Feature Detection of Acoustically Induced Sea Surface Micro-motions with Terahertz Radar
-
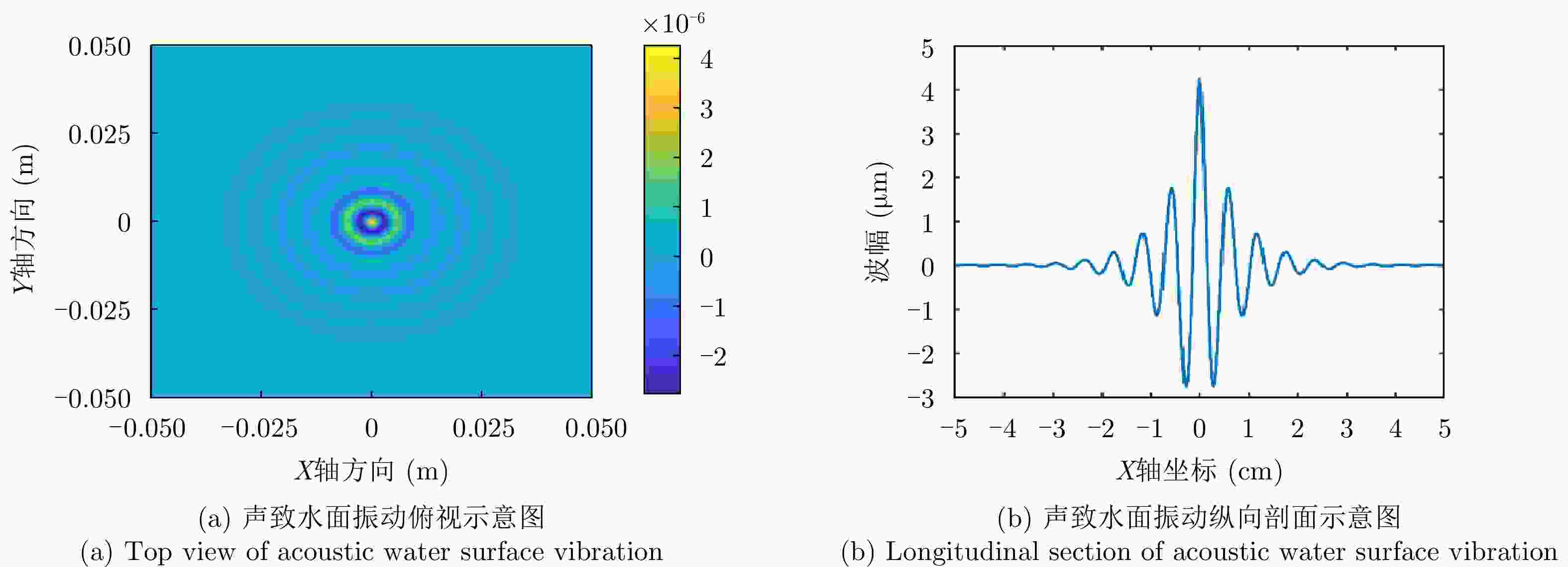
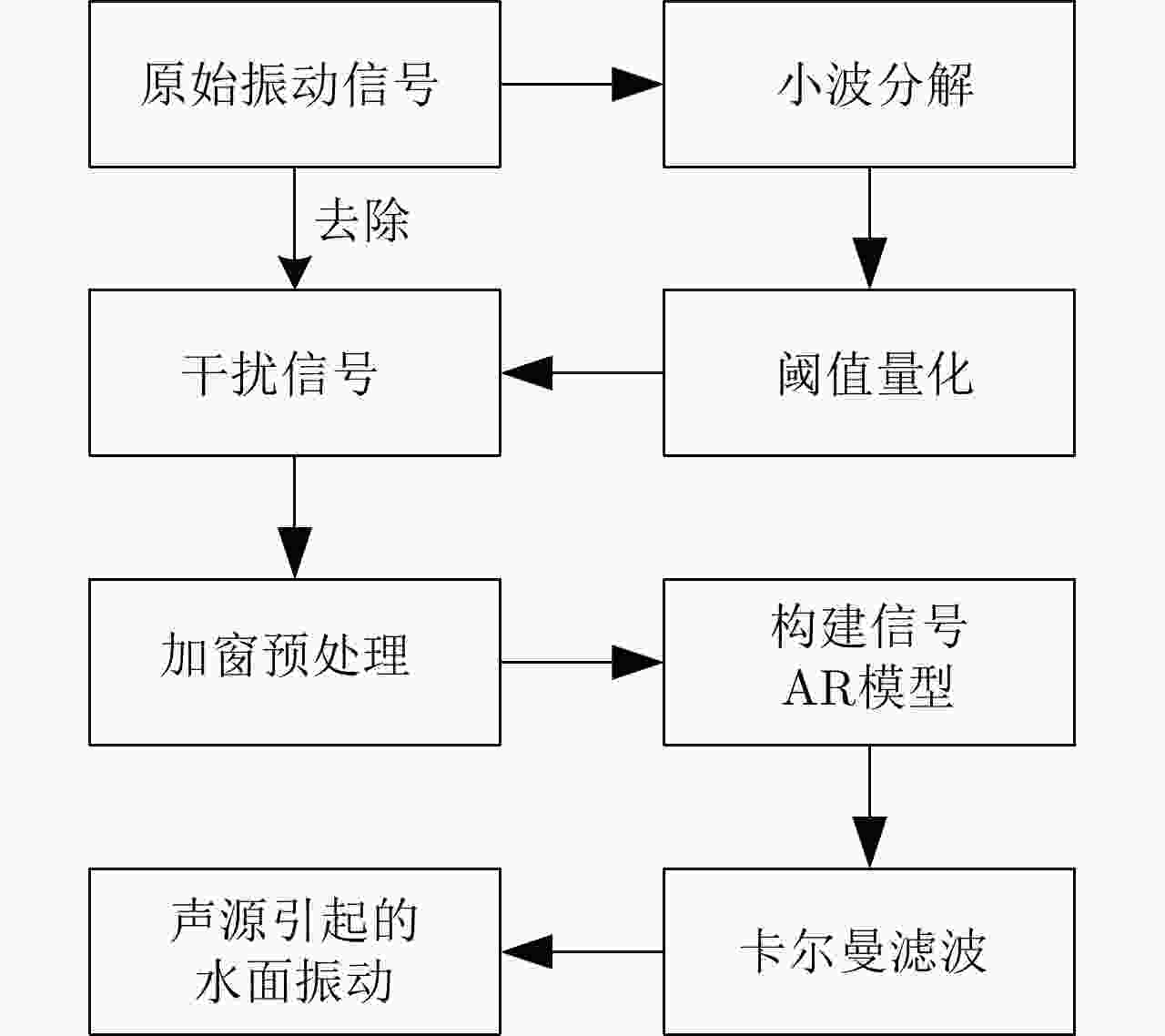
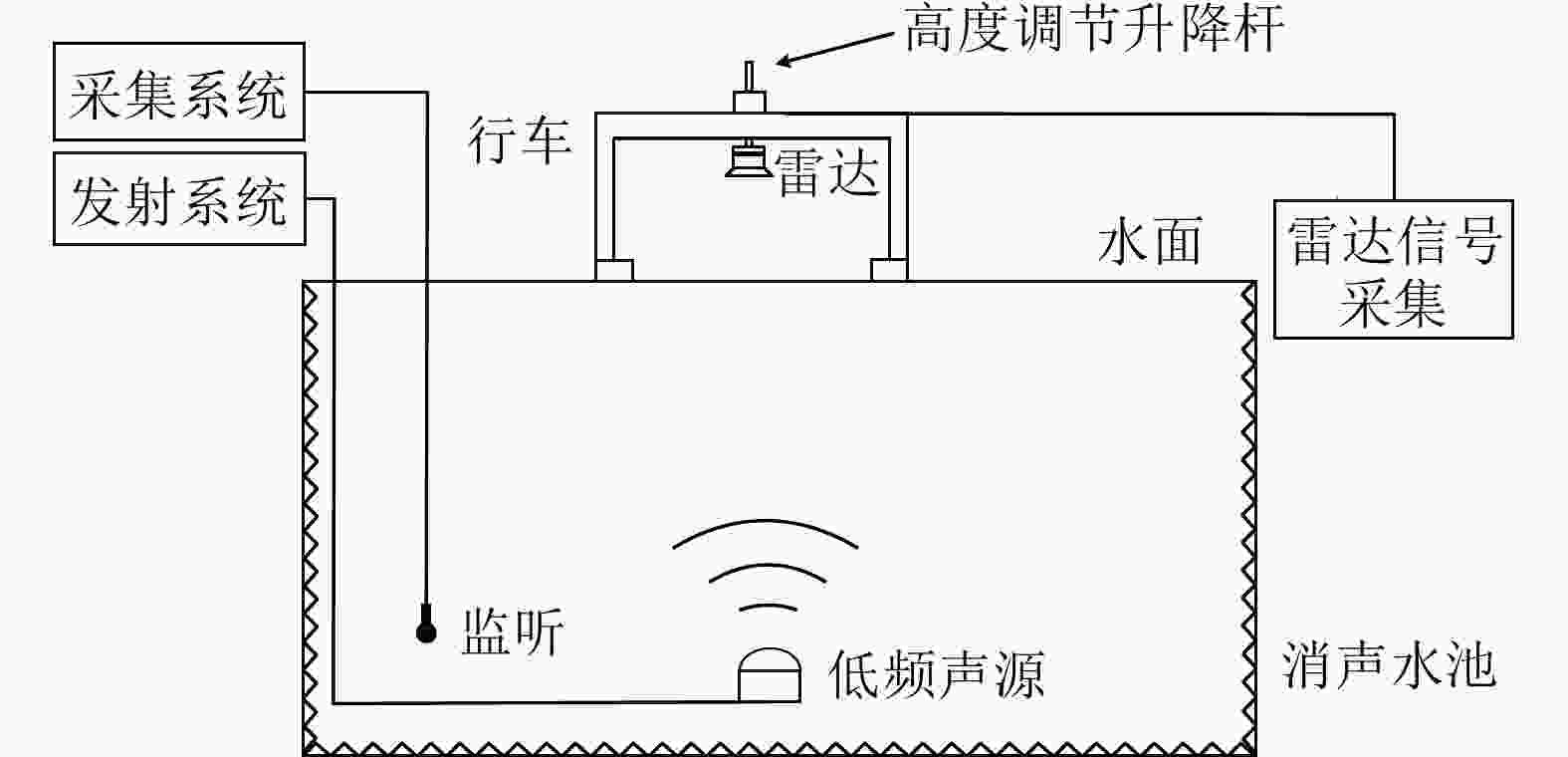
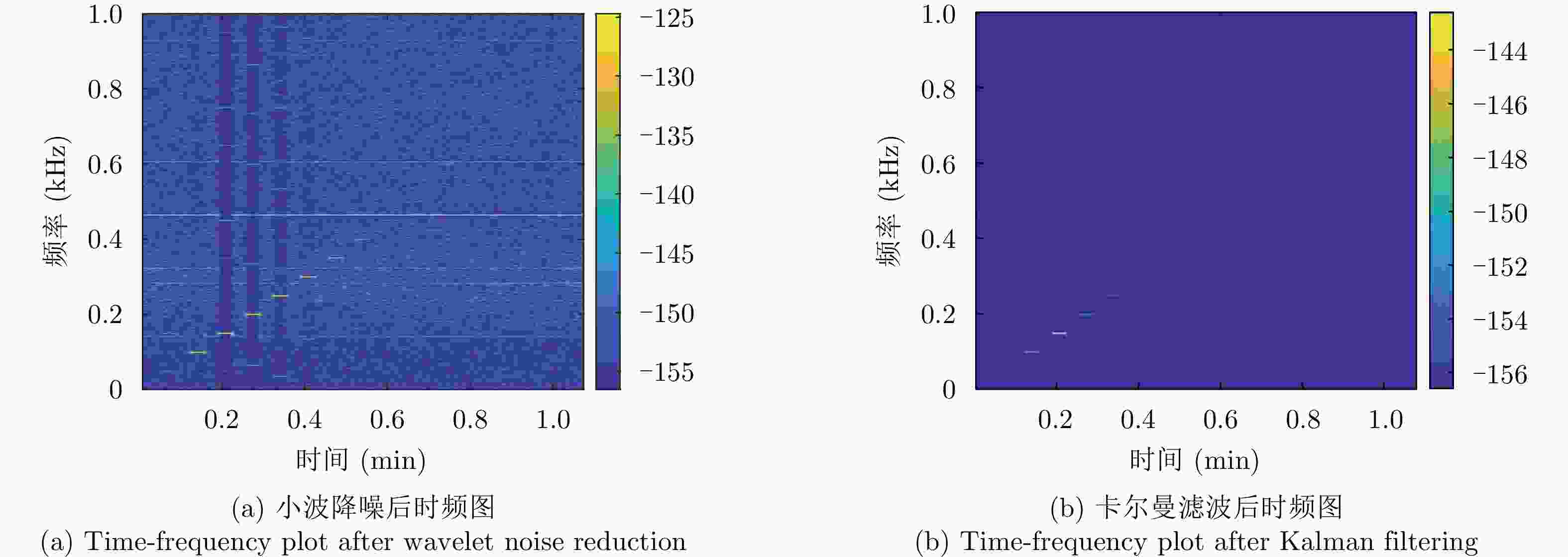
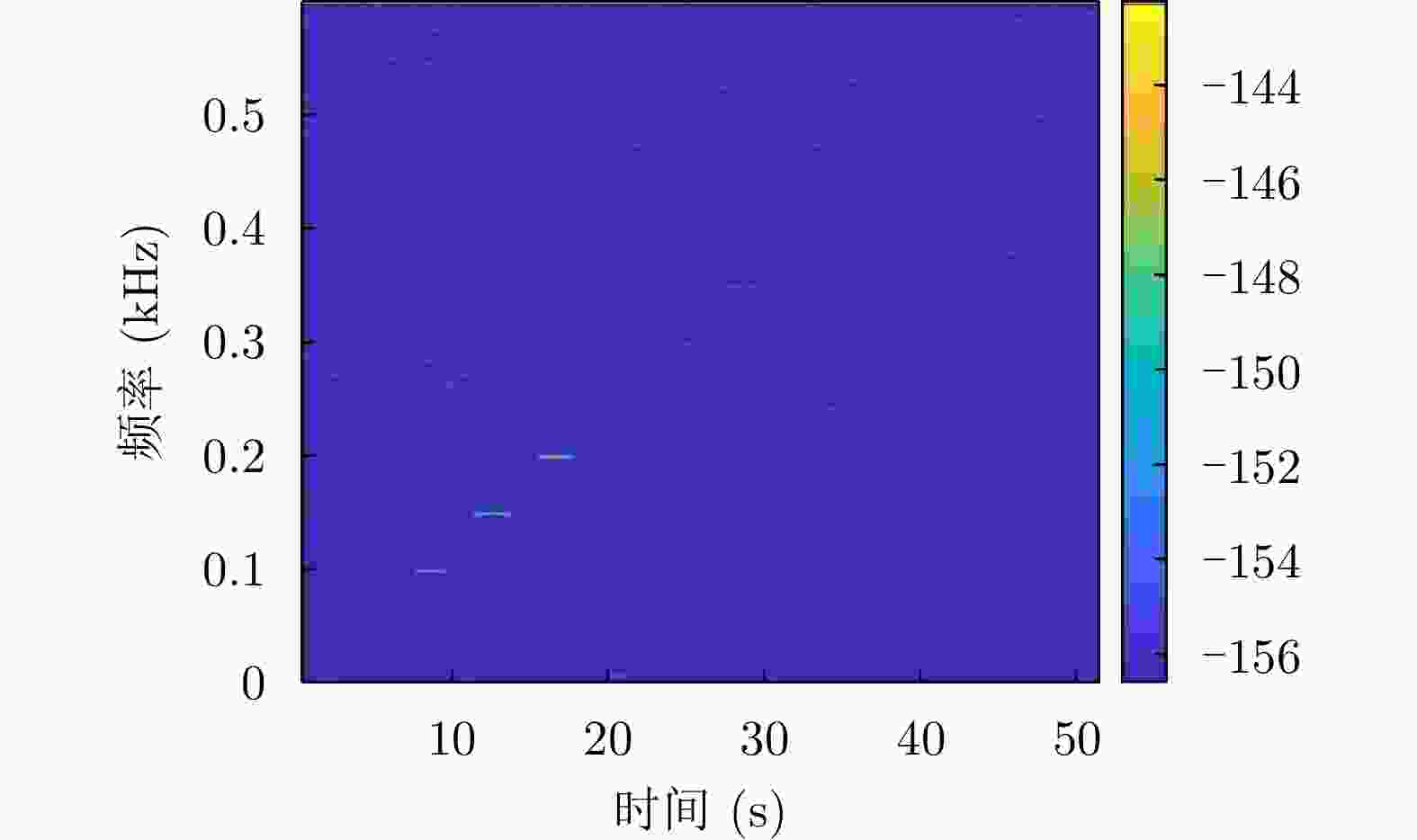
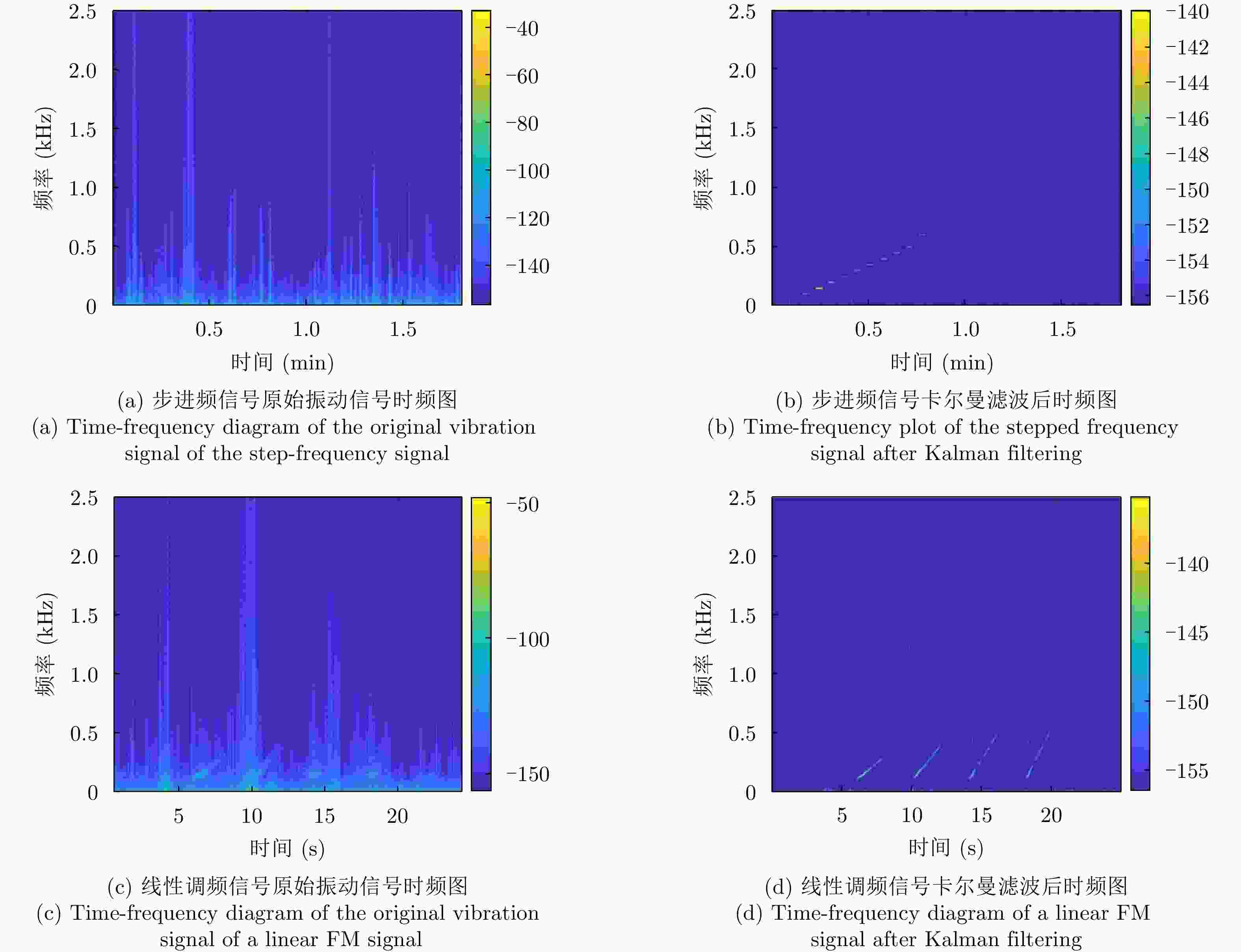
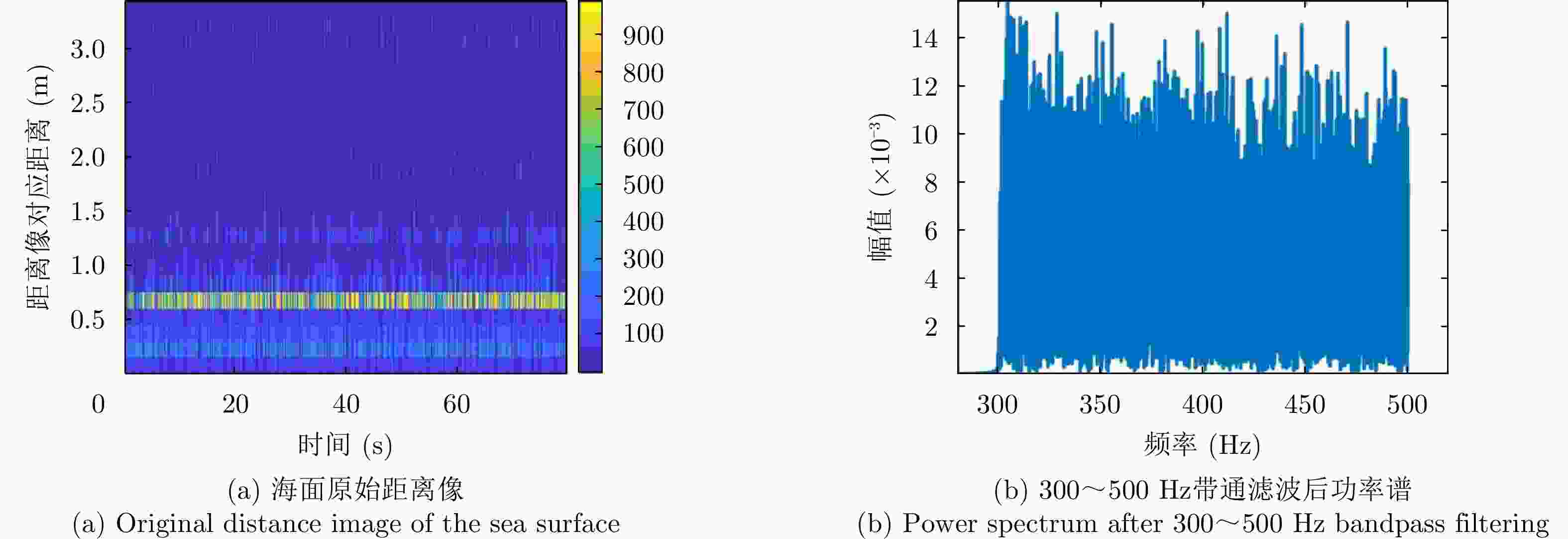
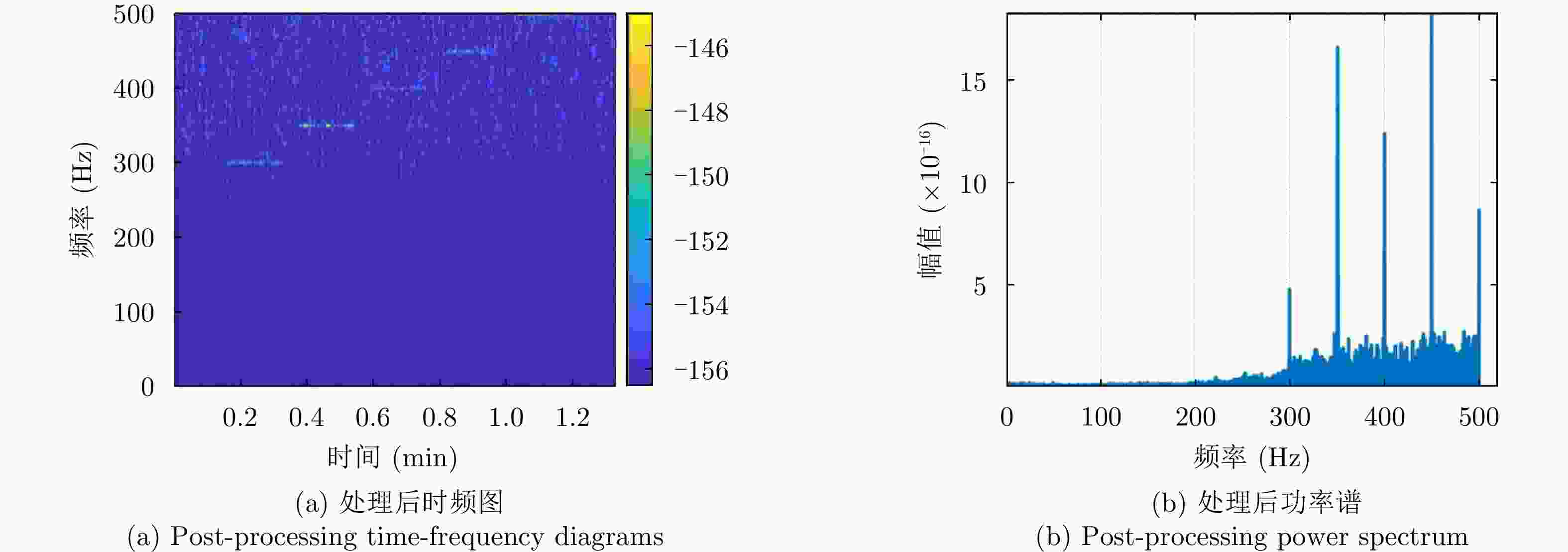
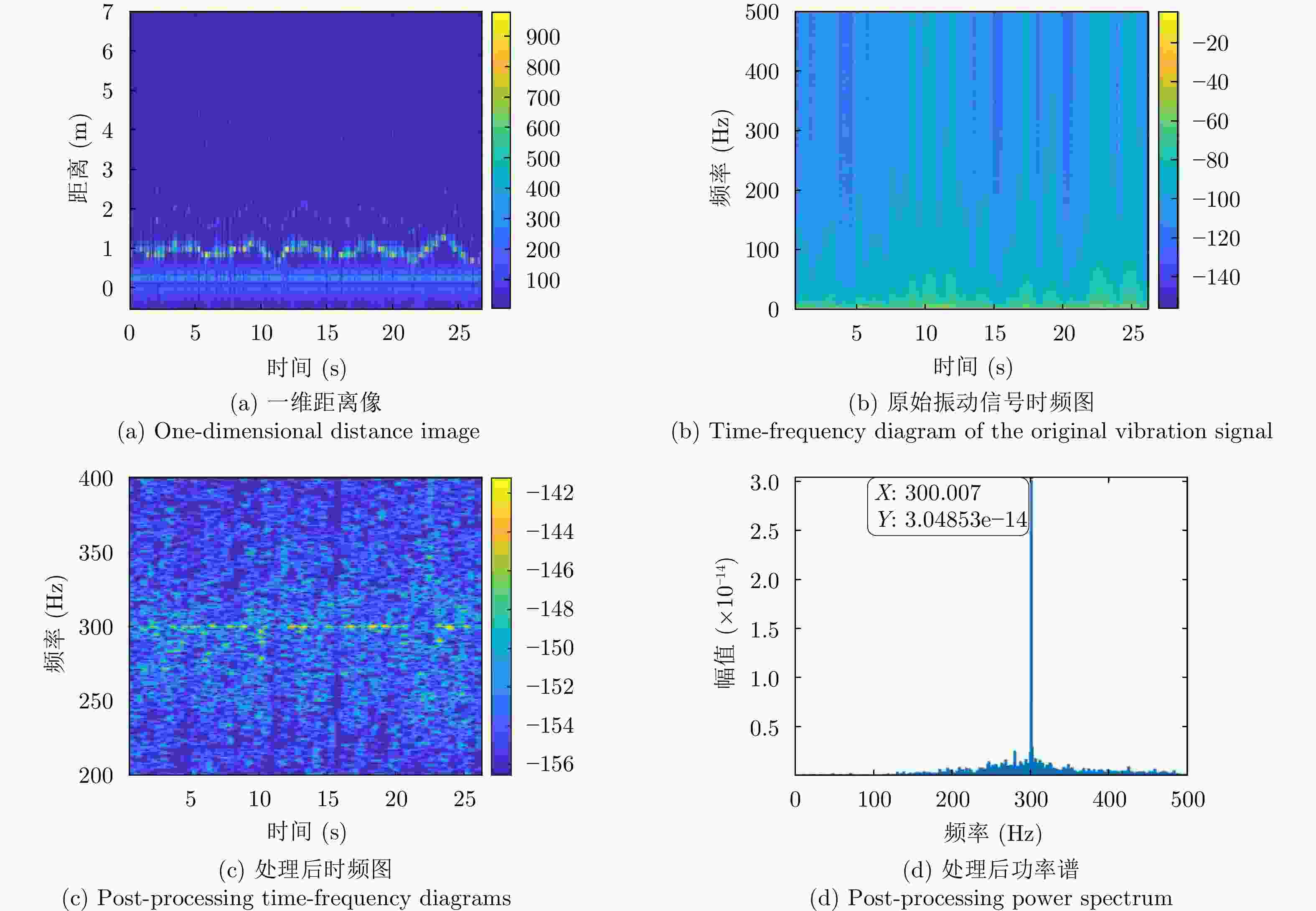
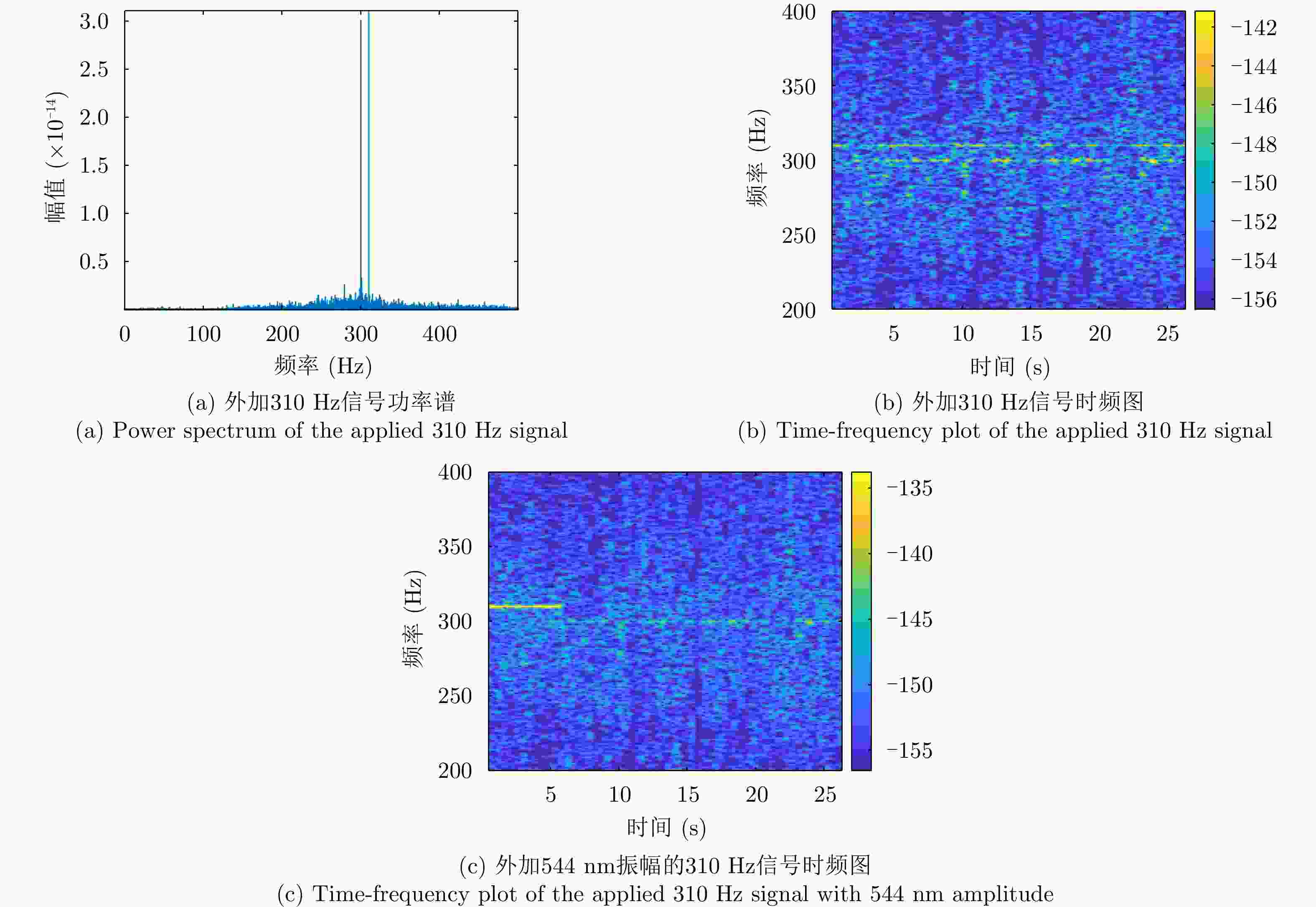
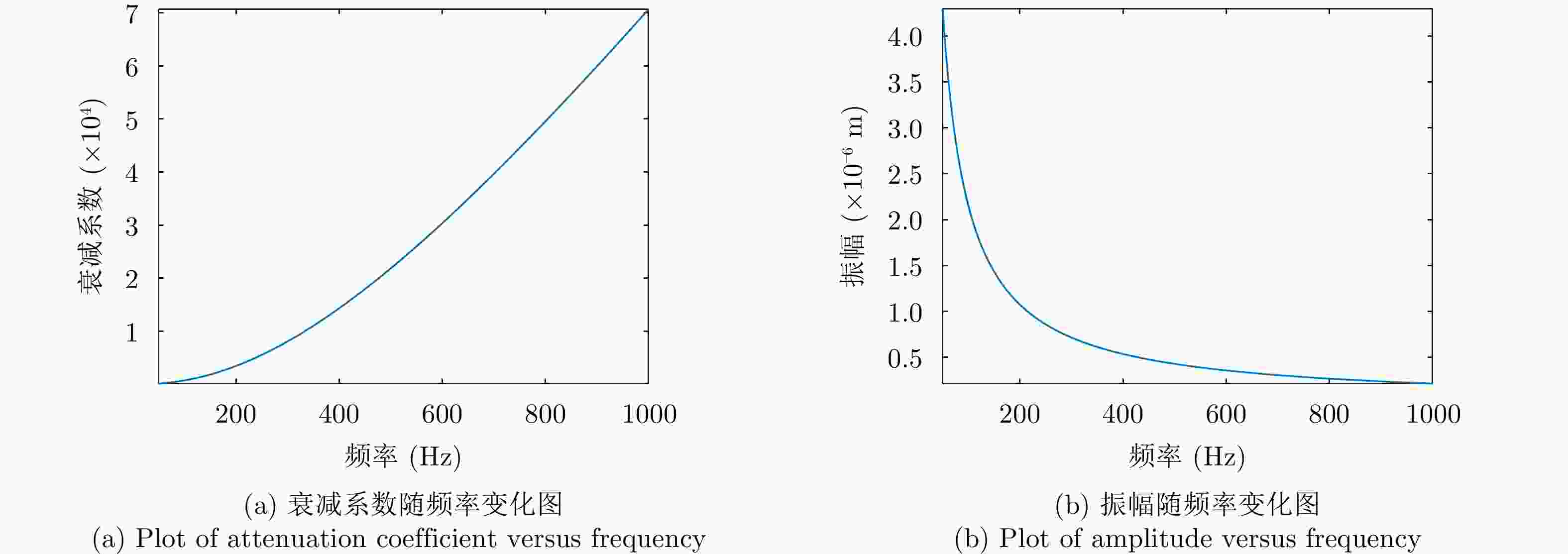
摘要: 水下声信号传播到水面时,由于水和空气的声阻抗差,会激发水表面横向微幅波,其振动信号包含了声源的相关信息。雷达通过目标回波间的相位差来检测目标的微小位移,因此可以利用雷达检测水面微小位移变化获取水面振动信号,进而反演水下声源信息。该文首先分析了水下声传播的衰减特性及水面振动的物理模型,然后基于雷达回波模型对声致水面振动检测进行理论分析,提出了小波-卡尔曼滤波信号检测方法,最后在大型综合消声水池和黄海水域开展了基于太赫兹雷达的声致水面微动信号检测实验。实验结果表明所用太赫兹雷达能够检测声致水面的细微振动,所提算法能有效滤除水面干扰和雷达相位噪声并提取振动信号。实验首次在二级海况下检测到了亚微米级的振动信号,为水-空跨介质信息传输与水下航行器探测提供了依据。Abstract: When underwater acoustic signals propagate to the water surface, the acoustic impedance difference between water and air leads to transverse microamplitude waves on the water surface. These waves carry vibration frequencies containing relevant information about the sound source. Radar systems detect the slight displacement of the target through the phase difference between the target echoes; hence, radar systems can be used to detect small displacement changes on the water surface, thereby obtaining the water-surface vibration signal and subsequently inverting the underwater sound source information. In this study, we first analyzed the attenuation characteristics of underwater sound propagation and the physical model of water-surface vibration. Building upon the radar echo model for detecting acoustic water-surface vibration, we proposed a wavelet-Kalman filter signal detection method through theoretical analysis. Lastly, experiments were conducted in the large-scale comprehensive anechoic pool and the Yellow Sea water using terahertz radar for acoustic water-surface micromotion signal detection. The results demonstrate the capability of the terahertz radar to successfully detect acoustic water-surface microvibrations. The proposed method effectively filters water-surface interference and radar phase noise and extracts vibration signals. For the first time, submicron vibration signals were detected under a secondary sea state, providing a foundation for water-space transmedia information transmission and underwater vehicle detection.
-
表 1 雷达实验参数设置
Table 1. Radar experiment parameter setting
参数 第1组 第2组 中心频率(GHz) 122.5 24.5 带宽(GHz) 1 1 扫频时间(ms) 0.1 0.5 扫频周期(ms) 0.2 0.5 采样频率(kHz) 1000 256 波束宽度(°) 1 30 -
[1] ZHOU Chenbo, LIU Kaihua, HE Junqing, et al. Experimental method for underwater acoustic field detection from water surface using laser probe[C]. Automated Optical Inspection for Industry: Theory, Technology, and Applications II, Beijing, China, 1998. [2] 戴振宏, 孙金祚, 隋鹏飞. 水下声源引起的水表面横向微波的理论研究[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2004, 26(1): 95–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2004.01.022DAI Zhenhong, SUN Jinzuo, and SUI Pengfei. Theoretical study on the water surface transversal mini-wave due to the underwater sound field[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2004, 26(1): 95–98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2004.01.022 [3] 章文勋. 电磁波应用研究的当代课题[J]. 电子科技导报, 1997(12): 6–7, 32.ZHANG Wenxun. Contemporary topics in applied electromagnetic wave research[J]. Electronic Science and Technology Herald, 1997(12): 6–7, 32. [4] 朱敏, 武岩波. 水声通信技术进展[J].中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34(3): 289–296.ZHU Min and WU Yanbo. Development of underwater acoustic communication technology[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences , 2019, 34(3): 289–296. [5] 王俊, 王世练. 电磁波在水-空气两层媒质中的传播特性研究[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2019, 39(10): 227–231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2019.10.051WANG Jun and WANG Shilian. Research on propagation characteristics of electromagnetic waves in water-air two-layer media[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2019, 39(10): 227–231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2019.10.051 [6] 夏维华, 王一璐. 潜艇通信系统综述[J]. 计算机与网络, 2002(17): 55–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1739.2002.17.038XIA Weihua and WANG Yilu. Overview of submarine communication systems[J]. China Computer &Network, 2002(17): 55–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1739.2002.17.038 [7] 师于杰, 任海刚. 国外非声探潜与隐身技术发展趋势[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2015, 35(1): 5–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2015.01.002SHI Yujie and REN Haigang. Trends of foreign non-acoustics exploration potential and stealth technology[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2015, 35(1): 5–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1672-9730.2015.01.002 [8] 刘伯胜. 水声学原理[M].北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 279–280.LIU Bosheng. Principles of Underwater Acoustics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 279–280. [9] LEE M S, BOURGEOIS B S, HSIEH S T, et al. A laser sensing scheme for detection of underwater acoustic signals[C]. Conference Proceedings’88., IEEE Southeastcon, Knoxville, TN, USA, 1988: 253–257. [10] 宫彦军, 江荣熙, 李晓伟, 等. 利用激光从散射光中提取水下声信号的探测技术[J]. 烟台大学学报: 自然科学与工程版, 2003, 16(1): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8820.2003.01.008GONG Yanjun, JIANG Rongxi, LI Xiaowei, et al. Detect technique of extracting underwater acoustic signal from scattered light by using laser[J]. Journal of Yantai University:Natural Science and Engineering Edition, 2003, 16(1): 38–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8820.2003.01.008 [11] 王秀芳, 王江, 杨向东, 等. 相位激光测距技术研究概述[J]. 激光杂志, 2006, 27(2): 4–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2006.02.002WANG Xiufang, WANG Jiang, YANG Xiangdong, et al. Phase laser rang finding technology and research summarization[J]. Laser Journal, 2006, 27(2): 4–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2743.2006.02.002 [12] 孔琪. 相位式激光测距技术研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 四川师范大学, 2018.KONG Qi. Research and implementation of phase laser ranging technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Sichuan Normal University, 2018. [13] 刘继勇, 赵磊. 相位式激光测距系统关键技术探究[J]. 电子测试, 2014(5): 17–19.LIU Jiyong and ZHAO Lei. Phase laser ranging system key technology research[J]. Electronic Test, 2014(5): 17–19. [14] TONOLINI F and ADIB F. Networking across boundaries: Enabling wireless communication through the water-air interface[C]. 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 2018: 117–131. [15] 贾刚, 汪力, 张希成. 太赫兹波(terahertz)科学与技术[J]. 中国科学基金, 2002, 16(4): 200–203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8217.2002.04.003JIA Gang, WANG Li, and ZHANG Xicheng. Terahertz science and technology[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2002, 16(4): 200–203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8217.2002.04.003 [16] 杨琪, 邓彬, 王宏强, 等. 太赫兹雷达目标微动特征提取研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(1): 22–45. doi: 10.12000/JR17087YANG Qi, DENG Bin, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Advancements in research on micro-motion feature extraction in the terahertz region[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(1): 22–45. doi: 10.12000/JR17087 [17] 马大猷. 现代声学理论基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 65–68.MA Dayou. Fundamentals of Modern Acoustic Theory[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 65–68. [18] 张烈山. 声波激励水面微幅波的光学外差检测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.ZHANG Lieshan. Research on optical heterodyne detection technology for acoustically induced water surface capillary waves[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [19] 张晓琳, 毛红杰, 李凯, 等. 相位解调实现低频水表面声波振幅探测[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(5): 0506001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0506001ZHANG Xiaolin, MAO Hongjie, LI Kai, et al. Amplitude detection of low frequency water surface acoustic wave based on phase demodulation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(5): 0506001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0506001 [20] 朱得糠, 刘永祥, 李康乐, 等. 基于雷达相位测距的微动特征获取[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(4): 574–582. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.04.018ZHU Dekang, LIU Yongxiang, LI Kangle, et al. Feature extraction for target with micro-motion based on radar phase derived range[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(4): 574–582. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.04.018 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: