Research on Calculation Method of Doppler Centroid Shift from Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar for Ocean Feature Retrieval
-
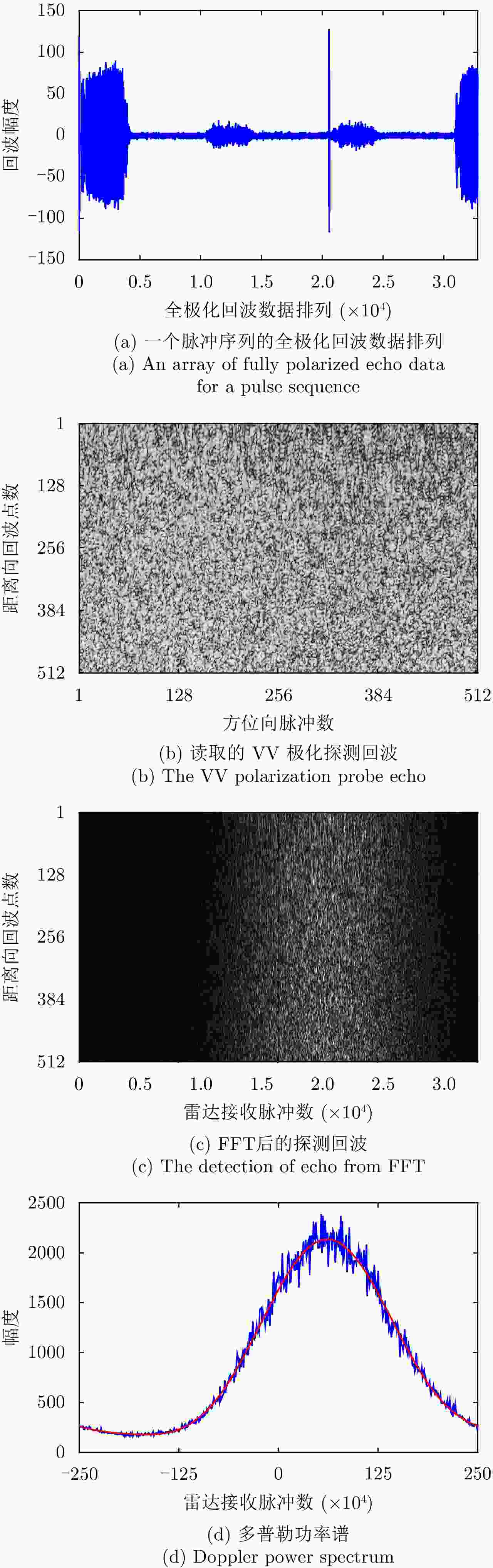
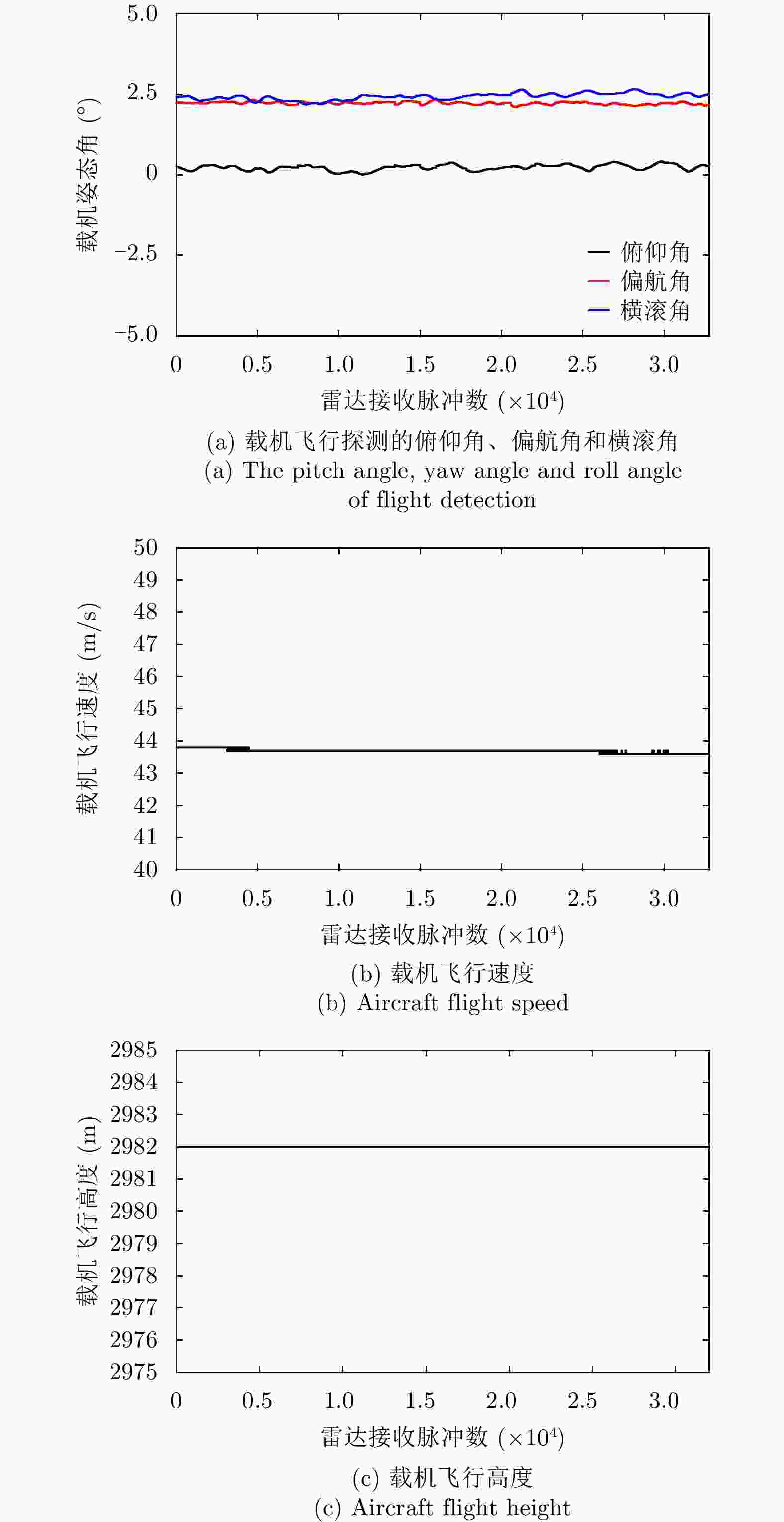
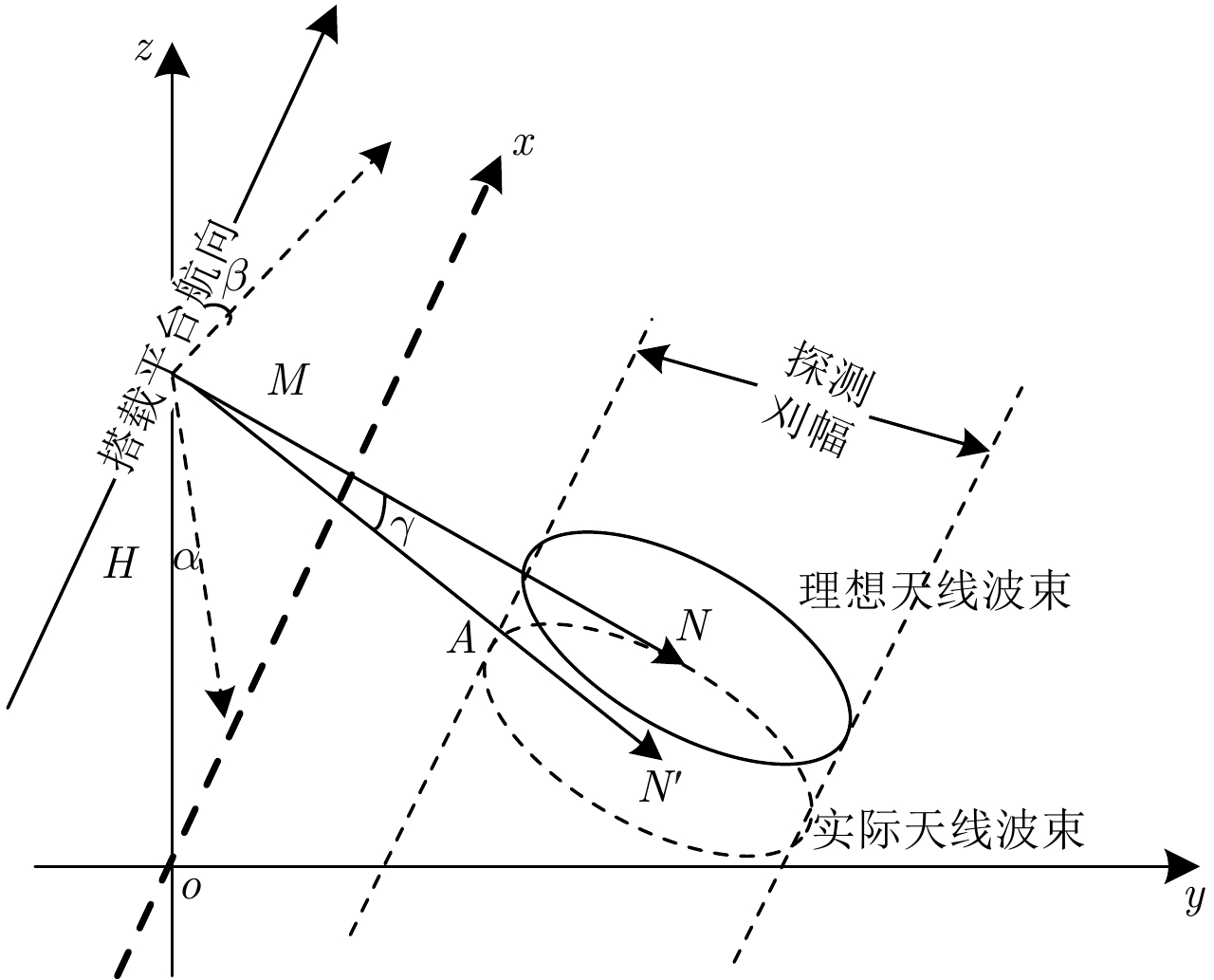
摘要: 多普勒中心偏移是合成孔径雷达(SAR)反演海面风场、海表流场的重要参数。该文针对机载正侧视提出一种多普勒中心偏移计算方法,分别利用载机运动状态数据和海洋探测回波数据计算多普勒中心频率,再作差求解多普勒中心偏移,并在多普勒谱分析中加入小波分析去除噪声的影响来提高计算精度。以CDOP经验模型计算结果作为比对真值,机载SAR飞行探测试验结果表明,9组探测数据多普勒中心偏移计算误差的绝对值均小于2 Hz,均方根误差为1.4 Hz,满足海洋环境要素反演的精度要求。实验表明高精度的平台运动状态数据和探测回波数据是多普勒中心偏移海洋应用的关键。
-
关键词:
- 机载正侧视合成孔径雷达 /
- 多普勒中心偏移 /
- 计算方法 /
- 多普勒中心频率
Abstract: Doppler center shift is an important parameter for Synthetic Aperture Radar(SAR) to retrieve ocean surface wind field and ocean surface current field. We present a calculation method of Doppler centroid shift for airborne side-looking SAR. We compute Doppler centroid frequency by aircraft motion status data and ocean detection echo data respectively, and make difference to solve the Doppler centroid shift. In order to remove the influence of noise, we add wavelet analysis in Doppler spectrum analysis method to improve Doppler centroid frequency accuracy from ocean detection echo data. We carry out flight detection experiment by airborne SAR to obtain the Doppler centroid shift, while put buoy wind direction and wind speed in detection area into CDOP geophysical model function to simulate the Doppler centroid shift as compared to the validation true value. Flight detection results of 9 group data show that the calculation error absolute value of Doppler centroid shift are less than 2 Hz, and the RMS error is 1.4 Hz. It is meets the accuracy requirements of marine environmental factors retrieval, and proves the effective of Doppler centroid shift calculation method. In practical applications, the accuracy of Doppler centroid shift calculation is the key to the application of marine environment research, which requires high-precision platform motion data and sounding echo data to ensure application value. -
表 1 惯导参数测量误差对多普勒中心频率计算精度的影响
Table 1. The influence of inertial parameter measurement error to Doppler center frequency calculation accuracy
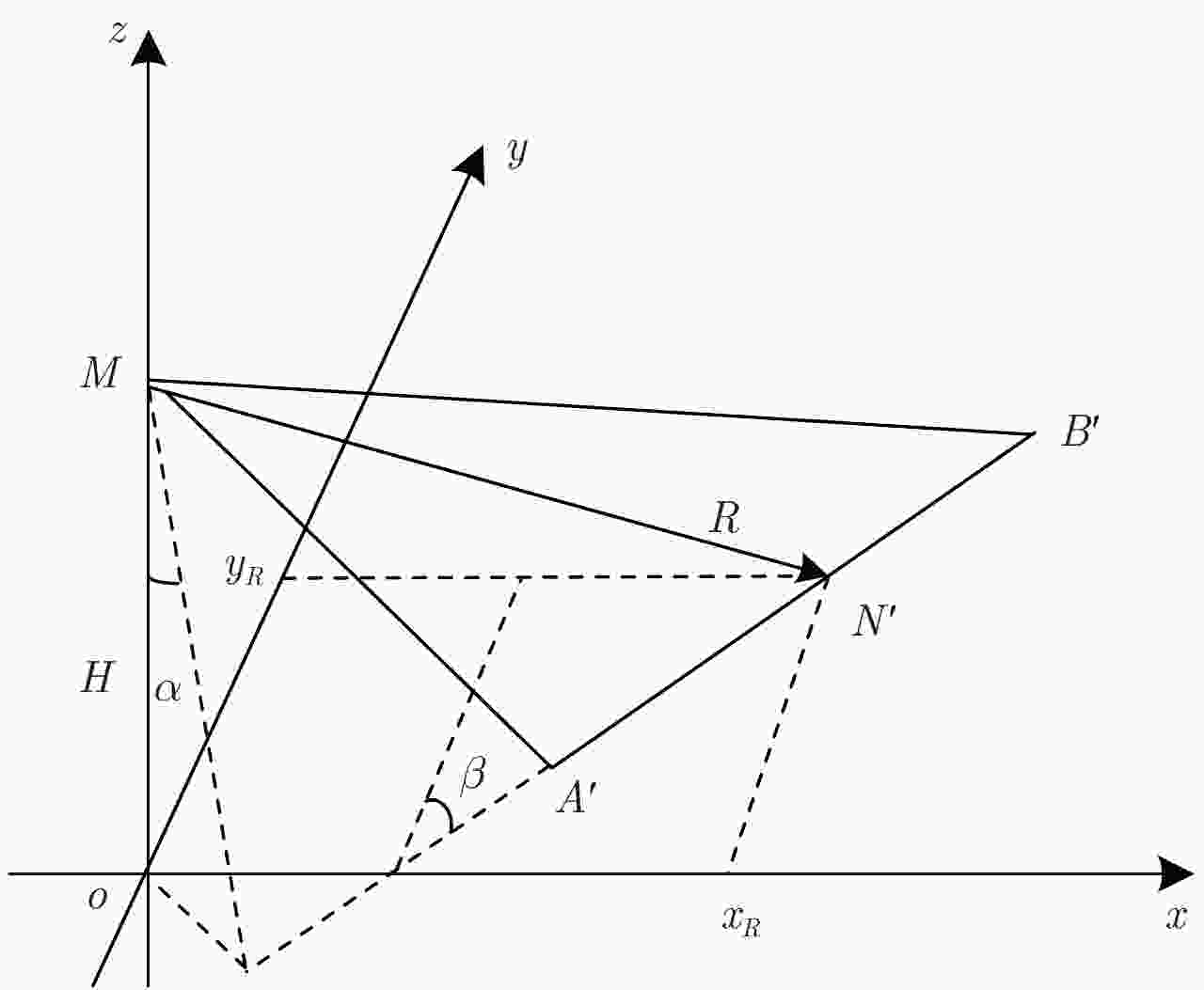
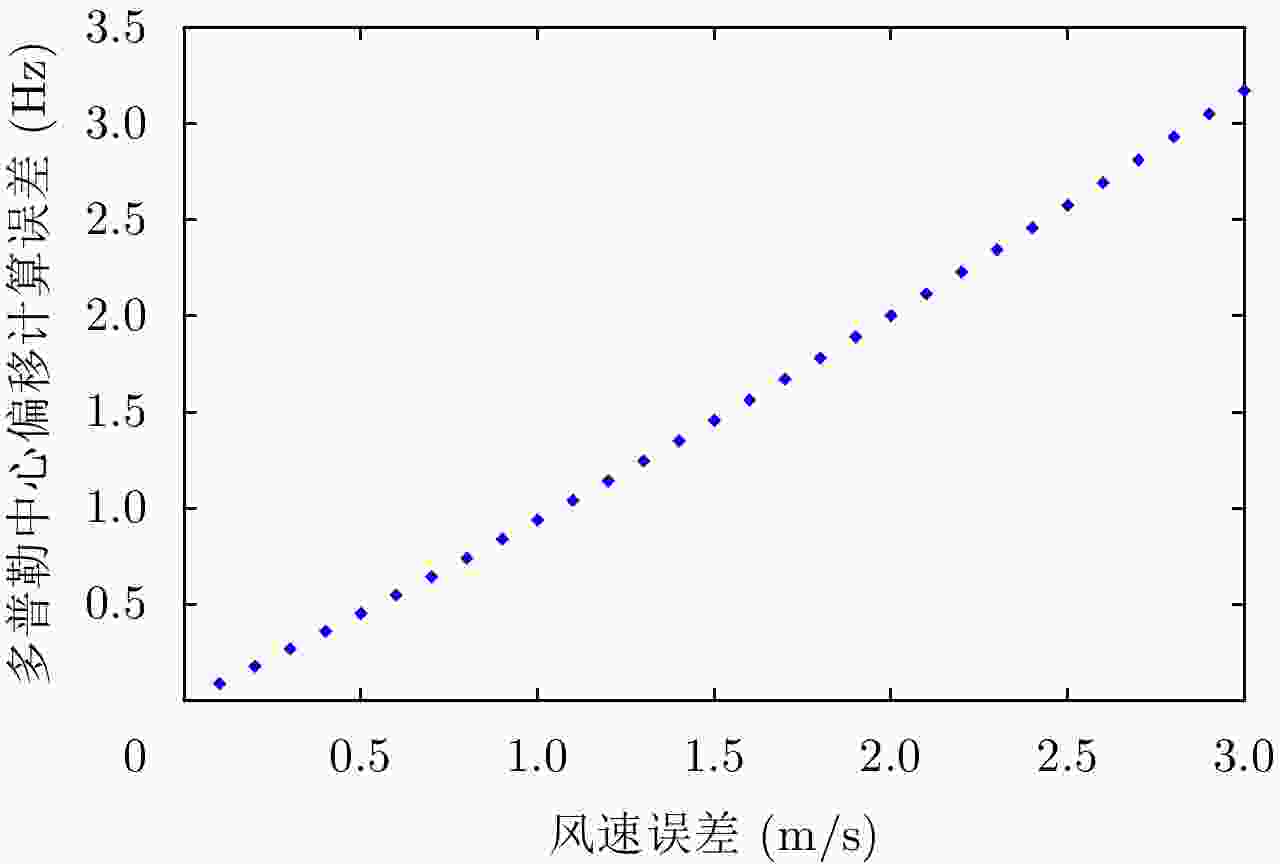
惯导参数 测量误差 多普勒中心频率误差(Hz) 俯仰角 0.1° 2.0 偏航角 0.1° 1.8 飞行速度 1 m/s 1.0 飞行高度 / / 表 2 机载SAR工作参数及指标
Table 2. Operating parameters and indicators of airborne SAR
工作参数 指 标 工作模式 条带 极化方式 HH, HV, VH, VV 雷达频率 5.3 GHz 雷达波长 0.056 m 信号带宽 80 MHz, 150 MHz 脉冲宽度 15 μs PRF 500 Hz 表 3 多普勒中心偏移计算结果比对验证(Hz)
Table 3. Comparison of Doppler centroid shift calculation verification (Hz)
条带名称 回波数据 惯导数据 探测数据 CDOP模型 计算误差 20120726-011 61.5 46.2 15.3 14.5 0.8 20120726-021 53.7 61.1 –7.4 –9.2 1.8 20120726-031 27.3 36.8 –9.5 –10.8 1.3 20120726-041 47.9 28.9 19.0 19.6 –0.6 20120726-051 10.7 18.6 –7.9 –6.7 –1.2 20120726-061 66.4 47.4 19.0 17.4 1.6 20120726-071 –13.7 –3.5 –10.2 –11.4 1.2 20120726-081 –15.6 –31.2 15.6 17.3 –1.7 20120726-091 31.3 10.1 21.2 19.6 1.6 RMS 1.4 -
[1] MARTIN S. An Introduction to Ocean Remote Sensing[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014: 15–27. [2] HASSELMANN S, BRÜNING C, HASSELMANN K, et al. An improved algorithm for the retrieval of ocean wave spectra from synthetic aperture radar image spectra[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1996, 101(C7): 16615–16629. doi: 10.1029/96JC00798 [3] HERSBACH H, STOFFELEN A, and DE HAAN S. An improved C-band scatterometer ocean geophysical model function: CMOD5[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2007, 112(C3): C03006. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003743 [4] 张杰, 张晰, 范陈清, 等. 极化SAR在海洋探测中的应用与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Xi, FAN Chenqing, et al. Discussion on application of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in marine surveillance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124 [5] 王绍清. 星载SAR多普勒中心实时估计技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院研究生院(电子学研究所), 2005: 12–17.WANG Shaoqing. Research on the Doppler centroid real-time estimation technology of space-borne SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Electronics, 2005: 12–17. [6] MOUCHE A A, COLLARD F, CHAPRON B, et al. On the use of Doppler shift for sea surface wind retrieval from SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(7): 2901–2909. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2174998 [7] CHAPRON B, COLLARD F, and ARDHUIN F. Direct measurements of ocean surface velocity from space: Interpretation and validation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C7): C07008. doi: 10.1029/2004JC002809 [8] ROUAULT M J, MOUCHE A, COLLARD F, et al. Mapping the Agulhas Current from space: An assessment of ASAR surface current velocities[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C10): C10026. doi: 10.1029/2009JC006050 [9] RANEY R K. Doppler properties of radars in circular orbits[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1986, 7(9): 1153–1162. doi: 10.1080/01431168608948916 [10] BEZVESILNIY O O and VAVRIV D M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Systems for Small Aircrafts: Data Processing Approaches[M]. London: INTECH Open Access Publisher, 2012: 465–498. [11] HERLAND E A. Seasat SAR processing at the Norwegian defence research establishment[C]. Proceedings of an EALSel-ESA Symposium, Voss, Norway, 1981: 247–253. [12] MCDONOUGH R N, RAFF B E, and KERR J L. Image formation from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar signals[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 1985, 6(4): 300–312. [13] BENNETT J R, CUMMING I G, and DEANE R A. The digital processing of seasat synthetic aperture radar data[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, Washington, USA, 1980: 168–175. [14] LI F K, HELD D N, CURLANDER J C, et al. Doppler parameter estimation for spaceborne synthetic-aperture radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1985, GE-2(1): 47–56. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1985.289499 [15] CURLANDER J C, WU C, and PANG A. Automated preprocessing of spaceborne SAR data[C]. Proceedings of 1982 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 1982: 6. [16] HANSEN M W, COLLARD F, DAGESTAD K F, et al. Retrieval of sea surface range velocities from Envisat ASAR Doppler centroid measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3582–3592. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2153864 [17] 闫龙. 机载SAR多普勒参数估计及运动补偿技术研究[D]. [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2009: 10–20.YAN Long. Research on Doppler parameters estimation and motion compensation of air-born SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2009: 10–20. [18] ROMEISER R and THOMPSON D R. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 446–458. doi: 10.1109/36.823940 [19] 刘银中. 机载SAR实测数据多普勒参数估计与成像算法研究[D]. [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006: 12–18.LIU Yinzhong. Study on Doppler parameters estimation of airborne SAR raw data and imaging algorithms[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006: 12–18. [20] LEITE G C, USHIZIMA D M, MEDEIROS F N S, et al. Wavelet analysis for wind fields estimation[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(6): 5994–6016. doi: 10.3390/s100605994 [21] 郝胜勇, 王小青, 盛新庆, 等. 一种提高海洋SAR定位精度的方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(8): 1213–1216.HAO Shengyong, WANG Xiaoqing, SHENG Xinqing, et al. A means of improving accuracy of positioning for ocean SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2005, 27(8): 1213–1216. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
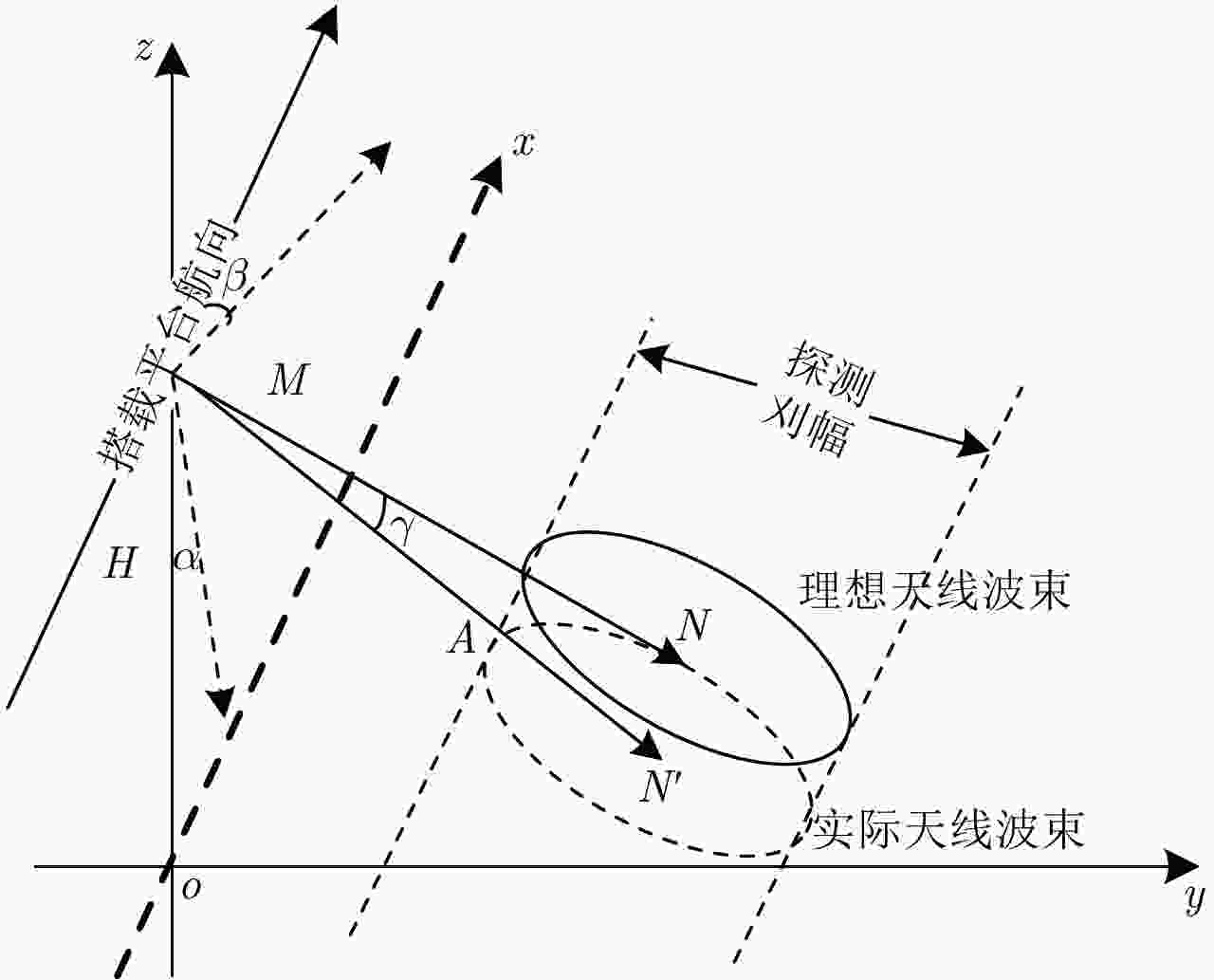
 下载:
下载: