A Water Segmentation Algorithm for SAR Image Based on Dense Depthwise Separable Convolution
-
摘要: SAR图像的水域分割在舰船目标检测、灾害监测等军事和民用领域具有重要意义。针对传统水域分割算法鲁棒性差、难以准确进行分割等问题,该文首先建立了基于高分三号的SAR图像水域分割数据集,并基于深度学习技术提出了基于密集深度分离卷积的分割网络架构,该网络以SAR图像作为输入,通过密集分离卷积和扩张卷积提取图像高维特征,并构造基于双线性插值的上采样解码模块用于输出分割结果。在水域分割数据集上的实验结果表明,与传统方法相比,该方法不仅在分割准确度上有大幅提高,在算法的鲁棒性和分割速度上也具有部分优势,具备较好的工程实用价值。Abstract: Water segmentation of real SAR images is of great significance in military and civilian applications such as ship target detection and disaster monitoring. To solve the issues of poor robustness and inaccurate segmentation of traditional water segmentation algorithms, this paper first establishes a SAR water segmentation dataset based on the GF3 satellite and then presents a segmentation network architecture based on depthwise separable convolution. The network takes real SAR images as inputs, extracts high-dimensional features through depthwise separable and dilated convolutions, constructs an up-sampling and decoding module based on bilinear interpolation, and then outputs the corresponding segmentation results. The segmentation results of a water segmentation dataset show that the proposed segmentation method remarkably improves the segmentation accuracy, the segmentation robustness and running speed than traditional method. Therefore, the findings demonstrate the excellent practical engineering value of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 高分三号成像模式
Table 1. The imaging modes of GF3 satellite
工作模式 分辨率(m) 极化方式 成像幅宽(km) 滑块聚束(SL) 1 单极化 10 超精细条带(UFS) 3 单极化 30 精细条带1(FSI) 5 双极化 50 精细条带2(FSII) 10 双极化 100 标准条带1(QPSI) 8 全极化 30 表 2 数据集图像组成
Table 2. The composition of dataset
图像类型 数量 图像尺寸(像素) 原始图像 10 $ \approx 10,000 \times 10,000$ 裁剪图像 480 $513 \times 513$ 扩充图像 21180 $513 \times 513$ 表 3 数据扩充对分割性能的影响
Table 3. Segmentation effects of data augmentation
扩充方法 像素准确度 交并比 未扩充 0.9569 0.9497 旋转 0.9806 0.9758 翻转 0.9620 0.9603 旋转+翻转 0.9887 0.9844 表 4 网络结构对分割性能的影响
Table 4. Segmentation effects of network structure
连接方式 像素准确度 交并比 直连 0.9312 0.9289 仅残差 0.9703 0.9681 仅密集 0.9679 0.9638 残差+密集 0.9887 0.9844 表 5 各水域分割算法性能对比
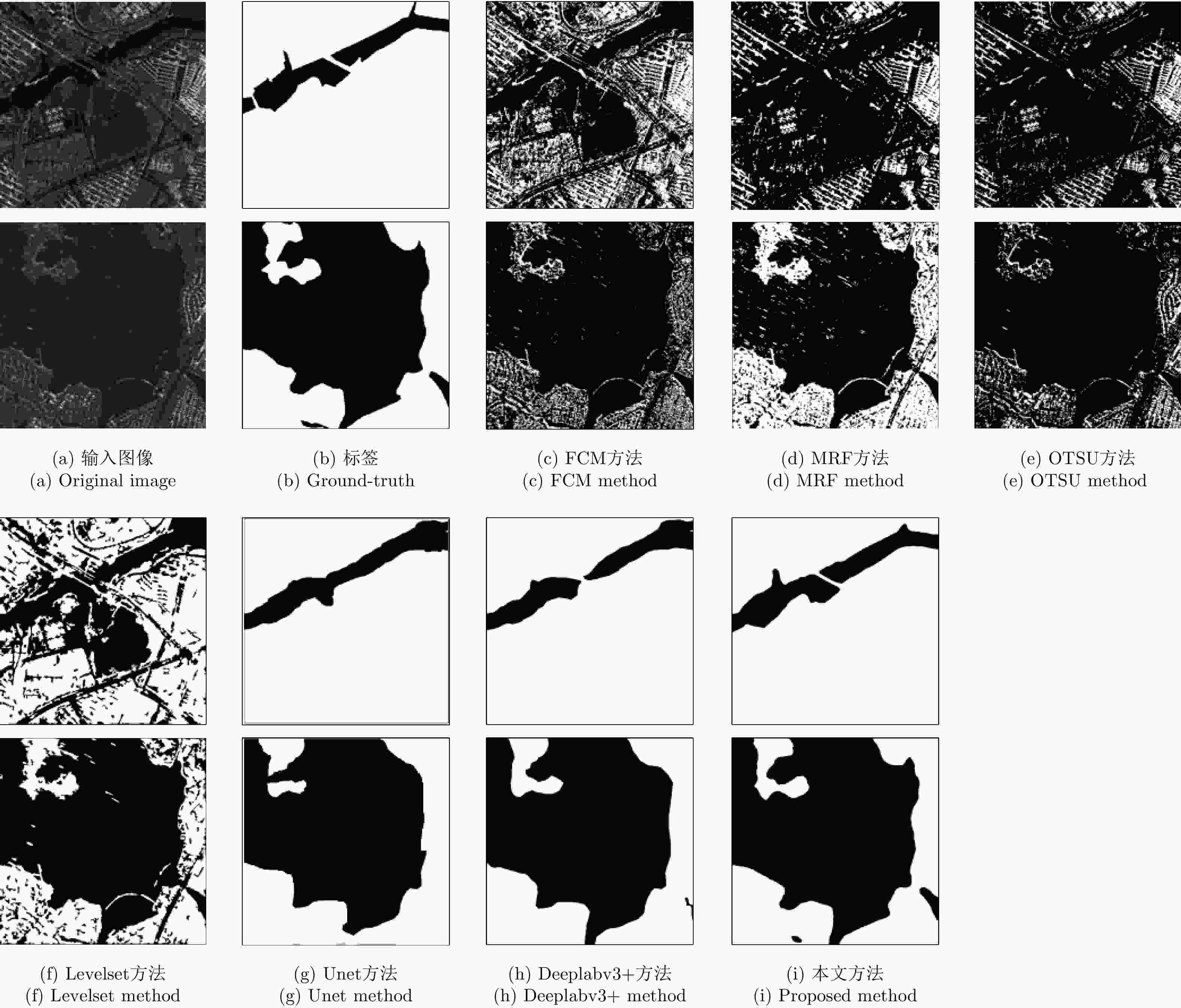
Table 5. Segmentation performance of different methods
方法类别 具体方法 像素准确度 交并比 小图速度(s) 大图速度(s) 传统方法 FCM 0.6710 0.4644 8.24 206.0 MRF 0.5961 0.5430 2.29 57.25 OTSU 0.6303 0.6108 0.06 1.50 Levelset 0.7134 0.6868 3.41 85.25 深度学习 Unet 0.9533 0.9496 0.07 1.75 DeepLabv3+ 0.9672 0.9566 0.10 2.50 所提方法 0.9887 0.9844 0.14 3.50 理想值 1.0000 1.0000 – – 表 6 本文方法对多模式多极化下SAR图像的IoU分割结果
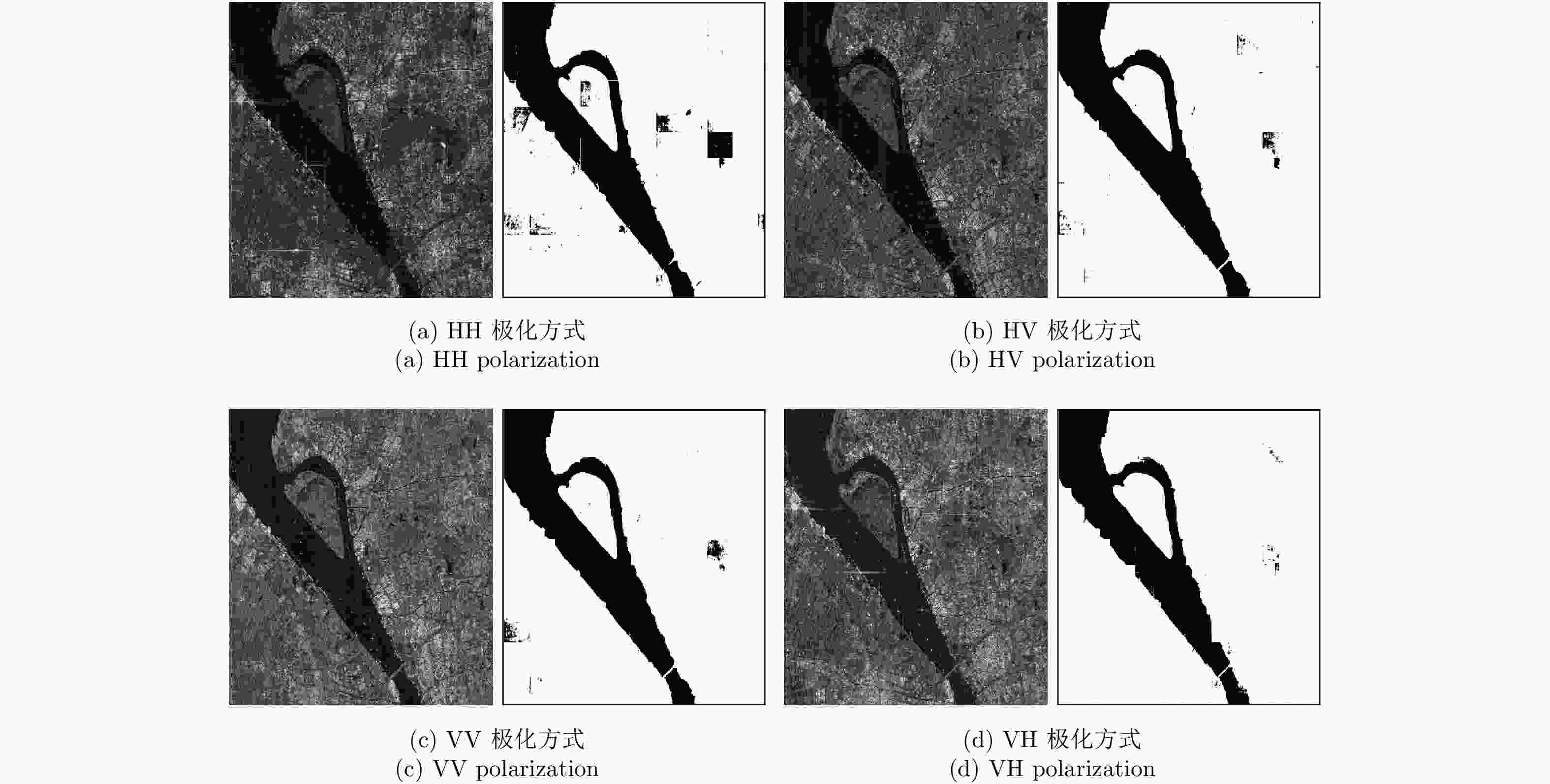
Table 6. IoU under multi-mode and multi-polarization by the proposed method
工作模式/极化方式 HH HV VH VV SL (1 m) 0.9844 – – – UFS (3 m) 0.9240 – – – FSI (5 m) 0.9365 0.9542 – – FSII (10 m) 0.9549 0.9454 – – QPSI (8 m) 0.9605 0.9684 0.9686 0.9717 -
[1] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047WU Yirong. Concept of multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047 [2] 艾加秋, 齐向阳, 禹卫东. 改进的SAR图像双参数CFAR舰船检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(12): 2881–2885. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01707AI Jiaqiu, QI Xiangyang, and YU Weidong. Improved two parameter CFAR ship detection algorithm in SAR images[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(12): 2881–2885. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01707 [3] 牛世林, 郭拯危, 李宁, 等. 星载SAR水域分割研究进展与趋势分析[J]. 聊城大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 31(2): 72–86.NIU Shilin, GUO Zhengwei, LI Ning, et al. Research progress and trend analysis of water extraction by spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Liaocheng University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 31(2): 72–86. [4] 安成锦, 牛照东, 李志军, 等. 典型Otsu算法阈值比较及其SAR图像水域分割性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426AN Chengjin, NIU Zhaodong, LI Zhijun, et al. Otsu threshold comparison and SAR water segmentation result analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426 [5] 李智, 曲长文, 周强, 等. 基于SLIC超像素分割的SAR图像海陆分割算法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2017, 15(4): 354–358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.04.003LI Zhi, QU Changwen, ZHOU Qiang, et al. A sea-land segmentation algorithm of SAR image based on the SLIC superpixel division[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2017, 15(4): 354–358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.04.003 [6] AMITRANO D, CIERVO F, DI MARTINO G, et al. Modeling watershed response in semiarid regions with high-resolution synthetic aperture radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(7): 2732–2745. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2014.2313230 [7] OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076 [8] SUI H G and XU C. Automatic extraction of water in high-resolution SAR images based on multi-scale level set method and Otsu algorithm[C]. Proceedings of International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Melbourne, Australia, 2012: 453–457. doi: 10.5194/isprsarchives-XXXIX-B7-453-2012. [9] LIU Chun, YANG Jian, YIN Junjun, et al. Coastline detection in SAR images using a hierarchical level set segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(11): 4908–4920. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2016.2613279 [10] 侯彪, 胡育辉, 焦李成. SAR图像水域的改进Shearlet边缘检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2010, 15(10): 1549–1554. doi: 10.11834/jig.20101019HOU Biao, HU Yuhui, and JIAO Licheng. Improved shearlet edge detection for waters of SAR images[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2010, 15(10): 1549–1554. doi: 10.11834/jig.20101019 [11] LIU Zhongling, LI Fei, LI Ning, et al. A novel region-merging approach for coastline extraction from sentinel-1A IW mode SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 324–328. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2510745 [12] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [13] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [14] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [15] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.660. [16] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [17] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs[EB/OL]. arXiv: 1412.7062, 2014. [18] 张庆君. 高分三号卫星总体设计与关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049ZHANG Qingjun. System design and key technologies of the GF-3 satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049 [19] 丁赤飚, 刘佳音, 雷斌, 等. 高分三号SAR卫星系统级几何定位精度初探[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024DING Chibiao, LIU Jiayin, LEI Bin, et al. Preliminary exploration of systematic geolocation accuracy of GF-3 SAR satellite system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024 [20] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195. [21] YU F and KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[EB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015. [22] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308. [23] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [24] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. [25] NAIR V and HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 807–814. [26] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[EB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1502.03167, 2015. [27] MIKOLOV T, SUTSKEVER I, CHEN Kai, et al. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2013: 3111–3119. [28] HANSEN L K and SALAMON P. Neural network ensembles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1990, 12(10): 993–1001. doi: 10.1109/34.58871 [29] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848. [30] VESE L A and CHAN T F. A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and shah model[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 50(3): 271–293. doi: 10.1023/a:1020874308076. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: