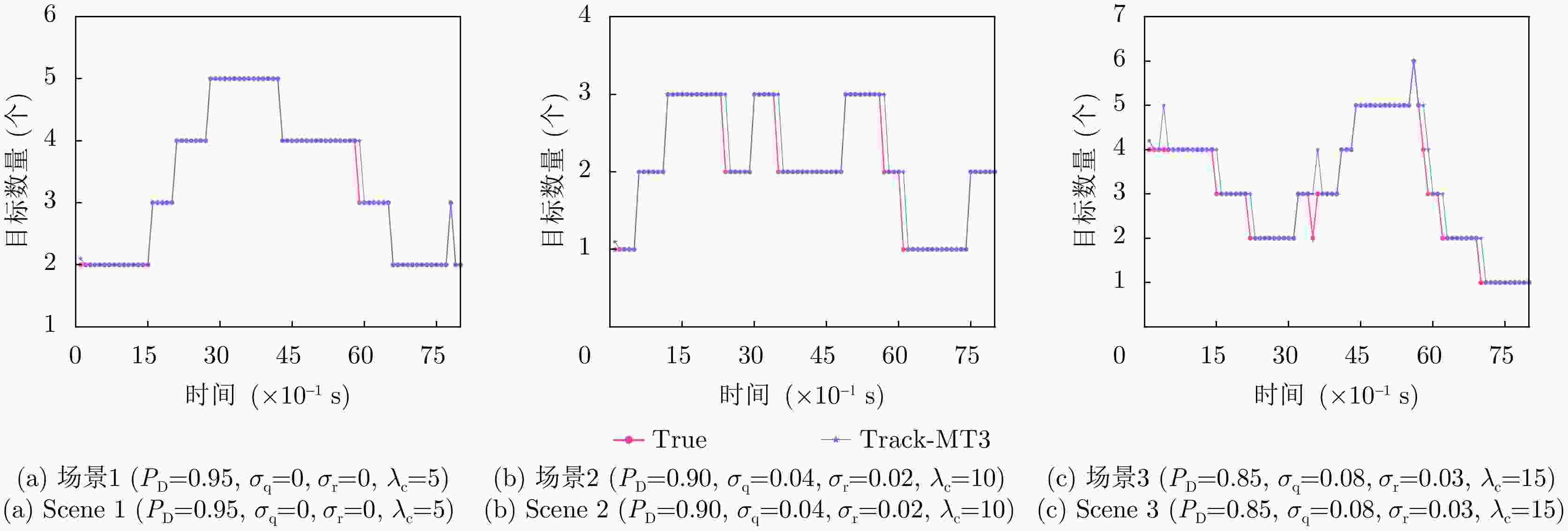
场景 目标数量(个) 出生率 死亡率 场景1 6 0.04 0.01 场景2 6 0.08 0.02 场景3 10 0.12 0.03 表 6 跟踪准确性对比
Table 6. Tracking accuracy comparison
跟踪方法 定位误差 漏检误差 虚警误差 JPDA 0.1629 0.6208 4.2812 MHT 0.6006 1.5921 3.8717 Track-MT3 0.0588 2.3683 2.3708 表 7 计算效率对比
Table 7. Computational efficiency comparison
跟踪方法 单帧运行时间(s) 平均内存占用(MB) JPDA 0.0041 169.6641 MHT 0.1714 209.8398 Track-MT3 0.0123 253.6656 表 8 QTM消融实验
Table 8. QTM ablation experiment
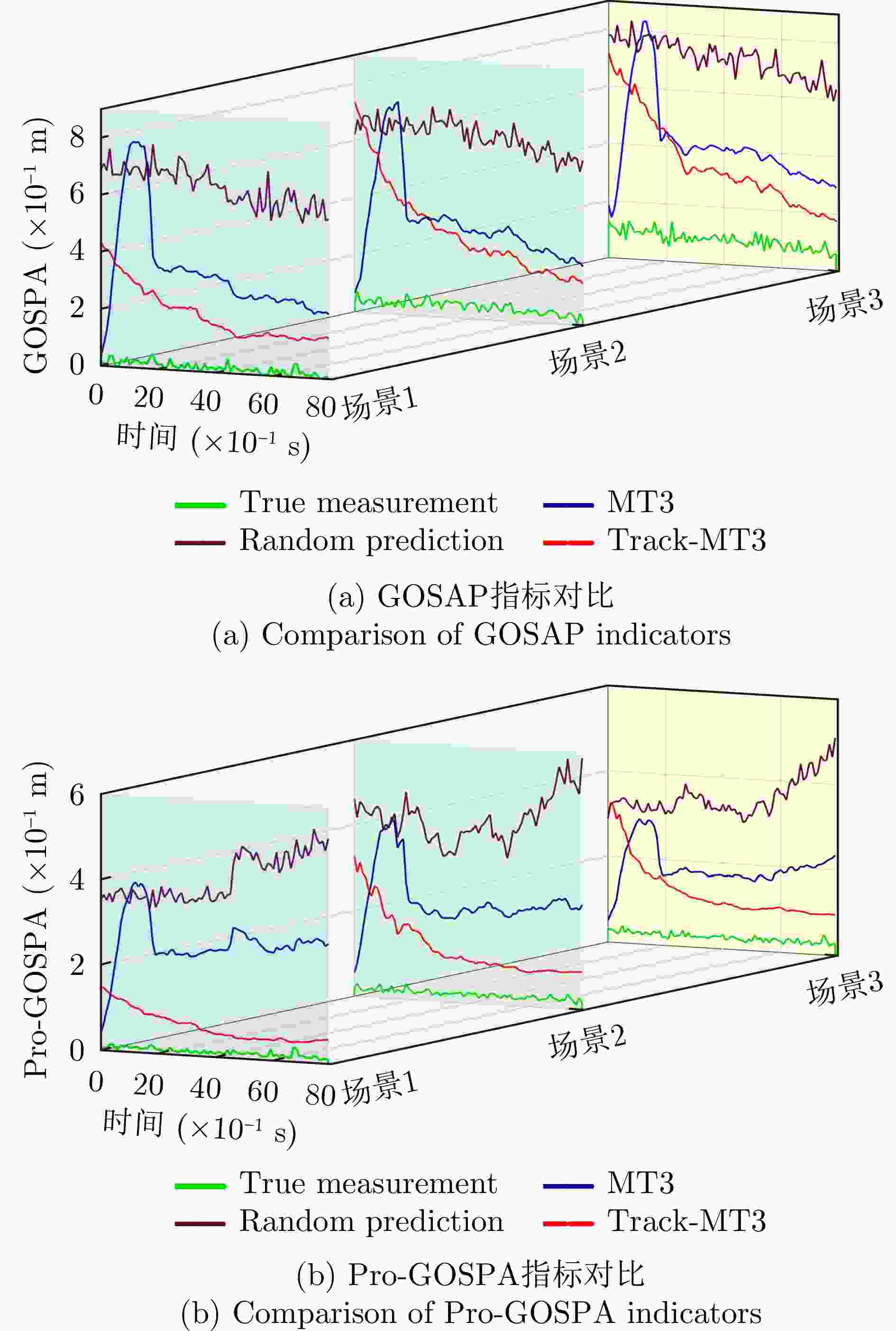
评价指标 Full No-QTM GOSPA (×10–1 m) 3.546362 4.760920 Pro-GOSPA (×10–1 m) 1.340019 1.925471 表 9 实验参数设置
Table 9. Experimental parameter settings
实验组 ${P_{\mathrm{D}}}$ ${\sigma _{\mathrm{q}}}$ ${\sigma _{\mathrm{r}}}$ ${\lambda _{\mathrm{c}}}$ 实验1 0.95 0.01 0.1 5 实验2 0.90 0.02 0.9 10 实验3 0.85 0.03 2.0 15 表 1 Training sample information
Parameter Value Total samples (valid measurements) 401651991 Real target measurements 81664937 Clutter measurements 319987054 Average samples per batch 8034 Average samples per time window 252 表 2 Experimental environment
Component Specification CPU 12th Gen Intel(R) Core i5- 12400 GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 TiPython 3.7.4 Pytorch 1.6.0 Torchvision 0.7.0 CUDA 4.14.0 表 3 Track-MT3 network parameters
Parameter Value Encoder layers 6 Decoder layers 6 Encoder input dimension 256 Decoder input dimension 256 Attention heads 8 Query vectors 16 FFN hidden dimension 2048 Dropout rate 0.1 MLP predictor layers 3 Predictor hidden dimension 128 表 4 Model training hyperparameters
Hyperparameter Value Optimizer Adam Epochs 50000 Batch size 32 Initial learning rate 0.0002 Learning rate decay patience 5000 Learning rate decay factor 0.5 表 5 Parameter settings for different simulation scenarios
Scenario Number of targets Birth rate Death rate Scenario 1 6 0.04 0.01 Scenario 2 6 0.08 0.02 Scenario 3 10 0.12 0.03 表 6 Tracking accuracy comparison
Method Location Missed False alarm JPDA 0.1629 0.6208 4.2812 MHT 0.6006 1.5921 3.8717 Track-MT3 0.0588 2.3683 2.3708 表 7 Computational efficiency comparison
Method Execution time (s) Memory usage (MB) JPDA 0.0041 169.6641 MHT 0.1714 209.8398 Track-MT3 0.0123 253.6656 表 8 QTM ablation experiment
Evaluation metric Full No-QTM GOSPA ( $ \times {10^{ - 1}}m$) 3.546362 4.760920 Pro-GOSPA ( $ \times {10^{ - 1}}m$) 1.340019 1.925471 表 9 Robustness test parameter settings
Experiment ${P_{\mathrm{D}}}$ ${\sigma _{\mathrm{q}}}$ ${\sigma _{\mathrm{r}}}$ ${\lambda _{\mathrm{c}}}$ Experiment 1 0.95 0.01 0.1 5 Experiment 2 0.90 0.02 0.9 10 Experiment 3 0.85 0.03 2.0 15 -
[1] BAI Xianglong, LAN Hua, WANG Zengfu, et al. Robust multitarget tracking in interference environments: A message-passing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(1): 360–386. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3323629. [2] YANG Jialin, JIANG Defu, TAO Jin, et al. A sector-matching probability hypothesis density filter for radar multiple target tracking[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(5): 2834. doi: 10.3390/app13052834. [3] HEM A G, BAERVELDT M, and BREKKE E F. PMBM filtering with fusion of target-provided and exteroceptive measurements: Applications to maritime point and extended object tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 55404–55423. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3389824. [4] CHEN Jiahui, GUO Shisheng, LUO Haolan, et al. Non-line-of-sight multi-target localization algorithm for driver-assistance radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5332–5337. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3227971. [5] HERZOG F, CHEN Junpeng, TEEPE T, et al. Synthehicle: Multi-vehicle multi-camera tracking in virtual cities[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops. Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/WACVW58289.2023.00005. [6] RAKAI L, SONG Huansheng, SUN Shijie, et al. Data association in multiple object tracking: A survey of recent techniques[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 192: 116300. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116300. [7] LI Tiancheng, LIANG Haozhe, XIAO Bing, et al. Finite mixture modeling in time series: A survey of Bayesian filters and fusion approaches[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 98: 101827. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.101827. [8] LIU Zongxiang, LUO Junwen, and ZHOU Chunmei. Multi-hypothesis marginal multi-target bayes filter for a heavy-tailed observation noise[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(21): 5258. doi: 10.3390/rs15215258. [9] QIU Changzhen, ZHANG Zhiyong, LU Huanzhang, et al. A survey of motion-based multitarget tracking methods[J]. Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, 2015, 62: 195–223. doi: 10.2528/PIERB15010503. [10] Vo B N and MA W K. The gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881190. [11] Vo B T, Vo B N, and CANTONI A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3553–3567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894241. [12] Vo B T, Vo B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924. [13] Vo B N, Vo B T, and PHUNG D. Labeled random finite sets and the bayes multi-target tracking filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(24): 6554–6567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2364014. [14] GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, WILLIAMS J L, GRANSTRÖM K, et al. Poisson multi-Bernoulli mixture filter: Direct derivation and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1883–1901. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805153. [15] CHONG C Y. An overview of machine learning methods for multiple target tracking[C]. 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Information Fusion, Sun City, South Africa, 2021: 1–9. doi: 10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9627045. [16] JONDHALE S R and DESHPANDE R S. Kalman filtering framework-based real time target tracking in wireless sensor networks using generalized regression neural networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(1): 224–233. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2873357. [17] LIU Huajun, ZHANG Hui, and MERTZ C. DeepDA: LSTM-based deep data association network for multi-targets tracking in clutter[C]. 22th International Conference on Information Fusion, Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION43075.2019.9011217. [18] BECKER P, PANDYA H, GEBHARDT G H W, et al. Recurrent Kalman networks: Factorized inference in high-dimensional deep feature spaces[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 544–552. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1905.07357. [19] SHI Zhuangwei. Incorporating Transformer and LSTM to Kalman filter with EM algorithm for state estimation[OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.00250. [20] GAO Chang, YAN Junkun, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Long short-term memory-based deep recurrent neural networks for target tracking[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 502: 279–296. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.039. [21] ZHANG Yongquan, SHI Zhenyun, JI Hongbing, et al. Online multi-target intelligent tracking using a deep long-short term memory network[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2023, 36(9): 313–329. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2023.02.006. [22] LI Jing, LIANG Xinru, YUAN Shengzhi, et al. A strong maneuvering target-tracking filtering based on intelligent algorithm[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2024, 2024(1): 9981332. doi: 10.1155/2024/9981332. [23] EMAMBAKHSH M, BAY A, and VAZQUEZ E. Deep recurrent neural network for multi-target filtering[C]. MultiMedia Modeling: 25th International Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2019: 519–531. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-05716-9_42. [24] LIU Jingxian, WANG Zulin, and XU Mai. DeepMTT: A deep learning maneuvering target-tracking algorithm based on bidirectional LSTM network[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 53: 289–304. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.06.012. [25] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All you Need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [26] ZENG Ailing, CHEN Muxi, ZHANG Lei, et al. Are transformers effective for time series forecasting?[C]. 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 11121–11128. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i9.26317. [27] PINTO J, HESS G, LJUNGBERGH W, et al. Next generation multitarget trackers: Random finite set methods vs transformer-based deep learning[C]. 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Information Fusion, Sun City, South Africa, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9626990. [28] PINTO J, HESS G, LJUNGBERGH W, et al. Can deep learning be applied to model-based multi-object tracking?[OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2202.07909. [29] MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXÉ L, et al. TrackFormer: Multi-object tracking with transformers[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8844–8854. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00864. [30] ZENG Fangao, DONG Bin, ZHANG Yuang, et al. MOTR: end-to-end multiple-object tracking with transformer[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 659–675. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19812-0_38. [31] WANG Qiang, LI Bei, XIAO Tong, et al. Learning deep transformer models for machine translation[C]. 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 1810–1822. doi: 10.18653/v1/P19-1176. [32] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. 16th European conference on computer vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13. [33] BEARD M, VO B T, and VO B N. Bayesian multi-target tracking with merged measurements using labelled random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(6): 1433–1447. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2393843. [34] RAHMATHULLAH A S, GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, and SVENSSON L. Generalized optimal sub-pattern assignment metric[C]. 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Xi’an, China, 2017: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/ICIF.2017.8009645. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: