Few-shot Ship Classification of SAR Images via Scattering Point Topology and Dual-branch Convolutional Neural Network
-
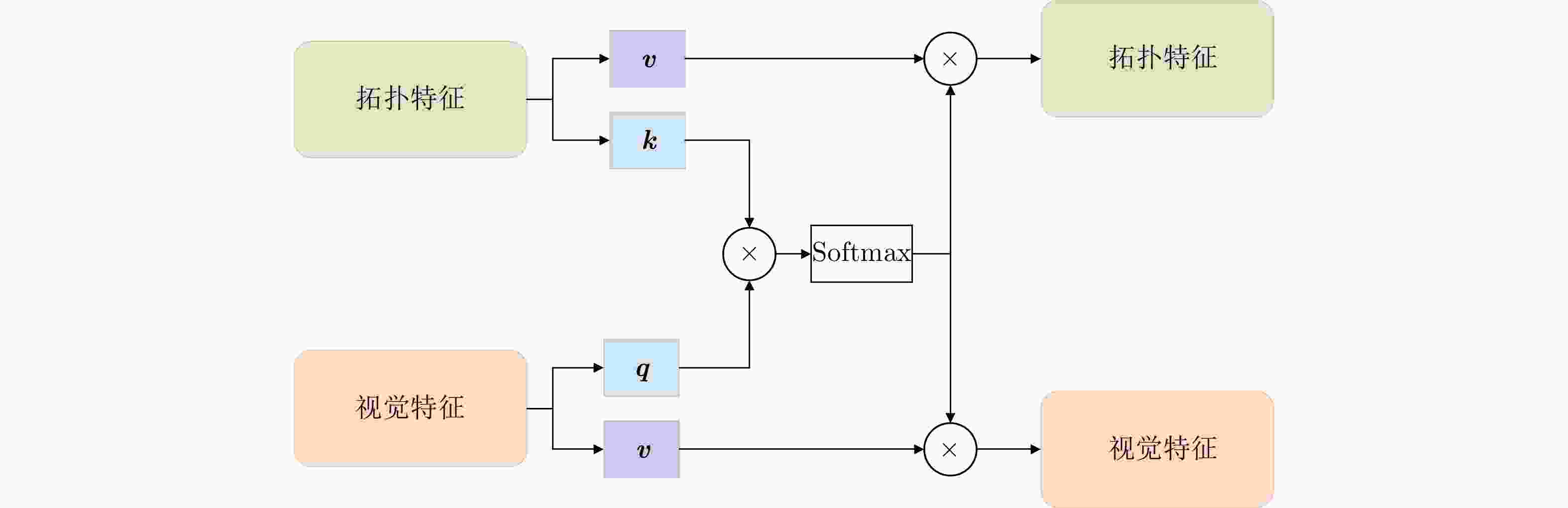
摘要: 随着合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像在舰船检测和识别领域的广泛应用,准确而高效地进行舰船分类已经成为一个亟待解决的问题。在小样本学习场景下,一般的方法面临着泛化能力不足的问题,因此该文引入了额外的信息和特征,旨在增加模型对目标的理解和泛化能力。该文通过散射关键点构建拓扑结构以表征舰船目标的结构和形状特征,并计算拓扑结构的拉普拉斯矩阵,将散射点之间的拓扑关系转化为矩阵形式,最后将SAR图像和拉普拉斯矩阵分别作为双分支网络的输入进行特征提取。在网络结构方面,该文设计了一个由两个独立的卷积分支组成的双分支卷积神经网络,分别负责处理视觉特征和拓扑特征,并用两个交叉融合注意力模块分别对两个分支的特征进行交互融合。该方法有效地将目标散射点拓扑关系与网络的自动学习过程相结合,从而增强模型的泛化能力并提高分类精度。实验结果表明,在OpenSARShip数据集上,所提方法在1-shot和5-shot任务的平均准确率分别为53.80%和73.00%。而在FUSAR-Ship数据集上,所提方法分别取得了54.44%和71.36%的平均准确率。所提方法在1-shot和5-shot的设置下相比基础方法准确率均提升超过15%,证明了散射点拓扑的应用对SAR图像小样本舰船分类的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 舰船分类 /
- 小样本学习 /
- 散射点拓扑 /
- 双分支卷积神经网络
Abstract: With the widespread application of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images in ship detection and recognition, accurate and efficient ship classification has become an urgent issue that needs to be addressed. In few-shot learning, conventional methods often suffer from limited generalization capabilities. Herein, additional information and features are introduced to enhance the understanding and generalization capabilities of the model for targets. To address this challenge, this study proposes a few-shot ship classification method for SAR images based on scattering point topology and Dual-Branch Convolutional Neural Network (DB-CNN). First, a topology structure was constructed using scattering key points to characterize the structural and shape features of ship targets. Second, the Laplacian matrix of the topology structure was calculated to transform the topological relations between scattering points into a matrix form. Finally, the original image and Laplacian matrix were used as inputs to the DB-CNN for feature extraction. Regarding network architecture, a DB-CNN comprising two independent convolution branches was designed. These branches were tasked with processing visual and topological features, employing two cross-fusion attention modules to collaboratively merge features from both branches. This approach effectively integrates the topological relations of target scattering points into the automated learning process of the network, enhancing the generalization capabilities and enhancing the classification accuracy of the model. Experimental results demonstrated that the proposed approach obtained average accuracies of 53.80% and 73.00% in 1-shot and 5-shot tasks, respectively, on the OpenSARShip dataset. Similarly, on the FUSAR-Ship dataset, it achieved average accuracies of 54.44% and 71.36% in 1-shot and 5-shot tasks, respectively. In the case of both 1-shot and 5-shot tasks, the proposed approach outperformed the baseline by >15% in terms of accuracy, underscoring the effectiveness of incorporating scattering point topology in few-shot ship classification of SAR images. -
表 1 实验数据集设置
Table 1. The dataset settings in our experiment
数据集 基础类别 样本数量 新颖类别 样本数量 Cargo 8240 Dredgin 80 OpenSARShip Fishing 126 Passeng 38 Tanker 1670 Pilot 14 Tug 176 Search 24 合计 10212 合计 156 Cargo 1289 HighSpeedCraft 15 Dredger 51 LawEnforce 27 FUSAR-Ship Fishing 563 Reserved 28 Tanker 157 Passenger 31 Unspecified 111 Tug 44 合计 2171 合计 145 表 2 实验数据设置
Table 2. Experimental data setting
数据集 1-shot 5-shot 支持集 查询集 支持集 查询集 OpenSARShip 1×4 5 5×4 5 FUSAR-Ship 1×5 5 5×5 5 表 3 本文方法和其他方法性能的对比(%)
Table 3. Comparison of performance of our method and other methods (%)
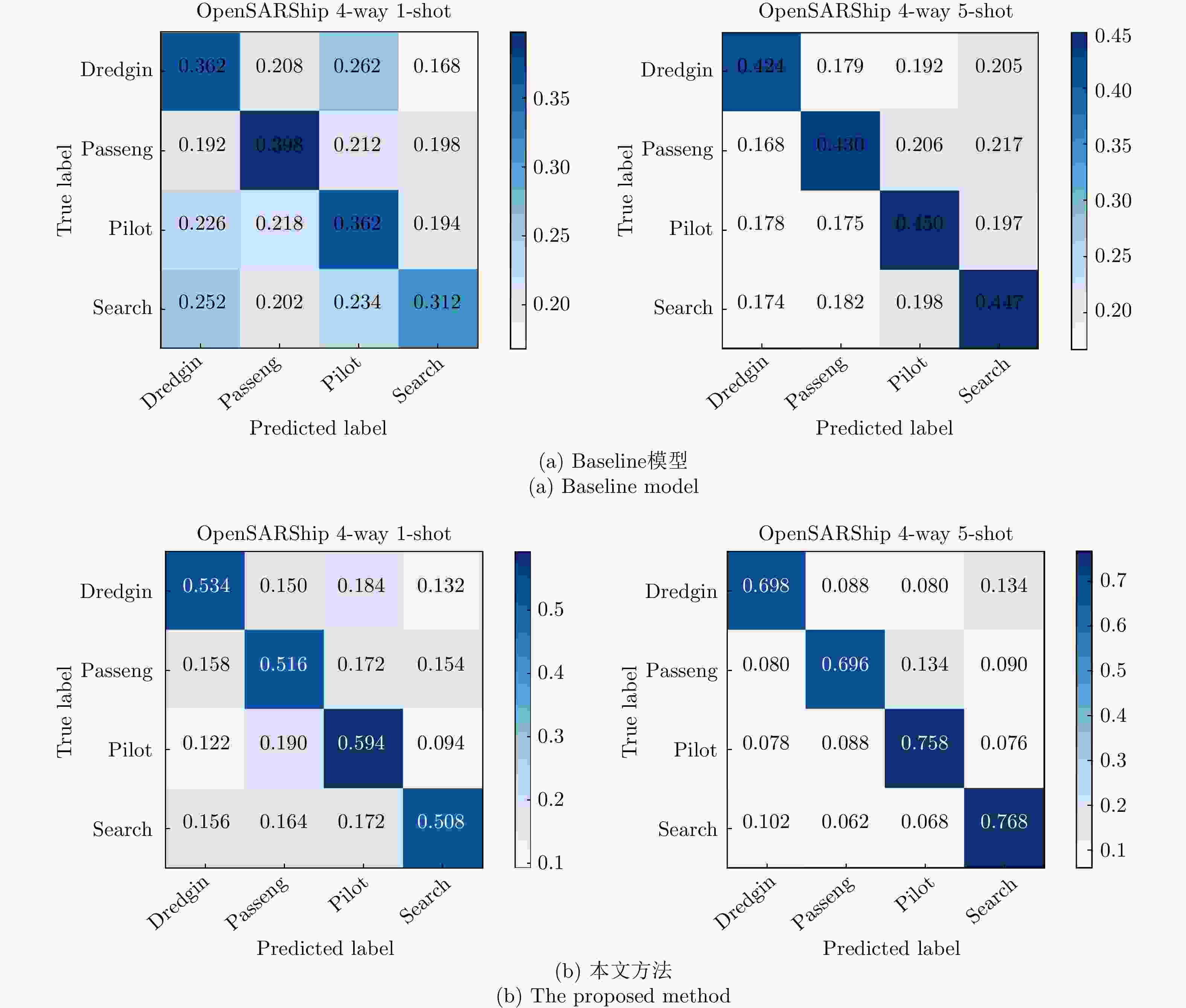
方法 OpenSARShip FUSAR-Ship 1-shot 5-shot 1-shot 5-shot MatchingNet[16] 30.20±1.66 33.30±1.70 31.88±1.96 34.00±1.44 ProtoNet[14] 32.00±1.97 37.35±2.19 30.64±2.01 35.40±1.68 RelationNet[15] 29.64±2.04 30.60±1.73 31.12±1.53 31.12±1.53 MAML[13] 29.60±2.13 33.10±1.87 31.32±1.81 32.40±1.71 Baseline[18] 35.85±2.00 43.40±2.04 31.68±1.56 37.32±2.00 Baseline++[18] 35.35±2.09 40.90±1.84 31.96±1.79 35.64±1.83 NegMargin[34] 36.15±2.15 41.05±1.86 30.68±1.91 35.68±1.89 MetaBaseline[19] 32.51±2.03 38.60±1.86 30.32±1.88 34.52±1.83 基于GCN的方法 47.50±2.47 71.05±2.48 55.76±2.28 68.04±1.64 本文方法 53.80±2.28 73.00±2.21 54.44±2.02 71.36±1.75 注:表3—表6中数值的下标表示标准差。 表 4 不同最近邻数量k对模型的影响(%)
Table 4. The effect of different nearest neighbor number k on the model (%)
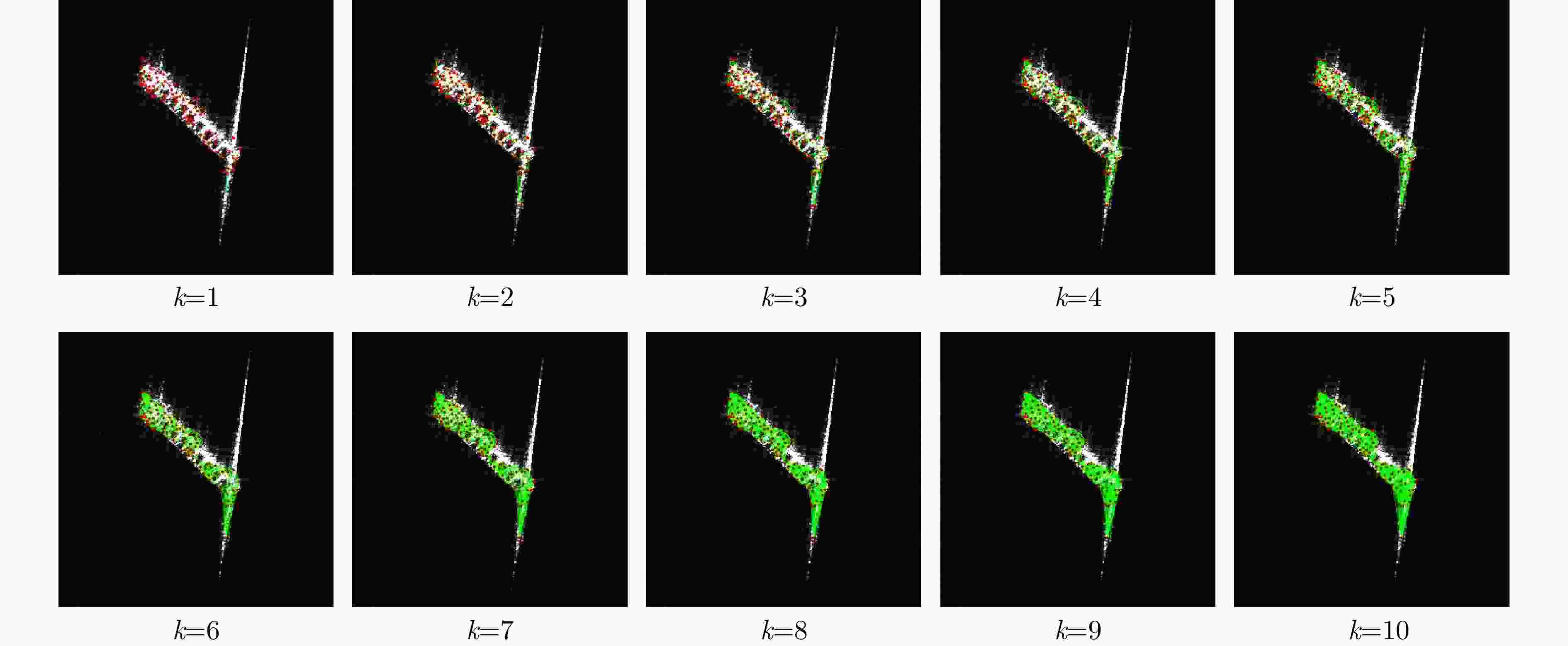
k OpenSARShip FUSAR-Ship 1-shot 5-shot 1-shot 5-shot 1 38.85±2.61 52.85±2.24 47.64±1.73 60.76±1.75 2 37.25±2.23 48.00±2.24 59.48±1.92 63.04±1.78 3 41.50±2.22 59.75±2.14 51.32±2.34 73.44±1.61 4 47.45±2.49 67.45±2.31 49.68±2.18 66.36±1.95 5 49.80±2.30 74.82±2.22 53.40±2.16 71.84±1.76 6 51.75±2.41 69.50±2.28 50.76±2.03 66.56±1.84 7 49.05±2.60 72.30±2.45 49.76±1.91 70.12±1.79 8 53.80±2.28 73.00±2.21 54.44±2.02 71.36±1.75 9 50.35±2.63 72.40±2.16 49.28±2.34 71.12±1.64 10 51.00±2.27 70.05±2.20 50.36±2.13 71.16±1.77 表 5 拓扑特征支路和视觉特征支路消融(%)
Table 5. Topological feature branch and visual feature branch ablation (%)
分支1 分支2 OpenSARShip FUSAR-Ship 1-shot 5-shot 1-shot 5-shot 图像特征 无 35.85±2.00 43.40±2.04 31.68±1.56 37.32±2.00 图像特征 图像特征 42.20±2.21 69.60±2.16 43.88±2.31 62.92±1.87 拓扑特征 拓扑特征 35.50±2.30 44.85±1.40 21.80±1.05 28.52±1.64 图像特征 拓扑特征 53.80±2.28 73.00±2.21 54.44±2.02 71.36±1.75 表 6 交叉融合注意力机制对模型的影响(%)
Table 6. The effect of cross-fusion attention mechanism on the model (%)
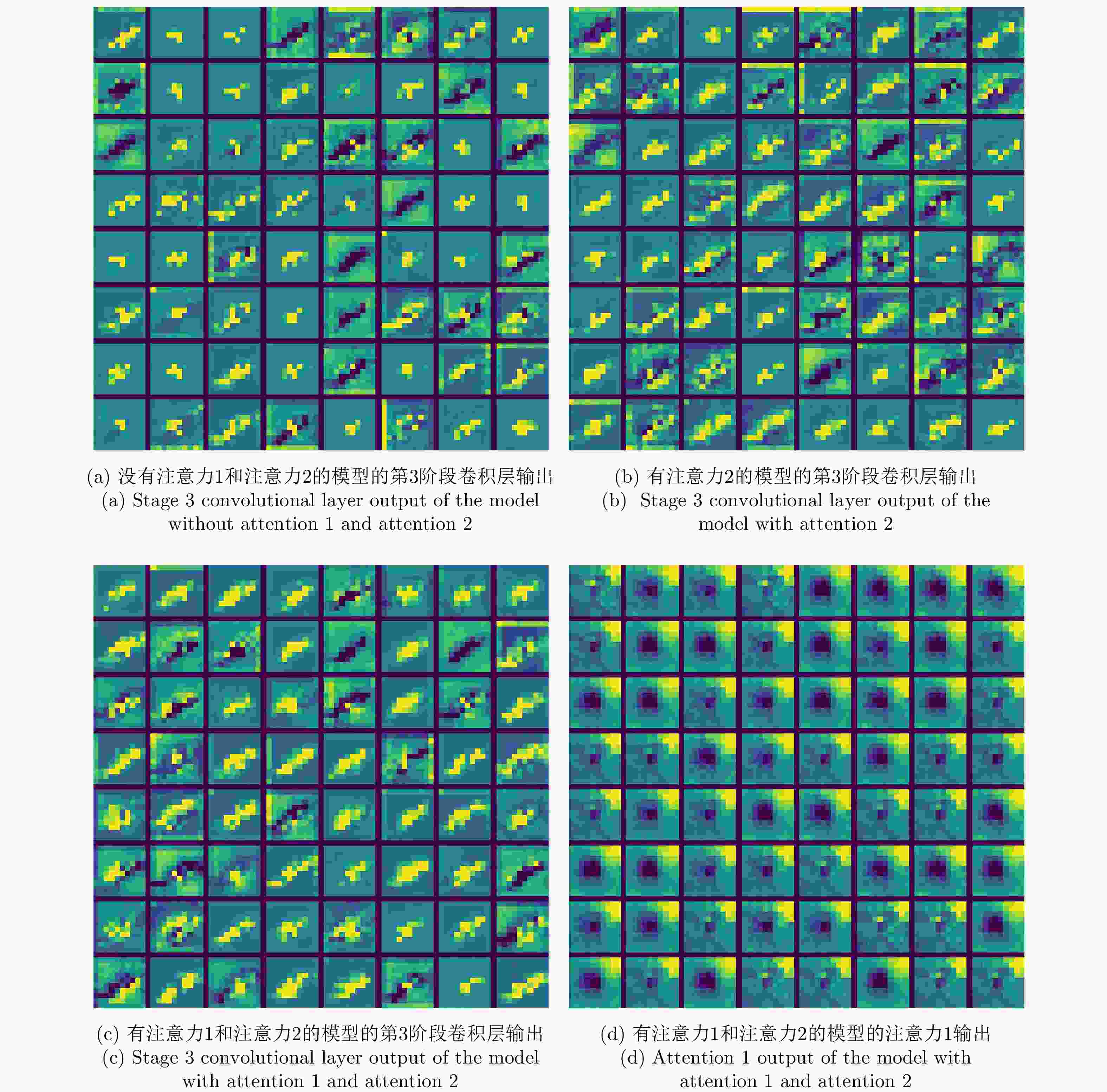
注意力1 注意力2 OpenSARShip FUSAR-Ship 1-shot 5-shot 1-shot 5-shot × × 34.45±1.95 41.20±2.14 30.24±1.75 35.48±1.75 × √ 47.45±2.57 64.65±2.14 38.72±2.19 53.52±2.02 √ √ 53.80±2.28 73.00±2.21 54.44±2.02 71.36±1.75 注:“×”表示未使用相应的注意力机制,“√”表示使用了相应的注意力机制。 -
[1] HASHIMOTO S, SUGIMOTO Y, HAMAMOTO K, et al. Ship classification from SAR images based on deep learning[C]. SAI Intelligent Systems Conference, Cham, Switzerland, 2019: 18–34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01054-6_2. [2] 雷禹, 冷祥光, 孙忠镇, 等. 宽幅SAR海上大型运动舰船目标数据集构建及识别性能分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 347–362. doi: 10.12000/JR21173.LEI Yu, LENG Xiangguang, SUN Zhongzhen, et al. Construction and recognition performance analysis of wide-swath SAR maritime large moving ships dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 347–362. doi: 10.12000/JR21173. [3] 胡思茹, 马福民, 秦天奇, 等. 基于多特征组合的红外舰船目标识别技术[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2022, 42(2): 185–189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.02.040.HU Siru, MA Fumin, QIN Tianqi, et al. Infrared ship target recognition technology based on multi feature combination[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(2): 185–189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.02.040. [4] OUCHI K. Current status on vessel detection and classification by synthetic aperture radar for maritime security and safety[C]. 38th Symposium on Remote Sensing for Environmental Sciences, Gamagori, Japan, 2016: 3–5. [5] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037.TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037. [6] JI Yongjie, ZENG Peng, ZHANG Wangfei, et al. Forest biomass inversion based on KNN-FIFS with different alos data[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 4540–4543. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554712. [7] ZHANG Xin, HUO Chunlei, XU Nuo, et al. Multitask learning for ship detection from synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 8048–8062. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3102989. [8] 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104.DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. [9] ZHANG Liangpei, ZHANG Legei, and DU Bo. Deep learning for remote sensing data: A technical tutorial on the state of the art[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2016, 4(2): 22–40. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2016.2540798. [10] HOSPEDALES T, ANTONIOU A, MICAELLI P, et al. Meta-learning in neural networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(9): 5149–5169. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3079209. [11] CAO Changjie, CUI Zongyong, CAO Zongjie, et al. An integrated counterfactual sample generation and filtering approach for SAR automatic target recognition with a small sample set[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3864. doi: 10.3390/rs13193864. [12] NICHOL A, ACHIAM J, and SCHULMAN J. On first-order meta-learning algorithms[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02999, 2018. [13] FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126–1135. [14] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. [15] SUNG F, YANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1199–1208. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131. [16] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637–3645. [17] BENGIO Y. Deep learning of representations: Looking forward[C]. International conference on statistical language and speech processing. Berlin, Germany, 2013: 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39593-2_1. [18] CHEN Weiyu, LIU Y C, KIRA Z, et al. A closer look at few-shot classification[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 241–268. [19] CHEN Yinbo, LIU Zhuang, XU Huijuan, et al. Meta-baseline: Exploring simple meta-learning for few-shot learning[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9042–9051. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00893. [20] CUI Zongyong, ZHANG Mingrui, CAO Zongjie, et al. Image data augmentation for SAR sensor via generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 42255–42268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907728. [21] DING Jun, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2513754. [22] WANG Ke, ZHANG Gong, XU Yanbing, et al. SAR target recognition based on probabilistic meta-learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 682–686. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983988. [23] PAN Zongxu, BAO Xianjie, ZHANG Yueting, et al. Siamese network based metric learning for SAR target classification[C]. IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1342–1345. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898210. [24] LU Da, CAO Lanying, and LIU Hongwei. Few-shot learning neural network for SAR target recognition[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/APSAR46974.2019.9048517. [25] TAI Yuan, TAN Yihua, XIONG Shengzhou, et al. Few-shot transfer learning for SAR image classification without extra SAR samples[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 2240–2253. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3155406. [26] KANG Yuzhuo, WANG Zhirui, FU Jiamei, et al. SFR-Net: Scattering feature relation network for aircraft detection in complex SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5218317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3130899. [27] SUN Yuanrui, WANG Zhirui, SUN Xian, et al. SPAN: Strong scattering point aware network for ship detection and classification in large-scale SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 1188–1204. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3142025. [28] SUN Xian, LV Yixuan, WANG Zhirui, et al. SCAN: Scattering characteristics analysis network for few-shot aircraft classification in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5226517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3166174. [29] 吕艺璇, 王智睿, 王佩瑾, 等. 基于散射信息和元学习的SAR图像飞机目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 652–665. doi: 10.12000/JR22044.LYU Yixuan, WANG Zhirui, WANG Peijin, et al. Scattering information and meta-learning based SAR images interpretation for aircraft target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 652–665. doi: 10.12000/JR22044. [30] KANG Yuzhuo, WANG Zhirui, ZUO Haoyu, et al. ST-Net: Scattering topology network for aircraft classification in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5202117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3236987. [31] HARRIS C G and STEPHENS M J. A combined corner and edge detector[C]. Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 1988: 1–6. [32] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672. [33] HOU Xiyue, AO Wei, SONG Qian, et al. FUSAR-Ship: Building a high-resolution SAR-AIS matchup dataset of Gaofen-3 for ship detection and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63: 140303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2772-5. [34] LIU Bin, CAO Yue, LIN Yutong, et al. Negative margin matters: Understanding margin in few-shot classification[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 438–455. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_26. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: