Adaptive Region Proposal Selection for SAR Target Detection Using Reinforcement Learning
-
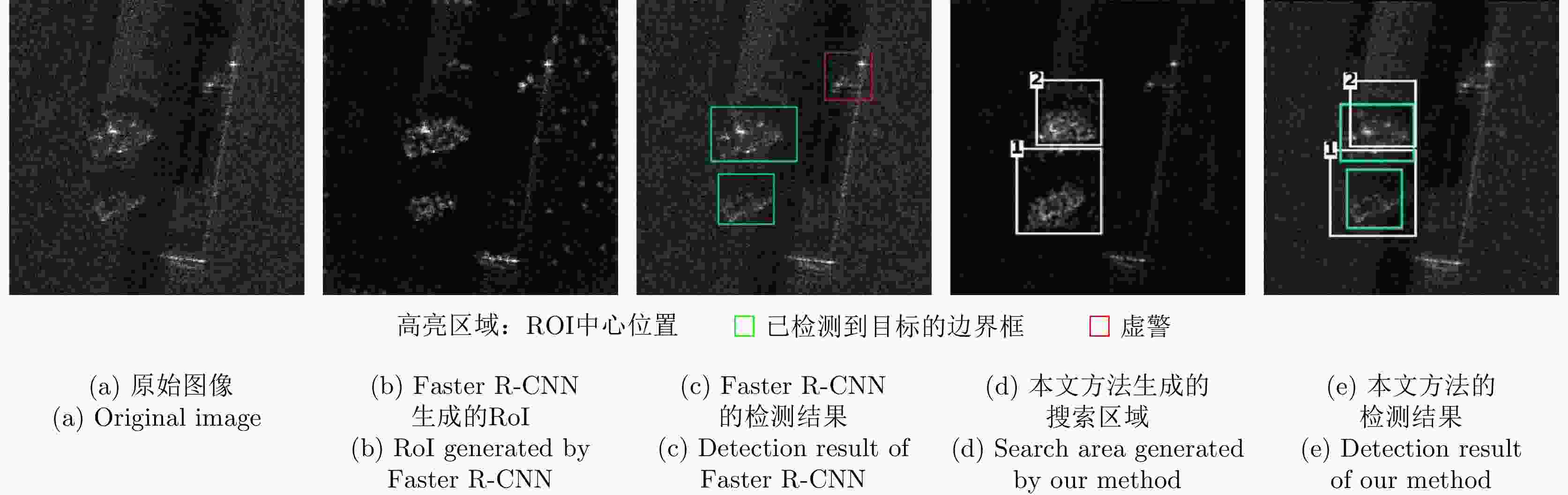
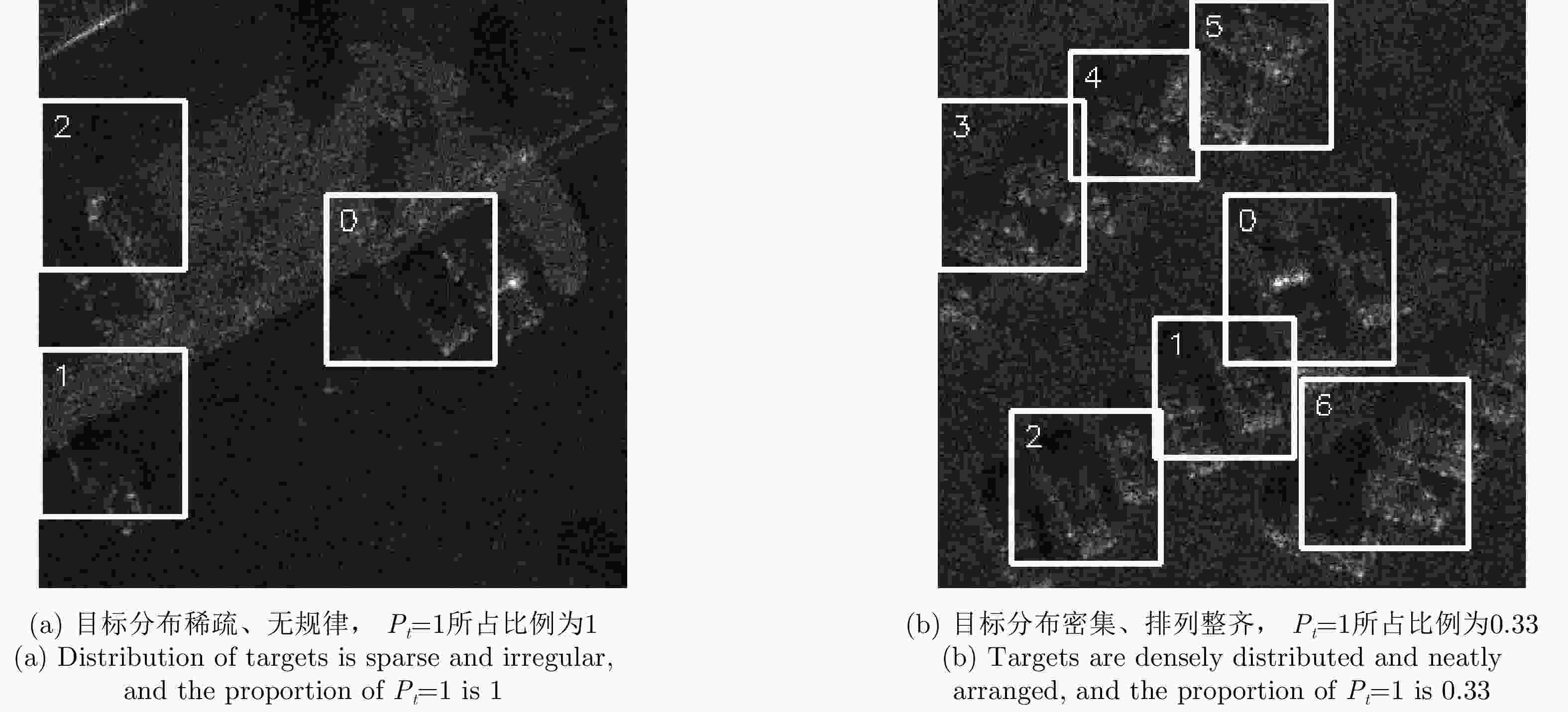
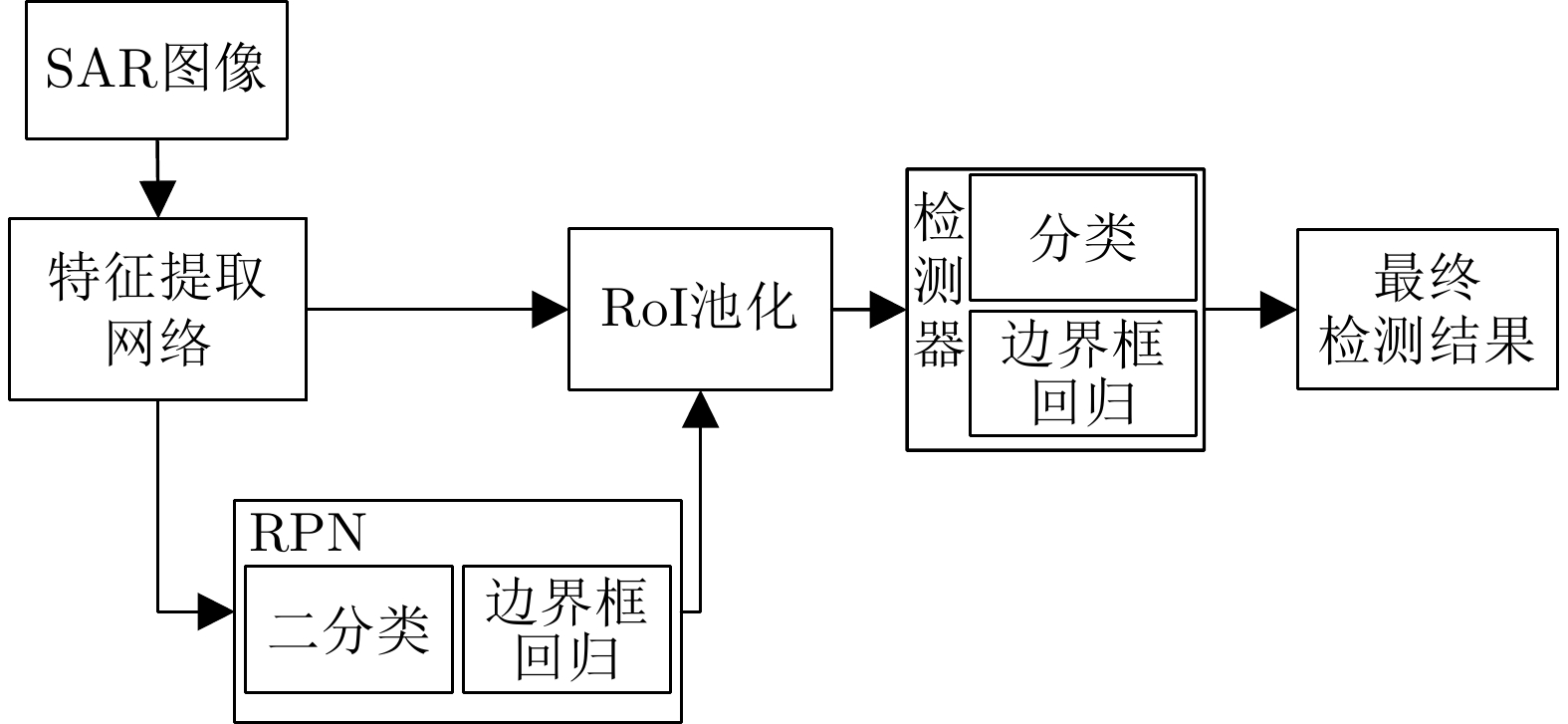
摘要: 大场景合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像相对于通用光学图像,复杂背景杂波对目标特征提取影响更大,由于传统基于候选框的深度目标检测算法会在整张特征图上产生大量冗余候选框,因而在SAR图像复杂背景杂波影响下会产生大量的虚警,降低目标检测精度。针对该问题,该文基于Faster R-CNN检测模型,提出结合强化学习自适应候选框挑选的SAR目标检测方法。该方法能够通过强化学习自适应搜索特征图中可能含有目标的区域,并挑选搜索区域内的候选框继续进行分类、回归。通过准确搜索到含有目标的区域,可以减少复杂背景杂波的影响并减少传统强化学习应用于检测问题的计算量。所提方法利用强化学习序列决策的特点,能够根据图像信息通过强化学习迭代搜索自适应确定图像中可能含有目标的搜索区域的位置。同时,该方法通过在强化学习中使用距离约束,可以根据之前的搜索结果自适应调整下一次搜索区域的尺寸。基于实测数据的实验结果表明,所提方法能够提升传统深度学习目标检测方法的检测性能。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达 /
- 目标检测 /
- 强化学习 /
- Faster R-CNN算法
Abstract: Compared with optical images, the background clutter has a greater impact on feature extraction in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. Due to the traditional redundant region proposals on the entire feature map, these algorithms generate large quantities of false alarms under the influence of clutter in SAR images, thereby lowering the target detection accuracy. To address this issue, this study proposes a Faster R-CNN model-based SAR target detection method, which uses reinforcement learning to realize adaptive region proposal selection. This method can adaptively locate areas that may contain targets on the feature map using the sequential decision-making characteristic of reinforcement learning and simultaneously adjust the scope of the next search area according to previous search results using distance constraints in reinforcement learning. Thus, this method can reduce the impact of complex background clutter and the computation of reinforcement learning. The experimental results based on the measured data indicate that the proposed method improves the detection performance.-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Target detection /
- Reinforcement learning /
- Faster R-CNN
-
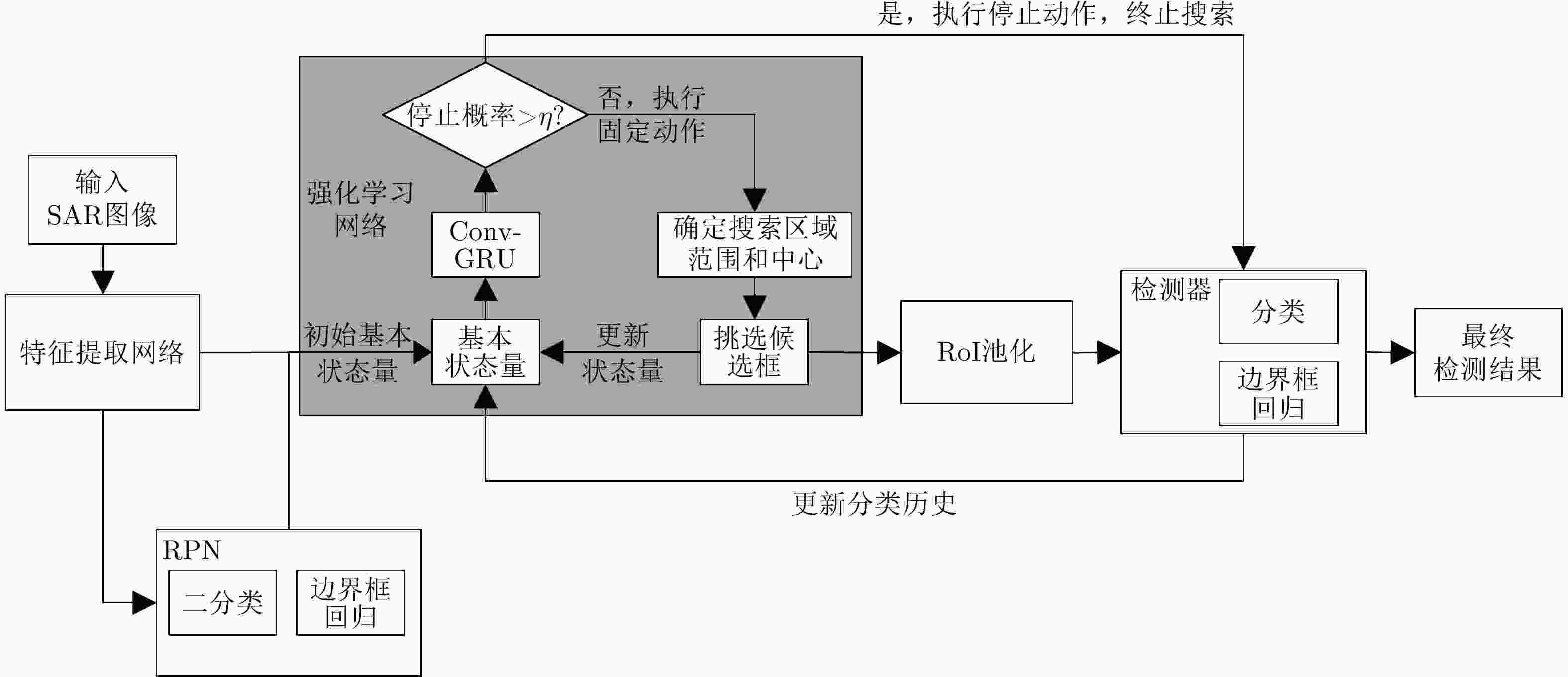
算法 1 自适应候选框挑选方法 Alg. 1 Adaptive region proposal selection 输入:状态${s_t} = $$\{ {R_t},{S_t},{H_t}\} $,最大迭代次数为$M = 10$ 输出:搜索区域中心坐标和范围参数$\{ {z_t},{p_t}\} $ 1:初始化状态量${s_t} = \{ {R_{t - 1}},{S_{t - 1}},{H_t}\} $ 2:for $t = 1 \to M$ do //t表示迭代次数 3: if $(\pi (a_t^d = 1|{s_t}) > \eta )$ then //$ \eta $为概率阈值,取0.5 4: break //结束迭代搜索 5: else 6: ${z_t} \Leftarrow \max \pi (a_t^d = 0,{\text{ }}a_t^f = {z_t}|{s_t})$ 7: ${p_t} \Leftarrow {z_t},{z_{t - 1}}$ //计算搜索区域中心坐标和范围 8: end if 9: 输出${z_t},{p_t}$ // 挑选候选框并送入后续检测器部分进行检测 10: ${R_t} \Leftarrow {R_{t - 1}},{\text{ }}{S_t} \Leftarrow {S_{t - 1}}$ //更新状态${R_t},{\text{ }}{S_t}$ 11:end for 表 1 不同方法实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results of different methods
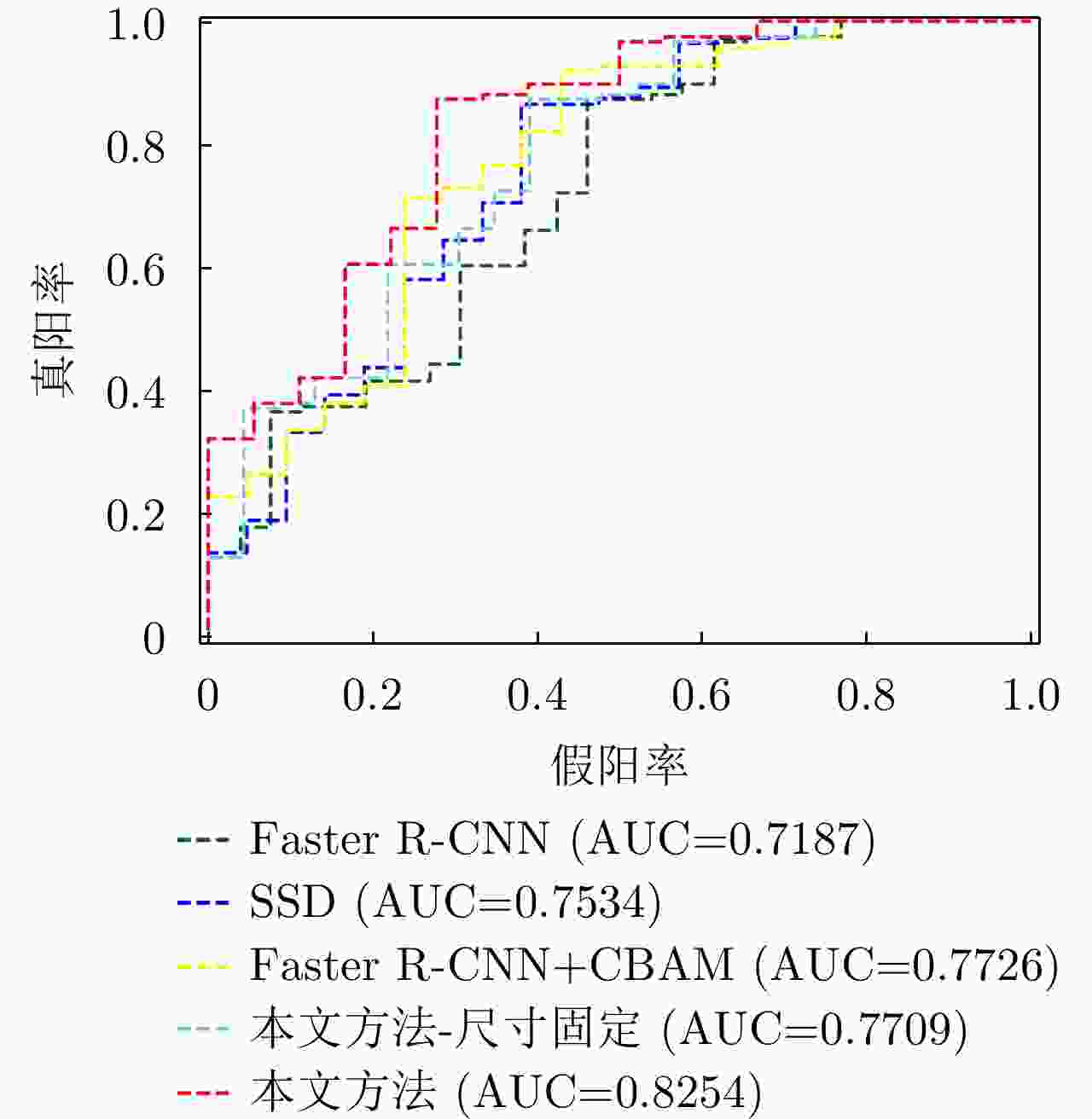
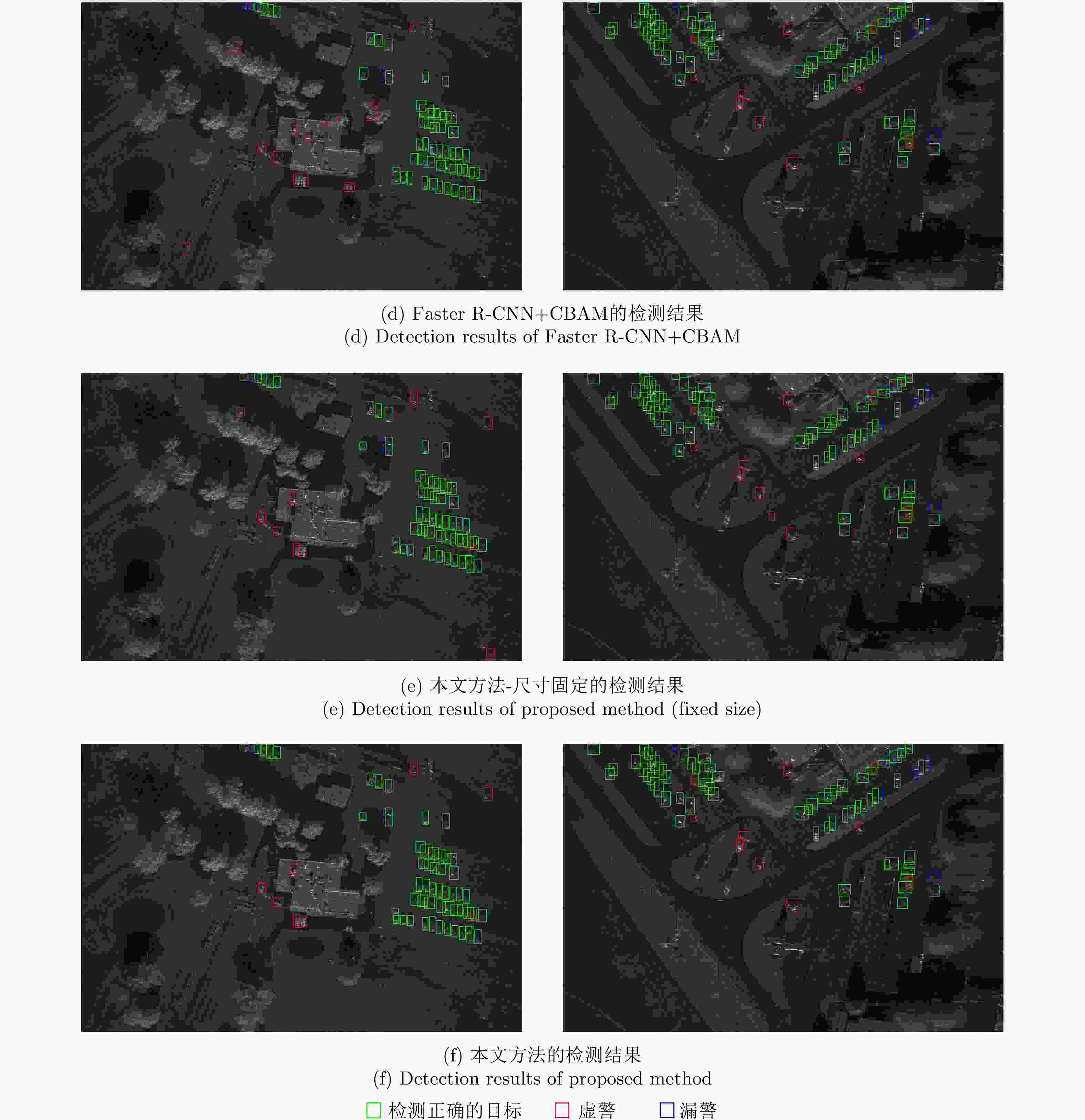
方法 P R F1-score Gaussian-CFAR 0.3789 0.7966 0.5135 Faster R-CNN 0.8156 0.9268 0.8677 SSD 0.8451 0.9106 0.8750 Faster R-CNN+CBAM 0.8409 0.9268 0.8818 本文方法-尺寸固定 0.8369 0.9350 0.8832 本文方法 0.8686 0.9350 0.9006 -
[1] BURL M C, OWIRKA G J, and NOVAK L M. Texture discrimination in synthetic aperture radar imagery[C]. Twenty-Third Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1989: 399–400. [2] NOVAK L M, BURL M C, and IRVING W W. Optimal polarimetric processing for enhanced target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(1): 234–244. doi: 10.1109/7.249129 [3] AI Jiaqiu, MAO Yuxiang, LUO Qiwu, et al. Robust CFAR ship detector based on bilateral-trimmed-statistics of complex ocean scenes in SAR imagery: A closed-form solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1872–1890. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3050654 [4] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [5] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [6] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. [7] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. [8] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [9] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [10] 杜兰, 刘彬, 王燕, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3018–3025. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161032DU Lan, LIU Bin, WANG Yan, et al. Target detection method based on convolutional neural network for SAR image[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3018–3025. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161032 [11] AI Jiaqiu, TIAN Ruitian, LUO Qiwu, et al. Multi-scale rotation-invariant Haar-like feature integrated CNN-based ship detection algorithm of multiple-target environment in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10070–10087. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931308 [12] ZHANG Shaoming, WU Ruize, XU Kunyuan, et al. R-CNN-based ship detection from high resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(6): 631. doi: 10.3390/rs11060631 [13] 杜兰, 魏迪, 李璐, 等. 基于半监督学习的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783DU Lan, WEI Di, LI Lu, et al. SAR target detection network via semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 154–163. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190783 [14] SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018: 1–526. [15] CHUNG J. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv: 1312.5602. [16] BUENO M B, GIRO-I-NIETO X, MARQUÉS F, et al. Hierarchical Object Detection with Deep Reinforcement Learning[M]. HEMANTH D J and ESTRELA V V. Deep Learning for Image Processing Applications. 2017: 164–1276. [17] CAICEDO J C and LAZEBNIK S. Active object localization with deep reinforcement learning[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2488–2496. [18] PIRINEN A and SMINCHISESCU C. Deep reinforcement learning of region proposal networks for object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6945–6954. [19] CHUNG J, GULCEHRE C, CHO K H, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[J]. arXiv: 1412.3555, 2014. [20] WILLIAMS R J. Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3/4): 229–256. doi: 10.1023/A:1022672621406 [21] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [22] GUTIERREZ D. MiniSAR: A review of 4-inch and 1-foot resolution Ku-band imagery[EB/OL]. https://www.sandia.gov/app/uploads/sites/124/2022/04/SAND2005-3706P-miniSAR-flight-SAR-images.pdf, 2005. [23] AI Jiaqiu, MAO Yuxiang, LUO Qiwu, et al. SAR target classification using the multikernel-size feature fusion-based convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5214313. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3106915 [24] 魏迪. 基于半监督卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标检测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.WEI Di. The research on target detection of SAR image based on semi-supervised convolutional neural network[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [25] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: