-
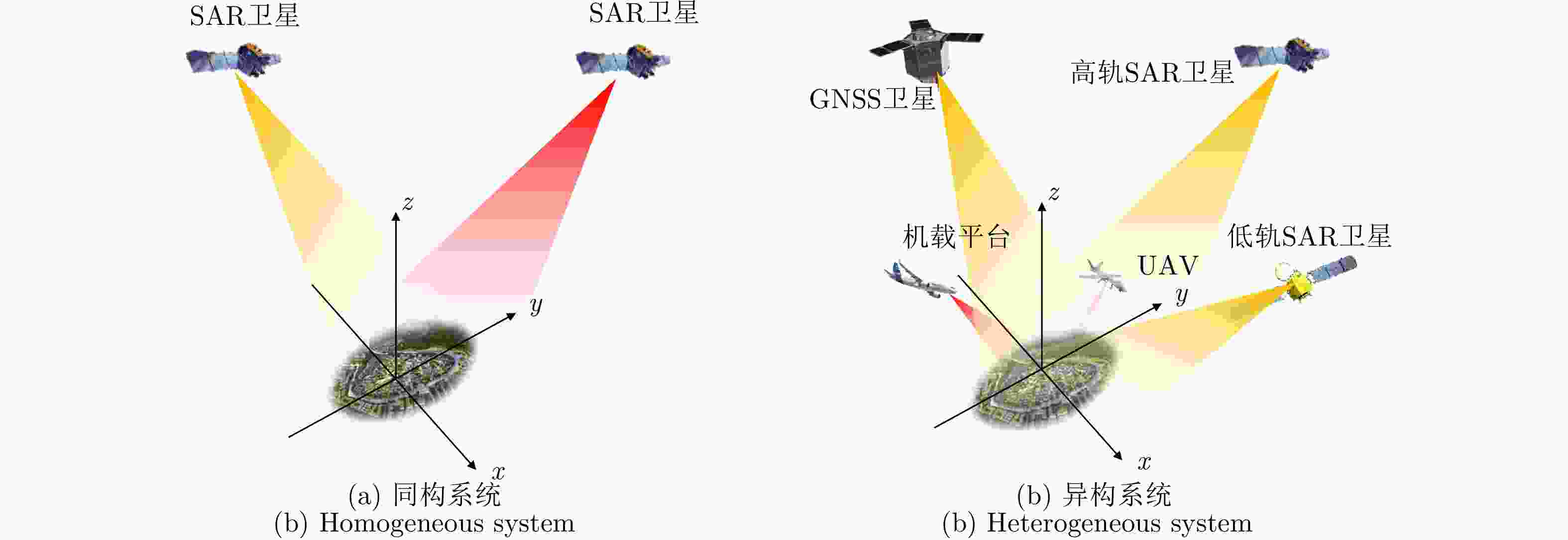
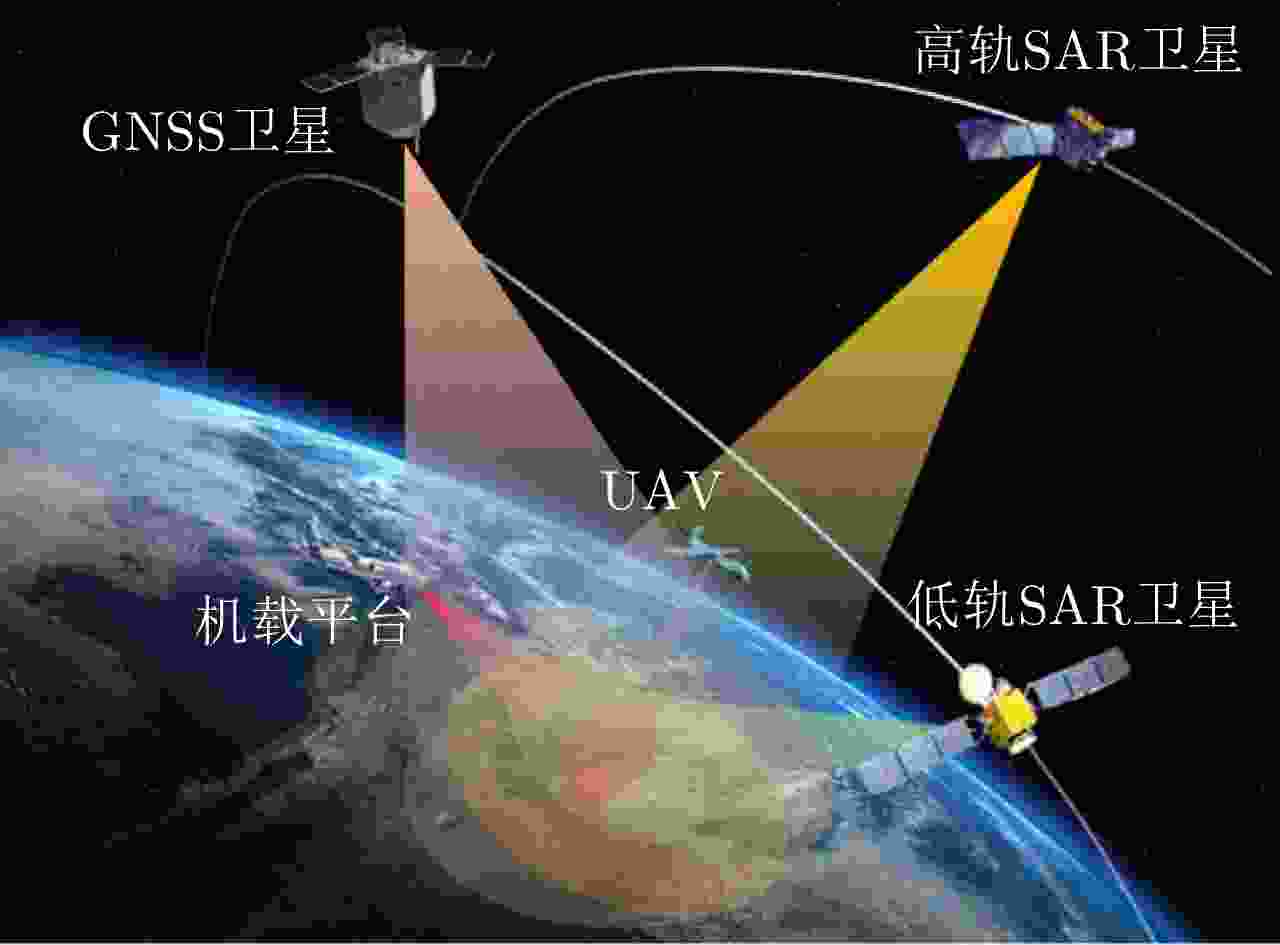
摘要: 星源照射双/多基地合成孔径雷达(SAR),采用卫星发射,卫星、临近空间、飞机、地面等平台接收,实现对地海面场景和目标的高分辨成像。该技术具有可成像范围广、隐蔽性好、抗干扰能力强等优点,且可以通过波束调控实现扫描、聚束、滑动聚束等多种组合成像模式,从而获取更加丰富的成像信息,具有十分广阔的民用和军事应用前景。目前,国内外针对星源照射双/多基地SAR成像技术开展了多年的研究,积累了诸多研究成果。该文分别从系统组成、构型方法、回波模型、成像方法、收发同步与试验验证等方面对该技术进行阐述与分析,同时对相关的研究工作进行较系统的回顾,并展望了星源照射双/多基地SAR成像技术未来的发展方向。Abstract: Bi/multistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) using spaceborne illuminator utilizes spaceborne platforms as transmitters and satellites, near-space vehicles, aircraft, and ground platforms as receivers, which allows high-resolution imaging of ground and marine scenes and targets. The system’s benefits include a broad imaging field of view, high concealment, and potent antijamming abilities. By using beam steering methods, a variety of imaging modes can be achieved, such as staring spotlight and sliding spotlight modes, which obtain abundant information about the imaging scene and offer broad application prospects both in civil and military fields. Thus far, the bi/multistatic SAR using spaceborne illuminator has been intensively investigated, and several research findings have been reported. This paper examines the technology from the aspects of system components, configuration design, echo model, imaging techniques, bistatic synchronization, and experimental verification and systematically reviews the state-of-the-art research progress. Finally, it is anticipated that spaceborne illuminator technology will be used to develop bi/multistatic SAR in the future.
-
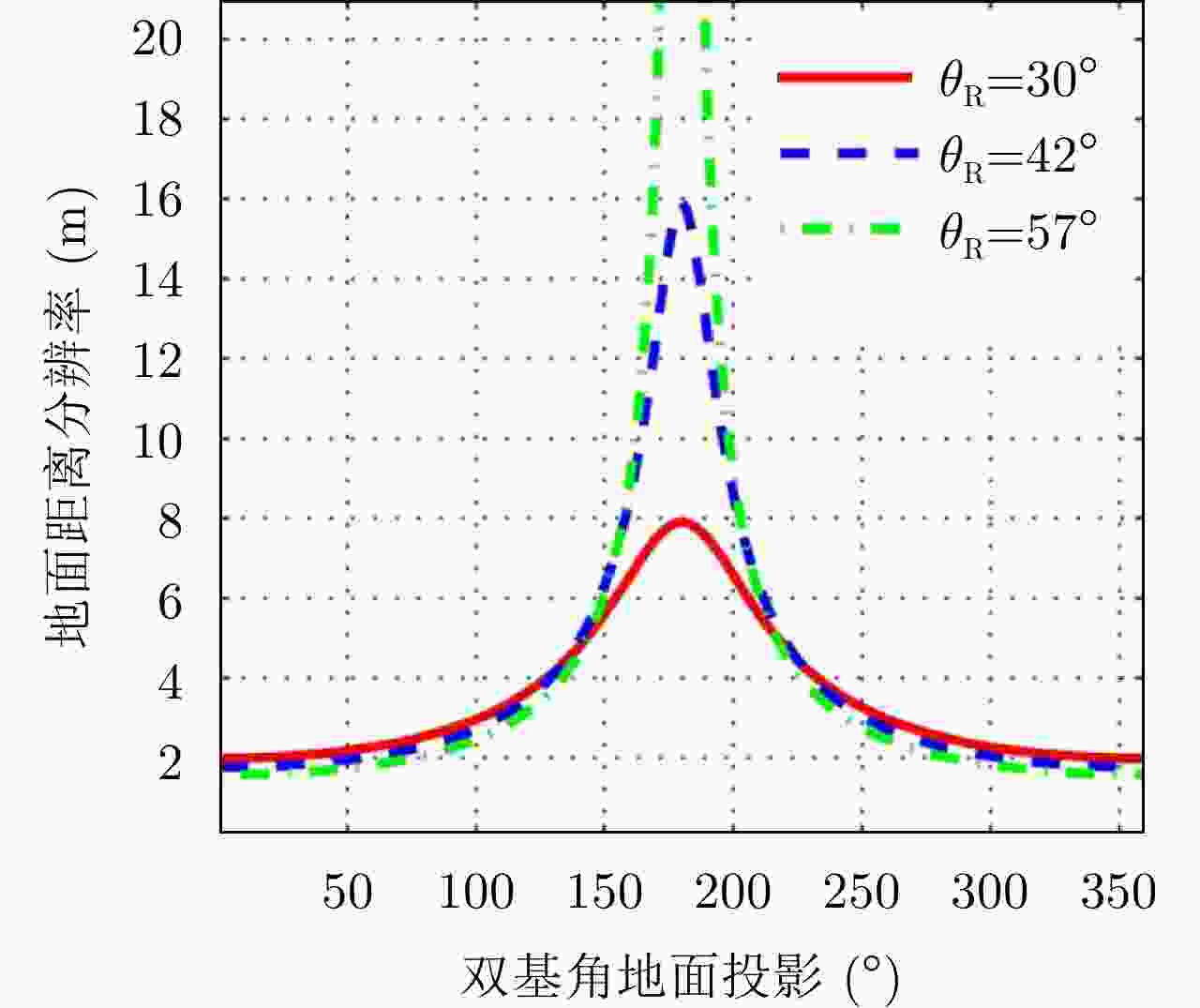
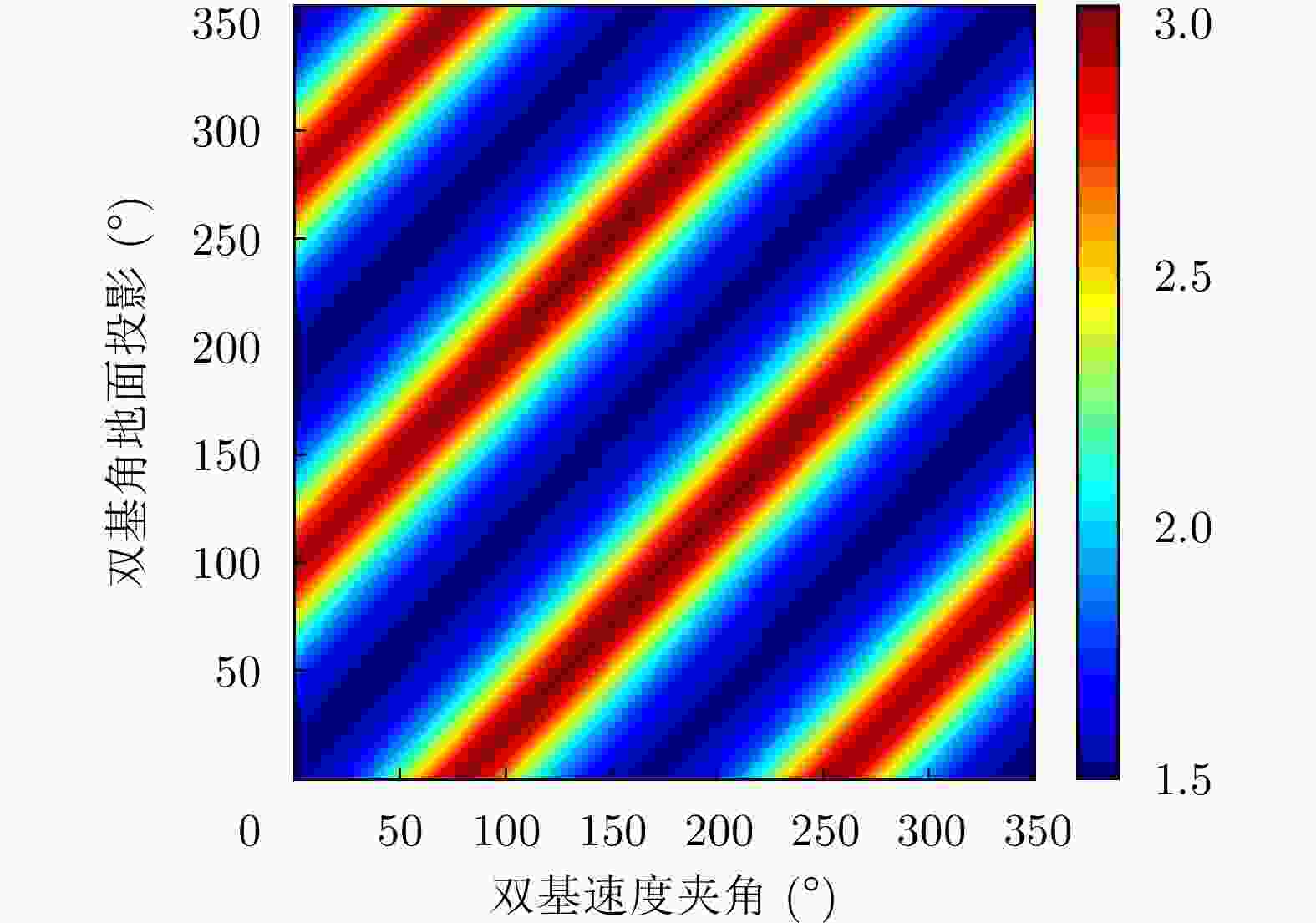
表 1 GEO星机双基SAR系统仿真参数
Table 1. The simulation parameters of geosynchronous spaceborne/airborne bistatic SAR
系统参数 数值 平台参数 数值 载频 1.25 GHz GEO轨道离心率 0.07 带宽 100 MHz GEO轨道倾角 53° 峰值功率 5 kW GEO半长轴长度 42164.17 km 发射天线增益 50 dB 接收站速度 200 m/s 接收天线增益 20.8 dB 接收站高度 10 km 表 2 星源照射双/多基SAR典型系统/试验介绍
Table 2. Typical system introduction of bi/multi-static SAR system with spaceborne illuminators
类别 平台组合 典型系统/试验 国家 研制状态 优劣势与应用价值 发射 接收 同构 SAR卫星 SAR卫星 陆探1号 中国 在轨运行 可实现高精度干涉测量,
用于地表DEM生成与运动目标检测等TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X 德国 在轨运行 TanDEM-L 德国 正在研制 异构 SAR卫星
GNSS卫
星等飞机、地
面等挑战者号+CV990飞机 美国 验证了星机双基SAR成像可行性 机载接收站:观测视角丰富、响应速度快
地面接收站:感兴趣区域
长时间观测
GNSS卫星:全球覆盖,
带宽与功率受限
SAR卫星:大带宽、
功率密度较高ERS-2/ENVISAT+地面固定站(SABRINA系统) 西班牙 星地双基干涉SAR试验 TerraSAR-X+飞机
(F-SAR/PAMIR)中国、德国、美国 星机SAR成像试验 遥感-1+地面固定站 中国 对比单双基成像结果 TerraSAR-X +地面固定站 中国 DBF提升信噪比 高分-3+飞机 中国 星机双基SAR成像试验 GLONASS/GPS/Galileo +地面固定接收 中国、英国 GNSS星地双基SAR成像试验 GLONASS+飞机 英国、中国 GNSS星机双基SAR成像试验 北斗-2+地面固定接收 中国 GNSS星地双基SAR成像试验 -
[1] 杨建宇. 双基合成孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017.YANG Jianyu. Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017. [2] 曾涛. 双基地合成孔径雷达发展现状与趋势分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 329–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20093ZENG Tao. Bistatic SAR: State of the art and development trend[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 329–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20093 [3] WANG R and DENG Yunkai. Bistatic SAR System and Signal Processing Technology[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018. [4] CHERNIAKOV M, ZENG Tao, and PLAKIDIS E. Galileo signal-based bistatic system for avalanche prediction[C]. IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 784–786. [5] ANTONIOU M and CHERNIAKOV M. GNSS-based bistatic SAR: A signal processing view[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013(1): 98. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-98 [6] WILLIS N J , GRIFFITHS H D. Advances in Bistatic Radar[M]. Scitech Publishing Inc, 2007. [7] MARTONE M, BRÄUTIGAM B, RIZZOLI P, et al. Enhancing interferometric SAR performance over sandy areas: Experience from the TanDEM-X mission[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1036–1046. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2418537 [8] ZHANG Yanyan, ZHANG Heng, OU Naiming, et al. First demonstration of multipath effects on phase synchronization scheme for LT-1[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2590–2604. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2952471 [9] HOMER J, MOJARRABI B, PALMER J, et al. Non-cooperative bistatic SAR imaging system: Spatial resolution analysis[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1446–1448. [10] ZENG Tao, CHERNIAKOV M, and LONG Teng. Generalized approach to resolution analysis in BSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(2): 461–474. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1468741 [11] ENDER J H G. The meaning of k-space for classical and advanced SAR techniques[C]. International Symposium Physics in Signal and Image Processing, Marseille, France, 2001: 23–38. [12] WANG Jingen, WANG Yanfei, ZHANG Jianming, et al. Resolution calculation and analysis in bistatic SAR with geostationary illuminator[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(1): 194–198. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2197850 [13] HU Cheng, CHEN Zhiyang, DONG Xichao, et al. Multistatic geosynchronous SAR resolution analysis and grating lobe suppression based on array spatial ambiguity function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6020–6038. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2969573 [14] SUN Zhichao, WU Junjie, PEI Jifang, et al. Inclined geosynchronous spaceborne–airborne bistatic SAR: Performance analysis and mission design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 343–357. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2457034 [15] SANTI F, BUCCIARELLI M, PASTINA D, et al. Spatial resolution improvement in GNSS-Based SAR using multistatic acquisitions and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6217–6231. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2583784 [16] JIANG Yicheng and WANG Zhuoqun. Analysis for resolution of bistatic SAR configuration with geosynchronous transmitter and UAV receiver[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 2013: 237463. doi: 10.1155/2013/237463 [17] 邓云凯, 禹卫东, 张衡, 等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008 [18] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004. [19] SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley, 1999. [20] 孙稚超. 基于GEO辐射源的星机SAR成像理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.SUN Zhichao. Research on the imaging theory and algorithms of geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [21] GEBHARDT U, LOFFELD O, NIES H, et al. Bistatic airborne/spaceborne hybrid experiment: Basic considerations[C]. SPIE 5978, Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites IX, Bruges, Belgium, 2005. [22] 周鹏. 星机双基地SAR系统总体与同步技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008.ZHOU Peng. System design and synchronization technique of spaceborne/airborne hybrid bistatic synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008. [23] SUN Zhichao, WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, et al. Path planning for GEO-UAV bistatic SAR using constrained adaptive multiobjective differential evolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(11): 6444–6457. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2585184 [24] LIU Qi, LI Qiang, YU Weidong, et al. Automatic building detection for multi-aspect SAR images based on the variation features[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 1409. doi: 10.3390/rs14061409 [25] 安洪阳. 基于高轨照射源的双基SAR成像与动目标检测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.AN Hongyang. Research on imaging and moving target detection technology of bistatic SAR with geosynchronous illuminator[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [26] RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, PRATS P, SCHULZE D, et al. First bistatic spaceborne SAR experiments with TanDEM-X[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 33–37. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2158984 [27] CUI Chang, DONG Xichao, and HU Cheng. Performance analysis and configuration design of geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic moving target indication system[C]. IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020; 6559–6562. [28] MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yongchao, PEI Jifang, et al. Forward-looking geometric configuration optimization design for spaceborne-airborne multistatic synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 8033–8047. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3103802 [29] GRAZIANO M D and D’ERRICO M. Novel constellation design method for spaceborne/airborne bistatic SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 2082–2095. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130161 [30] DONG Xichao, CUI Chang, LI Yuanhao, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic moving target indication system: Performance analysis and configuration design[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(11): 1810. doi: 10.3390/rs12111810 [31] SUN Zhichao, YEN G G, WU Junjie, et al. Mission planning for energy-efficient passive UAV radar imaging system based on substage division collaborative search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(1): 275–288. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3090662 [32] 王跃锟, 李真芳, 张金强, 等. GEO-LEO双站SAR地面分辨特性及轨道构型分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(5): 996–1001. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.07WANG Yuekun, LI Zhenfang, ZHANG Jinqiang, et al. Ground resolution characteristic and orbital configuration analysis for GEO-LEO BiSAR[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 996–1001. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.07 [33] MASSONNET D. Capabilities and limitations of the interferometric cartwheel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(3): 506–520. doi: 10.1109/36.911109 [34] 郝继刚, 张育林. SAR干涉测高分布式小卫星编队构形优化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2006, 27(4): 654–658, 669. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.04.017HAO Jigang and ZHANG Yulin. Formation optimized design for the height measurement of InSAR using distributed micro-satellites[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2006, 27(4): 654–658, 669. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.04.017 [35] 黄海风, 邓泳, 梁甸农. 基于测高精度最优值的星载分布式InSAR编队构形设计方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2005, 27(4): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.04.020HUANG Haifeng, DENG Yong, and LIANG Dianlong. A formation design approach of the distributed spaceborne InSAR based on height-measure optimal accuracy value[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2005, 27(4): 85–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.04.020 [36] 何峰, 梁甸农, 董臻. 主星带伴随小卫星编队SAR系统干涉测高精度与编队构形设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2005, 26(4): 455–460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.04.014HE Feng, LIANG Diannong, and DONG Zhen. Height-measure accuracy of InSAR in spaceborne parasitic SAR system and flying formation design[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2005, 26(4): 455–460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2005.04.014 [37] 陈雯雯, 邵晓巍, 段登平. 基于DEM和GMTI的收发同置分布式InSAR编队构型设计[J]. 上海航天, 2012, 29(1): 12–18, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2012.01.003CHEN Wenwen, SHAO Xiaowei, and DUAN Dengping. Formation design of distributed satellites InSAR based on DEM and GMTI[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2012, 29(1): 12–18, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2012.01.003 [38] 伍升钢, 钱山, 谭炜, 等. 分布式InSAR卫星绕飞角设计与控制方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(9): 1224–1230. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.09.007WU Shenggang, QIAN Shan, TAN Wei, et al. Research on the flying-around angle design and orbit control for distributed InSAR satellites[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(9): 1224–1230. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.09.007 [39] 胡程, 陈志扬, 董锡超. 分布式GEO SAR: 编队构型设计及性能分析[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 12(2): 236–245. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.012HU Cheng, CHEN Zhiyang, and DONG Xichao. Formation design and performance analysis for distributed geosynchronous SAR[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 12(2): 236–245. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.012 [40] MOREIRA A and HUANG Yonghong. Airborne SAR processing of highly squinted data using a chirp scaling approach with integrated motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1029–1040. doi: 10.1109/36.312891 [41] LI F K, HELD D N, CURLANDER J C, et al. Doppler parameter estimation for spaceborne synthetic-aperture radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1985, GE-23(1): 47–56. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1985.289499 [42] WU Yuan, SUN Guangcai, YANG Chun, et al. Processing of very high resolution spaceborne sliding spotlight SAR data using velocity scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1505–1518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2481923 [43] SUN Guangcai, WU Yuan, YANG Jun, et al. Full-aperture focusing of very high resolution spaceborne-squinted sliding spotlight SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3309–3321. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2669205 [44] HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Focusing of medium-earth-orbit SAR With advanced nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 500–508. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053211 [45] ZHAO Bingji, QI Xiangyang, DENG Yukai, et al. Accurate fourth-order Doppler parameter estimation approach for geosynchronous SAR[C]. EUSAR 2012; 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 615–618. [46] ZHANG Qianghui, WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, et al. PFA for bistatic forward-looking SAR mounted on high-speed maneuvering platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6018–6036. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2903878 [47] TANG Shiyang, GUO Ping, ZHANG Linrang, et al. Modeling and precise processing for spaceborne transmitter/missile-borne receiver SAR signals[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 346. doi: 10.3390/rs11030346 [48] WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. A generalized omega-K algorithm to process translationally variant bistatic-SAR data based on two-dimensional stolt mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6597–6614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2299069 [49] SUN Zhichao, CHEN Tianfu, SUN Huarui, et al. A novel frequency-domain focusing method for geosynchronous low-earth-orbit bistatic SAR in sliding-spotlight mode[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(13): 3178. doi: 10.3390/rs14133178 [50] SUN Zhichao, WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR data focusing using a novel range model based on one-stationary equivalence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1214–1230. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3002900 [51] NEO Y L, WONG F, and CUMMING I G. A two-dimensional spectrum for bistatic SAR processing using series reversion[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(1): 93–96. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.885862 [52] LIU Baochang, WANG Tong, WU Qisong, et al. Bistatic SAR data focusing using an omega-K algorithm based on method of series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(8): 2899–2912. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2017522 [53] ZENG Tao, HU Cheng, WU Lixin, et al. Extended NLCS algorithm of BiSAR systems with a squinted transmitter and a fixed receiver: Theory and experimental confirmation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(10): 5019–5030. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2276048 [54] ZENG Tao, WANG Rui, LI Feng, et al. A modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR based on series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3108–3118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219057 [55] FOCSA A, DATCU M, and ANGHEL A. Compressed sensing-based multi-aperture focusing of spaceborne transmitter/stationary receiver bistatic SAR data[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–4. [56] ZHANG Heng, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Spaceborne/Stationary bistatic SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator in staring-spotlight mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5203–5216. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2558294 [57] WANG Wenqin and SHAO Huaizong. Azimuth-variant signal processing in high-altitude platform passive SAR with spaceborne/airborne transmitter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2013, 5(3): 1292–1310. doi: 10.3390/rs5031292 [58] LIU Zhe, YANG Jianyu, ZHANG Xiaoling, et al. Frequency domain imaging algorithm for spaceborne/airborne hybrid bistatic SAR[C]. 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007: 842–845. [59] LIU Zhe, YANG Jianyu, and ZHANG Xiaoling. Nonlinear RCM compensation method for spaceborne/airborne forward-looking bistatic SAR[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 4233–4236. [60] LIU Zhe, LI Zhe, DAI Chunyang, et al. Efficient nonuniform fourier reconstruction for spaceborne/airborne bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 191–195. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2252144 [61] RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, PRATS P, KRIEGER G, et al. Efficient time-domain image formation with precise topography accommodation for general bistatic SAR configurations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2949–2966. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034676 [62] WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, AN Hongyang, et al. Azimuth signal multichannel reconstruction and channel configuration design for geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 1861–1872. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2869835 [63] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, et al. Azimuth ambiguity suppression for multichannel geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR[C]. IGARSS 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 3663–3666. [64] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR imaging based on fast low-rank and sparse matrices recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5207714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3081099 [65] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, HE Zhiwei, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne multichannel bistatic SAR imaging using weighted fast factorized backprojection method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1590–1594. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2902036 [66] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, et al. A two-step nonlinear chirp scaling method for multichannel GEO spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR spectrum reconstructing and focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3713–3728. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2886817 [67] GUO Yukun, YU Ze, LI Jingwen, et al. Focusing spotlight-mode bistatic GEO SAR with a stationary receiver using time-doppler resampling[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(18): 10766–10778. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2994752 [68] MIAO Yuxuan, YANG Jianyu, WU Junjie, et al. Spatially variable phase filtering algorithm based on azimuth wavenumber regularization for bistatic spotlight SAR imaging under complicated motion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5223115. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3139965 [69] ANTONIOU M, SAINI R, and CHERNIAKOV M. Results of a space-surface bistatic SAR image formation algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3359–3371. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.902124 [70] LI Chuang, ZHANG Heng, DENG Yunkai, et al. Focusing the L-band spaceborne bistatic SAR mission data using a modified RD algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 294–306. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2936255 [71] ESPETER T, WALTERSCHEID I, KLARE J, et al. Synchronization techniques for the bistatic spaceborne/airborne SAR experiment with TerraSAR-X and PAMIR[C]. 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007: 2160–2163. [72] 王淑芳, 王礼亮. 卫星导航定位系统时间同步技术[J]. 全球定位系统, 2005, 30(2): 10–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9268.2005.02.003WANG Shufang and WANG Liliang. Time synchronization technology of satellite navigation and positioning system[J]. GNSS World of China, 2005, 30(2): 10–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9268.2005.02.003 [73] 李中余, 黄川, 武俊杰, 等. 基于GNSS的无源雷达海面目标检测技术综述[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(4): 404–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.04.009LI Zhongyu, HUANG Chuan, WU Junjie, et al. Overview of maritime target detection techniques using GNSS-based passive radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(4): 404–416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.04.009 [74] GUTTRICH G L, SIEVERS W E, and TOMLJANOVICH N M. Wide area surveillance concepts based on geosynchronous illumination and bistatic unmanned airborne vehicles or satellite reception[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 126–131. [75] KLEMM R. Comparison between monostatic and bistatic antenna configurations for STAP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(2): 596–608. doi: 10.1109/7.845248 [76] FANTE R L. Ground and airborne target detection with bistatic adaptive space-based radar[C]. 1999 IEEE Radar Conference. Radar into the Next Millennium, Waltham, USA, 1999: 7–11. [77] ZHANG Ying, XIONG Wei, DONG Xichao, et al. A novel azimuth spectrum reconstruction and imaging method for moving targets in geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic multichannel SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5976–5991. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2974531 [78] ZHANG Shuangxi, LI Shaojie, LIU Yanyang, et al. A novel azimuth Doppler signal reconstruction approach for the GEO-LEO bi-static multi-channel HRWS SAR system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39539–39546. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904653 [79] XU Wei, WEI Zhengbin, HUANG Pingping, et al. Azimuth multichannel reconstruction for moving targets in geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(11): 1703. doi: 10.3390/rs12111703 [80] CUI Chang, DONG Xichao, HU Cheng, et al. An adaptive moving target indication method for GEO spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 5243–5246. [81] WANG Pengfei, LIU Mei, WANG Shuwen, et al. 3D velocity estimation for moving targets via geosynchronous bistatic SAR[C]. 2018 China International SAR Symposium (CISS), Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–5. [82] AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Simultaneous moving and stationary target imaging for geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR based on sparse separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6722–6735. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3025802 [83] GOLDSTEIN R, ROSEN P, and WERNER C. ERS-1 bistatic radar images[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Pasadena, USA, 1994: 1–7. [84] DUQUE S, LOPEZ-DEKKER P, and MALLORQUI J J. Single-pass bistatic SAR interferometry using fixed-receiver configurations: Theory and experimental validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(6): 2740–2749. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2041063 [85] RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, BAUMGARTNER S V, KRIEGER G, et al. Bistatic TerraSAR-X/F-SAR spaceborne-airborne SAR experiment: Description, data processing, and results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 781–794. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2029984 [86] WALTERSCHEID I, ESPETER T, BRENNER A R, et al. Bistatic SAR experiments with PAMIR and TerraSAR X—Setup, processing, and image results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(8): 3268–3279. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2043952 [87] WAHL D E and YOCKY D A. Bistatic SAR: Signal processing and image formation[R]. SAND2014-18347, 2014. [88] WANG Rui, LI Feng, and ZENG Tao. Bistatic SAR experiment, processing and results in spaceborne/stationary configuration[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 393–397. [89] ZENG Tao, ZHU Mao, HU Cheng, et al. Experimental results and algorithm analysis of DEM generation using bistatic SAR interferometry with stationary receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(11): 5835–5852. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2422303 [90] WANG R, WANG Wei, SHAO Yunfeng, et al. First bistatic demonstration of digital beamforming in elevation with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 842–849. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2467176 [91] SUN Zhichao, WU Junjie, LV Zheng, et al. Spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR experiment using GF-3 illuminator: Description, processing and results[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 2699–2702. [92] 武俊杰, 孙稚超, 杨建宇, 等. 基于GF-3照射的星机双基SAR成像及试验验证[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(3): 241–247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.03.002WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, YANG Jianyu, et al. Spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR using GF-3 illumination—Technology and experiment[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(3): 241–247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.03.002 [93] KRIEGER G, MOREIRA A, FIEDLER H, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3317–3341. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900693 [94] SAINI R, ZUO Rui, and CHERNIAKOV M. Development of space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar with GNSS trasmnitter of opportunity[C]. 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–6. [95] ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. Space-surface bistatic SAR image enhancement based on repeat-pass coherent fusion with beidou-2/compass-2 as illuminators[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614337 [96] ZHANG Qilei, CHANG Wen’ge, ZENG Zhangfan, et al. An integrative synchronization and imaging algorithm for GNSS-based BSAR[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5319-5 [97] MA Hui, ANTONIOU M, and CHERNIAKOV M. Passive GNSS-based SAR imaging and opportunities using Galileo E5 signals[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5335-5 [98] ZHOU Xinkai, CHEN Jie, WANG Pengbo, et al. An efficient imaging algorithm for GNSS-R Bi-static SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 2945. doi: 10.3390/rs11242945 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: