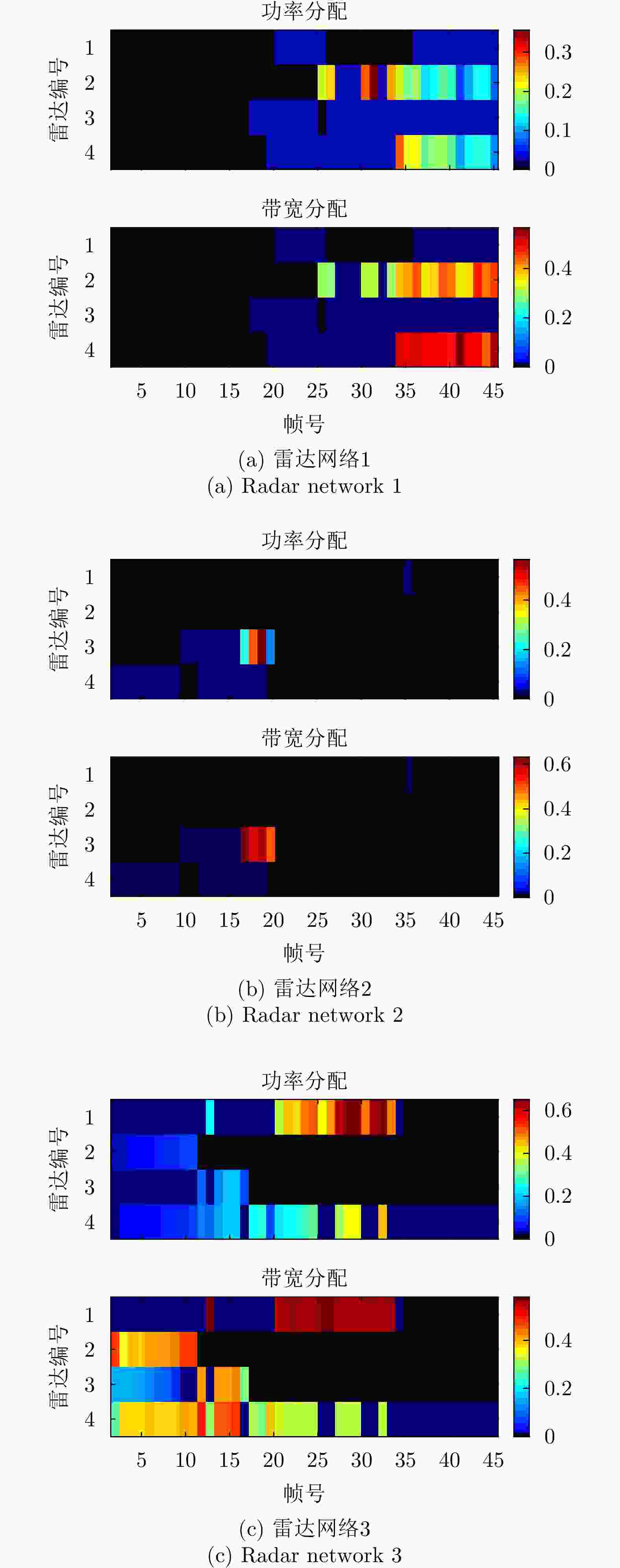
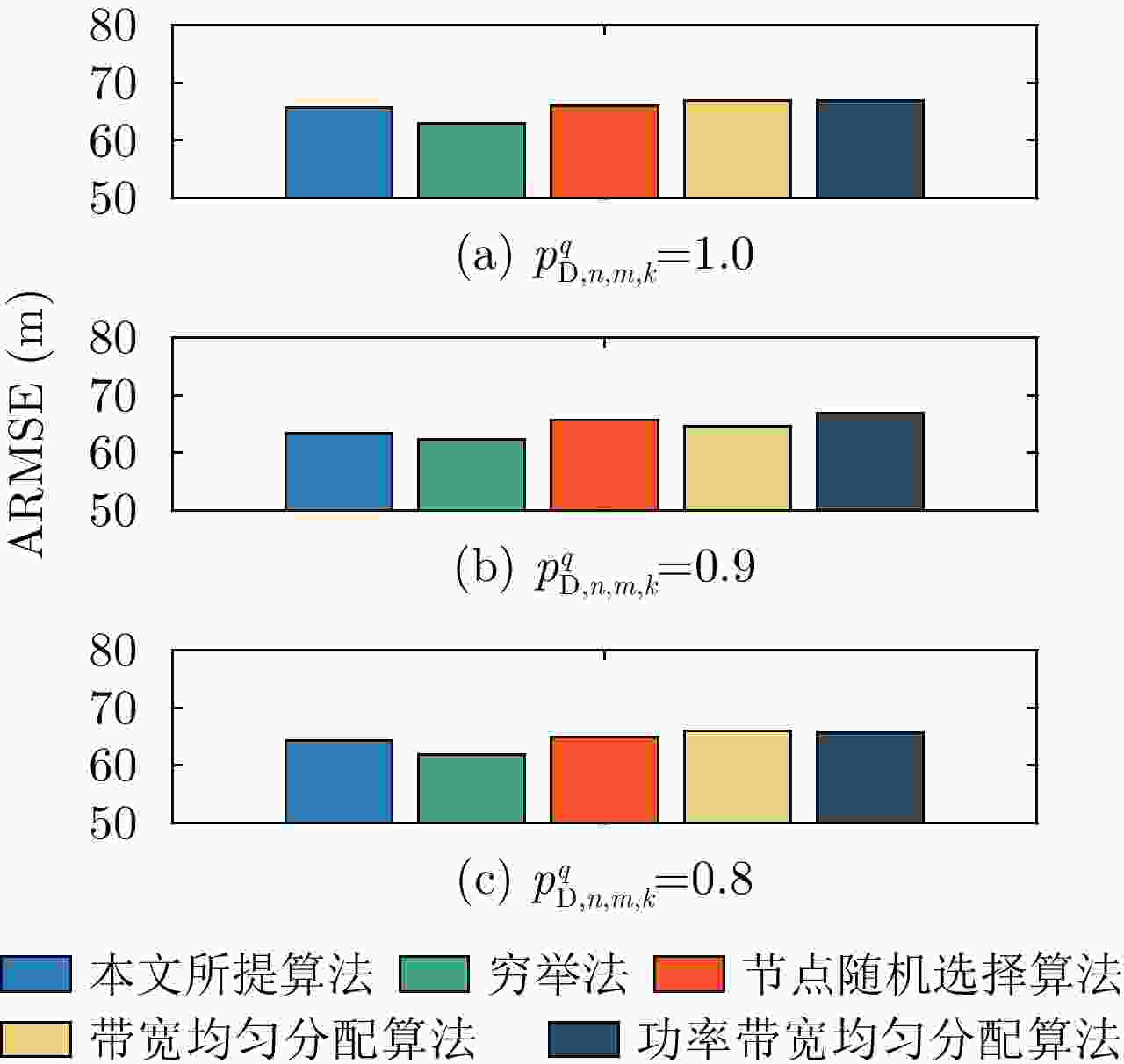
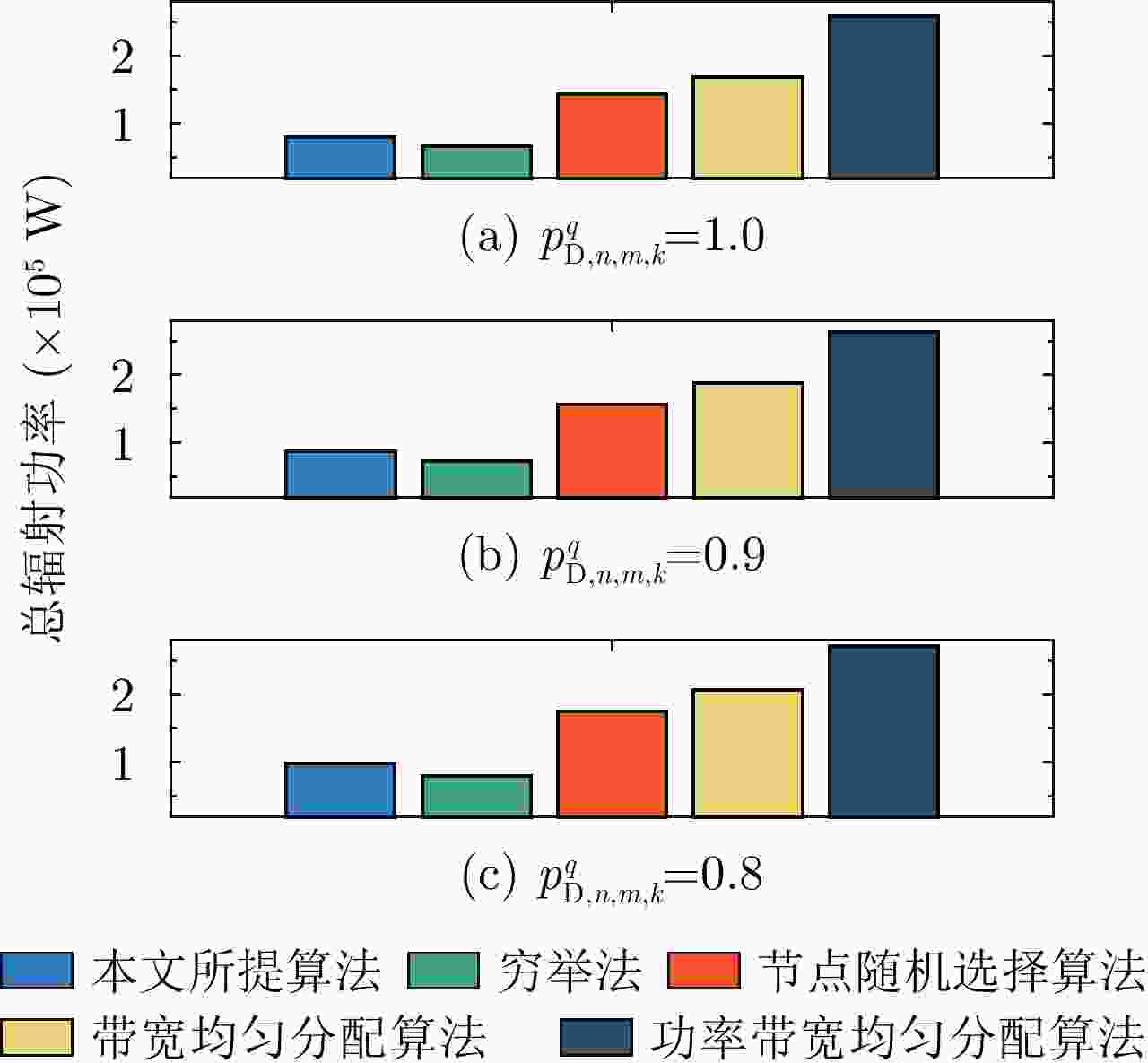
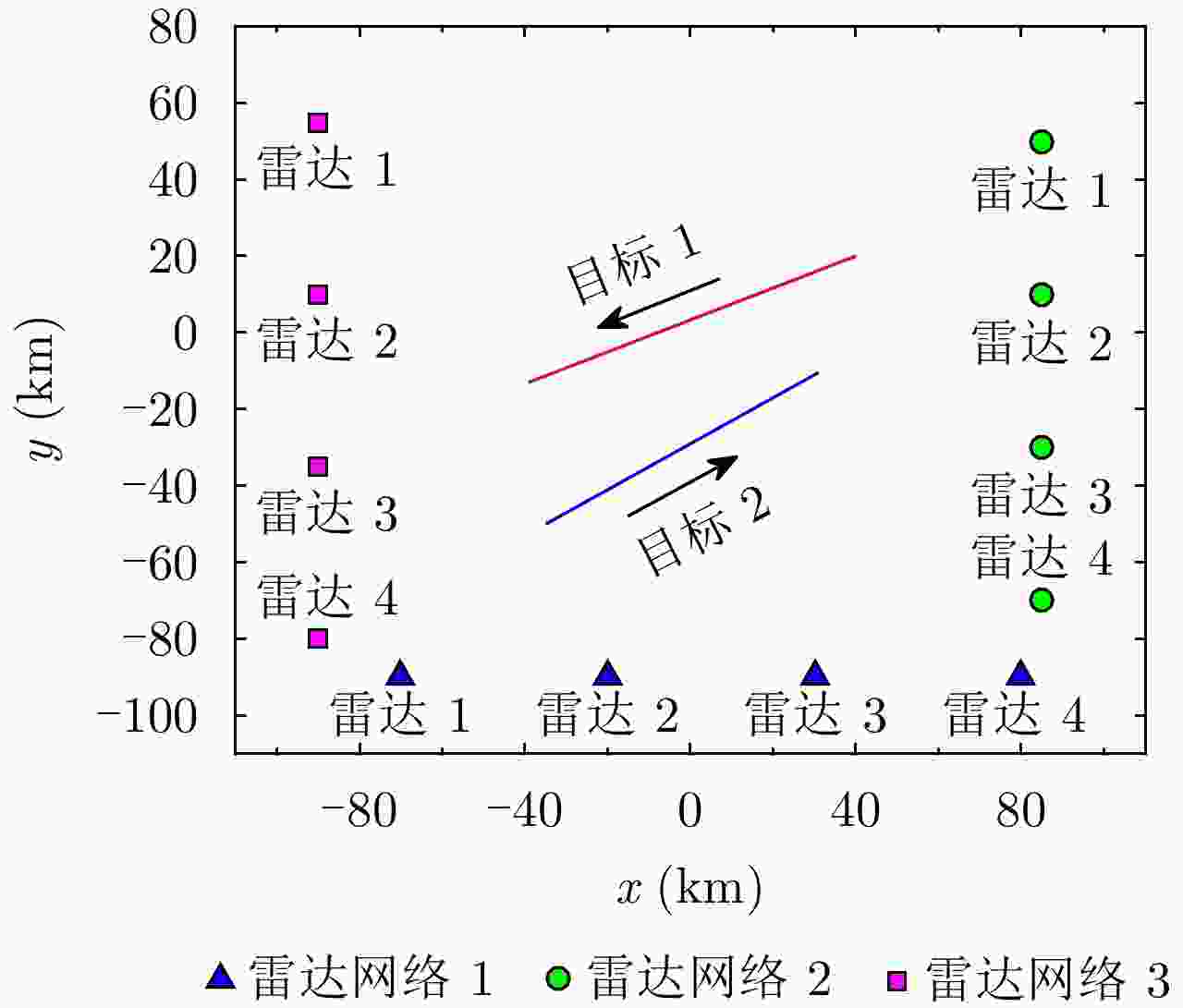
Joint Collaborative Radar Selection and Transmit Resource Allocation in Multiple Distributed Radar Networks with Imperfect Detection Performance
-
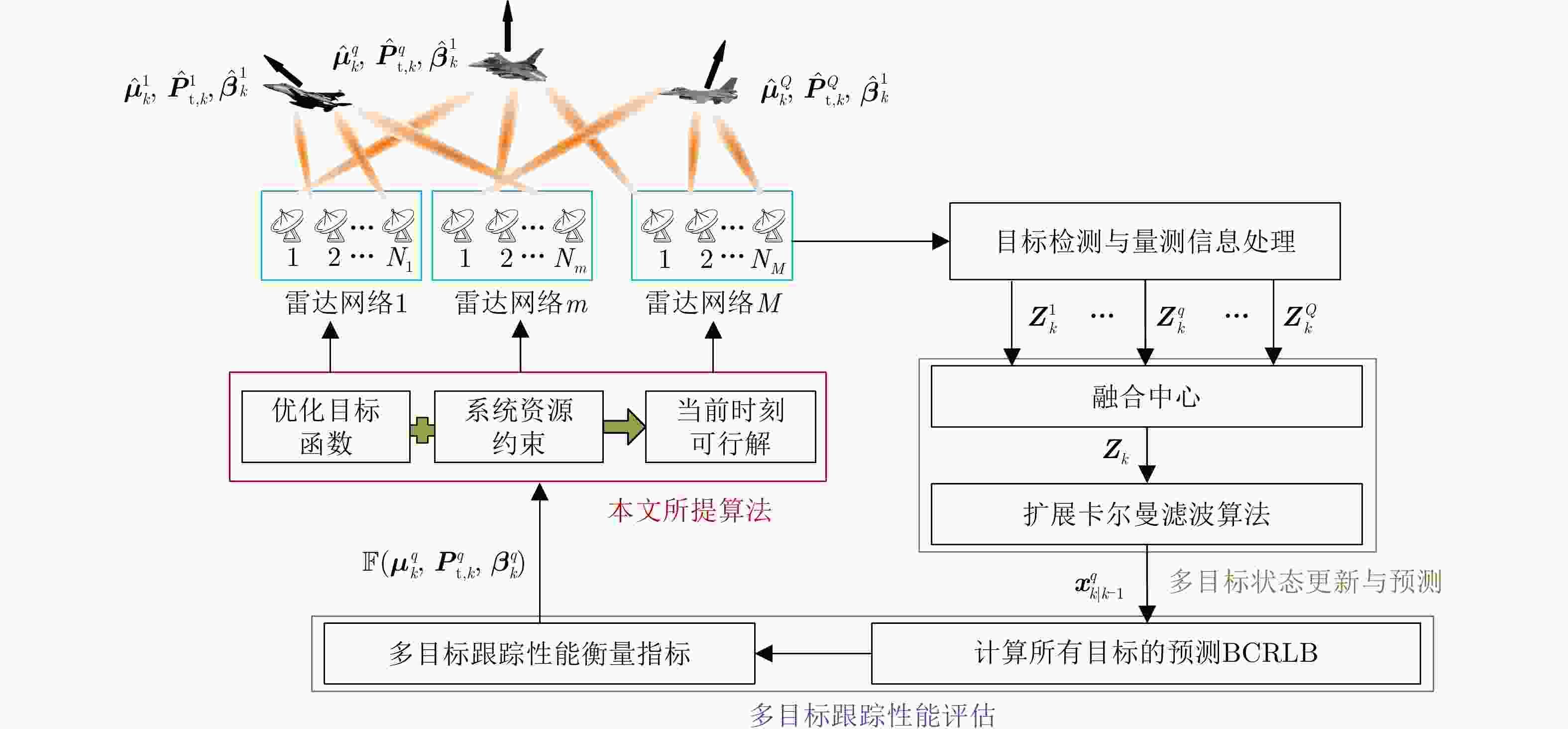
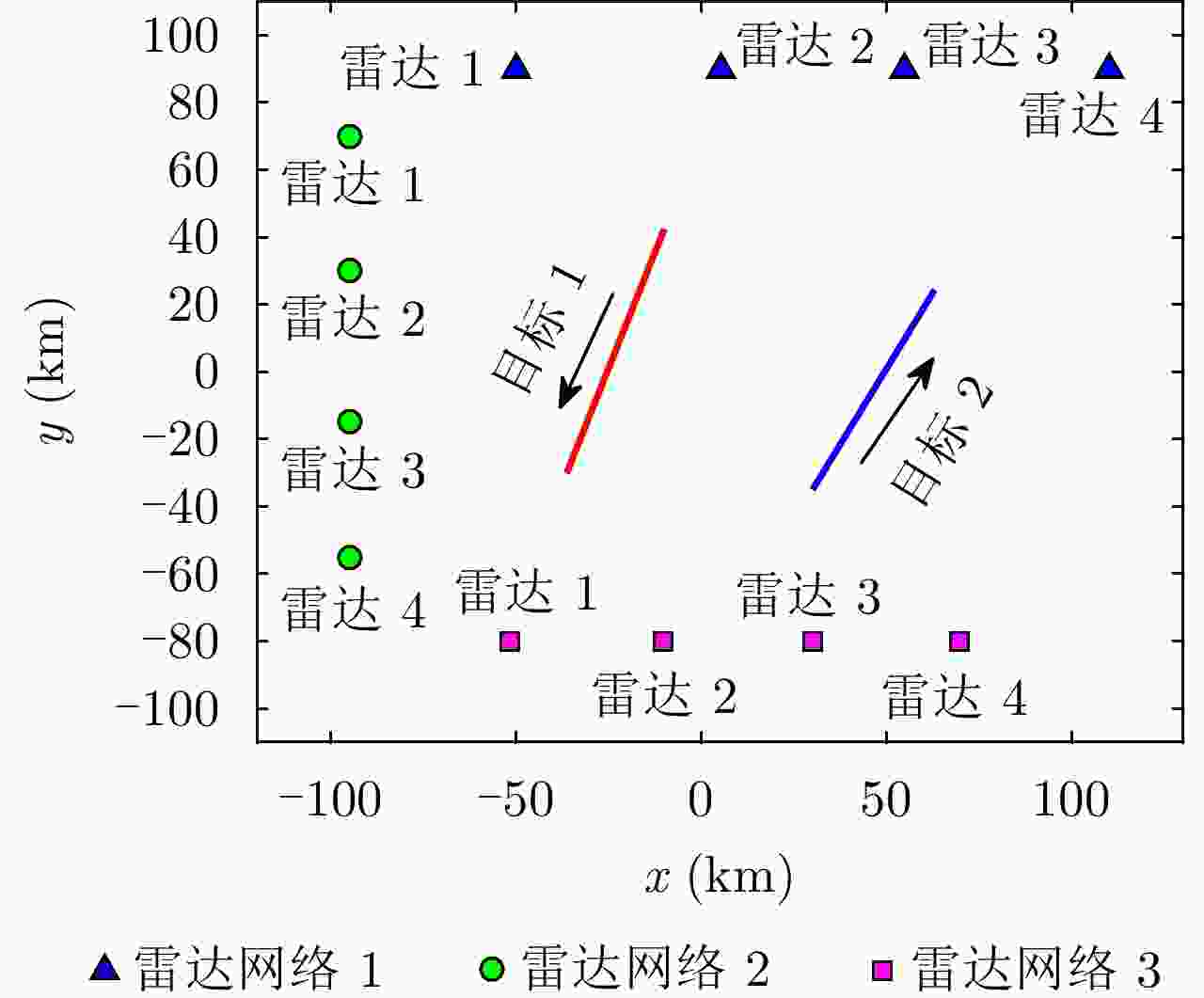
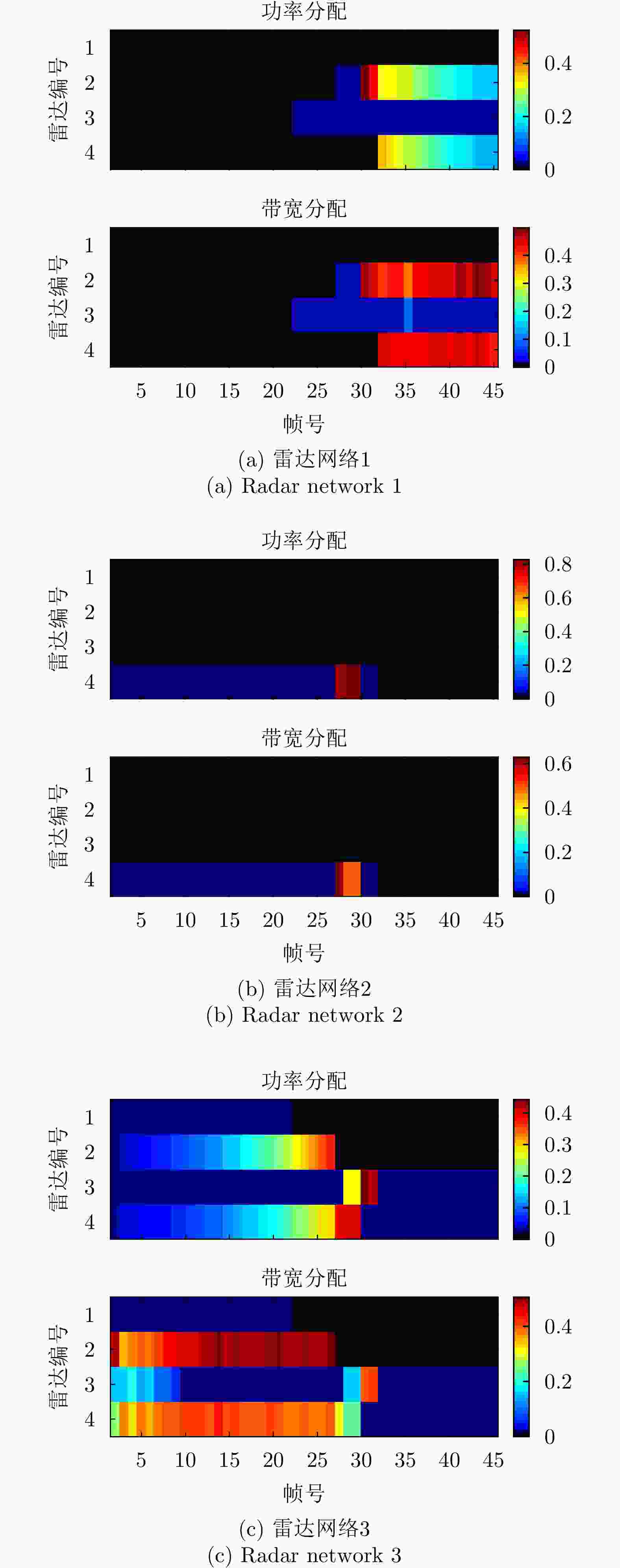
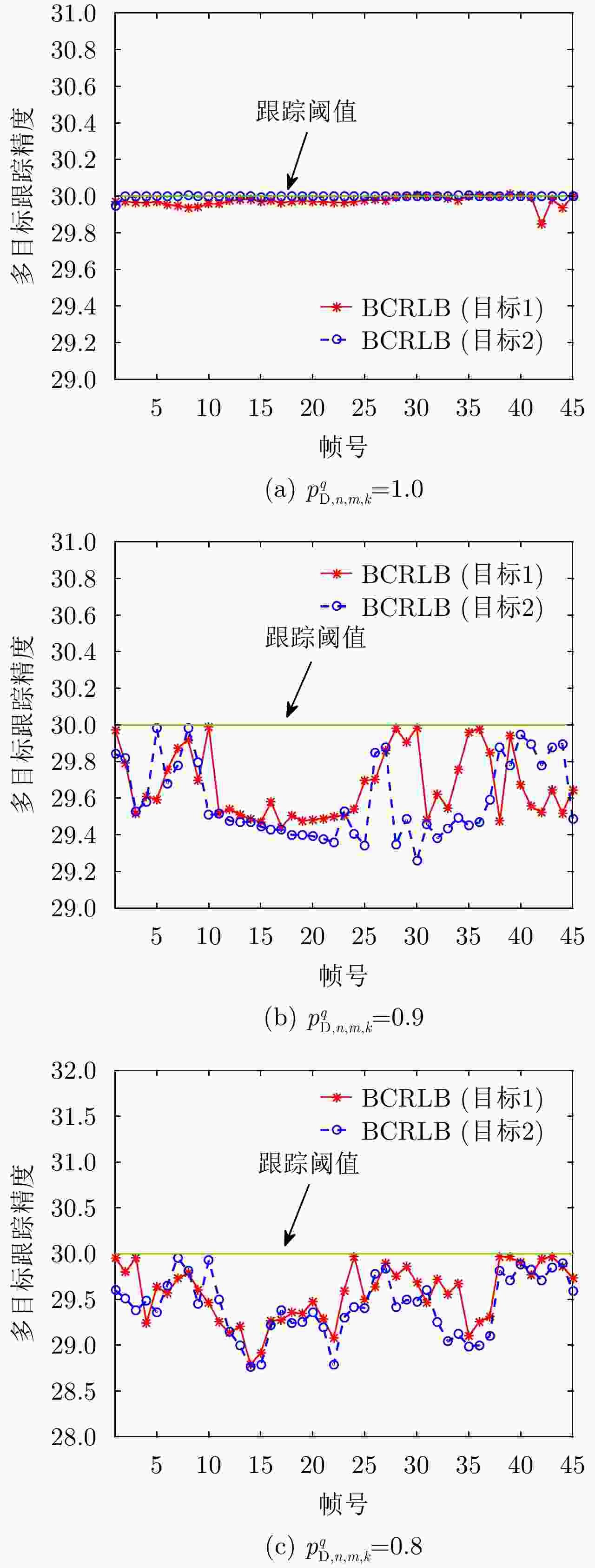
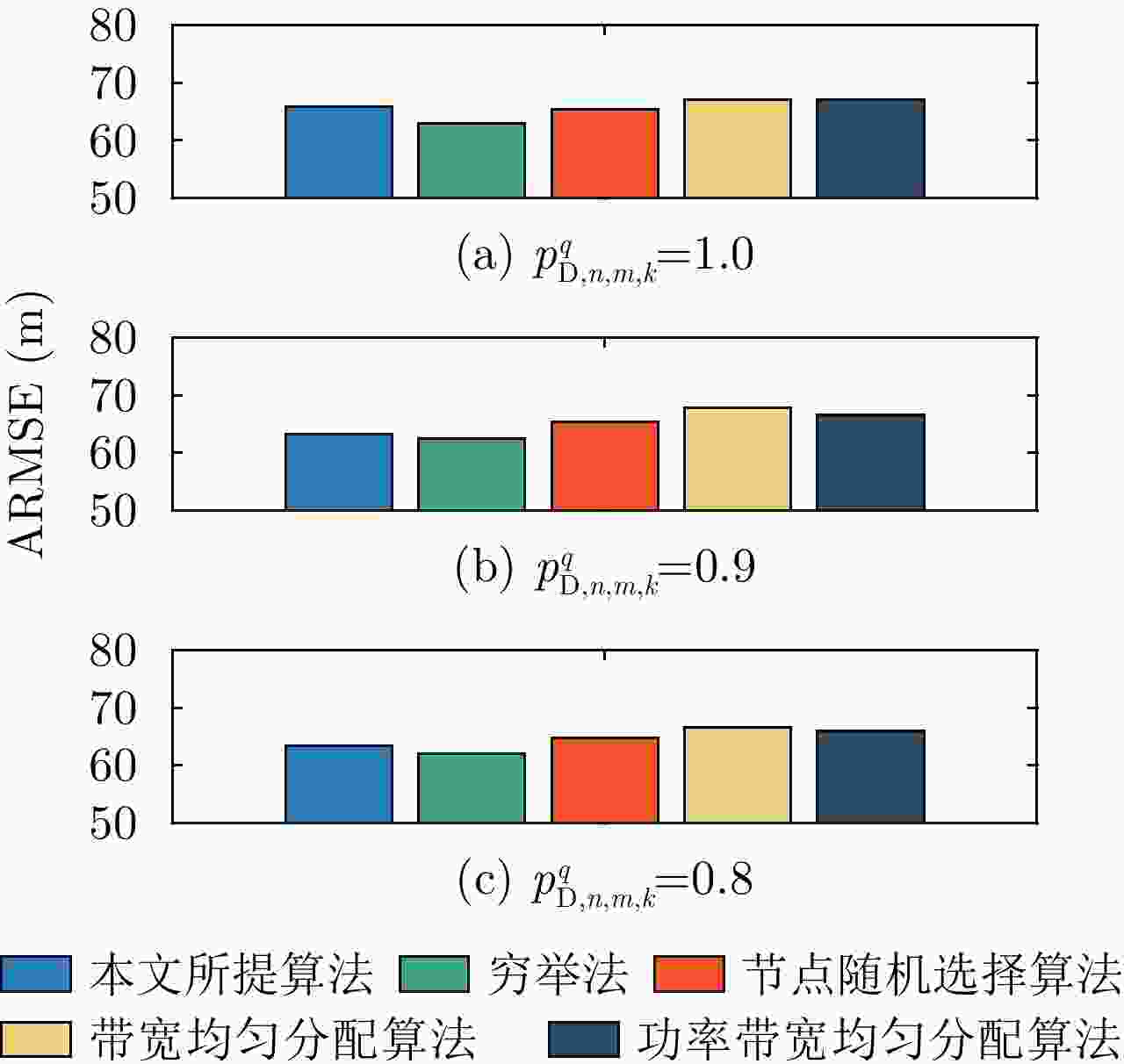
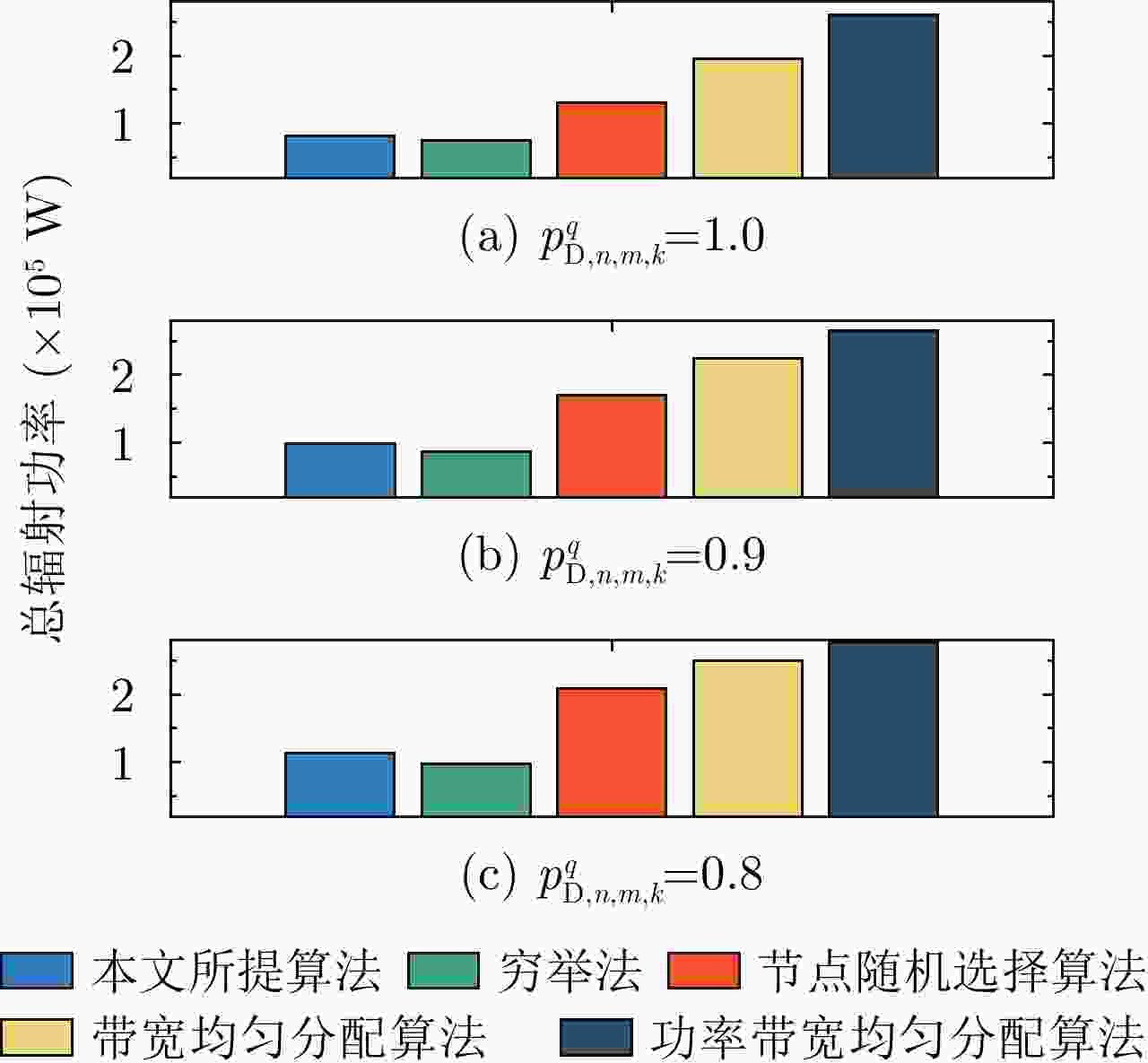
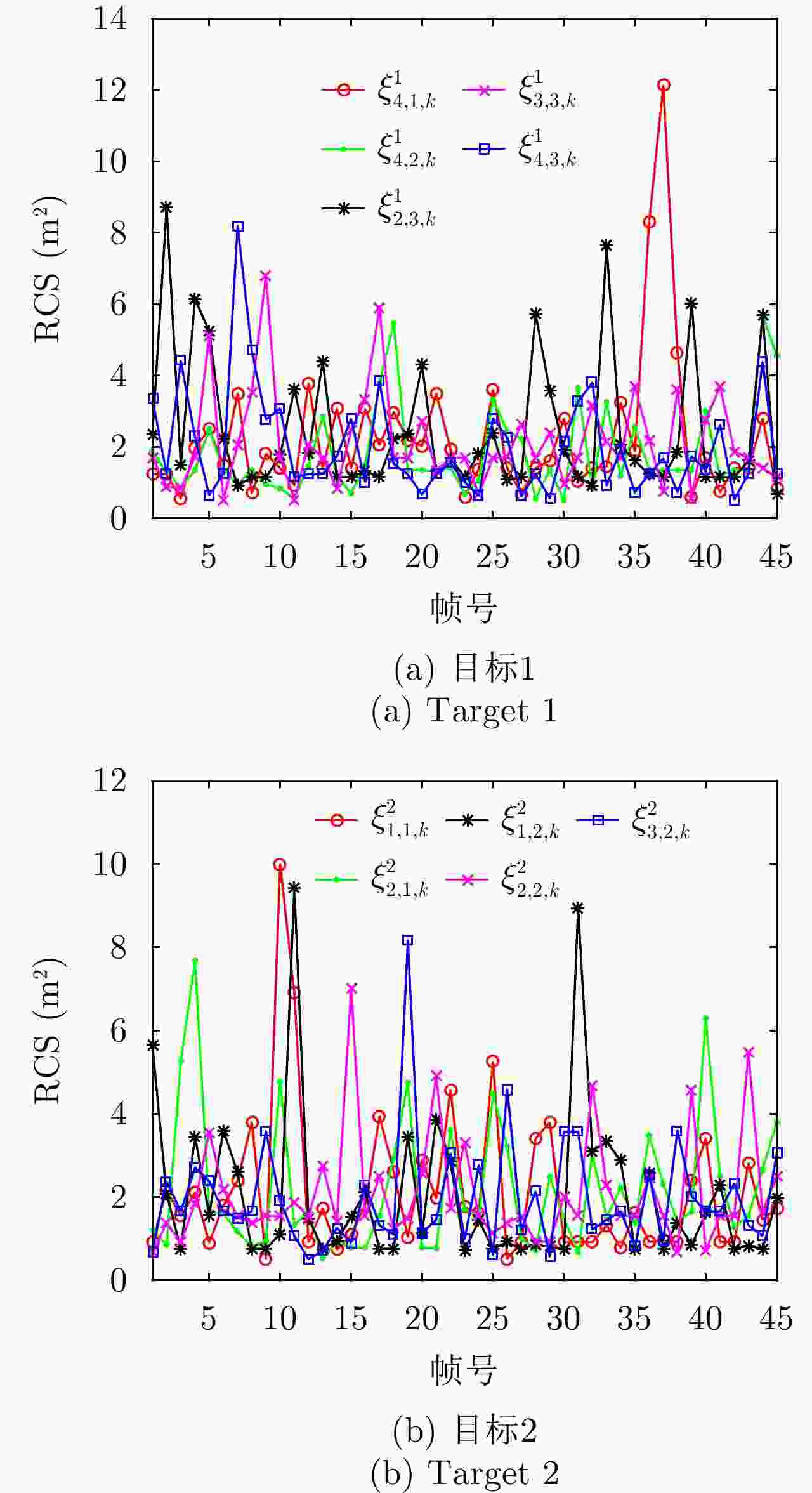
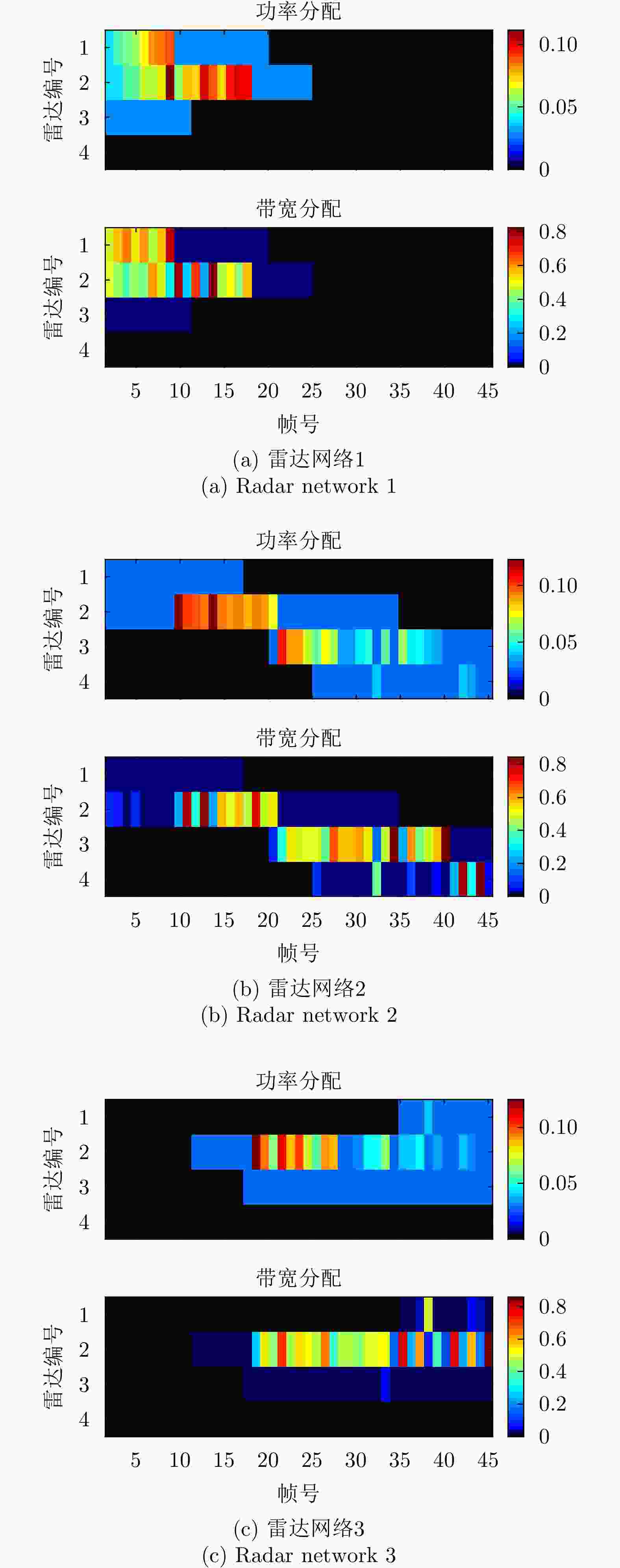
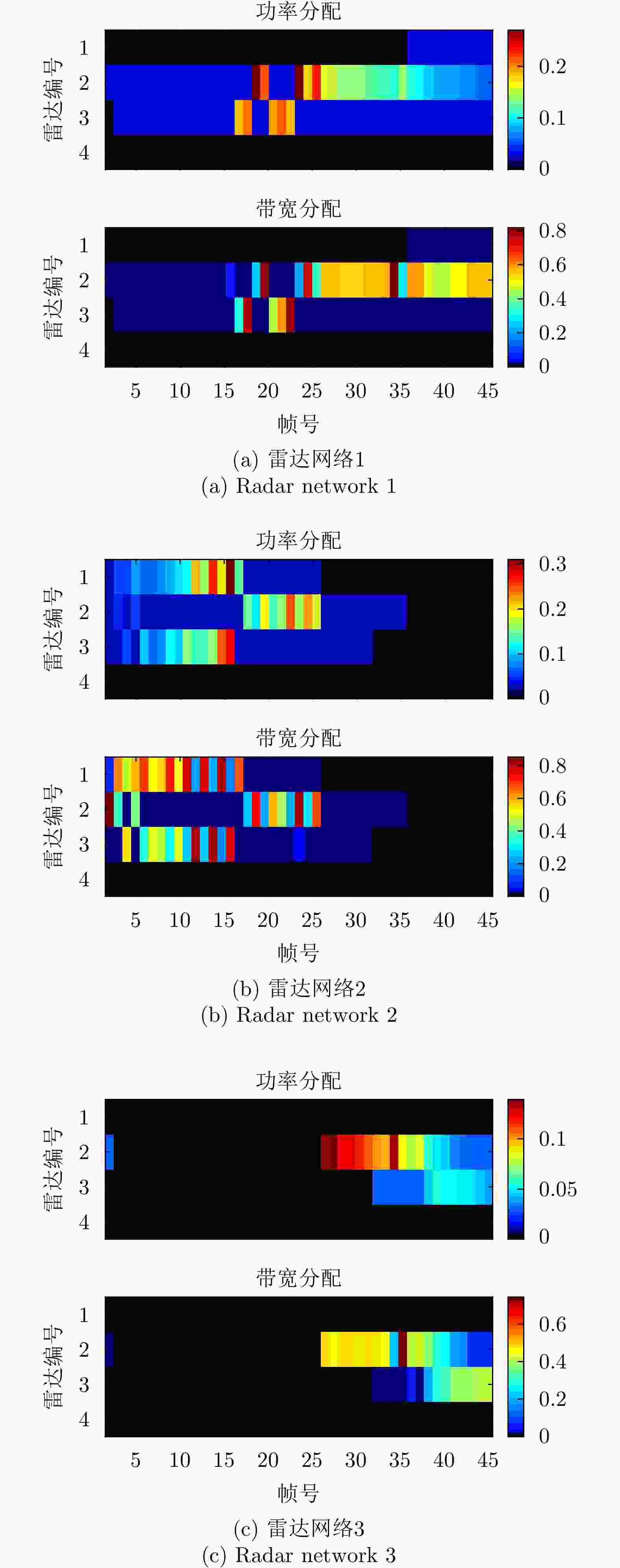
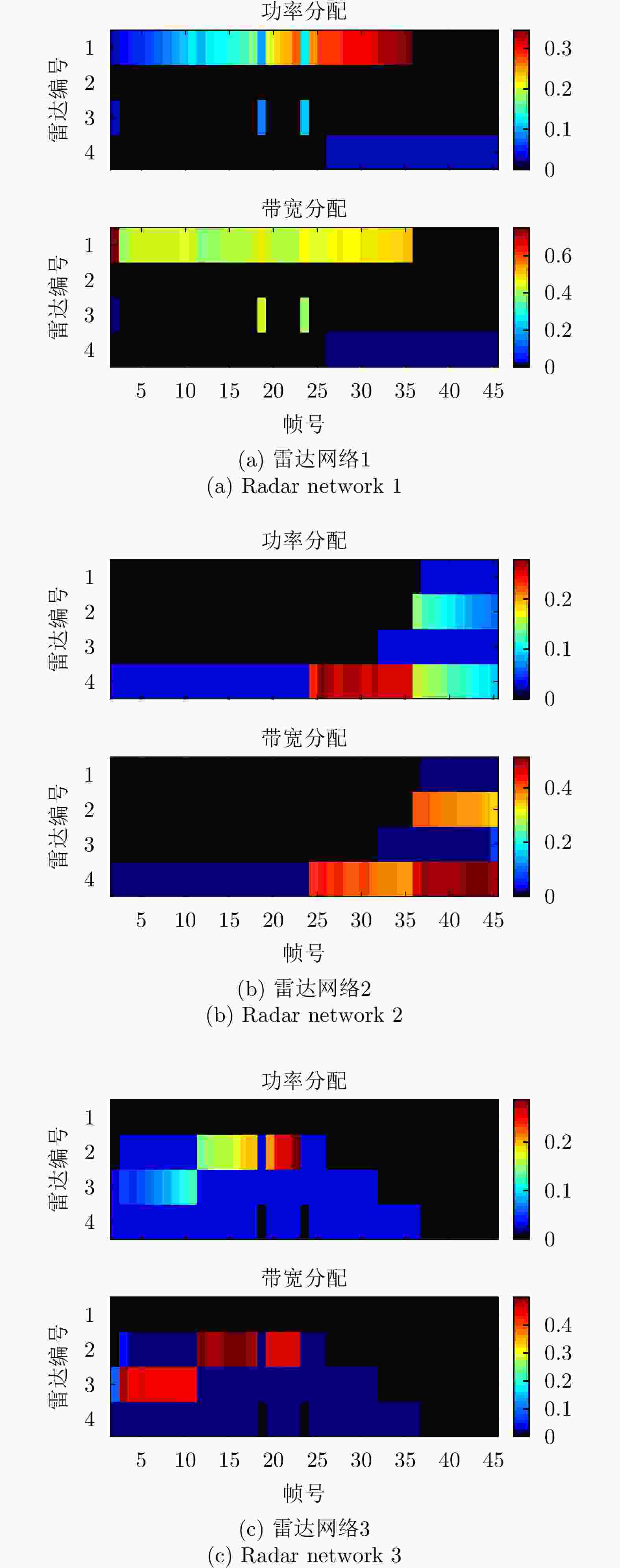
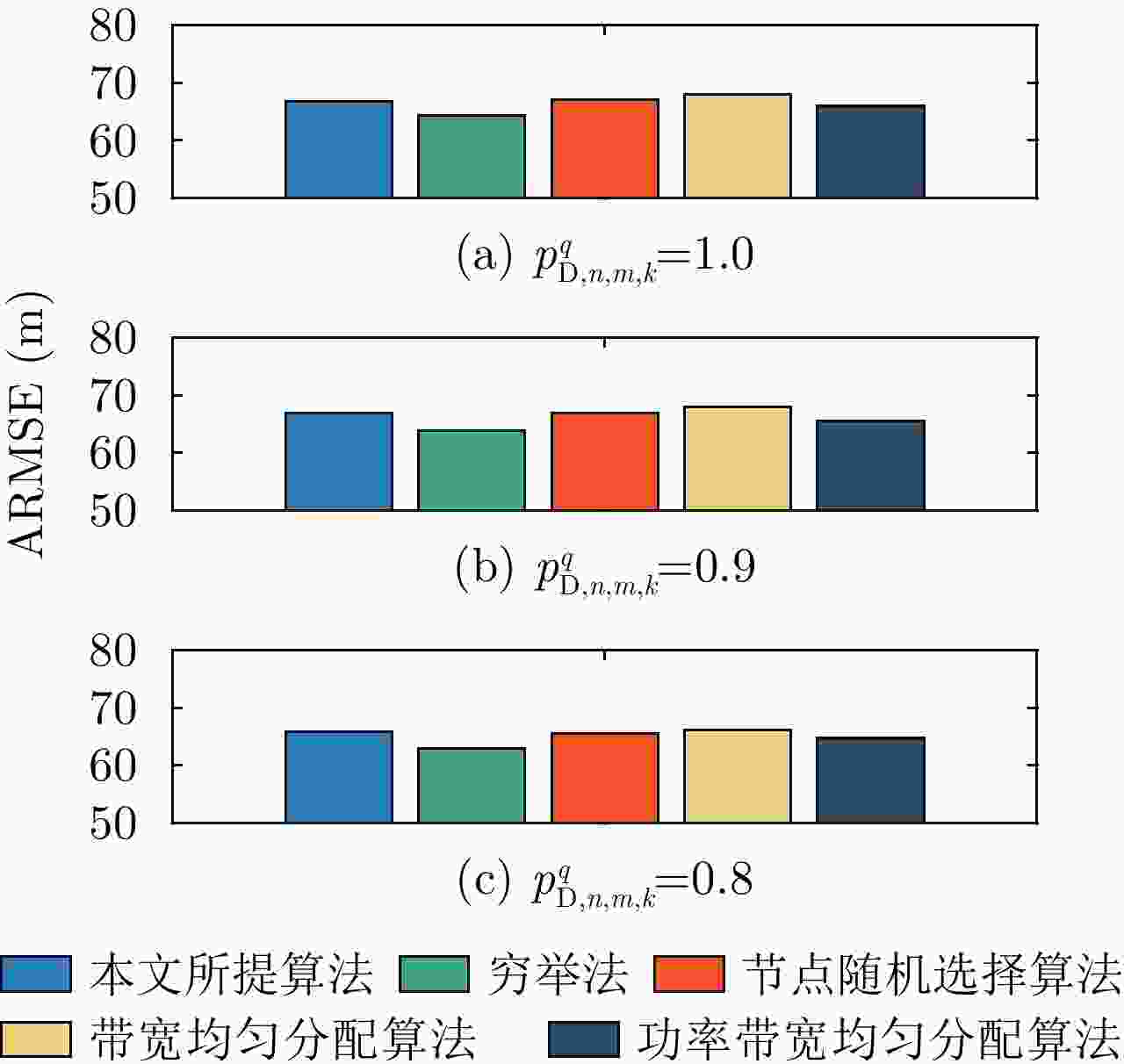
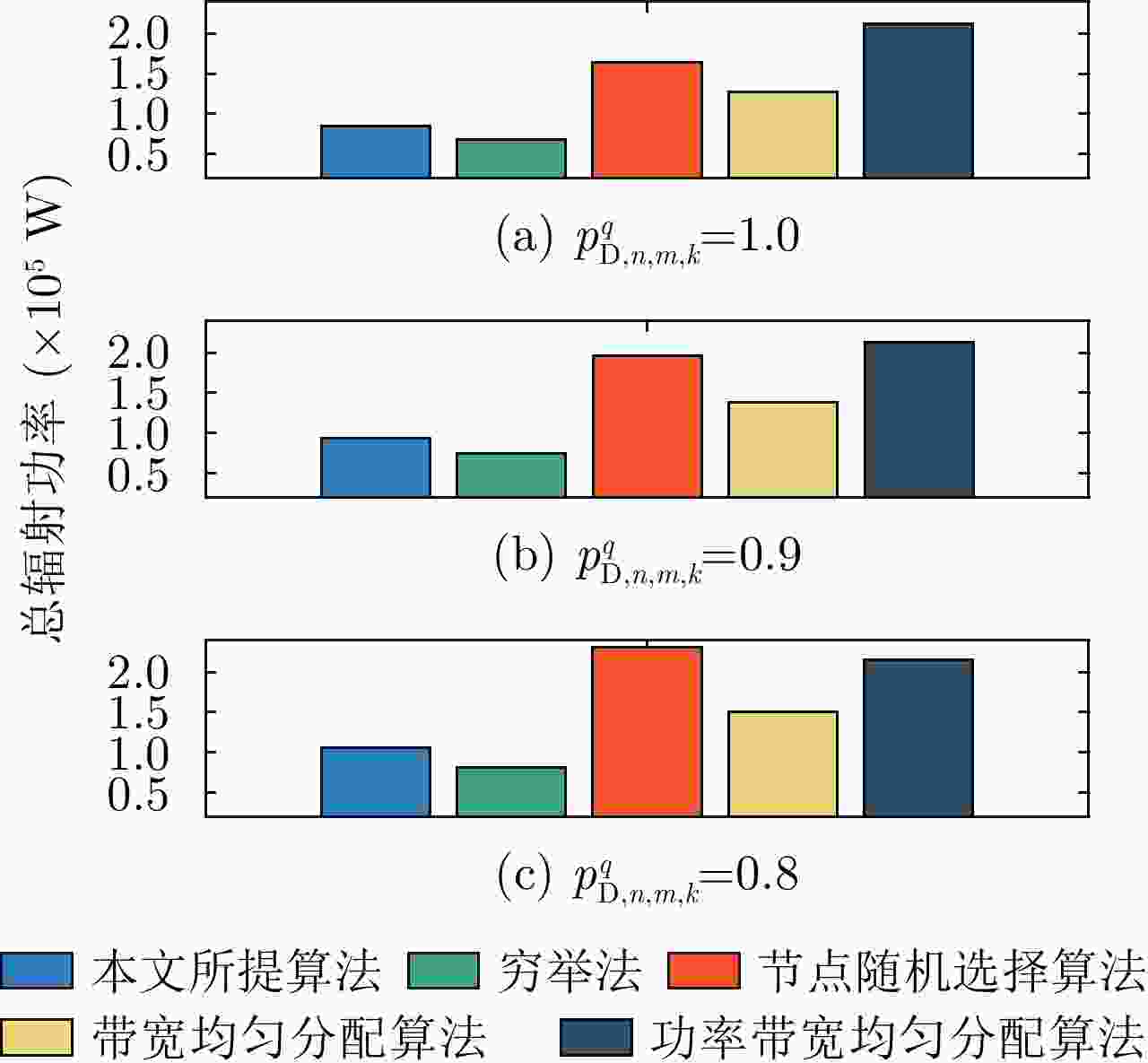
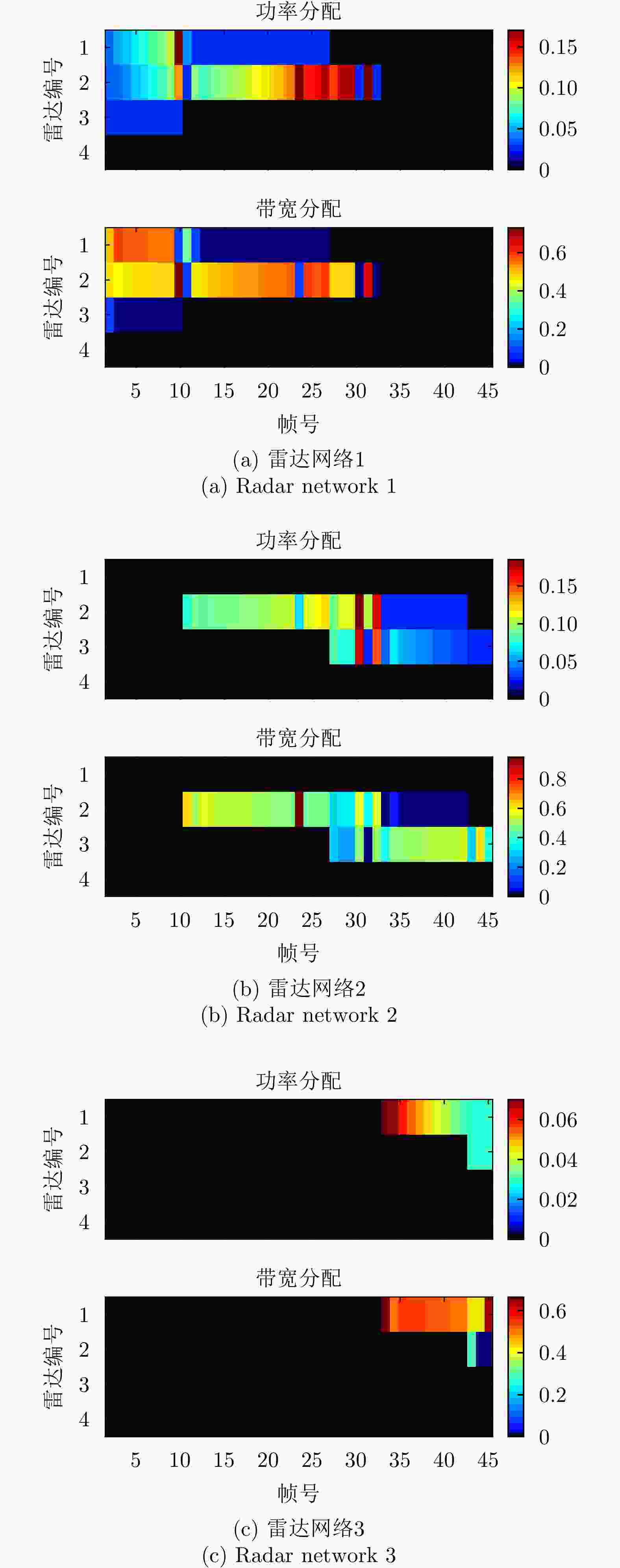
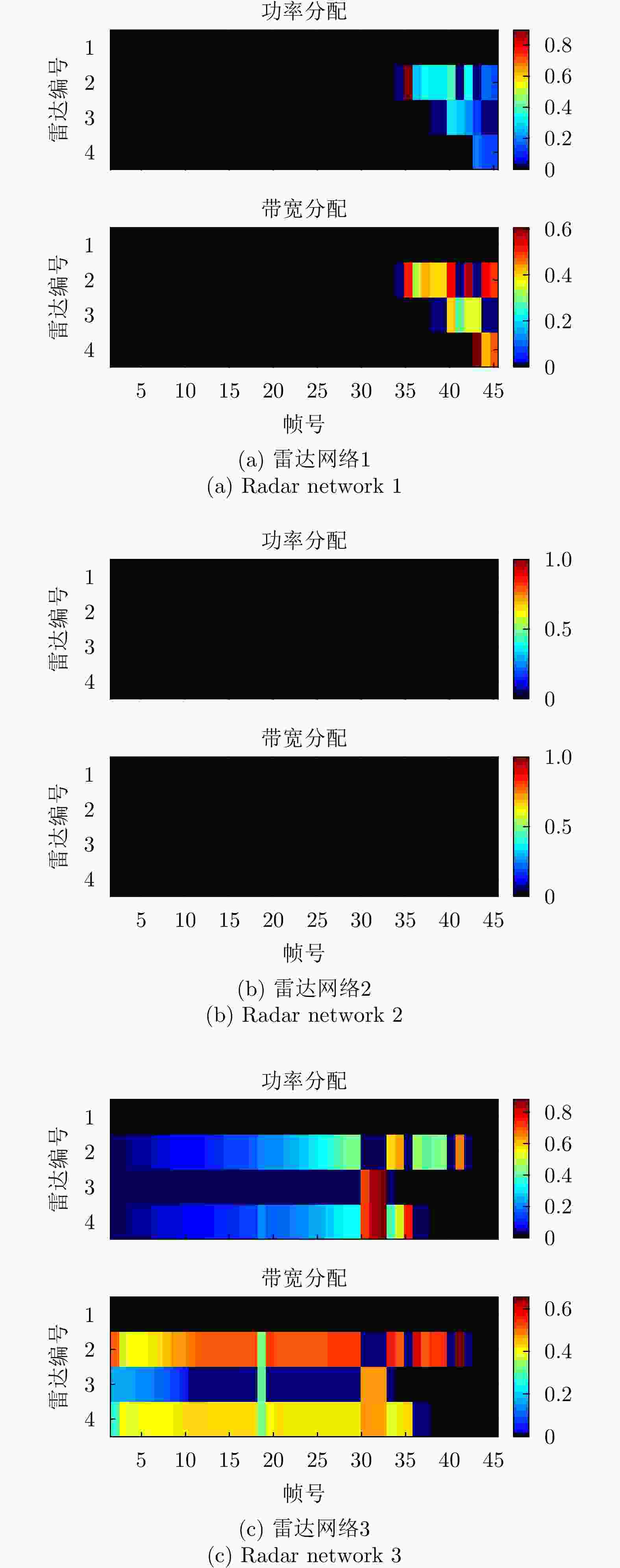
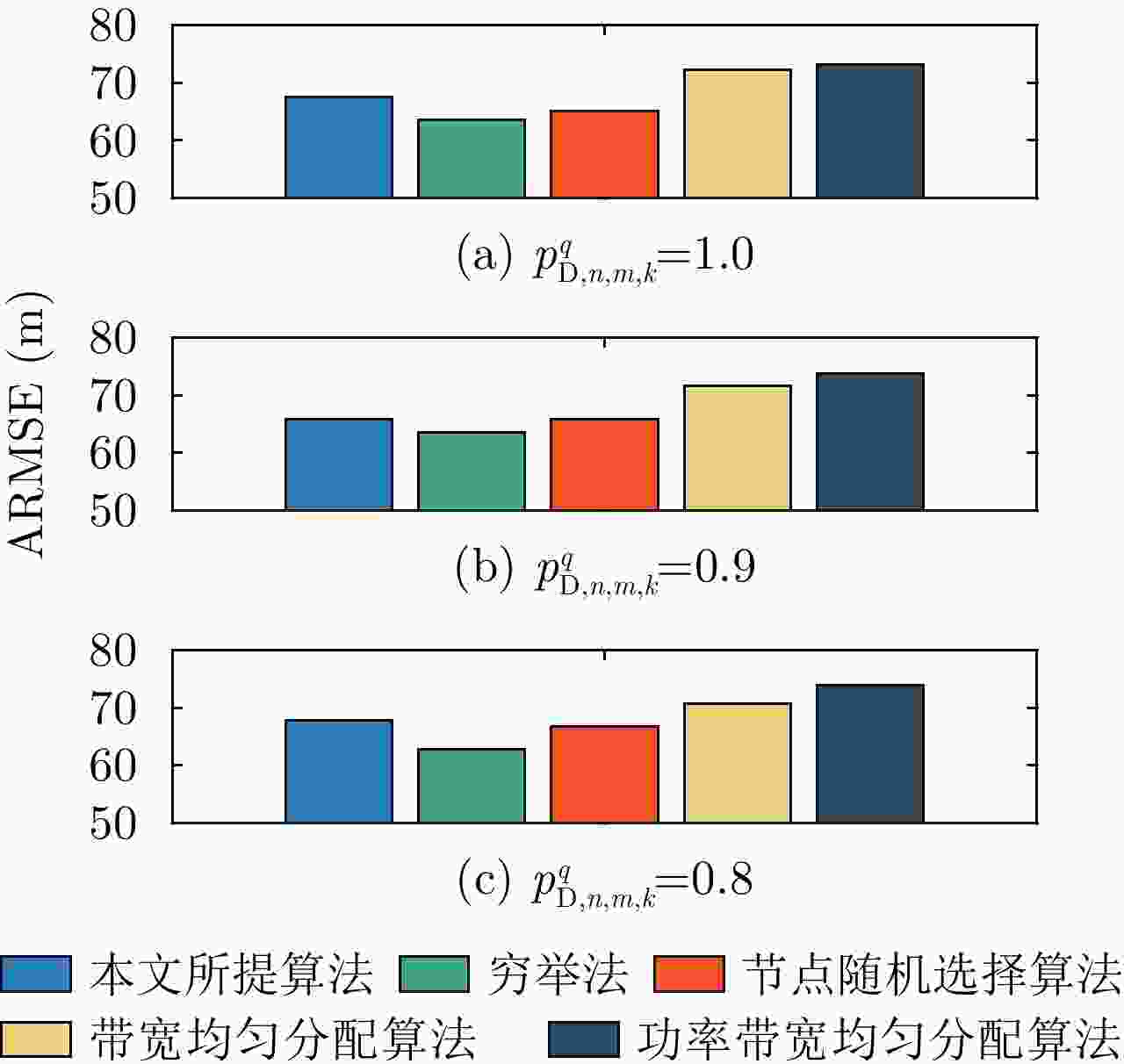
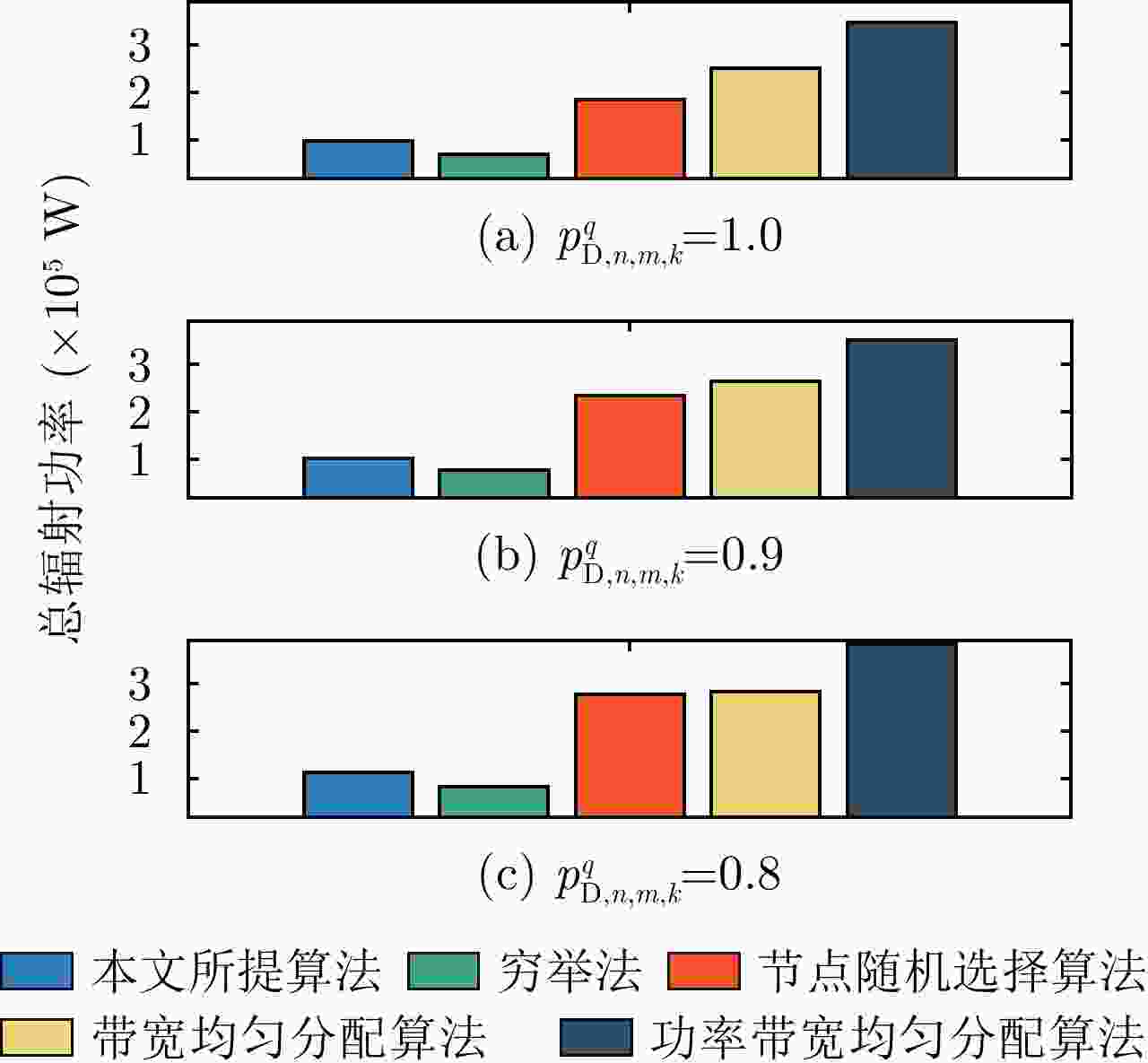
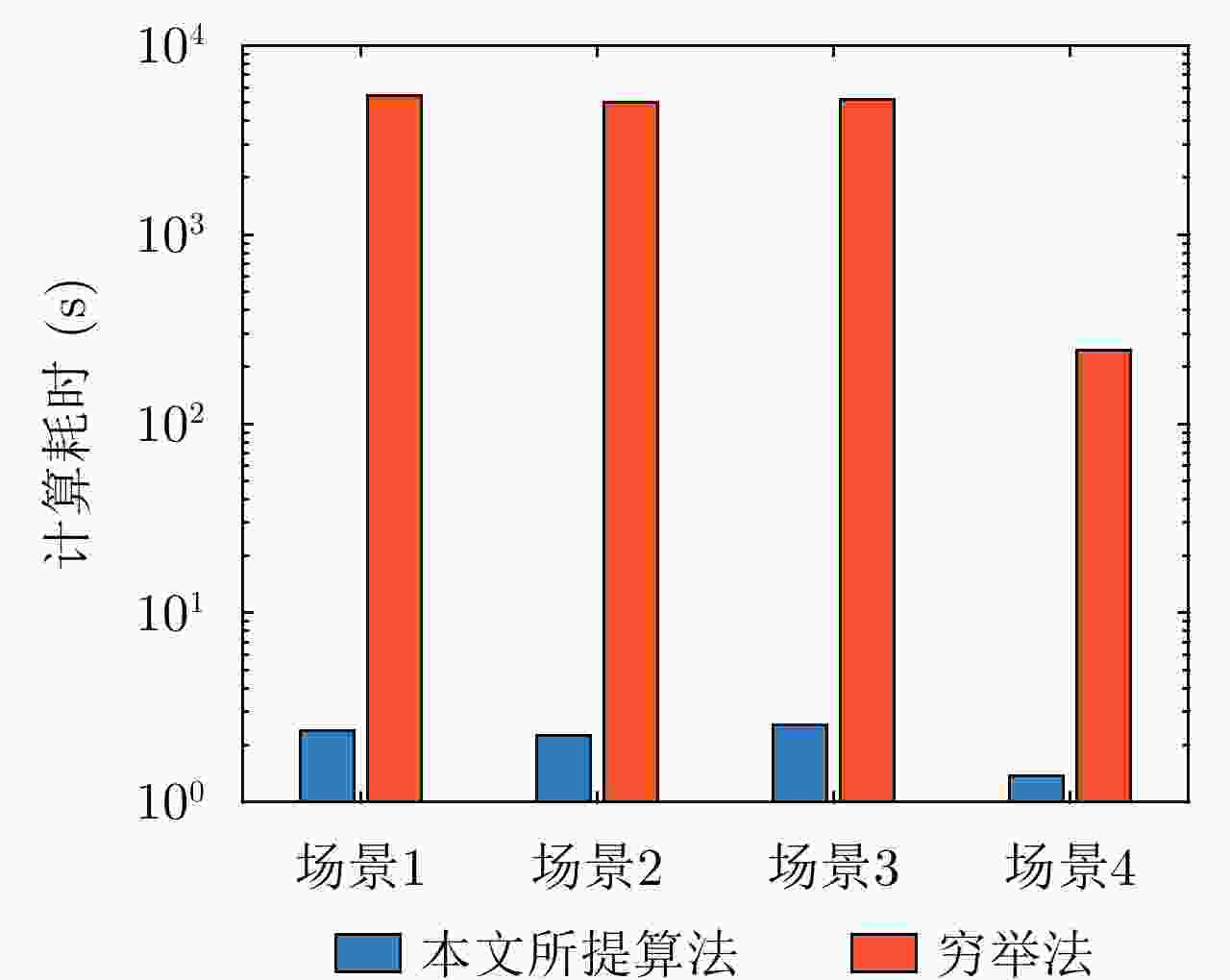
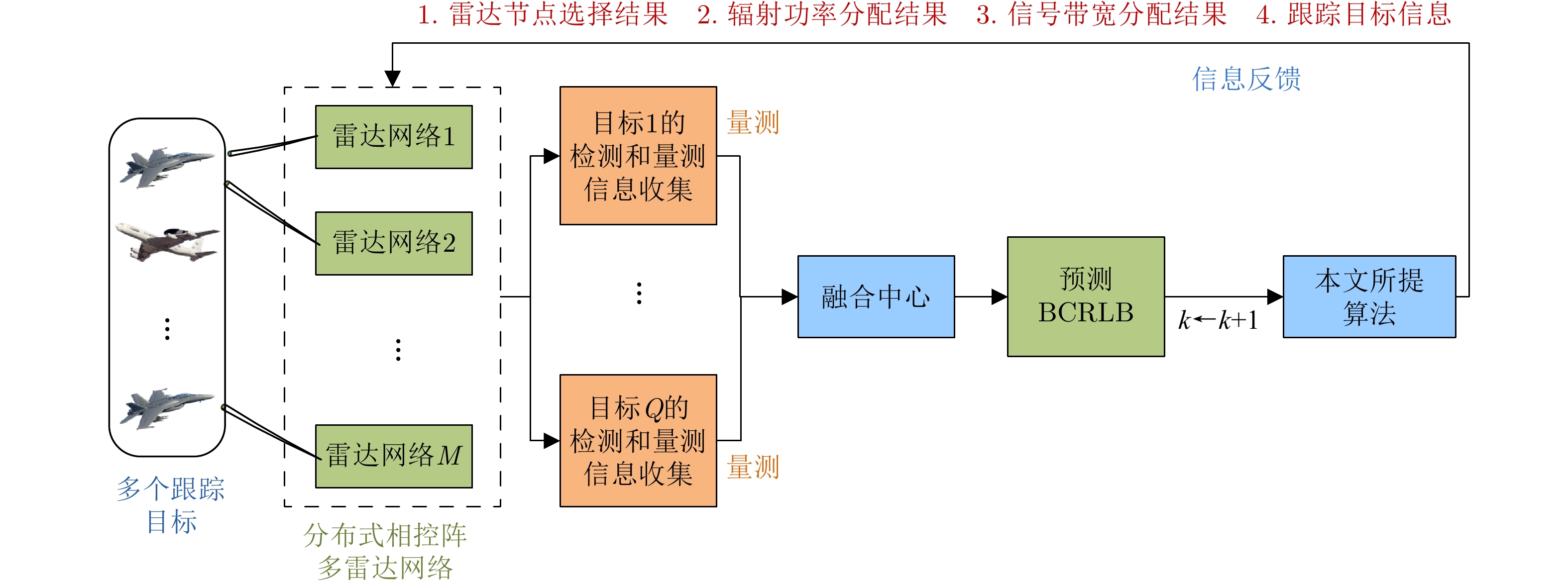
摘要: 该文针对分布式相控阵多雷达网络的多目标跟踪场景,研究非理想检测条件下的节点选择与辐射资源联合优化分配算法。首先,根据分布式相控阵多雷达网络构成、目标运动模型、雷达量测模型以及雷达节点检测情况,推导非理想检测下以雷达节点选择、辐射功率和信号带宽为变量的贝叶斯克拉默-拉奥下界(BCRLB)闭式解析表达式,并以此作为多目标跟踪精度衡量指标。在此基础上,以最小化系统各雷达节点对所有目标的总辐射功率为优化目标,以满足目标跟踪精度门限以及给定的系统射频辐射资源限制为约束条件,建立非理想检测条件下多雷达网络节点选择与辐射资源联合优化分配模型,对各时刻雷达节点选择、辐射功率和信号带宽等参数进行联合优化设计,以提升多雷达网络的射频隐身性能。最后,针对上述非线性、非凸优化问题,采用基于障碍函数法和循环最小化算法的4步分解算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,与现有算法相比,所提算法能在满足给定多目标跟踪精度的条件下有效降低分布式相控阵多雷达网络的总辐射功率,至少降低了约32.3%,从而提升其射频隐身性能。
-
关键词:
- 雷达资源分配 /
- 分布式多雷达网络 /
- 多目标跟踪 /
- 非理想检测 /
- 贝叶斯克拉默-拉奥下界
Abstract: In this study, a collaborative radar selection and transmit resource allocation strategy is proposed for multitarget tracking applications in multiple distributed phased array radar networks with imperfect detection performance. The closed-form expression for the Bayesian Cramér-Rao Lower Bound (BCRLB) with imperfect detection performance is obtained and adopted as the criterion function to characterize the precision of target state estimates. The key concept of the developed strategy is to collaboratively adjust the radar node selection, transmitted power, and effective bandwidth allocation of multiple distributed phased array radar networks to minimize the total transmit power consumption in an imperfect detection environment. This will be achieved under the constraints of the predetermined tracking accuracy requirements of multiple targets and several illumination resource budgets to improve its radio frequency stealth performance. The results revealed that the formulated problem is a mixed-integer programming, nonlinear, and nonconvex optimization model. By incorporating the barrier function approach and cyclic minimization technique, an efficient four-step-based solution methodology is proposed to solve the resulting optimization problem. The numerical simulation examples demonstrate that the proposed strategy can effectively reduce the total power consumption of multiple distributed phased array radar networks by at least 32.3% and improve its radio frequency stealth performance while meeting the given multitarget tracking accuracy requirements compared with other existing algorithms. -
1 非理想检测下基于障碍函数法的雷达节点选择算法
1. Radar node selection algorithm based on barrier function method with imperfect detection
输入:令$ {g_1} = {\kern 1pt} \mathbb{F}\left( {{\boldsymbol{\mu }}_k^q,{\boldsymbol{\hat P}}_{{\text{t}},k}^q,{\boldsymbol{\hat \beta }}_k^q} \right) - {\eta ^q} $, $ {g_2} = {\kern 1pt} - \mu _{1,1,k}^q $,
$ {g_3} = {\kern 1pt} - \mu _{2,1,k}^q $, ···, $ {g_{{N_1} + 1}} = {\kern 1pt} - \mu _{{N_1},1,k}^q $, ···,
$ {g_{\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 1}} = {\kern 1pt} - \mu _{{N_M},M,k}^q $, $ {g_{\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 2}} = {\kern 1pt} \mu _{1,1,k}^q - 1 $,
$ {g_{\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 3}} = {\kern 1pt} \mu _{2,1,k}^q - 1 $, ···, $ {g_{2\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 1}} = {\kern 1pt} \mu _{{N_M},M,k}^q - 1 $,
设置迭代索引$ \varphi = 1 $;设置可行域$ D = \left\{ {\mu _{n,m,k}^q\left| {{g_a}\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right) \le 0,a = 1,2, \cdots ,2\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 1} \right.} \right\} $,
其中$ {g_a}\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right) = {g_a} $;设置$ \varepsilon \gt 0 $为算法终止指标,$ {\xi ^{\left( \varphi \right)}} \gt 0 $,
$ e \ge 2 $。步骤1:取$ {\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right)^{\left( {\varphi - 1} \right)}} \in D $为初始点; 步骤2:求解如下问题:
$\begin{gathered} \min {\kern 1pt} {\mathbb{G}_1} - {\xi ^{\left( \varphi \right)} }\left[ {\frac{1}{ { {g_1} } } + \frac{1}{ { {g_2} } } + \cdots + \frac{1}{ { {g_{2 \sum\limits_{m = 1}^M { {N_m} } + 1} } } } } \right], \\ {\text{s} }{\text{.t} }{\text{.} }{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} \mu _{n,m,k}^q \in D. \\ \end{gathered}$式中,${\mathbb{G}_1}$表示优化模型(23)中的目标函数; 步骤3:令上述问题的极小值点为$ {\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right)^{\left( \varphi \right)}} $; 步骤4:检验终止条件,若
$ - {\xi ^{\left( \varphi \right)}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{g_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{g_2}}} + , \cdots , + \dfrac{1}{{{g_{2\sum\limits_{m = 1}^M {{N_m}} + 1}}}}} \right] \lt \varepsilon $,算法终止;若
未满足终止条件,令${\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right)^{\left( {\varphi + 1} \right)} } \leftarrow \dfrac{ { { {\left( {\mu _{n,m,k}^q} \right)}^{\left( \varphi \right)} } } }{e}$,
$ \varphi \leftarrow \varphi + 1 $。输出:雷达节点最优选择结果。 -
[1] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMIN L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448. [2] GODRICH H, PETROPULU A P, and POOR H V. Power allocation strategies for target localization in distributed multiple-radar architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3226–3240. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2144976. [3] CHAVALI P and NEHORAI A. Scheduling and power allocation in a cognitive radar network for multiple-target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(2): 715–729. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2174989. [4] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KONG Lingjiang, et al. Receive-beam resource allocation for multiple target tracking with distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2421–2436. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2818579. [5] ZHANG Haowei, ZONG Binfeng, and XIE Junwei. Power and bandwidth allocation for multi-target tracking in collocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9795–9806. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3002899. [6] 易伟, 袁野, 刘光宏, 等. 多雷达协同探测技术研究进展:认知跟踪与资源调度算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036.YI Wei, YUAN Ye, LIU Guanghong, et al. Recent advances in multi-radar collaborative surveillance: Cognitive tracking and resource scheduling algorithms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036. [7] ZHANG Weiwei, SHI Chenguang, SALOUS S, et al. Convex optimization-based power allocation strategies for target localization in distributed hybrid non-coherent active-passive radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 2476–2488. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3173756. [8] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Joint node selection and power allocation strategy for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2777394. [9] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, XIE Junwei, et al. Joint subarray selection and power allocation for cognitive target tracking in large-scale MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 2569–2580. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2960401. [10] YI Wei, YUAN Ye, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Resource scheduling for distributed multi-target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1602–1617. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2976587. [11] SUN Hao, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. Joint radar scheduling and beampattern design for multitarget tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1863–1867. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3108675. [12] YAN Junkun, DAI Jinhui, PU Wenqiang, et al. Target capacity based resource optimization for multiple target tracking in radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 2410–2421. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3071173. [13] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, ZHANG Zhaojian, et al. Joint target assignment and power allocation in multiple distributed MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 694–704. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2986020. [14] SUN Hao, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. Resource allocation for multitarget tracking and data reduction in radar network with sensor location uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4843–4858. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3101018. [15] AJORLOO A, AMINI A, and BASTANI M H. A compressive sensing-based colocated MIMO radar power allocation and waveform design[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(22): 9420–9429. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2871214. [16] DU Yi, LIAO Kefei, OUYANG Shan, et al. Time and aperture resource allocation strategy for multitarget ISAR imaging in a radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(6): 3196–3206. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2954711. [17] WANG Dan, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Joint optimization of time and aperture resource allocation strategy for multi-target ISAR imaging in radar sensor network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 19570–19581. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3090053. [18] SUN Hao, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. JPBA of ARN for target tracking in clutter[J]. IET Radar,Sonar &Navigation, 2019, 13(11): 2024–2033. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0038. [19] DAI Jinhui, YAN Junkun, LV Jindong, et al. Composed resource optimization for multitarget tracking in active and passive radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5119215. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3215228. [20] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, SHI Junpeng, et al. Joint detection threshold optimization and illumination time allocation strategy for cognitive tracking in a networked radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 5833–5847. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3188205. [21] LI Zhengjie, XIE Junwei, LIU Weijian, et al. Joint strategy of power and bandwidth allocation for multiple maneuvering target tracking in cognitive MIMO radar with collocated antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(1): 190–204. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3204939. [22] YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Collaborative detection and power allocation framework for target tracking in multiple radar system[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 55: 173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.08.010. [23] LI Xi, CHENG Ting, SU Yang, et al. Joint time-space resource allocation and waveform selection for the collocated MIMO radar in multiple targets tracking[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: 107650. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107650. [24] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, ZONG Binfeng, et al. An efficient power allocation strategy for maneuvering target tracking in cognitive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1591–1602. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047227. [25] ZUO Lei, HU Juan, SUN Hao, et al. Resource allocation for target tracking in multiple radar architectures over lossy networks[J]. Signal Processing, 2023, 208: 108973. doi: 10.1016/J.SIGPRO.2023.108973. [26] SUN Hao, LI Ming, ZUO Lei, et al. Joint threshold optimization and power allocation of cognitive radar network for target tracking in clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 172: 107566. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107566. [27] LAWRENCE D E. Low probability of intercept antenna array beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(9): 2858–2865. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2052573. [28] GOVONI M A, LI Hongbin, and KOSINSKI J A. Low probability of interception of an advanced noise radar waveform with linear-FM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2): 1351–1356. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494419. [29] ZHANG Zhenkai and TIAN Yubo. A novel resource scheduling method of netted radars based on Markov decision process during target tracking in clutter[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2016, 2016(1): 16. doi: 10.1186/s13634-016-0309-3. [30] SHI Chenguang, WANG Fei, SELLATHURAI M, et al. Power minimization-based robust OFDM radar waveform design for radar and communication systems in coexistence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1316–1330. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2770086. [31] ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, HE Shibo, et al. A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1099–1112. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2704610. [32] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Low probability of intercept-based collaborative power and bandwidth allocation strategy for multi-target tracking in distributed radar network system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(12): 6367–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2977328. [33] YUAN Ye, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust power allocation for resource-aware multi-target tracking with colocated MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 443–458. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047519. [34] SHI Chenguang, WANG Yijie, SALOUS S, et al. Joint transmit resource management and waveform selection strategy for target tracking in distributed phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2762–2778. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3138869. [35] SU Yang, CHENG Ting, HE Zishu, et al. Joint waveform control and resource optimization for maneuvering targets tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(3): 3960–3971. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3098622. [36] YAN Junkun, DAI Jinhui, PU Wenqiang, et al. Quality of service constrained-resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking in radar sensor network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 771–779. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2990409. [37] SHI Yuchun, JIU Bo, YAN Junkun, et al. Data-driven simultaneous multibeam power allocation: When multiple targets tracking meets deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 1264–1274. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2984774. [38] DELIGIANNIS A, PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, et al. Game-theoretic power allocation and the Nash equilibrium analysis for a multistatic MIMO radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(24): 6397–6408. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2755591. [39] YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Optimal resource allocation for asynchronous multiple targets tracking in heterogeneous radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4055–4068. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3007313. [40] YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, LIU Hongwei, et al. Robust chance constrained power allocation scheme for multiple target localization in colocated MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(15): 3946–3957. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2841865. [41] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Joint target assignment and resource optimization framework for multitarget tracking in phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 4379–4390. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3025867. [42] ZHANG Weiwei, SHI Chenguang, and ZHOU Jianjiang. Power minimization-based joint resource allocation algorithm for target localization in noncoherent distributed MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(2): 2183–2194. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3126152. [43] FARINA A, RISTIC B, and TIMMONERI L. Cramér-Rao bound for nonlinear filtering with Pd<1 and its application to target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(8): 1916–1924. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.800411. [44] ANASTASIO V, FARINA A, COLONE F, et al. Cramér-Rao lower bound with Pd<1 for target localisation accuracy in multistatic passive radar[J]. IET Radar,Sonar &Navigation, 2014, 8(7): 767–775. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0213. [45] SUN Jun, LU Xiujuan, YUAN Ye, et al. Resource allocation for multi-target tracking in multi-static radar systems with imperfect detection performance[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence Italy, 2020. [46] SHI Chenguang, SHI Zhao, TANG Zhicheng, et al. Joint Radar Selection and Resource Allocation for Multi-target Tracking in Multiple Radar Networks with Non-ideal Detection Performance[M]. FU Wenxing, GU Mancang, and NIU Yifeng. Proceedings of 2022 International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems (ICAUS 2022). Singapore: Springer, 2023: 82–89. [47] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [48] YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, JIU Bo, et al. Simultaneous multibeam resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3110–3122. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2417504. [49] STOICA P and SELEN Y. Cyclic minimizers, majorization techniques, and the expectation-maximization algorithm: A refresher[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2004, 21(1): 112–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2004.1267055. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: