Simultaneous Direction of Arrival Estimation and Radar Cross-section Reduction Based on Space-time-coding Digital Metasurfaces(in English)
-
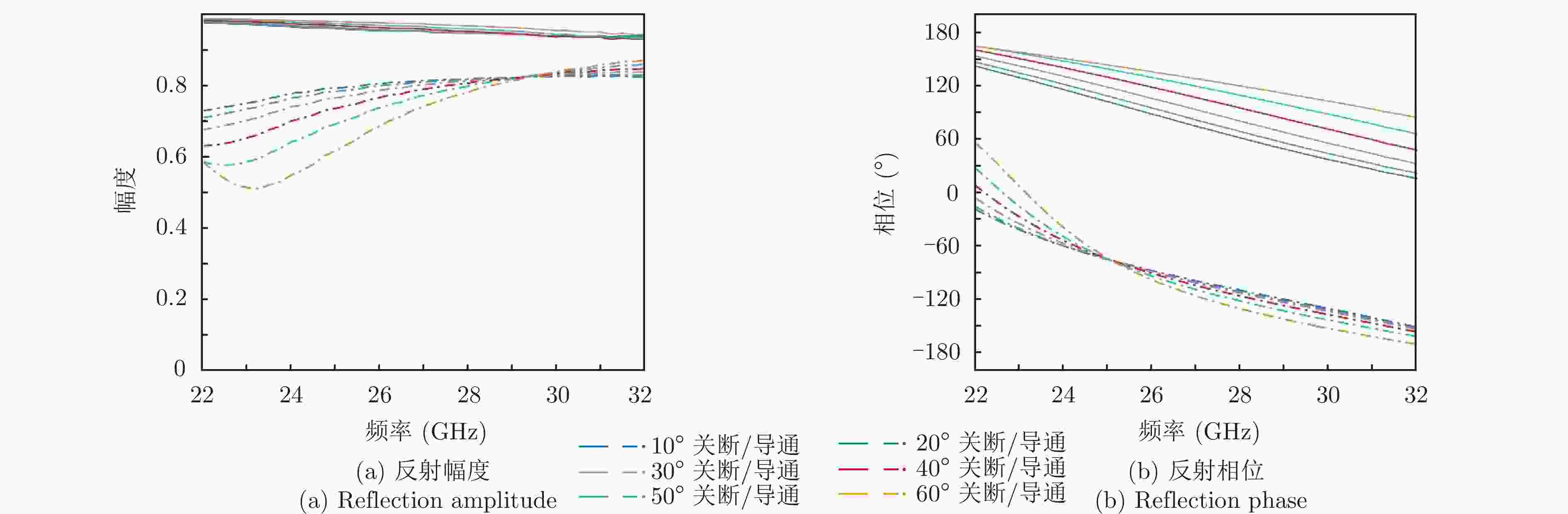
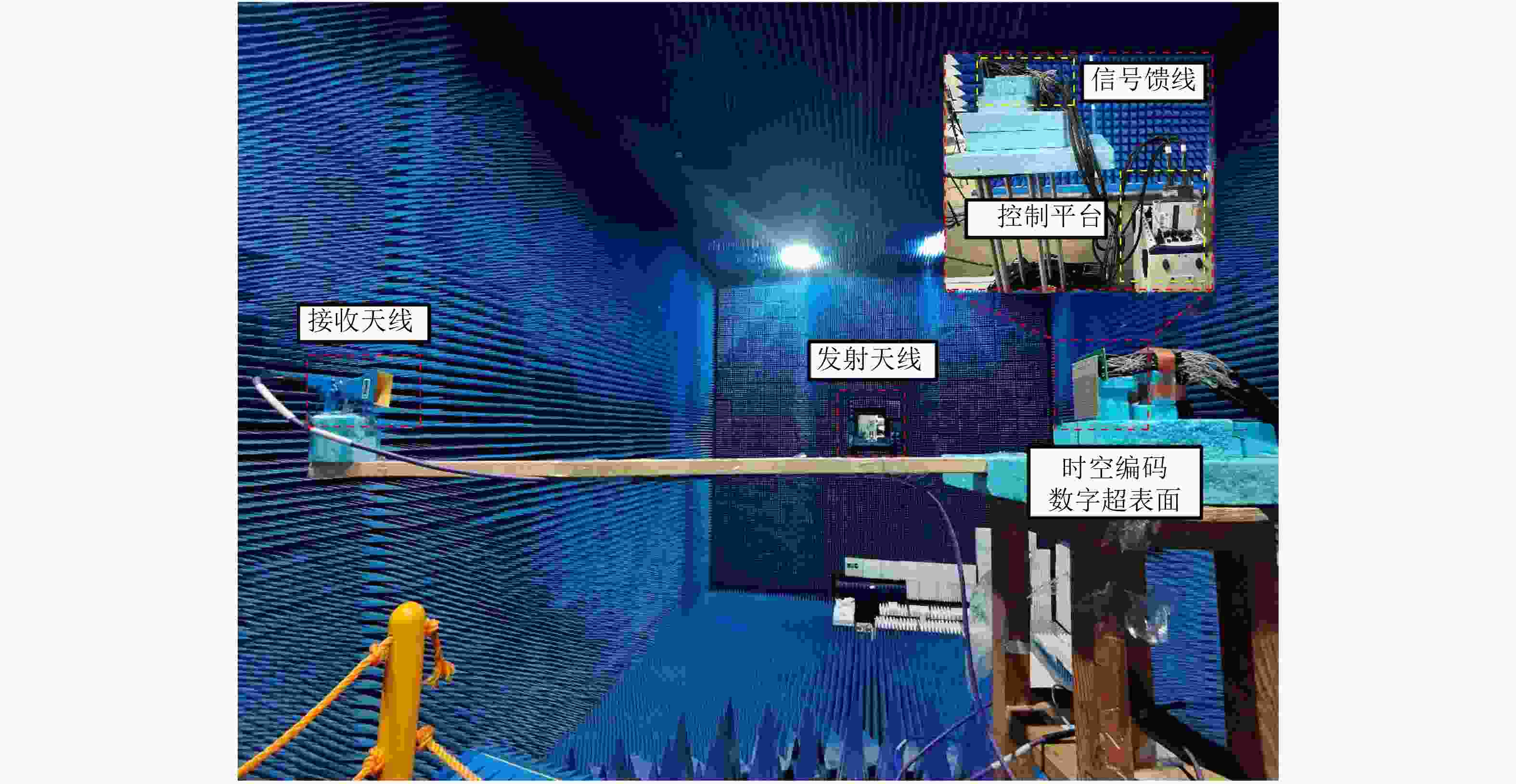
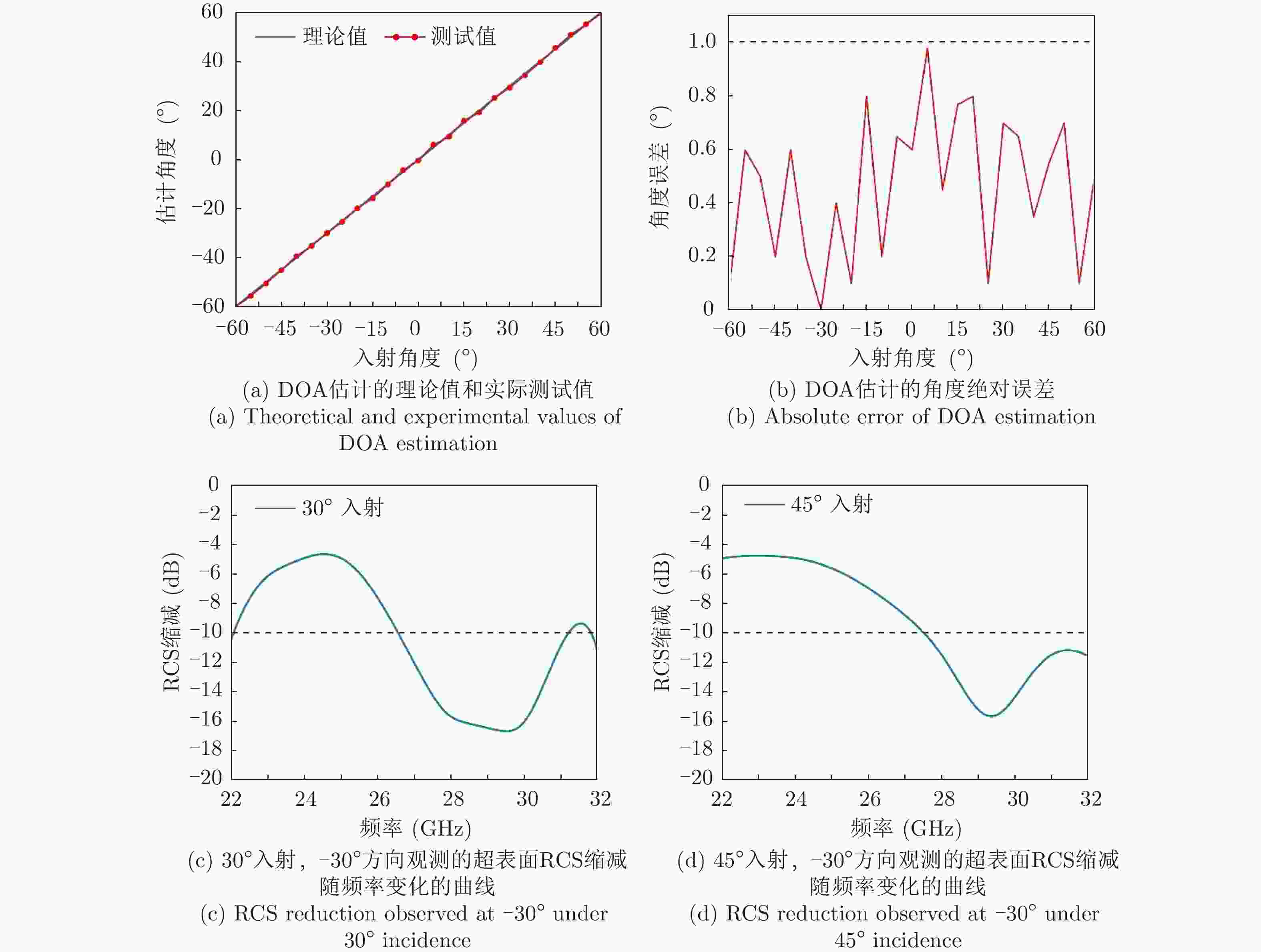
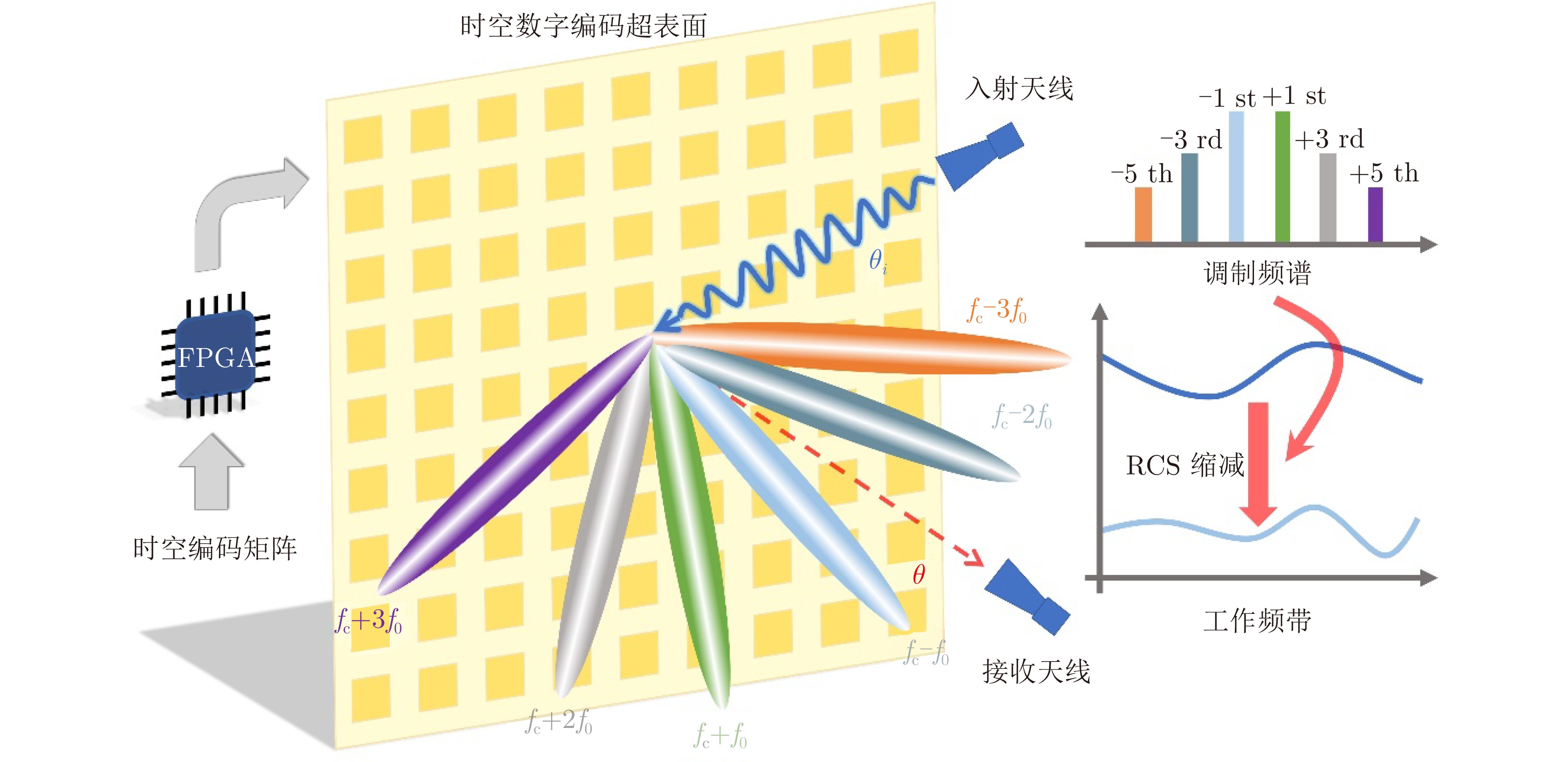
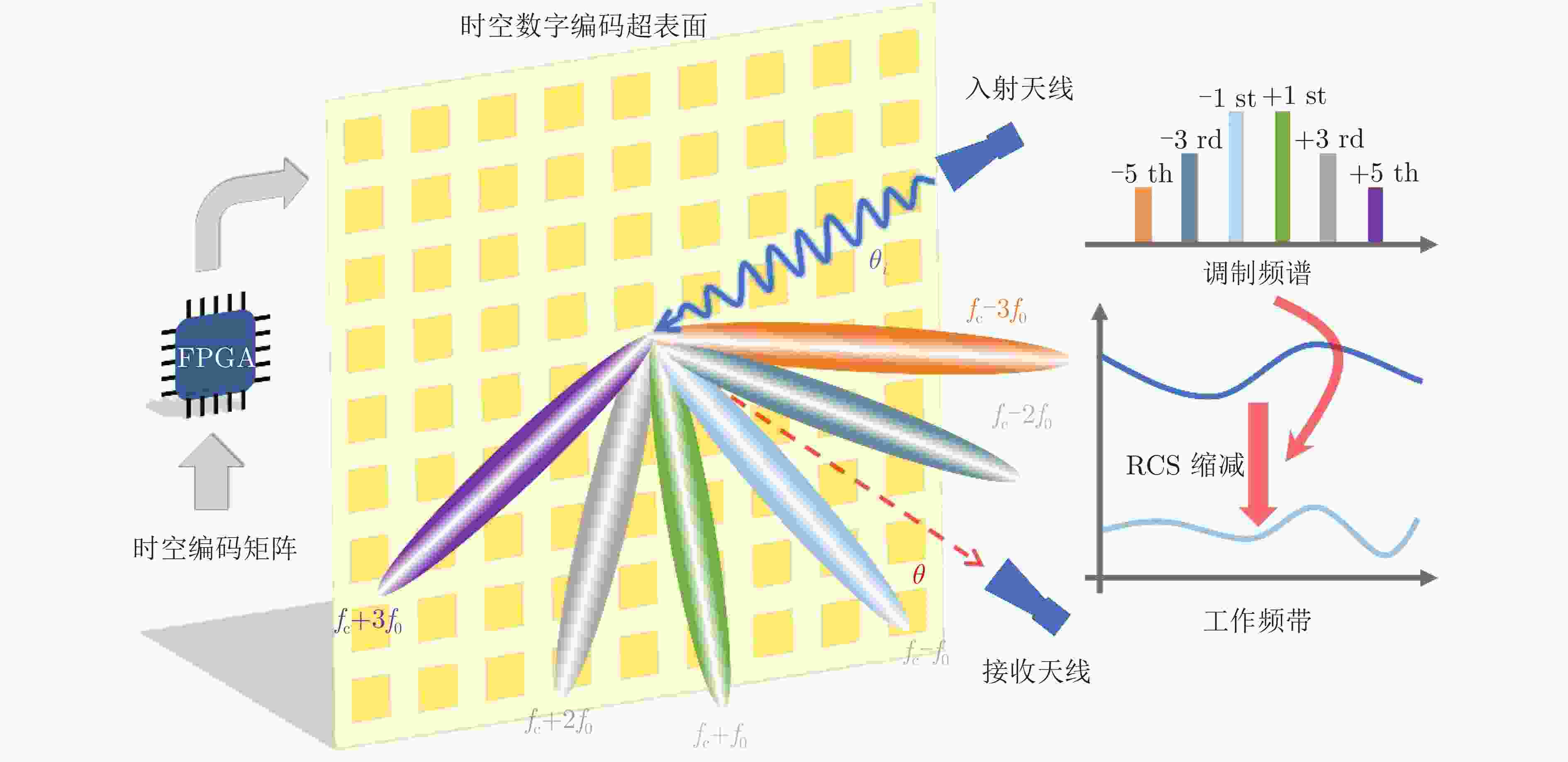
摘要: 传统的波达角(DOA)估计方法的实现通常基于相控阵天线系统,而其高昂的硬件成本限制该技术在不同领域的应用和推广,此外相控阵天线普遍不具备隐身性能,其在工作频段内雷达散射截面积(RCS)普遍较高。为解决上述问题,该文在时空编码(STC)理论的基础上提出了一种基于超表面同时实现RCS缩减和DOA估计的方法,并利用一款毫米波超表面对算法进行了验证。实验结果表明,该方法实现的波达角估计误差在1°以内,同时RCS缩减大于10 dB,为DOA估计和RCS缩减功能的集成提供了全新的思路,具有高性能、低成本等特点。Abstract: The traditional Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation is typically based on phased array antenna systems. However, it is greatly limited by the high hardware cost for applications in various fields. In addition, conventional phased array antennas also suffer from the high Radar Cross-Section (RCS), which cannot be employed for stealth purposes. To address these issues, we propose a new algorithm based on the Space-Time-coding (STC) strategy for simultaneous DOA estimation and RCS reduction, which is further experimentally verified using a metasurface in the millimeter band. The results demonstrate the excellent performance of the proposed DOA method with an error below 1°. Meanwhile, a good RCS reduction of over 10 dB is achieved in the bandwidth of interest. The proposed algorithm paves a new path to integrating DOA estimation and RCS reduction with a single metasurface, with the advantages of low cost and good performance.
-
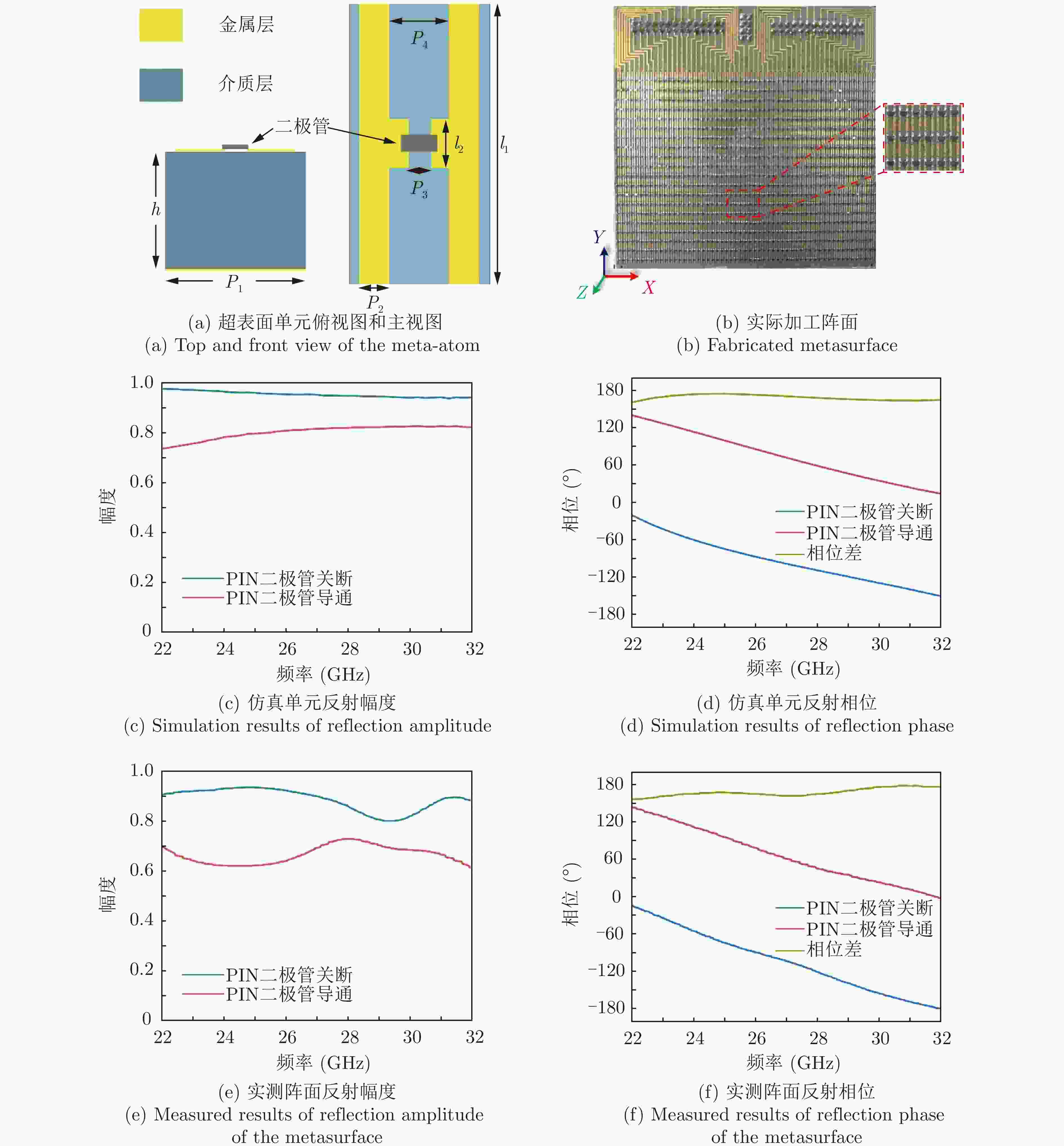
表 1 二极管等效串连电路参数
Table 1. Equivalent serial circuit parameters of the PIN diode
状态 电流(mA) 电阻R (Ω) 电感L (nH) 电容C (pF) 关断 0 6.5 0 0.063 导通 15 4.6 0.204 0 表 2 不同基于超表面DOA估计方法的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of metasurface-based DOA estimation in published works
表 1 Equivalent serial circuit parameters of the PIN diode
State Current (mA) Resistance
R (Ω)Inductance
L (nH)Capacitance
C (pF)OFF 0 6.5 0 0.063 ON 15 4.6 0.204 0 -
[1] BENCHEIKH M L, WANG Yide, and HE Hongyang. Polynomial root finding technique for joint DOA DOD estimation in bistatic MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(9): 2723–2730. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.03.023. [2] ENDER J H G. On compressive sensing applied to radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(5): 1402–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.11.009. [3] HUANG Hongji, YANG Jie, HUANG Hao, et al. Deep learning for super-resolution channel estimation and DOA Estimation based massive MIMO system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(9): 8549–8560. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2851783. [4] PUCCI L, PAOLINI E, and GIORGETTI A. System-level analysis of joint sensing and communication based on 5G new radio[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2043–2055. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155522. [5] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830. [6] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276. [7] ZISKIND I and WAX M. Maximum likelihood localization of multiple sources by alternating projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(10): 1553–1560. doi: 10.1109/29.7543. [8] WANG Huafei, WAN Liangtian, DONG Mianxiong, et al. Assistant vehicle localization based on three collaborative base stations via SBL-based robust DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 5766–5777. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2905788. [9] WAN Liangtian, SUN Yuchen, SUN Lu, et al. Deep learning based autonomous vehicle super resolution DOA estimation for safety driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(7): 4301–4315. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3009223. [10] BURTOWY M, RZYMOWSKI M, and KULAS L. Low-profile ESPAR antenna for RSS-based DoA estimation in IoT applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 17403–17411. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2895740. [11] WAN Liangtian, ZHANG Mingyue, SUN Lu, et al. Machine learning empowered IoT for intelligent vehicle location in smart cities[J]. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 2021, 21(3): 71. doi: 10.1145/3448612. [12] AI Lingyu, JING Changqiang, CHEN Y, et al. Maximum likelihood estimators for three-dimensional rigid body localization in internet of things environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 201458–201467. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3035850. [13] MIAO Wang, LUO Chunbo, MIN Geyong, et al. Location-based robust beamforming design for cellular-enabled UAV communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 9934–9944. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3028853. [14] TENNANT A and CHAMBERS B. A two-element time-modulated array with direction-finding properties[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2007, 6: 64–65. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2007.891953. [15] HE Chong, LIANG Xianling, LI Zhaojin, et al. Direction finding by time-modulated array with harmonic characteristic analysis[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 642–645. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2373432. [16] CHEN Jingfeng, HE Chong, LIANG Xianling, et al. Direction finding of linear frequency modulation signal in time modulated array with pulse compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(1): 509–520. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2938815. [17] LI Gang, YANG Shiwen, and NIE Zaiping. Direction of arrival estimation in time modulated linear arrays with unidirectional phase center motion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(4): 1105–1111. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2041313. [18] LAN Jifeng, SANG Jian, ZHOU Mingyong, et al. Measurement and characteristic analysis of RIS-assisted wireless communication channels in Sub-6 GHz outdoor scenarios[C]. 2023 IEEE 97th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2023-Spring), Florence, Italy, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTC2023-Spring57618.2023.10200072. [19] TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887. [20] WANG Siran, CHEN Mingzheng, KE Junchen, et al. Asynchronous space-time-coding digital metasurface[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(24): 2200106. doi: 10.1002/advs.202200106. [21] KE Junchen, DAI Junyan, ZHANG Junwei, et al. Frequency-modulated continuous waves controlled by space-time-coding metasurface with nonlinearly periodic phases[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2022, 11(1): 273. doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00973-8. [22] LI Lianlin, CUI Tiejun, JI Wei, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9. [23] WU Junwei, WANG Zhengxing, ZHANG Lei, et al. Anisotropic metasurface holography in 3-D space with high resolution and efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(1): 302–316. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3008659. [24] CUI Tiejun, QI Meiqing, WAN Xiang, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.99. [25] KE Junchen, CHEN Xiangyu, TANG Wankai, et al. Space-frequency-polarization-division multiplexed wireless communication system using anisotropic space-time-coding digital metasurface[J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(11): nwac225. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac225. [26] GAO Xi, YANG Wanli, MA Huifeng, et al. A reconfigurable broadband polarization converter based on an active metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(11): 6086–6095. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2866636. [27] HUANG Cheng, LIAO Jianming, JI Chen, et al. Graphene-integrated reconfigurable metasurface for independent manipulation of reflection magnitude and phase[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(7): 2001950. doi: 10.1002/adom.202001950. [28] PHON R and LIM S. Dynamically self-reconfigurable multifunctional all-passive metasurface[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(37): 42393–42402. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c12203. [29] LIU Lixiang, ZHANG Xueqian, KENNEY M, et al. Broadband metasurfaces with simultaneous control of phase and amplitude[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(29): 5031–5036. doi: 10.1002/adma.201401484. [30] ZHANG Lei, WANG Zhengxing, SHAO Ruiwen, et al. Dynamically realizing arbitrary multi-bit programmable phases using a 2-bit time-domain coding metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(4): 2984–2992. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2955219. [31] CLEMENTE A, DUSSOPT L, SAULEAU R, et al. Wideband 400-element electronically reconfigurable transmitarray in X band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(10): 5017–5027. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2271493. [32] LI Weihan, QIU Tianshuo, WANG Jiafu, et al. Programmable coding metasurface reflector for reconfigurable multibeam antenna application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(1): 296–301. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3010801. [33] ZHANG Lei, CHEN Xiaoqing, LIU Shuo, et al. Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4334. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06802-0. [34] 许河秀, 王彦朝, 王朝辉, 等. 基于多元信息的多功能电磁集成超表面研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 191–205. doi: 10.12000/JR21037.XU Hexiu, WANG Yanzhao, WANG Chaohui, et al. Research progress of multifunctional metasurfaces based on the multiplexing concept[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 191–205. doi: 10.12000/JR21037. [35] LIN Mingtuan, XU Ming, WAN Xiang, et al. Single sensor to estimate DOA with programmable metasurface[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 10187–10197. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3051014. [36] HUANG Min, ZHENG Bin, CAI Tong, et al. Machine-learning-enabled metasurface for direction of arrival estimation[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(9): 2001–2010. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0663. [37] CHEN Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, LIU Shuo, et al. Artificial neural network for direction-of-arrival estimation and secure wireless communications via space-time-coding digital metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(23): 2201900. doi: 10.1002/adom.202201900. [38] DAI Junyan, TANG Wankai, WANG Manting, et al. Simultaneous in situ direction finding and field manipulation based on space-time-coding digital metasurface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(6): 4774–4783. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3145445. [39] ZHOU Qunyan, WU Junwei, WANG Siran, et al. Two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation based on time-domain-coding digital metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 121(18): 181702. doi: 10.1063/5.0124291. [40] WANG Jiawei, HUANG Ziai, XIAO Qiang, et al. High-precision direction-of-arrival estimations using digital programmable metasurface[J]. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2022, 4(4): 2100164. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202100164. [41] XIA Dexiao, WANG Xin, HAN Jiaqi, et al. Accurate 2-D DoA estimation based on active metasurface with nonuniformly periodic time modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023, 71(8): 3424–3435. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3222322. [42] LI Yongfeng, ZHANG Jieqiu, QU Shaobo, et al. Wideband radar cross section reduction using two-dimensional phase gradient metasurfaces[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(22): 221110. doi: 10.1063/1.4881935. [43] XU Hexiu, ZHANG Lei, KIM Y, et al. Wavenumber-splitting metasurfaces achieve multichannel diffusive invisibility[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(10): 1800010. doi: 10.1002/adom.201800010. [44] CHEN Ke, GUO Wenlong, DING Guowen, et al. Binary geometric phase metasurface for ultra-wideband microwave diffuse scatterings with optical transparency[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(9): 12638–12649. doi: 10.1364/OE.392182. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: