-
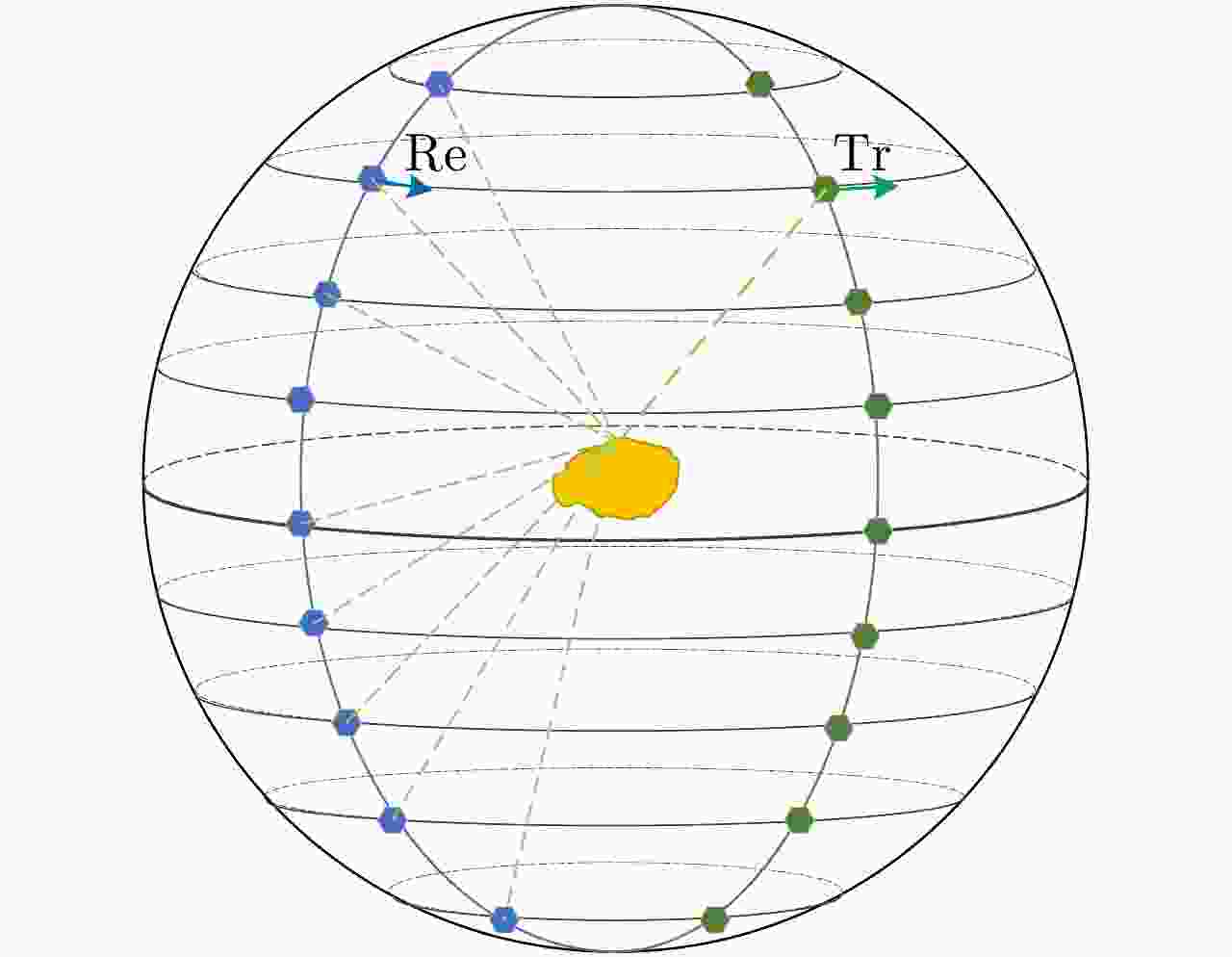
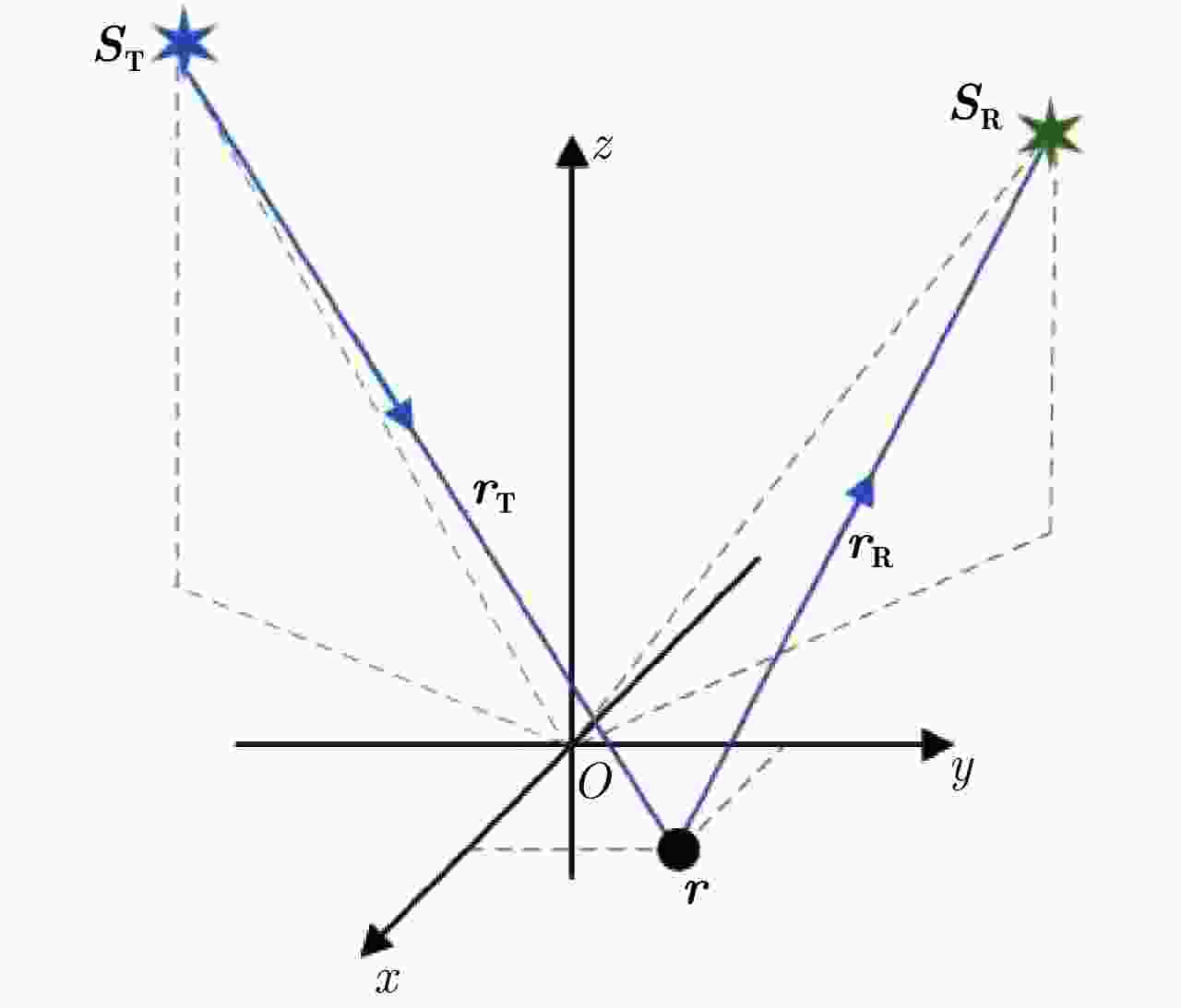
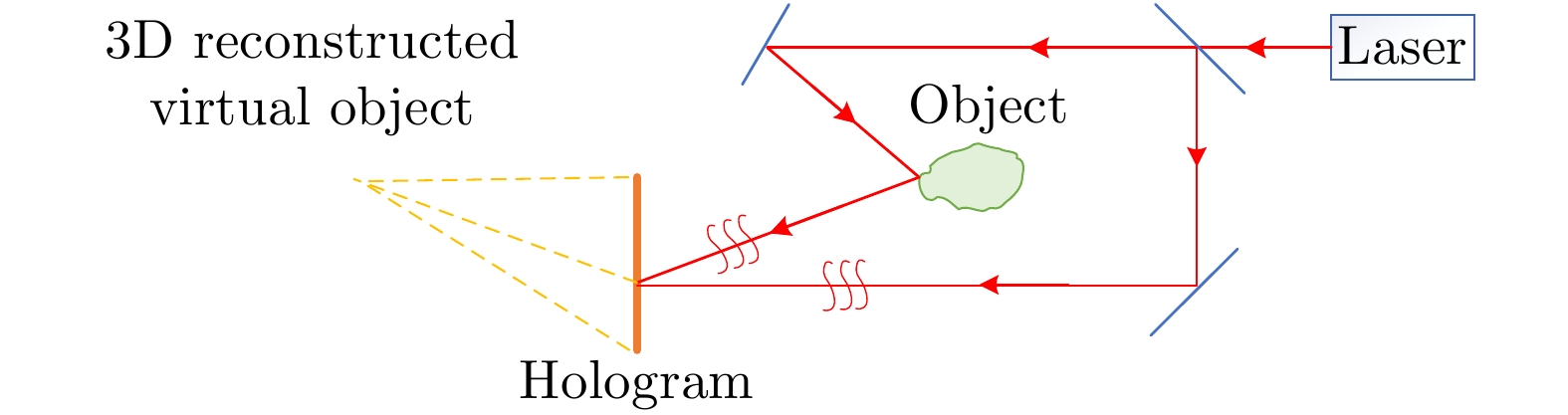
摘要: 合成孔径雷达技术经历了二维SAR、二维半SAR(InSAR)、三维SAR,已发展到如今的多维度SAR,取得了巨大的技术成就。该文在简要总结合成孔径雷达及其成像技术发展历程的基础上,提出了全息合成孔径雷达的概念并首次给出了明确的定义,指出该定义与现有全息雷达、多基线圆迹SAR、多维度SAR等概念的区别与联系。并且基于现有多维度SAR模型框架,给出了全息SAR的成像体制和信号模型,提出了初步的成像思路,为全息SAR技术的发展提供了初步的理论和技术框架基础。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology has undergone two-dimensional, two-and-a-half-dimensional, and three-dimensional SAR. It has also developed to multidimensional SAR and has made great technical achievements. After a brief summary of the development of SAR and its imaging technology, this study proposes the concept of holographic SAR and gives a clear definition of the concept for the first time. Furthermore, it points out the difference and connection between this holographic SAR definition and existing concepts, such as holographic radar, circular tomographic SAR, and multidimensional SAR. On this basis, the imaging system and signal model of holographic SAR are established under the framework of the existing multidimensional SAR, and preliminary imaging ideas are proposed. Thus, a preliminary theoretical and technical framework for the development of holographic SAR technology is provided.
-
Key words:
- Holographic SAR /
- Multi-dimensional SAR /
- SAR imaging model /
- Sparse imaging method
-
表 1 简缩全息SAR体制示例
Table 1. Examples of compact holographic SAR system
系统体制 观测度数 多维度数 频率 极化 入射角 散射角 时相 俯仰角 方位角 俯仰角 方位角 单波段全极化阵列干涉SAR多航过 1 4(完备) / / 1 1 K 2 单波段全极化圆迹层析3D-SAR 1 4(完备) / / 1 N(完备) 1 2 多波段全极化阵列干涉3D-SAR K 4(完备) / / 1 1 1 2 多波段全极化层析3D-SAR K 4(完备) / / 1 1 1 2 单全极化层析4D-SAR 1 4(完备) / / 1 1 K 2 全波段相参全极化层析3D-SAR M(完备) 4(完备) / / 1 1 1 2 全波段相参全极化圆迹层析3D-SAR M(完备) 4(完备) / / 1 N(完备) 1 3 全波段相参全极化圆迹层析4D-SAR M(完备) 4(完备) / / 1 N(完备) K 4 单波段分布式多发多收全极化3D-SAR 1 4(完备) K1 K2 K3 K4 1 3 多波段分布式多发多收全极化3D-SAR K 4(完备) K1 K2 K3 K4 1 4 表 1 Examples of compact holographic SAR system
System Observation degree Number of Dimension Frequency Polarization Incident angle Scattering angle Time
phaseElevation
angleAzimuth
angleElevation
angleAzimuth
angleSingle-band full-polarization array interferometric multipass SAR 1 4(complete) / / 1 1 K 2 Single-band full-polarization circular tomographic 3D-SAR 1 4(complete) / / 1 N(complete) 1 2 Multi-band full-polarization array interferometric 3D-SAR K 4(complete) / / 1 1 1 2 Multi-band full-polarization tomographic 3D-SAR K 4(complete) / / 1 1 1 2 Single-band full-polarization tomographic 4D-SAR 1 4(complete) / / 1 1 K 2 Multi-band coherent full-polarization tomographic 3D-SAR M(complete) 4(complete) / / 1 1 1 2 Multi-band coherent full-polarization circular tomographic 3D-SAR M(complete) 4(complete) / / 1 N(complete) 1 3 Multi-band coherent full-polarization circular tomographic 4D-SAR M(complete) 4(complete) / / 1 N(complete) K 4 Single-band distributed multiple-input multiple-output full-polarization 3D-SAR 1 4(complete) K1 K2 K3 K4 1 3 Multi-band distributed multiple-input multiple-output full-polarization 3D-SAR K 4(complete) K1 K2 K3 K4 1 4 -
[1] MOREIRA J, SCHWABISCH M, FORNARO G, et al. X-SAR interferometry: First results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 950–956. doi: 10.1109/36.406681 [2] GABRIEL A K and GOLDSTEIN R M. Crossed orbit interferometry: Theory and experimental results from SIR-B[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1988, 9(5): 857–872. doi: 10.1080/01431168808954901 [3] WERNER M. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM): Experience with the X-band SAR interferometer[C]. 2001 CIE International Conference on Radar, Beijing, China, 2001: 634-638. doi: 10.1109/ICR.2001.984798. [4] 张庆君. 高分三号卫星总体设计与关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(3): 269–277.ZHANG Qingjun. System design and key technologies of the GF-3 satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. [5] HAN Bing, DING Chibiao, ZHONG Lihua, et al. The GF-3 SAR data processor[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 835. doi: 10.3390/s18030835 [6] 袁新哲, 林明森, 刘建强, 等. 高分三号卫星在海洋领域的应用[J]. 卫星应用, 2018, (6): 17–21.YUAN Xinzhe, LIN Mingsen, LIU Jianqiang, et al. Application of CF-3 satellite in the marine field[J]. Satellite Application, 2018(6): 17–21. [7] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [8] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047WU Yirong. Concept on multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047 [9] BOUSSO R. The holographic principle[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2002, 74(3): 825–874. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.825 [10] BYRD M J, JERSAK B D, KRENEK B D, et al. Demonstration of 3D microwave holography[C]. IGARSS’94—1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 1994. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1994.399300. [11] BLANCHARD A J, WILLIAMS B, SCHINDEL R F, et al. Images of statistically distributed clutter targets made by the harc holographic imaging facility[C]. IGARSS’92 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Houston, USA, 1992. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1992.578298. [12] 林溪波. 航天微波全息雷达[J]. 上海航天, 1994, (2): 44–49.LIN Xibo. Space microwave holographic radar[J]. Shanghai Aerospace, 1994(2): 44–49. [13] KRZYSTOFIK W J. Microwave holography[C]. 13th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar and Wireless Communications, Wroclaw, Poland, 2000: 597–600. doi: 10.1109/MIKON.2000.914003. [14] IVASHOV S I, RAZEVIG V V, VASILIEV I A, et al. Holographic subsurface radar of RASCAN type: Development and applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2011, 4(4): 763–778. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2011.2161755 [15] ZHURAVLEV A V, IVASHOV S I, RAZEVIG V V, et al. Holographic subsurface radar RASCAN-5[C]. 2013 7th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar, Nantes, France, 2013: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/IWAGPR.2013.6601548. [16] BORGIOLI G, BOSSI L, CAPINERI L, et al. A hologram reconstruction algorithm for landmine recognition and classification based on microwave holographic radar data[C].2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Toyama, Japan, 2018: 1938–1944. doi: 10.23919/PIERS.2018.8597707. [17] PONCE O, PRATS P, SCHEIBER R, et al. Multibaseline 3-D circular SAR imaging at L-band[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012. [18] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. Polarimetric 3-D reconstruction from multicircular SAR at P-band[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 803–807. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2279236 [19] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. First airborne demonstration of holographic SAR tomography with fully polarimetric multicircular acquisitions at L-Band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6170–6196. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2582959 [20] 洪文. 圆迹SAR成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046HONG Wen. Progress in circular SAR imaging technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046 [21] 王本君. 圆周SAR三维成像技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012: 20–41.WANG Benjun. Research on circular SAR 3-D imaging[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012: 20–41. [22] 安道祥, 陈乐平, 冯东, 等. 机载圆周SAR成像技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 221–242. doi: 10.12000/JR20026AN Daoxiang, CHEN Leping, FENG Dong, et al. Study of the airborne circular synthetic aperture radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 221–242. doi: 10.12000/JR20026 [23] BAO Qian, LIN Yun, HONG Wen, et al. Holographic SAR tomography image reconstruction by combination of adaptive imaging and sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1248–1251. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2704601 [24] FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. A phase calibration method based on phase gradient autofocus for airborne holographic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(12): 1864–1868. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2911932 [25] FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, CHEN Leping, et al. Multicircular SAR 3-D imaging based on iterative adaptive approach[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 2019. doi: 10.1109/APSAR46974.2019.9048440. [26] 谭维贤. 合成孔径雷达三维成像理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2009: 1–141.TAN Weixian. Study on theory and algorithms for three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009: 1–141. [27] GABOR D. Microscopy by reconstructed wave fronts: Ⅱ[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1951, 64(6): 449–469. doi: 10.1088/0370-1301/64/6/301 [28] THORN C B. Reformulating string theory with the 1/N expansion[C]. International A.D. Sakharov Conference on Physics, Moscow, Russia, 1991. [29] SUSSKIND L. The world as a hologram[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1995, 36(11): 6377–6396. doi: 10.1063/1.531249 [30] 彭学明, 王彦平, 谭维贤, 等. 基于跨航向稀疏阵列的机载下视MIMO 3D-SAR三维成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720PENG Xueming, WANG Yanping, TAN Weixian, et al. Airborne downward-looking MIMO 3D-SAR imaging algorithm based on cross-track thinned array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720 [31] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [32] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1 -norm regularization—the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [33] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2005.843567 [34] FORNARO G, REALE D, and SERAFINO F. Four-dimensional SAR imaging for height estimation and monitoring of single and double scatterers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 224–237. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2000837 [35] LOMBARDINI F and VIVIANI F. New developments of 4D+ differential SAR tomography to probe complex dynamic scenes[C]. 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Quebec City, Canada, 2014. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6947201 [36] 陈晨, 魏中浩, 徐志林, 等. 基于高斯字典原子稀疏表示的高精度宽角SAR成像方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(11): 2471–2478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.10CHEN Chen, WEI Zhonghao, XU Zhilin, et al. High-precision wide angle SAR imaging method based on sparse representation of Gaussian dictionary atoms[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(11): 2471–2478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.11.10 [37] 洪文. 基于混合极化架构的极化SAR: 原理与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074HONG Wen. Hybrid-polarity architecture based polarimetric SAR: Principles and applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074 [38] 陈杰, 杨威, 王鹏波, 等. 多方位角观测星载SAR技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, WANG Pengbo, et al. Review of novel azimuthal multi-angle observation spaceborne SAR technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015 [39] 吴一戎, 洪文, 张冰尘. 稀疏微波成像导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 38–41.WU Yirong, HONG Wen, and ZHANG Bingchen. Introduction to Sparse Microwave Imaging[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018: 38–41. [40] 焦泽坤. 稀疏阵列雷达空间目标三维成像技术[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2019: 17–46.JIAO Zekun. 3D imaging technology of sparse array radar space target[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019: 17–46. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
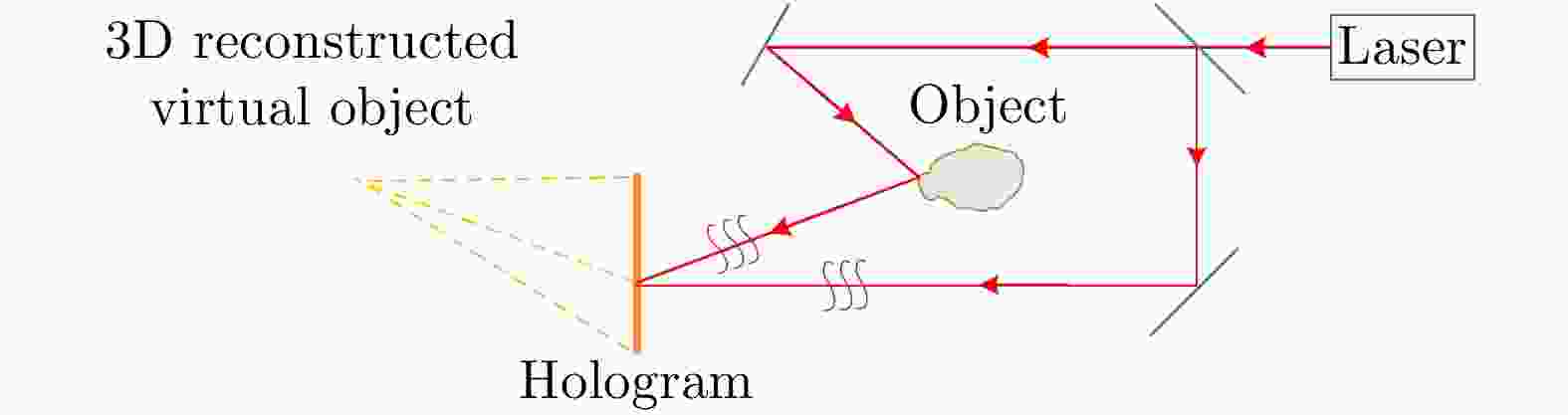
 下载:
下载: