SAR Time Series Despeckling Based on Additive Signal Component Decomposition in Logarithm Domain
-
摘要: 随着合成孔径雷达(SAR)在测绘带宽度、空间以及时间分辨率上的大幅提升,由不同时间获取的SAR图像配准得到的时间序列能更加精确地提供观测区域的动态变化信息。然而,相干斑噪声以及沿时间维度突变信号为后续的解译工作带来了严重挑战。尽管现有的主流方法可以对时序SAR图像的相干斑进行有效抑制,但沿时间维度突变信号会对去噪结果产生干扰。为更好地解决此问题,该文提出了一种基于对数域加性信号分解的方法,能同时抑制相干斑噪声并且对时序图像中的稳定信号和沿时间维度突变信号进行分离,从而消除突变信号对于去噪结果的影响。在仿真数据受到突变信号干扰的情况下,所提方法与其他主流方法相比,其去噪结果在峰值信噪比(PSNR)指标上取得了大约3 dB的提升。在哨兵1号数据上,所提方法能鲁棒地对时序图像中的相干斑噪声进行抑制,并且得到的突变信号成分也为后续的解译工作提供了参考数据。Abstract: With the substantial improvement of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) regarding swath width and spatial and temporal resolutions, a time series obtained by registering SAR images acquired at different times can provide more accurate information on the dynamic changes in the observed areas. However, inherent speckle noise and outliers along the temporal dimension in the time series pose serious challenges for subsequent interpretation tasks. Although existing state-of-the-art methods can effectively suppress the speckle noise in a SAR time series, outliers along the temporal dimension will interfere with the denoising results. To better solve this problem, this paper proposes an additive signal decomposition method in the logarithm domain that can suppress the speckle noise and separate stable data and outliers along the temporal dimension in a time series, thus eliminating the impact of outliers on the denoising results. When the simulated data are disturbed by outliers, the proposed method can achieve an approximately 3 dB improvement in the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) compared to the other state-of-the-art methods. On Sentinel-1 data, the proposed method robustly suppresses the speckle noise in a time series, and the obtained outliers along the temporal dimension provide reference data for subsequent interpretation tasks.
-
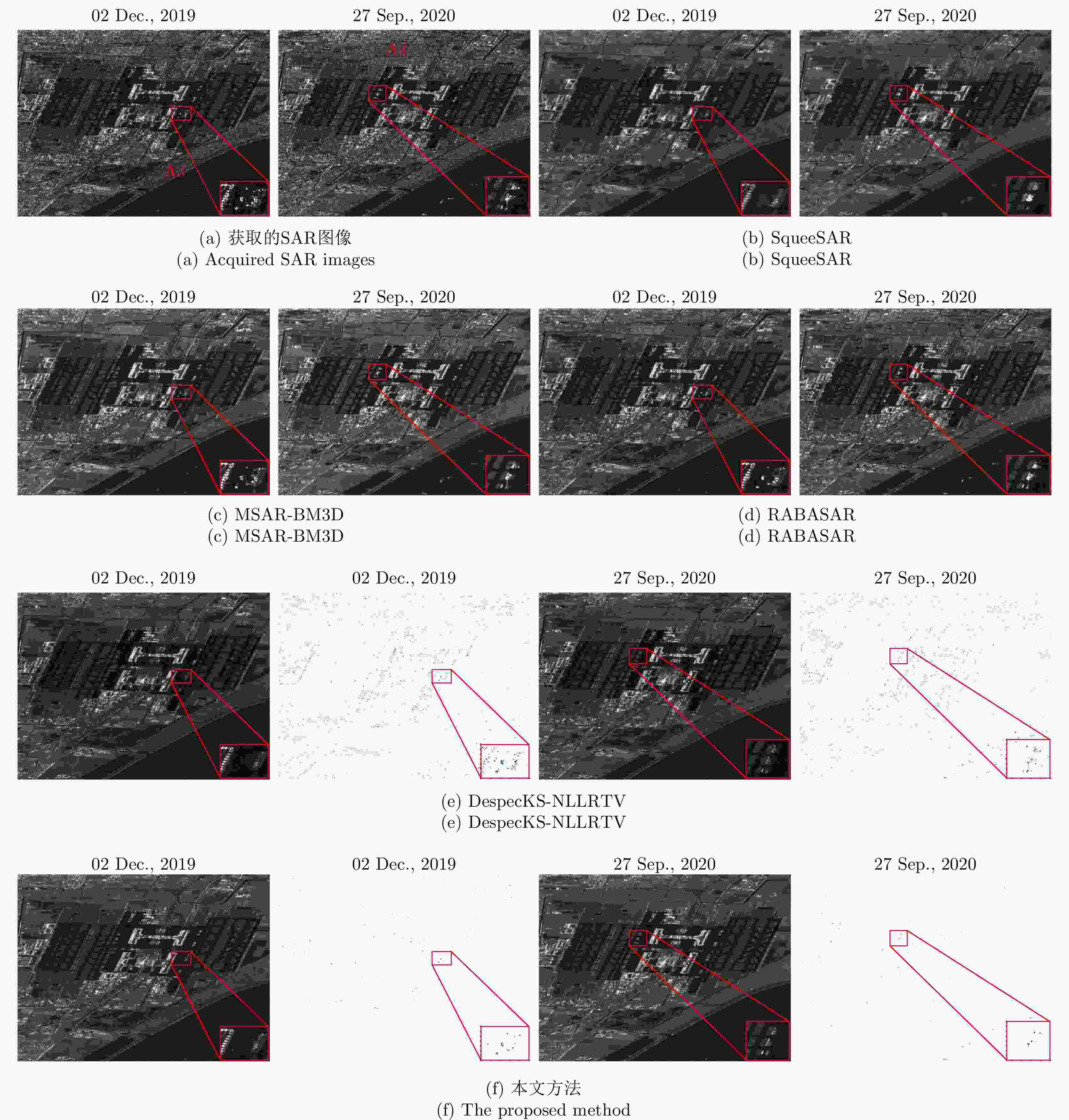
表 1 仿真数据相干斑抑制结果的定量分析
Table 1. Quantitative analysis of speckle suppression results in simulation data
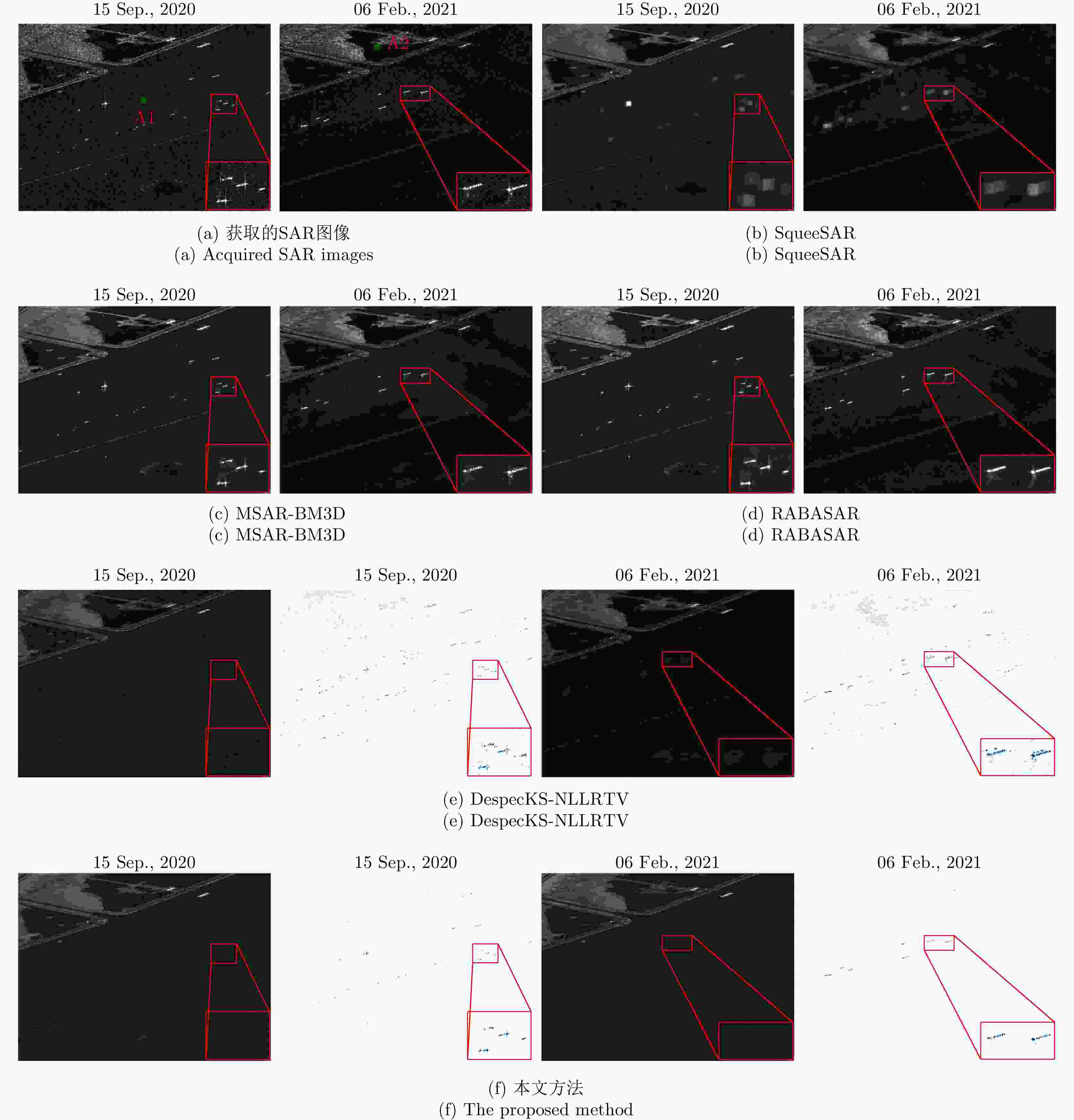
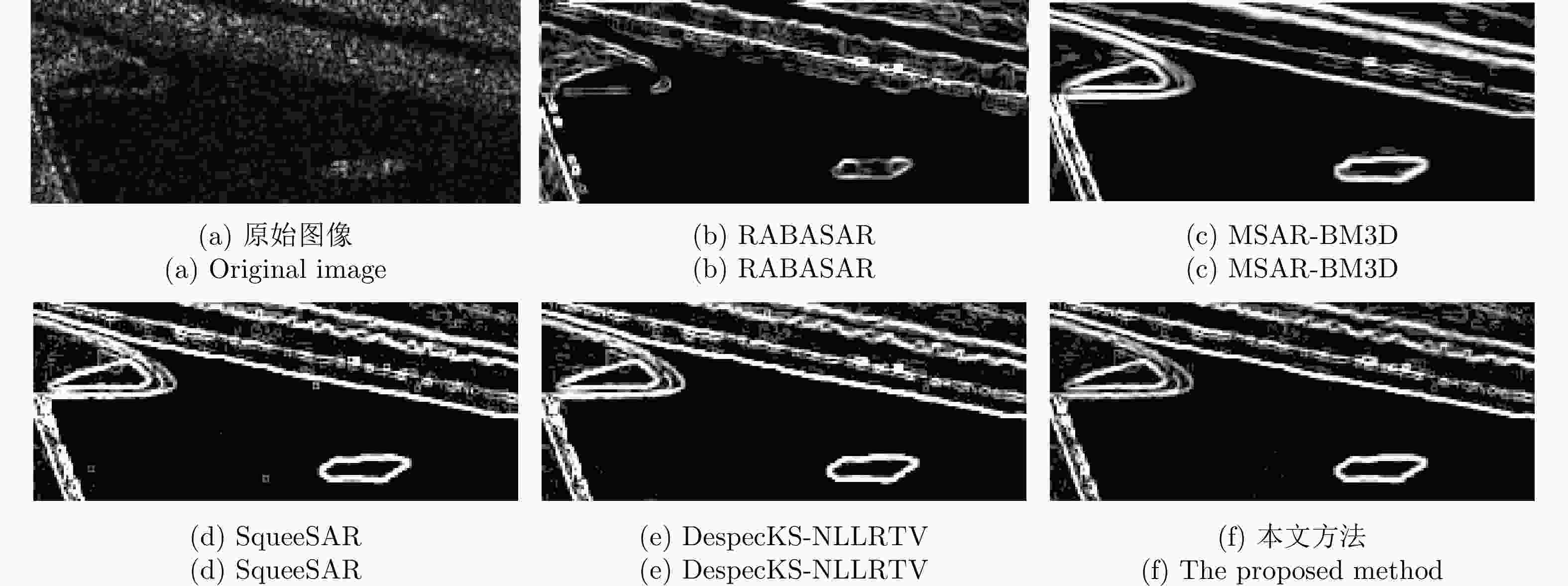
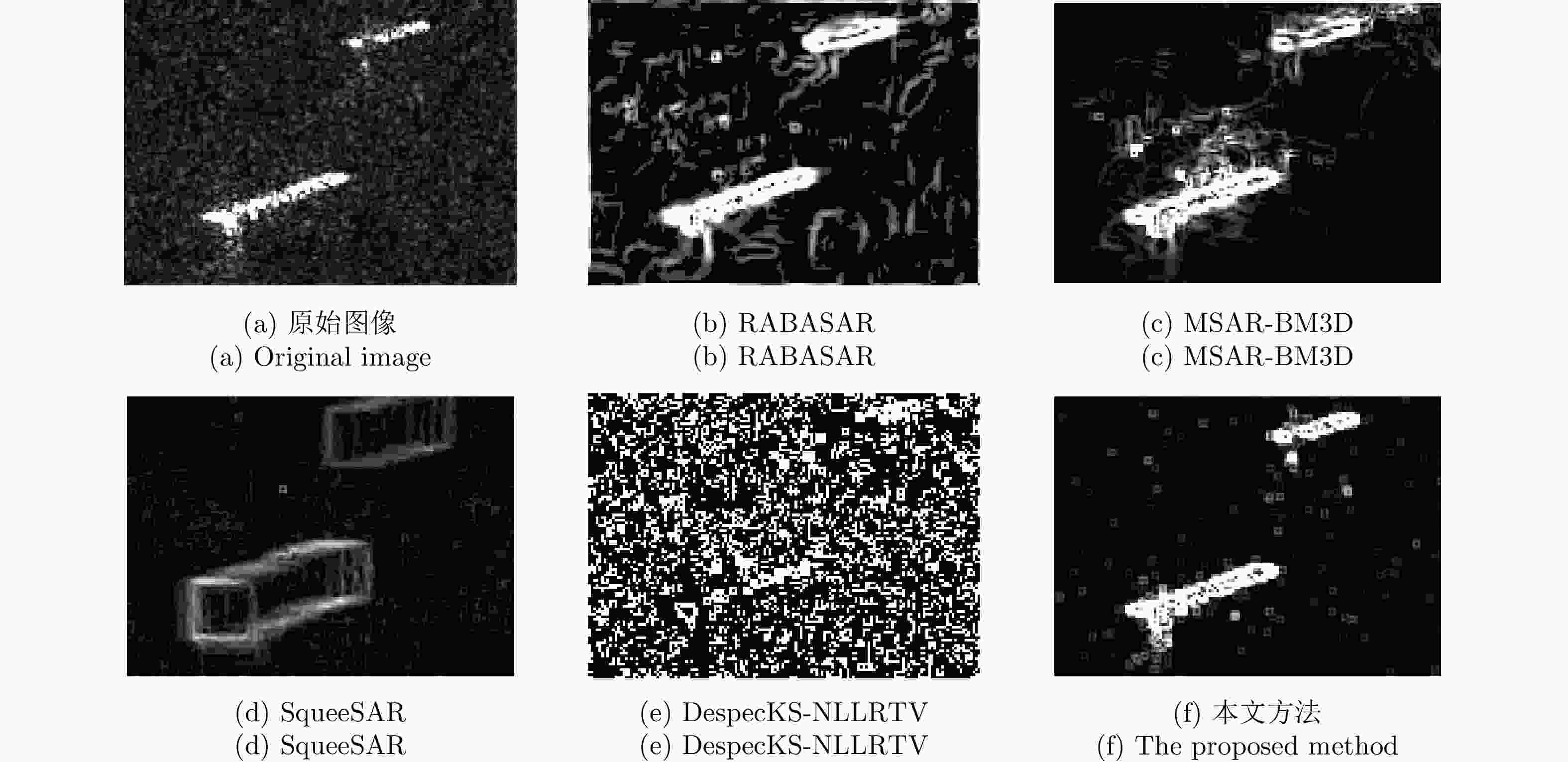
方法 PSNR (dB) MSSIM (dB) MCC – 0.5% 1.0% – 0.5% 1.0% – 0.5% 1.0% SqueeSAR 30.95 29.81 28.42 0.51 0.43 0.38 0.87 0.80 0.75 MSAR-BM3D 35.01 18.02 15.12 0.56 0.26 0.18 0.93 0.35 0.26 RABASAR 35.07 32.97 30.51 0.63 0.49 0.39 0.96 0.91 0.82 DespecKS-NLLRTV 29.53 28.70 28.41 0.54 0.31 0.28 0.90 0.88 0.88 本文方法 32.07 32.82 33.15 0.57 0.56 0.55 0.92 0.92 0.91 表 2 4块同质区域计算得到的等效视数
Table 2. The equivalent apparent number calculated by four homogeneous regions
方法 ENL A1 A2 A3 A4 原始图像 0.872 0.794 0.907 0.936 SqueeSAR 325.30 3.25 64.33 72.55 MSAR-BM3D 176.40 15.48 65.22 117.07 RABASAR 26.33 24.40 24.13 17.07 DespecKS-NLLRTV 54.86 59.32 110.70 85.61 本文方法 107.30 74.68 80.11 139.50 表 3 沿时间维度突变信号的熵值分析
Table 3. Entropy analysis of the outliers along the temporal dimension
地点 测试日期 DespecKS-NLLRTV 本文方法 近海 2020-09-15 14.618 0.306 2021-02-06 15.791 0.144 机场 2019-12-02 18.623 0.643 2020-09-27 16.032 0.736 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [3] 陈杰, 杨威, 王亚敏, 等. 高时相星载序贯SAR图像运动目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1048–1060. doi: 10.12000/JR22184CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, WANG Yamin, et al. Moving target monitoring algorithm based on high-frame-rate SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1048–1060. doi: 10.12000/JR22184 [4] XUE Feiyang, LV Xiaolei, DOU Fangjia, et al. A review of time-series interferometric SAR techniques: A tutorial for surface deformation analysis[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(1): 22–42. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2956165 [5] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 [6] ARGENTI F, LAPINI A, BIANCHI T, et al. A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(3): 6–35. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2277512 [7] VASILE G, TROUVE E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 [8] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, and GRANDI G D. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2363–2373. doi: 10.1109/36.789635 [9] BIOUCAS-DIAS J M and FIGUEIREDO M A T. Multiplicative noise removal using variable splitting and constrained optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(7): 1720–1730. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2045029 [10] DALSASSO E, YANG Xiangli, DENIS L, et al. SAR image despeckling by deep neural networks: From a pre-trained model to an end-to-end training strategy[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2636. doi: 10.3390/rs12162636 [11] XIONG Kai, ZHAO Guanghui, WANG Yingbin, et al. SPB-Net: A deep network for SAR imaging and despeckling with downsampled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9238–9256. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3034102 [12] MOLINI A B, VALSESIA D, FRACASTORO G, et al. Speckle2Void: Deep self-supervised SAR despeckling with blind-spot convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5204017. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3065461 [13] DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, POGGI G, et al. Exploiting patch similarity for SAR image processing: The nonlocal paradigm[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 69–78. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2311305 [14] XU Gang, GAO Yandong, LI Jinwei, et al. InSAR phase denoising: A review of current technologies and future directions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(2): 64–82. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2955120 [15] QUEGAN S, LE TOAN T, YU Jiongjiong, et al. Multitemporal ERS SAR analysis applied to forest mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(2): 741–753. doi: 10.1109/36.842003 [16] TROUVE E, CHAMBENOIT Y, CLASSEAU N, et al. Statistical and operational performance assessment of multitemporal SAR image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(11): 2519–2530. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817270 [17] SU Xin, DELEDALLE C A, TUPIN F, et al. Two-step multitemporal nonlocal means for synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6181–6196. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2295431 [18] FERRETTI A, FUMAGALLI A, NOVALI F, et al. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(9): 3460–3470. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2124465 [19] CHIERCHIA G, EL GHECHE M, SCARPA G, et al. Multitemporal SAR image despeckling based on block-matching and collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5467–5480. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2707806 [20] PARRILLI S, PODERICO M, ANGELINO C V, et al. A nonlocal SAR image denoising algorithm based on LLMMSE wavelet shrinkage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(2): 606–616. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2161586 [21] ZHAO Weiying, DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, et al. Ratio-based multitemporal SAR images denoising: RABASAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3552–3565. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2885683 [22] BAIER G, HE Wei, and YOKOYA N. Robust nonlocal low-rank SAR time series despeckling considering speckle correlation by total variation regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(11): 7942–7954. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2985400 [23] CHAMBOLLE A and POCK T. A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2011, 40(1/2): 120–145. doi: 10.1007/s10851-010-0251-1 [24] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [25] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [26] DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, TABTI S, et al. MuLoG, or how to apply Gaussian denoisers to multi-channel SAR speckle reduction?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4389–4403. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713946 [27] WANG Yilun, YANG Junfeng, YIN Wotao, et al. A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2008, 1(3): 248–272. doi: 10.1137/080724265 [28] PARIKH N and BOYD S. Proximal algorithms[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Optimization, 2014, 1(3): 127–239. doi: 10.1561/2400000003 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: