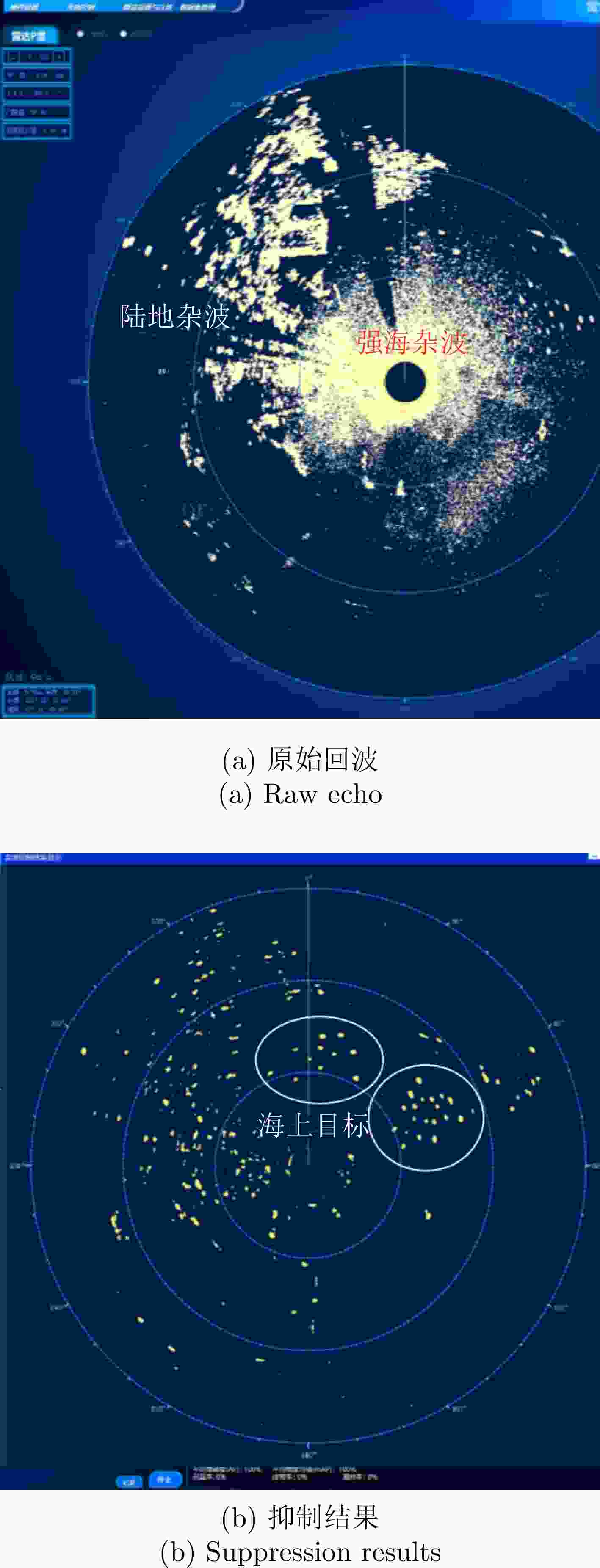
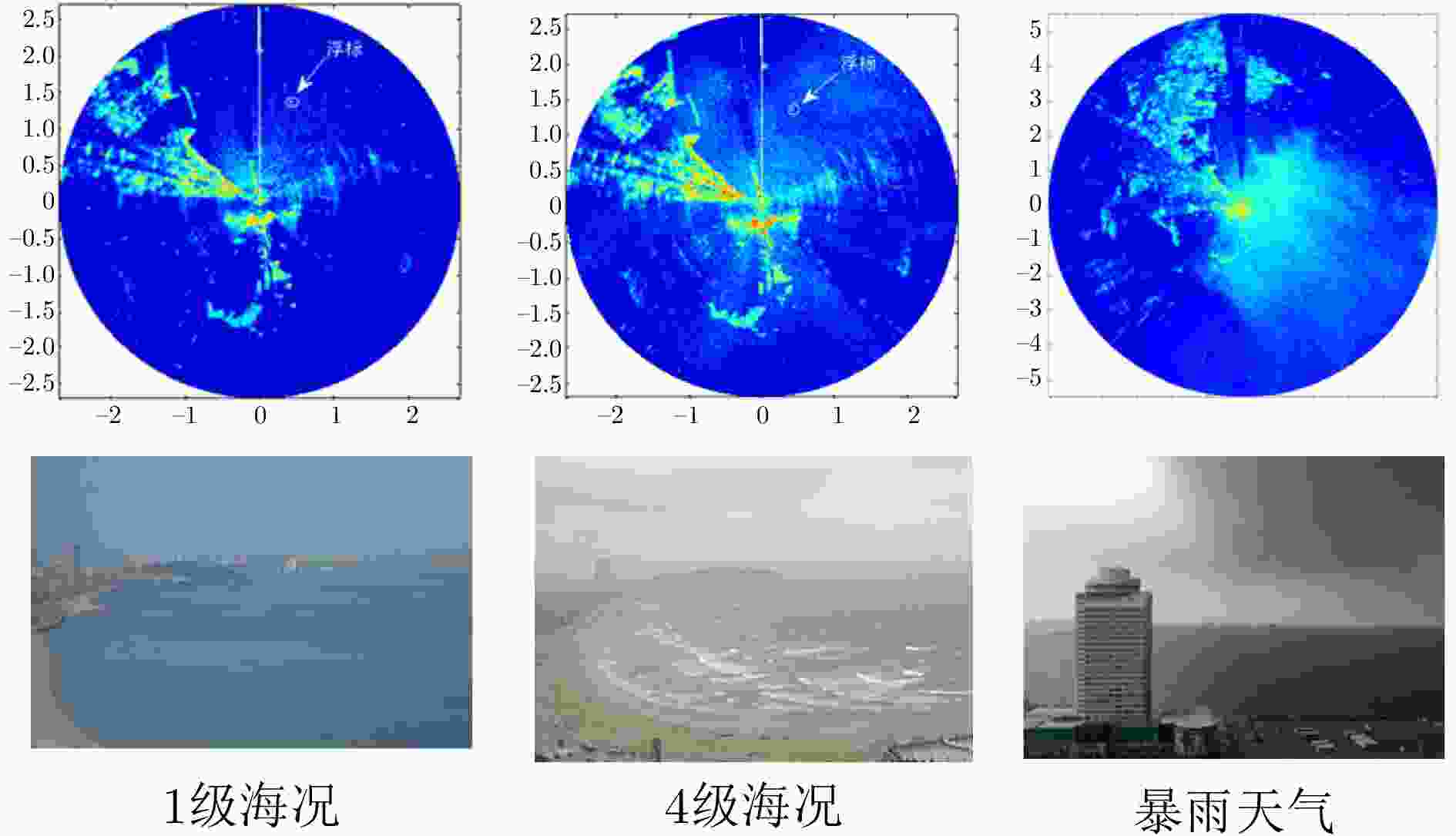
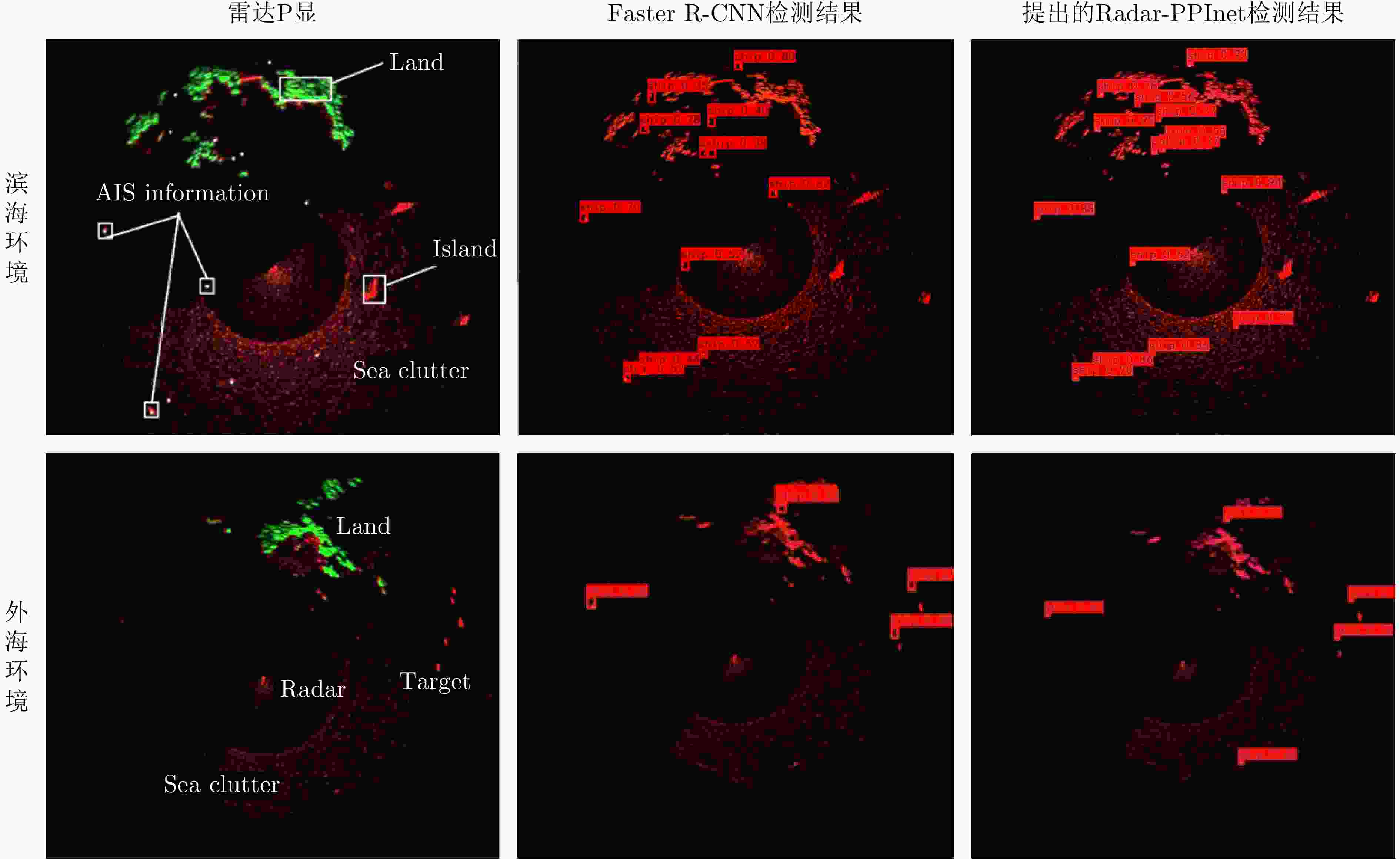
-
摘要: 雷达微弱目标处理是实现优异探测性能的基础和前提,在复杂的实际环境应用过程中,由于强杂波干扰、目标信号微弱、图像特征不明显、有效特征难提取等问题,导致雷达微弱目标检测与识别一直是雷达处理领域中的难点之一。传统模型类处理方法与实际工作背景和目标特性匹配不精准,导致通用性不强。近年来,深度学习在雷达智能信息处理领域取得了显著进展,深度学习算法通过构建深层神经网络,可以自动地从大量雷达数据中学习特征表示,提高目标检测和识别的性能。该文分别从雷达目标微弱信号处理、图像处理、特征学习等多个方面系统梳理和总结近年来雷达微弱目标智能化处理的研究进展,具体包括噪声与杂波抑制、微弱目标信号增强;低、高分辨雷达图像和特征图处理;特征提取、融合、目标分类与识别等。针对目前微弱目标智能化处理应用存在的泛化能力有限、特征单一、可解释性不足等问题,从小样本目标检测(迁移学习、强化学习)、多维多特征融合检测、网络模型可解释性、知识与数据联合驱动等方面对未来发展进行了展望。Abstract: Weak target signal processing is the cornerstone and prerequisite for radar to achieve excellent detection performance. In complex practical applications, due to strong clutter interference, weak target signals, unclear image features, and difficult effective feature extraction, weak target detection and recognition have always been challenging in the field of radar processing. Conventional model-based processing methods do not accurately match the actual working background and target characteristics, leading to weak universality. Recently, deep learning has made significant progress in the field of radar intelligent information processing. By building deep neural networks, deep learning algorithms can automatically learn feature representations from a large amount of radar data, improving the performance of target detection and recognition. This article systematically reviews and summarizes recent research progress in the intelligent processing of weak radar targets in terms of signal processing, image processing, feature extraction, target classification, and target recognition. This article discusses noise and clutter suppression, target signal enhancement, low- and high-resolution radar image and feature processing, feature extraction, and fusion. In response to the limited generalization ability, single feature expression, and insufficient interpretability of existing intelligent processing applications for weak targets, this article underscores future developments from the aspects of small sample object detection (based on transfer learning and reinforcement learning), multidimensional and multifeature fusion, network model interpretability, and joint knowledge- and data-driven processing.
-
表 1 舰船、干扰检测识别准确率(%)[50]
Table 1. Ship and interference detection and identification accuracy (%)[50]
模型名称 舰船 干扰 平均 恒虚警率检测方法CA-CFAR 84.2 80.4 82.3 自适应阈值分割OTSU 88.3 83.9 86.1 卷积网络CNN 97.1 87.7 92.4 非对称检测卷积神经网络AD-CNN 99.5 94.1 96.8 非对称检测卷积神经网络AD-CNN (Efficient) 99.6 94.4 97.0 表 2 不同网络性能对比分析
Table 2. Comparative analysis of different network performance
网络模型 雷达特征 数据集 模型组成结构 适用条件 LeNet, AlexNet, GoogLeNet[63] 海上微动特征 仿真目标和实测海杂波(Intelligent pixel-processing, IPIX雷达) 基于LeNet, AlexNet, GoogLeNe模型的
检测与分类网络杂波背景下的雷达微动目标 AlexNet[64] 飞机尾涡特征 某机场40天内航班起飞的情况 基于AlexNet模型的识别网络 大气风场中尾涡 Transformer
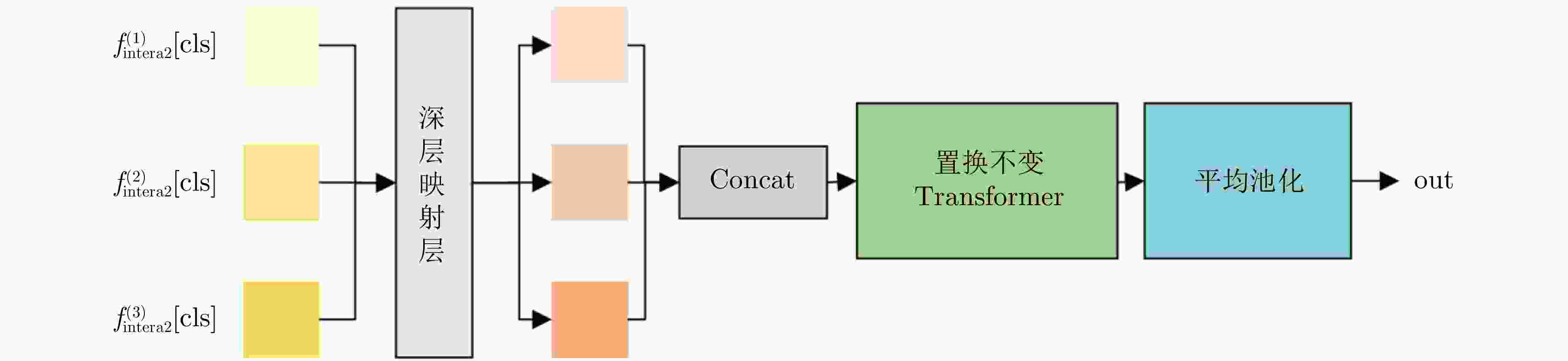
融合网络[61]多站协同雷达HRRP特征 单部雷达采集的某一航线的5型目标回波 以Transformer作为特征提取主体结构,并在此基础上设计了3个新的辅助模块:角度引导模块、前级特征交互模块以及深层注意力特征融合模块 多站协同雷达目标 -
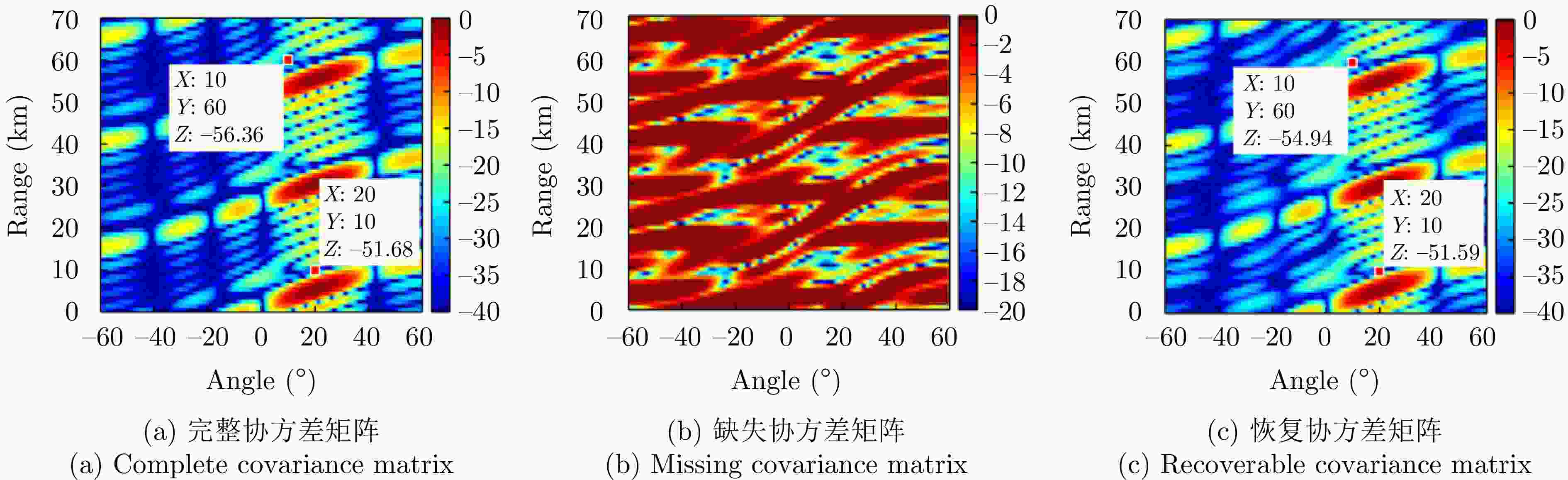
[1] 金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083.JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. [2] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040.WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040. [3] 杨建宇. 雷达技术发展规律和宏观趋势分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010.YANG Jianyu. Development laws and macro trends analysis of radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010. [4] 王珽, 赵晨, 陈泽宗, 等. 基于DnCNN网络的高频地波雷达海洋回波谱去噪方法研究[C]. 第十八届全国电波传播年会论文集, 青岛, 2023: 4–8. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2023.050865.WANG Ting, ZHAO Chen, CHEN Zezong, et al. Research on denoising method of high frequency ground wave radar ocean echo spectrum based on DnCNN network[C]. The 18th National Conference on Radio Wave Propagation, Qingdao, China, 2023: 4–8. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2023.050865. [5] YE Xin, QIAN Jiang, WANG Lu, et al. Noise suppression of ISAR micro cluster targets based on Generated Adversarial Network[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 704–707. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028484. [6] HU Minghuan, MAO Jiandong, LI Juan, et al. A novel lidar signal denoising method based on convolutional autoencoding deep learning neural network[J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(11): 1403. doi: 10.3390/atmos12111403. [7] 施端阳, 林强, 胡冰, 等. 遗传算法优化神经网络的雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 现代防御技术, 2021, 49(6): 74–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2021.06.011.SHI Duanyang, LIN Qiang, HU Bing, et al. Radar clutter suppression method based on neural network optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2021, 49(6): 74–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2021.06.011. [8] 施端阳, 林强, 胡冰, 等. 基于LVQ神经网络的雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2023, 48(4): 37–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.04.006.SHI Duanyang, LIN Qiang, HU Bing, et al. Radar clutter suppression method based on LVQ neural network[J]. Fire Control Command & Control, 2023, 48(4): 37–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.04.006. [9] TANG Xianhui, LI Dong, CHENG Wanru, et al. A novel sea clutter suppression method based on deep learning with exploiting time-frequency features[C]. The IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 2021: 2548–2552. doi: 10.1109/IAEAC50856.2021.9390660. [10] WANG Yumiao, ZHAO Wenjing, WANG Xiang, et al. Nonhomogeneous sea clutter suppression using complex-valued U-Net model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4027705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3214633. [11] MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Sea clutter suppression for Radar PPI images based on SCS-GAN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(11): 1886–1890. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3012523. [12] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Maritime target detection based on radar graph data and graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133473. [13] 耿常青, 杨承志, 吴宏超, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的微弱雷达信号增强技术研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2018(6): 101–105. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2018.8.108.GENG Changqing, YANG Chengzhi, WU Hongchao, et al. Research on weak radar signal enhancement technology based on convolutional neural network[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2018(6): 101–105. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2018.8.108. [14] 苏琮智, 吴宏超, 杨承志, 等. 基于RSETransformer的低截获概率雷达信号增强[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2022(5): 44–54. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220096.SU Congzhi, WU Hongchao, YANG Chengzhi, et al. LPI radar signal enhancement based on RSETransformer[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2022(5): 44–54. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220096. [15] 曹鹏宇, 杨承志, 石礼盟, 等. 基于DAE-GAN网络的LPI雷达信号增强[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(9): 2493–2500. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.09.16.CAO Pengyu, YANG Chengzhi, SHI Limeng, et al. LPI radar signal enhancement based on DAE-GAN network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(9): 2493–2500. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.09.16. [16] KONG Yameng, FENG Dejun, and ZHANG Jiang. Radar HRRP target recognition based on composite deep networks[C]. 2022 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES-China), Xuzhou, China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ACES-China56081.2022.10064953. [17] TANG Tao, WANG Cai, and GAO Meiguo. Radar target recognition based on micro-doppler signatures using recurrent neural network[C]. The IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China, 2021: 189–194. doi: 10.1109/ICET51757.2021.9450934. [18] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于深度学习的海上目标一维序列信号目标检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. One-dimensional sequence signal detection method for marine target based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004. [19] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 陈宝欣, 等. 雷达海上目标双通道卷积神经网络特征融合智能检测方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(10): 47–52, 57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.10.009.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, et al. Dual-channel convolutional neural networks feature fusion method for radar maritime target intelligent detection[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(10): 47–52, 57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.10.009. [20] CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. [21] 王治飞, 于俊朋, 杨予昊, 等. 基于帧间多维特征的深度学习雷达目标检测技术[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(12): 48–54. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.007.WANG Zhifei, YU Junpeng, YANG Yuhao, et al. Radar target detection with multi-frame multi-dimensional features based on deep learning[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(12): 48–54. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.007. [22] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Graph data and GCN based maritime target detection of multi-frame scanning radar[C]. 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Sydney, Australia, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR54928.2023.10371140. [23] 许述文, 焦银萍, 白晓惠, 等. 基于频域多通道图特征感知的海面小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188.XU Shuwen, JIAO Yinping, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Small target detection based on frequency domain multichannel graph feature perception on sea surface[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188. [24] HUANG Hao, PENG Yang, YANG Jie, et al. Fast beamforming design via deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(1): 1065–1069. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2949122. [25] 任燕飞, 杜盈, 张劲东. 基于深度神经网络的自适应波束形成算法[J]. 电讯技术, 2022, 62(7): 852–858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.07.002.REN Yanfei, DU Ying, and ZHANG Jindong. An adaptive beamforming algorithm based on deep neural network[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2022, 62(7): 852–858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.07.002. [26] 丁梓航, 谢军伟, 王博. 基于深度学习的FDA-MIMO雷达协方差矩阵缺失数据恢复方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1112–1124. doi: 10.12000/JR23002.DING Zihang, XIE Junwei, and WANG Bo. Missing covariance matrix recovery with the FDA-MIMO radar using deep learning method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1112–1124. doi: 10.12000/JR23002. [27] THORNTON C E, KOZY M A, BUEHRER R M, et al. Deep reinforcement learning control for radar detection and tracking in congested spectral environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(4): 1335–1349. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3019605. [28] HU Jinfeng, WEI Zhiyong, LI Yuzhi, et al. Designing unimodular waveform(s) for MIMO radar by deep learning method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(2): 1184–1196. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3037406. [29] ELBIR A M, MISHRA K V, and ELDAR Y C. Cognitive radar antenna selection via deep learning[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(6): 871–880. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5438. [30] 王超, 孙丽婷, 王翔, 等. 基于脉内线性调频的雷达脉冲分裂信号分选与参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(7): 1222–1232. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.07.009.WANG Chao, SUN Liting, WANG Xiang, et al. Deinterleaving and parameter estimation methods of radar signal with pulse splitting based on intra-pulse linear frequency modulation[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(7): 1222–1232. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.07.009. [31] 韩文草. 基于深度学习的雷达信号检测与参数估计[D]. [硕士论文], 杭州电子科技大学, 2023. doi: 10.27075/d.cnki.ghzdc.2022.000329.HAN Wencao. Radar signal detection and parameter estimation based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2023. doi: 10.27075/d.cnki.ghzdc.2022.000329. [32] 牟效乾, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于INet的雷达图像杂波抑制和目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090.MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Clutter suppression and marine target detection for radar images based on INet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090. [33] 陈小龙, 牟效亁, 关键. 对海雷达多维图像特征融合智能检测方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2022, 20(10): 1006–1016. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2022119.CHEN Xiaolong, MU Xiaoqian, and GUAN Jian. Detection method of multi-dimensional images feature intelligent fusion for marine radar[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2022, 20(10): 1006–1016. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2022119. [34] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, MU Xiaoqian, et al. Multi-dimensional automatic detection of scanning radar images of marine targets based on radar PPInet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3856. doi: 10.3390/rs13193856. [35] CHEN Xiaolong, MU Xiaoqian, GUAN Jian, et al. Marine target detection based on Marine-Faster R-CNN for navigation radar PPI images[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2022, 23(4): 630–643. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2000611. [36] TAN Yihua, LI Qingyun, LI Yansheng, et al. Aircraft detection in high-resolution SAR images based on a gradient textural saliency map[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(9): 23071–23094. doi: 10.3390/s150923071. [37] 杜兰, 刘彬, 王燕, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3018–3025. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161032.DU Lan, LIU Bin, WANG Yan, et al. Target detection method based on convolutional neural network for SAR image[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3018–3025. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161032. [38] 李健伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像舰船目标检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(9): 1953–1959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.09.LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, PENG Shujuan, et al. Ship detection in SAR images based on convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1953–1959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.09. [39] CUI Zongyong, WANG Xiaoya, LIU Nengyua, et al. Ship detection in large-scale SAR images via spatial shuffle-group enhance attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 379–391. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2997200. [40] 李广帅, 苏娟, 李义红. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的SAR图像飞机检测算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(1): 159–168. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0004.LI Guangshuai, SU Juan, and LI Yihong. An aircraft detection algorithm in SAR image based on improved Faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(1): 159–168. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0004. [41] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084.XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084. [42] 牟效乾, 陈小龙, 苏宁远, 等. 基于时频图深度学习的雷达动目标检测与分类[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2019, 17(1): 105–111. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0105.MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, et al. Radar detection and classification of moving target using deep convolutional neural networks on time-frequency graphs[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2019, 17(1): 105–111. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0105. [43] CHEN Xiaolong, ZHANG Hai, SONG Jie, et al. Micro-motion classification of flying bird rotor drones via data augmentation modified multi-scale CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1107. doi: 10.3390/rs14051107. [44] 施赛楠, 董泽远, 杨静, 等. 基于时频图自主学习的海面小目标检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(1): 33–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.05.SHI Sainan, DONG Zeyuan, YANG Jing, et al. Sea-surface small target detection based on autonomic learning of time-frequency graph[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(1): 33–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.01.05. [45] 裴家正, 黄勇, 陈宝欣, 等. 联合脉压与Radon傅里叶变换的长时间相参积累方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 956–969. doi: 10.12000/JR21068.PEI Jiazheng, HUANG Yong, CHEN Baoxin, et al. Long time coherent integration method based on combining pulse compression and Radon-Fourier transform[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 956–969. doi: 10.12000/JR21068. [46] PÉREZ R, SCHUBERT F, RASSHOFER R, et al. Deep learning radar object detection and classification for urban automotive scenarios[C]. 2019 Kleinheubach Conference, Miltenberg, Germany, 2019: 1–4. [47] WANG Chenxing, TIAN Jiangmin, and CAO Jiuwen. Deep learning-based UAV detection in pulse-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3104907. [48] 张暄, 高跃清. 基于卷积神经网络的雷达目标检测方法[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2021, 29(2): 49–52, 57. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.02.011.ZHANG Xuan and GAO Yueqing. Radar target detection based on convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2021, 29(2): 49–52, 57. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.02.011. [49] BRODESKI D, BILIK I, and GIRYES R. Deep radar detector[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835792. [50] 宋海凌, 孙宇航, 何良, 等. 雷达回波信号的深度学习目标检测识别方法研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2021(2): 117–126. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2021.9.114.SONG Hailing, SUN Yuhang, HE Liang, et al. Research on deep learning target detection and recognition method based on radar echo signal[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2021(2): 117–126. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2021.9.114. [51] KIM Y, ALNUJAIM I, YOU S, et al. Human detection with range-Doppler signatures using 3D convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 2440–2442. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9324052. [52] 张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049.ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. [53] LIAO Leiyao, DU Lan, and CHEN Jian. Interpretable deep probabilistic model for hrr radar signal and its application to target recognition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(4): 775–790. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3160241. [54] 田野, 丁赤飚, 张福博, 等. 一种基于深度学习的SAR城市建筑区域叠掩精确检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 441–455. doi: 10.12000/JR23033.TIAN Ye, DING Chibiao, ZHANG Fubo, et al. SAR building area layover detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 441–455. doi: 10.12000/JR23033. [55] 李毅, 杜兰, 杜宇昂. 基于特征分解卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1069–1080. doi: 10.12000/JR23004.LI Yi, DU Lan, and DU Yuang. Convolutional neural network based on feature decomposition for target detection in SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1069–1080. doi: 10.12000/JR23004. [56] 吴礼洋, 呙鹏程, 刘超, 等. 基于注意力机制增强残差网络的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(8): 2310–2318. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0302.WU Liyang, GUO Pengcheng, LIU Chao, et al. Radar signal modulation type recognition based on attention mechanism enhanced residual networks[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(8): 2310–2318. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0302. [57] BALTRUŠAITIS T, AHUJA C, and MORENCY L P. Multimodal machine learning: a survey and taxonomy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(2): 423–443. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2798607. [58] ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264. [59] 周雪珂, 刘畅, 周滨. 多尺度特征融合与特征通道关系校准的SAR图像船舶检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 531–543. doi: 10.12000/JR21021.ZHOU Xueke, LIU Chang, and ZHOU Bin. Ship detection in SAR images based on multi-scale features fusion and channel relation calibration of features[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 531–543. doi: 10.12000/JR21021. [60] LIAN Xiaoqin, HUANG Xue, GAO Chao, et al. A multiscale local-global feature fusion method for SAR image classification with Bayesian hyperparameter optimization algorithm[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(11): 6806. doi: 10.3390/app13116806. [61] 郭帅, 陈婷, 王鹏辉, 等. 基于角度引导Transformer融合网络的多站协同目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014.GUO Shuai, CHEN Ting, WANG Penghui, et al. Multistation cooperative radar target recognition based on an angle-guided Transformer fusion network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. [62] YU Xiaopeng and YU Xiaogao. The research on an adaptive k-nearest neighbors classifier[C]. The 5th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Informatics, Beijing, China, 2006: 535–540. doi: 10.1109/COGINF.2006.365542. [63] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077. [64] 潘卫军, 段英捷, 张强, 等. 基于AlexNet卷积神经网络的激光雷达飞机尾涡识别研究[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 190082. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190082.PAN Weijun, DUAN Yingjie, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Research on aircraft wake vortex recognition using AlexNet[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(7): 190082. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190082. [65] 员娇娇, 胡永利, 孙艳丰, 等. 基于深度学习的小目标检测方法综述[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(3): 293–302. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020090019.YUAN Jiaojiao, HU Yongli, SUN Yanfeng, et al. Survey of small object detection methods based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(3): 293–302. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020090019. [66] YANG Yonghu, CHU Na, and LIU Zhenyu. Target detection in sea clutter based on transfer learning[C]. The IEEE 14th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE), Dalian, China, 2019: 795–799. doi: 10.1109/ISKE47853.2019.9170451. [67] LI Xuefei, WU Di, and ZHU Daiyin. Multi-channel SAR moving target detection based on simulation samples and transfer learning[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 2054–2057. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028221. [68] 王金强, 孙闽红, 唐向宏, 等. 小样本下雷达复合干扰半监督迁移学习识别方法[J]. 电信科学, 2023, 39(10): 15–28. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2023182.WANG Jinqiang, SUN Minhong, TANG Xianghong, et al. A semi-supervised transfer learning recognition method for radar compound jamming under small samples[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2023, 39(10): 15–28. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2023182. [69] 杨立儒, 刘永祥, 杨威. 基于迁移学习的雷达杂波幅度统计模型选择[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(8): 2457–2467. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.09.YANG Liru, LIU Yongxiang, and YANG Wei. Radar clutter amplitude statistical model selection based on transfer learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2457–2467. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.09. [70] 杜兰, 王梓霖, 郭昱辰, 等. 结合强化学习自适应候选框挑选的SAR目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121.DU Lan, WANG Zilin, GUO Yuchen, et al. Adaptive region proposal selection for SAR target detection using reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121. [71] ZHAI Weitong, WANG Xiangrong, GRECO M S, et al. Weak target detection in massive MIMO radar via an improved reinforcement learning approach[C]. ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 4993–4997. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746472. [72] WANG Yuedong, LIANG Yan, ZHANG Huixia, et al. Domain knowledge-assisted deep reinforcement learning power allocation for MIMO radar detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(23): 23117–23128. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3211606. [73] 赵会盼, 刘环宇. 基于多模态数据融合学习网络的微弱目标群检测方法[J]. 空天防御, 2021, 4(3): 41–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2021.03.006.ZHAO Huipan and LIU Huanyu. Low signature target group detection based on multimodal data learning fusion network[J]. Air & Space Defense, 2021, 4(3): 41–47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2021.03.006. [74] 陈小龙, 黄勇, 关键, 等. MIMO雷达微弱目标长时积累技术综述[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001.CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Review of long-time integration techniques for weak targets using MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001. [75] 郭瑞, 张月, 田彪, 等. 全息凝视雷达系统技术与发展应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Review of the technology, development and applications of holographic staring radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153. [76] 陈小龙, 陈宝欣, 黄勇, 等. 频控阵雷达空距频聚焦信号处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 183–193. doi: 10.12000/JR18018.CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, HUANG Yong, et al. Frequency diverse array radar signal processing via space-range-Doppler focus (SRDF) method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 183–193. doi: 10.12000/JR18018. [77] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059.GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. [78] 罗迎, 倪嘉成, 张群. 基于“数据驱动+智能学习”的合成孔径雷达学习成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103.LUO Ying, NI Jiacheng, and ZHANG Qun. Synthetic aperture radar learning-imaging method based on data-driven technique and artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103. [79] 黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165.HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. -



 作者中心
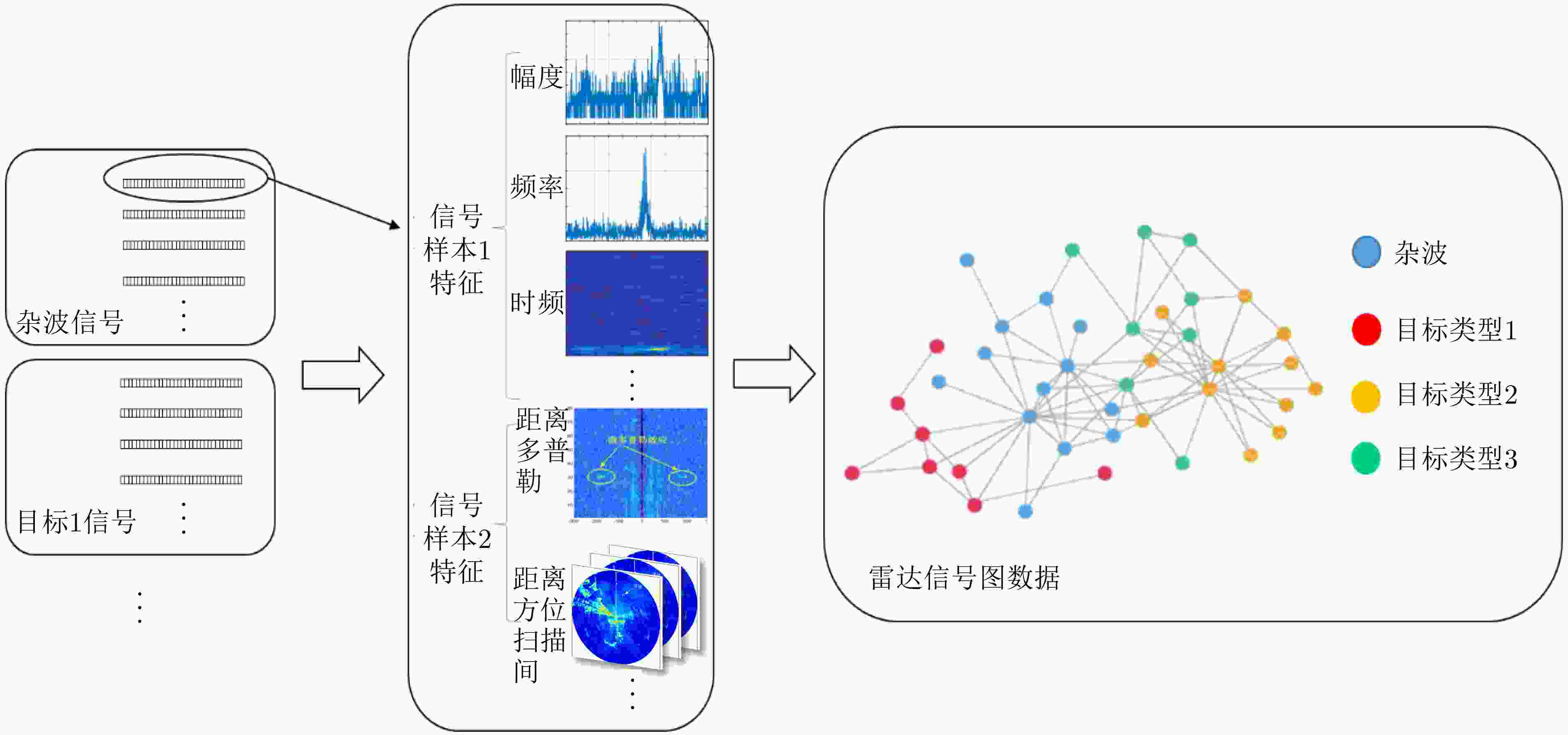
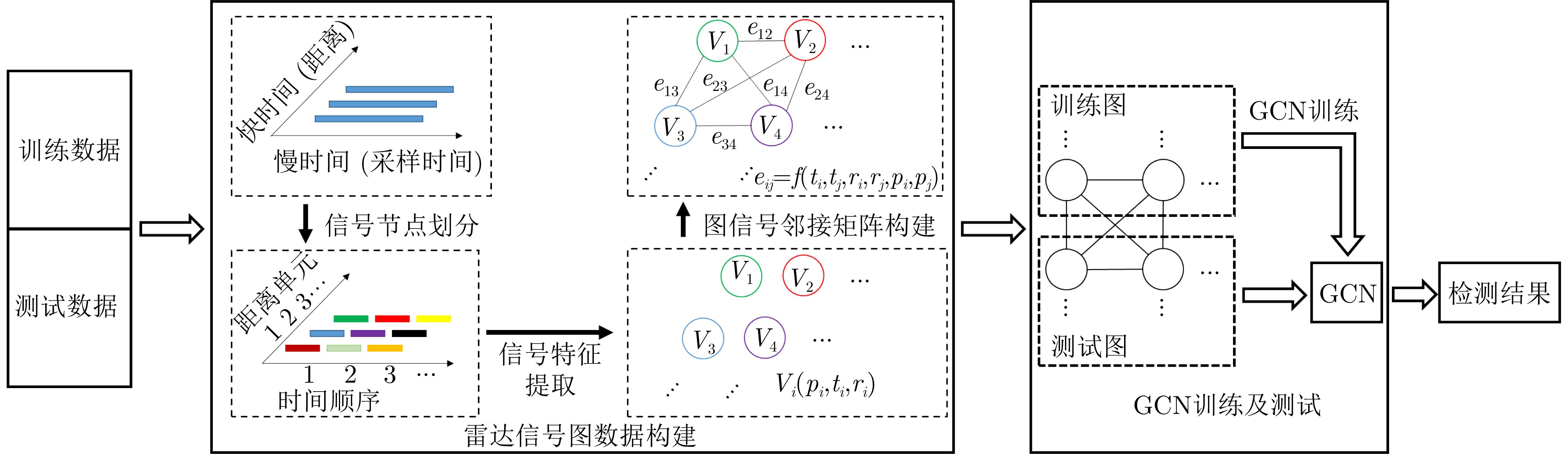
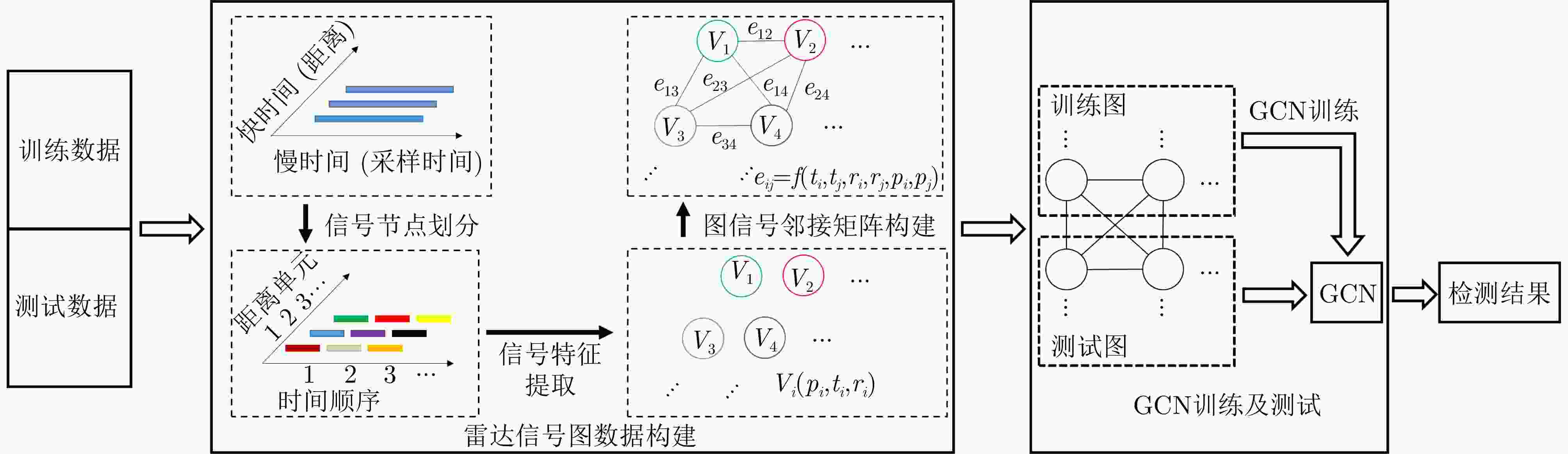
作者中心 专家审稿
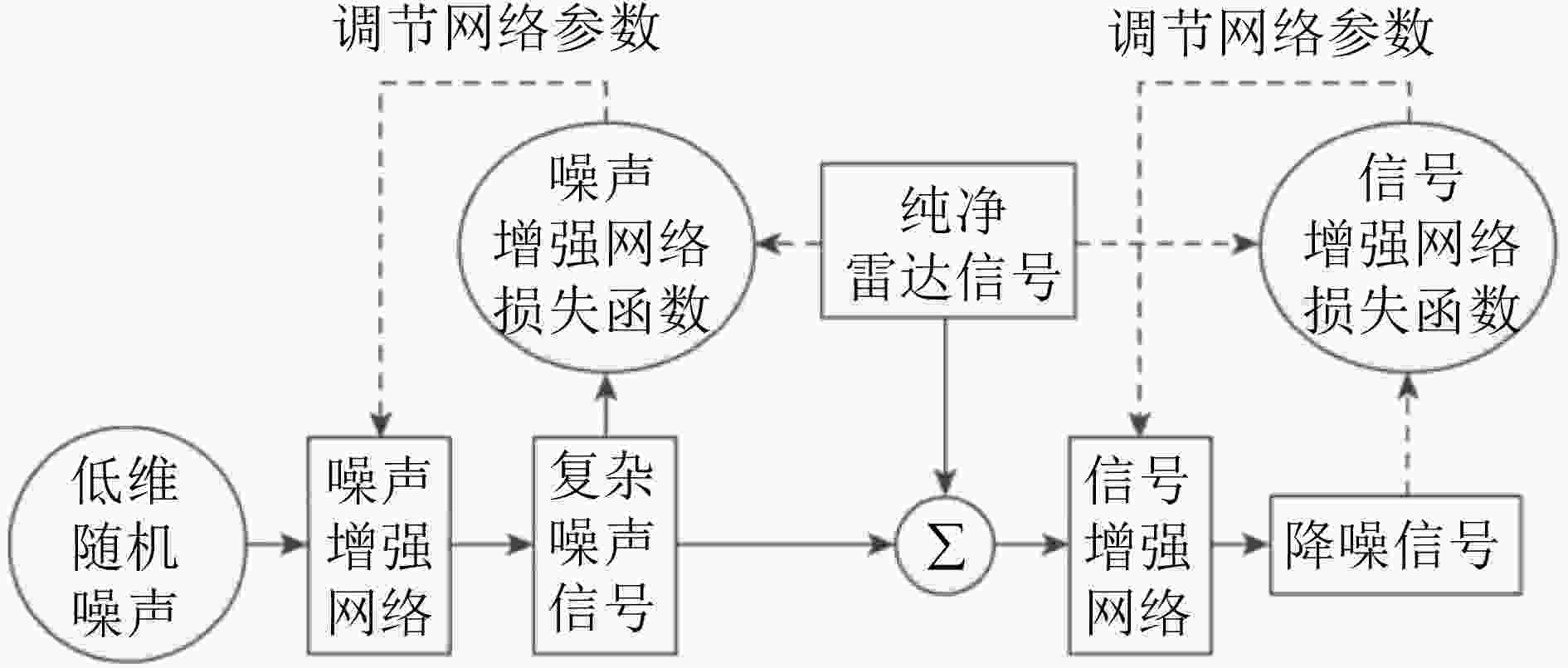
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: